Topic 3 Hardware CIE IGCSE Computer Science
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Describe the purpose of the control unit within this computer
It sends control signals; [1 mark]
● … that manage the transfer of data and instructions within the CPU; [1 mark]
● It decodes an instruction; [1 mark]
● … using an instruction set; [1 mark]
State purpose of a core in a CPU
process an instruction
to carry out an FDE cycle
Literally most sensor questions
Infrared sensor
Send signal to microprocessor
Signal is analogue and converted to digital using ADC
data compared to stored value
If does not match
Increment counter by 1
Continue process
Devices that can be used for input
Keyboard
Mouse
Microphone
Keypad
Touchscreen
Touchpad
Ron is attending a music concert. He has bought three tickets.
Each ticket number is displayed as a hexadecimal number.
Each ticket also has a QR code. TheQR code is scanned at the entrance to the venue.
A person can only enter the venue with a validQR code that allows entry.
When a person enters, a count is incremented to show how many people have entered the venue.
Explain how the system scans the QR code, checks if a person can enter and counts how many people have entered
Camera captures code // Laser/light shone on code; [1 mark]
− Black squares reflect different light to white; [1 mark]
− Corner squares are used for alignment; [1 mark]
− Pattern converted to digital data // by example; [1 mark]
− (Digital) data sent to microprocessor; [1 mark]
− There is a database of valid QR codes; [1 mark]
− Data compared to stored values/valid QR codes …; [1 mark]
− … If data matches entry is granted is raised; [1 mark]
− … If data matches count is incremented; [1 mark]
− … If data does not match, entry is denied; [1 mark]
What is LED?
− Light emitting diodes (technology); [1 mark]
− The display is made up of pixels; [1 mark]
− … that are arranged together as a matrix; [1 mark]
− … each is formed of three LEDs/filters; [1 mark]
− Shades of colour are achieved by mixing red, blue and green; [1 mark]
− The screen can be back-lit/edge-lit; [1 mark]
Benefits of LED
− Energy efficient // low power consumption; [1 mark]
− Long lasting // longevity; [1 mark]
− Focussed beam // less light strays from beam ; [1 mark]
− Brighter/vivid colours ; [1 mark]
− High resolution; [1 mark]
− No flicker; [1 mark]
− Display is thinner; [1 mark]
− Mercury free technology // environmentally friendly; [1 mark]
− Fewer pixel failure; [1 mark]
− Increased viewing in sunlight; [1 mark]
LED table
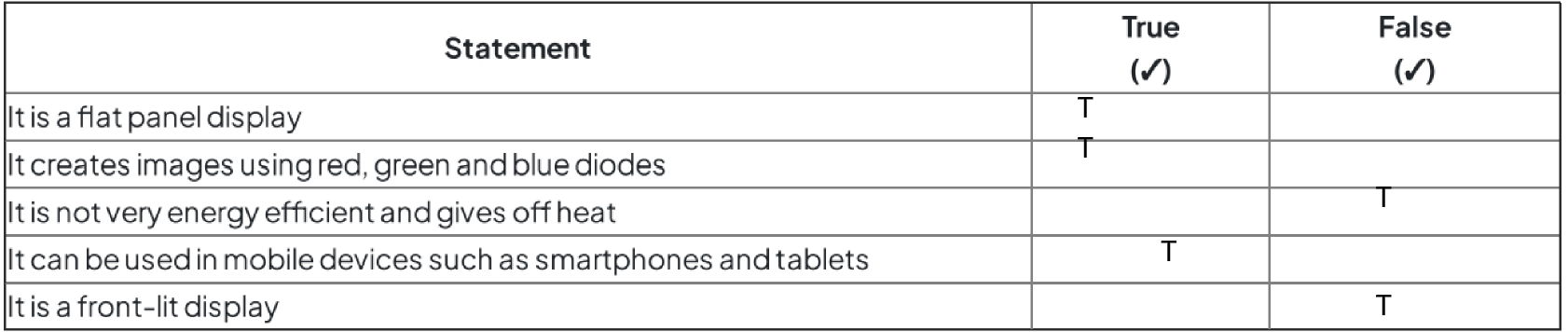
What is LCD?
