BTECH LEGIT ATA
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
Staking-out
It is the driving of stakes for batter boards to locate the corners and foundations of a building for excavation
Stakes
These are wooden sticks used as posts sharpened at one end driven into the ground to serve as boundaries or supports of the batter boards
Strings
Are either plastic cords or galvanized wires strung across batter boards and used to indicate the outline of the building wall and foundation
Batter Boards
- horizontal boards
- establishes height of the footing trenches and foundations
- establishes height of finish floor levels
Leveling
Done with a line level or carpenter's level, or with a transit;
height of the batter boards may be level with or a little higher that the top of the finished foundation
Batter Boards
wood sticks or boards nailed horizontally at the stake which serve as the horizontal plane where the reference point of the building measurements are established
Spirit Level
An instrument or tool capable of vertical and horizontal line check
Plumb Bob
A weight attached to a string, used for vertical line check
Plastic Hose Filled with Water
A method of leveling horizontally batter boards without transit
3-4-5 Multiples with the Use of Steel Tape Measure
A manual method of squaring the corners of building lines in staking
Formworks
used to shape and support fresh concrete until cured and able to support itself
Shoring
- temporary supports designed to carry forms for beams and slabs
- also used to support scaffolding works
(1) Lumber
(2) Steel
what are the two major materials used for forms and shoring construction
Yokes
Are clamping devices for keeping column forms and tops of wall forms from spreading under the fluid pressure of newly placed concrete
Spreaders
Usually of wood, space and keep the wall or space and keep the wall or forms apart
Snap Ties
- have notches or crimps that allow their ends to be snapped off below the concrete surface after stripping off the forms
- small, truncated cones of wood, steel or plastic attached to form ties
She Bolts
consist of waler rods that are inserted through the form and threaded onto the ends of an inner rod. After striping the water rods are removed for reuse while the inner rod remains in the concrete
Scaffolds
Temporary platforms designed to support workers and materials on the face of a structure and to provide access to work areas above the ground
- Ledgers
- Brace or the diagonal
- Standard or the Vertical Component
- Accessories: heads, jacks, and bases
What are the major components of metal shoring?
Hand Tools
are the tools that use power delivered by man only
Power Tools
are tools that employ power supplied by forces other than that coming from humans
Equipment
is a term that refers to large, complex tools and machines that is designed to do a particular job
Heavy Equipment
is equipment which is very large and very powerful.
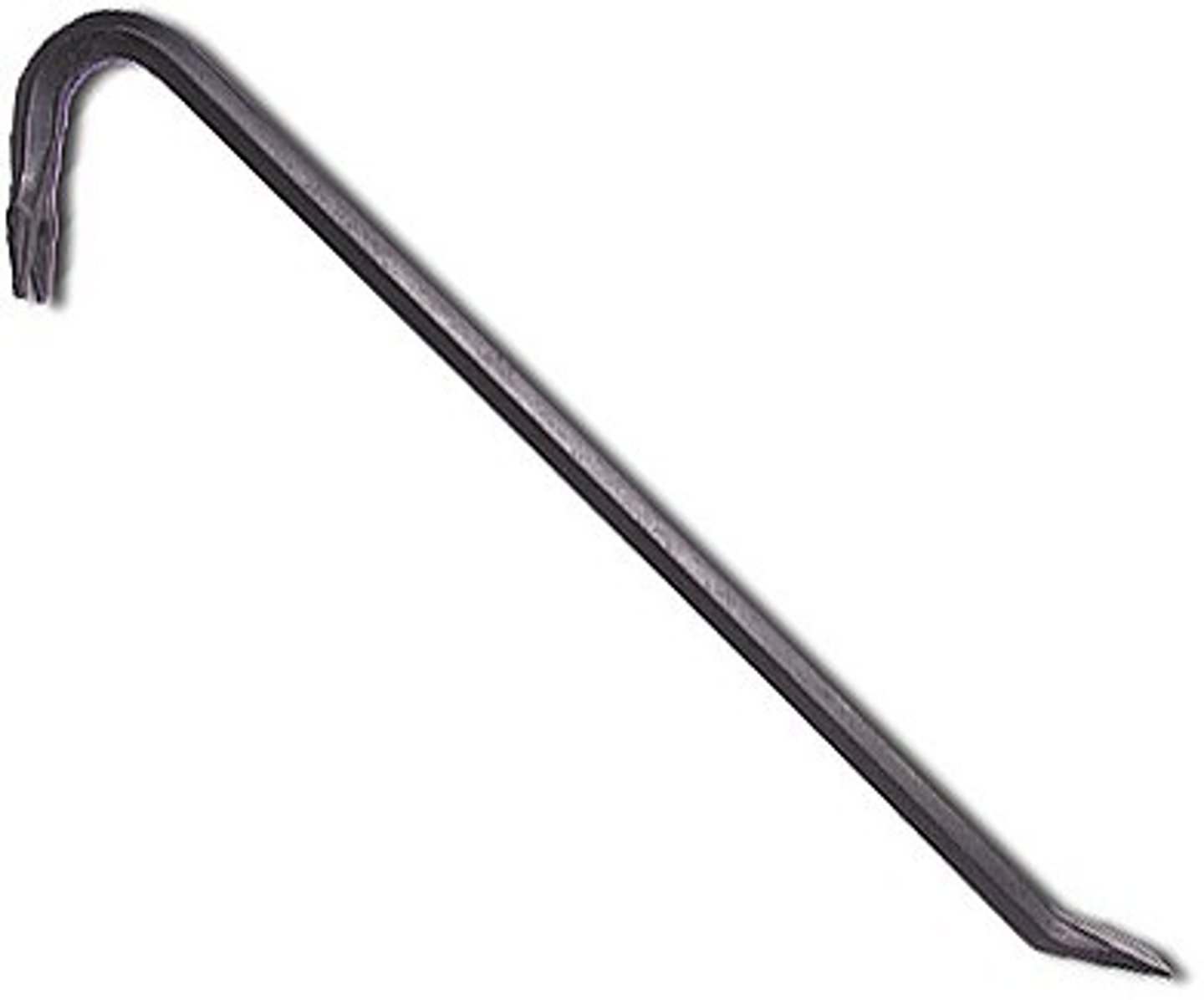
Pry Bar
is used to force open boards used in forming concrete.

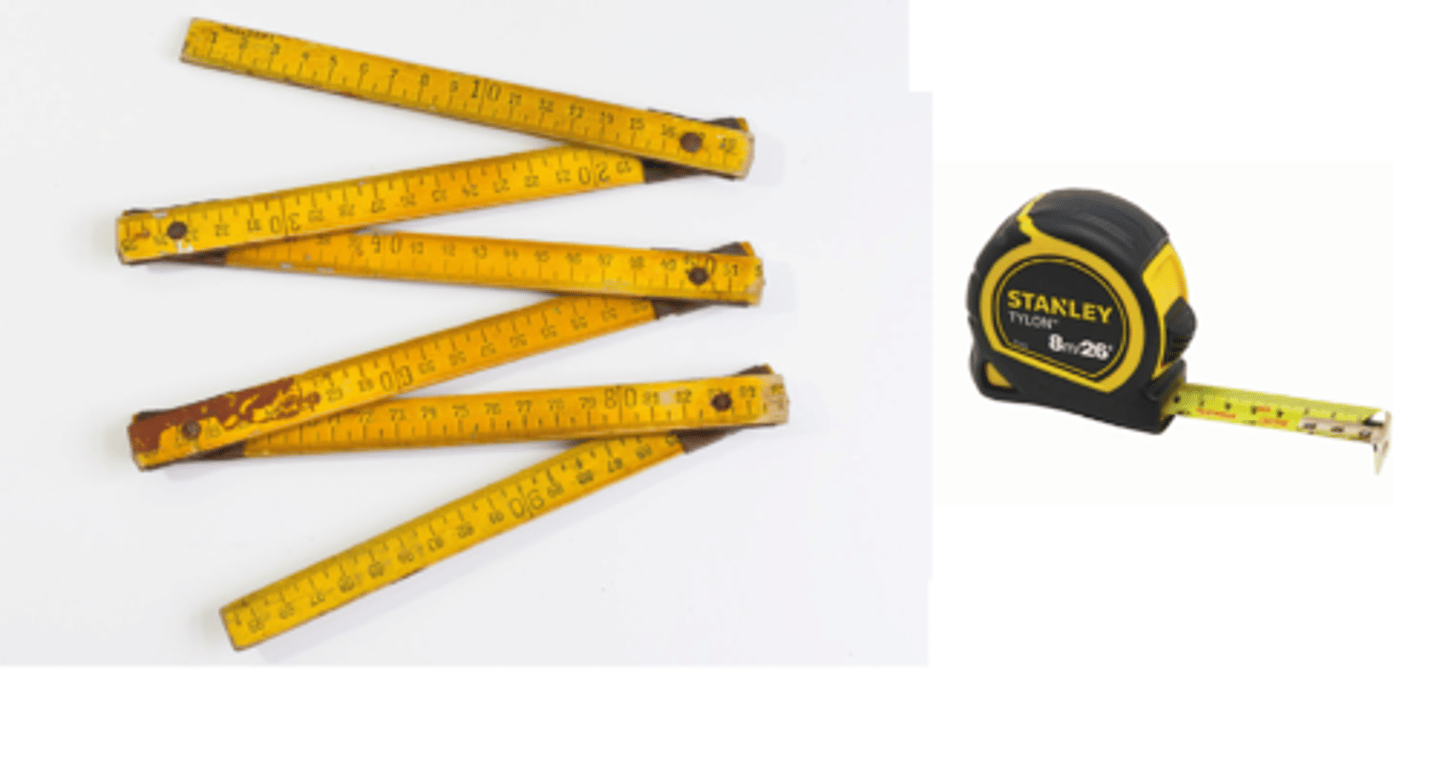
Folding rule and Tape measure
are the most common tools for measuring boards, pipe, wire, etc.

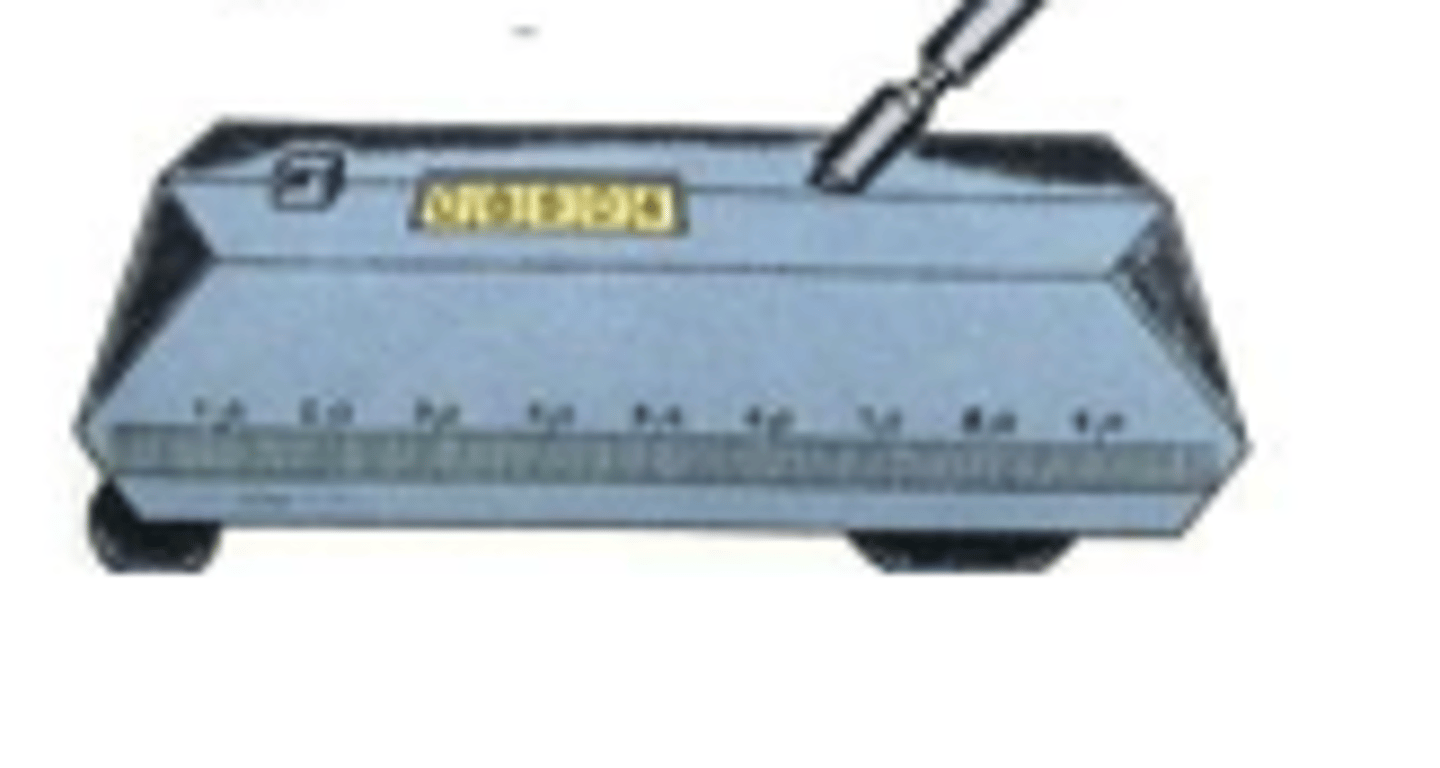
Digital Rule
is used to measure relatively long distances such as those in highway construction

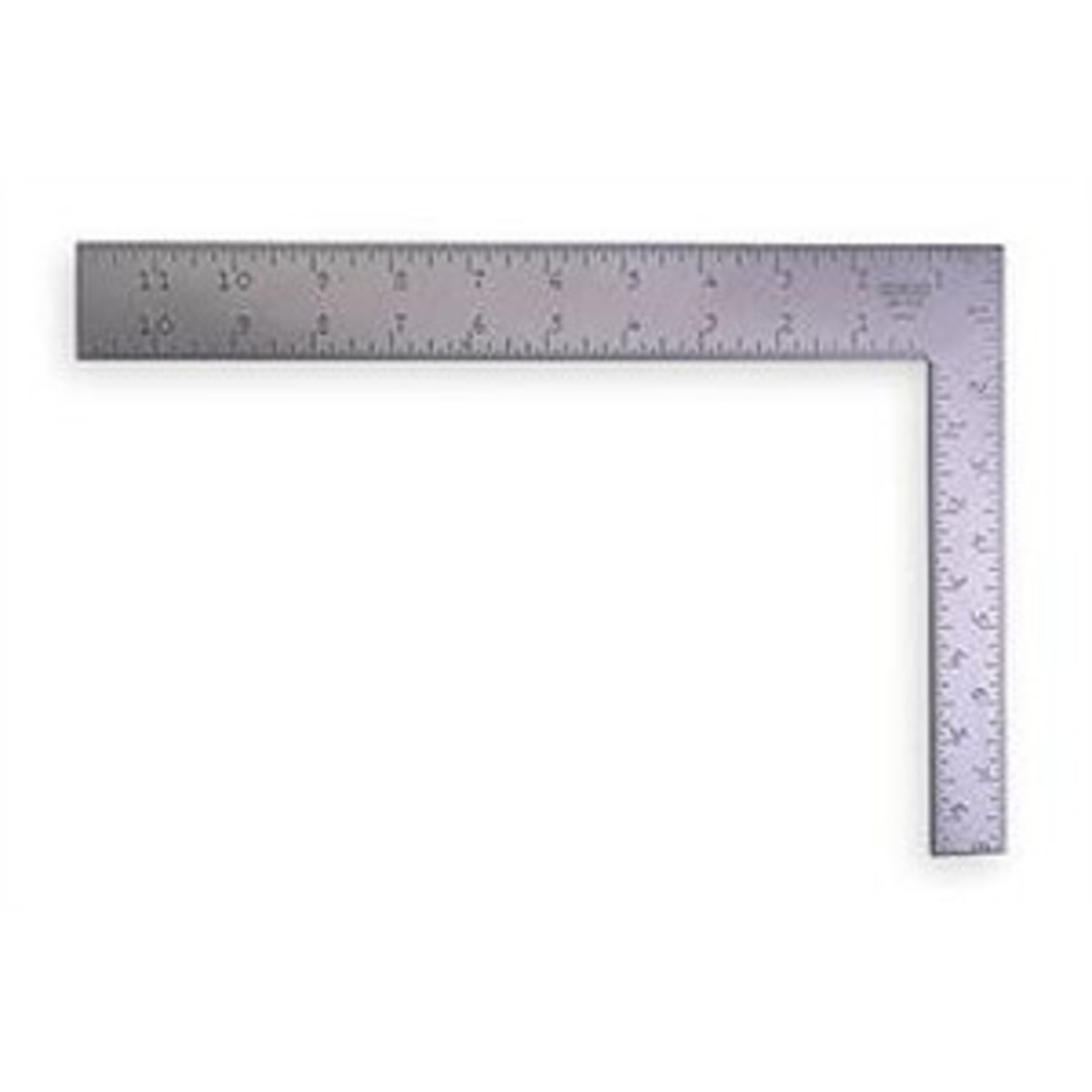
Framing Square
Is a layout tool that is used to measure 90 degree angles at the corners of framework and joints. They can also be employed to determine cutting angles on dimension lumber.

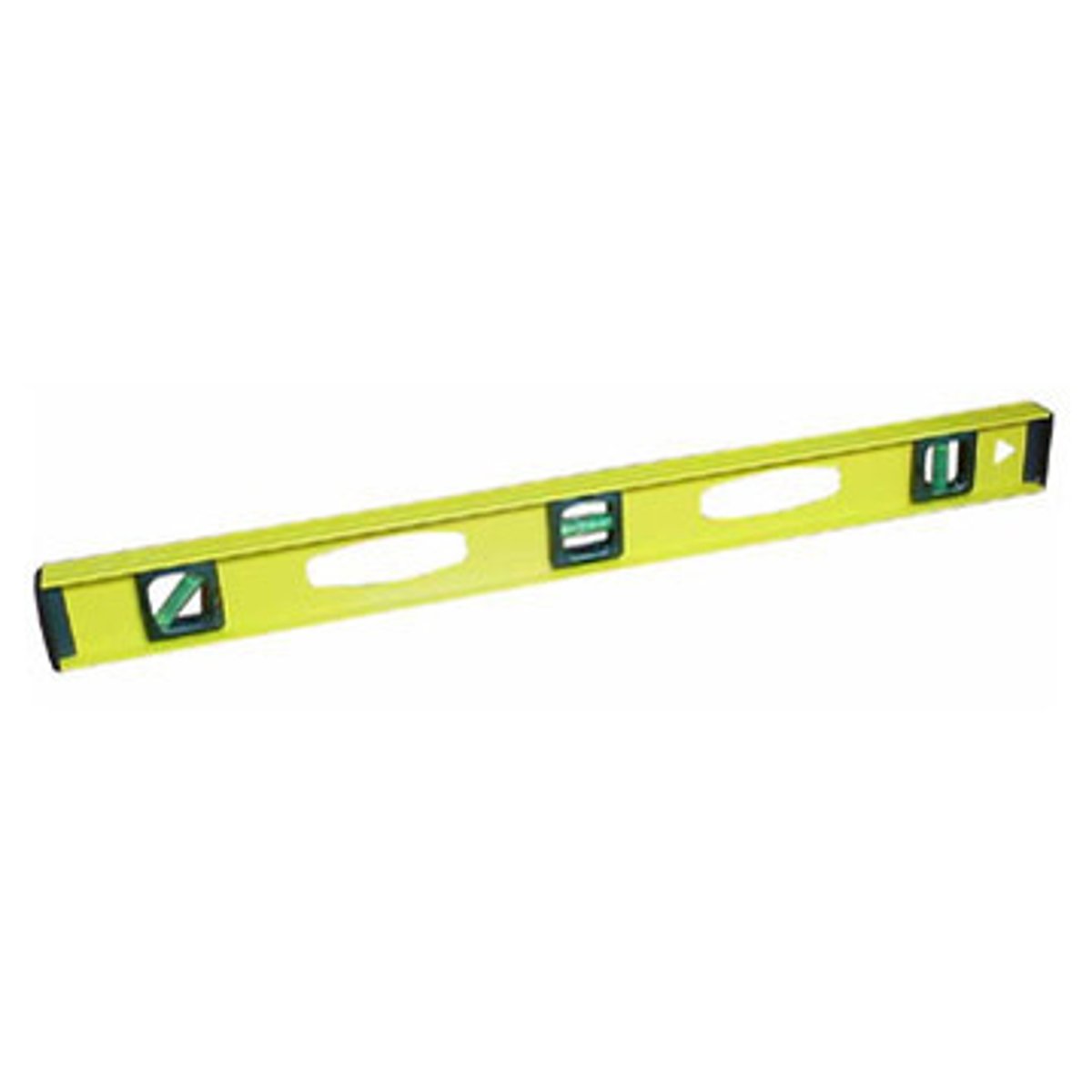
Level
Is a long, straight tool that contains one or more vials of liquid and used to determine if the horizontal or vertical is exact

