AP Environmental Science Comprehensive Study Guide
1/563
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
564 Terms
Geologic Time Scale
Chronological timeline of Earth's geological history.
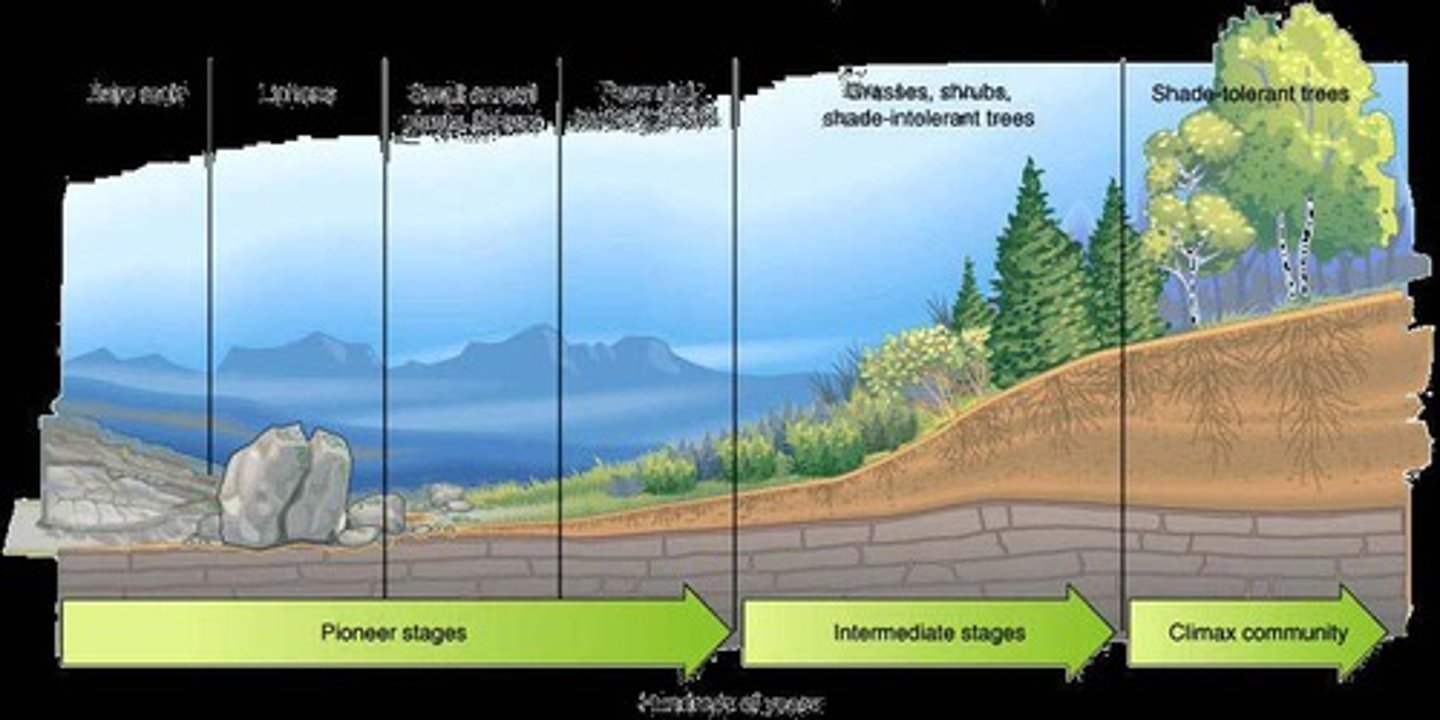
