Dialysis Access Management
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to dialysis access management, kidney failure stages, symptoms, and treatment options.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
To remove extra fluid and waste products from the blood when the kidneys are not able to. means what
What is the main purpose of dialysis?
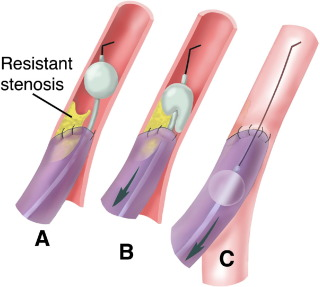
what type of thrombectomy is this and what types of vessels is it used on
AVG
fogarty thrombectomy
arterial plugs can be treated in two ways
performed with a fogarty balloon
mechanical thrombectomy device (only one device- Arrow Tretola PT(thrombolytic)Device)
when using a mechanical thrombectomy device to treat a AVG clot what is it best to avoid
avoid deployment at the anastomosis to prevent an embolus
Advance the **** balloon beyond the arterial anastomosis, inflate it under fluoroscopy, and pull it back through the anastomosis. Several passes may be needed due to the firm clot.
what balloon is this
fogarty balloon
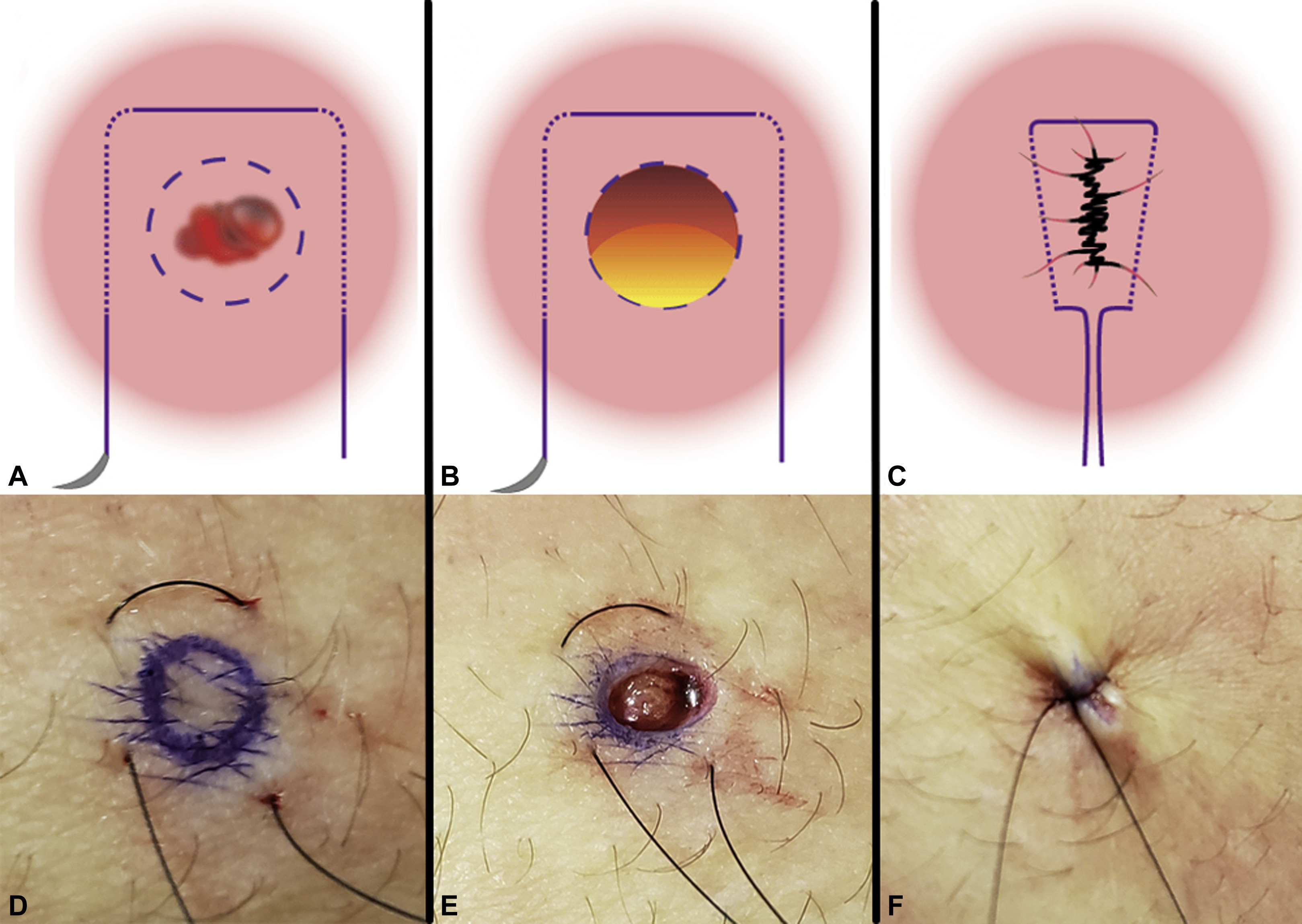
What are three ways to achieve post intervention hemostasis
manual compression
manual compression with clotting agent
purse string stuture
pic is purse string
tunneled catheters should be on what side of the maturing AVF/AVG
opposite side
In summary, ******* catheters are for short-term use and are inserted directly into the vein, while********* catheters are for longer-term use, with the catheter portion tunneled under the skin to offer better security and lower infection risk.
In summary, non-tunneled catheters are for short-term use and are inserted directly into the vein, while tunneled catheters are for longer-term use, with the catheter portion tunneled under the skin to offer better security and lower infection risk.