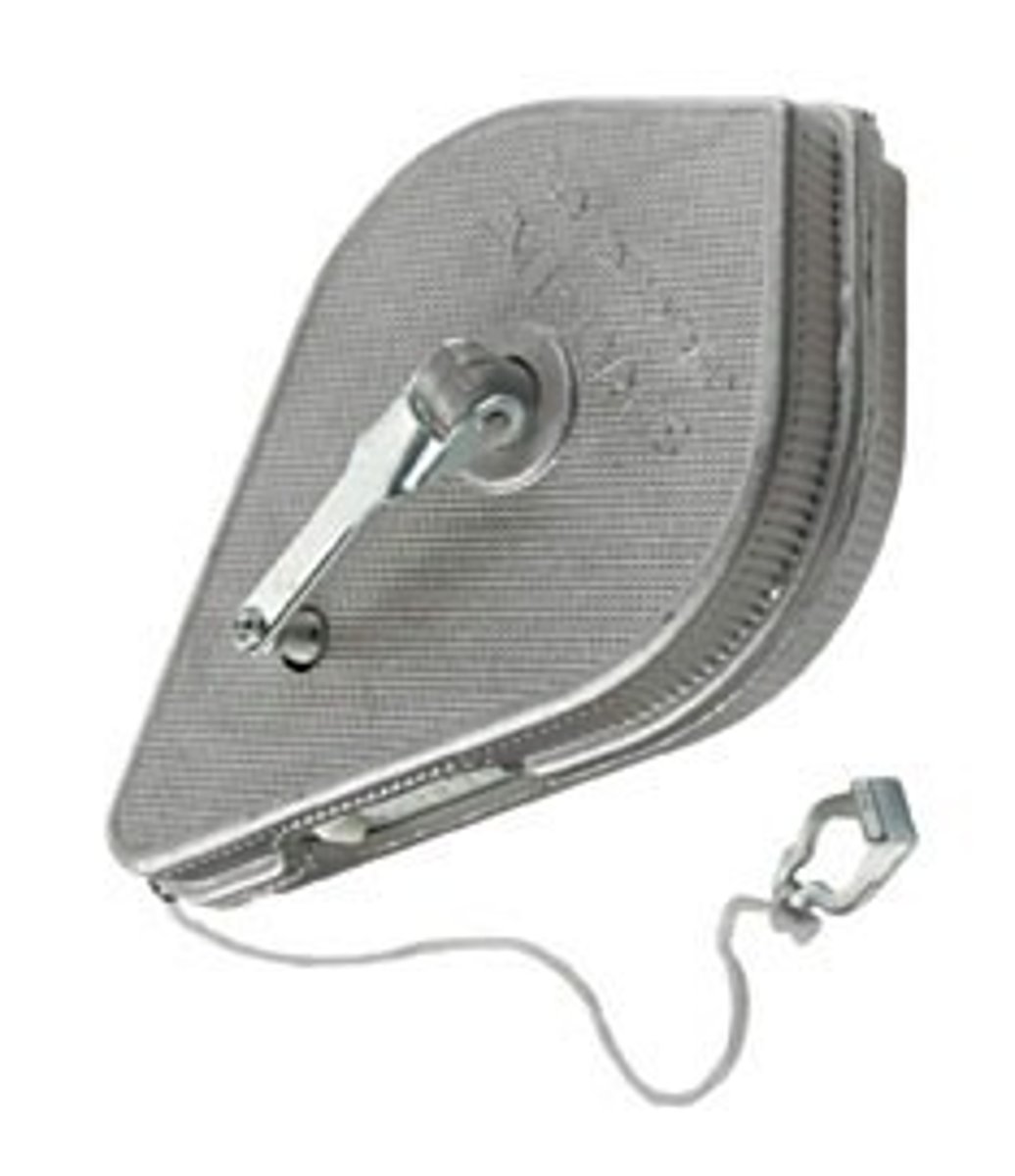
chalk line or chalk box
Is used for marking lines

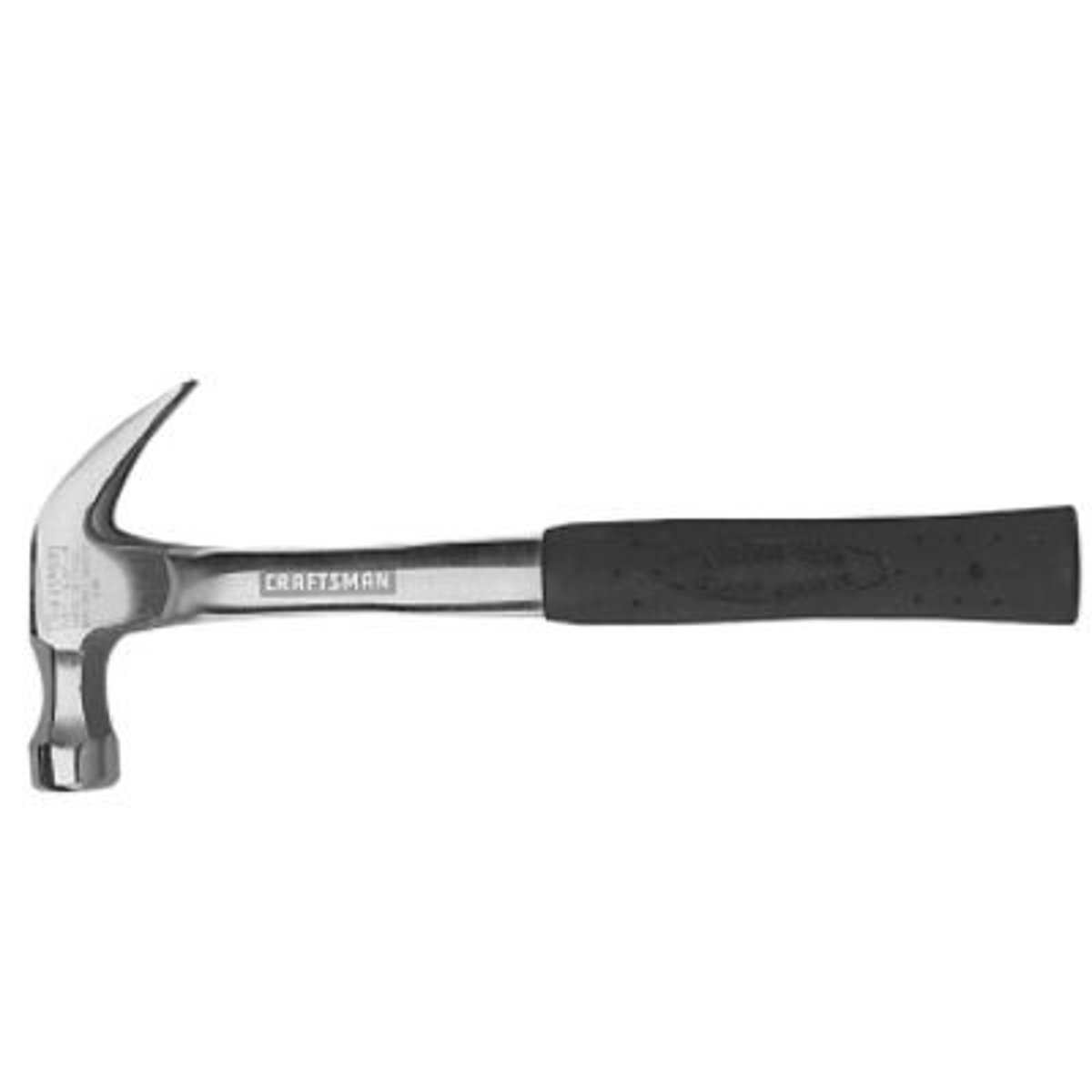
Claw Hammer
is an ordinary hammer used to drive or remove nails.

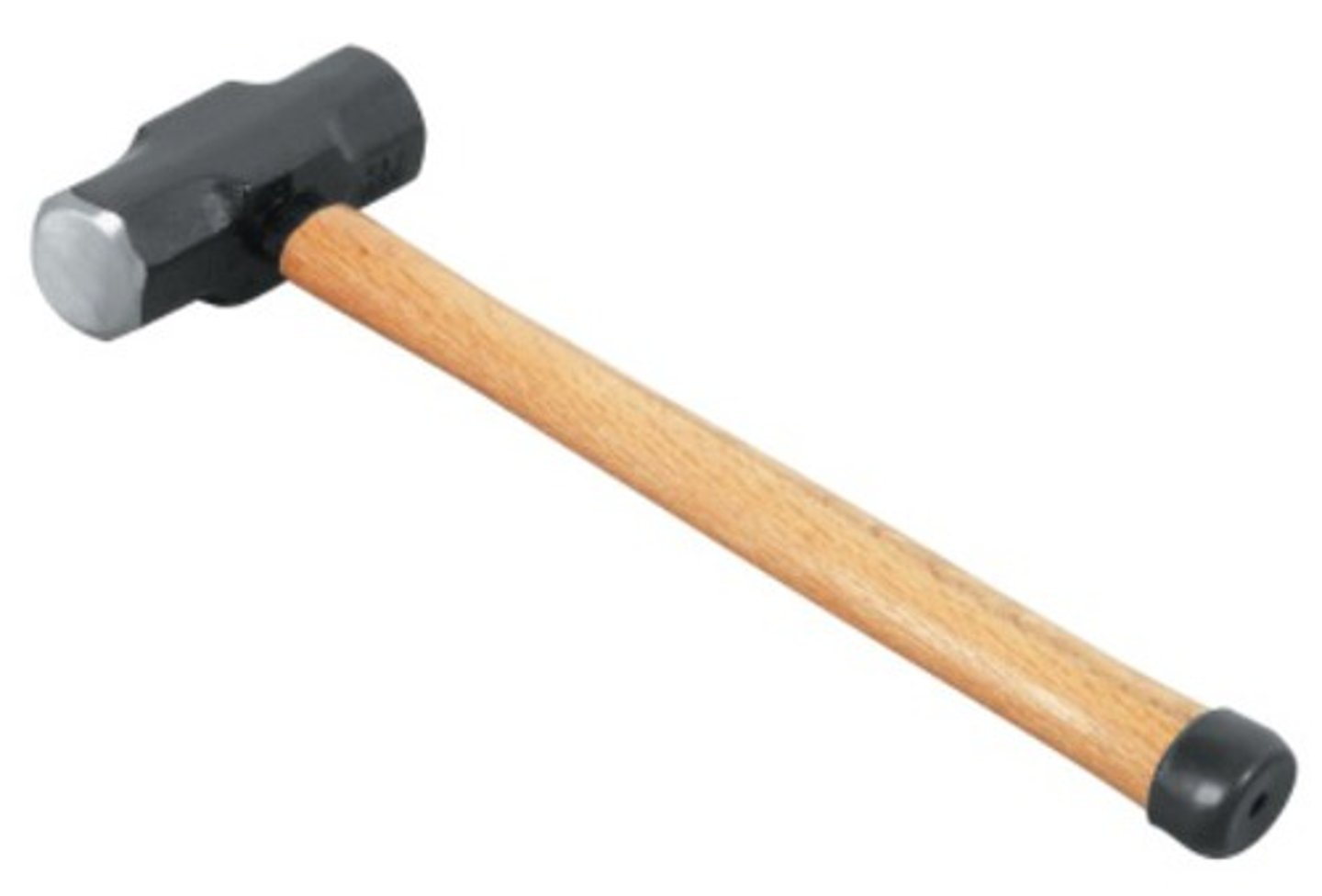
Sledgehammer
is a heavy hammer used to drive stakes into the ground and to break up concrete and stone

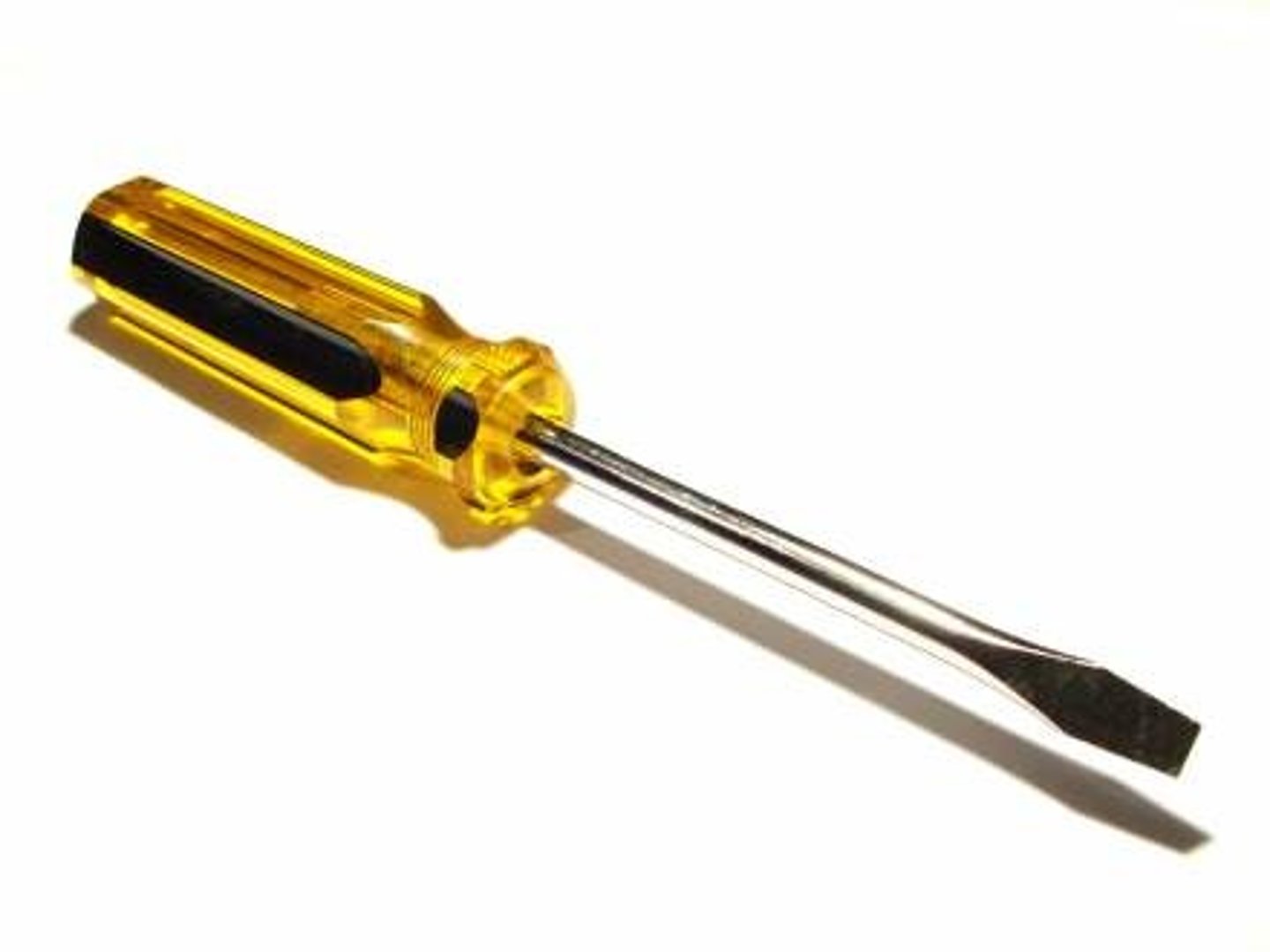
Standard Screwdriver
has a flat tip and is designed to fit a standard slotted screw

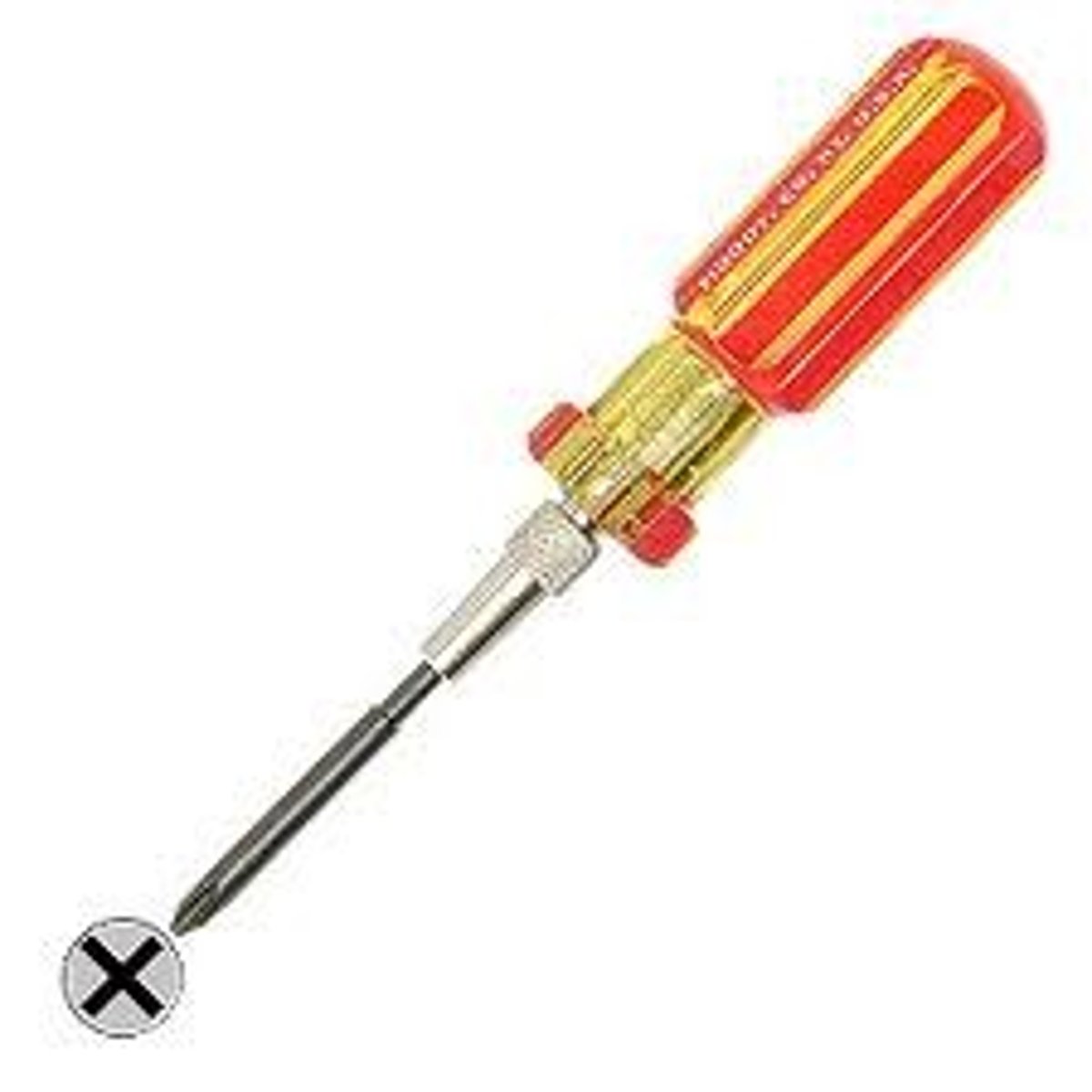
Phillips Screwdriver
has an X-shaped tip and is used to turn Philips-head screw only

