Integ Bio: Finals
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Tissues
Group of cells with similar structure and function plus extracellular matrix, “glue”
Cytology
Study of individual, normal cells of the body
Histology
Study of tissues
4 Types of Human Tissues
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Covers and lines body surfaces, organs, and cavities.
Protects against physical, chemical, and biological agents.
Absorbs and secretes substances.
Examples: skin, lining of the digestive tract, respiratory tract, and glands.
Connective Tissue
Supports and connects body structures.
Provides structural framework, protection, and insulation.
Transports substances throughout the body.
Examples: bone, cartilage, blood, adipose tissue, and tendons
Muscle Tissue
Enables movement and generates force.
Three types:
Skeletal: Attached to bones, voluntary control.
Smooth: Found in organs like the stomach and intestines, involuntary control.
Cardiac: Found in the heart, involuntary control.
Nervous Tissue
Receives, processes, and transmits information.
Composed of neurons (nerve cells) and glial cells.
Responsible for sensory perception, thought, emotion, and motor control.
Free Cell Surfaces
Surface not in contact with other cells
Smooth to reduce friction, Ex. Blood vessels
Microvilli
Increase cell’s surface area
Cilia
Move materials across cells’ surface
Goblet cells
Produce mucus
Ex. Stomach, intestine lining, respiratory tract
Glandular Epithelium
Structures that secrete substances onto a surface, a cavity, or into blood such as sweat, saliva, breast milk, digestive enzymes, and hormones.
Exocrine glands
Glands with ducts
Ex. Sweat, oil
Endocrine glands
Secrete their substances directly into bloodstream; ductless glands
Ex. Thyroid, thymus, pituitary glands
Aerolar Tissue
Structure: Loosely packed cells and fibers embedded in a gel-like matrix.
Function:
Provides support and flexibility.
Connects tissues and organs.
Helps in nutrient and waste exchange.
Location: Found beneath the epithelia, between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves.
Adipose Tissue
Structure: Densely packed adipocytes (fat cells) that store lipids.
Function:
Stores energy in the form of triglycerides.
Insulates the body.
Cushions organs.
Secretes hormones.
Location: Subcutaneous layer, around internal organs, and in specific areas like the buttocks and thighs.
Cartilage
is a firm, flexible connective tissue that plays a crucial role in various parts of the body. It's like a strong, rubbery material that provides support, protection, and flexibility.
Hyaline cartilage
Location: covers ends of bones
Structure: some collagen fibers
Function: reduces friction (cushion)
Fibrocartilage
Location: between vertebra
Structure: lots of collagen fibers
Function: can withstand compression
Elastic cartilage
Location: ear and tip of nose
Structure: elastic fibers
Function: can recoil
Bone
Hard connective tissue
Solid calcium carbonate matrix
2 Types: Compact & Spongy
Compact Bone
consist of osteons/haversian system
Ground of matrix is solid (calcium carbonate
Osteons consist of central canal that allow blood vessels and nerves to travel through them to supply the osteocytes / bone cells
Spongy bone
Also known as cancellous bone is composed of spongy, porous, bone tissue that is filled with red bone marrow.
Mostly concentrated in the vertebrae, ribs, pelvis, and skull, cancellous bone
Responsible for the production of red blood cells.
Muscle Tissue
Composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts
Highly cellular and is well supplied with blood vessels
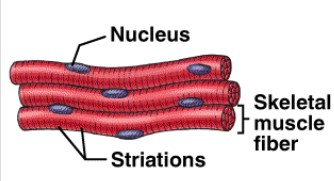
Skeletal muscle
striated, voluntary
Parallel elongated cells (fibers)
Multinucleated; attached to skeleton
Light meat, dark meat (stripes)
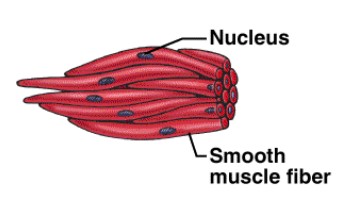
Smooth muscle
Visceral, involuntary
Cells are long and tapered
No striations; move by peristalsis
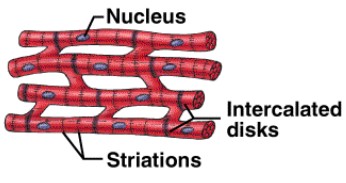
Cardiac muscle
Intercalated disc
Myogenic
Branched
Nervous tissue
the main tissue component of the nervous system. It is responsible for coordinating and controlling body functions and activities.