Ecosystems
Complex networks of interacting organisms and environments.
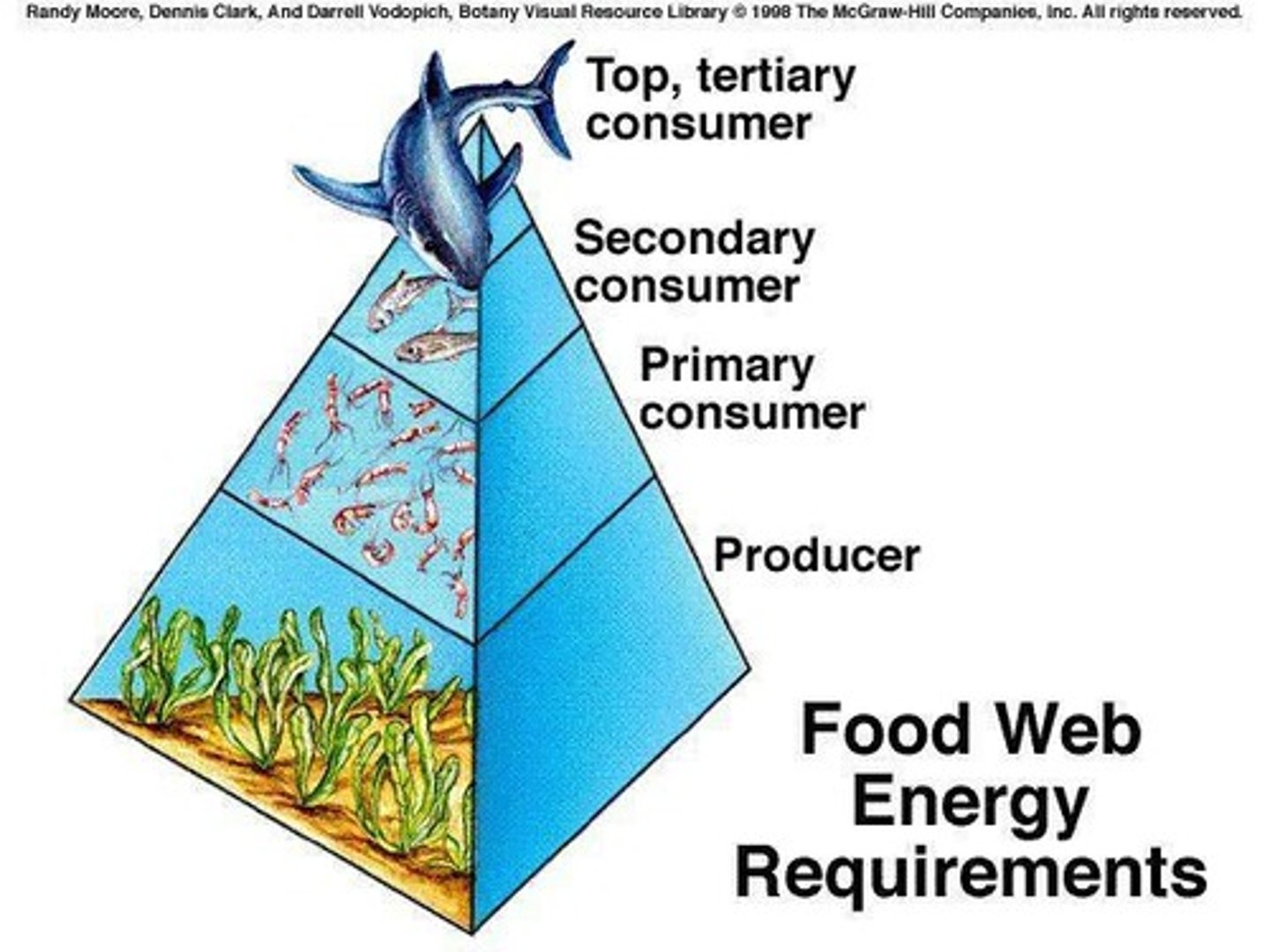
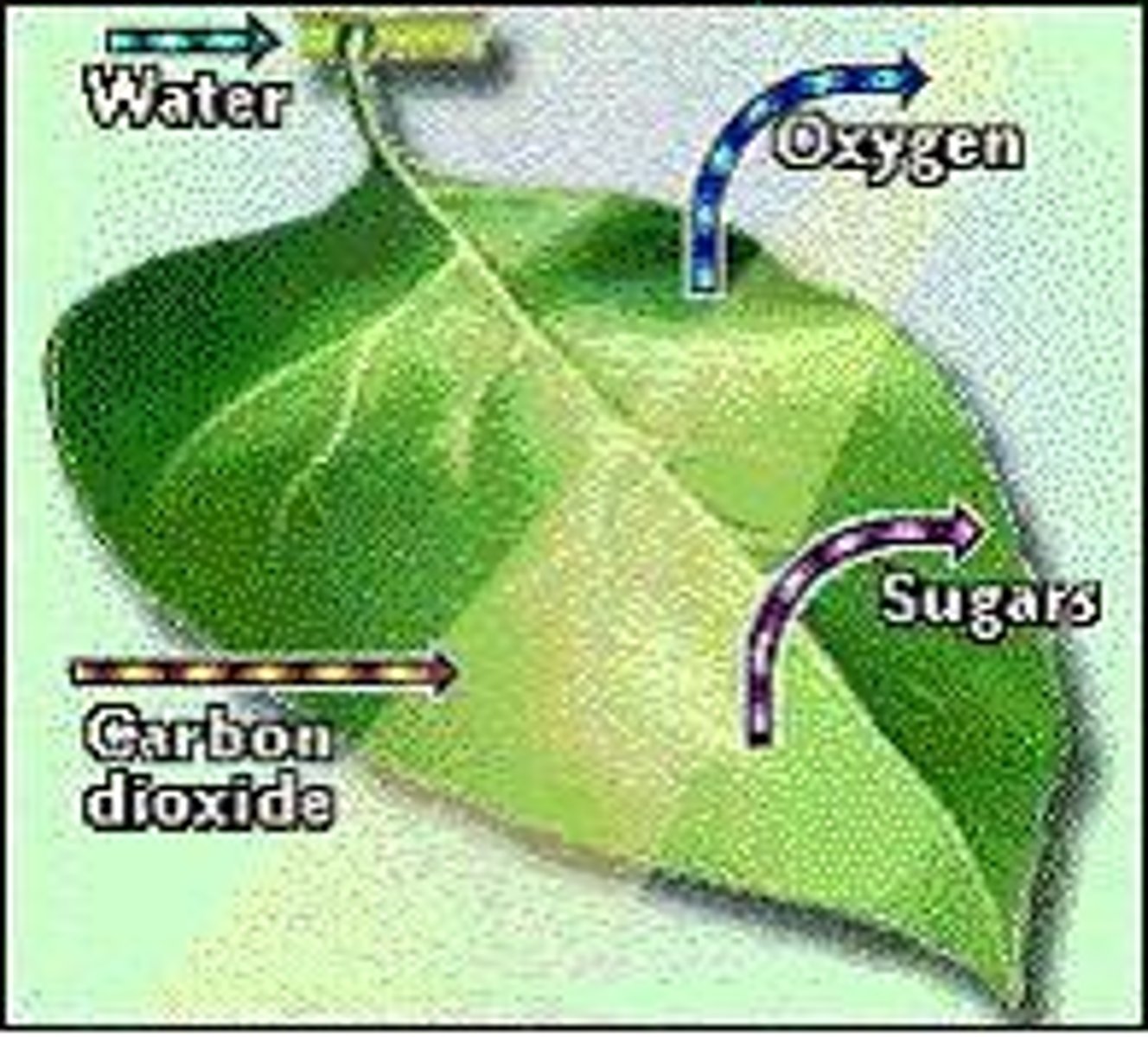
Energy Flow
Transfer of energy through food chains and webs.