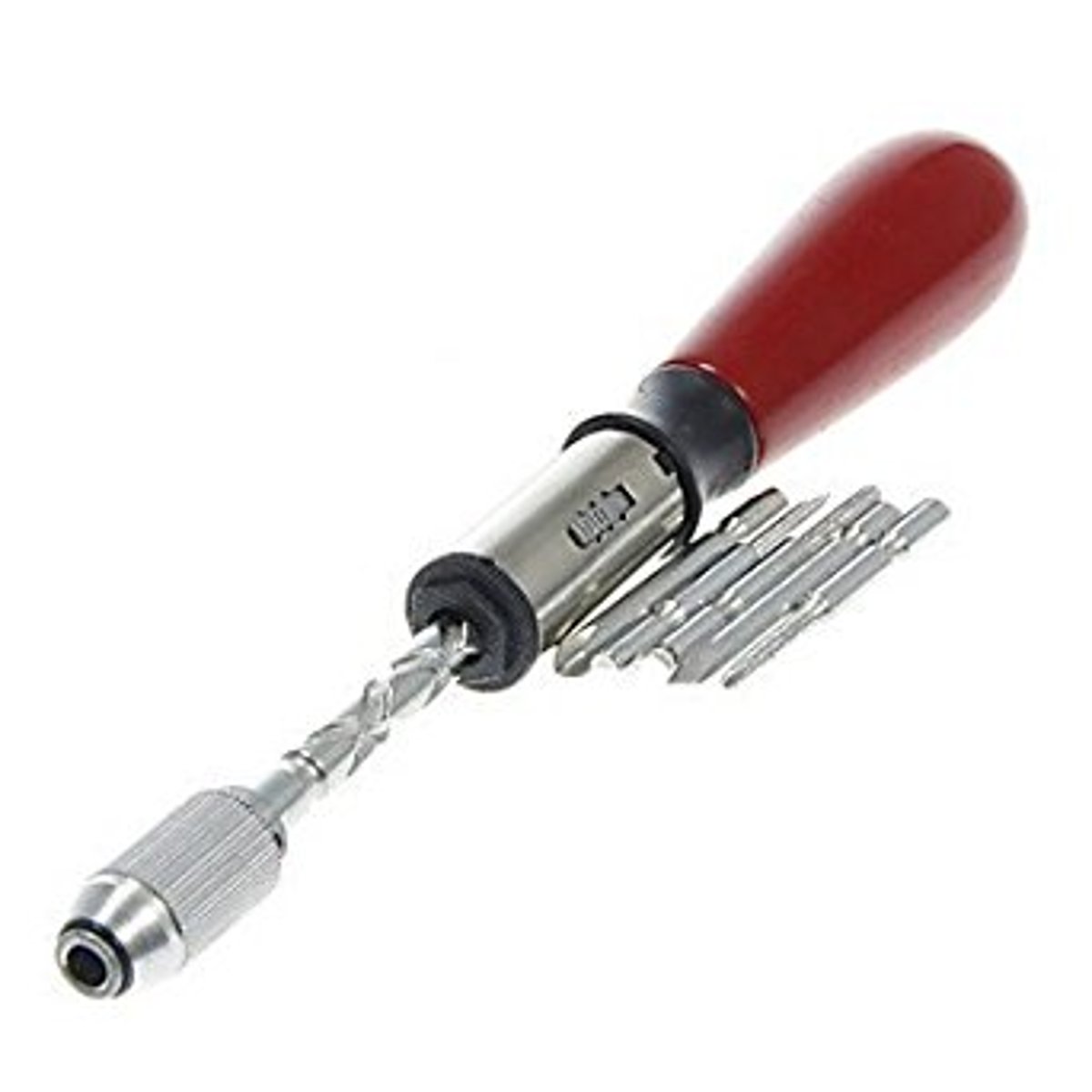
Spiral Ratchet Screwdriver
is that which relies on a pushing force rather than a twisting force

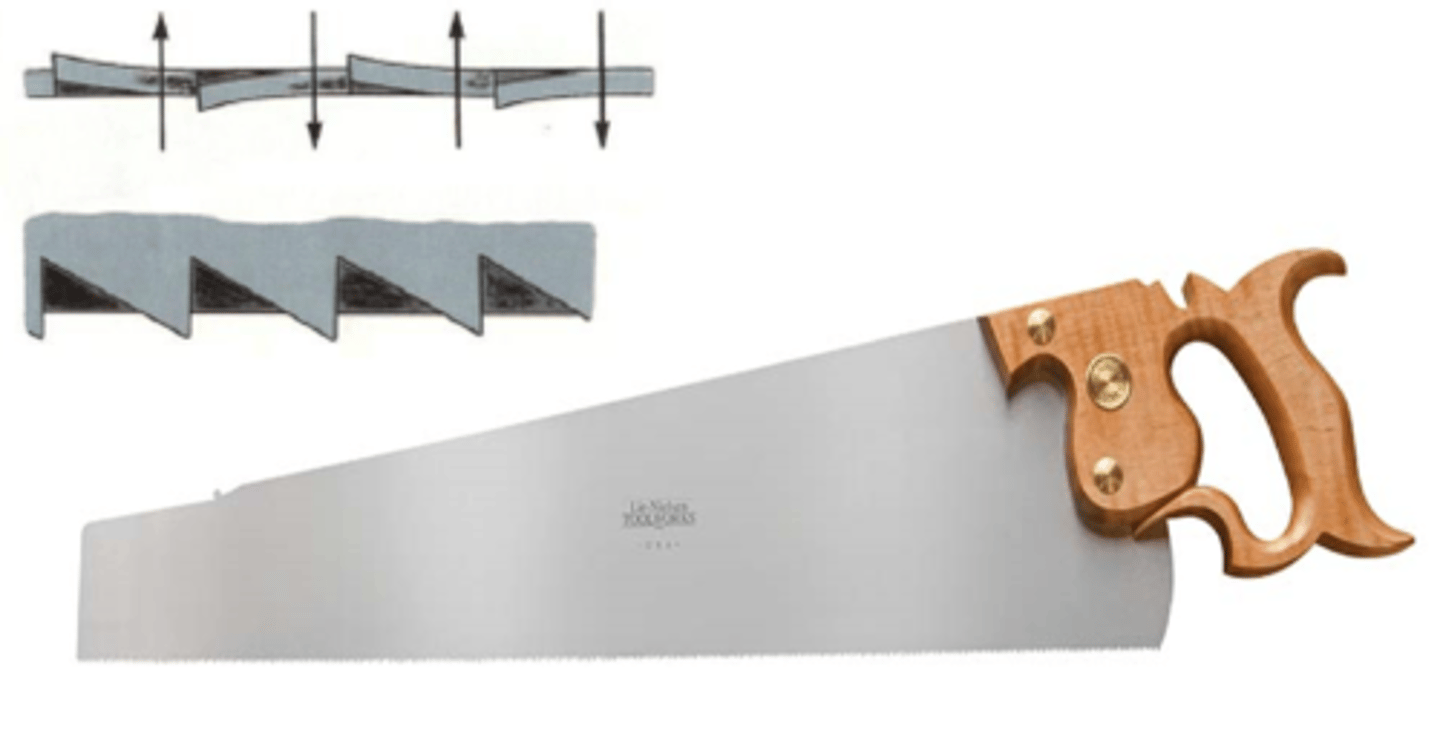
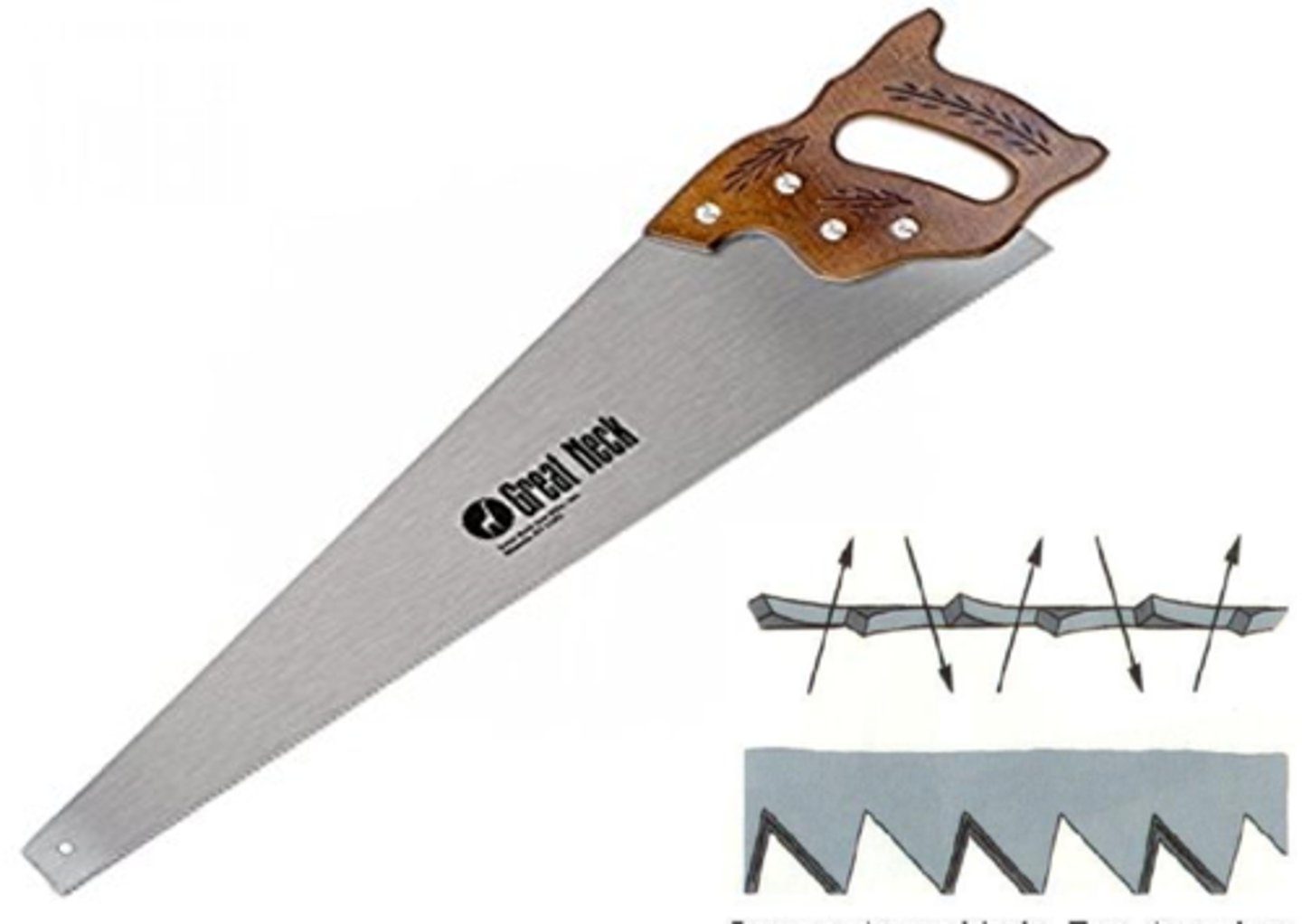
Ripsaw
has chisel-like teeth designed for ripping or cutting with the grain of wood

Crosscut saw
is used to cut across the grain of wood

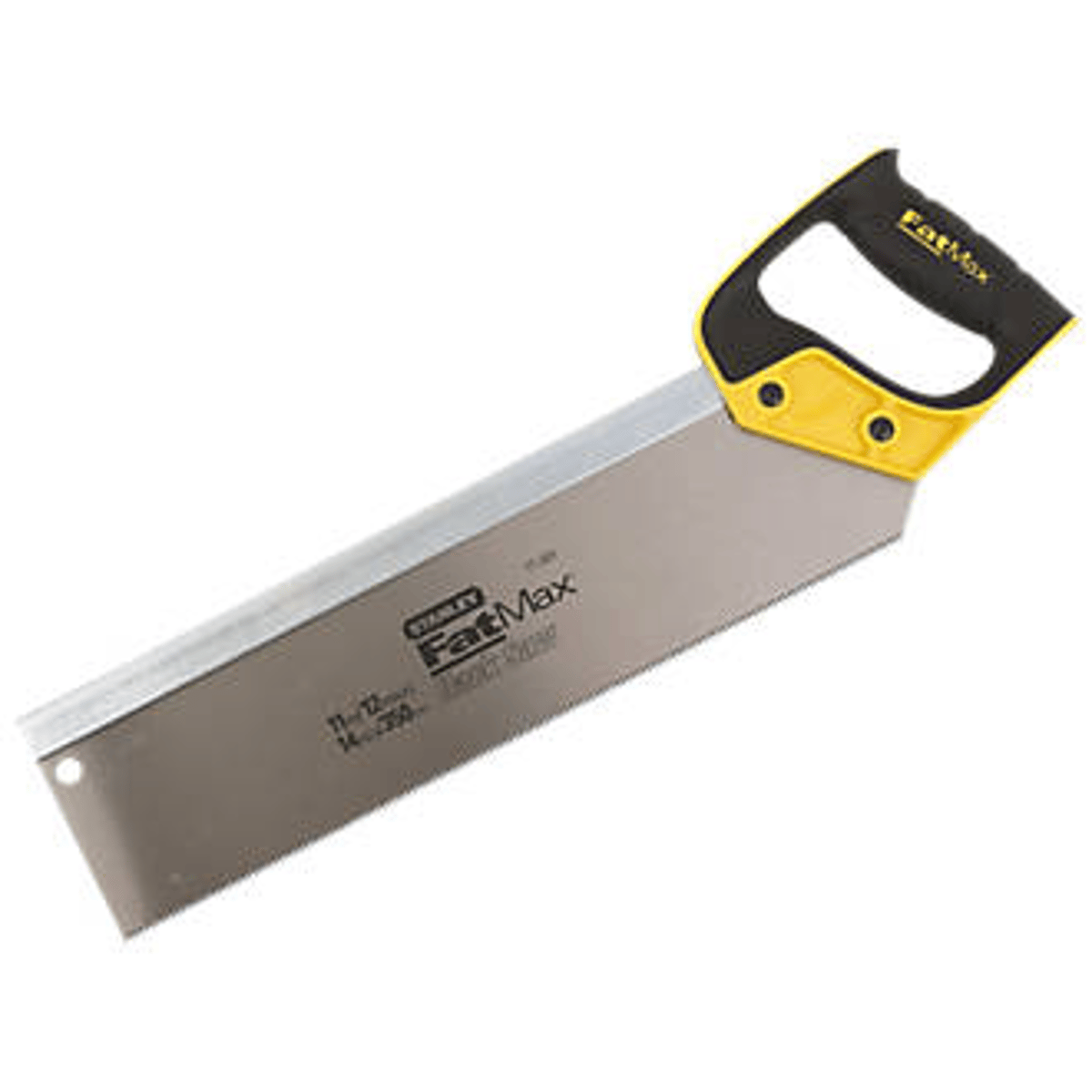
Backsaw
is a special type of handsaw that has a very thin blade and makes very straight cuts such as those on trims and mouldings

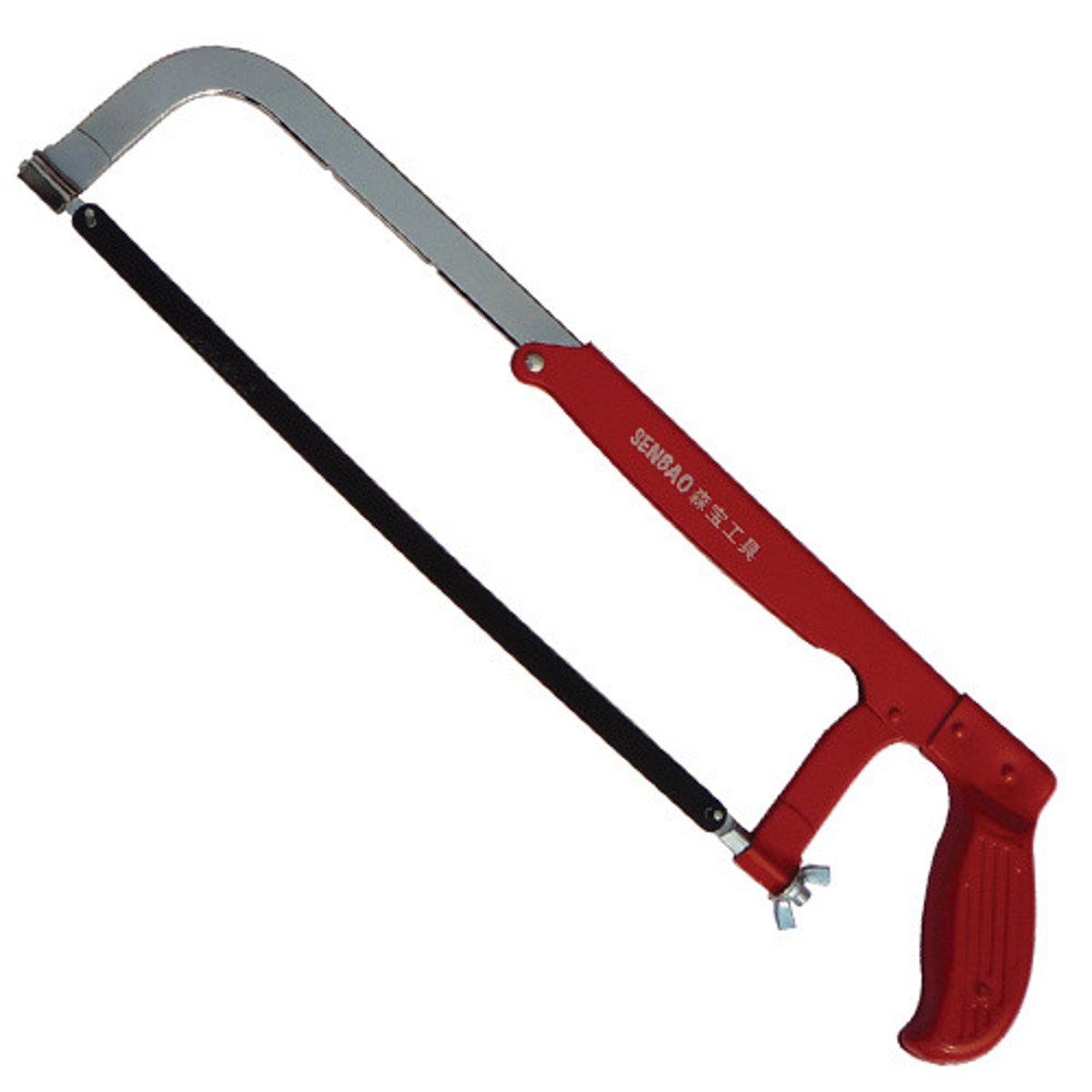
Hacksaw
is used to cut metals

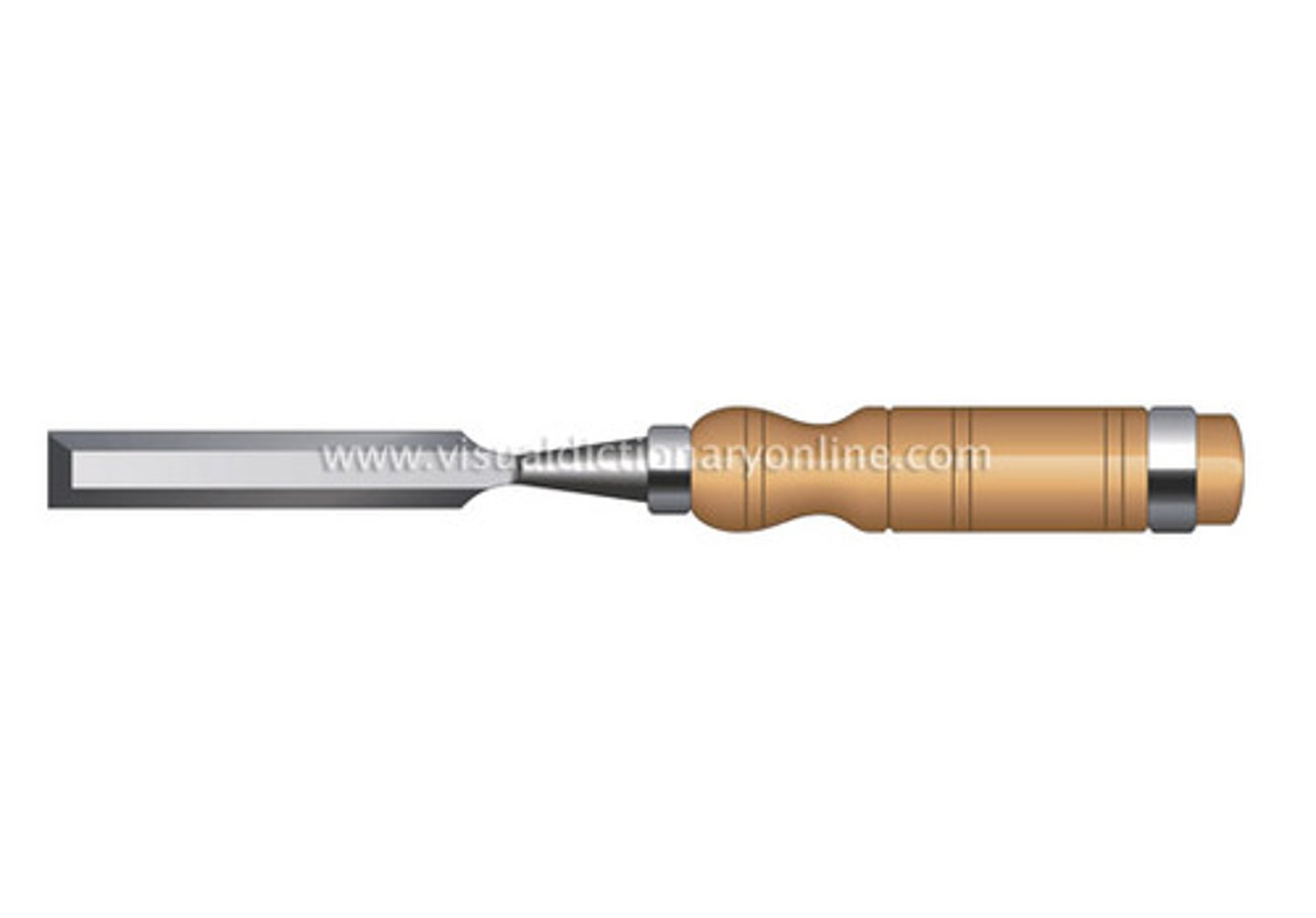
Wood Chisel
is used to trim wood and clear away excess material from wood joints