what are four advantages of CVC (hemodialysis catheters)
simplicity of insertion
************
*******************
ease of replacement and removal
simplicity of insertion
immediate utility
access without needle cannulation
ease of replacement and removal
what are the three preferred access sites for CVC placement
with what caviet
R internal jugular vein
R external jugular vein
L internal jugular vein
must be placed on opposite side of the maturing AVF/AVG
when is the use or placement of a nontunneled temporary catheter appropriate
short term use and temporary. for hospitalized patients without existing function access
what AVG site or access is considered a last resort
lower extremity graft
order of AVG creation
4x
forearm
upper arm graft
chest wall prosthetic graft (necklace graft)
lower extremity AVG
order of AVG creation 4x
forearm
*****
*****
lower extremity AVG
forearm
upper arm graft
chest wall prosthetic graft (necklace graft)
lower extremity AVG
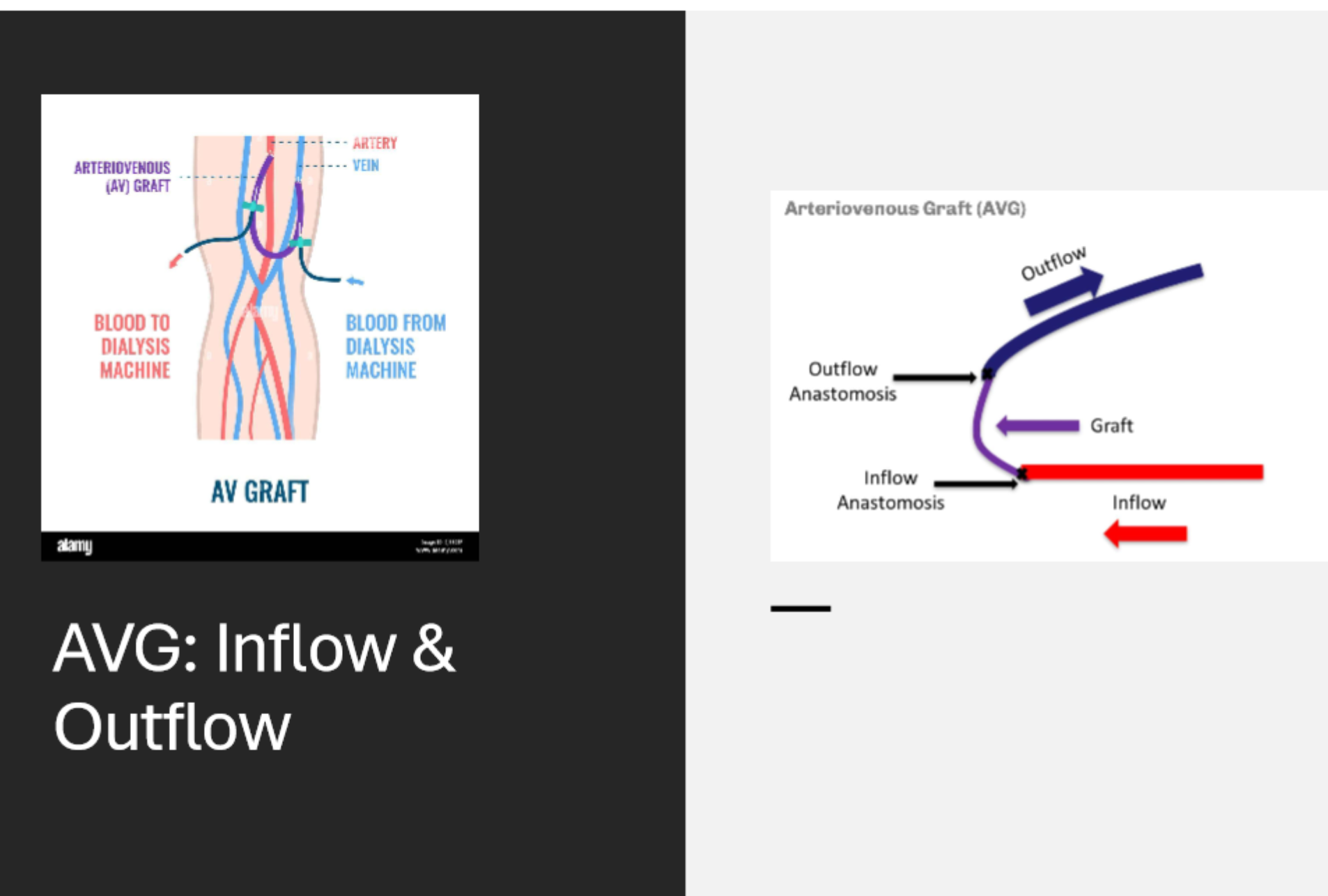
where is the inflow tract of an AVG
graft anastomosed to the arterial side
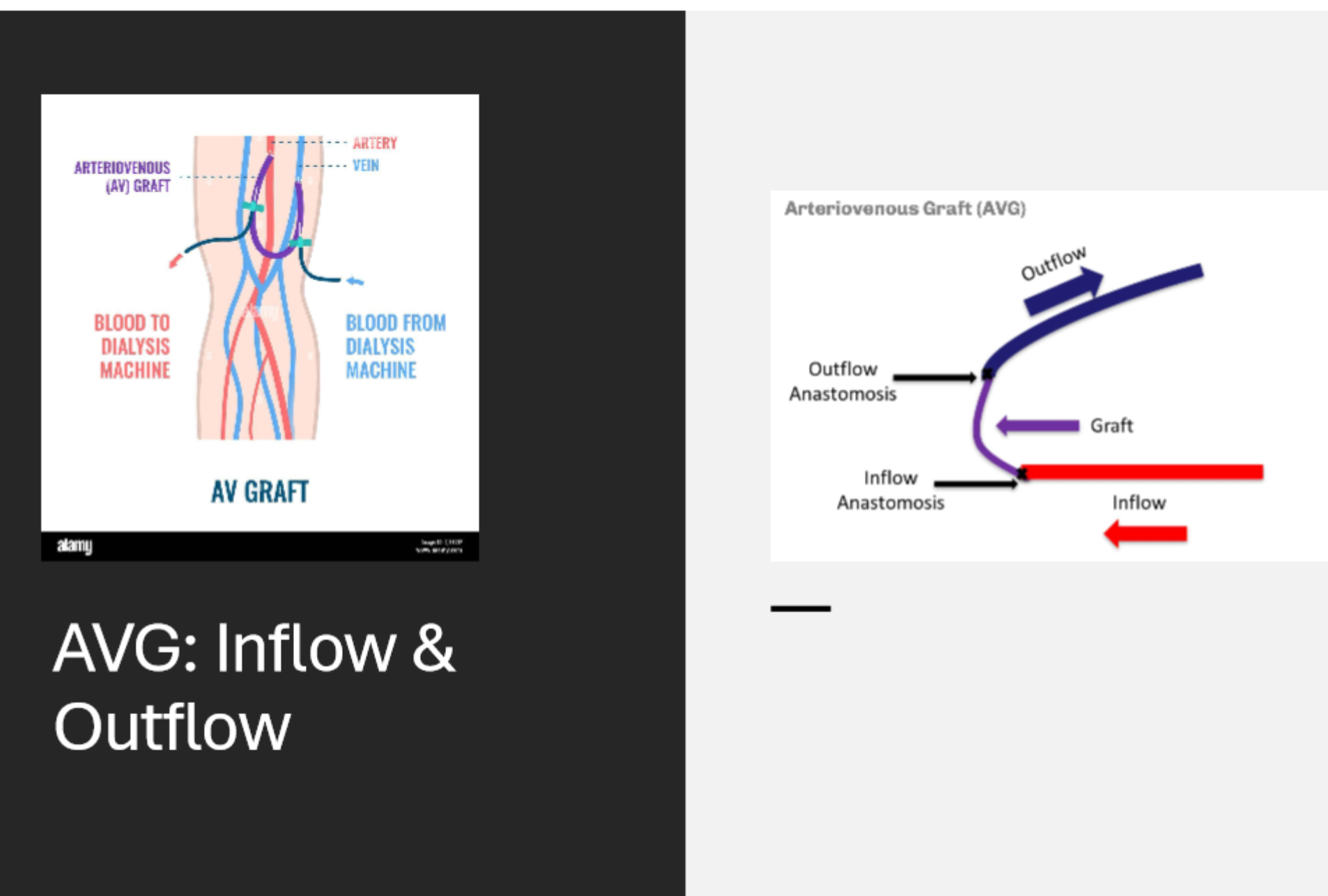
where is the outflow tract of an AVG
it is anastomosed to the vein to allow for venous return
Where should the start of diagnostic fistulogram be performed?
From the arterial inflow to the right atrium to visualize the entire circuit
what is the recommended treatment for any stenosis of 50% or greater that explains the presenting symptoms
PTA (percutaneous transluminal angioplasty)
when should a stent graft placement be considered
4x
graft venous anastomotic stenosis and in stent stenosis
*******
********
recurrent stenoses
Graft-venous anastomotic stenosis and in-stent stenosis, as self-expanding stent-grafts have been shown to improve patency at 6 months, and KDOQI recommends using them over angioplasty alone.
