AP Biology: Plasma Membrane
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
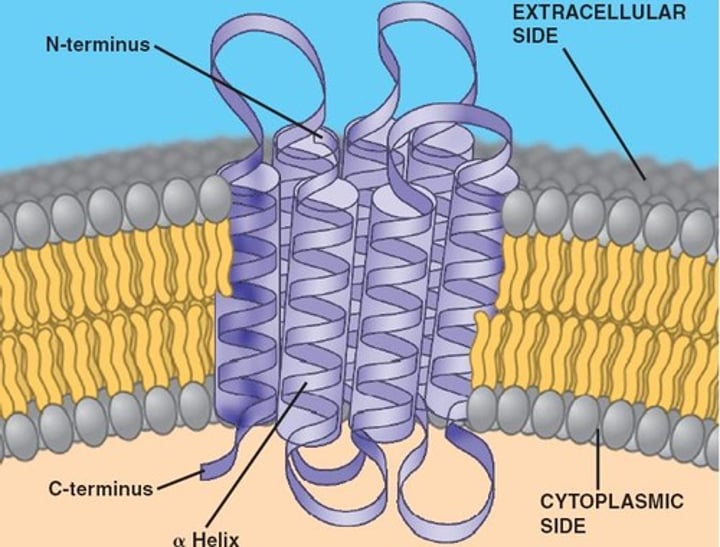
transmembrane proteins
the integral protein completely spans the membrane.
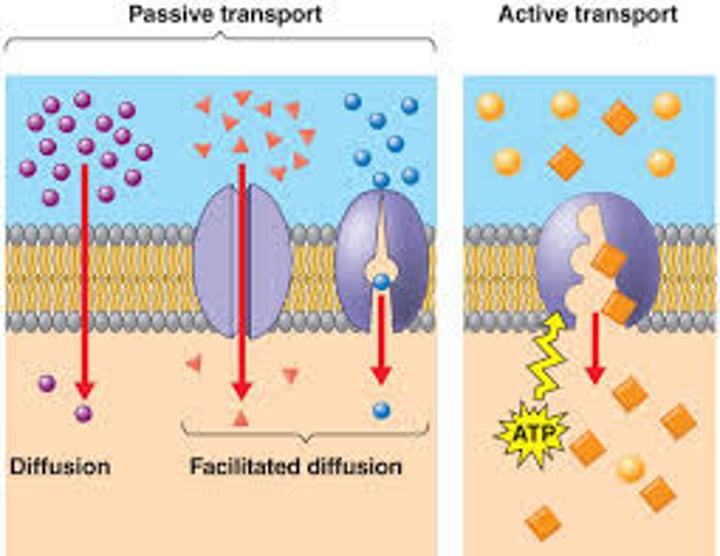
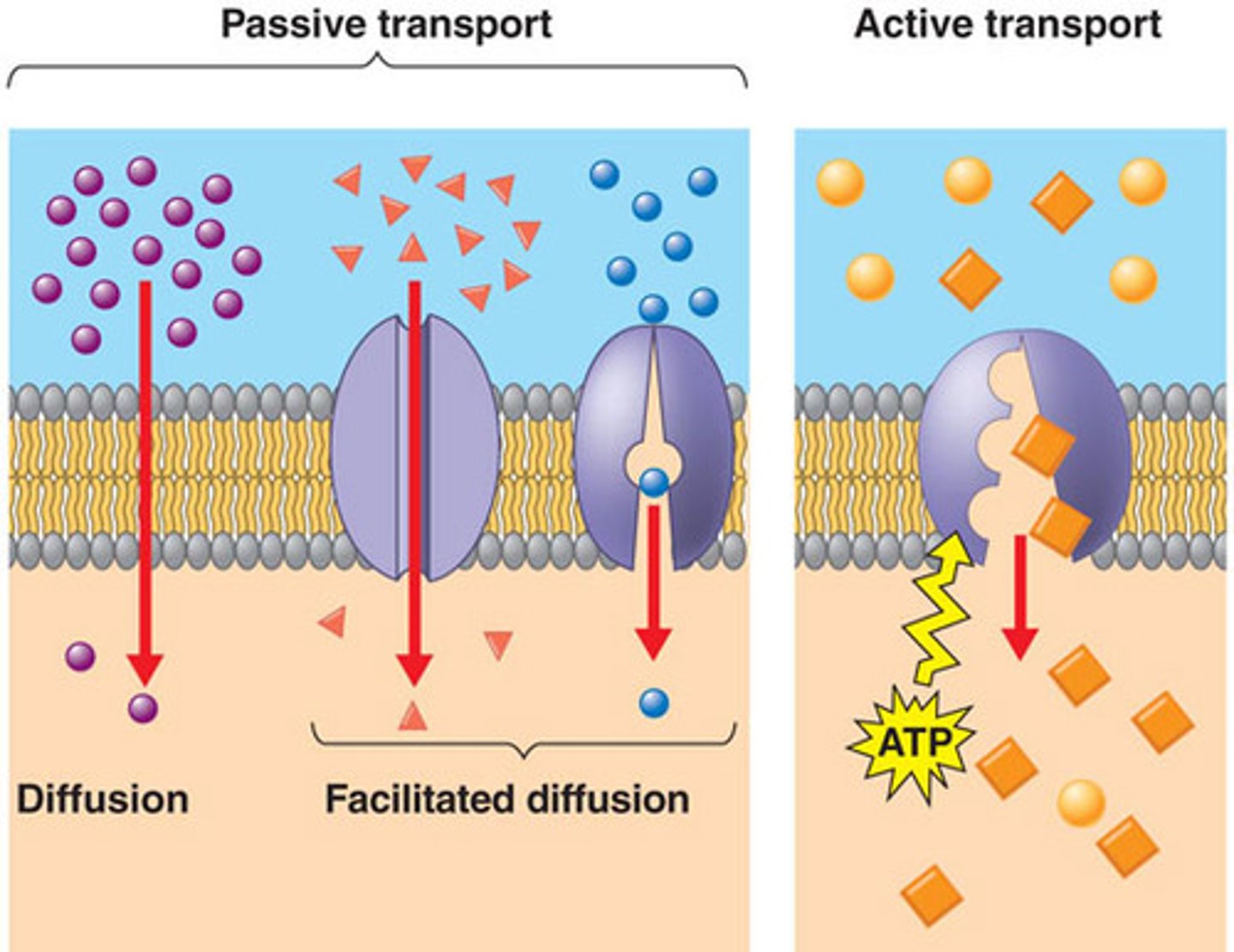
passive transport
transport that requires no energy input from the cell (ATP) for transport to occur. Simple diffusion and channel proteins like Aquaporins are examples of this.
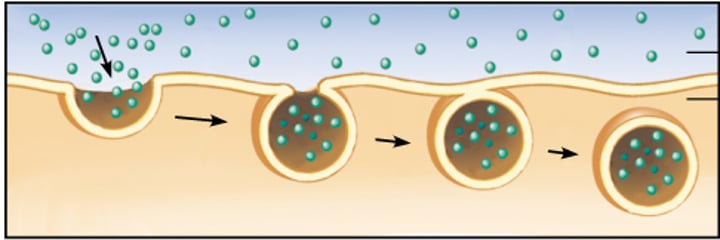
endocytosis
the taking in of matter by a living cell by invagination of its membrane to form a vacuole.
plasma membrane
a microscopic membrane of lipids and proteins that form the external boundary of the cytoplasm of a cell or encloses a vacuole and that regulates the passage of molecules in and out of the cytoplasm.
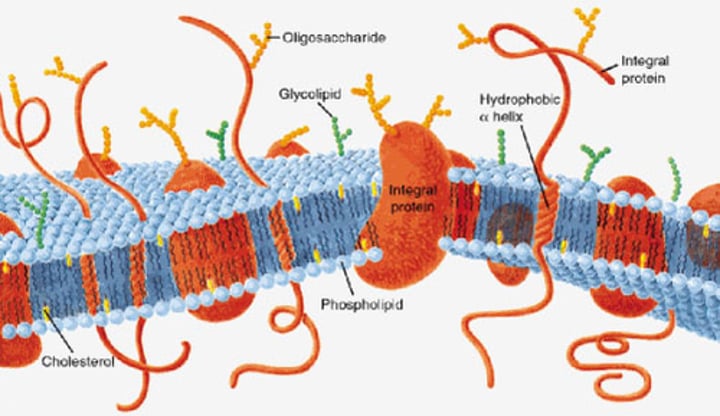
selectively permeable
A membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through more easily than other, by means of active or passive transport.