Cold Chisel
is used to trim metals
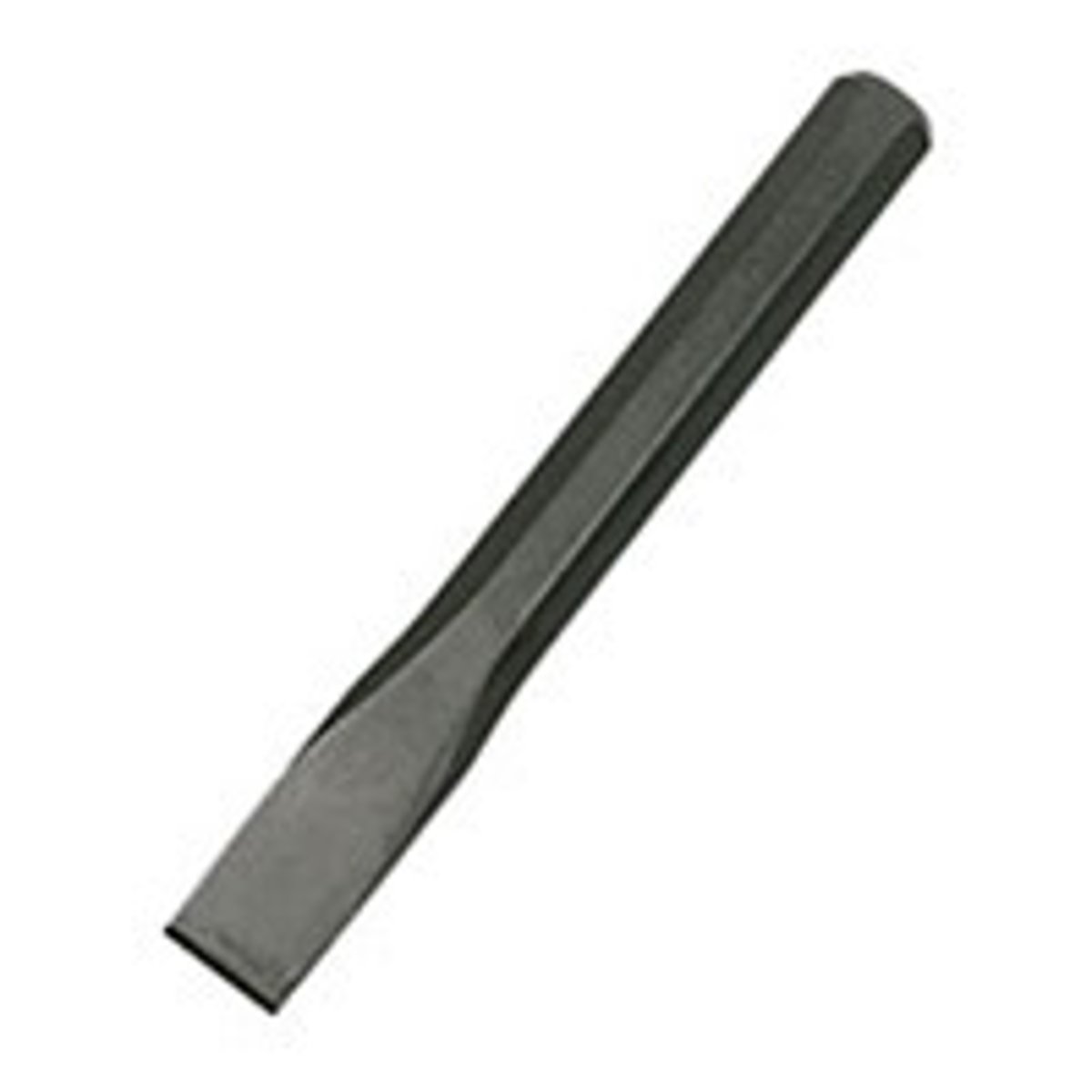

Nail Set
is used to drive finishing nails below the surface of a wooden trim or molding
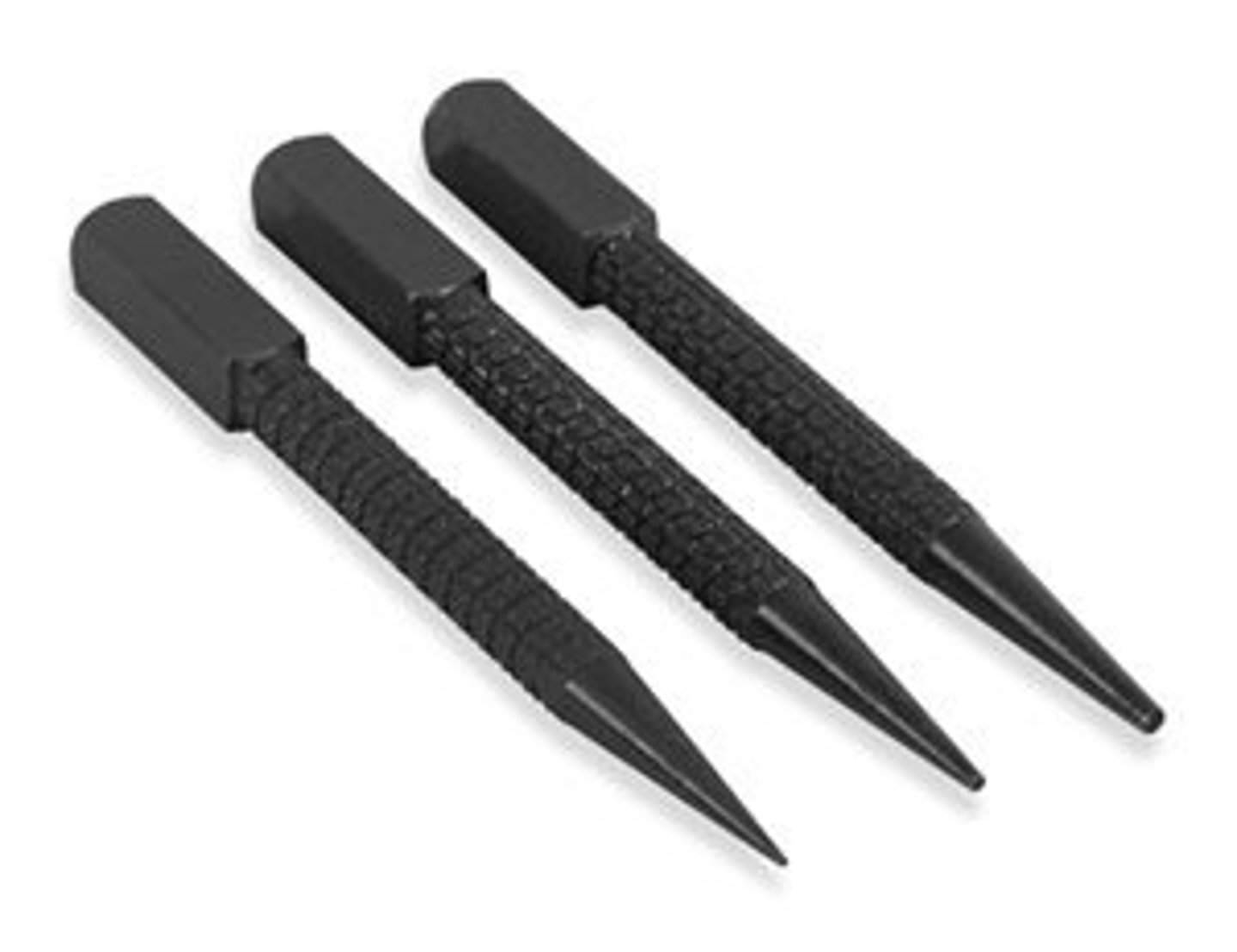

Pipe Wrench
is used to turn round objects like pipes
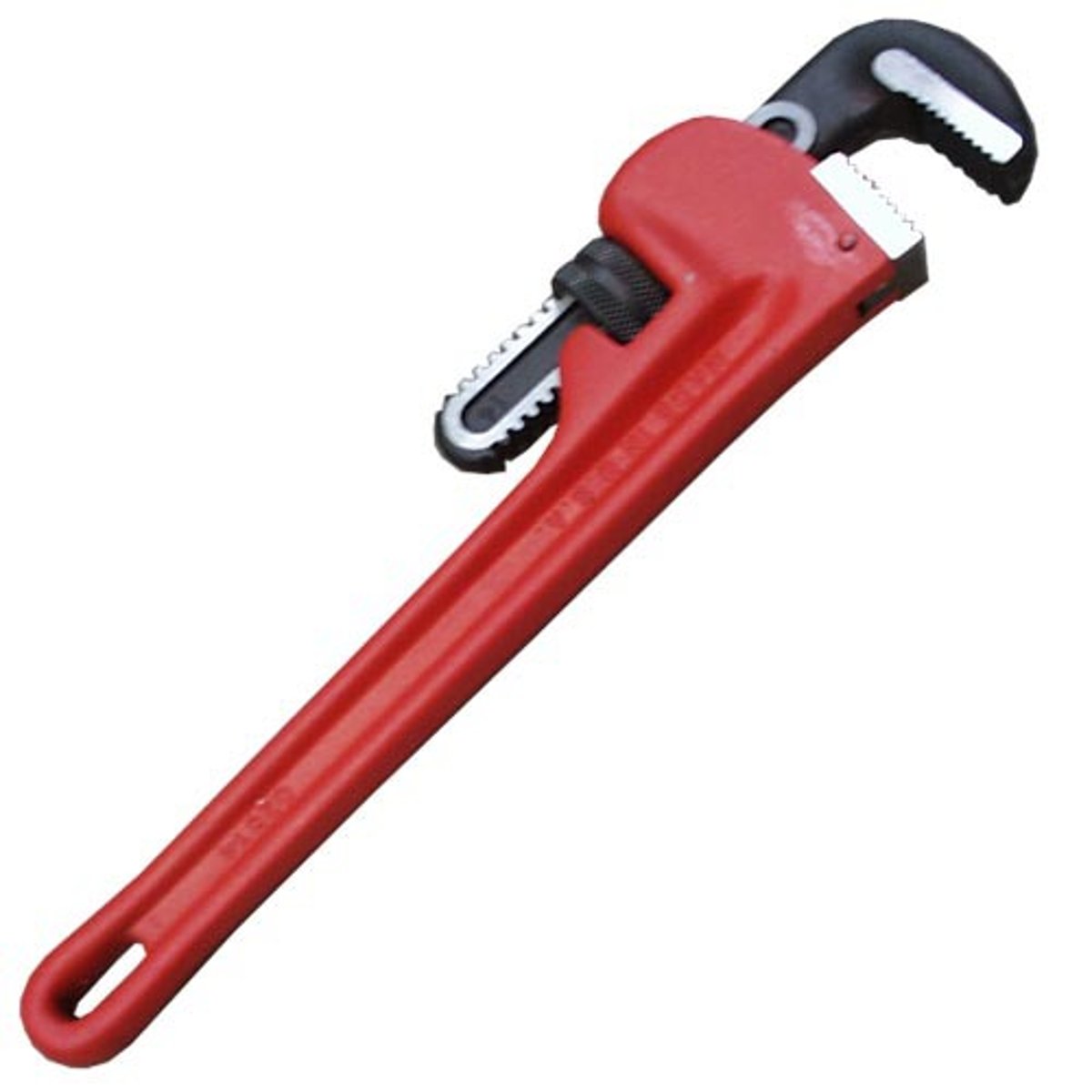

Brick Trowel
is used to place and trim mortar between bricks and concrete blocks

Bull Float
is used to smoothen out the surface of wet concrete

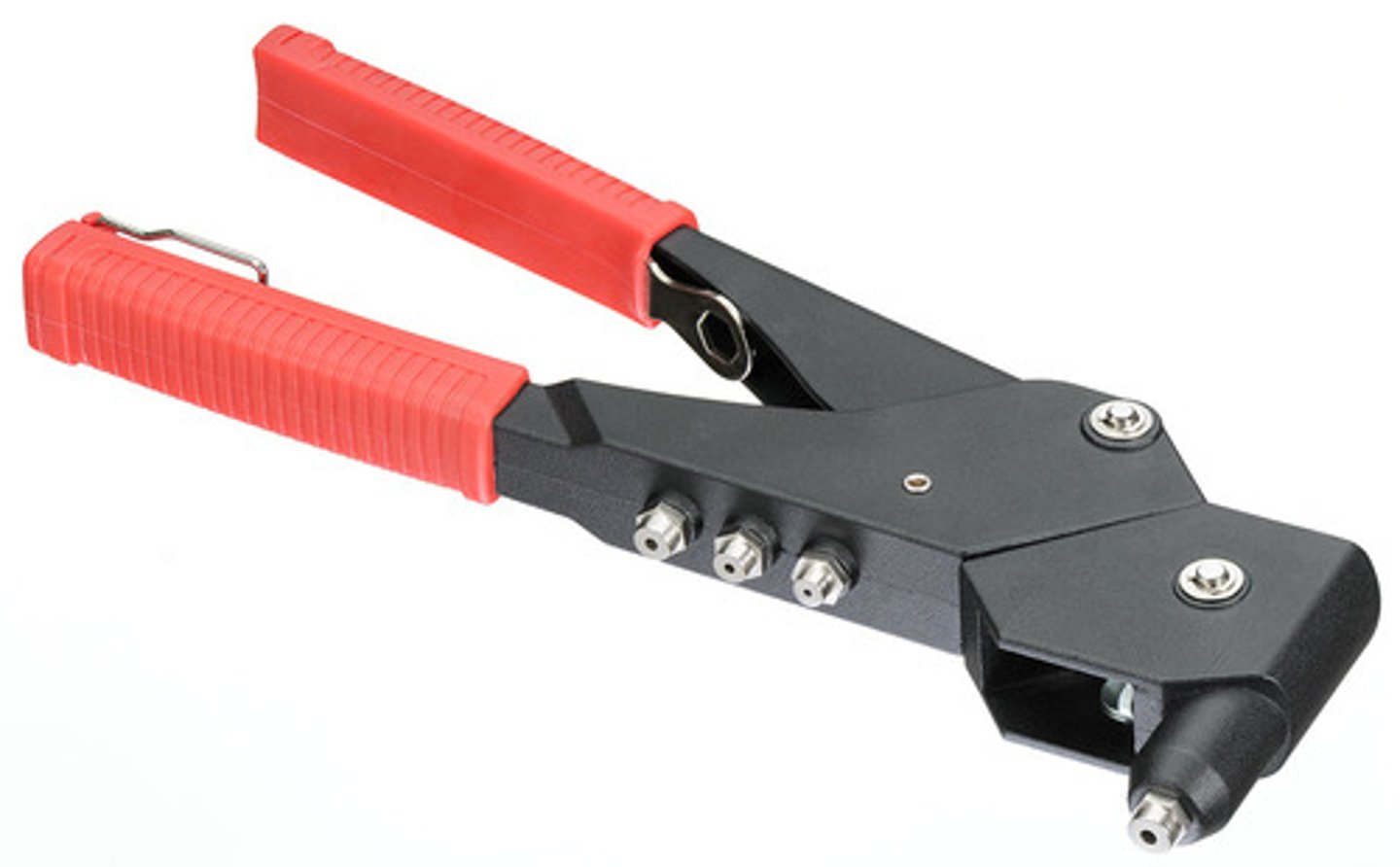
Blind Riveter
is used to fasten pieces of sheet metal together

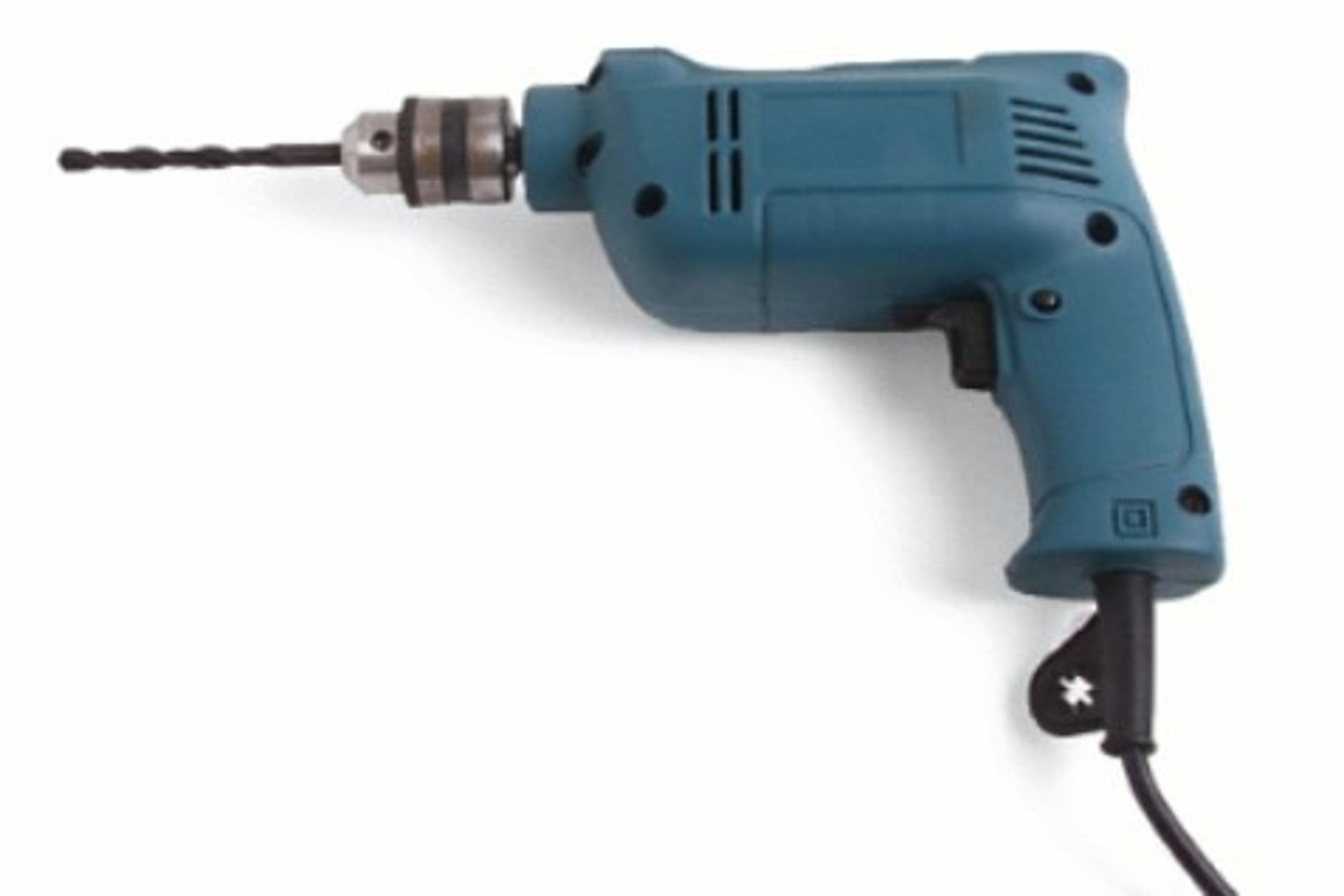
Power Drill
is used to drill holes in wood, metal, and concrete

