Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Osmosis
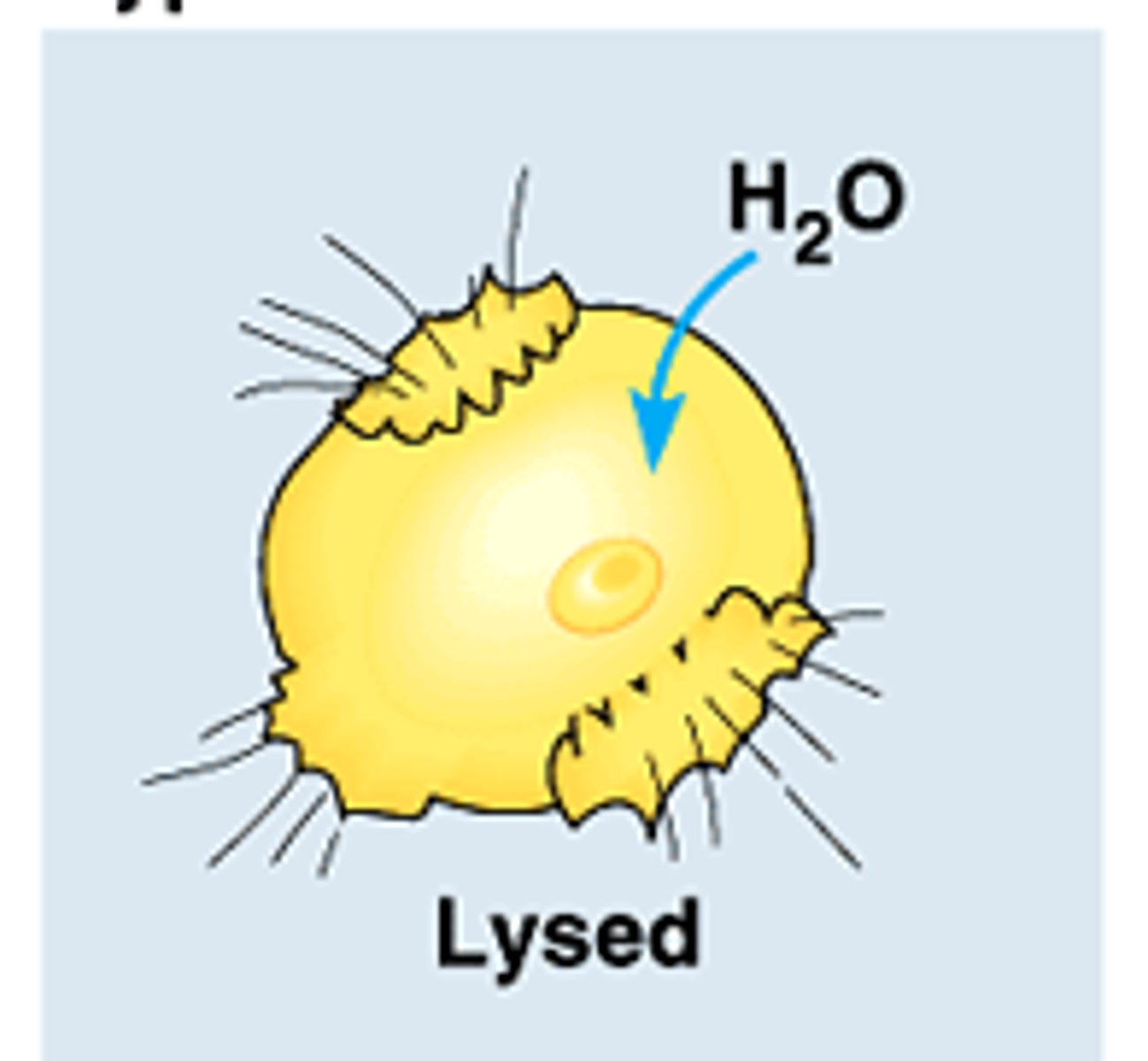
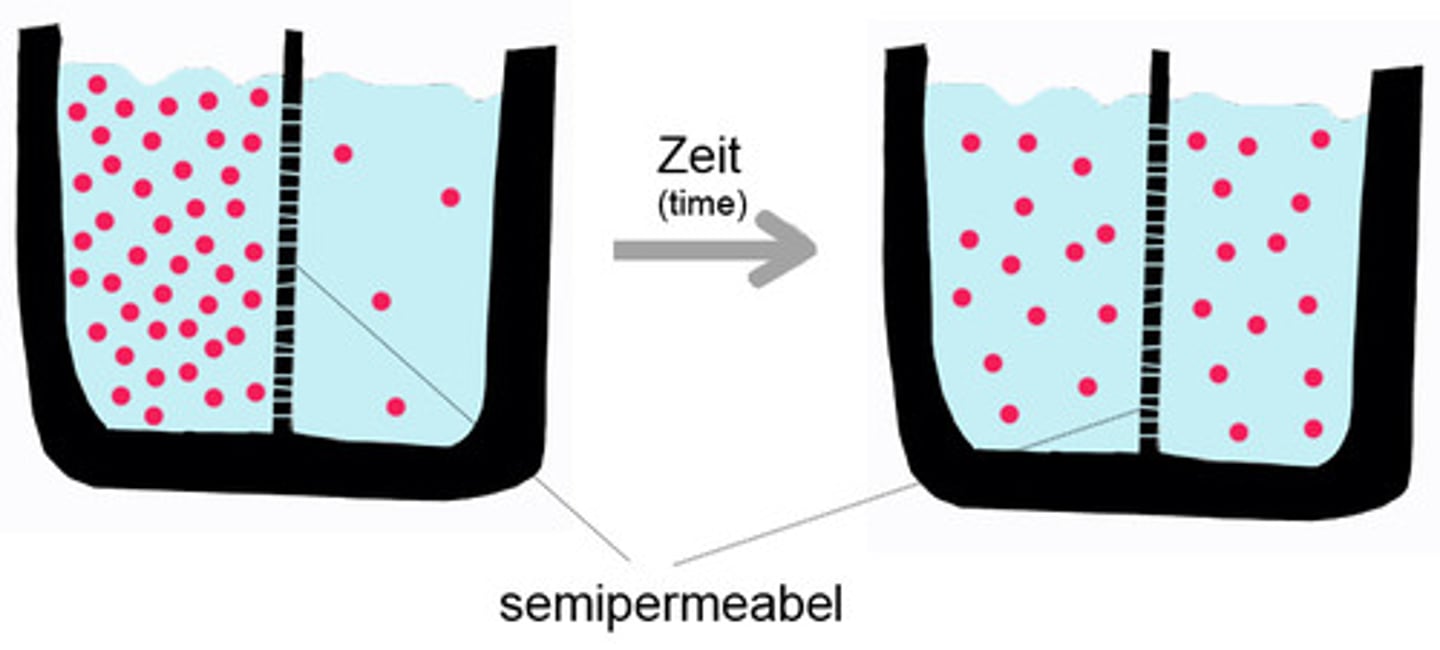
The movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane through diffusion. (semi-permeable means lets some things in and not others)
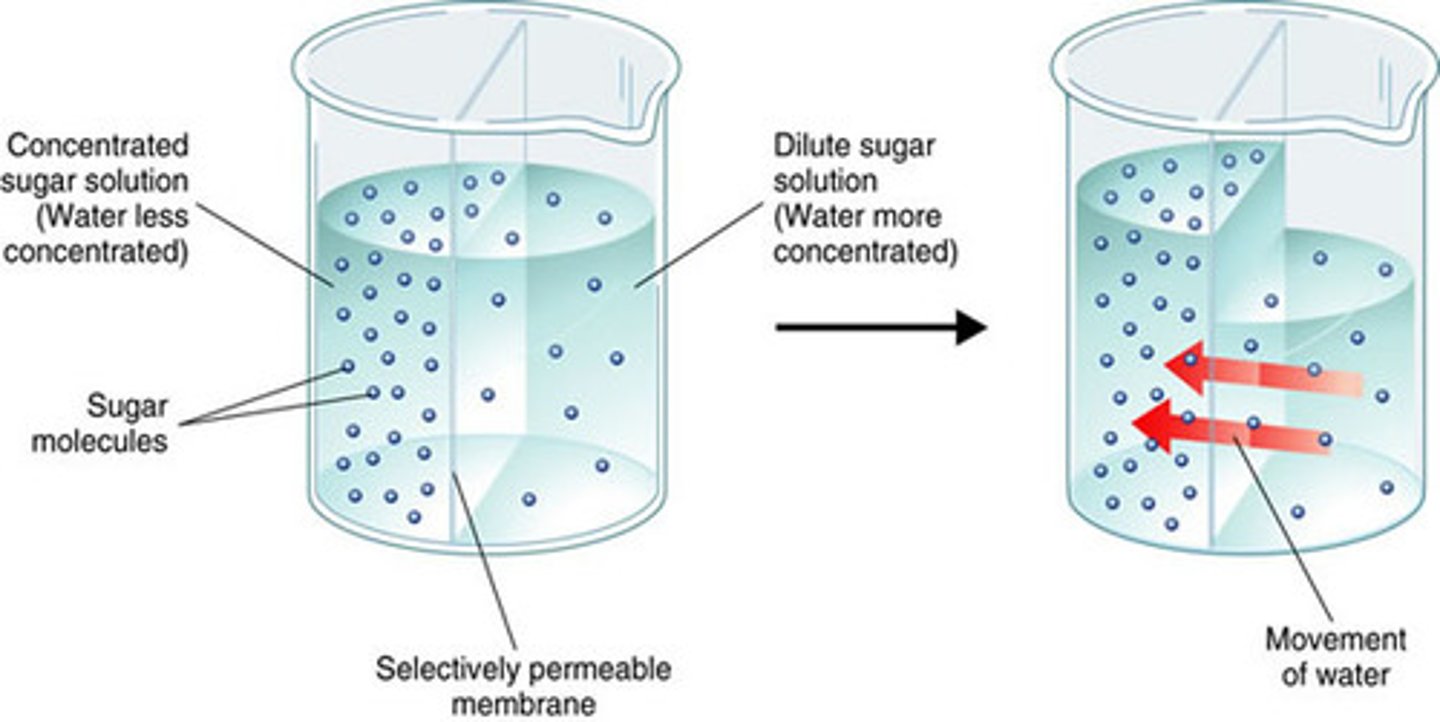
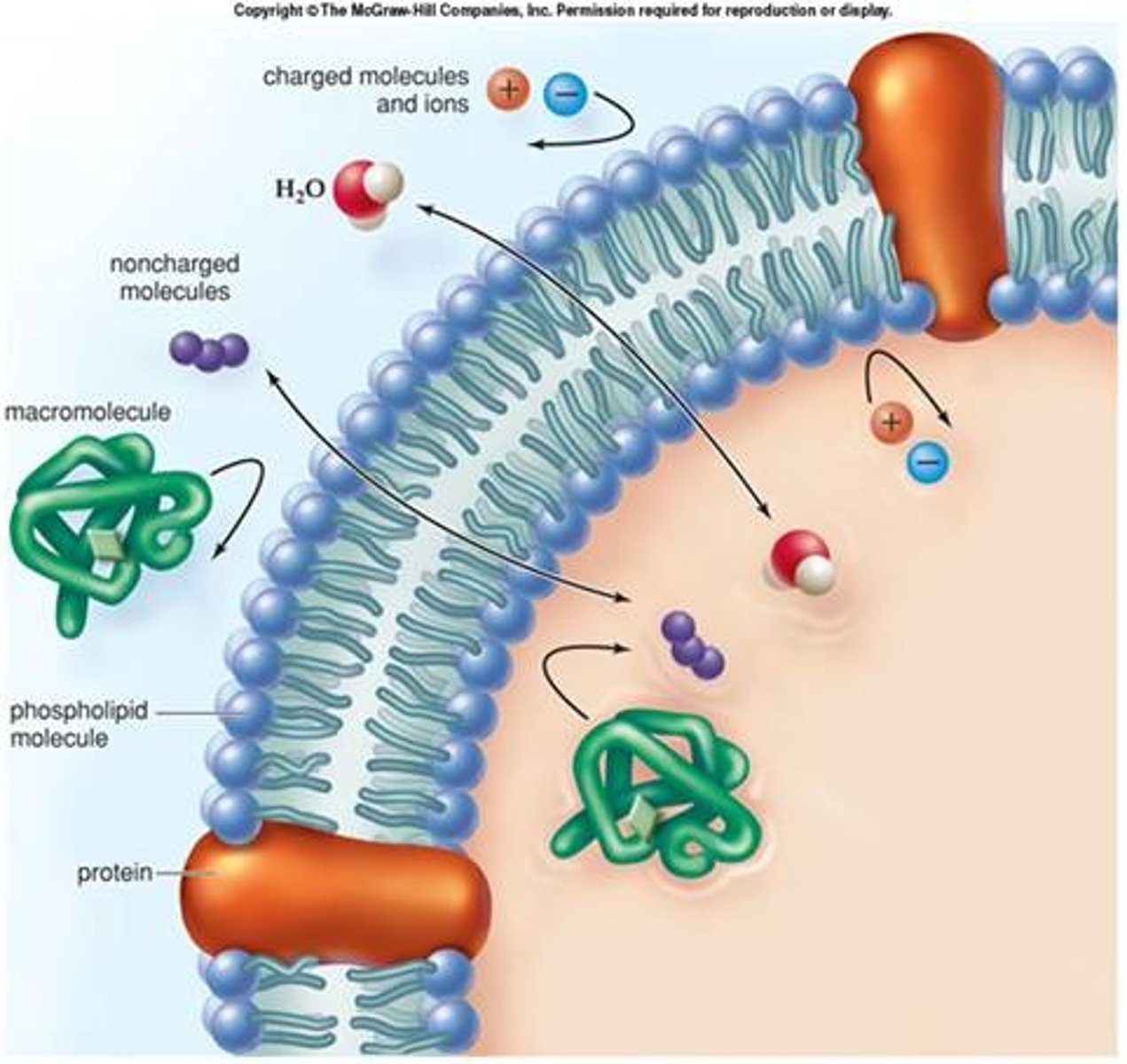
Selectively Permeable Membrane