− Liquid crystal display; [1 mark]
− The display is made of pixels; [1 mark]
− … arranged in a matrix; [1 mark]
− Uses a flat panel display; [1 mark]
− Backlit display; [1 mark]
− … with CCFLs/LEDs; [1 mark]
− Uses light-modulating properties of liquid crystals; [1 mark]
− Crystals can be turned between opaque and transparent (to allow light to pass); [1 mark]
− Colours created using RGB; [1 mark]
Benefits of LCD
Low power consumption; [1 mark]
− Runs at cool temperature; [1 mark]
− Do not suffer image burn; [1 mark]
− Do not suffer flicker issues; [1 mark]
− Bright image/colours; [1 mark]
− High resolution image; [1 mark]
− Cheaper to purchase than e.g. LED screen; [1 mark]
CD & DVD similarities
Both need a red laser to read/write data; [1 mark]
− Both are spun to be read; [1 mark]
− Both use spiral tracks for data; [1 mark]
− Both are optical storage; [1 mark]
− Both are off-line storage // both non-volatile; [1 mark]
− Both use pits and lands to store data; [1 mark]
CD & DVD differences
− DVD can be dual layer, but CD can only be single; [1 mark]
− DVD has higher storage capacity; [1 mark]
− DVD has a shorter wavelength laser; [1 mark]
− DVD are spun faster; [1 mark]
− DVDs have a higher data transfer rate; [1 mark]
Explain to Kamil why it is better to use DVD-RAM rather than DVD+RW or DVD-RW
– direct access because of concentric tracks; [1 mark]
– can read and write at the same time because it has a read/write head; [1 mark]
Draw a diagram to represent how virtual memory is created and used
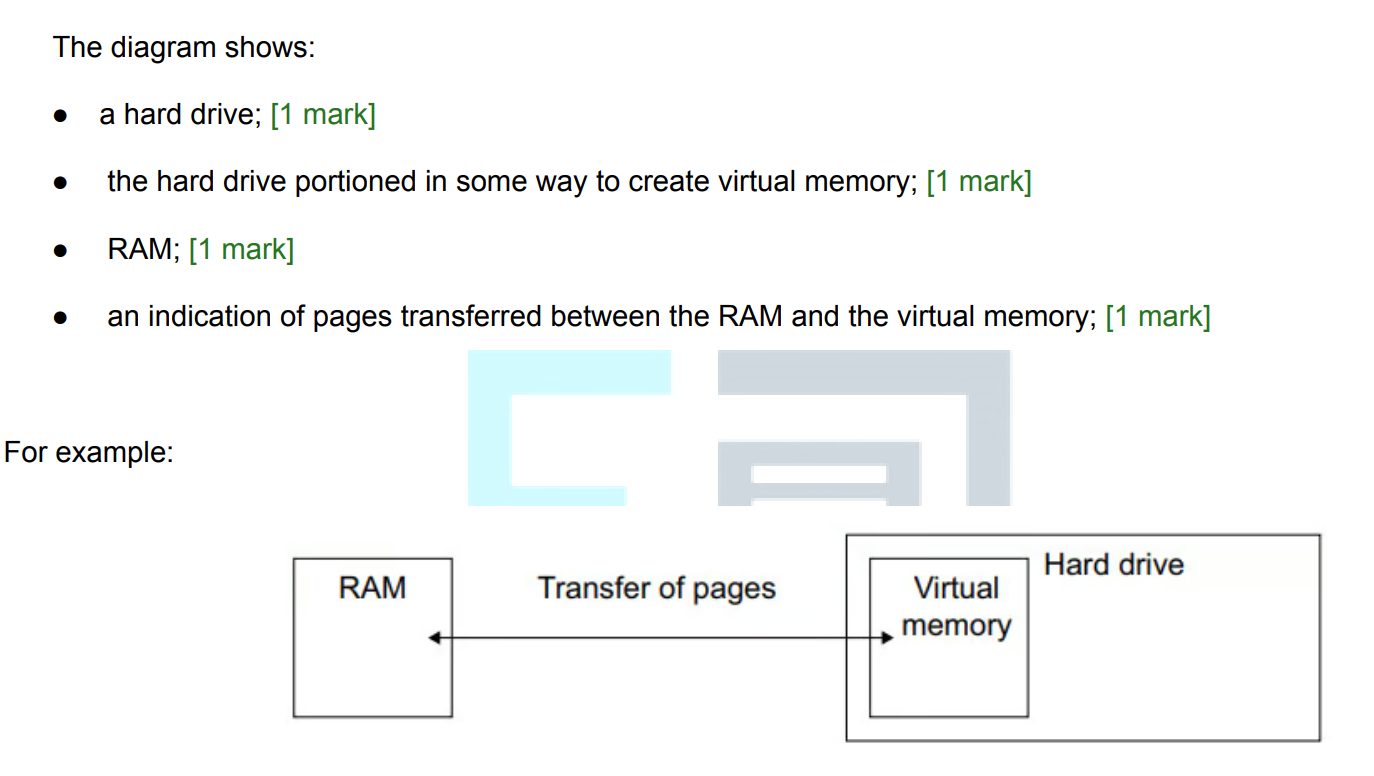
Explain why virtual memory is needed
to extend the RAM capacity; [1 mark]
● … to stop the 3D modelling software from freezing/crashing when the physical RAM is full; [1 mark]
● to allow the computer to process the large amount of data required for 3D modelling; [1 mark]
What is SSD, how does it work?