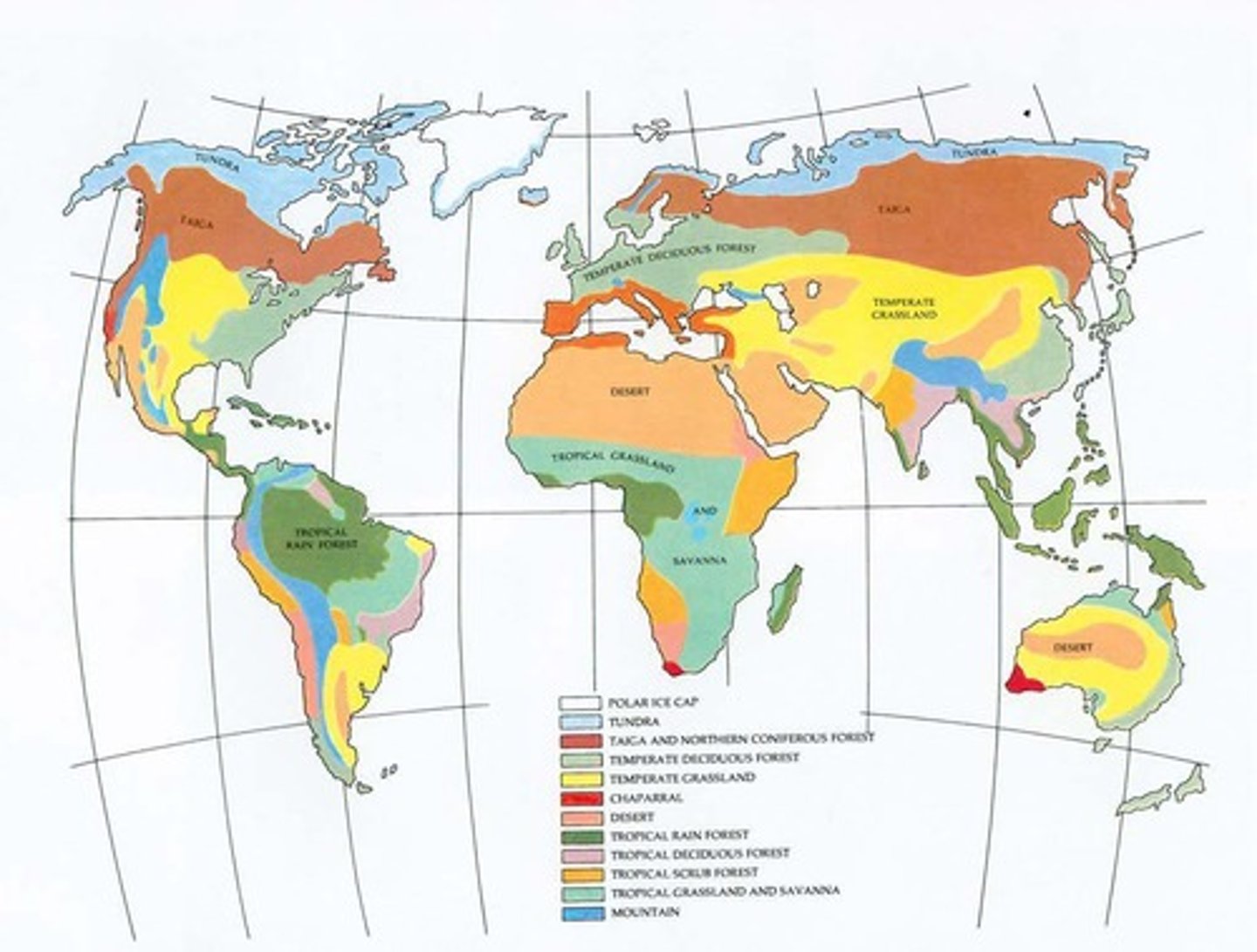
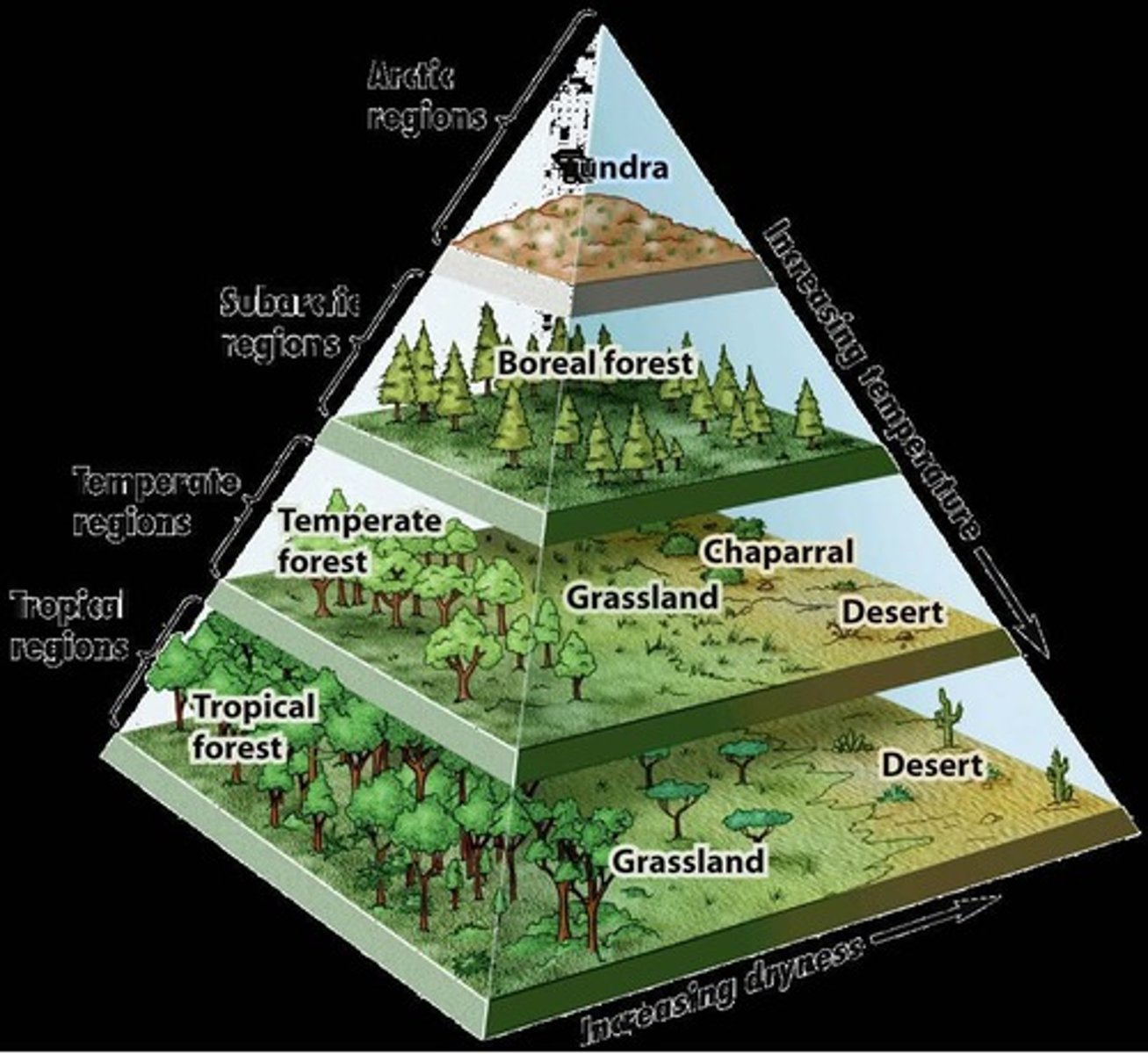
Ecosystem Diversity
Variety of ecosystems within a specific area.