A membrane that allows CERTAIN (only some) molecules to pass through it by diffusion. (Selective means to choose)

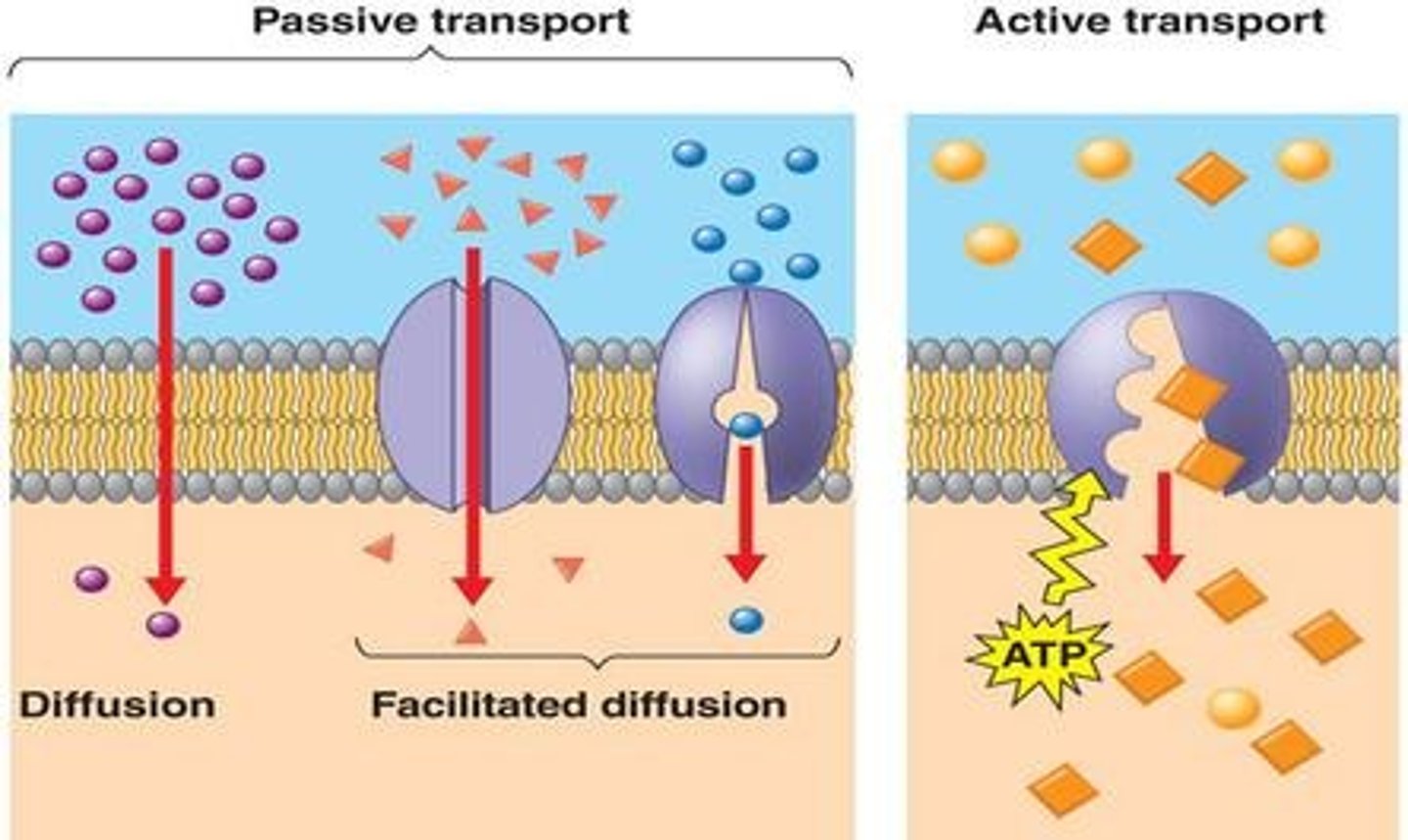
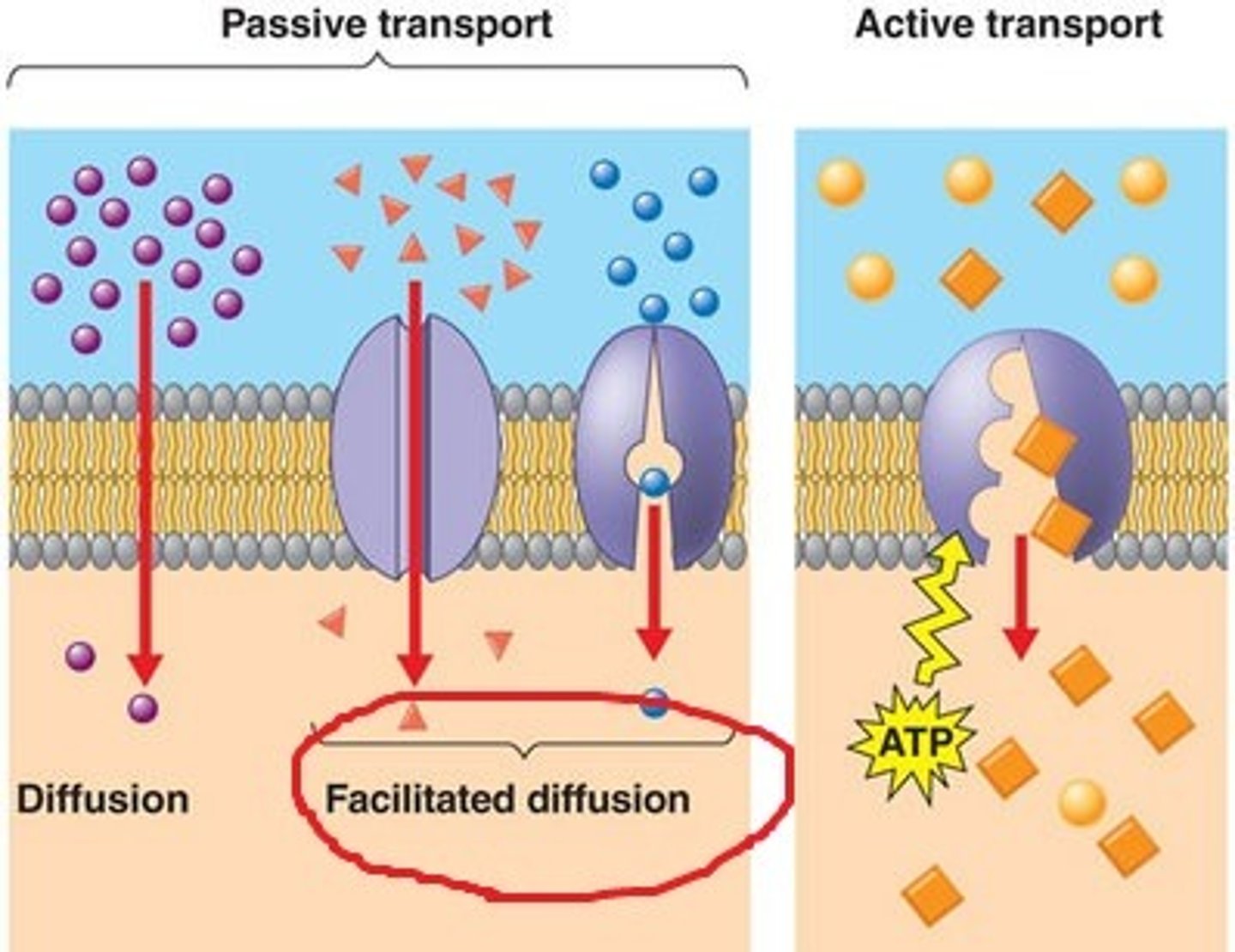
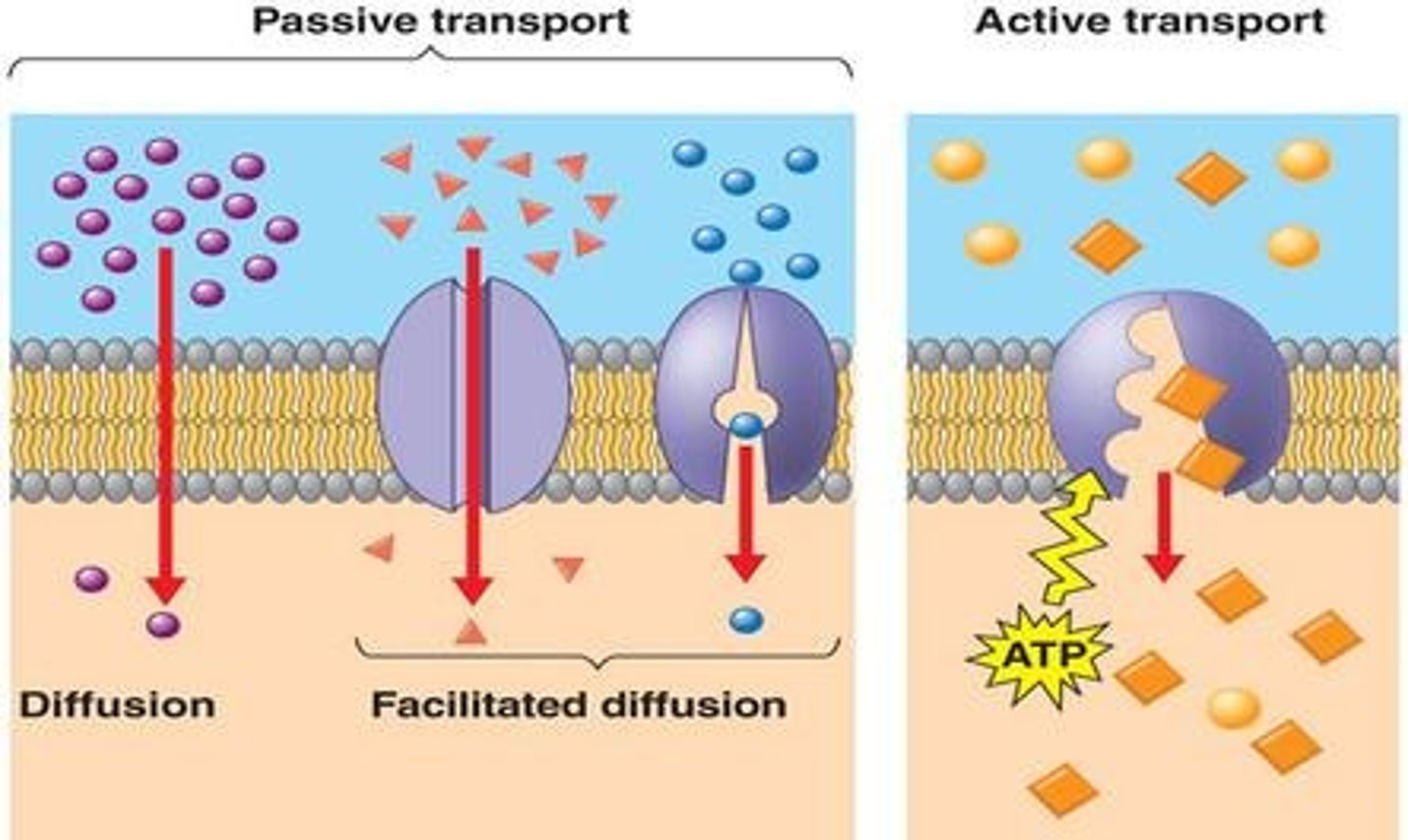
Passive Transport (definition)
Does NOT require energy....the movement of molecules (matter) from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Diffusion is a kind of passive transport.