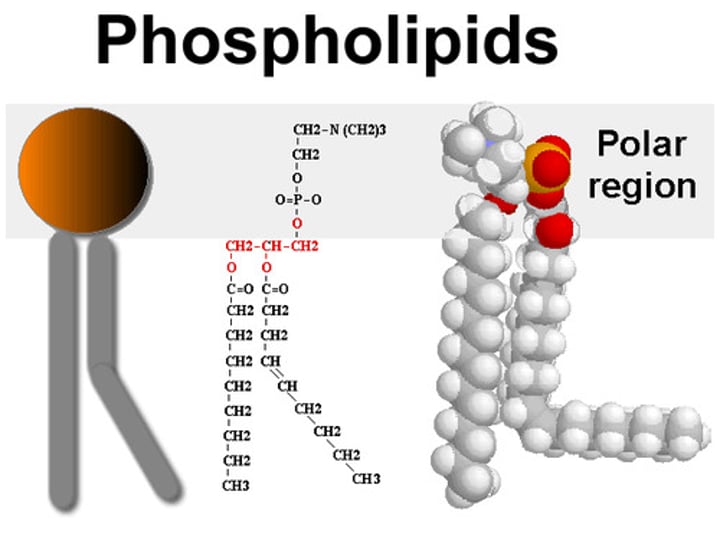
phospholipids
consist of a glycerol molecule, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group that is modified by an alcohol. The phosphate group is the negatively-charged polar head, which is hydrophilic. The fatty acid chains are the uncharged, nonpolar tails, which are hydrophobic.
lipids and proteins
primary macromolecules found in membranes
fluid mosaic model
Name the model that explains various observations regarding the structure of functional cell membranes. In this model, the cell membrane as a two-dimensional liquid that restricts the lateral diffusion of membrane components.
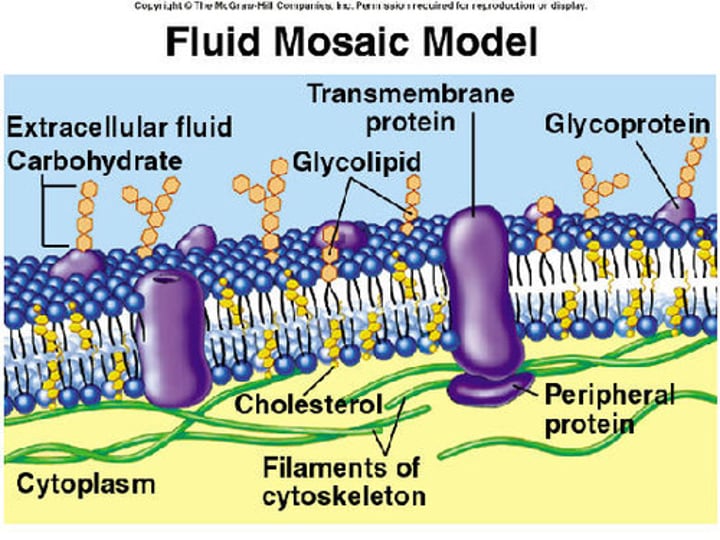
integral proteins
proteins integrated into the membrane: they have at least one hydrophobic region that anchors them to the hydrophobic core of the phospholipid bilayer. Some stick only partway into the membrane, while others stretch from one side of the membrane to the other and are exposed on either side