− Solid state drive; [1 mark]
− Non-volatile; [1 mark]
− Secondary storage; [1 mark]
− Flash memory; [1 mark]
− Has no mechanical/moving parts; [1 mark]
− Uses transistors; [1 mark]
− … and cells that are laid out in a grid; [1 mark]
− Uses control gates and floating gates; [1 mark]
− Can be NAND/NOR (technology); [1 mark]
− Use EEPROM technology; [1 mark]
Operating
− Stores data by flashing it onto the chips; [1 mark]
− Data stored by controlling the flow of electrons through/using transistors/chips/gates; [1 mark]
− The electric current reaches the control gate and flows through to the floating gate to be stored; [1 mark]
− When data is stored the transistor is converted from 1 to 0; [1 mark]
Differences between flash memory and CD-RW
Flash memory
– solid state memory
– no formatting issues
– plugs directly into the USB port
– direct transfer of data
CD-RW
– optical media
– slower access speed/flash memory has faster access speed
– requires a separate drive
– data needs to be burnt/finalised/finished (before being used on another device)
What is meant by a MAC address
used to identify a device; [1 mark]
● it is a unique (address); [1 mark]
● it is a static address // it does not change; [1 mark]
● it is set by the manufacturer; [1 mark]
● the first part is the manufacturer ID / number / identifies the manufacturer; [1 mark]
● the second part is the serial number / ID; [1 mark]
Characteristics of an IP address
consists of values between 0–255 / 0–FFF; [1 mark]
● values are separated by full stops / colons; [1 mark]
● it is a unique address; [1 mark]
● can be static or dynamic; [1 mark]
● can be public or private; [1 mark]
● can be IPv4 / have four groups of digits; [1 mark]
● can be IPv6 / have eight groups of digits; [1 mark]
● in IPv6 :: can replace groups of zeros; [1 mark]
IP address and MAC address similarities
Both addresses can be used to identify a computer/device; [1 mark]
− Both are unique; [1 mark]
− Both can be represented as hexadecimal; [1 mark]
− Both addresses do not change if IP address is static; [1 mark]
IP address & MAC addresses
− An IP address is assigned by the network/router/ISP, A MAC address is assigned by the manufacturer; [1
mark]
− An IP address can be changed (if dynamic), MAC address cannot be changed; [1 mark]
− IP address has 4/8 groups of values, MAC address has 6 groups/pairs of values; [1 mark]