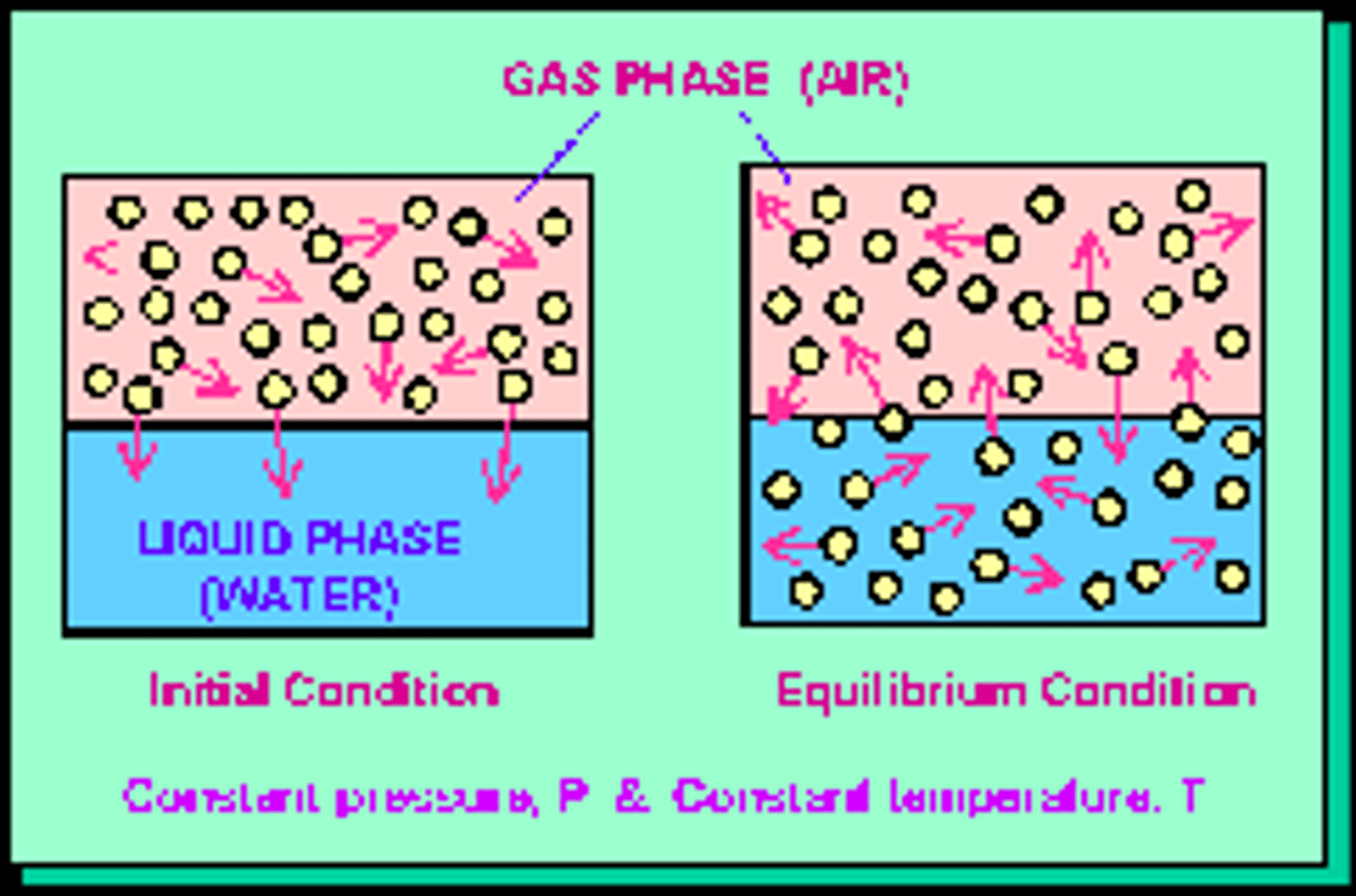
Equilibrium
A system in which things become equal; all particles (molecules or matter) become equal
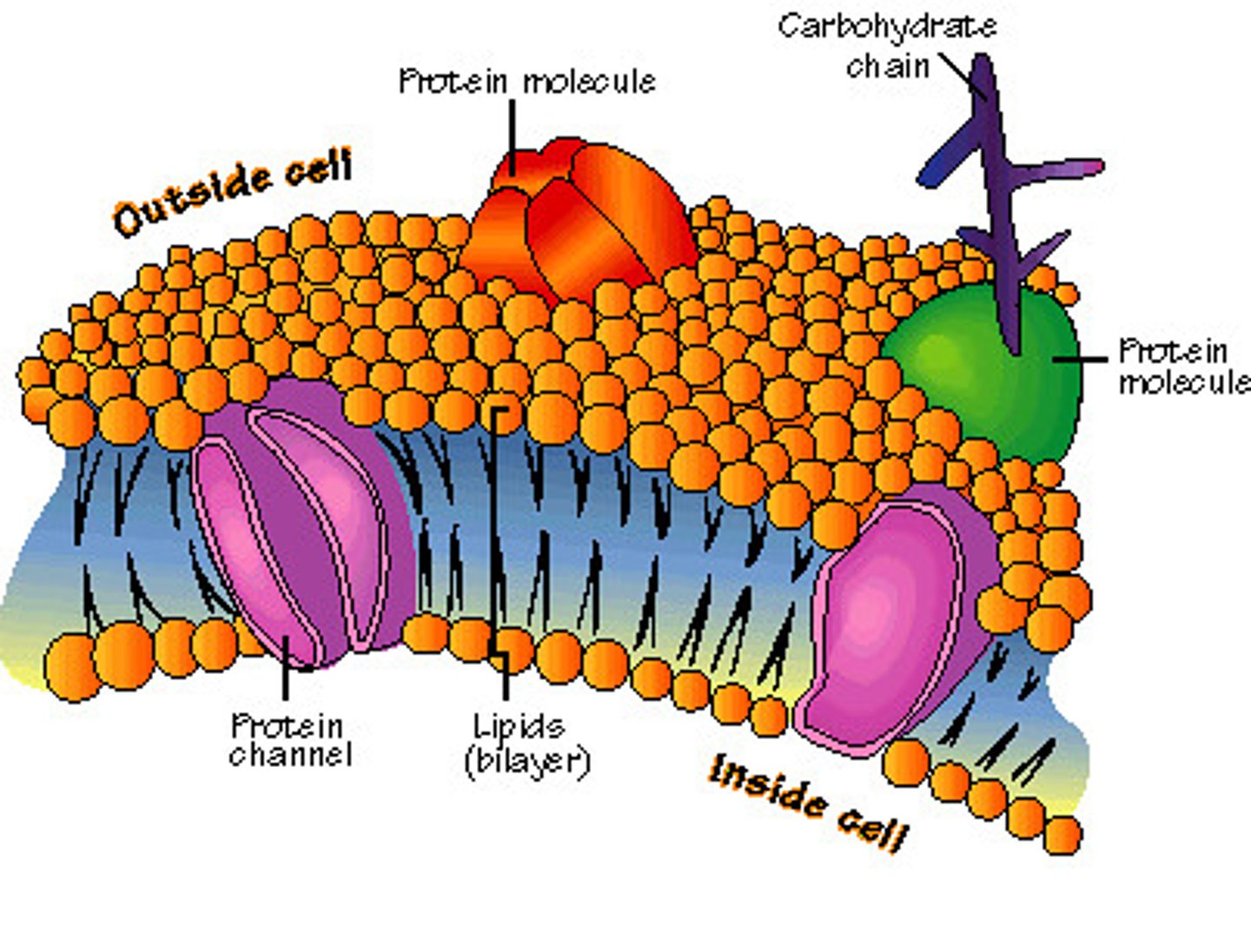
Cell Membrane (definition)
Double layer of phospholipids. Holds everything in. Decides what can enter or leave the cell.
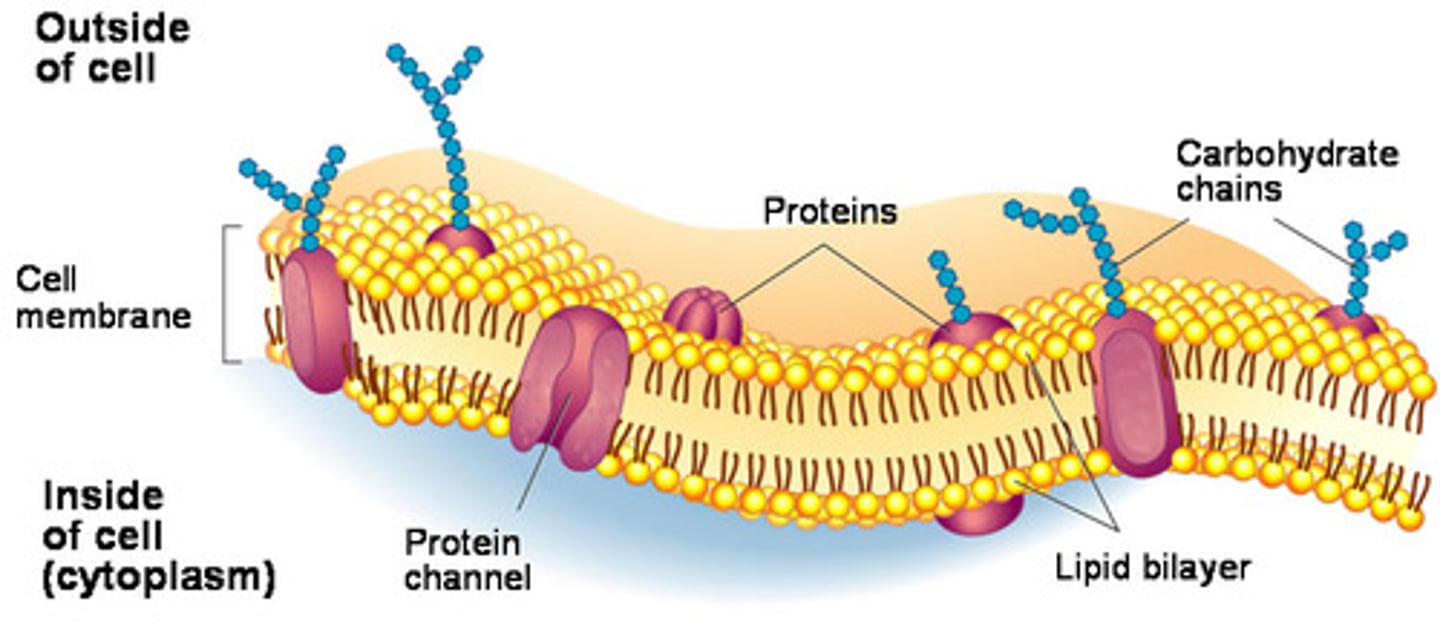
Selectively Permeable
Selective= pick and choose
Permeable= things can pass through
The cell membrane is said to be selectively permeable because it allows certain things to pass through and prevents other things from passing through.