Venous rupture that is refractory to prolonged PTA (percutaneous transluminal angioplasty).
Elastic stenoses in locations where surgical intervention is not easily possible.
Recurrent stenoses within 3 months or less, where no surgical options are available.
what are the three indications for AVF imaging/intervention
failing to mature (imaging)
failing AVF (intervention)
clotted AVF (intrv)
where should the diagnostic fistulogram be performed
from the arterial inflow
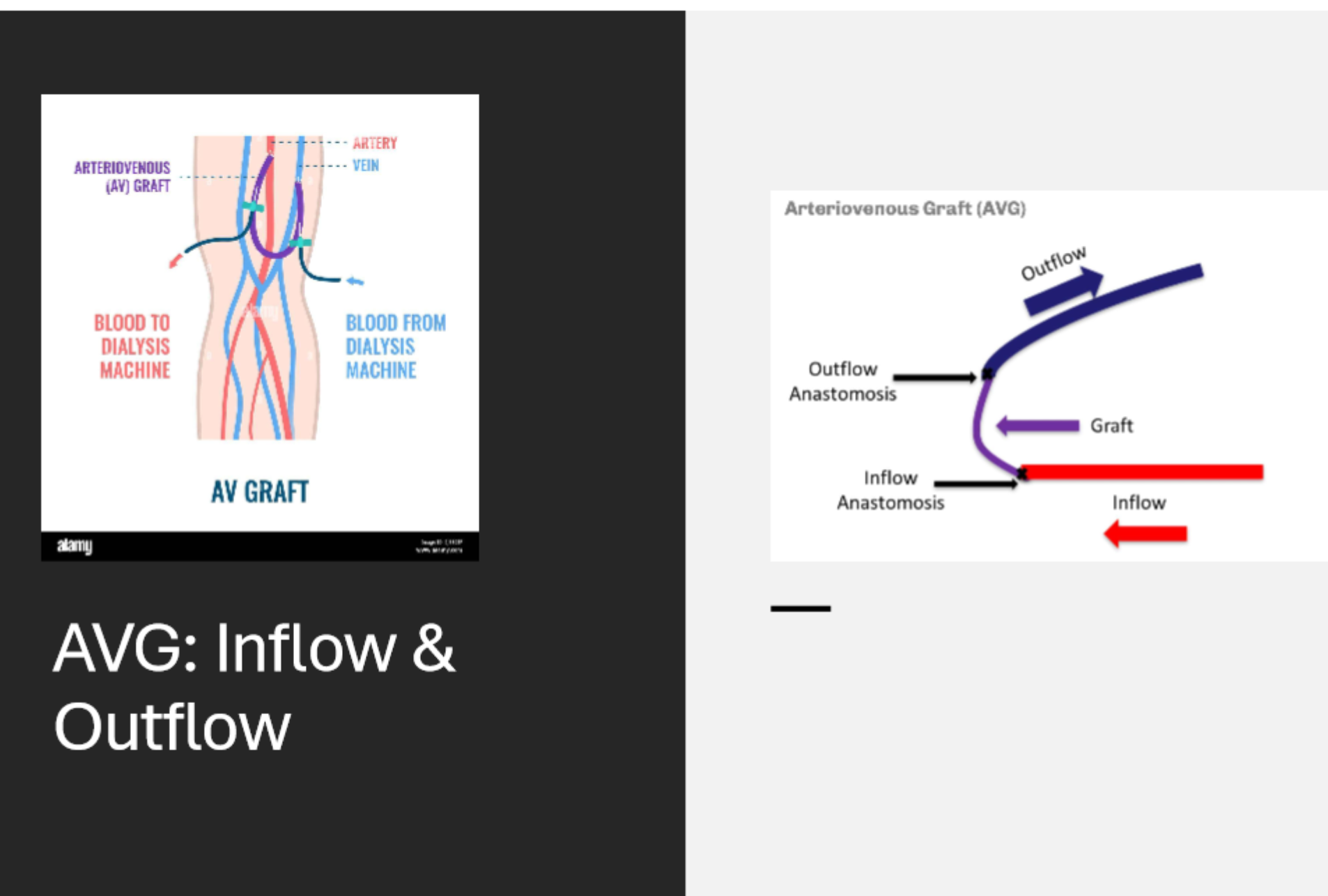
what is a AV anastomosis
a surgical procedure that creates a connection between two tubular structures in the body, such as blood vessels, intestines, or urinary tracts
What are the two main types of dialysis?
Hemodialysis (HD) and
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD).
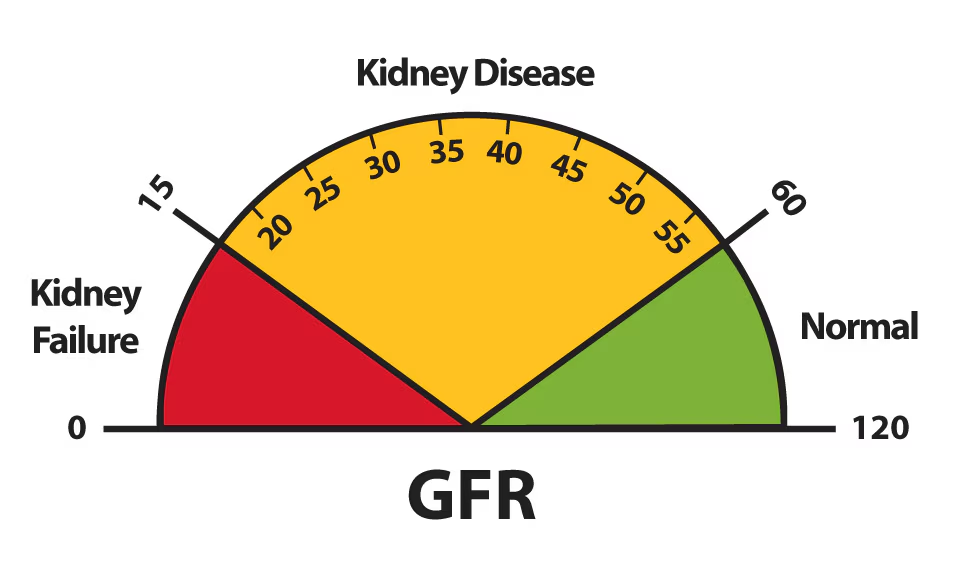
What does a GFR of less than 15 indicate?