Power Screwdriver
also known as "screw gun", used to install and remove screws

Radial Arm Saw
is used for crosscutting wood and consists of a motor-driven saw blade that is hung on an arm over a table

Table Saw
is used for cutting large sheets of wood and wood composites and consists of a blade mounted on an electric motor beneath a table-like surface

Portable Circular Saw
is used for cutting materials that are difficult to cut with stationary tools

Power Miter Saw
is a circular saw mounted over a small table used to cut various angles in wood

Saber Saw
is used to cut curves or holes in floors and roofs for pipes and has a small knife-shaped blade that moves up and down

Pneumatic Hammer
Also known as "Jackhammer", is used to break up concrete or asphalt paving

Rotary Hammer
is like an electric drill that operates with both rotating and reciprocating actions and is used to drill holes in concrete

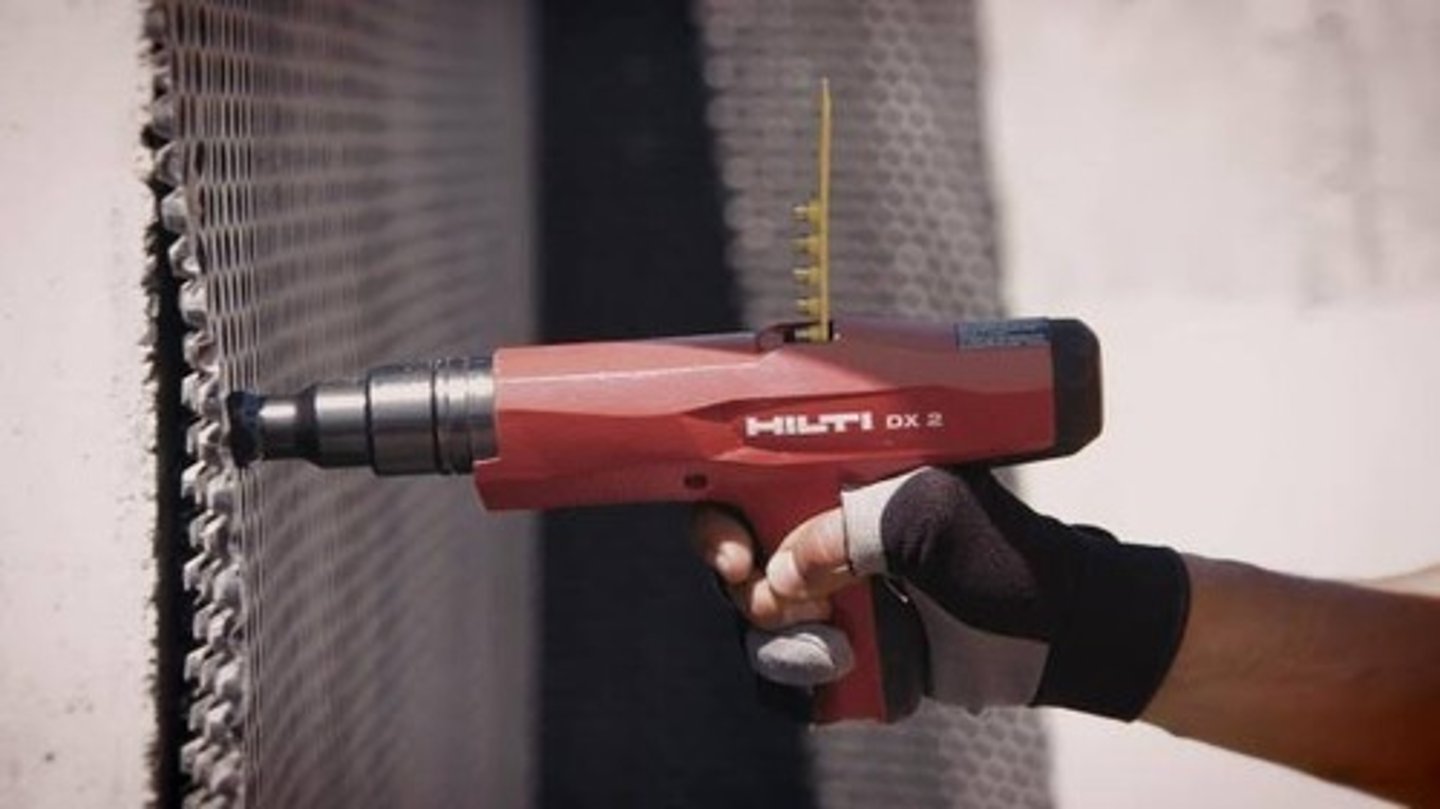
Nailers
Also known as "nail guns", fastens materials together by shooting nails into the building material

Powder-actuated stud driver
is a kind of nailer that is powered by gunpowder and is used to drive long pins into wood, steel or concrete.

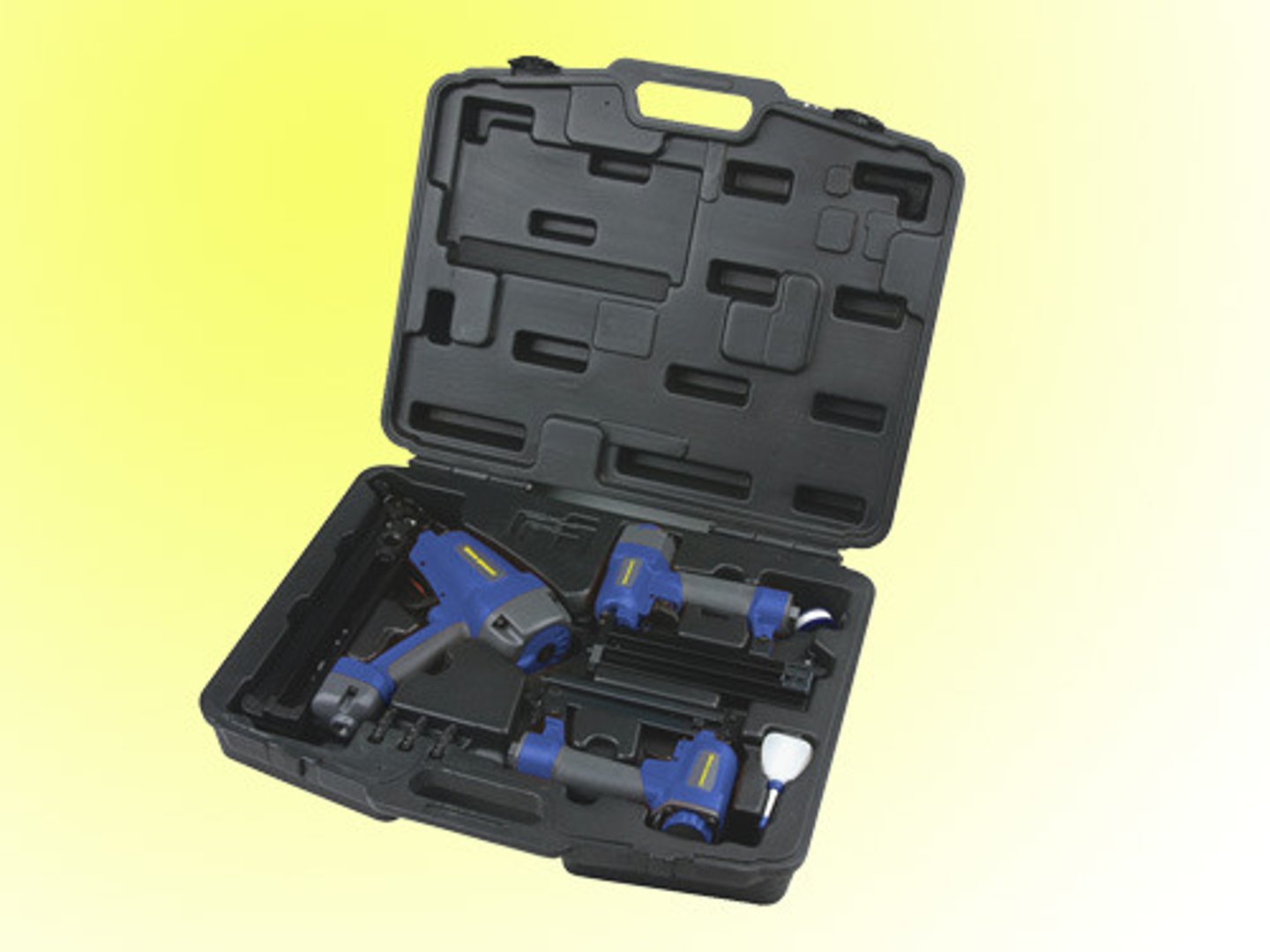
Staplers
are like nailers but are loaded with u-shaped staples instead of nails for fastening

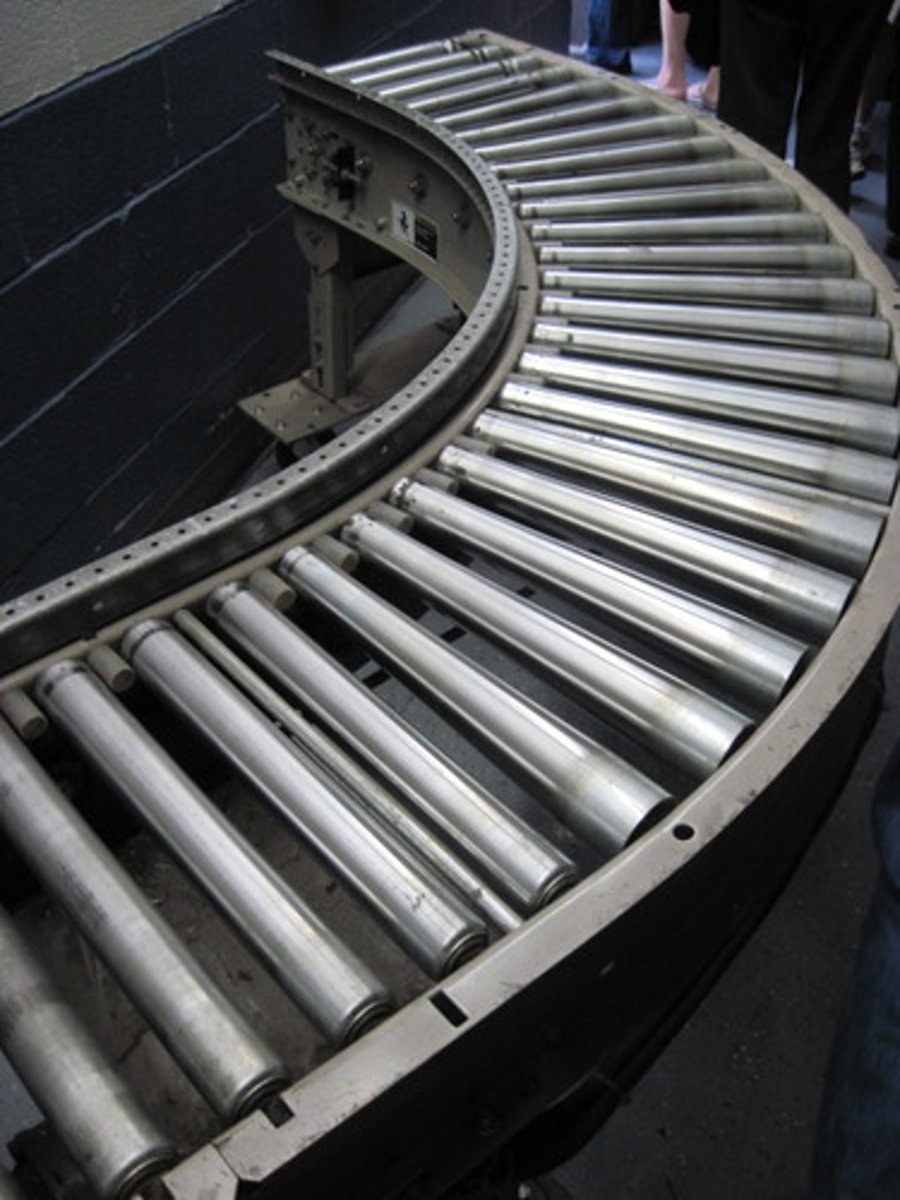
Conveyor
is an equipment which moves materials other than fluids

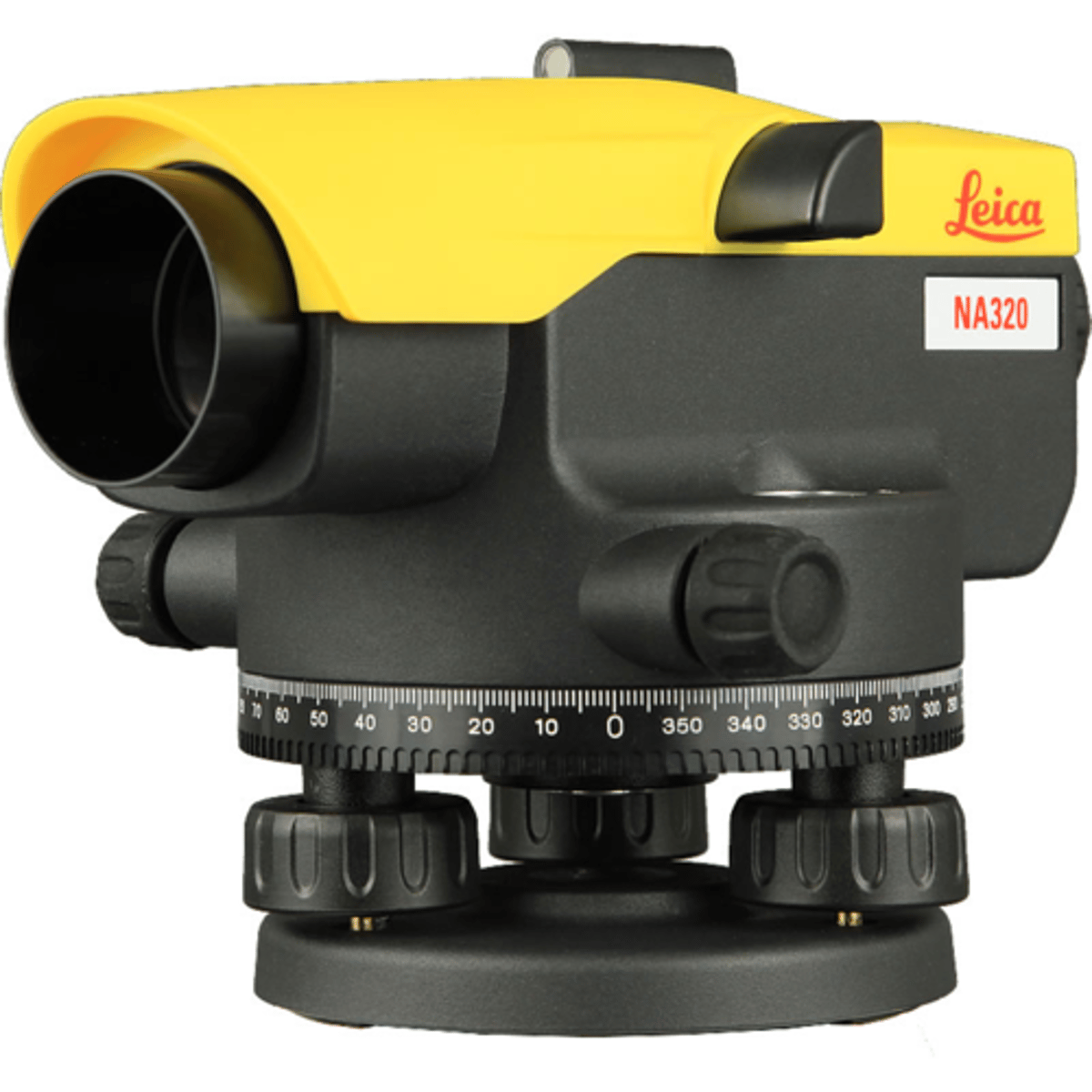
Transit
is an equipment used by surveyors to measure horizontal and vertical angles to obtain land elevation.
Surveyor's Level
is that which to determine an unidentified elevation from a known one

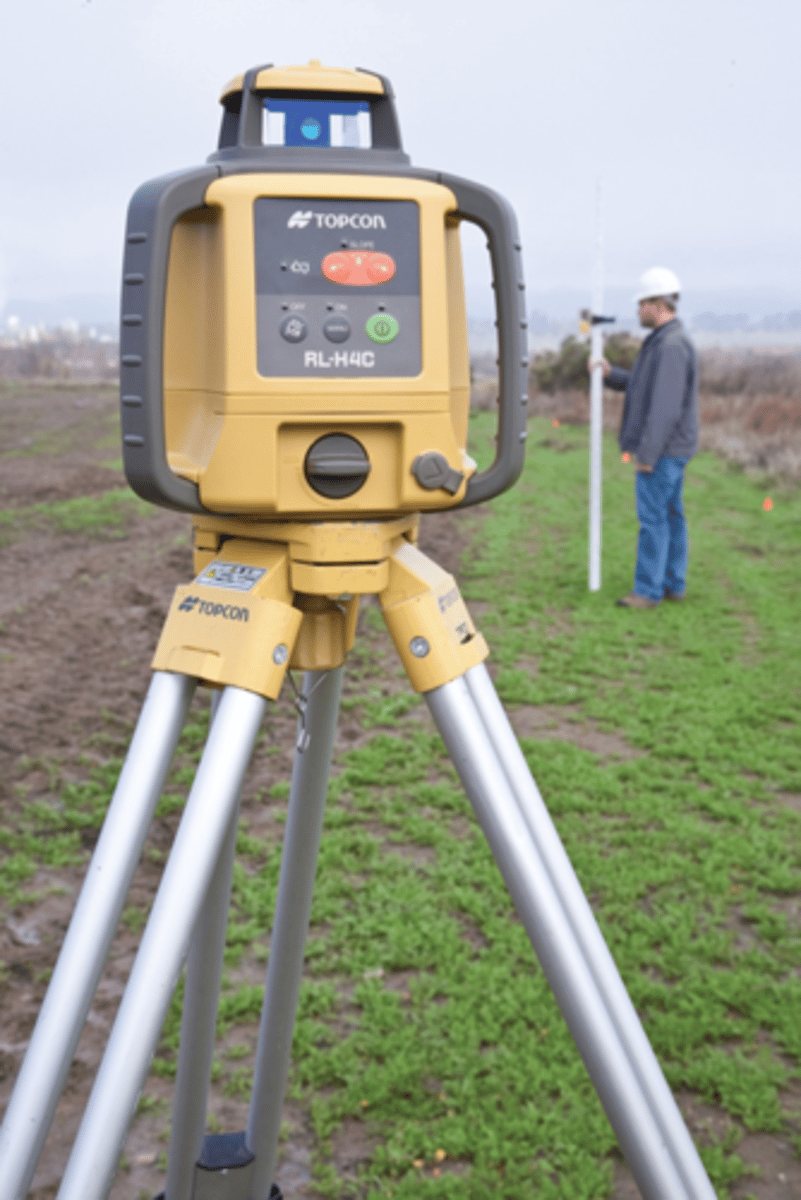
Construction Laser
flashes a narrow, accurate beam of light to make a baseline for additional measurements and is used as a level or as an alignment tool