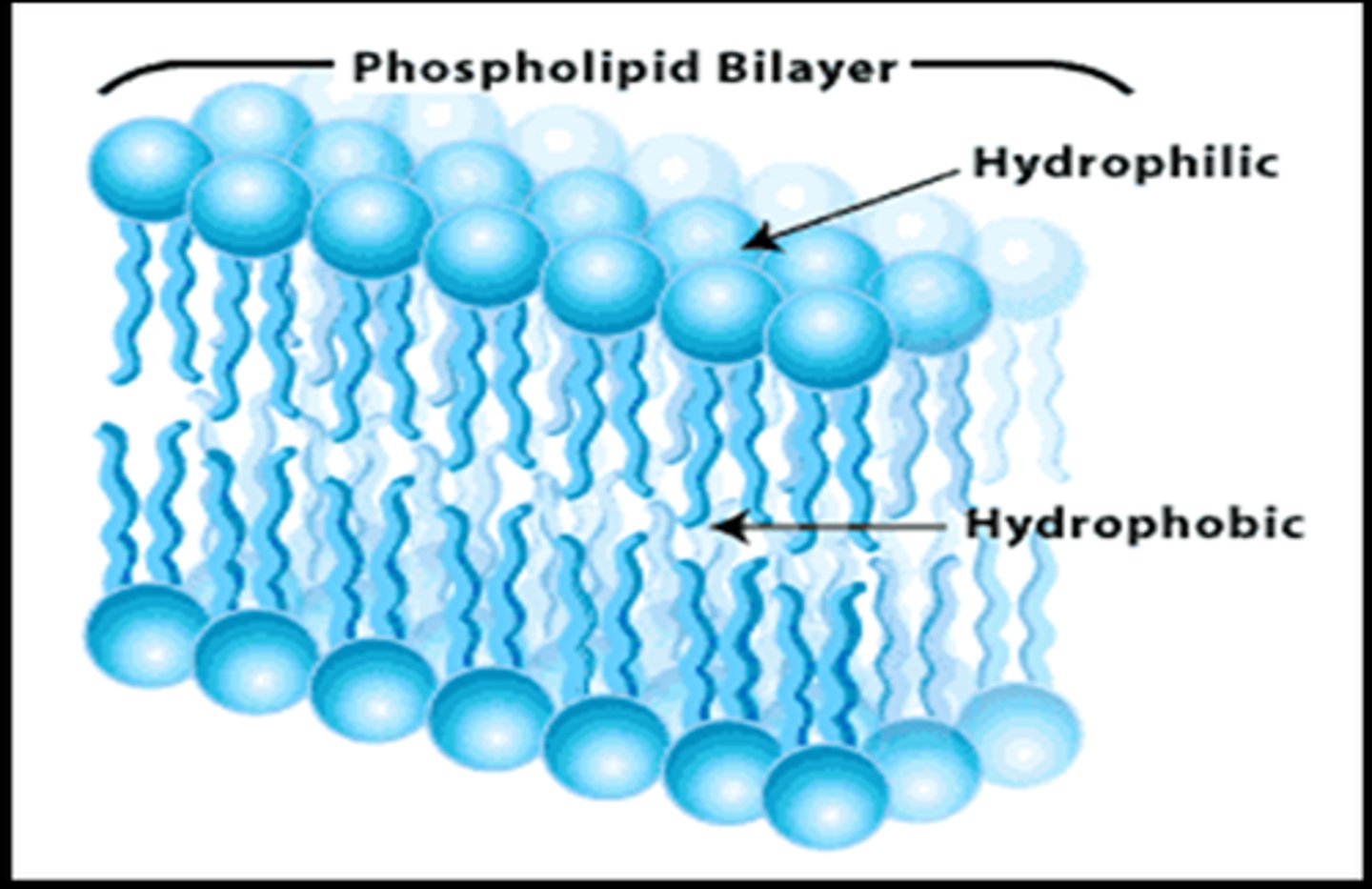
Polar
Will mix with water. Portion of membrane made up of phospholipid heads. Hydrophilic
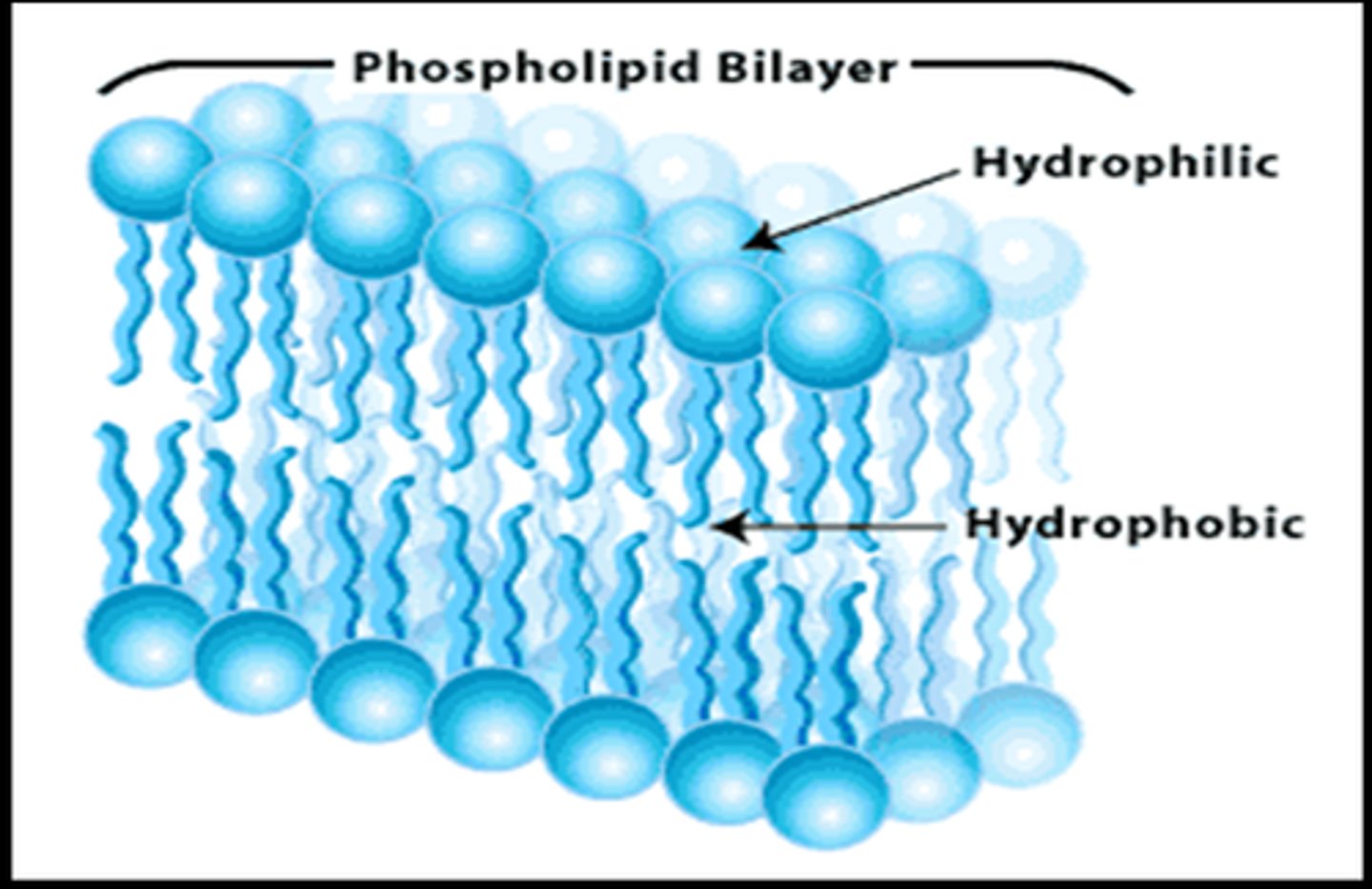
Non-polar
Will not mix with water. Portion of membrane made up of phospholipids tails. Hydrophobic
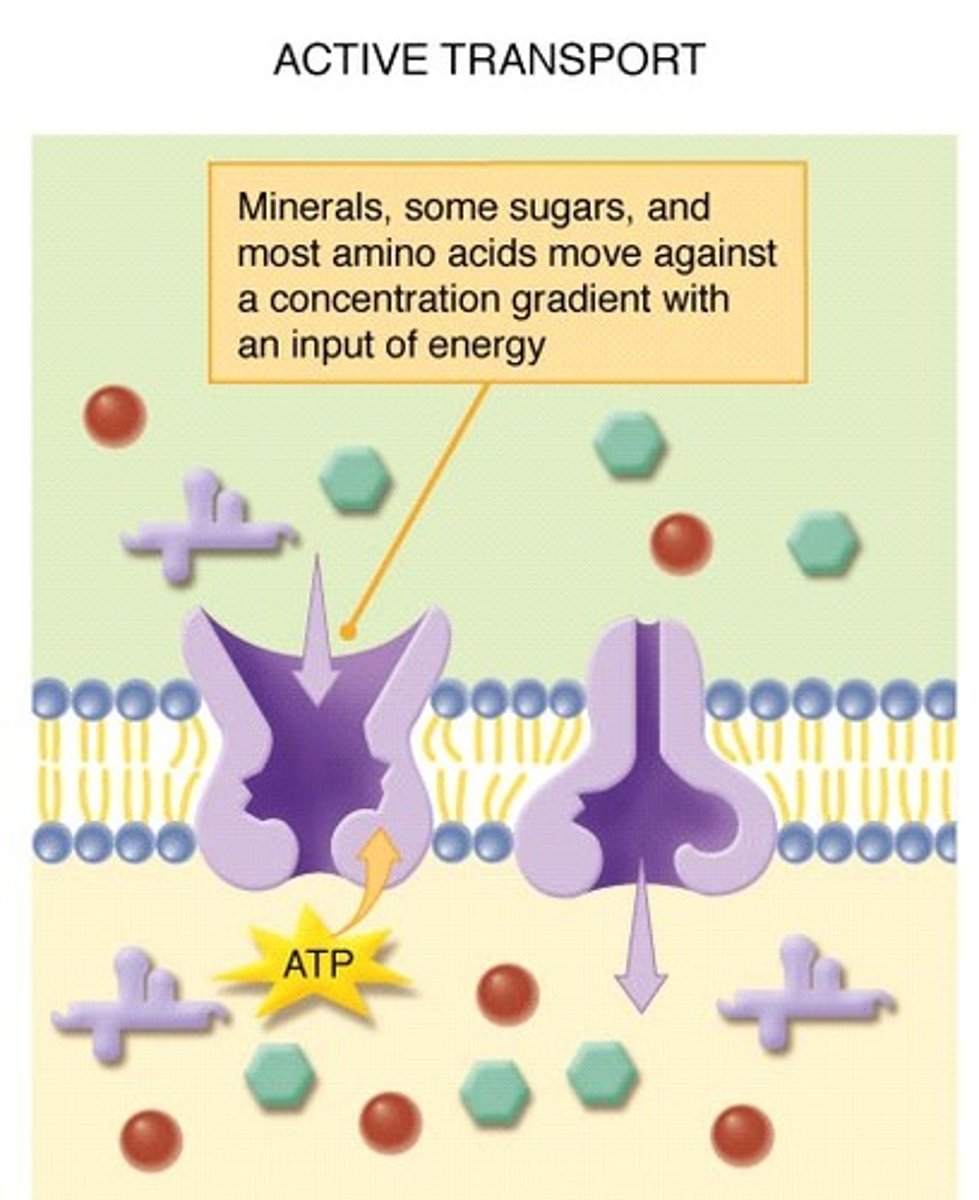
Active Transport (definition)
The movement of substances into/out of cell through the membrane, against the concentration gradient (from low to high). Requires ATP (i.e. proton pump, endocytosis)
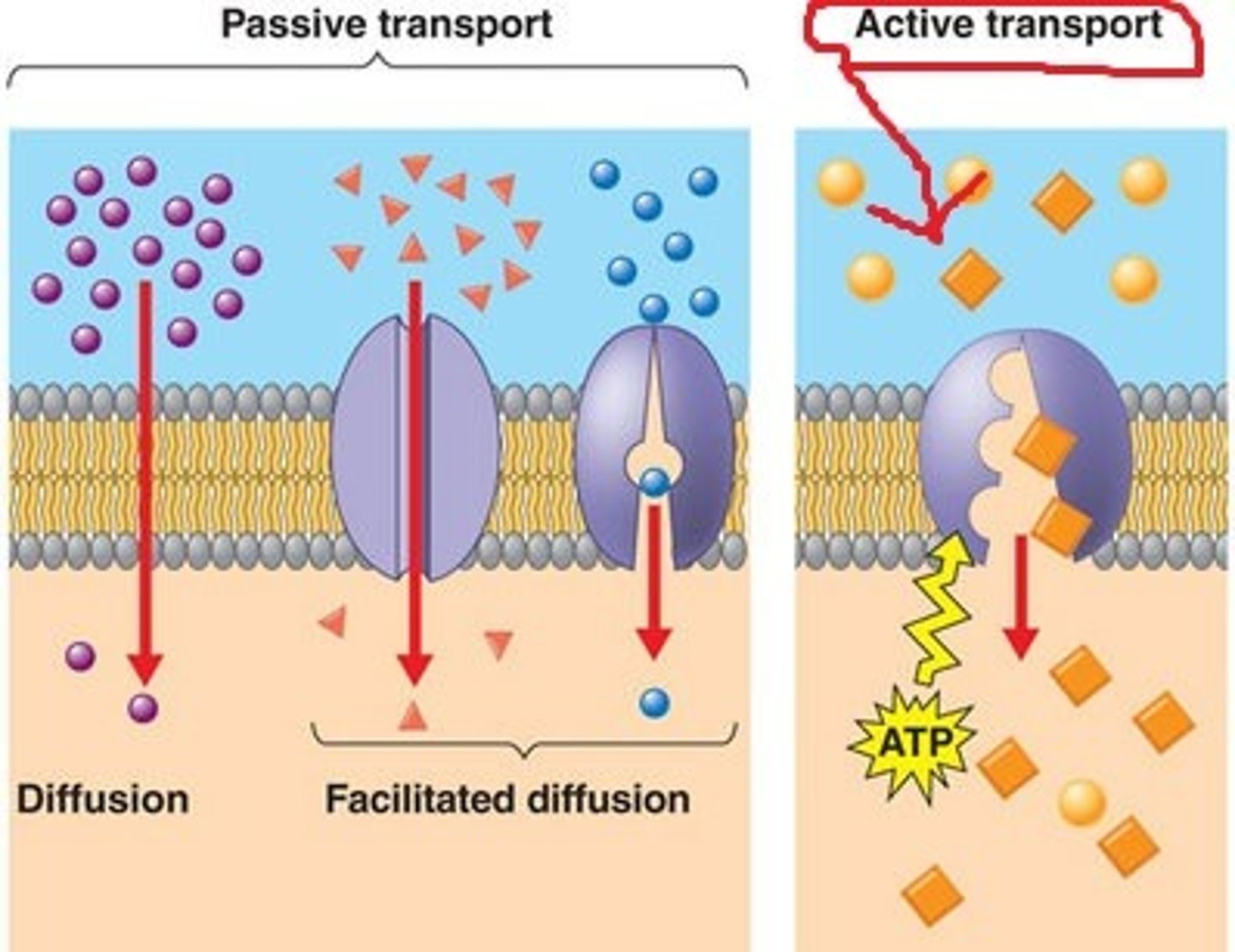
Protein Pump
Protein that can pump substances into/out of the cell against the concentration gradient(low to high). Requires ATP