peripheral proteins
found on the outside and inside surfaces of membranes, attached either to integral proteins or to phospholipids. Unlike integral membrane proteins, peripheral membrane proteins do not stick into the hydrophobic core of the membrane, and they tend to be more loosely attached.
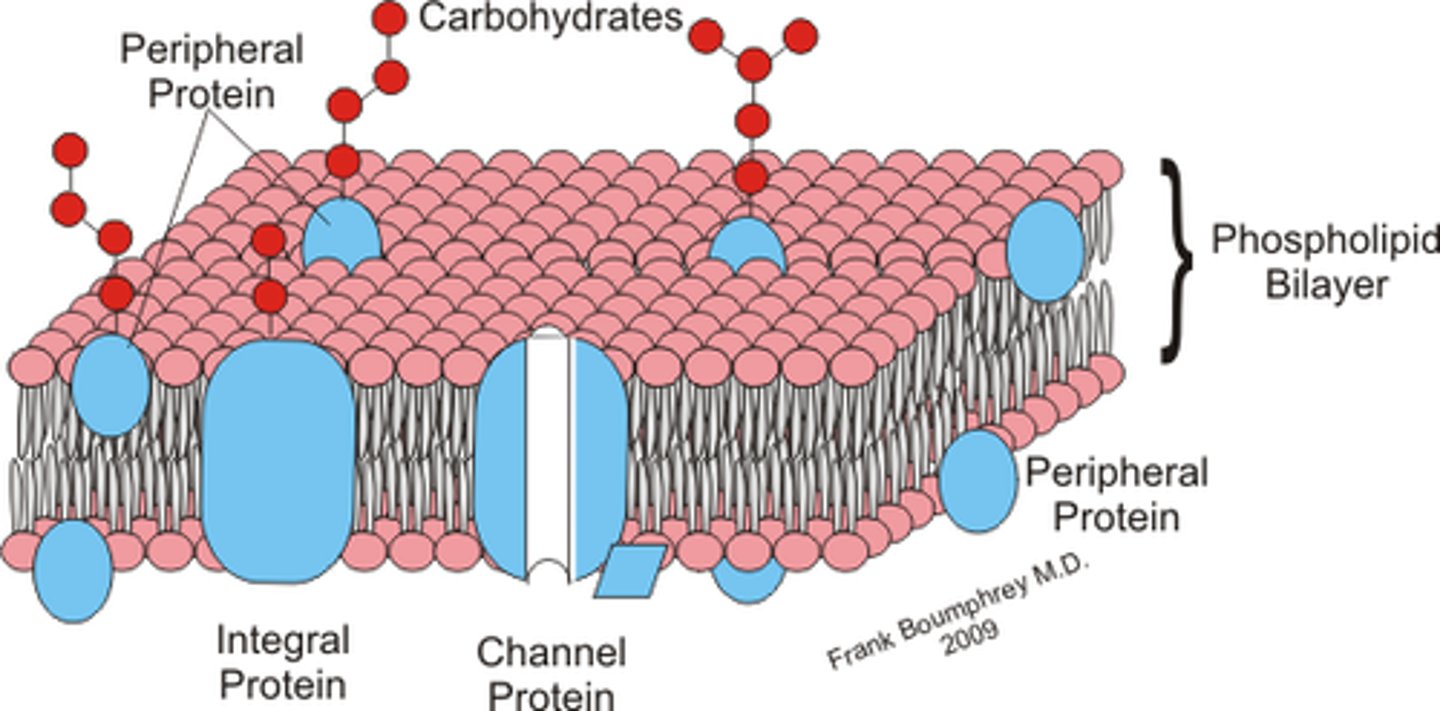
transport proteins
proteins that span the plasma membrane and aid in passive or active transport

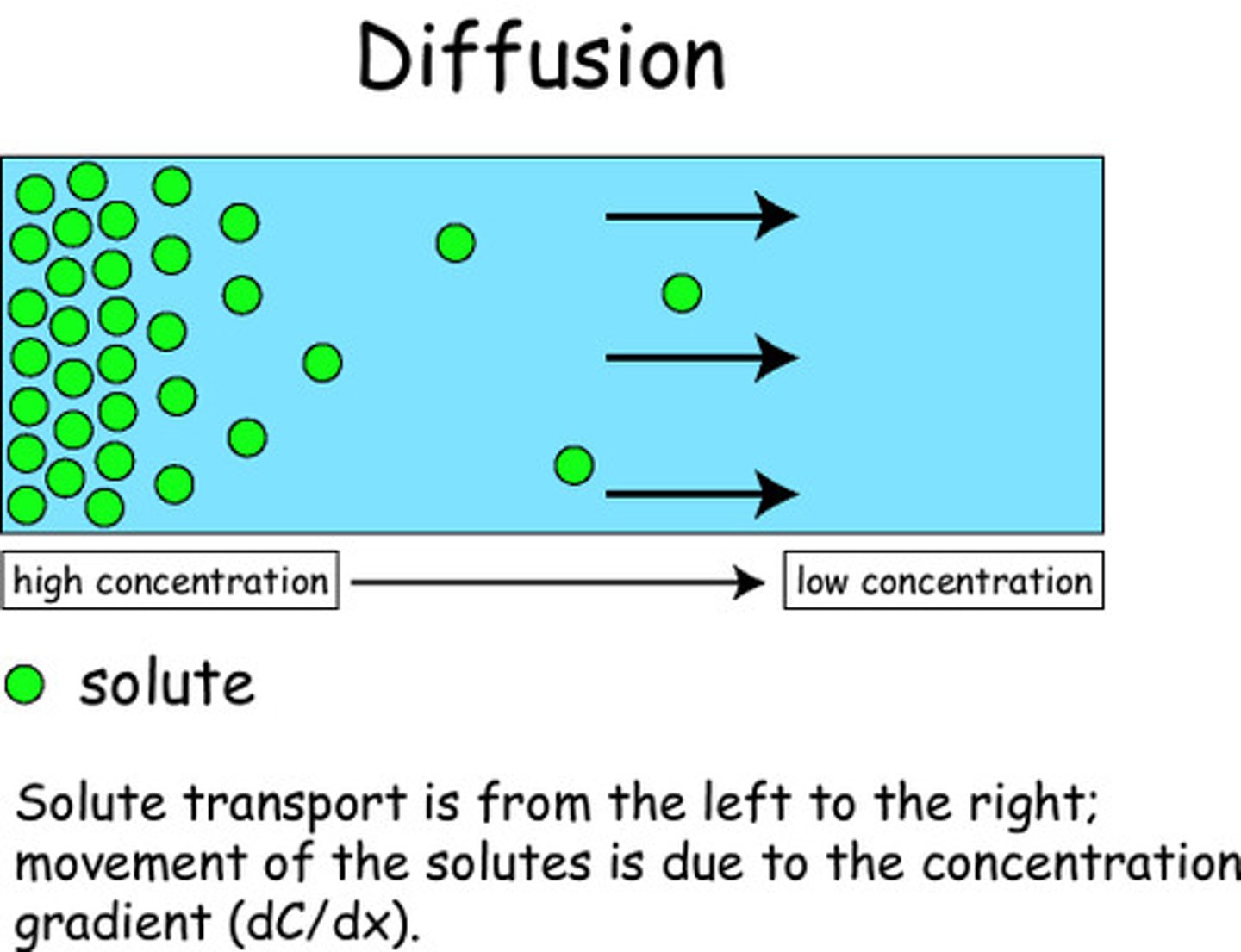
diffusion
the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
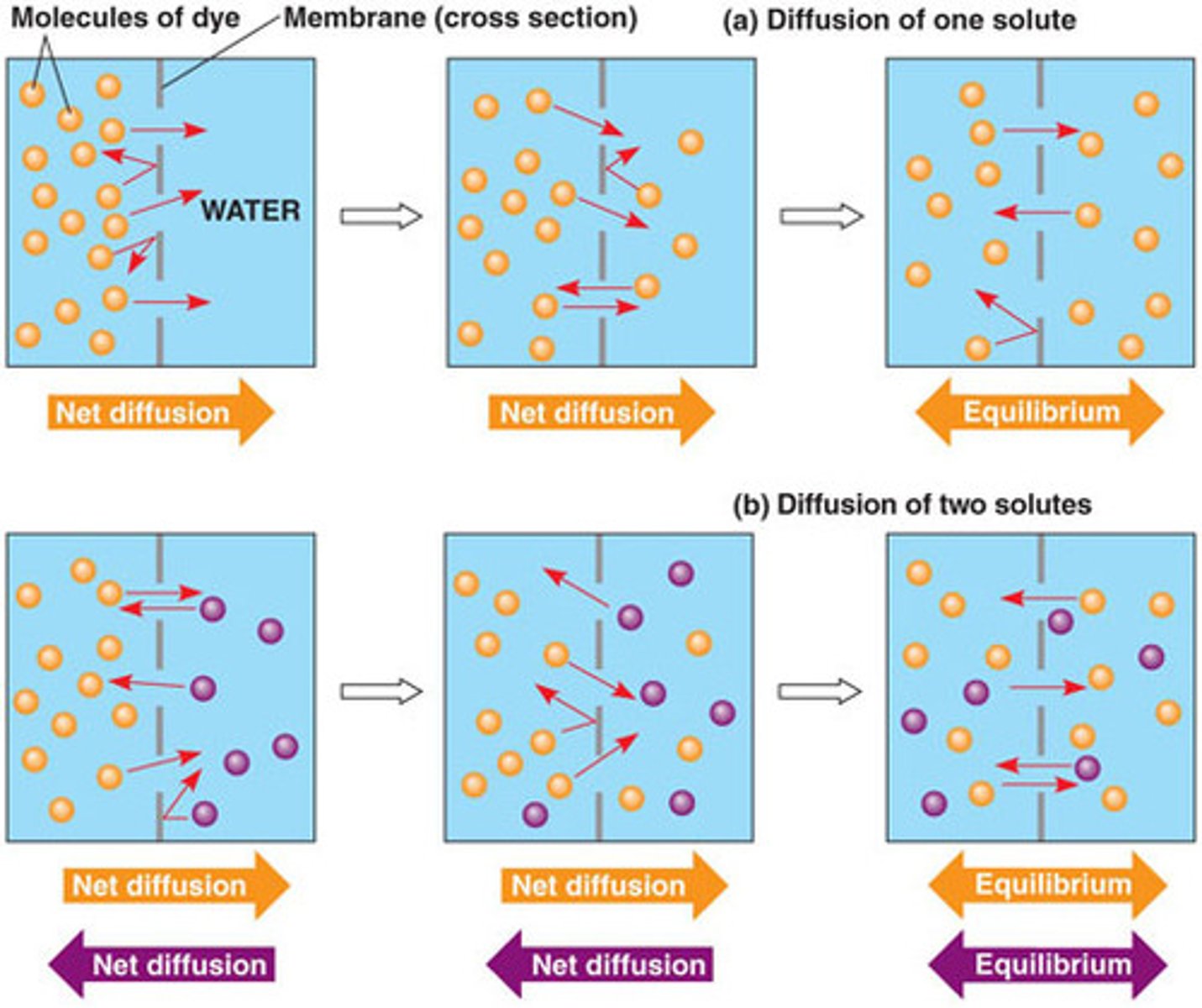
concentration gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance.
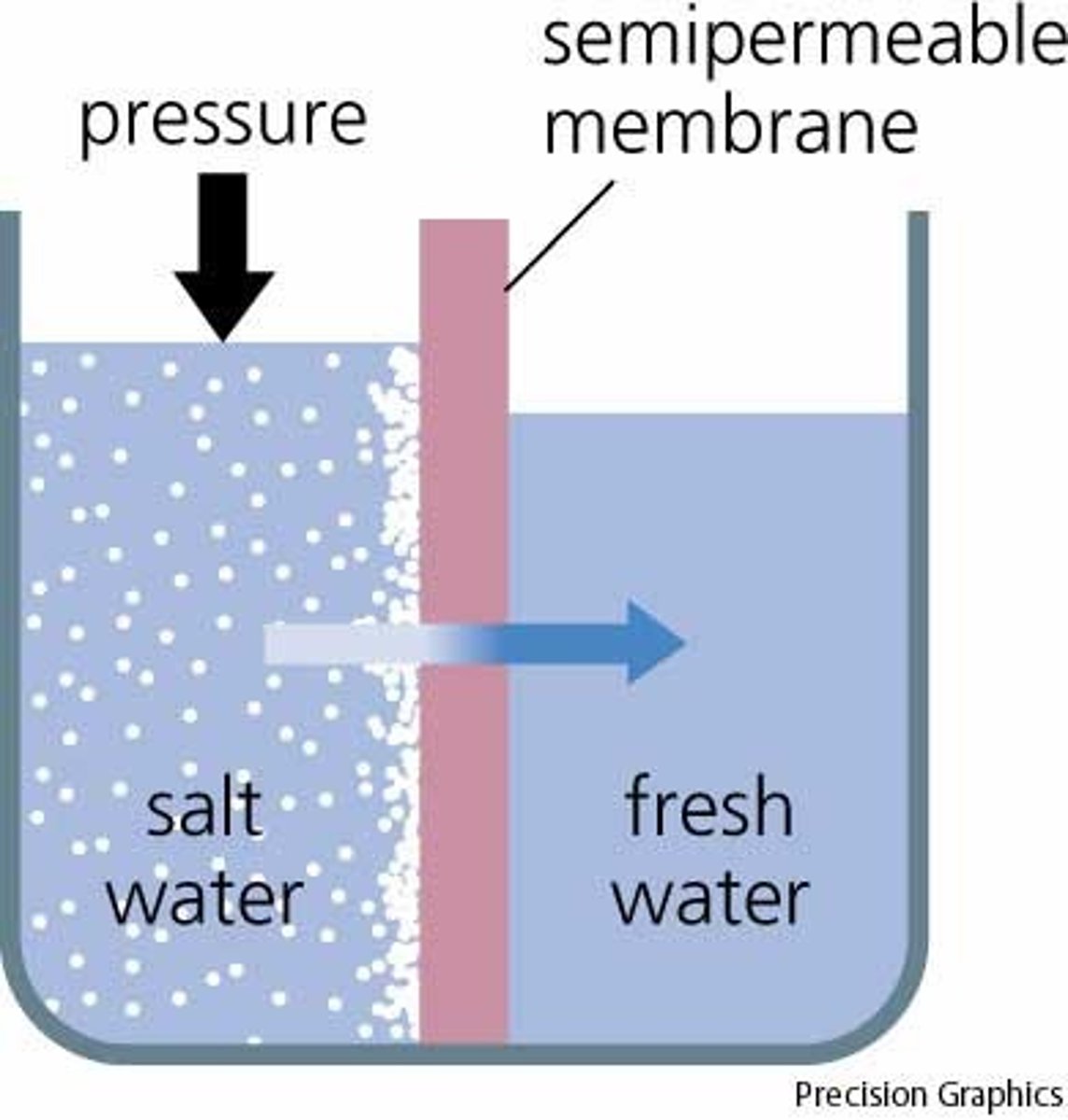
osmosis
a process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one, thus equalizing the concentrations on each side of the membrane.