Neurons
cell of the nervous system
Transmission of nerve impulses
Facilitate the transfer of information throughout the body by sending electrochemical signals.
Interneurons
Connect various neurons within the brain and spinal cord
Sensory neurons
Carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) into the central nervous system
Motor neurons
Carry signals from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body.
Neuroglial cells (glial cells / non-neuronal cells)
Support and protect neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS).
play a crucial role in maintaining the environment for neurons to function optimally
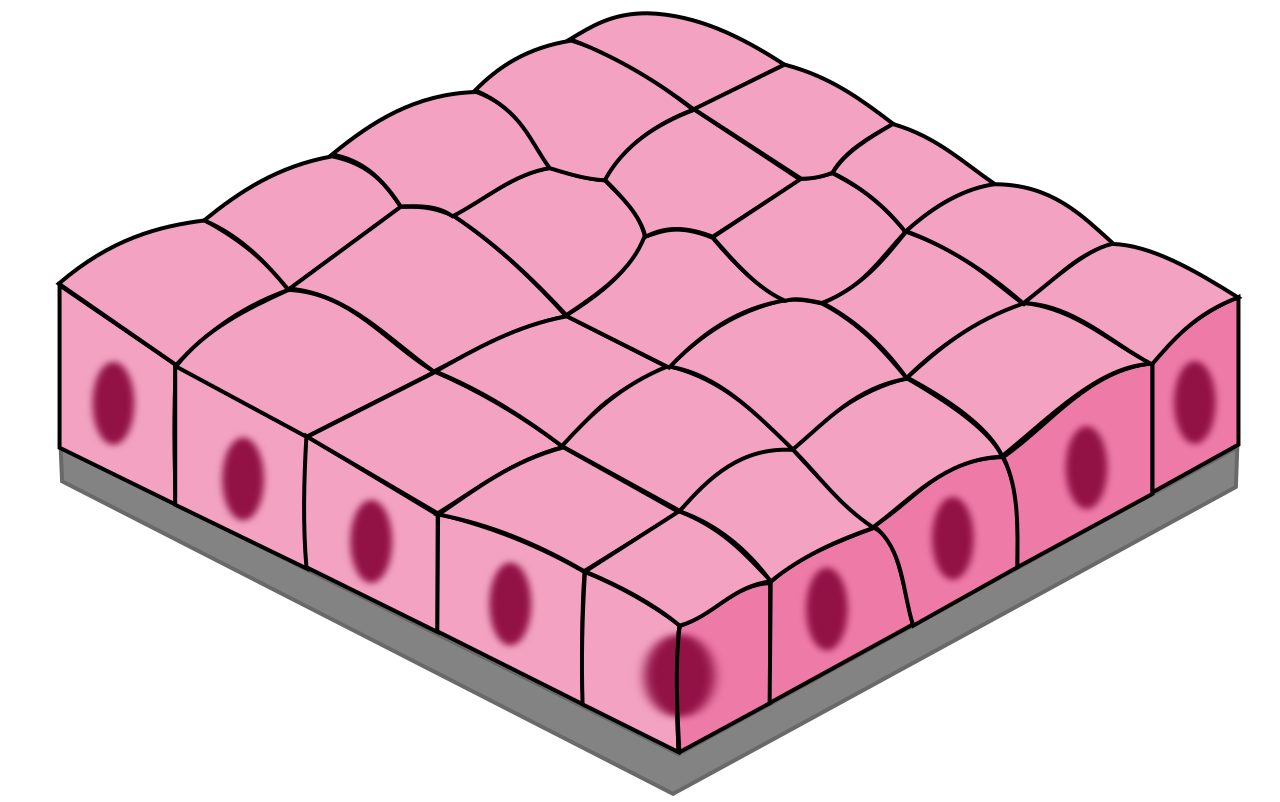
Simple Cuboidal
1 layer of square-shaped cells
Secretion
glands, ovaries, kidneys
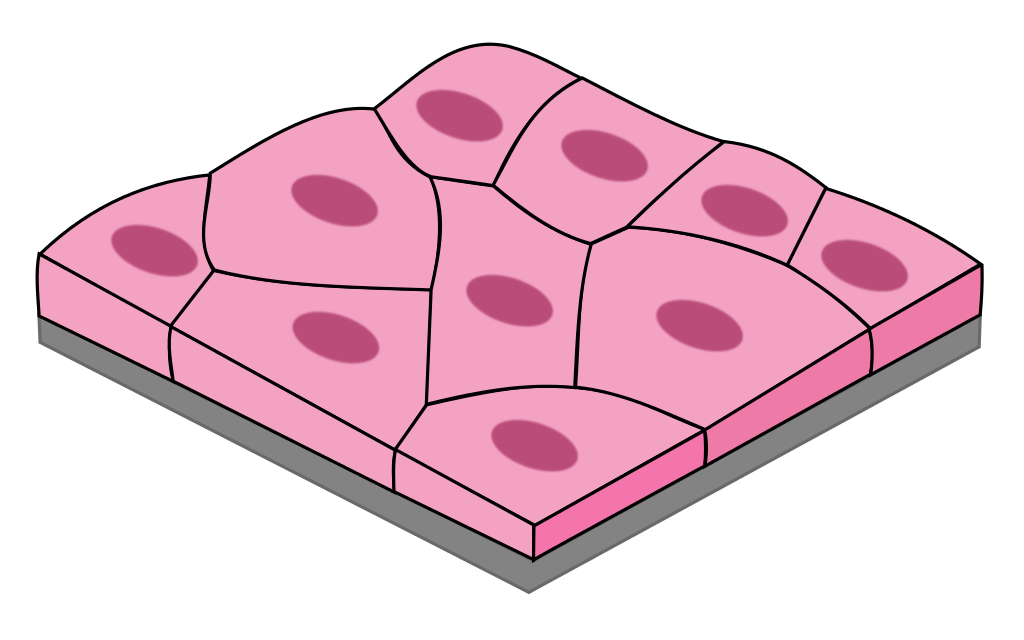