Population Dynamics
Study of how populations change over time.
Agriculture
Cultivation of plants and livestock for food production.
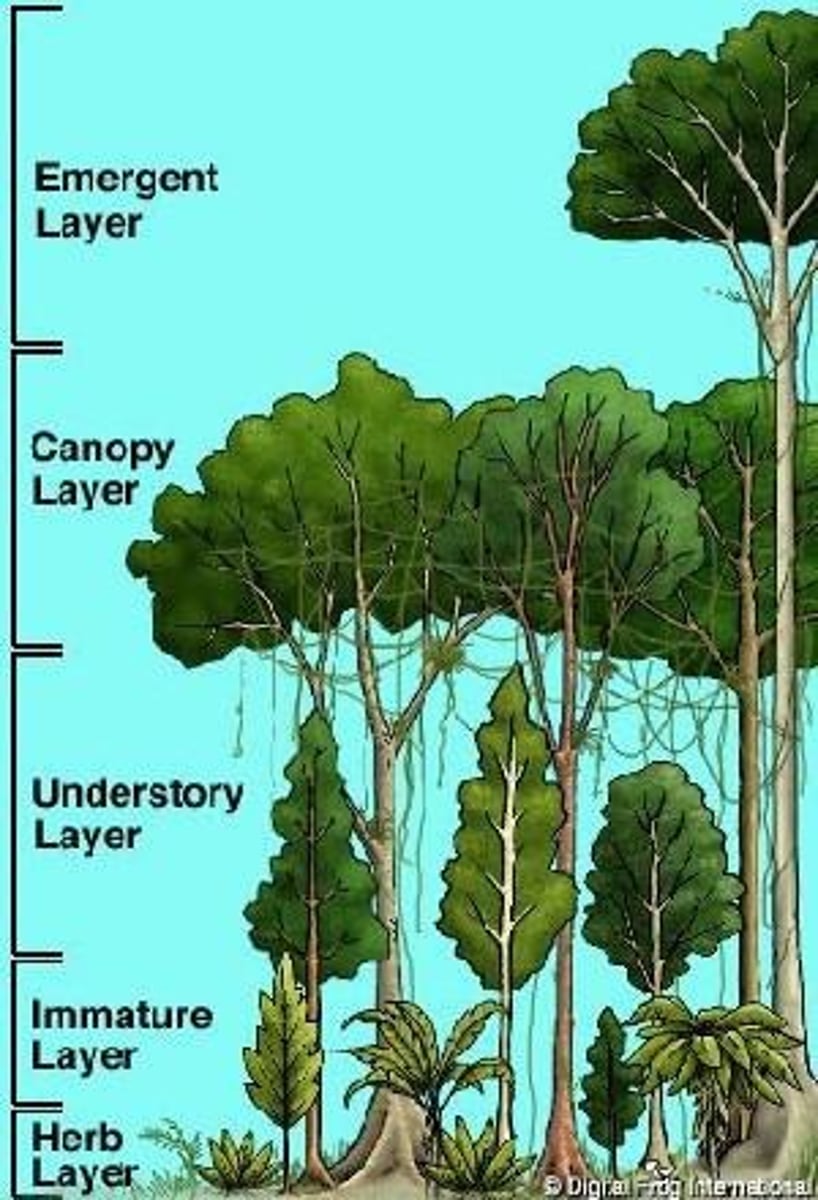
Forestry
Management of forests for timber and conservation.

Rangelands
Grasslands used for grazing livestock.

Mining
Extraction of minerals and resources from the Earth.
Fishing
Harvesting aquatic organisms for food or trade.
Global Economics
Study of economic systems on a worldwide scale.
Types of Pollution
Different forms of environmental contamination affecting ecosystems.
Energy Concepts
Fundamental principles governing energy use and conservation.
Environmental Health
Impact of environmental factors on human health.
Toxicology
Study of harmful effects of substances on living organisms.
Sustainable Cities
Urban areas designed for long-term ecological balance.
Climate Change
Long-term alteration of temperature and typical weather patterns.
Water Pollution
Contamination of water bodies affecting ecosystems and health.
Hazardous Waste
Waste posing substantial or potential threats to public health.