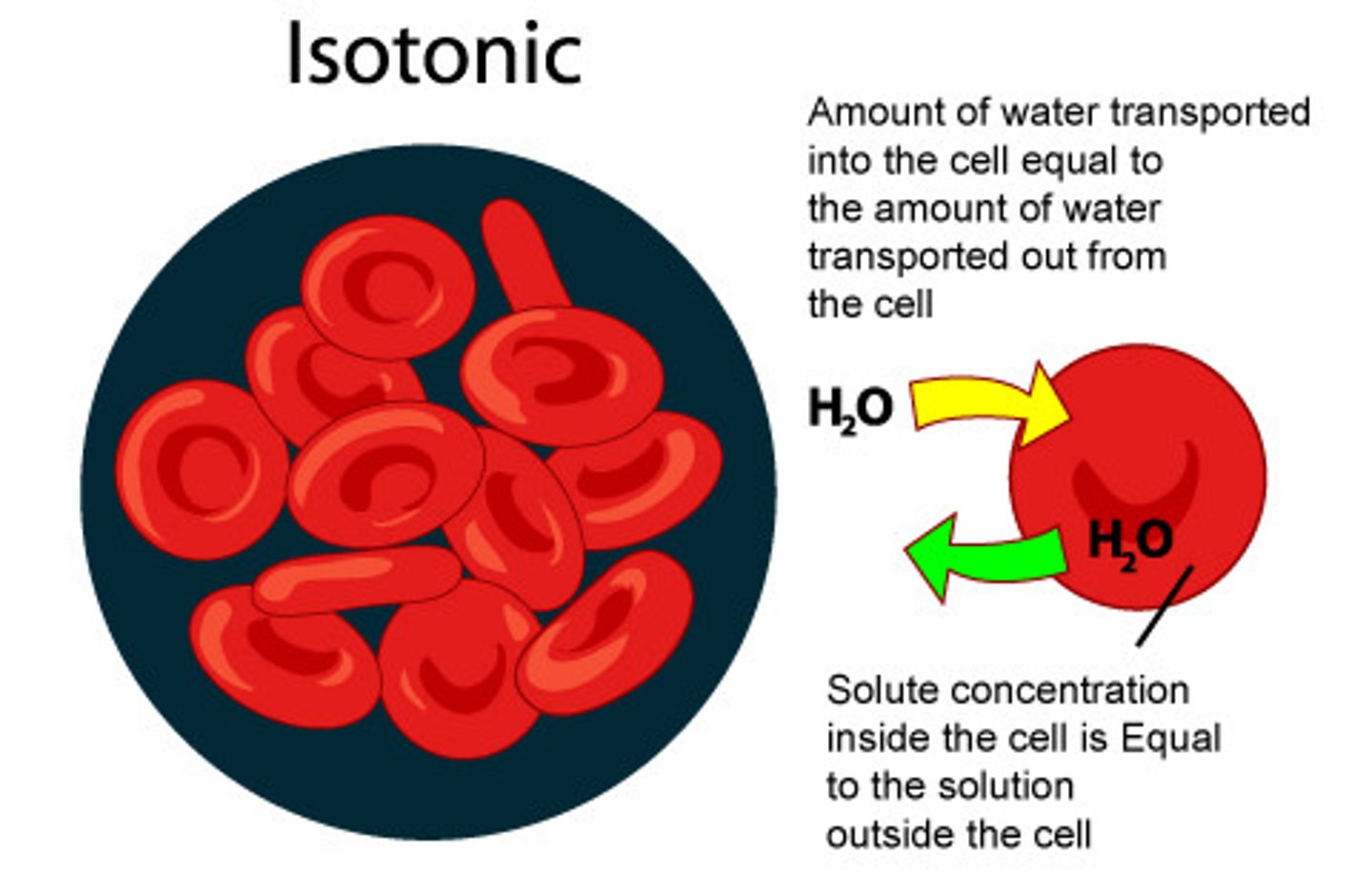
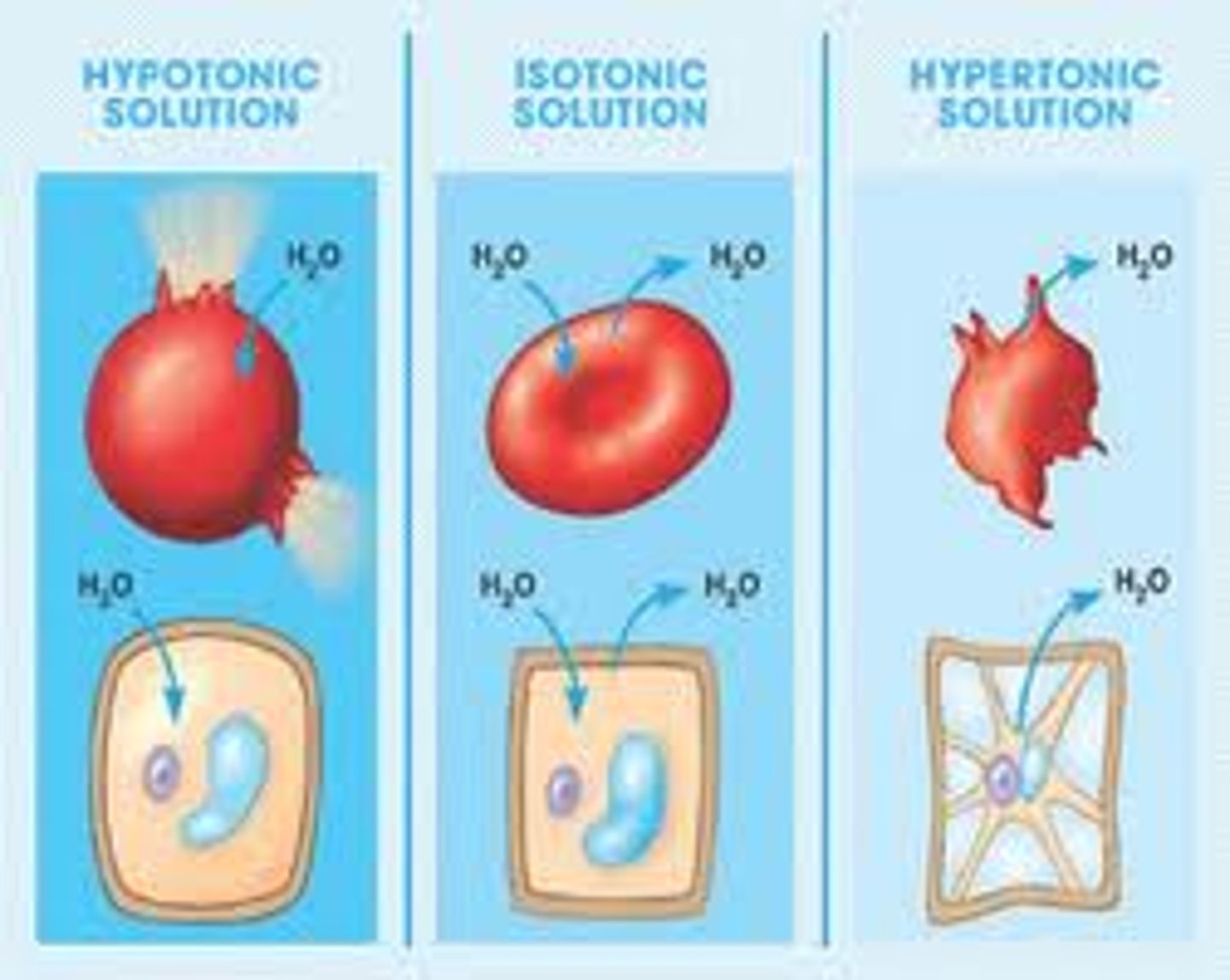
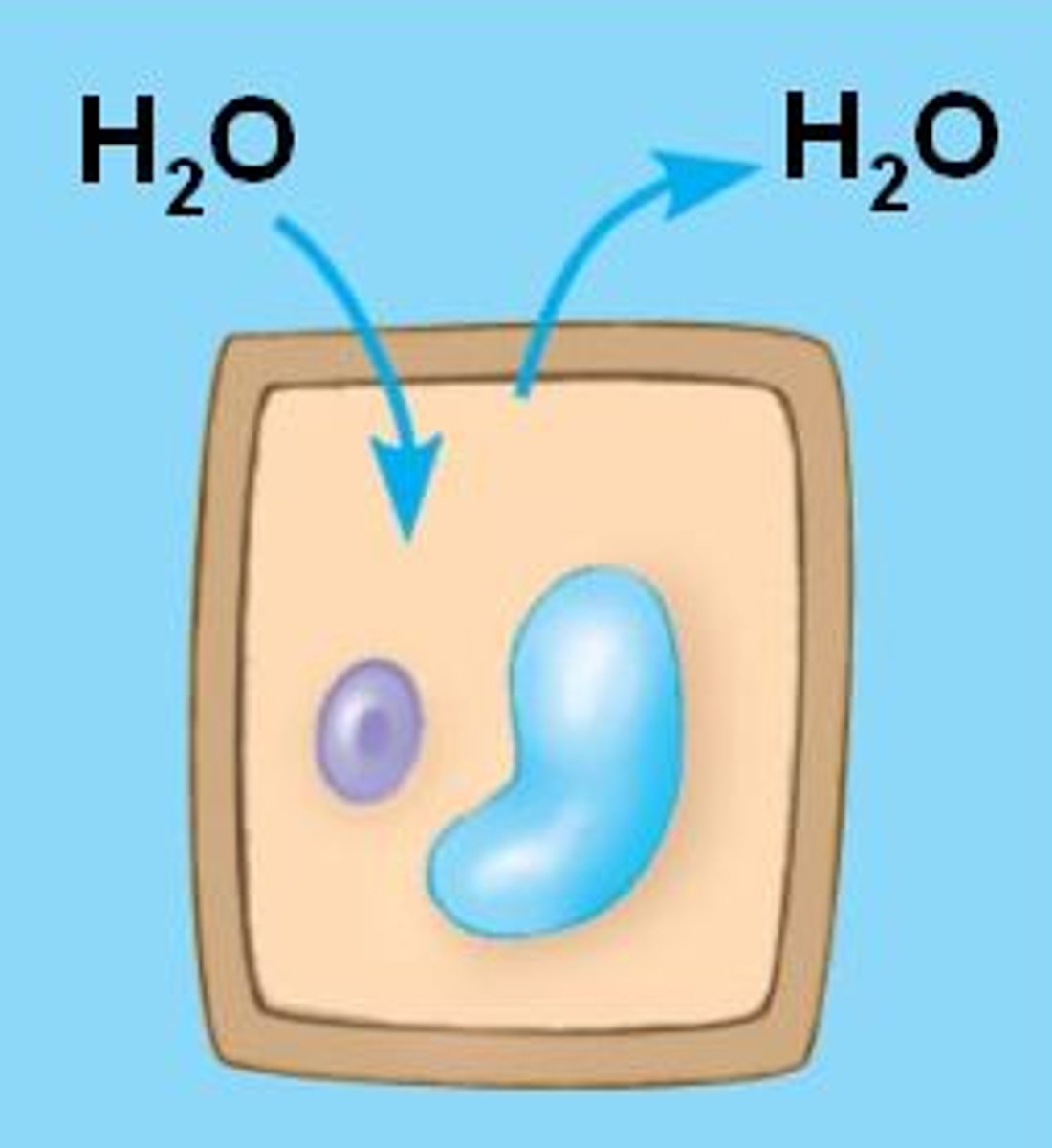
isotonic
Water enters and leaves the cell at the same rate, so no net change in the osmotic pressere. The cell stays the same.