Water Pump
is used to pump water out of holes in the ground so that construction work can commence
Concrete Pump
is used to move concrete from the concrete mixer to the concrete form.
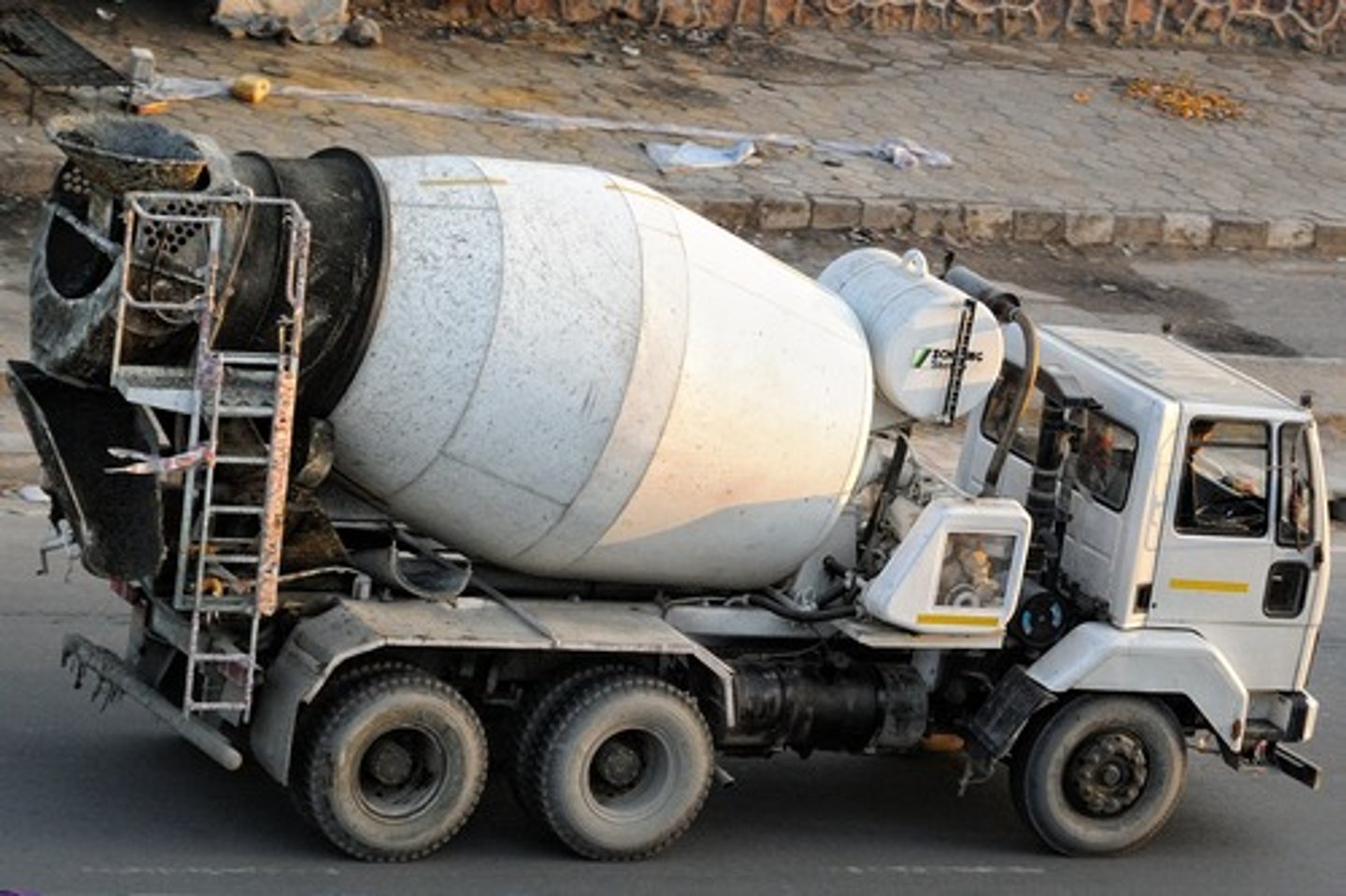
Concrete Mixer
a machine that mixes concrete ingredients by means of a rotating drum. raw materials are introduced into the mixing drum through its open end and discharged by tilting the mixing drum to allow the concrete to pour out

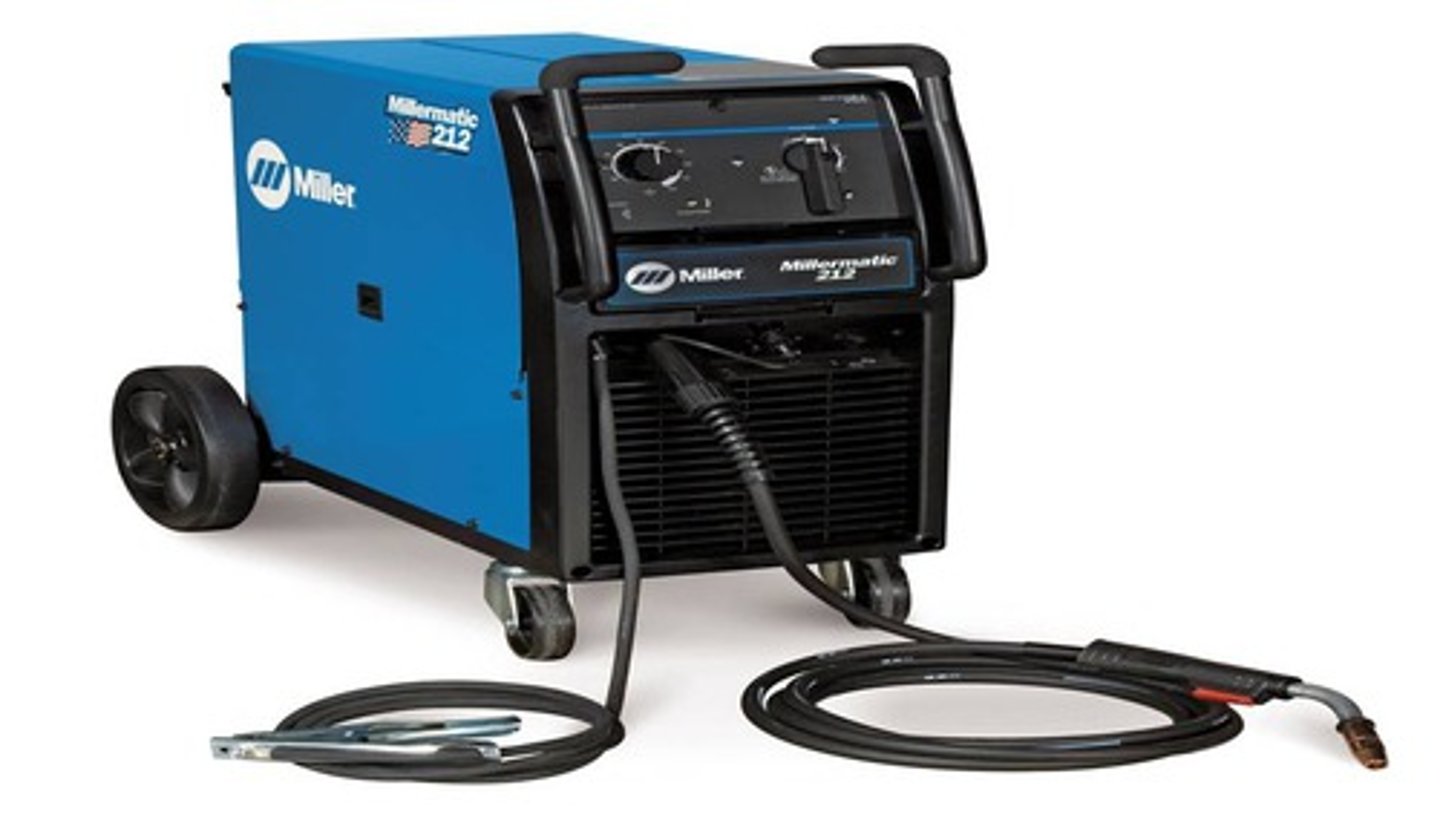
Arc Welding Machine
is used to weld materials by melting portions of the metal

Laser-powered Welder
is used to weld material by employing a laser to heat the metal
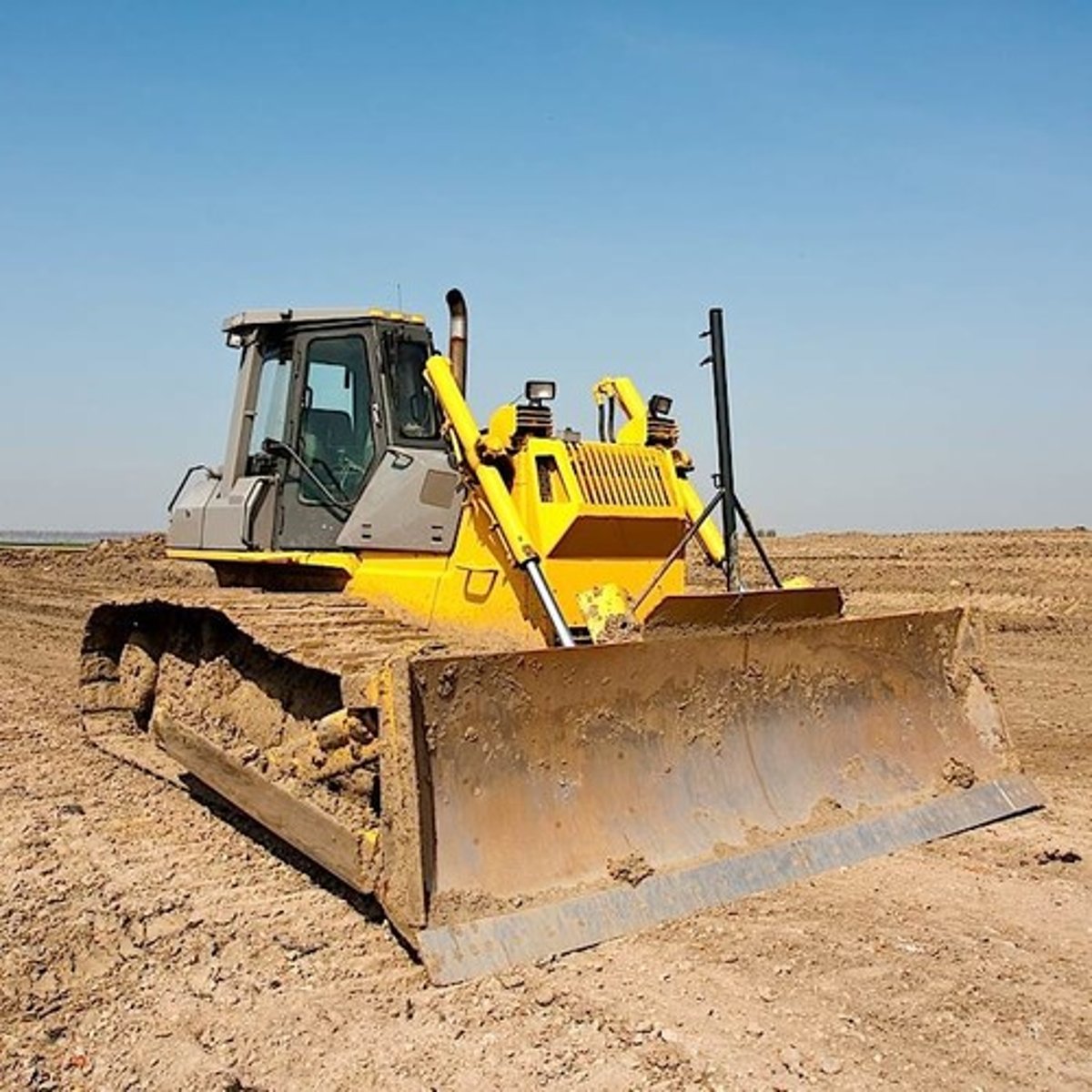
Bulldozer
is a tractor with a pushing blade which moves earth and clears land of bushes and trees

Cranes
are machines that lift large and heavy materials

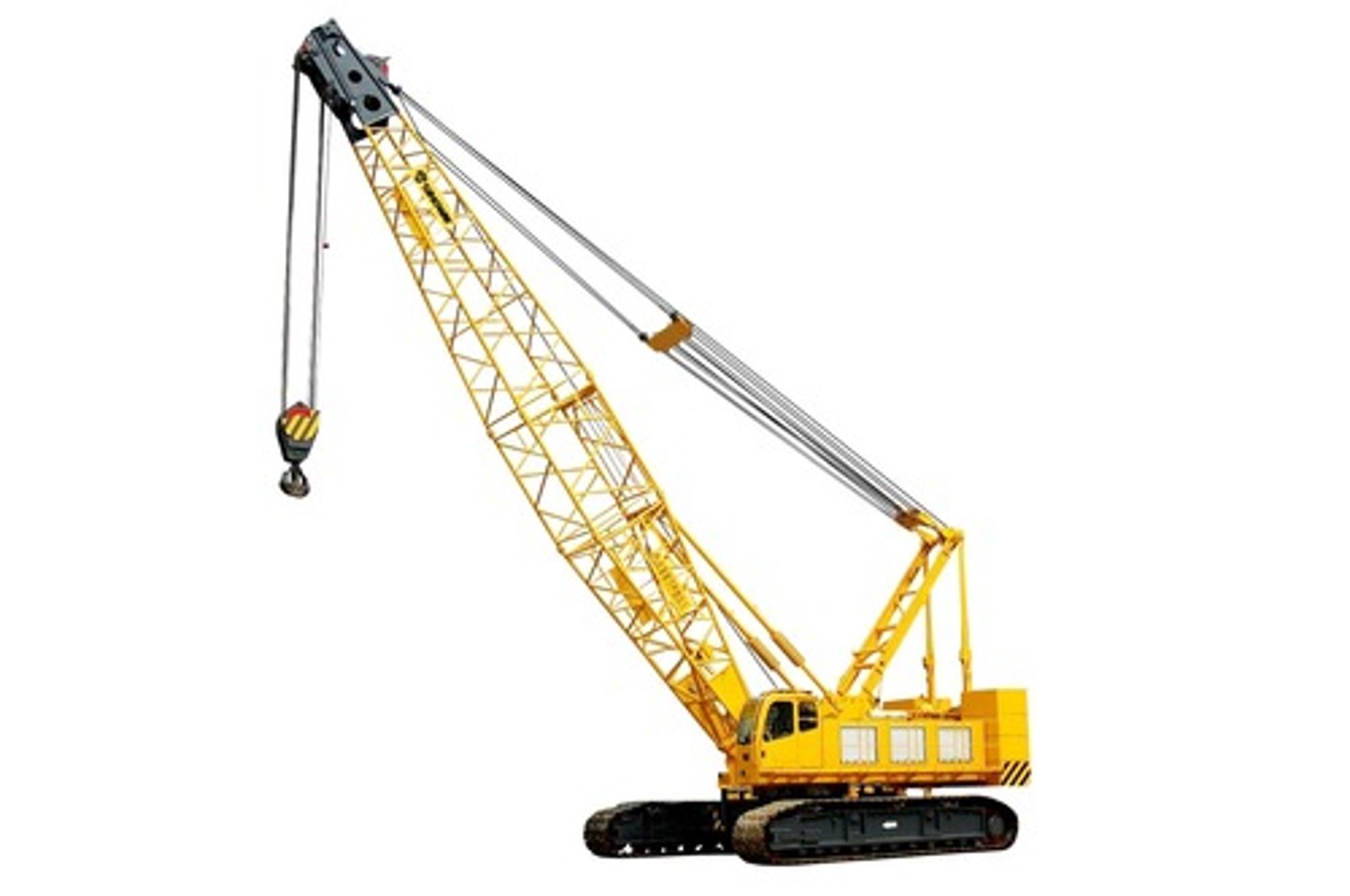
Crawler Crane
is a crane mounted on metal treads so that it can move over rough terrain

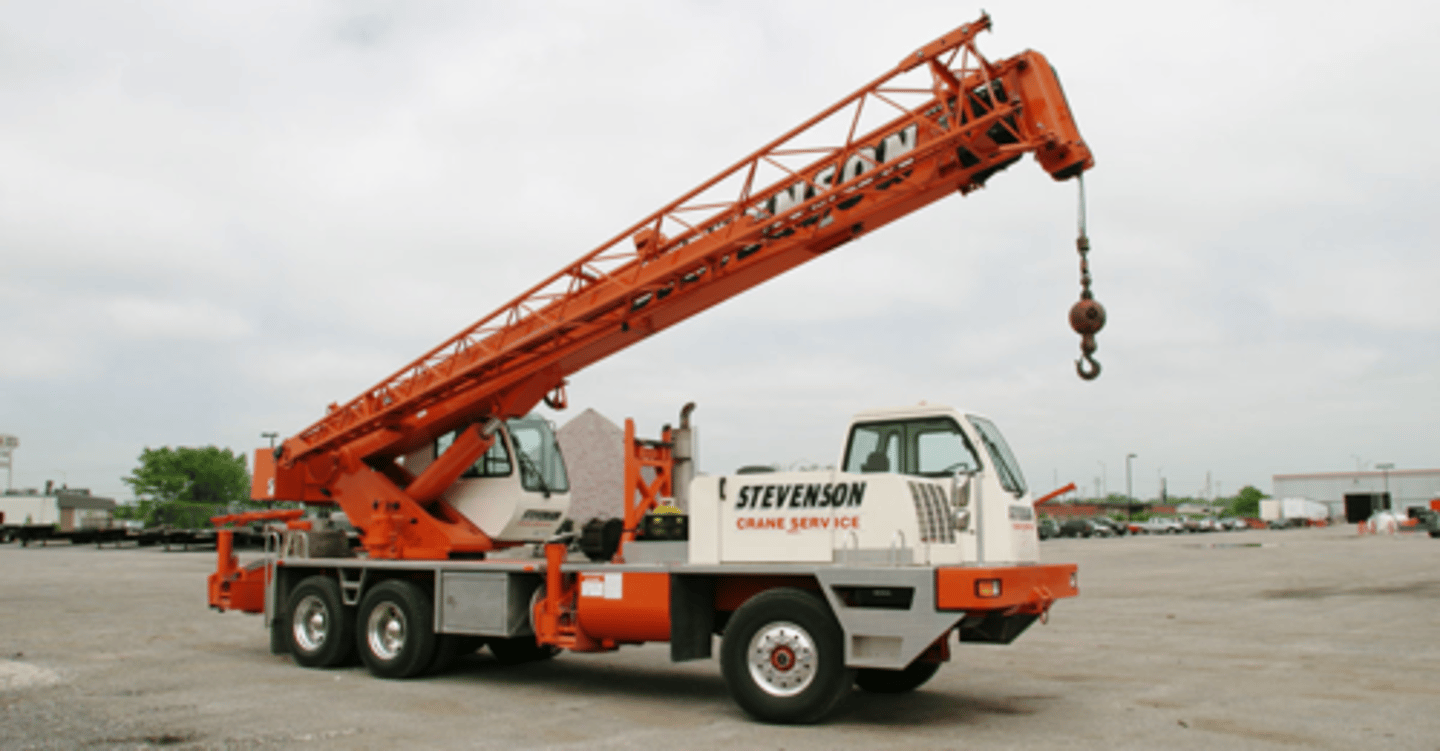
Truck Crane
is mounted on a truck frame so that it can be driven in the site