Stage 5, which is kidney failure.
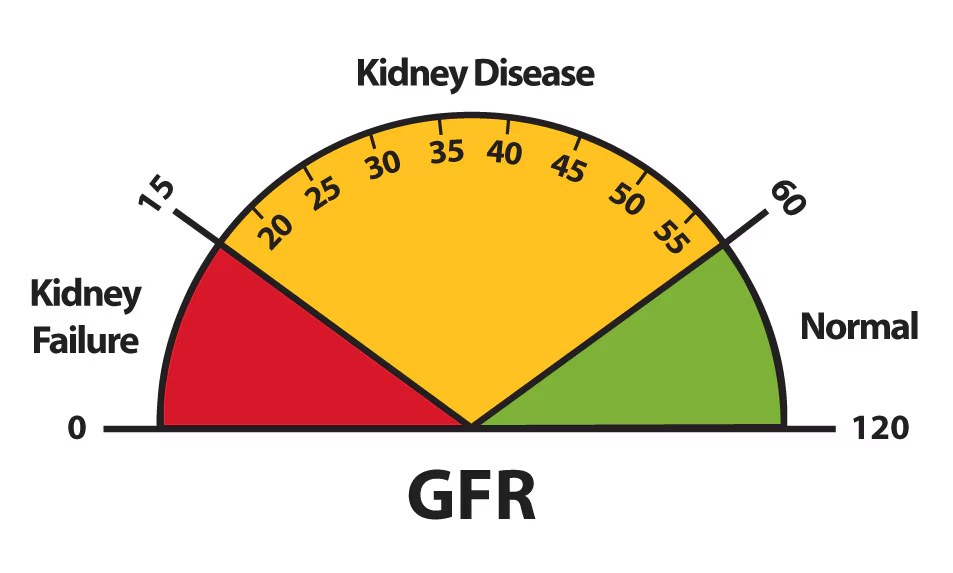
what does GFR measure
kidney function, measures the amount of blood filtered by your kidneys each minute
What is Oliguria?
low urine output
often defines as less than 400 mL
What is Anuria?
complete absence of urine production or less than 100 mL
What are two common causes of kidney failure?
Diabetes and hypertension.
What are the absolute contraindications for imaging/intervention of an AVF?
2x
Uncorrectable coagulopathy,
graft infection,
What is the typical placement site for an AVF?
could be 2 sites
Usually placed in the upper arm or lower forearm.
is a medical treatment that replaces the function of the kidneys in patients with kidney failure, using techniques like hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and kidney transplantation to remove waste, excess fluid, and electrolytes…. this is what kind of therapy
renal replacement therapy
What is the typical wait time before an AVF can be used?
About 6 months to allow the vein to mature.
What is the first stage of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
Kidney damage with normal kidney function (GFR of 90 or higher).
What does the abbreviation ESRD stand for?
End stage renal disease.
What is a sign of obstructive ureteral kidney stones?
Extreme flank or abdominal pain.
Utilizing a dialyzer to remove waste and extra fluid from the blood is what kind of dialysis
What does 'hemodialysis' involve?