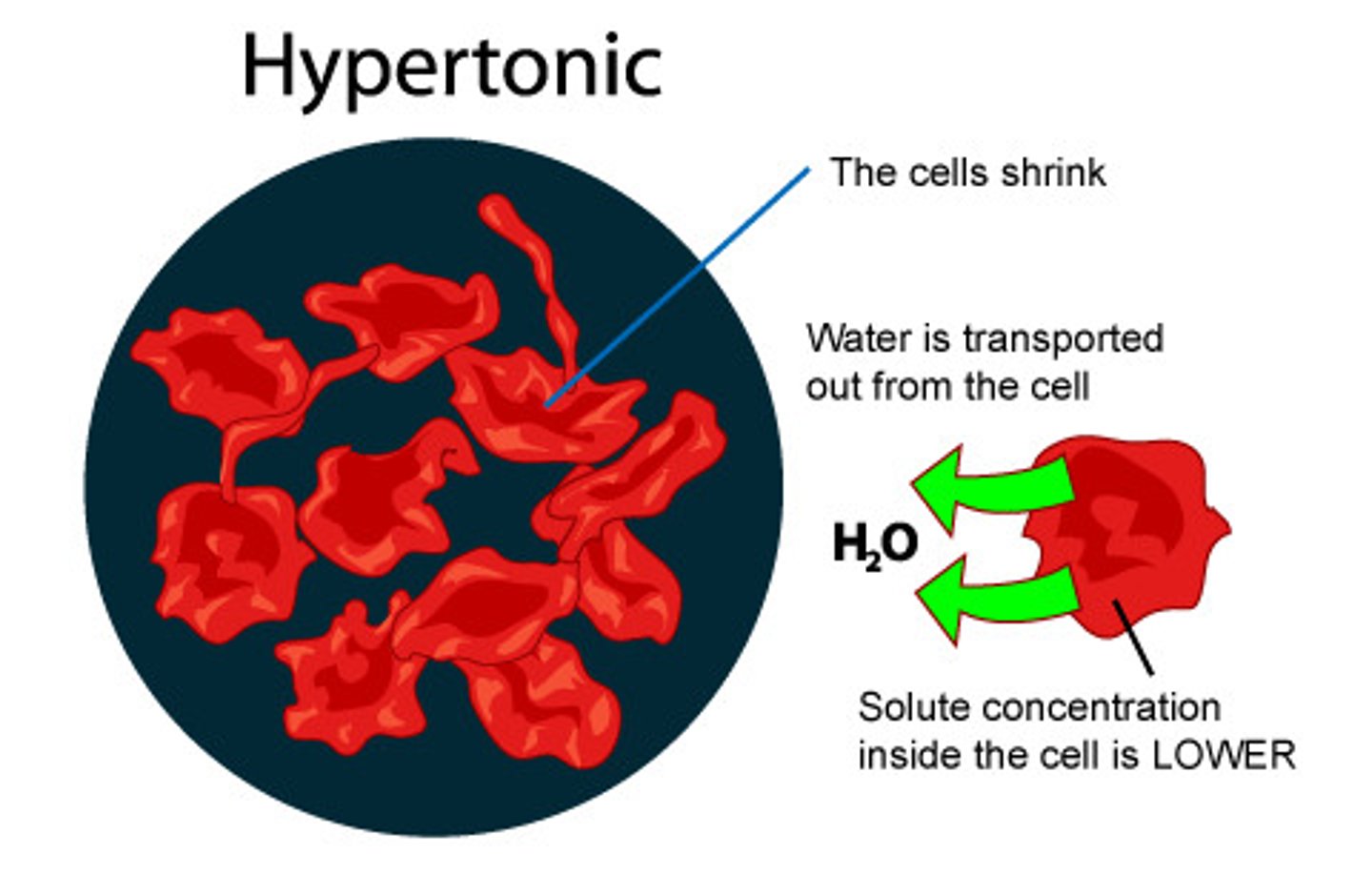
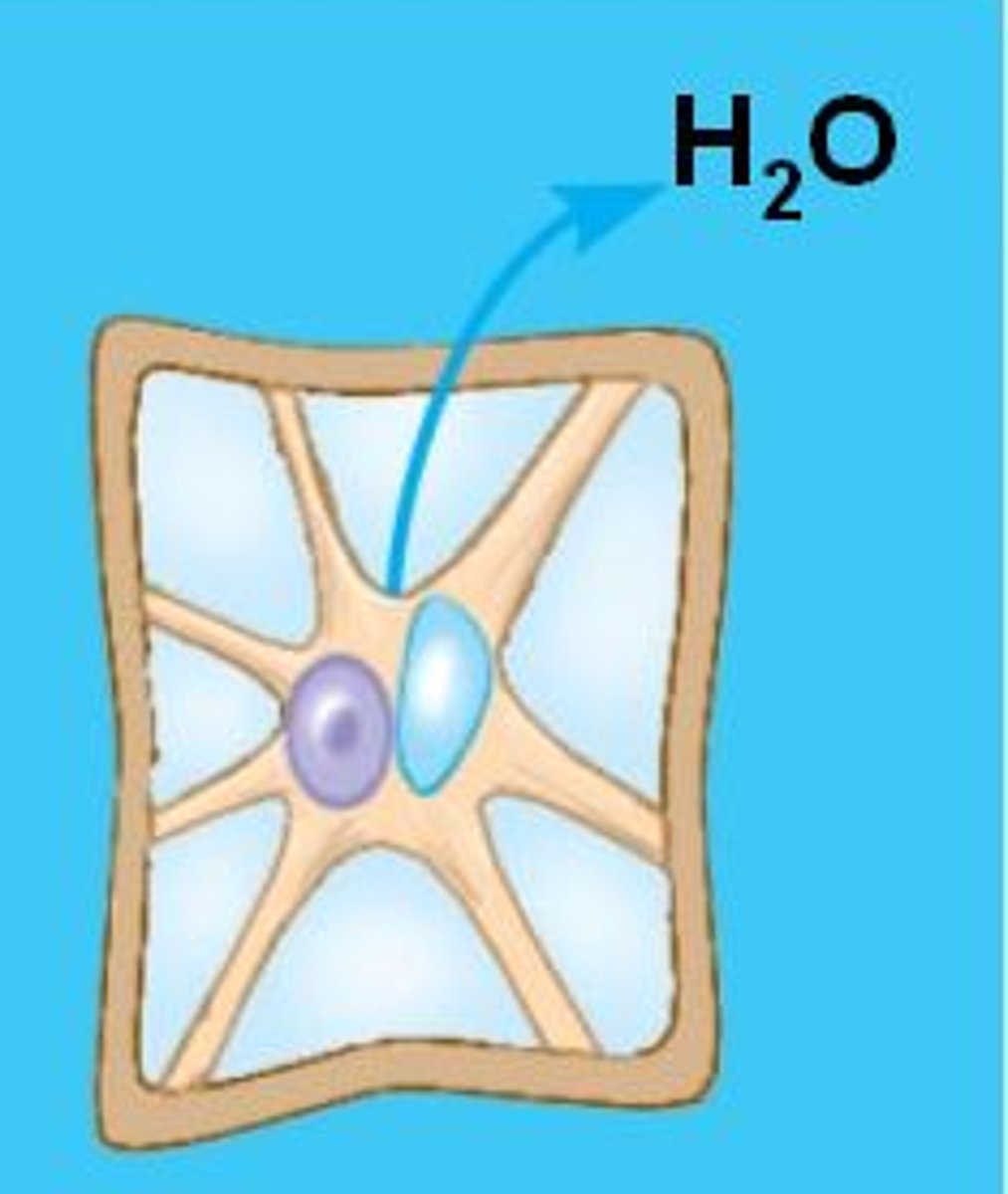
hypertonic
when the cell is immersed in a high solute concentrated solution where it loses water to its environment, shrivels and probably dies.