− IP address is 32-bit/128-bit, MAC address is 48-bit; [1 mark]
− IP address does not contain serial number/manufacturer number, MAC address does; [1 mark]
− IP(v4) address is denary and MAC address is hexadecimal; [1 mark]
Identify four events that take place during the fetch-execute cycle
An instruction is fetched from memory • The instruction is then decoded • The decoded instruction is then executed so that the CPU performs continuously • The process is repeated • The program counter is incremented • The instruction is transferred to the MDR • The address of the instruction to be fetched is placed in the MAR
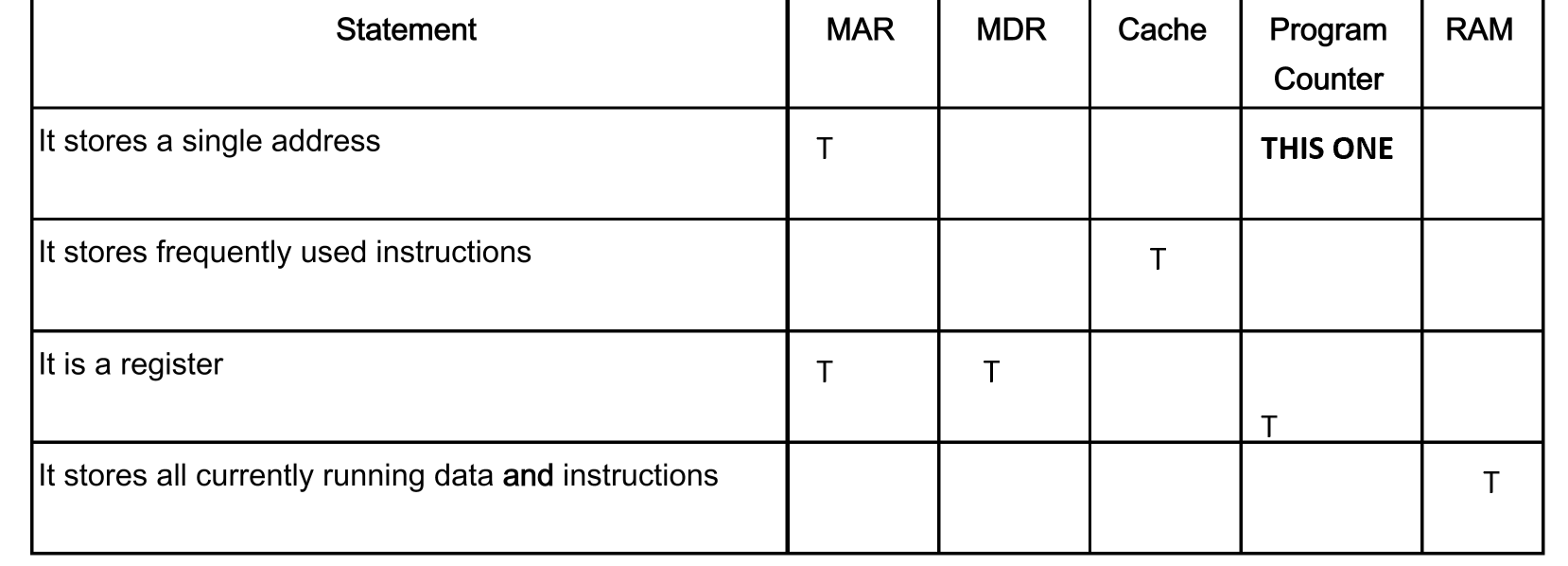
Describe purpose of registers that are used by Von Neumann architecture
MAR // memory address register
Stores the address/location where data
will be read/written/accessed/fetched
// address/location of data/instruction
being processed
// address/location of data/instruction
next to be processed
MDR // memory data register
Stores the data/instruction that is
fetched/read from memory
// stores the data that is to be written to
memory
// stores the data/instruction from the
address in the MAR
// data/instruction next to be processed
Program counter
Stores the address/location of the next
instruction to be run
// stores the address/location of the
current instruction being run
Accumulator
Stores the result of
manipulation/process/calculation
Why is more cores not always better?
Software may be designed to run on 1
core and not multiple cores
// depends on the task(s)
…some tasks cannot be split across
cores
Clock speed also affects speed
// dual core may have a faster clock
speed
// quad-core may have slower clock
speed
…so one task may be run faster/slower
RAM size also affects speed
// Quad-core may have less RAM
// amount of VM being used
Cache size also affects speed
// Quad-core may have less cache
What makes smart watch embedded system?
A smart watch is not a general-purpose
computer
… which means the smart watch has
one/limited/specific/dedicated
function(s)
Smart watch has a microprocessor
… on a single circuit board
It is a computer system that is built
within the watch
Runs firmware
Smart watch has built-in OS // difficult
to change/manipulate the OS/function
Smart watch has few components all
essential to its purpose
Smart watch has specific hardware
required to function i.e.