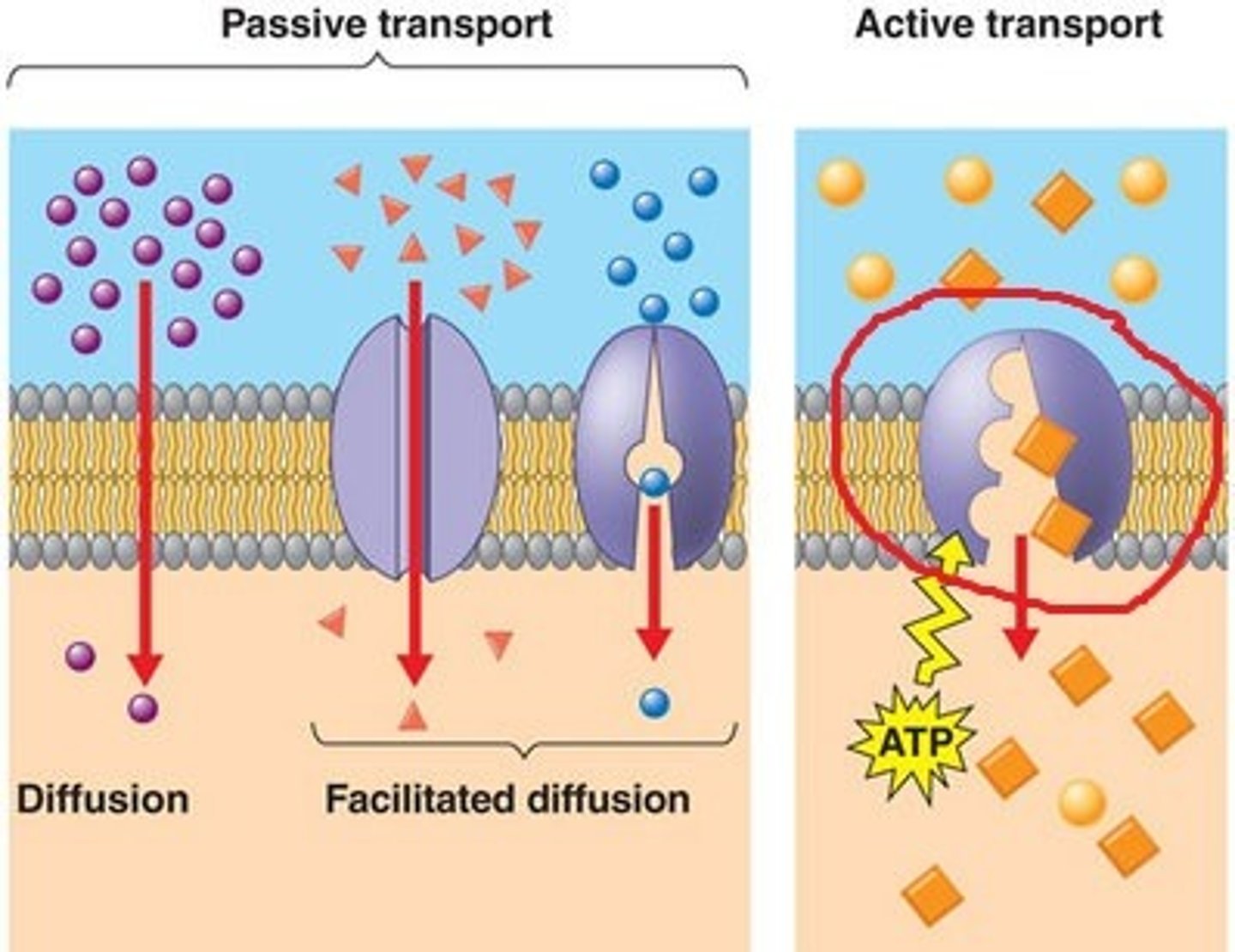
Facilitated diffusion
Channel proteins help polar substances enter/leave the cell. Does NOT require energy, so passive form of transport.
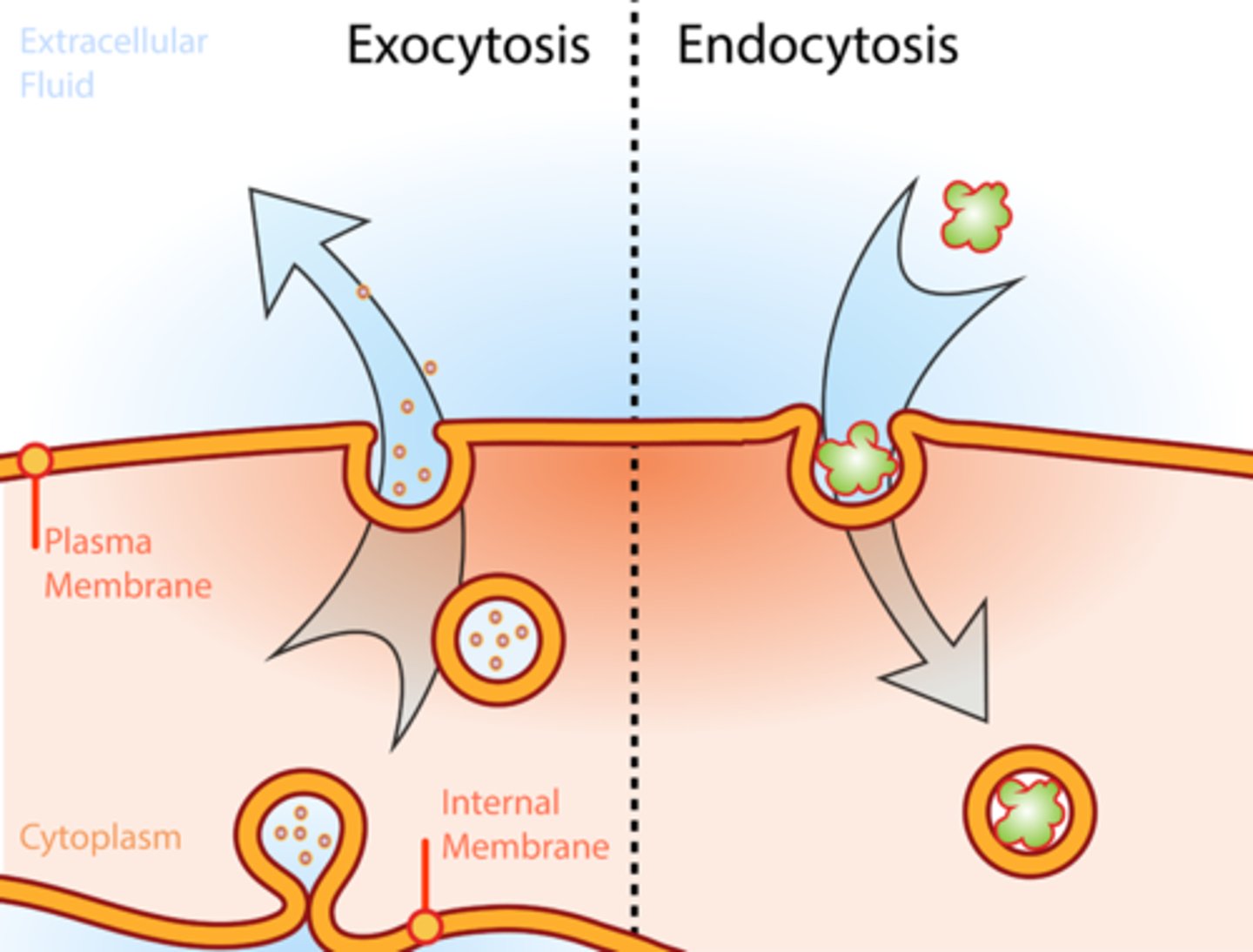
Endocytosis
Membrane folds around large substances so they can enter the cell. Requires ATP. Type of active transport
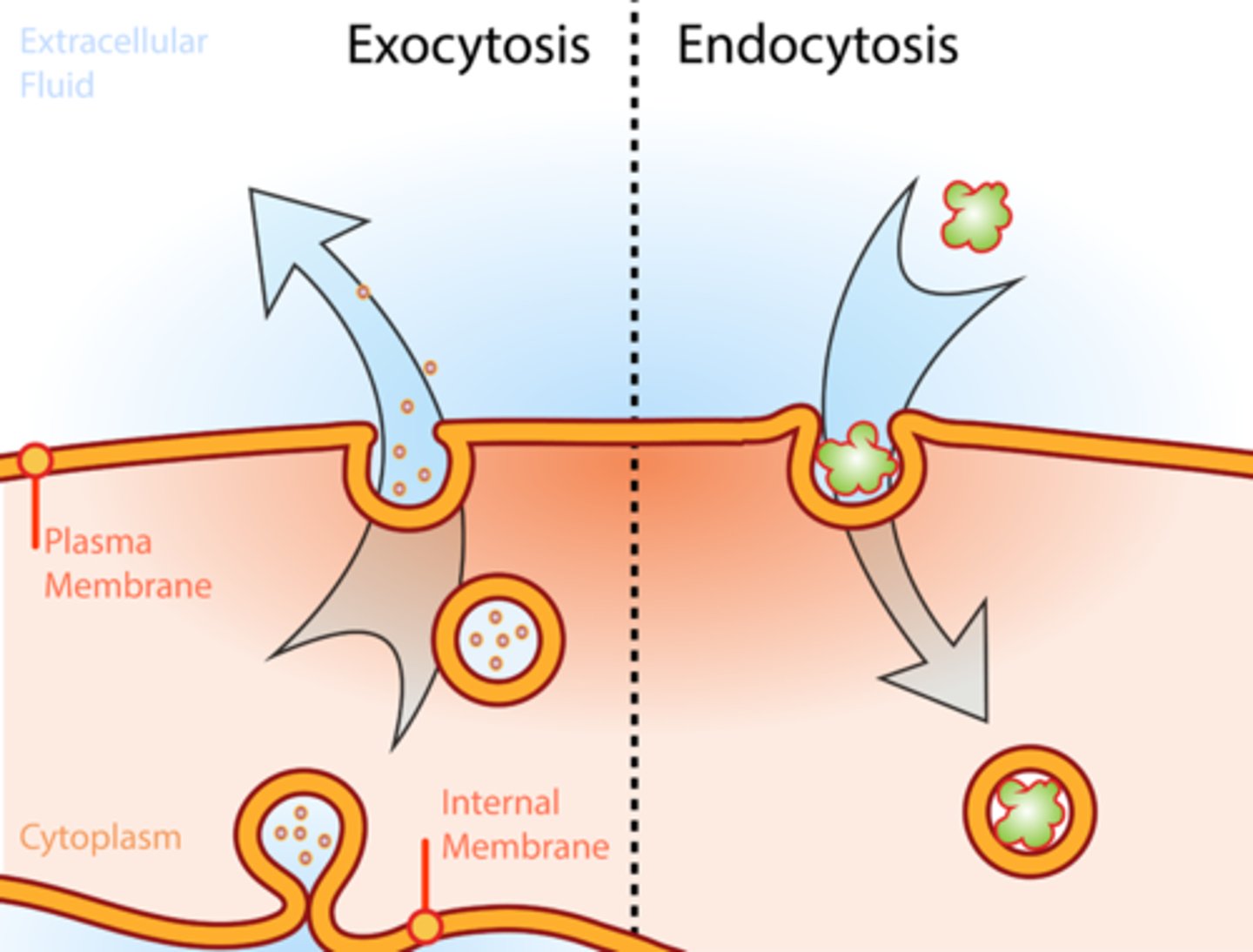
Exocytosis
Membrane folds around large substances so they can leave the cell. Requires ATP. Type of active transport
phospholipid
has a head and two tails and makes the membrane bilayer of this organelle