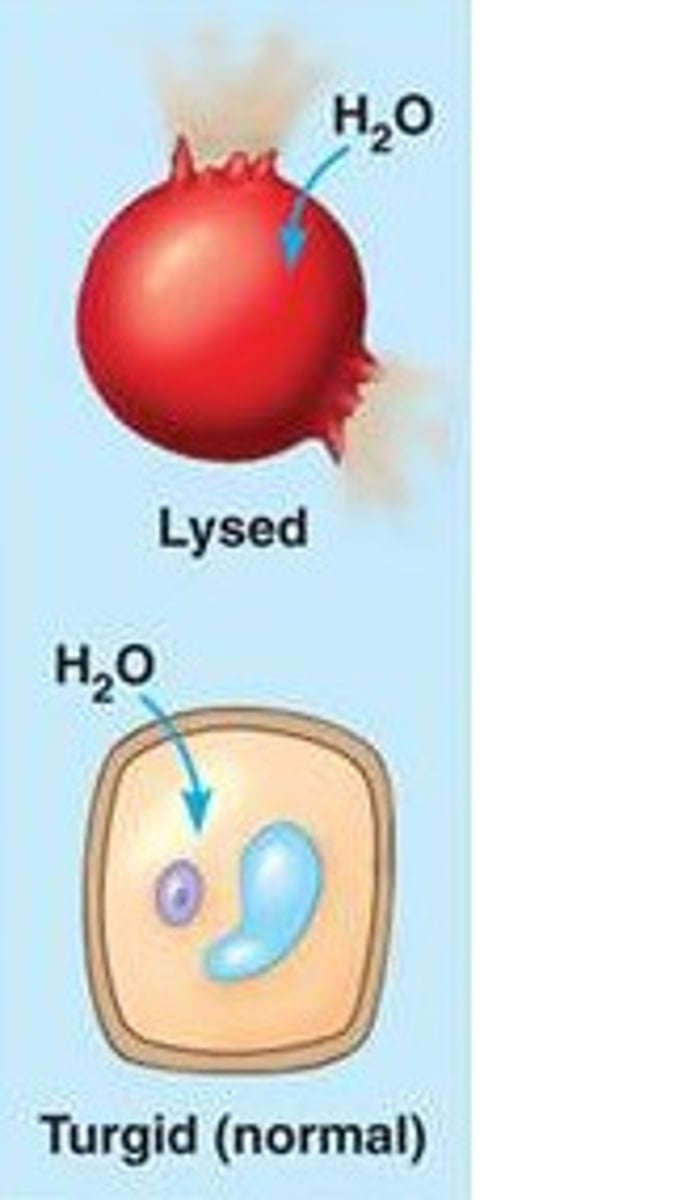
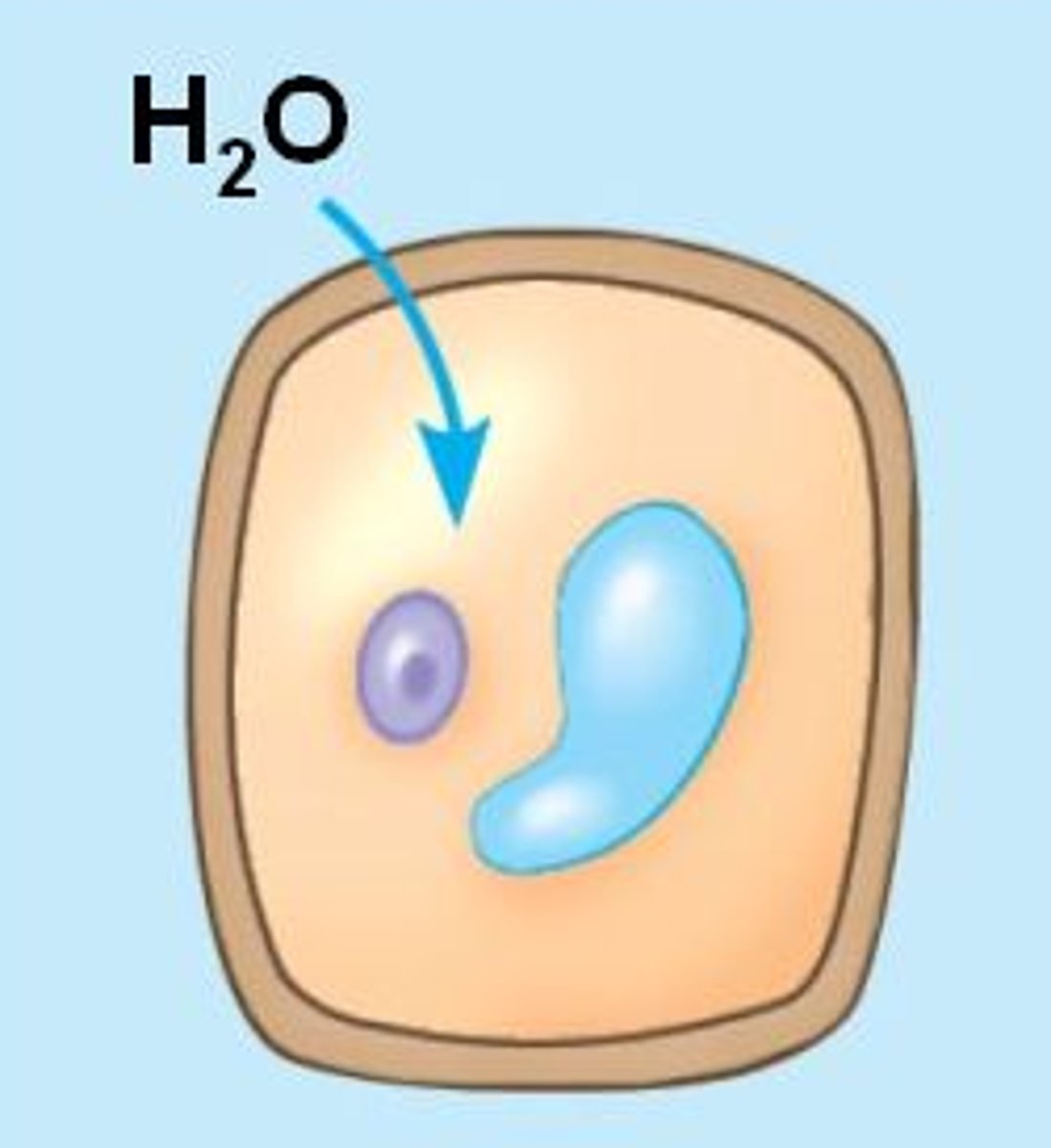
hypotonic
when a cell is immersed in a low solute concentrated solution, water enters the cell faster than it leaves, it swells and lyses (explodes) like an overfilled water balloon.
osmoregulation
the maintenance of constant osmotic pressure in the fluids of an organism by the control of water and salt concentrations.
turgid
when the plant cell is very firm, which is a healthy state for most plant cells.
flaccid
limp, not firm or strong (If a plant is not watered enough, its leaves become droopy and flaccid.)
plasmolysis
This happens when a cell shrinks inside its cell wall while the cell wall remains intact. The plasma membrane pulls away from the wall.
facilitated diffusion
the passive movement of molecules down their concentration gradient with the help of transport proteins.