Environmental Worldviews
Perspectives on humanity's relationship with the environment.
Sustainable Practices
Methods that meet current needs without compromising future generations.
Nutrient Cycles
Movement of nutrients through ecosystems.
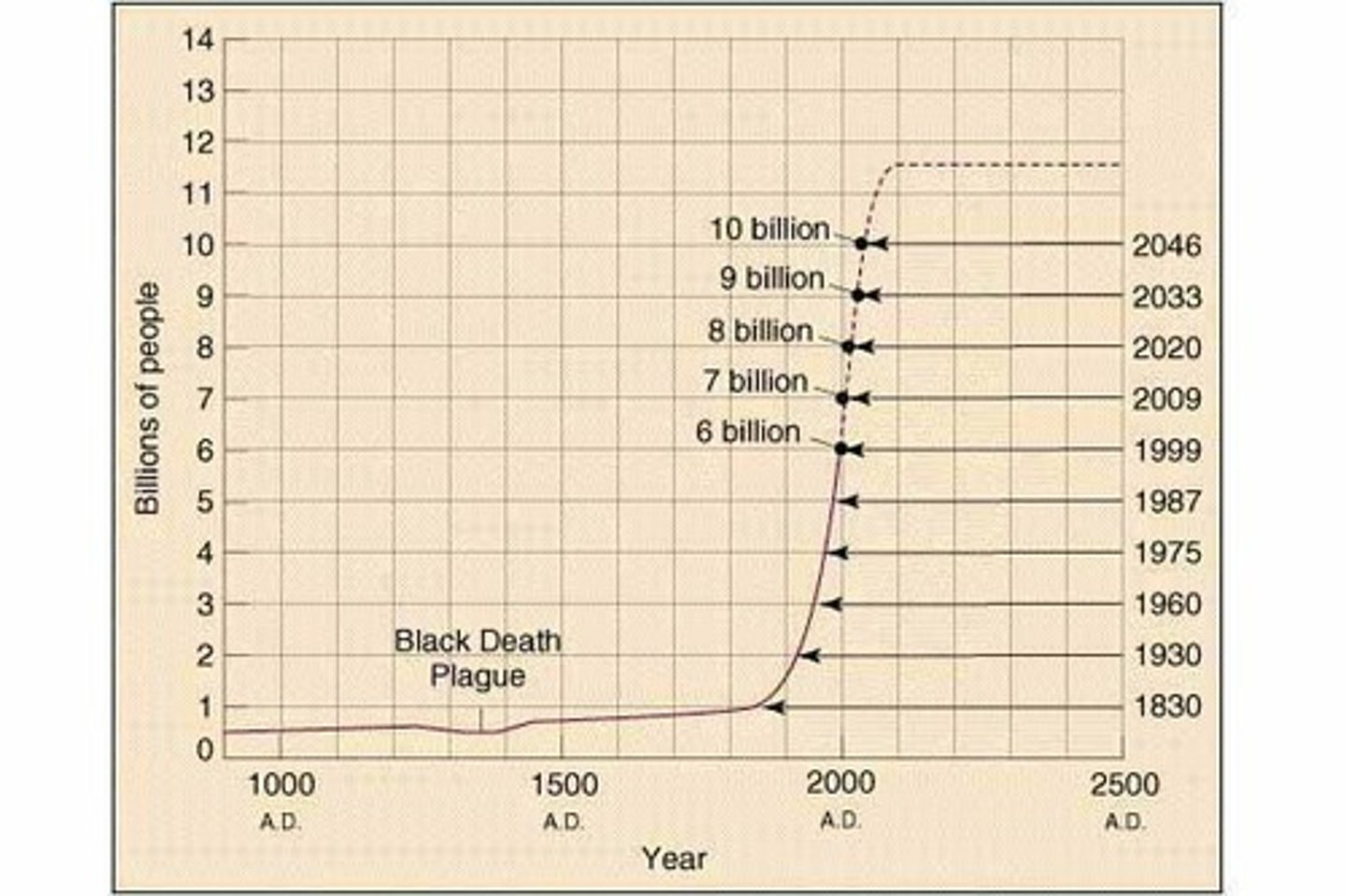
Human Population
Study of human demographics and their impacts on the environment.
APES Exam
Advanced Placement Environmental Science assessment.
Global Change
Significant alterations in global environmental conditions.
Nonrenewable Energy
Energy from finite resources like fossil fuels.
Solid Waste
Non-liquid waste materials generated by human activity.
Environmental Geology
Study of geological processes and their impact on the environment.
Economics and Environment
Relationship between economic activities and environmental health.
Pests
Organisms that cause damage to crops or human health.
Laws and Treaties
Regulations governing environmental protection and resource use.
Critical Thinking
Objective analysis and evaluation of issues to form judgment.