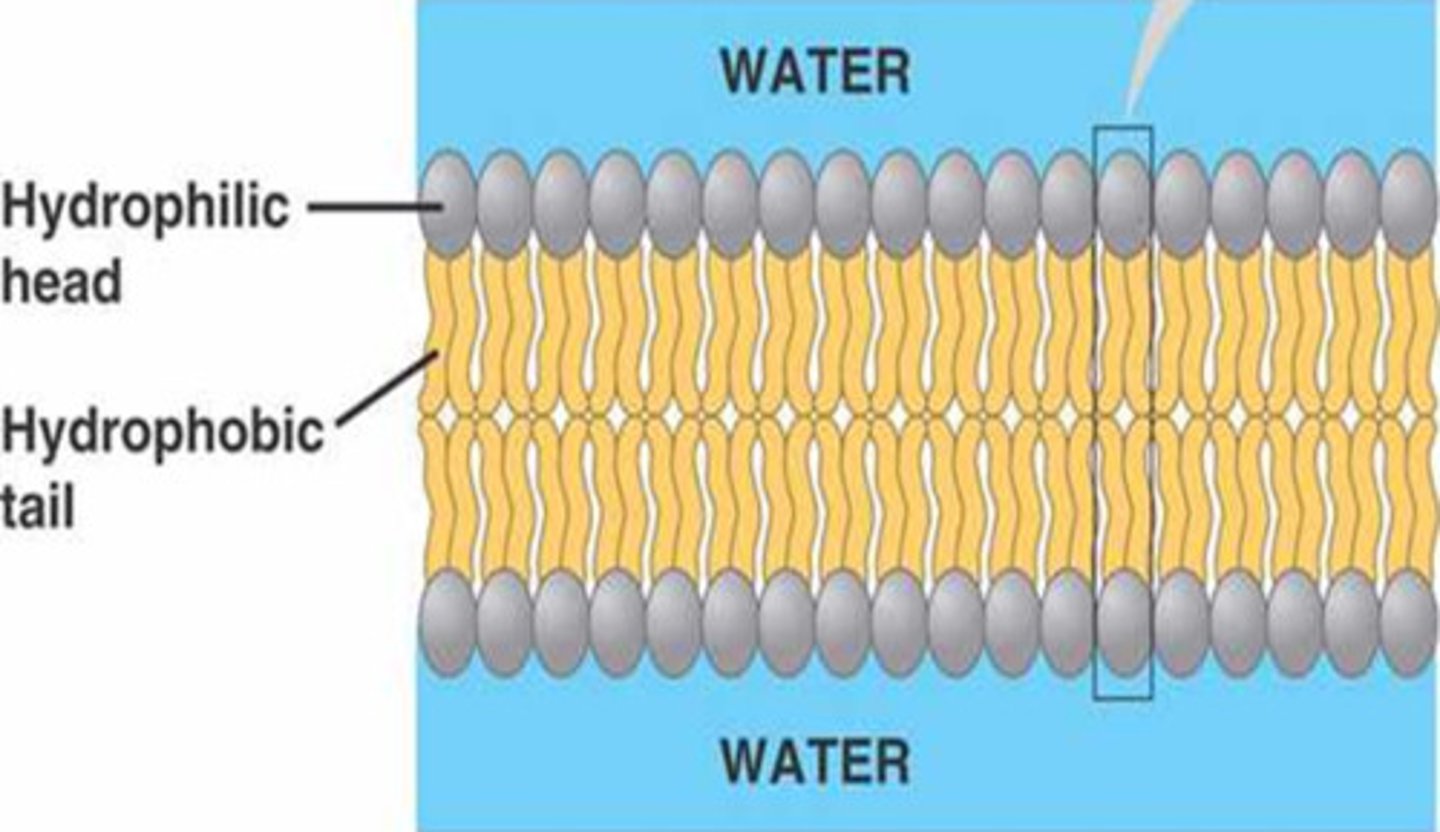
hydrophilic
water loving heads
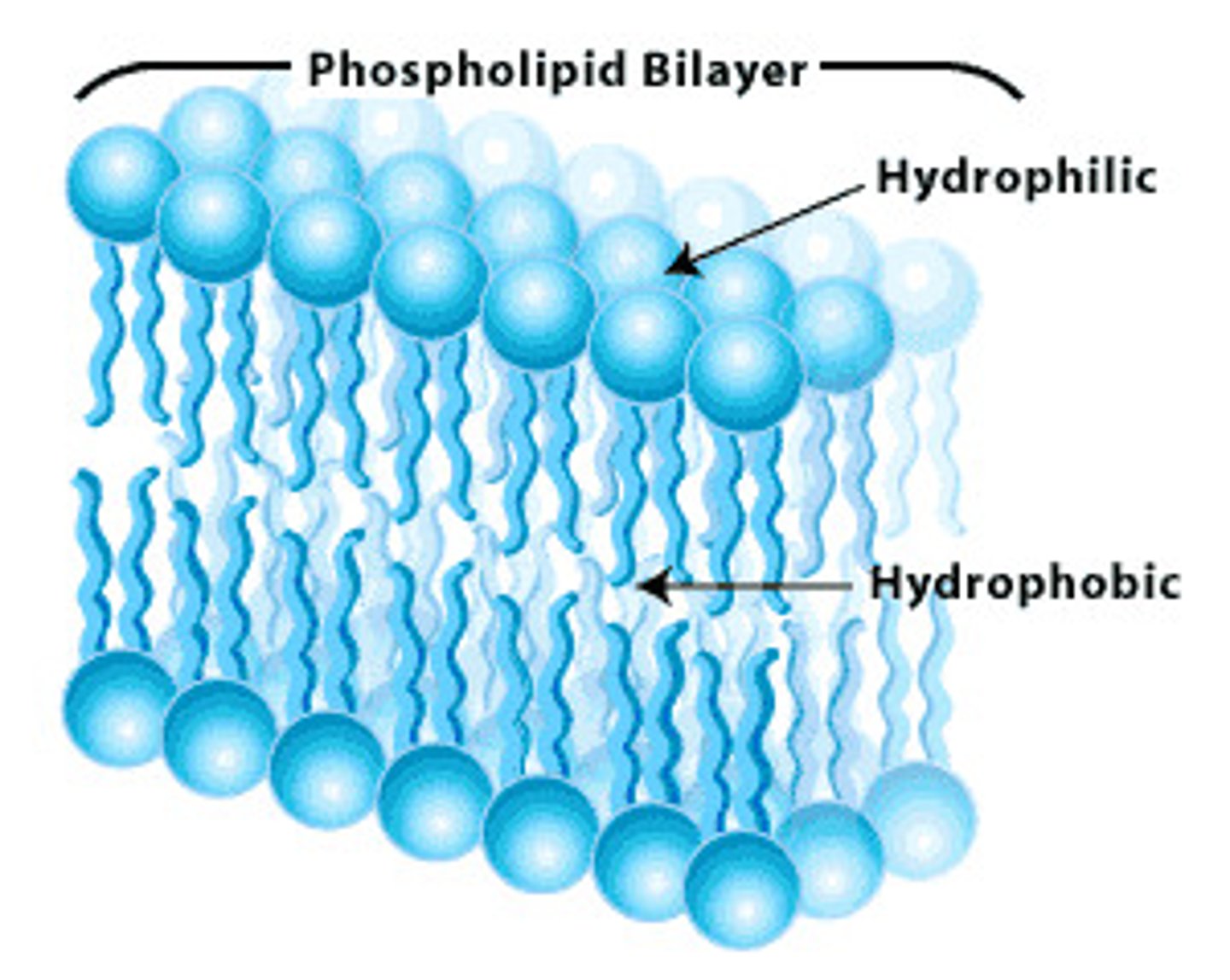
hydrophobic
water fearing tails
channel proteins
proteins that let molecules through the membrane and do NOT use energy
transport proteins
Proteins that let molecules through the membrane and DO use energy
Membrane proteins
Proteins that sit in the membrane and do the work of the membrane, such as Recognition, Receptors, and Transporters
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration
along the concentration gradient
solute
Substance dissolved in a solution