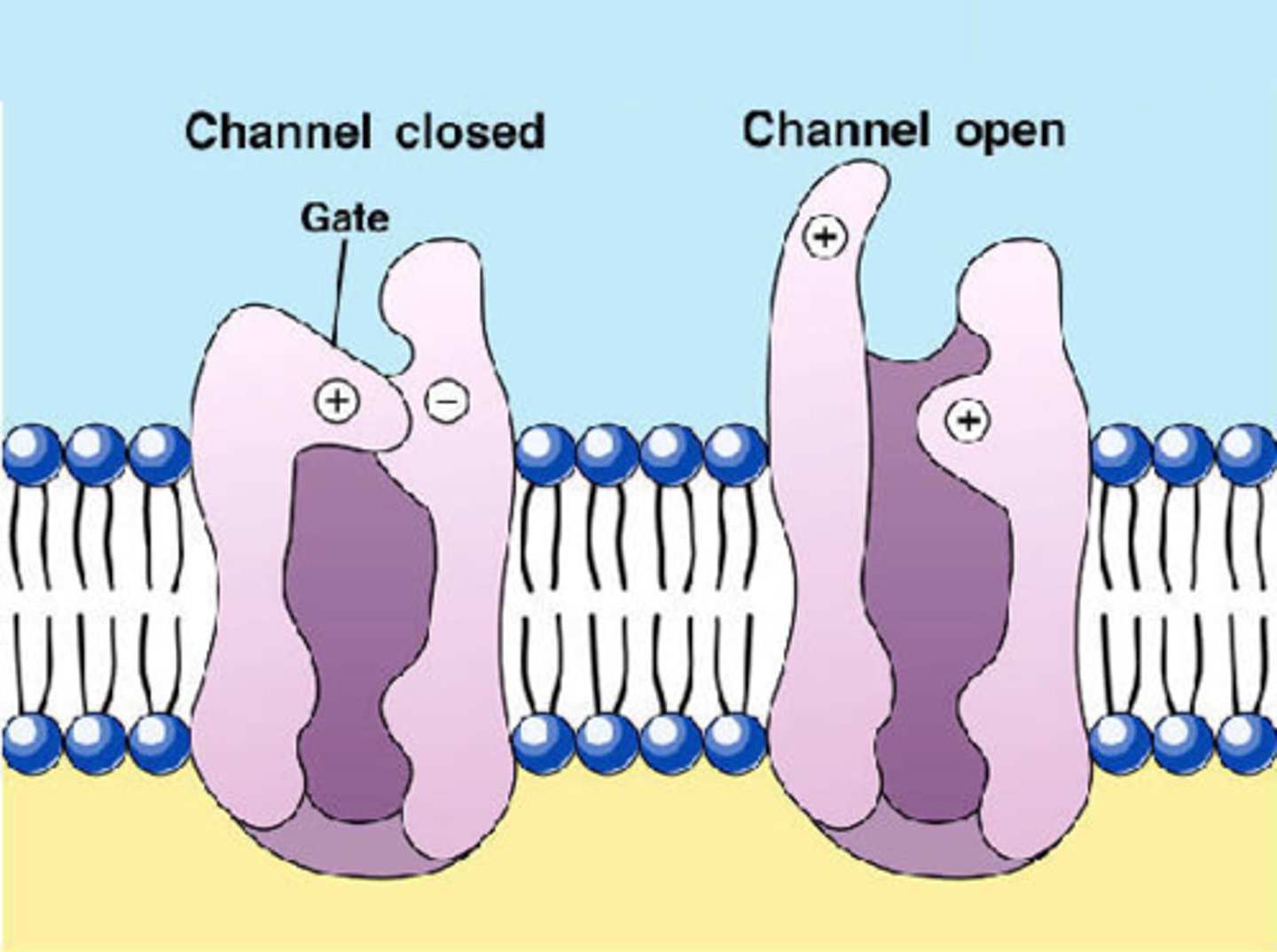
ion channels (gated channels)
Channels that open or close depending on the presence or abscence of an electrical, chemical, or physical stimulus.
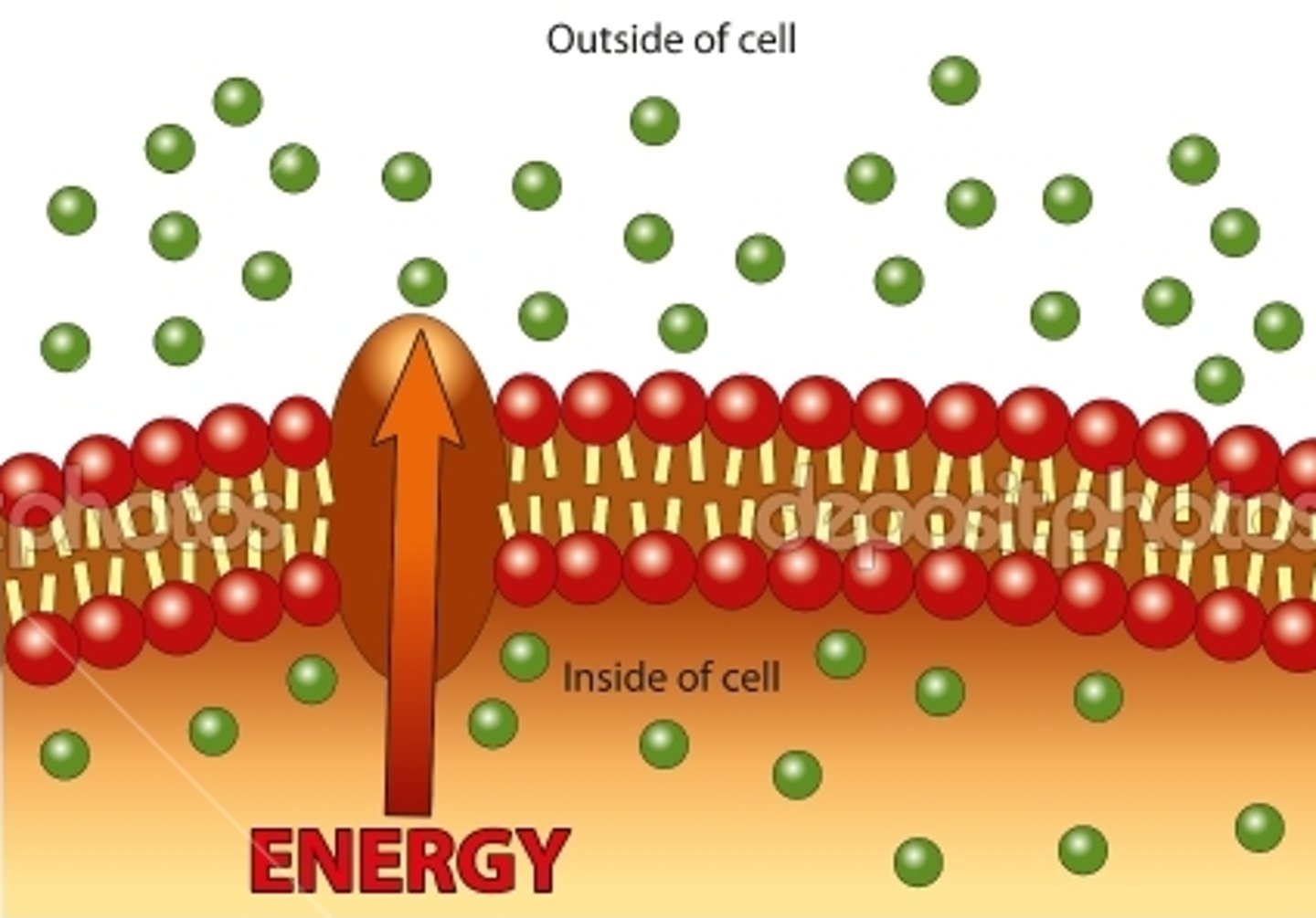
active transport
transport that requires the cell to expend metabolic energy and enables a cell to maintain internal concentrations of small molecules. Requires energy.
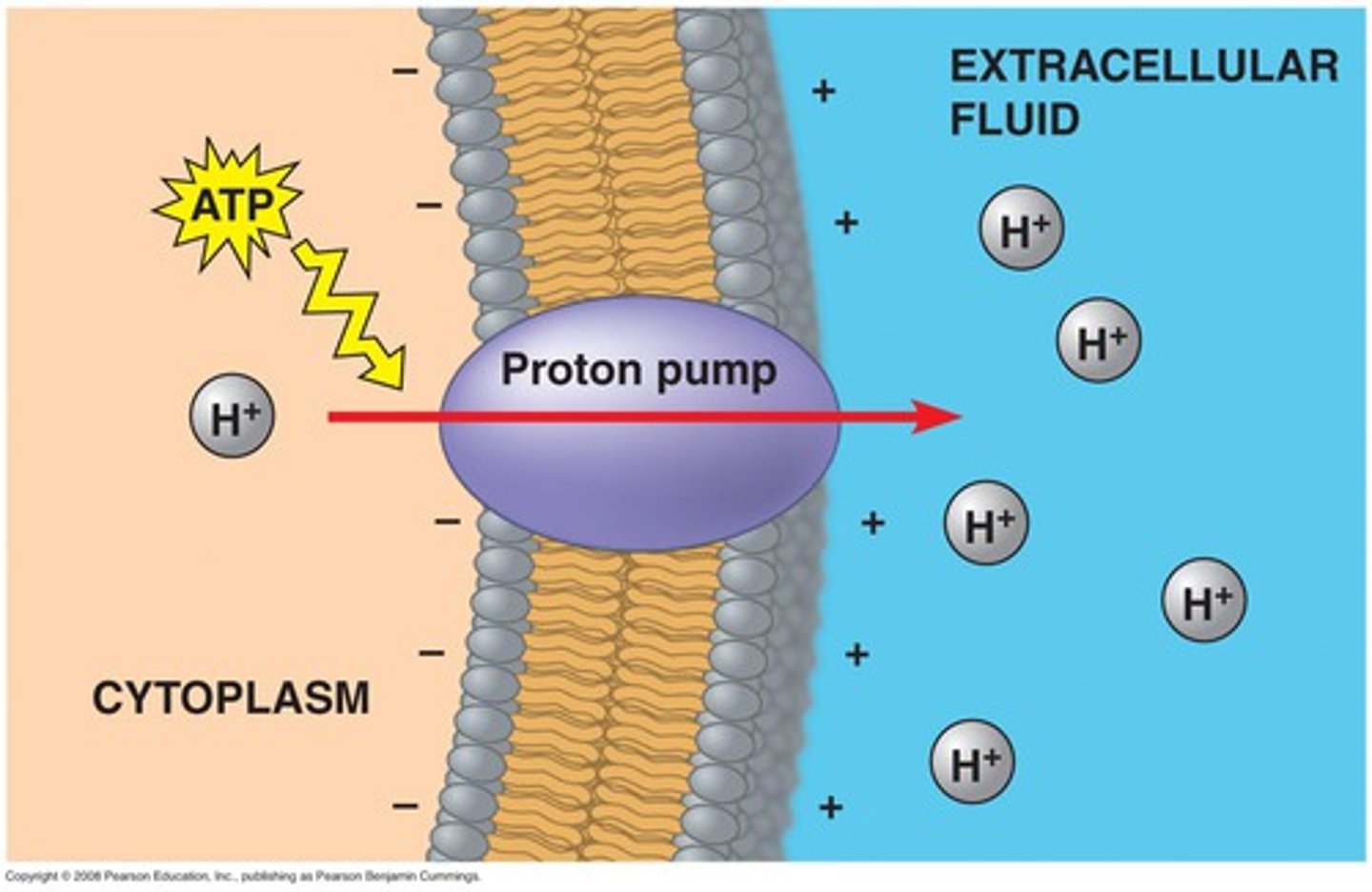
proton pumps
This protein is an integral membrane protein that is capable of moving protons across a biological membrane. Mechanisms are based on conformational changes of the protein structure.