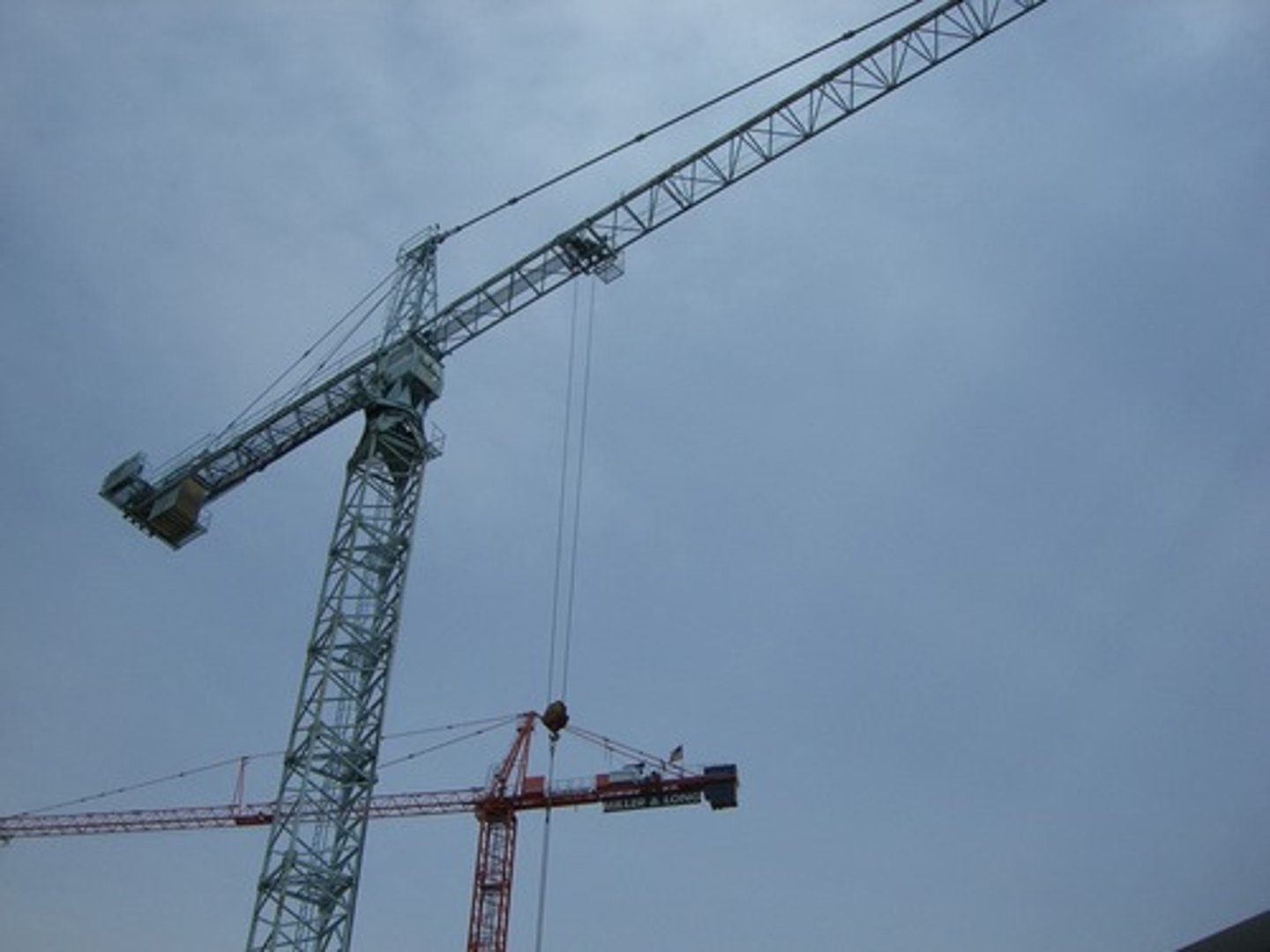
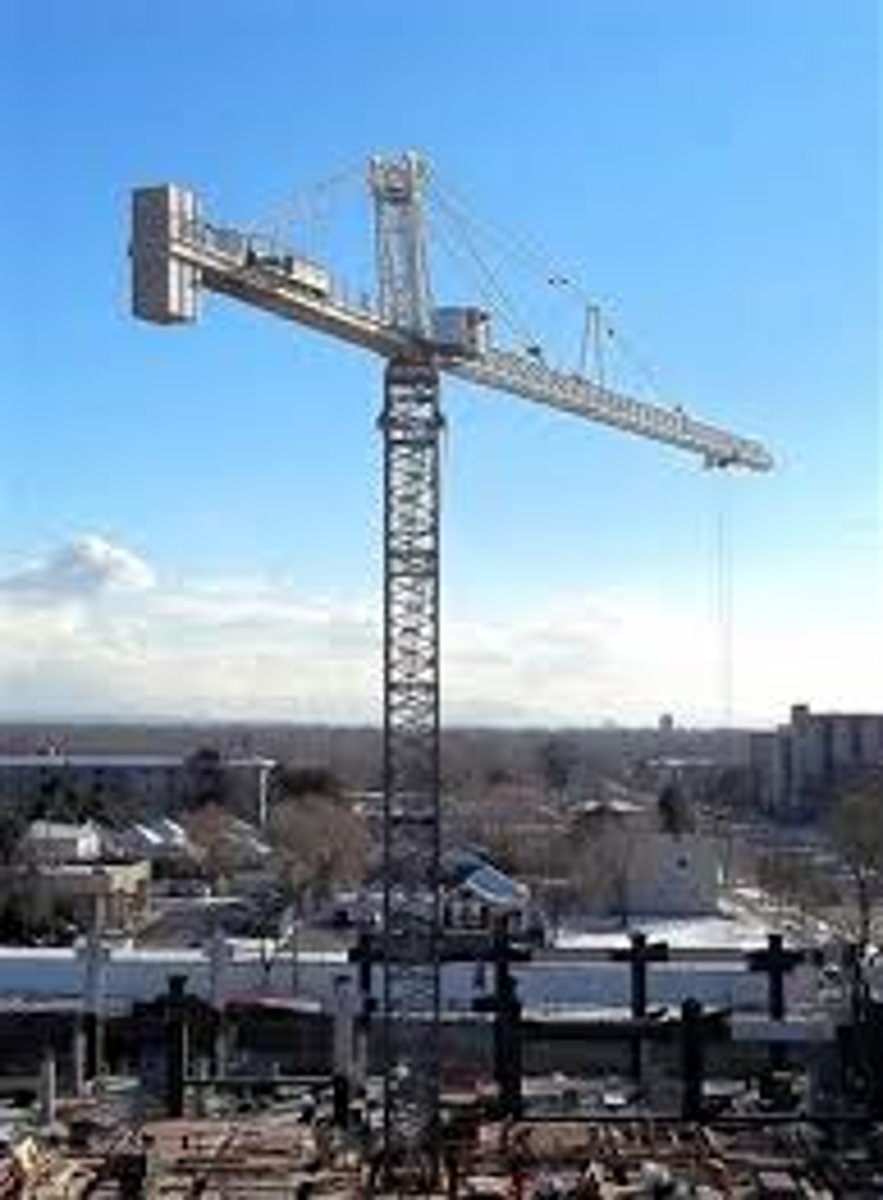
Tower Crane
Also known as "climbing crane", used in the construction of tall buildings because it has a built-in jack that raises the crane from floor to floor as the building is constructed

Excavator
is a machine used for digging or scooping earth from a place and depositing it in another
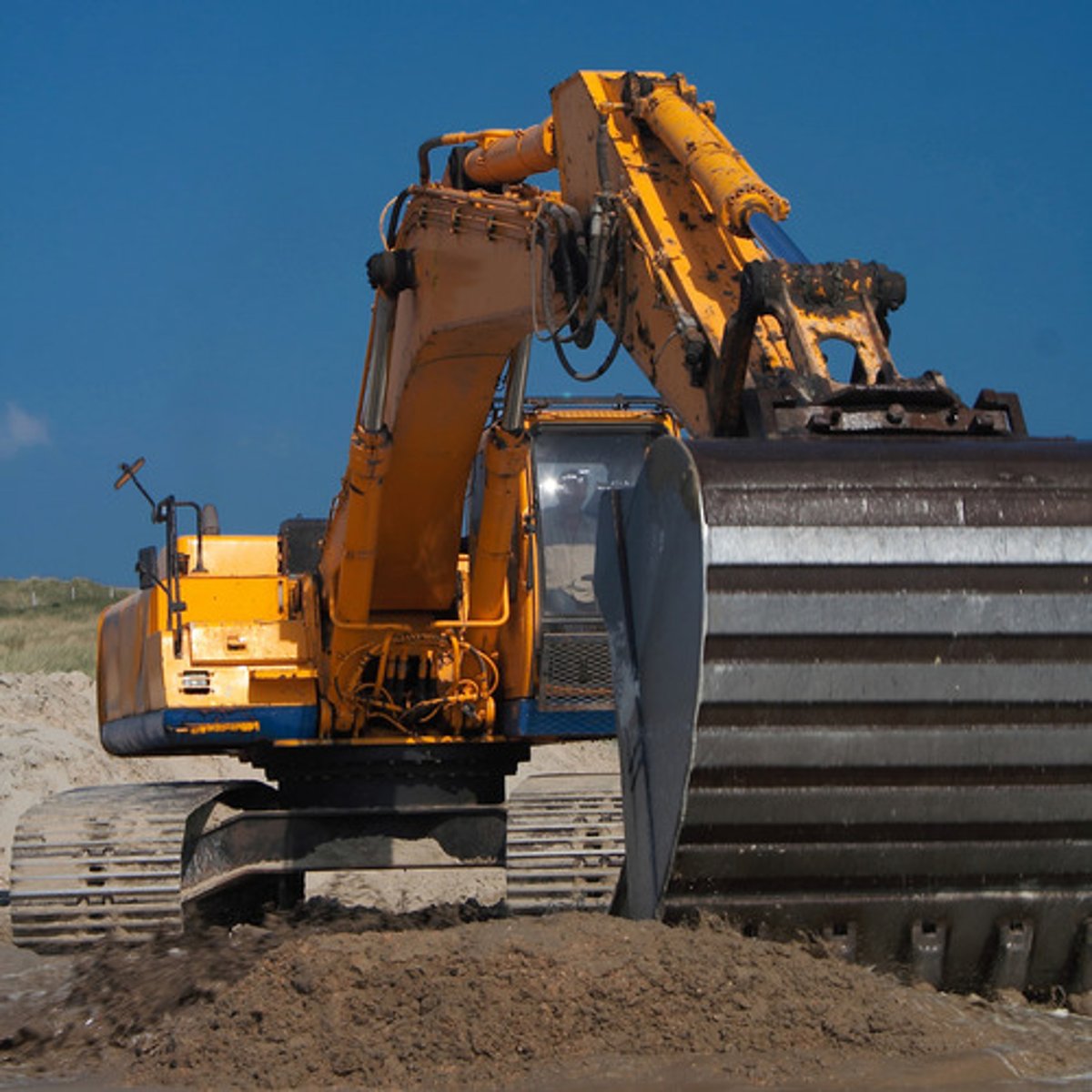

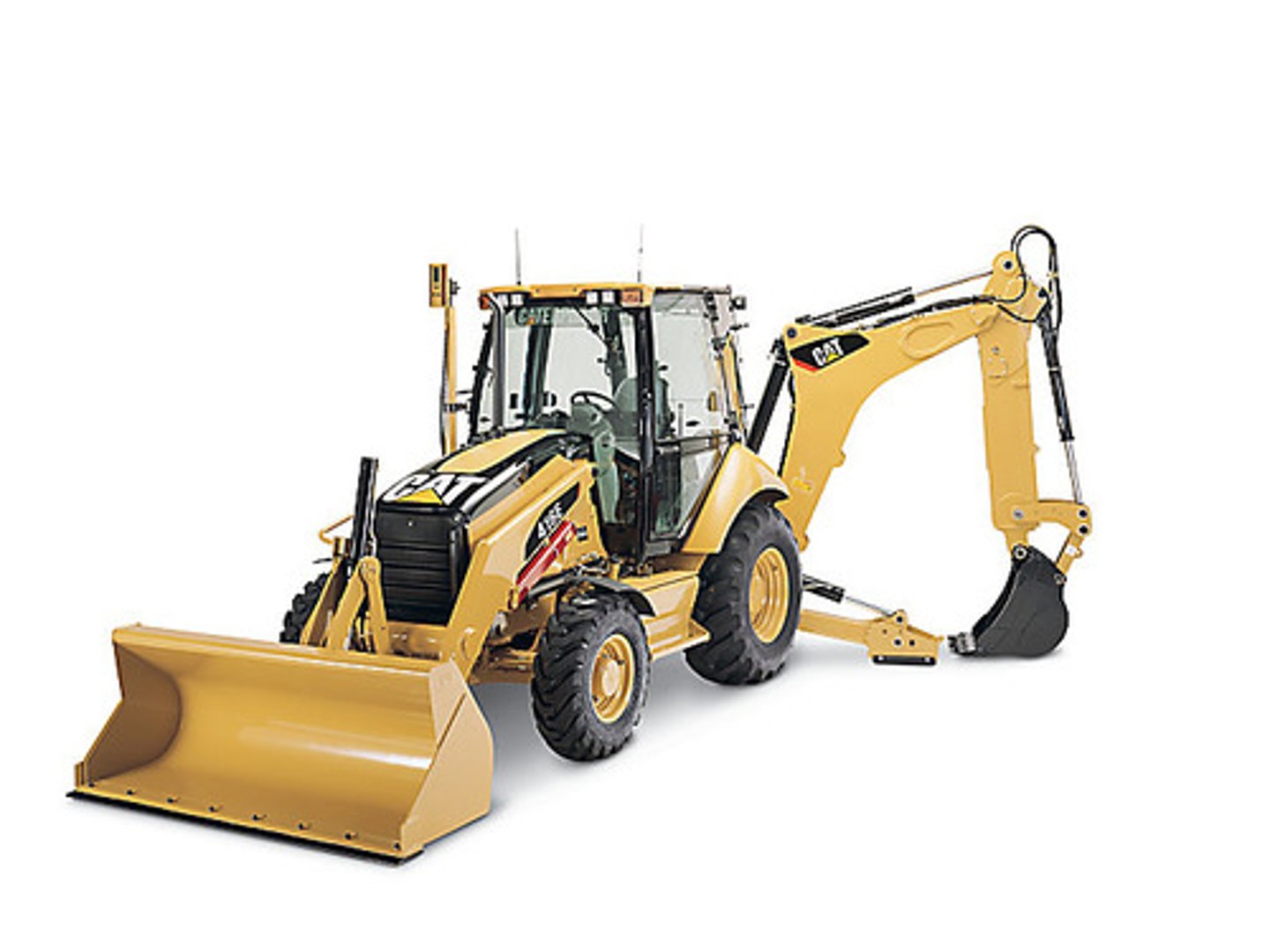
Backhoe
is used for general digging which is usually mounted on either a crawler or truck frame

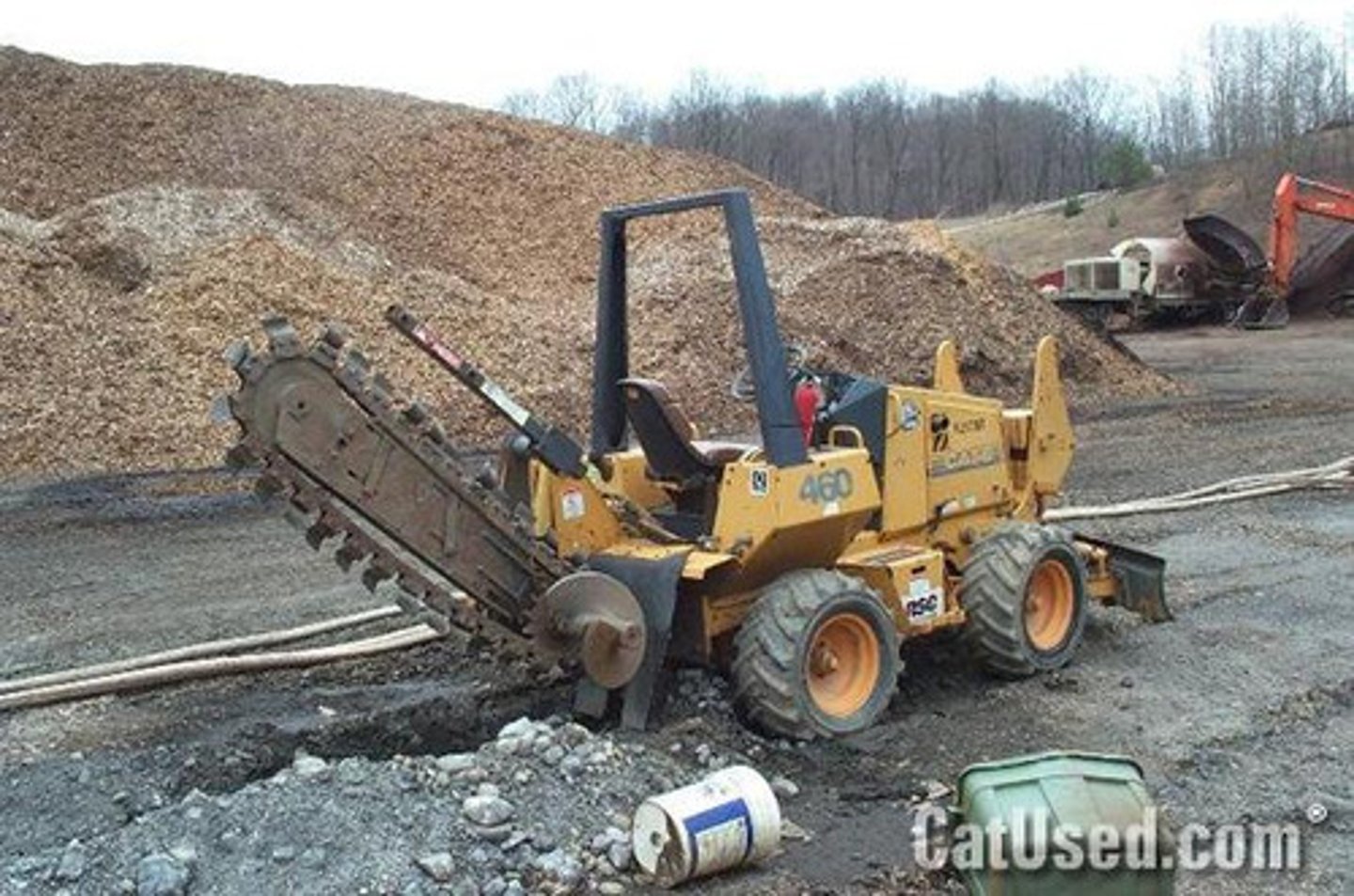
Trencher
is a special kind which digs trenches or long, narrow ditches for pipelines or cables

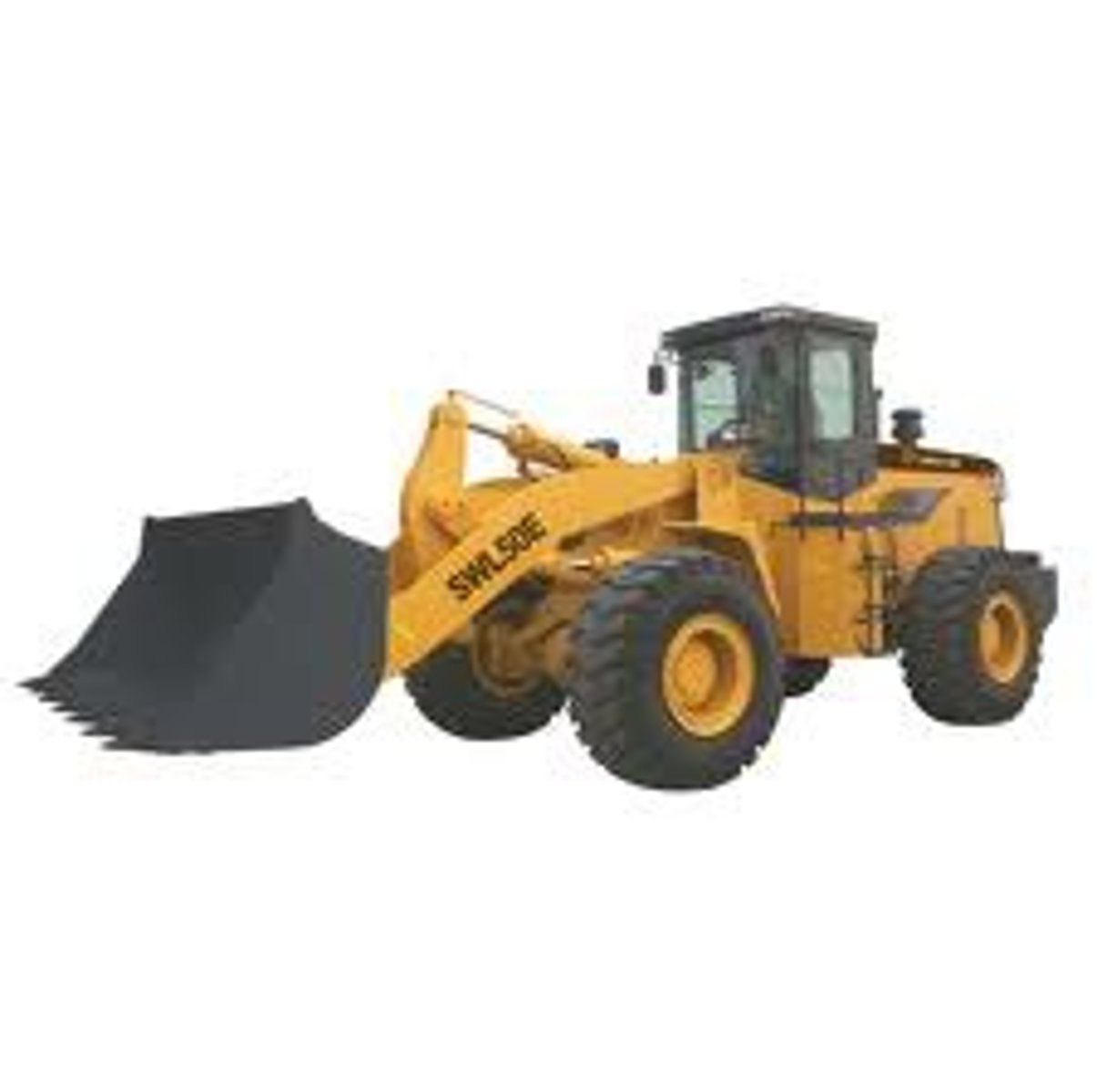
Front-end Loader
is a large shoveling machine that can scoop or deposit a large amount of material