Simple Squamous
1 layer of flat, tile-like cells
good for diffusion & filtration
blood vessels, lungs, heart, kidneys
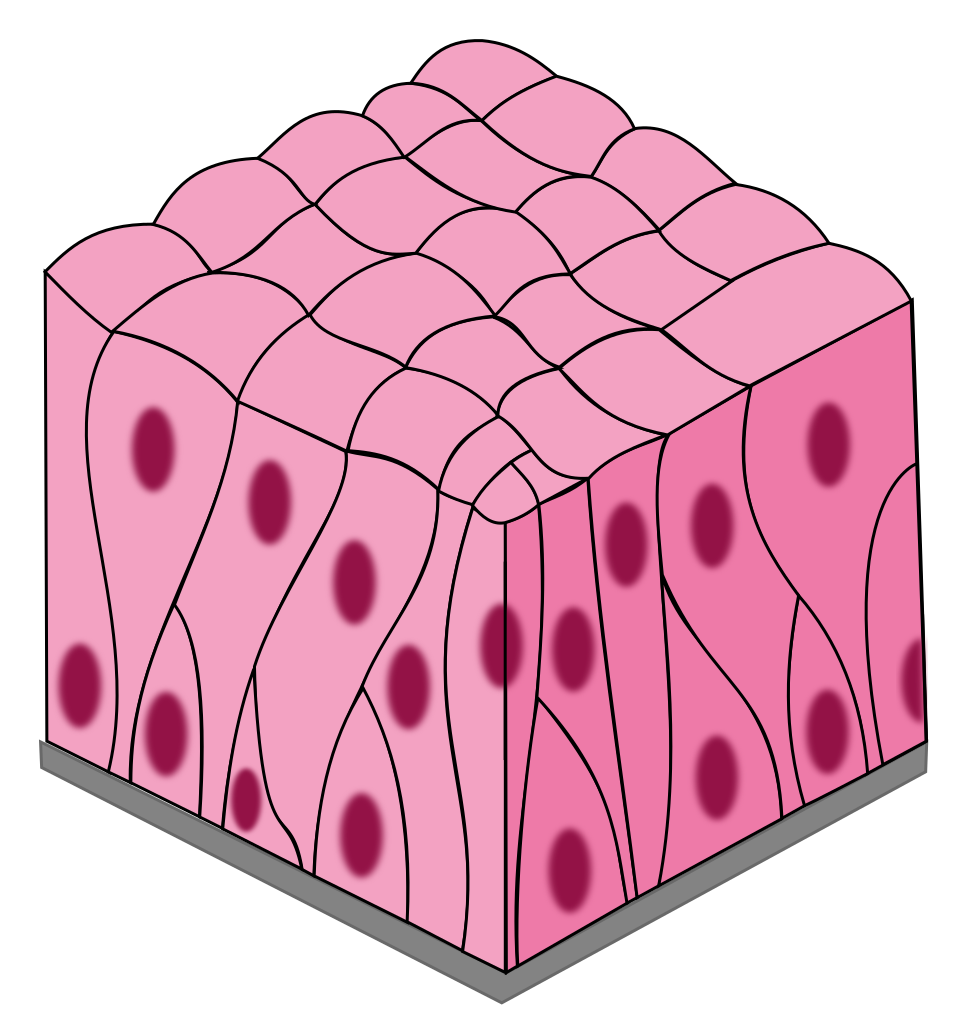
Pseudostratified Columnar
1 layer of tall, narrow cells appears stratified but isn’t
secretes mucus and propel debris out of respiratory tract (cilia)
nasal cavity and trachea
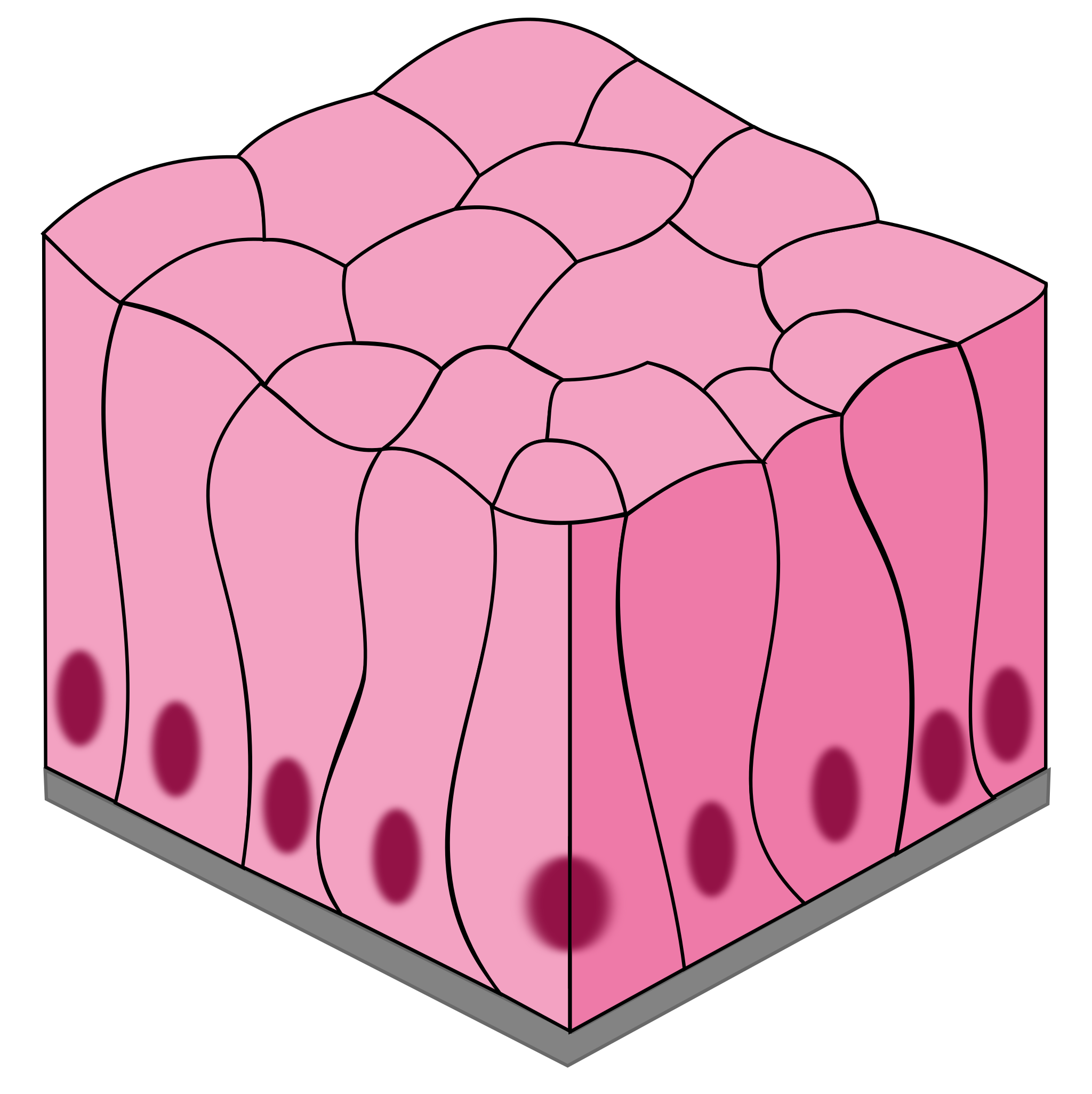
Simple Columnar