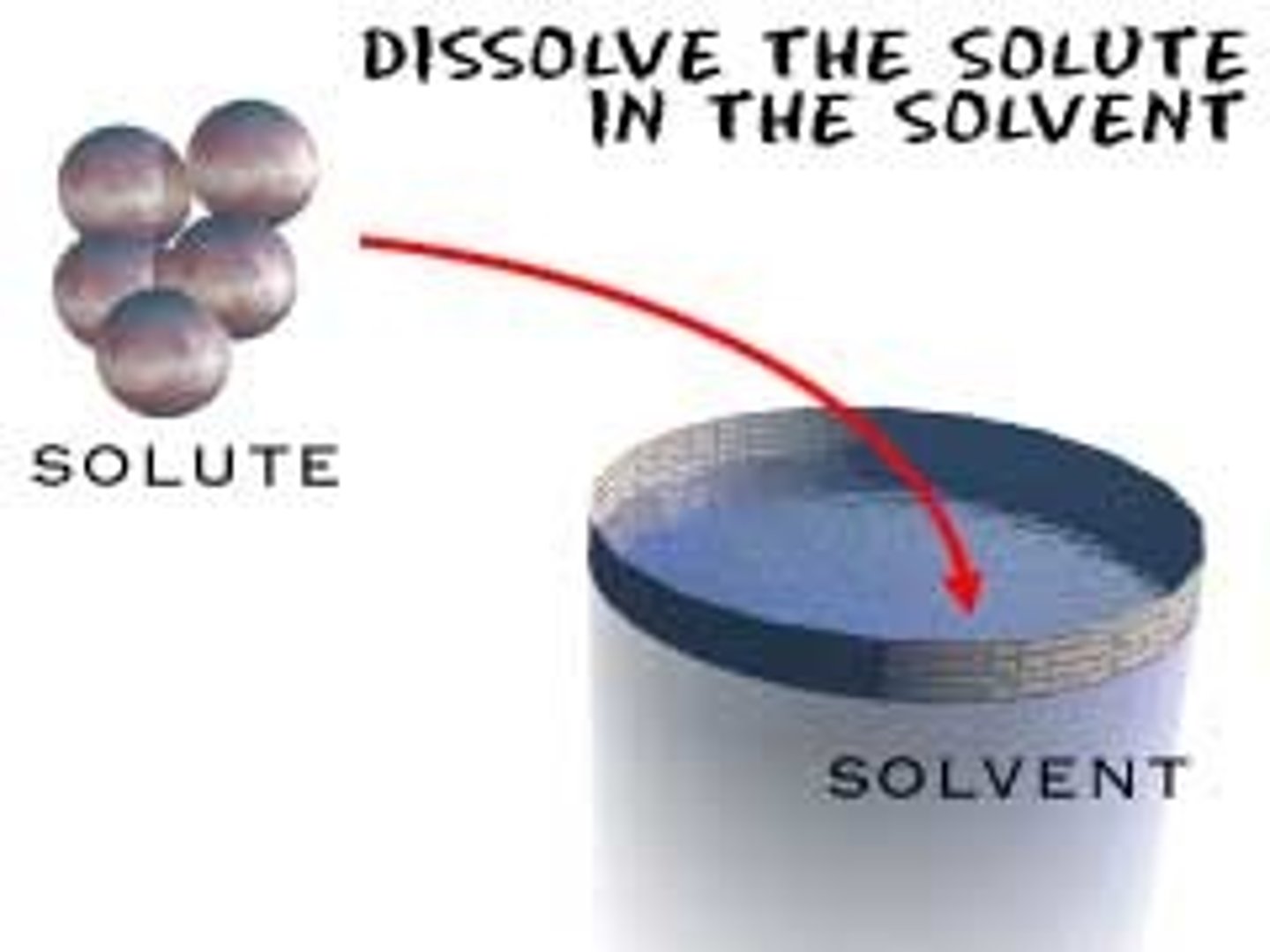
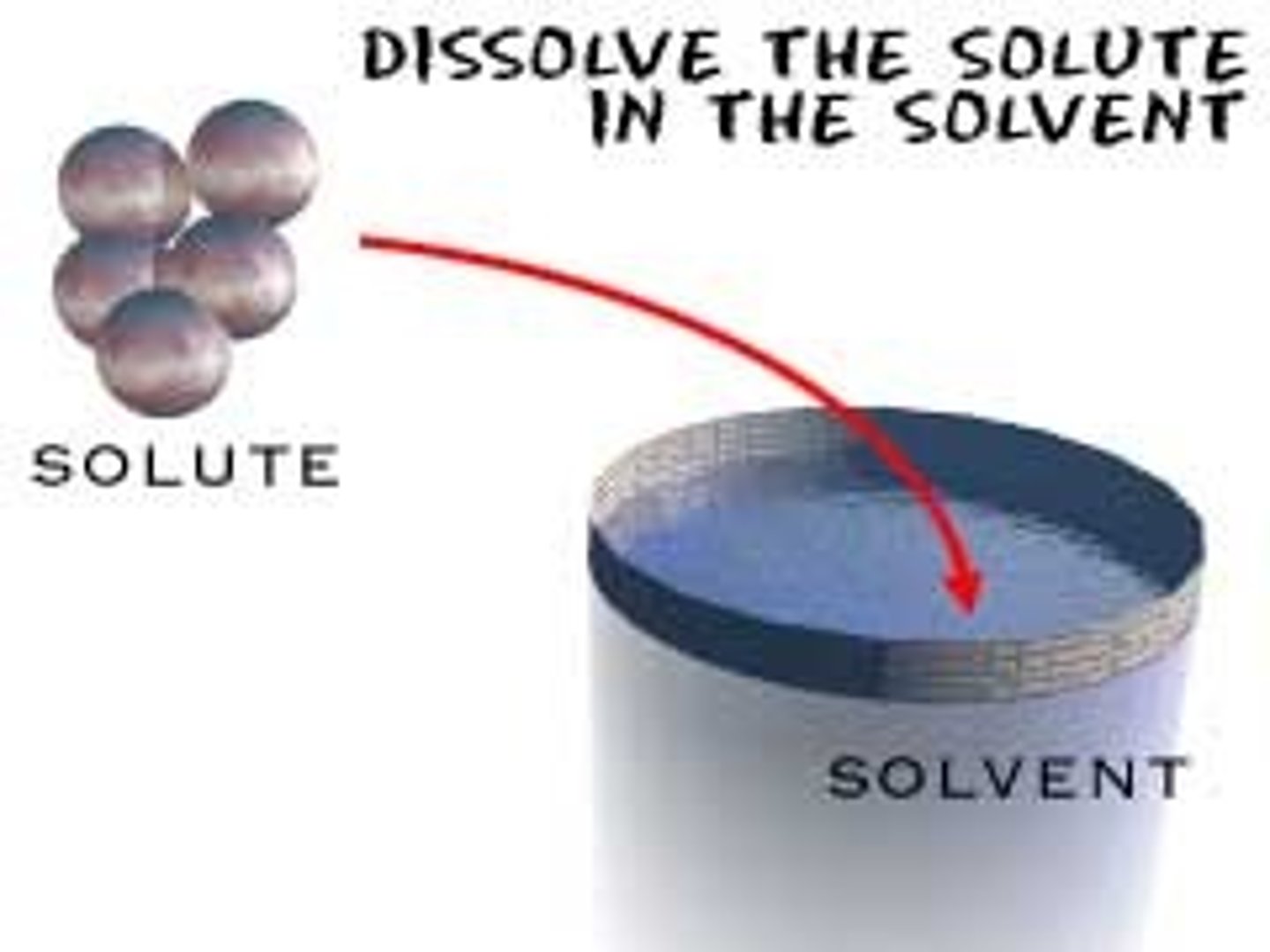
solvent
Substance in which something is dissolved - often WATER
Surface area
The amount of surface of the object that touches the outside world
plasma membrane ( aka cell membrane)
Controls the passage of materials in and out of the cell.
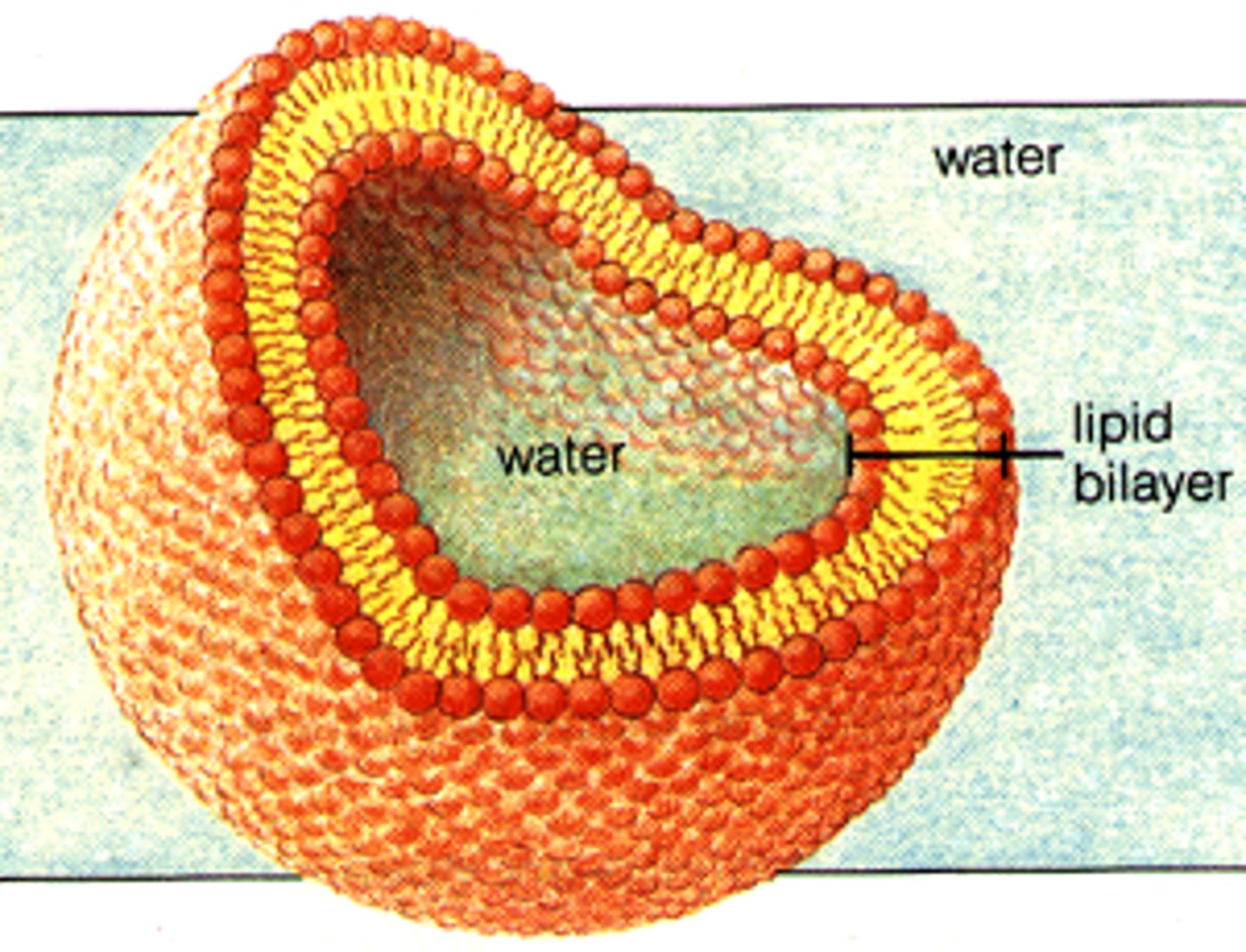
fluid mosaic model
Model that describes the arrangement and movement of molecules that make up a cell membrane (moves and made up of many things).
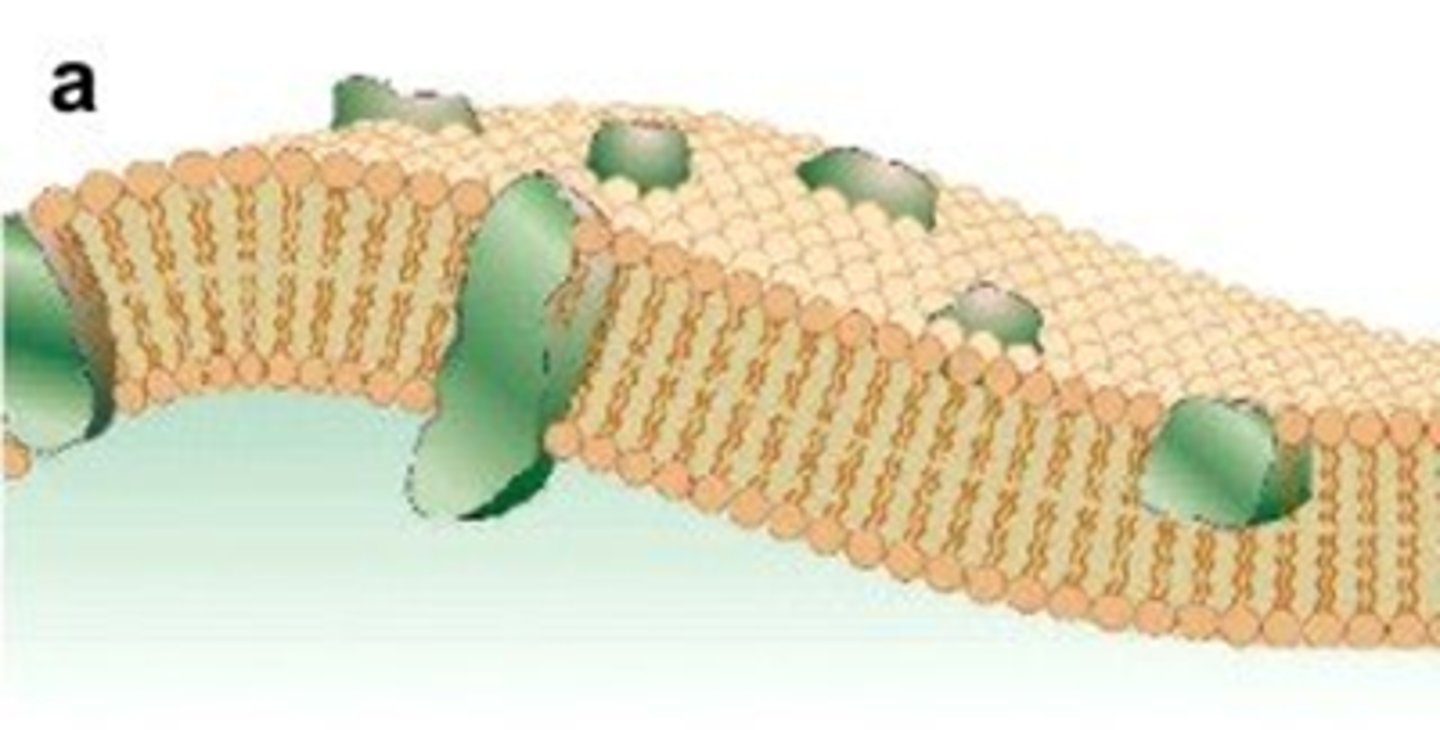
concentration gradient
Difference in concentration of a substance from one place to another.