speaker/headphones
Describe how the CPU and RAM work together to enable the computer to operate
Data stored in RAM
Fetched from RAM by CPU
Where they are executed
Purpose of cache memory
To store instructions / data that is
frequently used / previously used / next
to be used
Data does not need to be fetched from
RAM
Speeds up access
Components of computer table
Draw devices and connections in an office star network
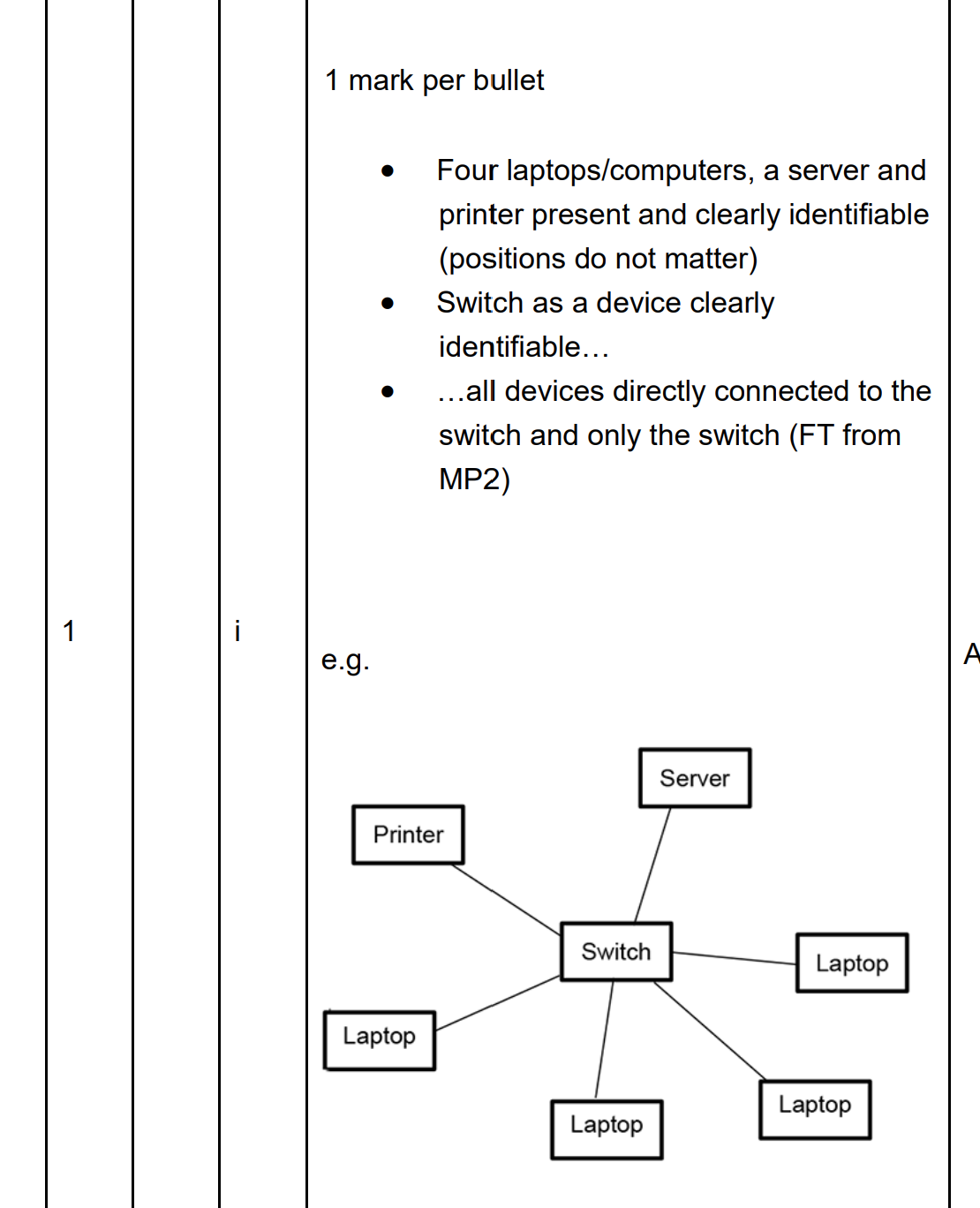
Describe role of switch in office network
To connect the devices together
Receives data/packets/traffic
Direct/send data/packets/traffic only
to its destination
Creates/generates a list of devices
connected to it as it receives signals
Uses MAC addresses of devices
connected to it
Describe what is meant by a character set
All the characters and symbols that can be represented by a computer system; [1 mark]
Each character and symbol is assigned a unique value; [1 mark]
Explain what is meant by MIDI and MP3
MIDI
− Musical Instrument Digital Interface (file)
− Stores a set of commands/instructions (for how the sound should be played)
− Does not store the actual sounds
− Data in the file has been recorded using digital instruments // produced by synthesizer
− Specifies pitch of the note // specifies the note to be played
− Specifies when each note plays and stops playing // Specifies key on/off
− Specifies duration of the note
− Specifies volume of the note
− Specifies the tempo
− Specifies the type of instrument
− Individual notes can be edited
MP3
− MP3 is a format for digital audio
− MP3 is an actual recording of the sound
− MP3 is a (lossy) compression format
− Recorded using a microphone