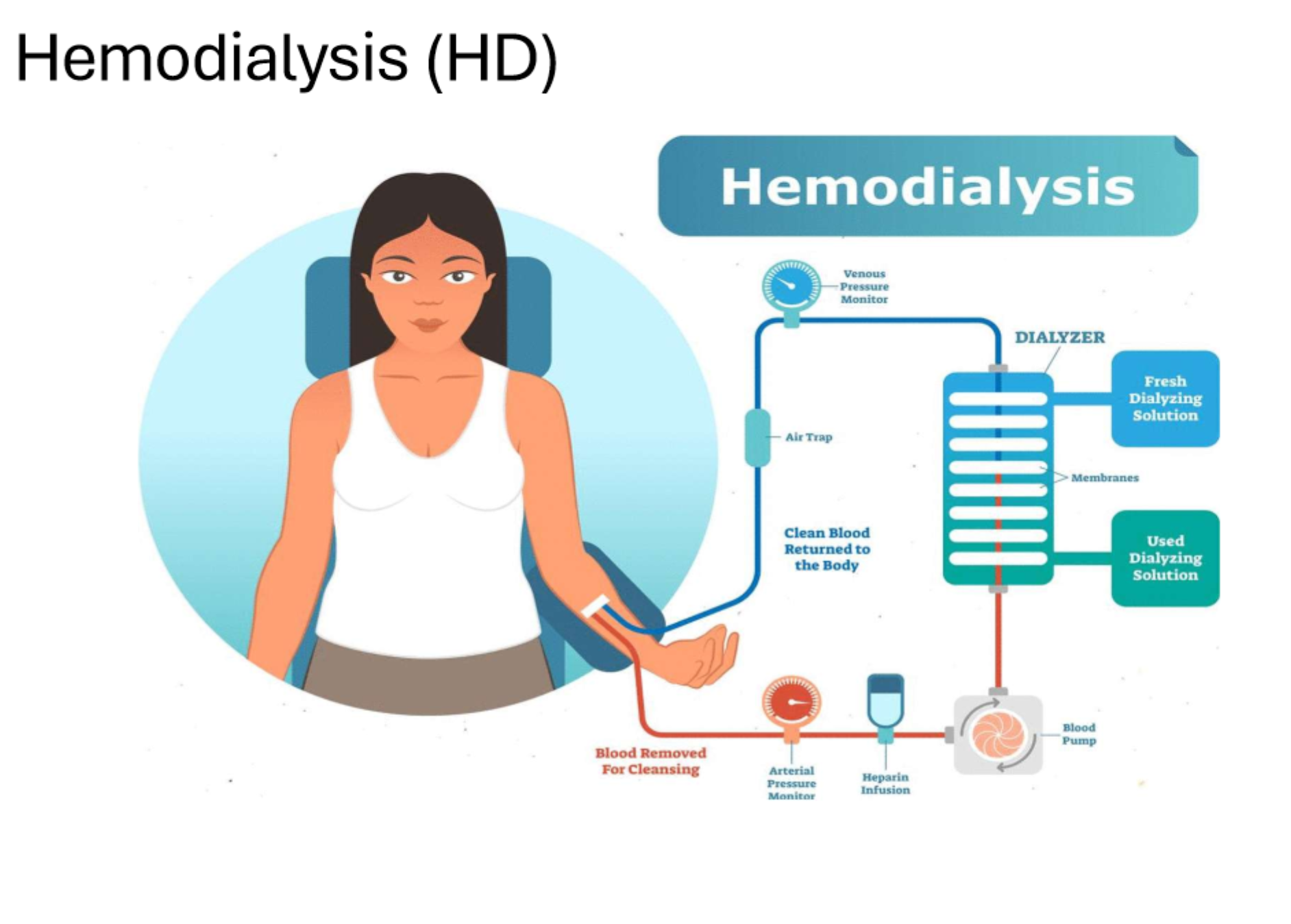
What does AVF imaging check for?
Signs of stenosis, clotted AVF, or failures to mature.
What are the common types of vascular access sites for tunneled catheters?
RIJV, REJV, LIJV, with tunneled catheters being the preferred option.
What are the three long term dialysis conduits a graft an AV shunt may be made out of
native conduits
artificial conduits
hybrid conduits
A conduit made entirely from the patients own vessels (e.g. radiocephalic AV fistula, saphenous vein graft in CABG)
Native conduit
A conduit made from synthetic material like PTFE or Dacron (ex. PTFE AV graft, synthetic vascular bypass)
artificial conduit
a combination of native vessels and synthetic material
ex. saphenous vein graft reinforced with a synthetic graft
hybrid conduit
A sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that happens within a few hours or days
AKI acute kidney injury
Kidneys are funcitoning at 10-15% and are no longer able to keep the patient alive without external assistance
chronic kidney/renal failure.