Scraper
is a machine that loads, hauls and dumps soil over medium to long distances
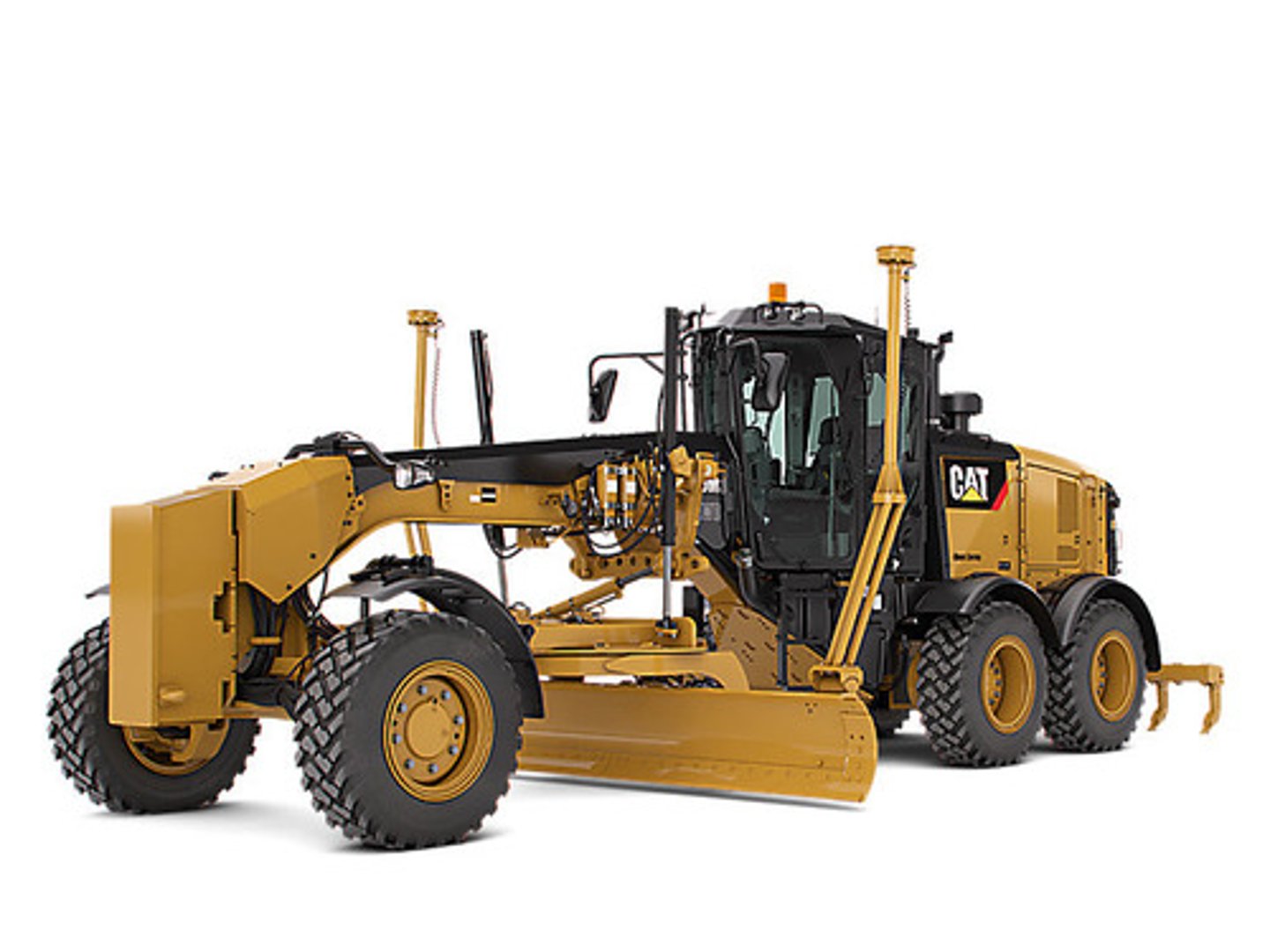
Grader
is an earth working machine that grades or levels the ground

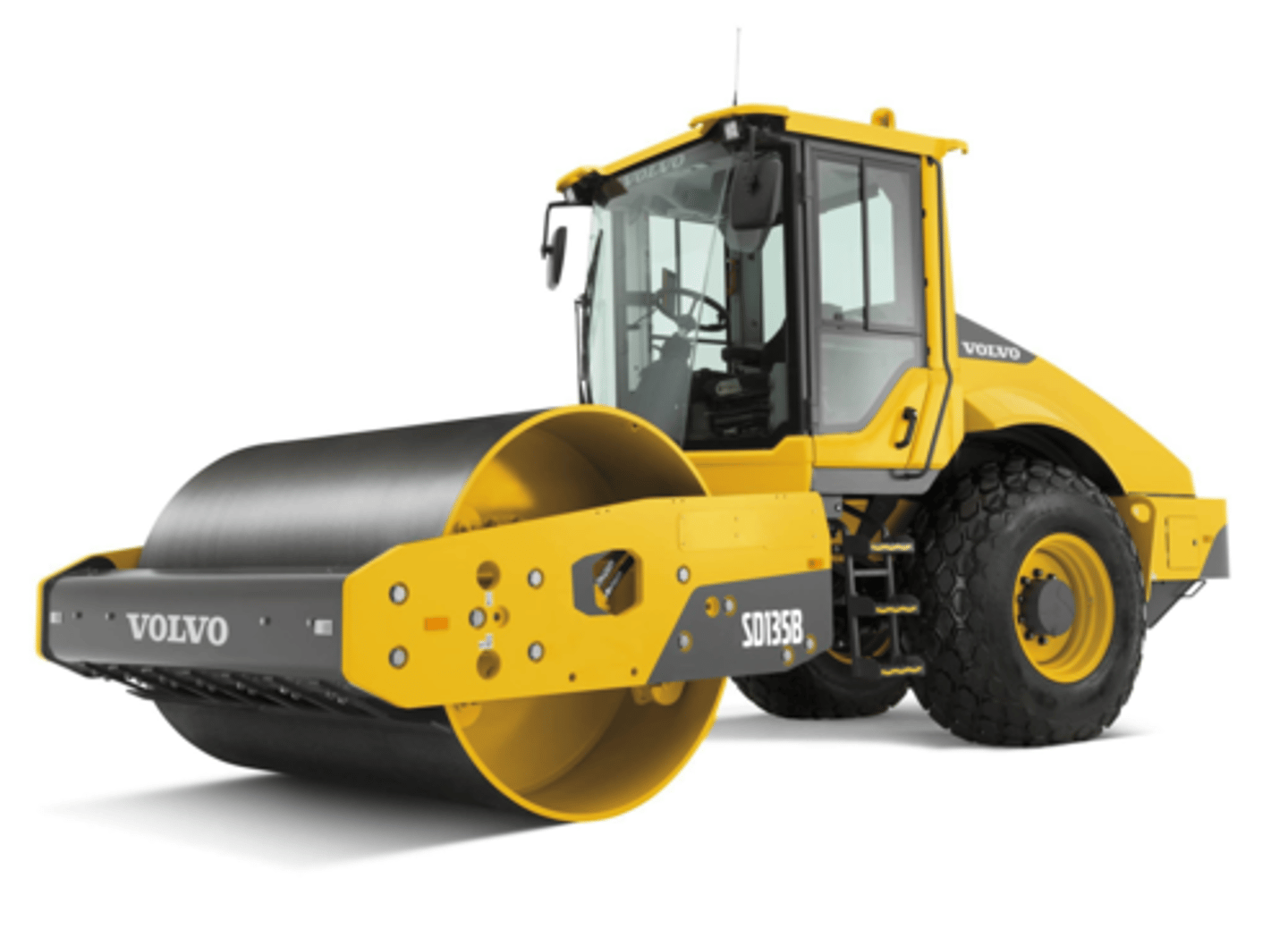
Compactor or roller
is a machine that compacts soil to prepare for road paving

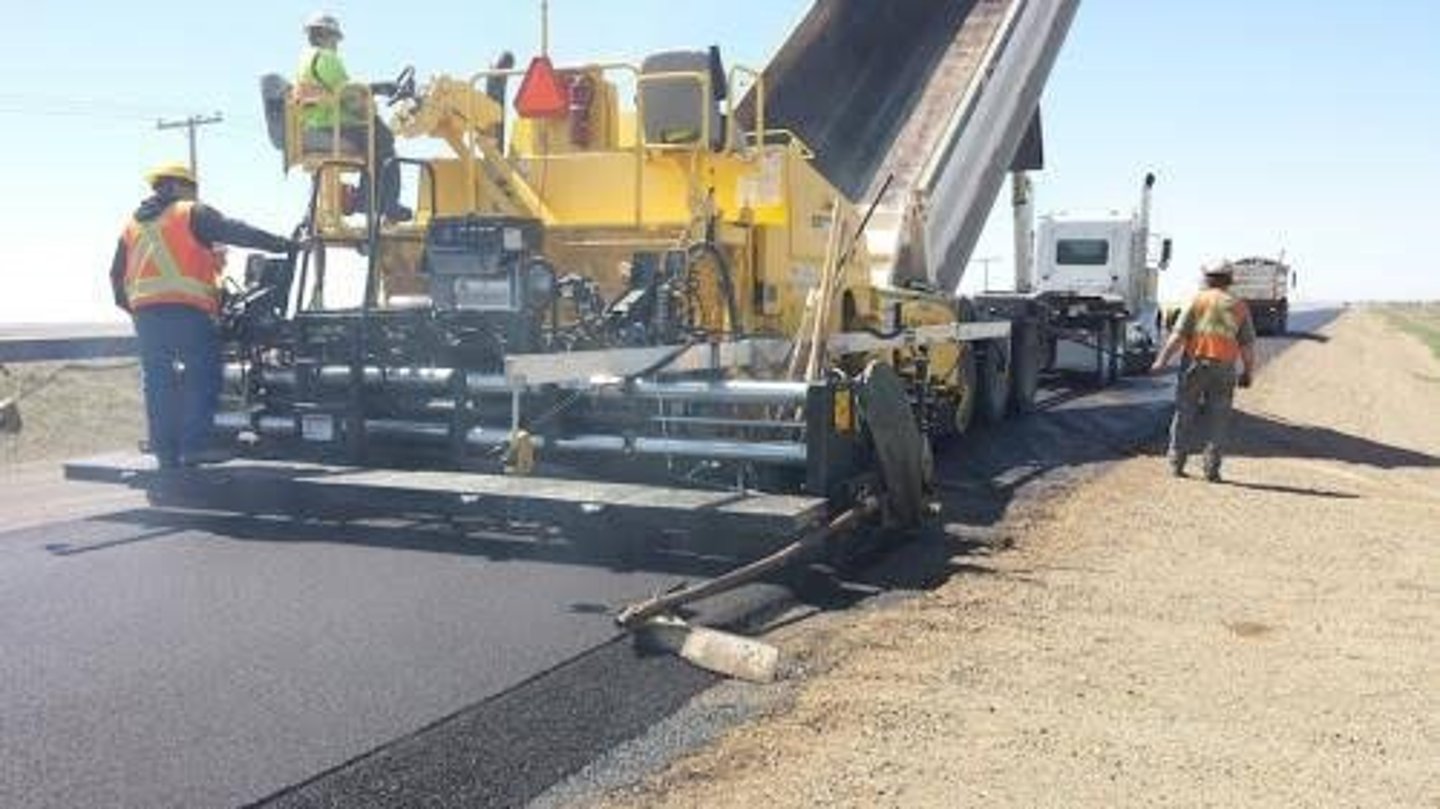
Paver
is a machine that places, spreads and finishes concrete or asphalt paving material

- Superstructure
- Substructure
- Foundation
What are the 3 major parts of a building?
Superstructure
the portion of the building ABOVE the ground
Substructure
the habitable portion of the building found BELOW the ground
Foundation
the STRUCTURAL portion of the building that transfer the building's load into the soil
- Slab on Fill
- Crawl Space
- Basement
What are the three types of substructures?
Slab on Fill
slab which rests on ground and not suspended
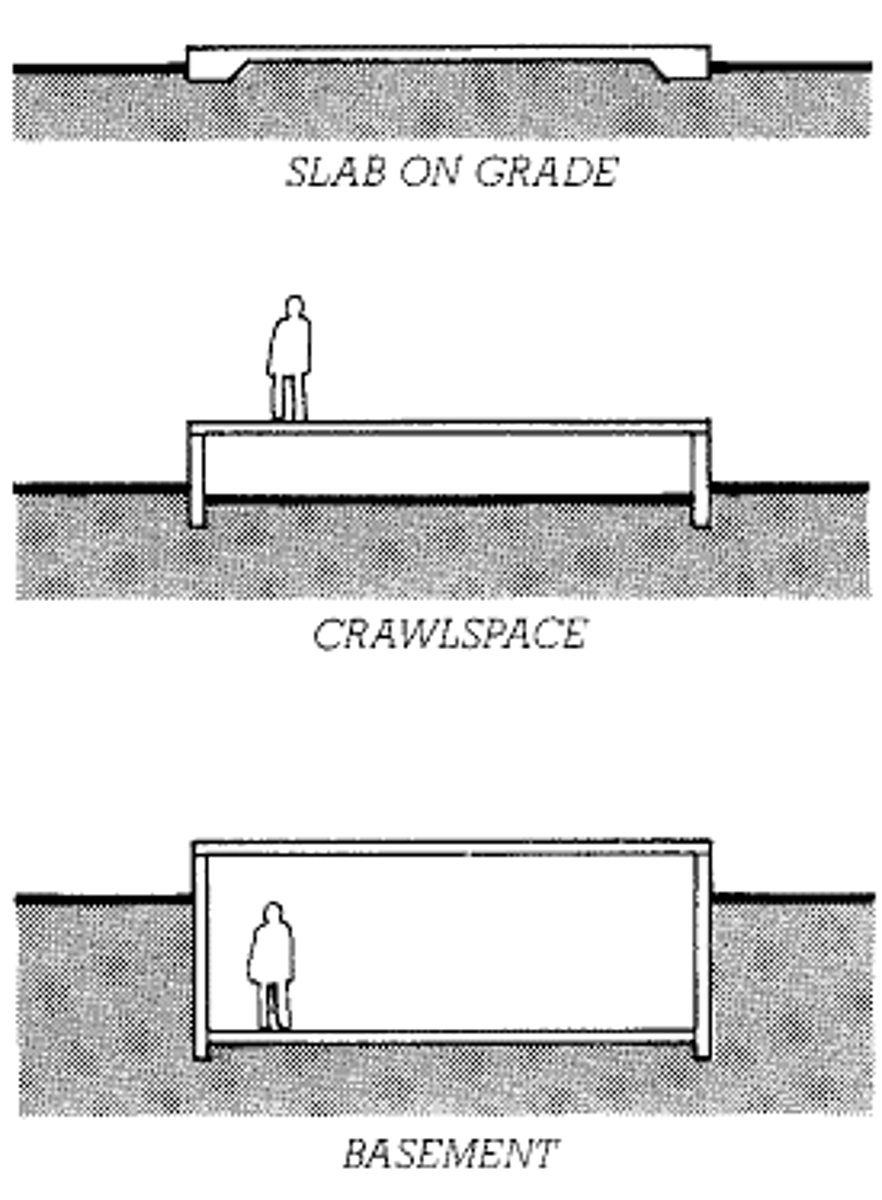
Crawl Space
in a building without a basement, an unfinished accessible space below the first floor which is usually less than a full story height
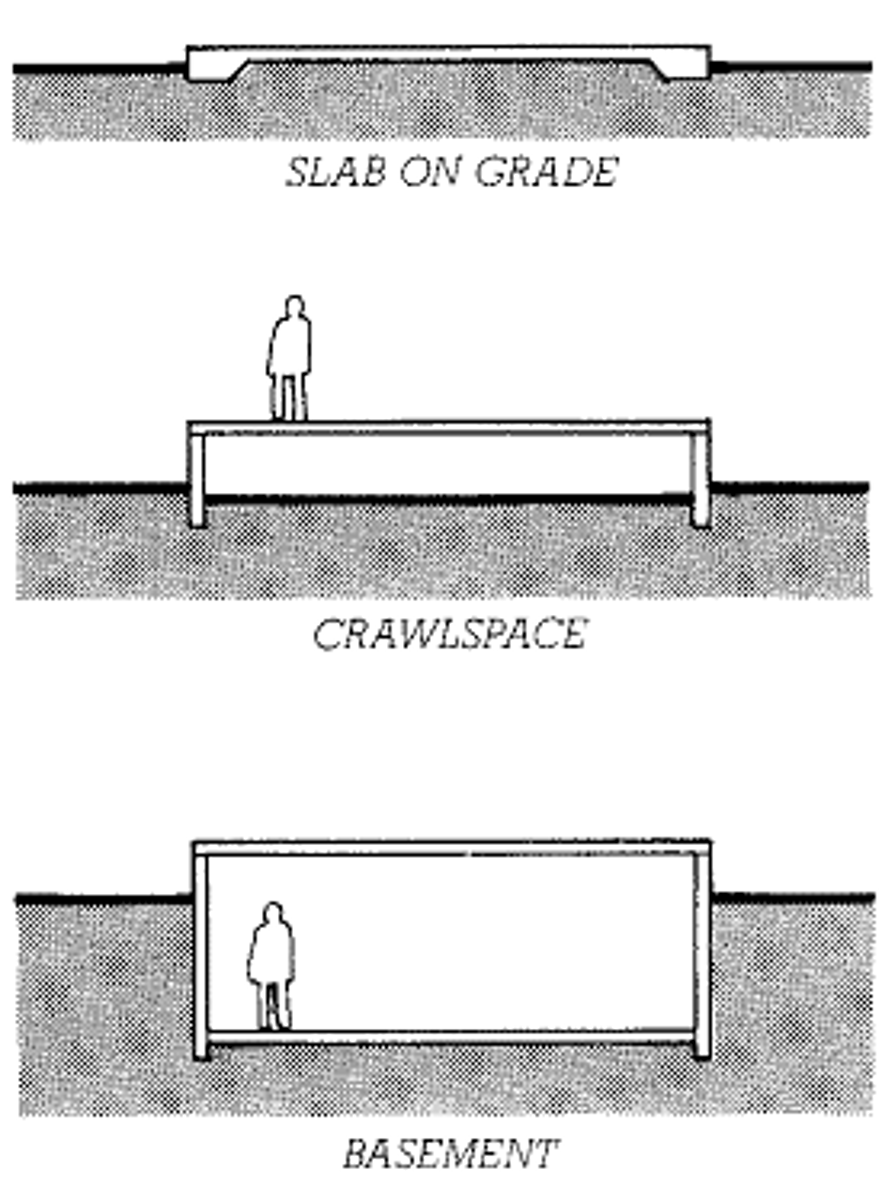
Basement
the lower story of a building, either partly or entirely below grade
Foundation Bed
The natural material on which the construction rests
Foundation Walls
That part of the building foundation which forms the permanent retaining wall of the structure below grade.
Foundation Piers/Columns
piers/columns below grade, to distinguish them from similar construction above grade
Grade Beam
that part of a foundation system which supports the exterior wall of the superstructure and bears directly on the column footing
Footing Courses
lower portions of walls, piers or columns which are spread to provide a safe base
Rock
Foundation Bed
Undisturbed rock masses forming an undisturbed part of the original rock-formation
Decayed Rock (Rotten Rock)
Foundation Bed
Sand, clays and other materials resulting from the disintegration of rock masses, lacking the coherent qualities but occupying the space formerly occupied by the original rock
Loose Rock
Foundation Bed
Rock masses detached from the ledge of which they originally formed a part
Gravel
Foundation Bed
Detached rock particles, generally water-worn, rounded and intermediate in size between sand particles and boulders
Boulders
Foundation Bed
detached rock masses larger than gravel, generally rounded and worn as a result of having been transported by water a considerable distance from the ledges of which they originally formed a part
Sand
Foundation Bed
Non-coherent rock particles smaller than 1/4" in maximum dimension
Clay
Foundation Bed
A plastic material resulting from the decomposition and hydration of feldspathic rocks, being hydrated silicate of alumina, generally mixed with powdered feldspar, quartz, and other materials
Hard-pan
Foundation Bed
any strong coherent mixture of clay or other cementing material with sand, gravel and boulders