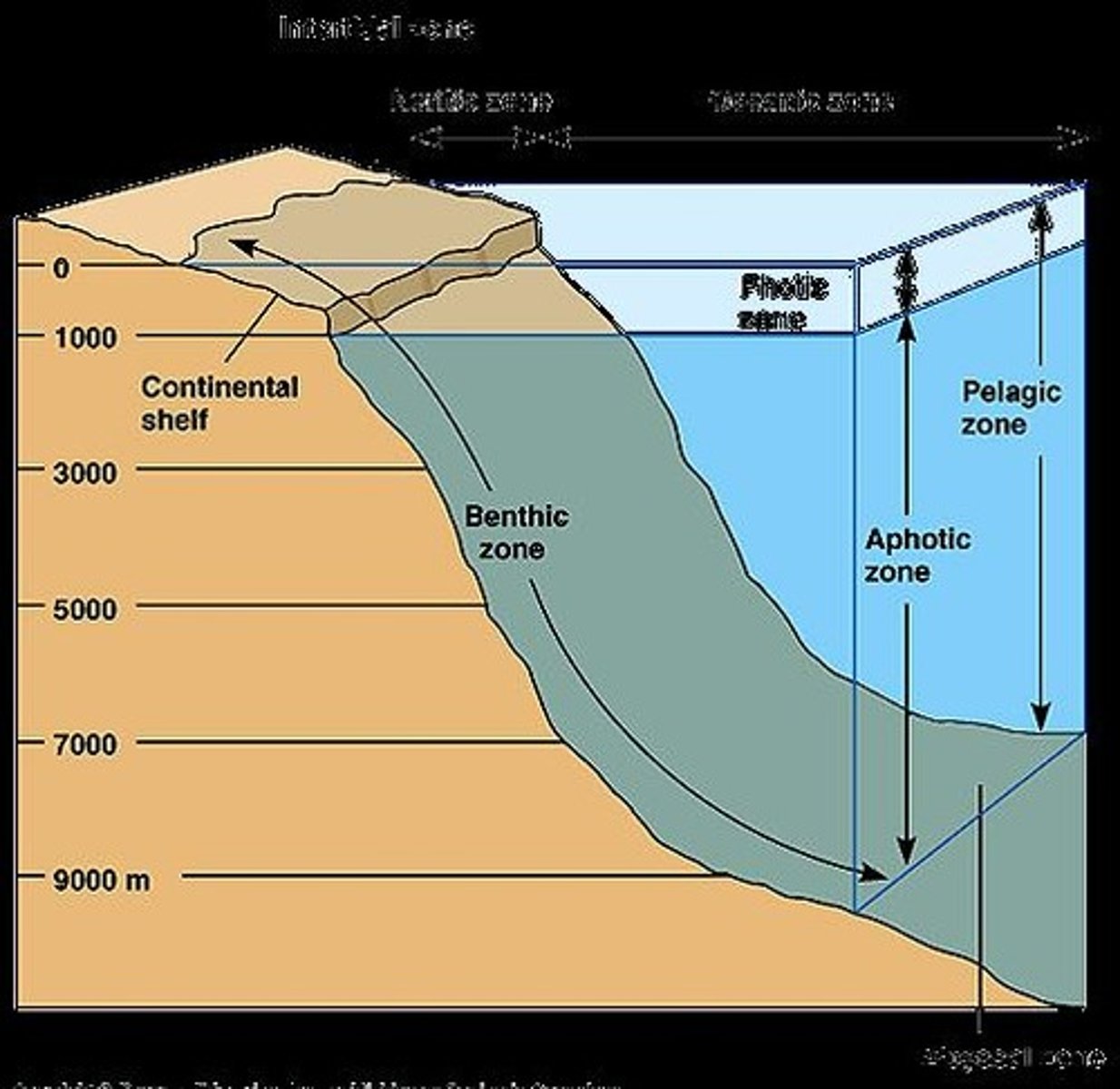
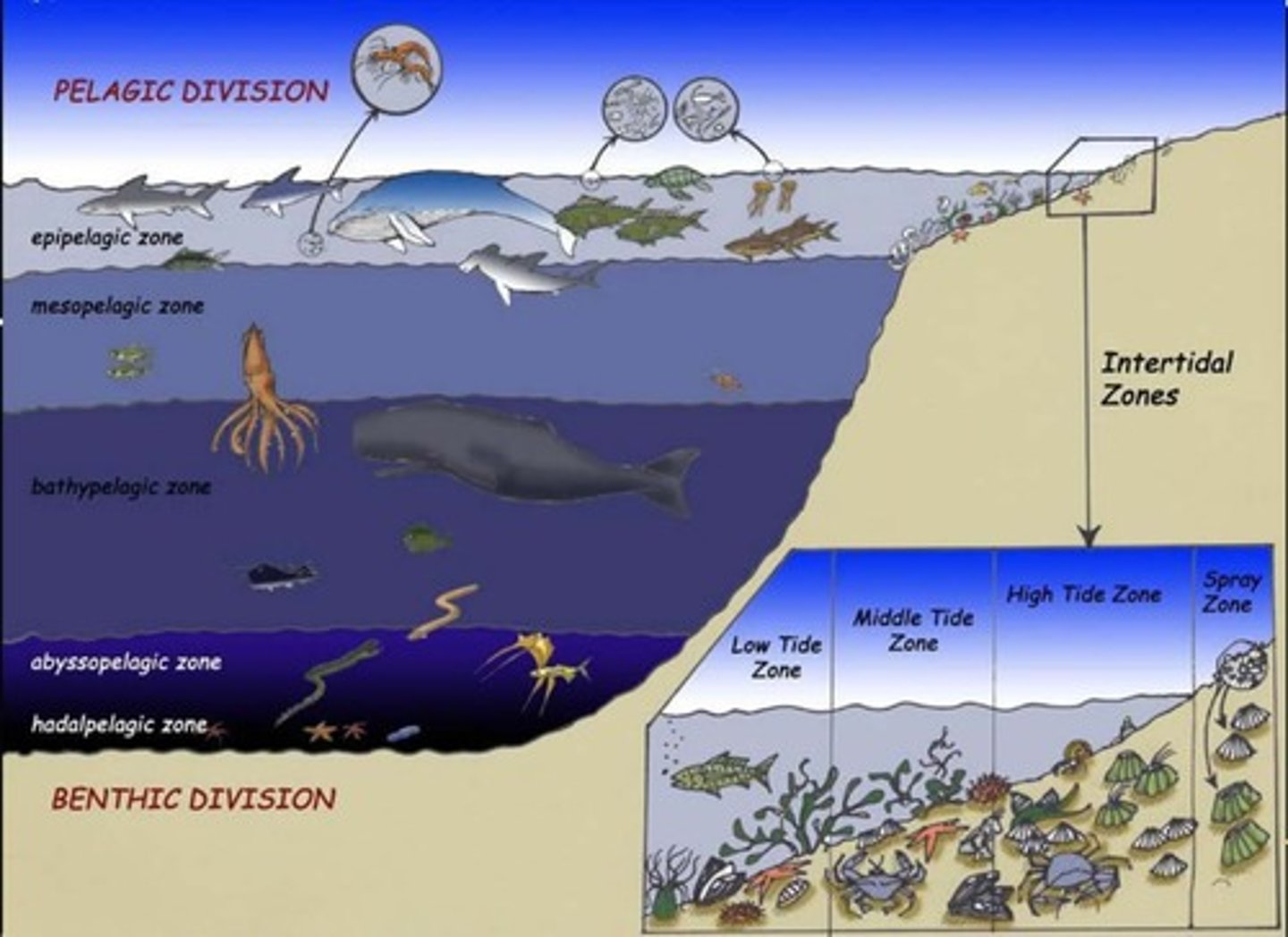
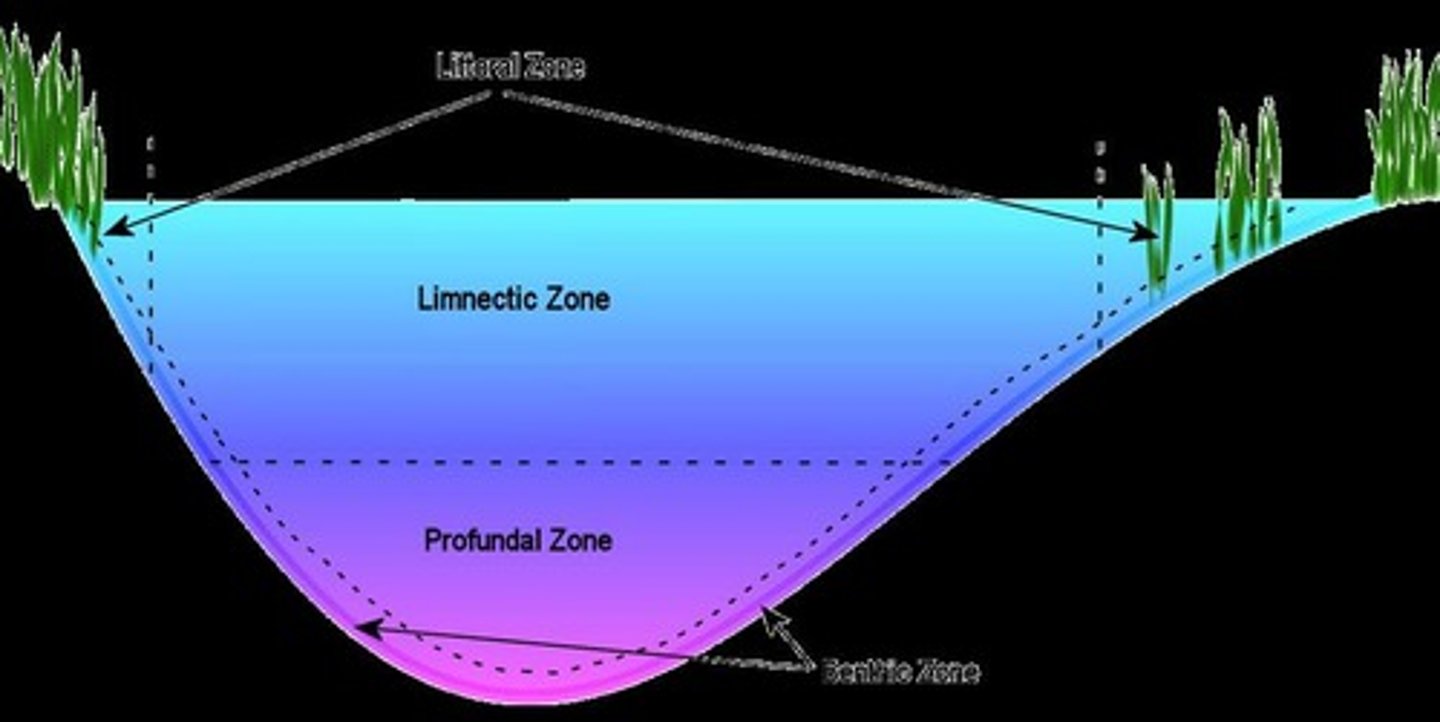
Aquatic Ecology
Study of ecosystems in water environments.
Sustainable Energy
Energy practices that meet current needs without compromising future.
Air Pollutants
Substances in the air that can harm human health.
Plate Tectonics
Movement of Earth's lithospheric plates.
ENSO
El Niño-Southern Oscillation; climate pattern affecting weather.
Freshwater Resources
Water with low salt concentration, essential for life.
Ocean Circulation
Movement of ocean water driven by wind and temperature.
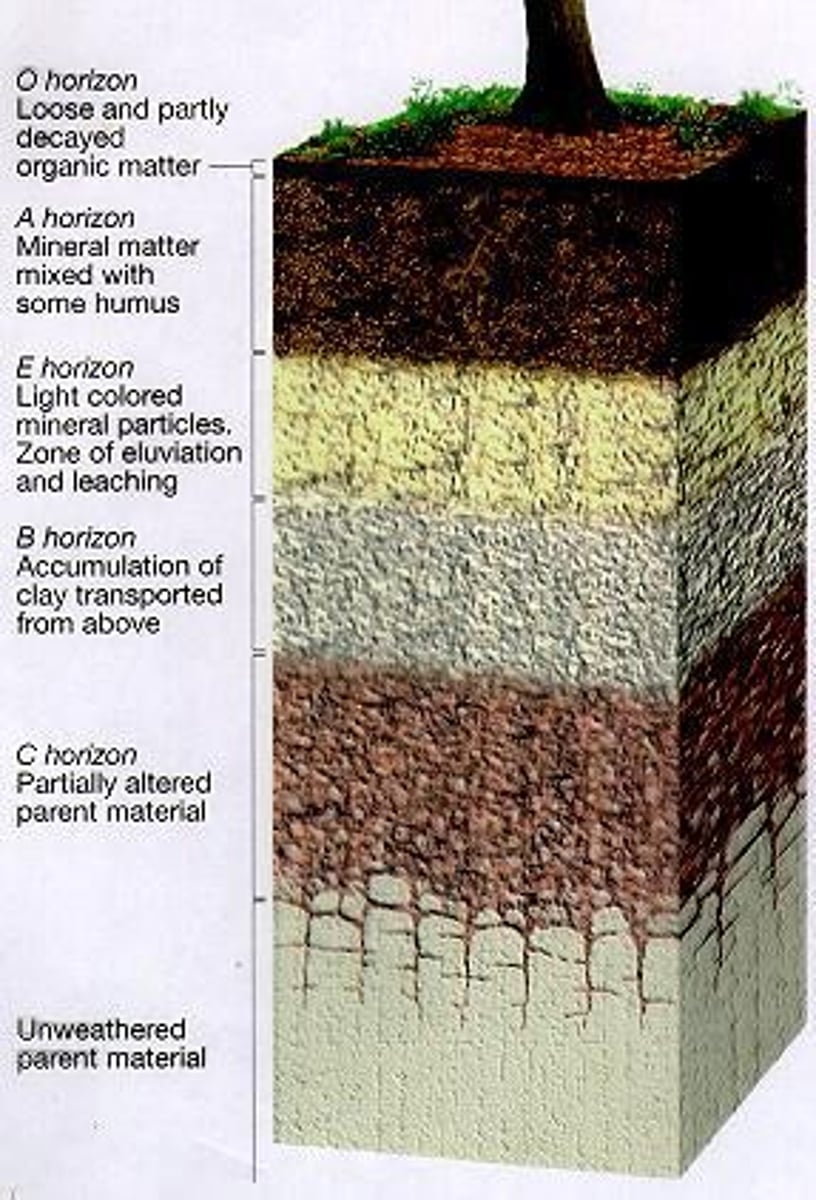
Soil Composition
Minerals, organic matter, water, and air in soil.
Ecosystem Structure
Organization of biological communities and populations.
Trophic Levels
Hierarchical levels in food chains and webs.
Carrying Capacity
Maximum population size an environment can sustain.
Demographic Transition
Model describing population change over time.
Integrated Pest Management
Combines biological, cultural, and chemical practices for pest control.
Urbanization
Increase in population living in urban areas.
Rangeland Management
Sustainable practices for grazing lands.
Nuclear Fission
Splitting of atomic nuclei to release energy.
Energy Efficiency
Using less energy to provide the same service.
Pollution Types
Various categories of environmental contamination.
Primary Pollutants
Directly emitted pollutants from sources.
Secondary Pollutants
Formed by reactions in the atmosphere.
Major Air Pollutants
Includes CO, NOx, SO2, PM, and O3.
Acid Deposition
Acidic rain caused by pollutants.
Heat Islands
Urban areas warmer than surrounding rural areas.
Clean Air Act
U.S. law regulating air quality standards.
Cultural Eutrophication
Nutrient enrichment causing excessive plant growth.
Groundwater Pollution
Contamination of underground water sources.
Water Purification
Processes to remove contaminants from water.
Sewage Treatment
Processes to treat wastewater before release.
Environmental Risk Analysis
Assessment of potential environmental hazards.
Dose Response Relationships
Correlation between exposure and effect severity.
Biomagnification
Increase in concentration of toxins in food chains.
Greenhouse Effect
Trapping of heat by greenhouse gases.
Loss of Biodiversity
Decline in variety of life forms.
Pangaea
Supercontinent existing during the late Paleozoic.
Holocene Epoch
Current geological epoch, began 0.01 million years ago.
Cenozoic Era
Current geological era, began 66 million years ago.
Proterozoic Eon
Time before abundant complex life, 2.5 billion years ago.
Archean Eon
Earliest geological eon, Earth formed 4.5 billion years ago.
Core
Earth's innermost layer, solid inner and molten outer.
Mantle
Layer of solid rock, includes flowing asthenosphere.
Lithosphere
Crust and upper mantle, divided into tectonic plates.
Tectonic Plates
Large sections of lithosphere that move.
Convergent Boundary
Where two tectonic plates push toward each other.
Divergent Boundary
Where two tectonic plates move away from each other.
Transform Fault Boundary
Where two plates slide past each other.
Active Volcano
Currently erupting or has erupted historically.
Dormant Volcano
Has not erupted in recorded history.
Extinct Volcano
Will never erupt again.
Rift Volcano
Formed where tectonic plates move apart.
Subduction Volcano
Formed where one plate slides over another.
Hot Spot Volcano
Volcanoes formed where magma rises to surface.
Focus
Location inside Earth where an earthquake begins.
Epicenter
Point on surface directly above earthquake focus.
Seismograph
Instrument measuring earthquake magnitude.
Sedimentary Rock
Formed from compressed sediments, e.g., limestone.
Metamorphic Rock
Rock transformed by heat and pressure, e.g., slate.
Igneous Rock
Formed from molten rock cooling, e.g., basalt.
Climate
Long-term weather patterns in a specific area.
Watershed
Area where water drains into a specific stream.
Delta
Deposited sediments where rivers meet the ocean.
Estuary
Where freshwater and saltwater mix, rich in biodiversity.
Groundwater
Water stored underground in aquifers or wells.
Soil Fertility
Soil's capacity to supply essential nutrients.
Soil Porosity
Volume of pore spaces in soil.
Infiltration
Process of water entering soil.
Plasticity
Soil's ability to expand and contract.
Compressibility
Soil's tendency to decrease in volume.
Erodibility
Ease of soil removal by wind or water.