1 layer of tall, narrow cells
secrete mucus and absorption
stomach, intestines, resp. tract
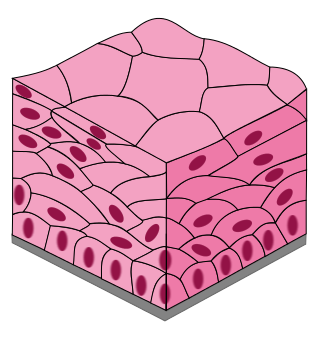
Stratified Squamous
many layers of flat, tile-like cells
protect and acts as a barrier
skin, mouth, throat, esophagus
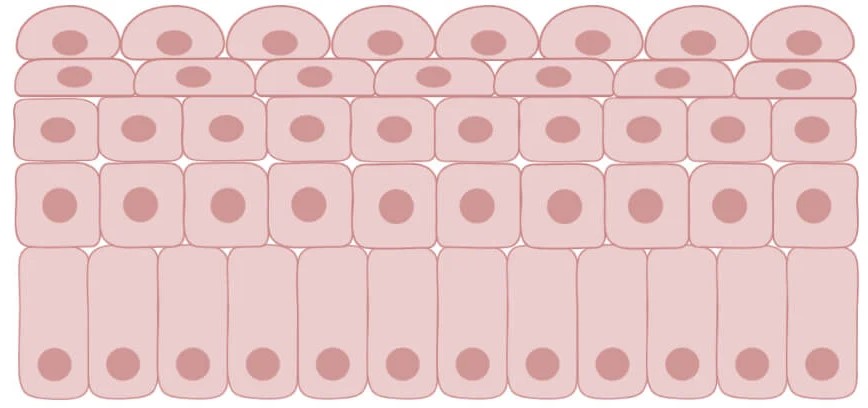
Transitional
special type of stratified epithelium; changes shape -stretched squamous.
hold fluids
urinary bladder