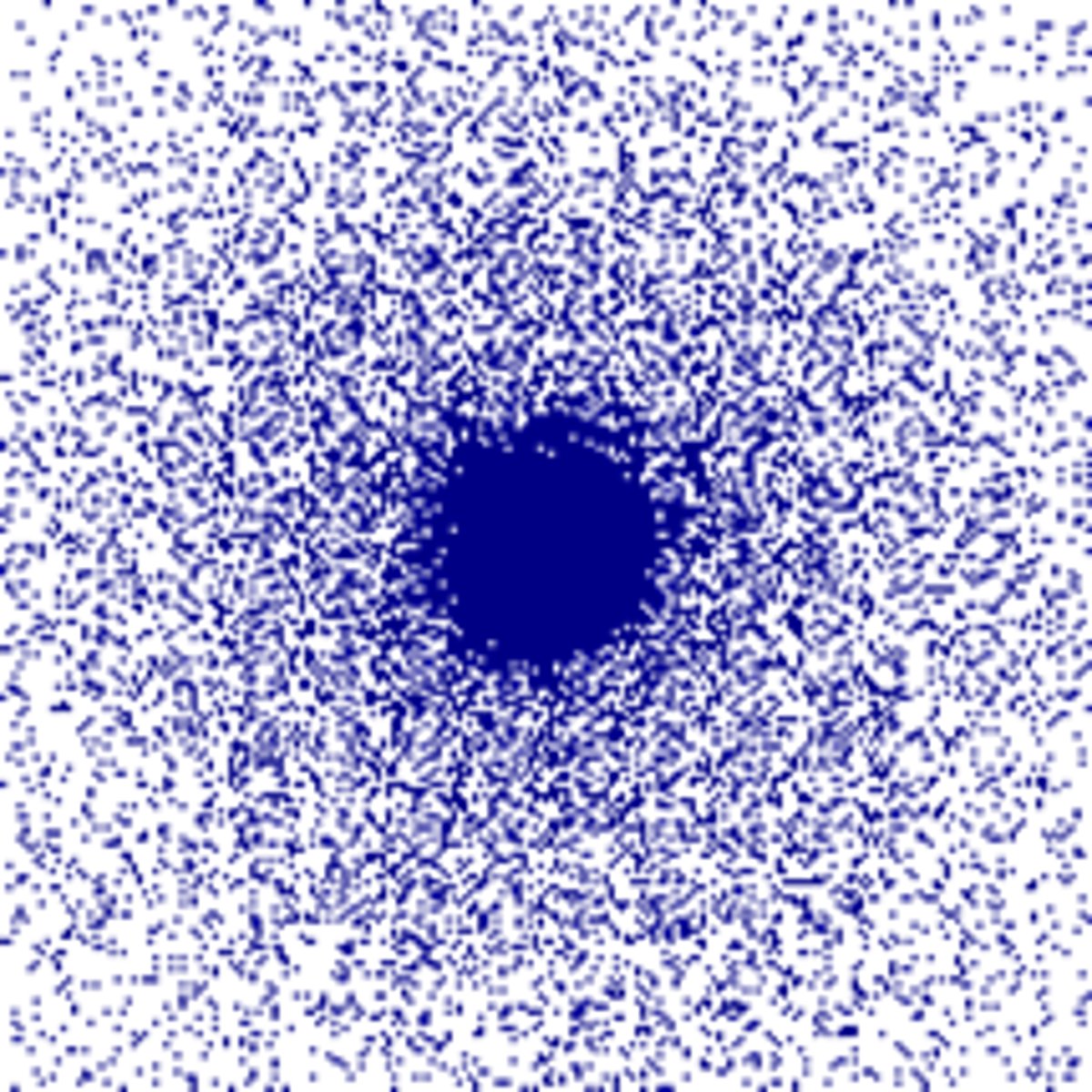
isotonic
Solution that has an equal concentration of solutes as another solution.
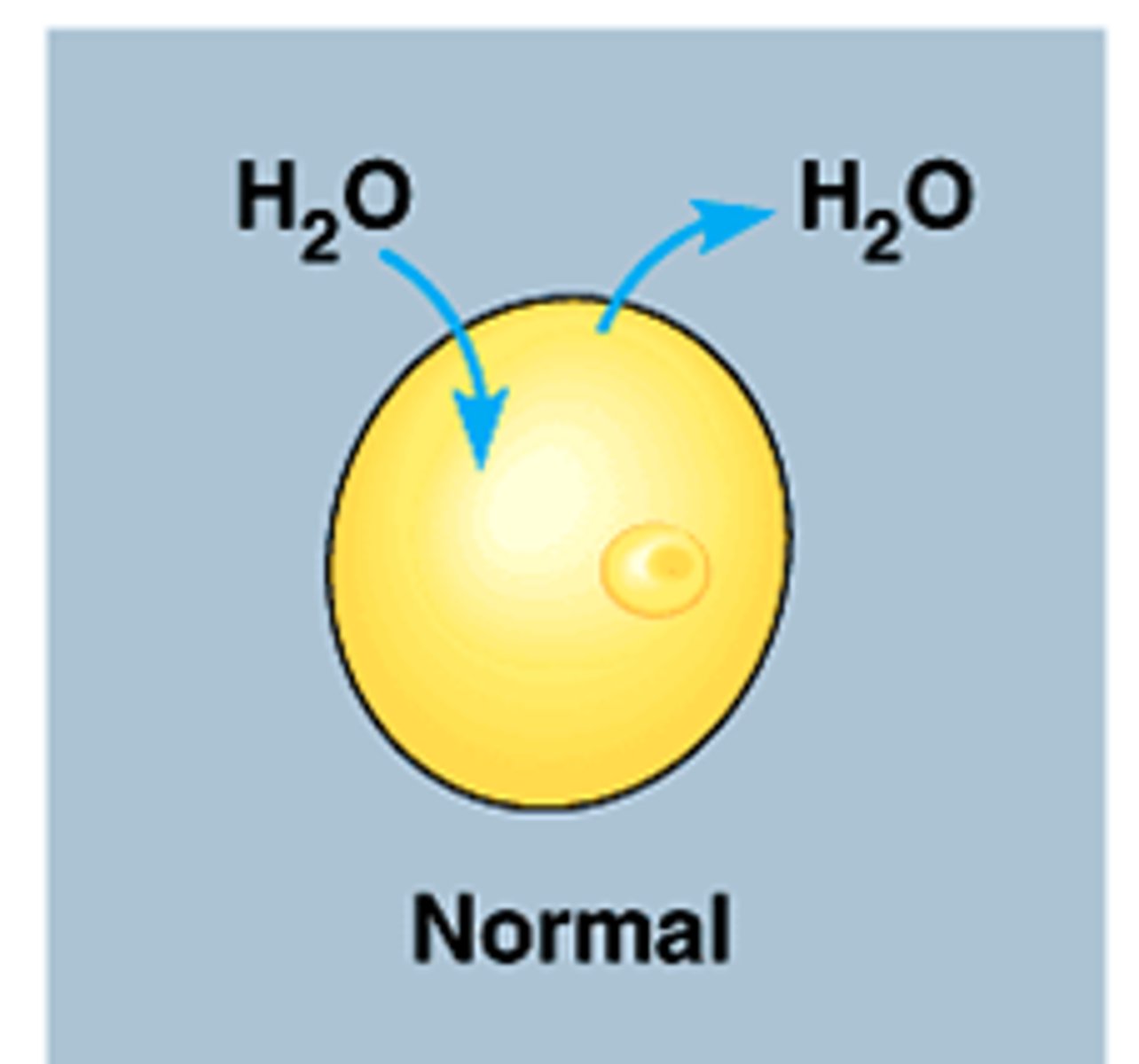
hypertonic
Solution that has a higher concentration of solutes as another solution.
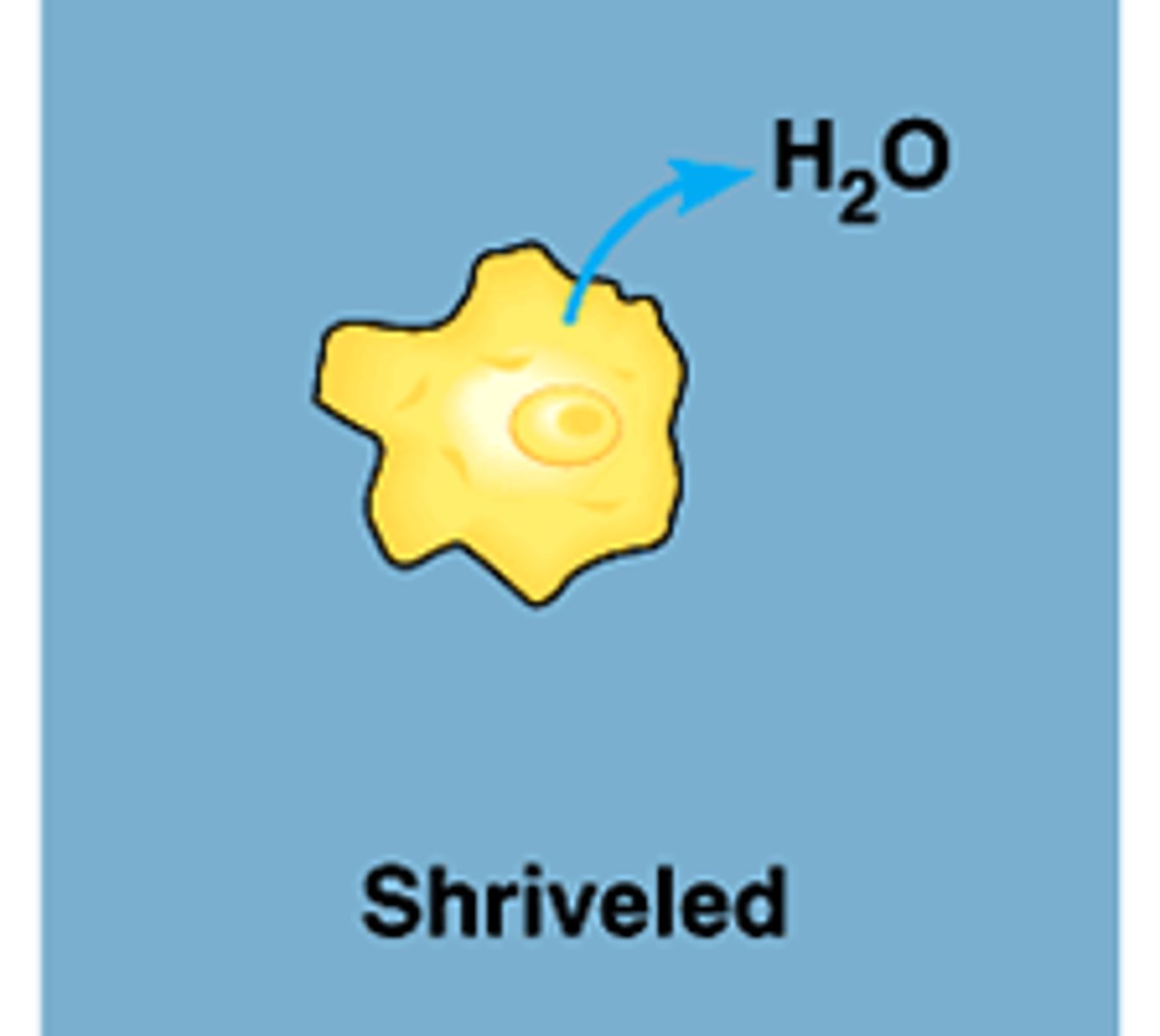
hypotonic
Solution that has a lower concentration of solutes as another solution.