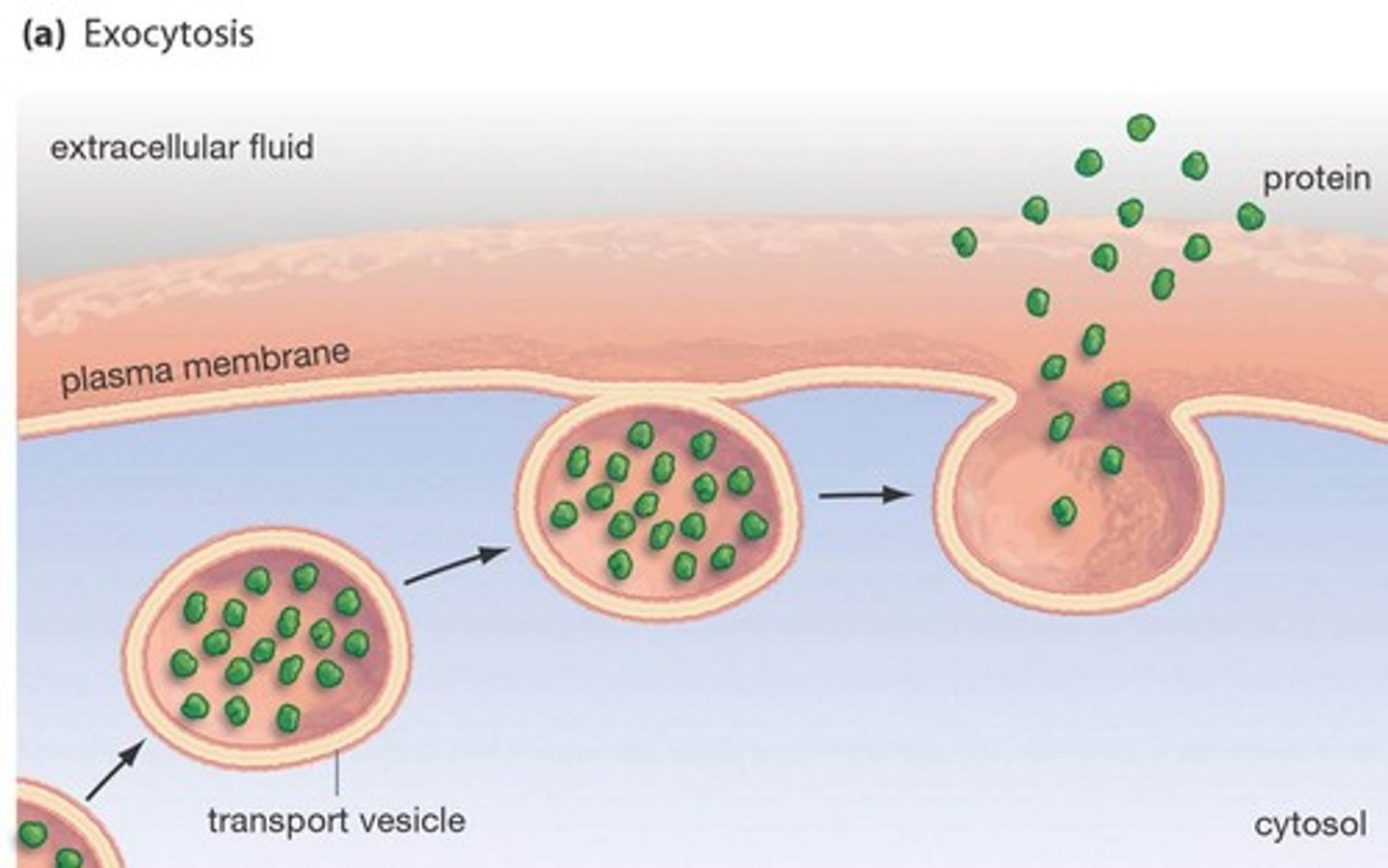
exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
phagocytosis
the ingestion of bacteria or other material by cells such as amoebas. "Cell Eating"
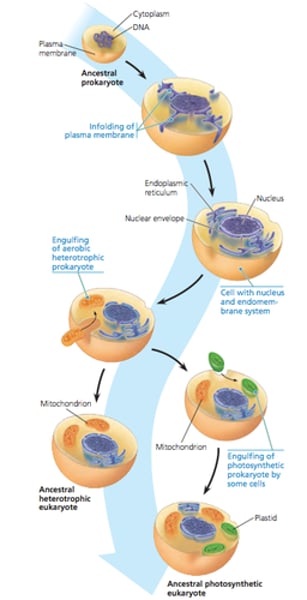
endosymbiotic theory
theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms. the prokaryotes that were engulfed are ancestors of mitochondria and chloroplasts. the prokaryotes that engulfed the other prokaryotes are ancestors of all eukaryotes around today.
Evidence includes
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes.
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts reproduce via binary fission like prokaryotes
cell compartmentalization
The formation in the cytosol of specialised structures enclosed by membranes, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, endosomes, lysosomes and chloroplasts.
It is advantageous to have functions in a cell compartmentalized because they can be done more efficiently when they are done separately in different areas.
Cell surface area to volume ratio
As a cell's size increases, its volume increases much more rapidly than its surface area.
This means that the ratio of surface area:volume decreases as the cell size increases.
This is why larger cells are less efficient at exchanging materials with the environment than smaller cells.
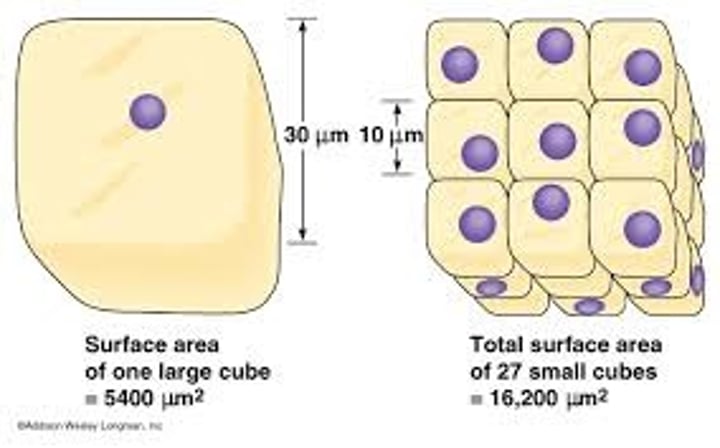
membrane folding
increases surface area of a membrane.
This means that exchange of materials of a cell with its environment can be done more efficiently. Think of gloves versus mittens!
Mittens hold onto more heat because they have less surface area with which they can lose heat.
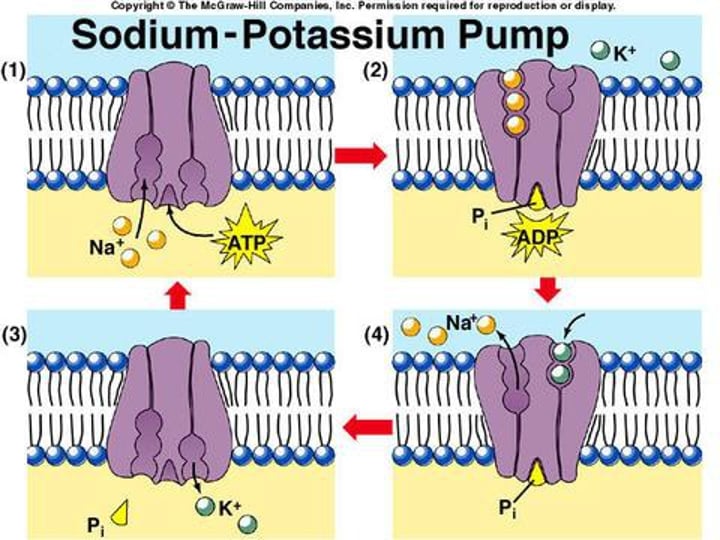
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell