Exam 2 psych
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
primary motor cortex
first gyrus in front of central sulcus
frontal lobe
involved in voluntary mvmt
topographical organization of body muscles→ maps the innervation of skeletal muscle groups → motor homunculus
secondary motor areas
anterior to primary motor cortex
programming of mvmt; assemble mvmt sequences
damage- person loses coordination of mvmts
brocas area
located on left, most ventral side of secondary motor area
paul broca
controls articulation of speech
lesions cause broca’s aphasia → impaired word production
broca’s aphasia
impaired word production
unimpaired word comprehension
prefrontal cortex
most anterior part of brain
involved in behavioral planning/organization
anticipating consequences of behavior, decision Making, impulse control
phineas gage
parietal lobe made up of
postcentral gyrus
association cortex/area
frontal lobe
primary somatosensory cortex
secondary motor area
prefrontal cortex
primary somatosensory cortex
in parietal lobe; posterior to central sulcus
processes skin senses, body position and mvmt topographical organization → somatosensory homunculus
sensory areas- projection cortices
association area
in parietal lobe
further sensory info processing
integrates info from other senses
location of obj in space → unilateral neglect
unilateral neglect
ignoring objects on the side opposite to the damage
only can draw one side of clock
occipital lobe contains
visual cortex
primary visual cortex (v1)
5 successive visual cortices
association areas (v4-v5)
sensory areas otherwise known as
projection cortices
visual cortex
in occipital lobe
process visual information
primary visual cortex (V1)
posterior part of occipital lobe
receives visual input from retina
process simple features
topographical organization of visual space (map of retina)
occipital association areas (V4-V5)
recieve input from V1,2,3
further computation
form/shape
movement
color
temporal lobe contains
auditory cortex
wernickes area
inferior temporal cortex
auditory cortex
dorsal part of temporal lobe
projection area
hearing
wernickes area
posterior to auditory cortex, dorsal part of temporal lobe
language comprehension
lesion- impaired word comprehension, word salad
inferior temporal cortex
ventral part of temporal lobe
visual identification of familiar objects
corpus callosum
large band of myelinated axons
carries info btwn 2 hemispheres
women have larger one than men
thalamus
made up of many different nuclei clustered together
acts as sensory relay station —> relays incoming sensory info to the cortex
in charge of senses(not olfaction)
hypothalamus
made up of nuclei
coordinates emotional and motivational fxns (sex, eating, emotion, and aggression)
controls pituitary gland which controls rest of endocrine system
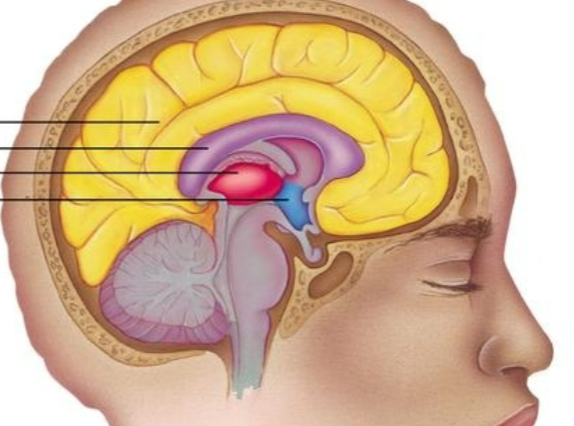
What is each arrow pointing to
top: cerebrum
2nd: corpus callosum
3rd: thalamus
4th: hypothalamus
midbrain
tectum - superior and inferior colliculus
tegmentum- substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area
tectum
dorsal portion of midbrain
superior colliculus- vision (coordinated eye mvmt)
inferior colliculus- hearing (location of sound)
tegmentum
ventral side of midbrain
control of movement
substantia nigra- dopamine producing neurons, impacted by parkinsons
ventral tegmental area
plays a role in the rewarding effects of food and rock and roll
hindbrain composed of
pons
cerebellum
medulla
pons
bridge
sensory nuerons pass through on the way to thalamus
motor neurons pass through btwn cerebral cortex and cerebellum
part of the reticular formation (sleep and arousal) (circadian rhythms)
cerebellum
motor coordination and balance, motor learning, cognitive fxns (even language)
medulla
life-sustaining fxns (heart activity and breathing)
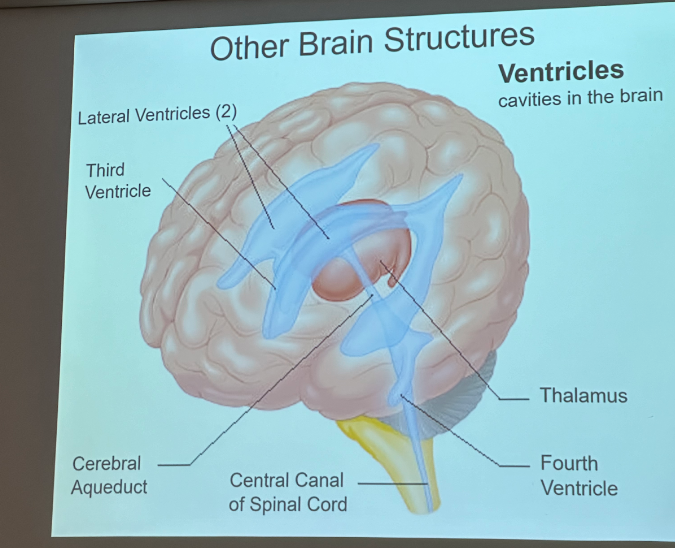
ventricles
cavities in brain
lateral ventricles on sides of thalamus
3rd wraps around thalamus
cerebral aqueduct leads to 4th ventricle
contain CSF
spinal cord
cable of neurons
carries signals from the brain to muscles (periphery)
carries sensory info from the periphery (sense organs ) to brain
Hub for reflex arcs
reflex arc
neural pathway that controls a reflex act
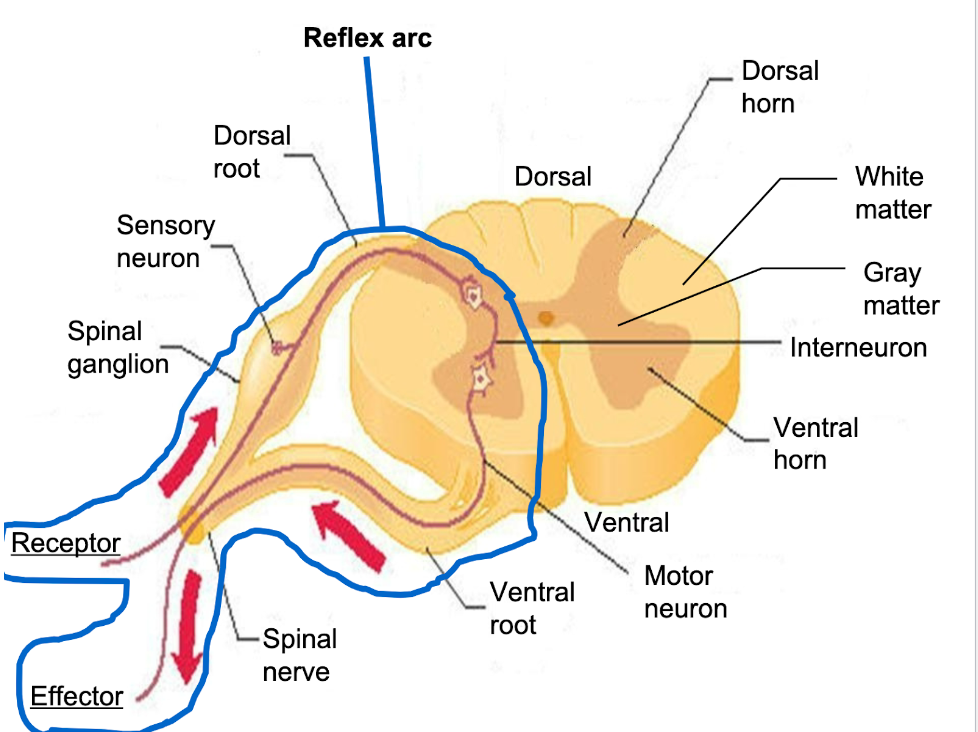
reflex act
simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus → response can be muscle contraction or gland secretion
meninges
provide structural support to brain and spinal cord
provide degree of protection against trauma
btwn 2 most innermost layers is CSF
blood brain barrier
provents harmful substances (toxins) from entering the brain
capillary mem cells are tightly packed
fat soluable subs freely pass through
some subs need transport proteins to get through
some areas of brain not protected- area postrema (medulla)- induces vomiting when certain toxins are in bloodstream
what area of the brain is not protected by the BBB?
- area postrema (medulla)- induces vomiting when certain toxins are in bloodstream
how many cranial and spinal nerves?
12 pairs of CN
31 SPinal nerves
CN 1
olfactory
smell
list cranial nerves
CN1- Olfactory
CN2- Optic
CN3-Oculomotor
CN4- troclear
CN5- trigeminal
CN6- Abducens
CN7- facial
CN8- vestibular/auditory
CN9- glossopharyngeal
CN10- Vagus
CN11- Accessory
CN12- hypoglossal
CN2
optic
vision
CN3
oculomotor
eye muscle mvmt
CN4
trochlear
eye muscle mvmt
CN5
trigeminal
facial sensations and jaw muscle
CN6
abducens
eye muscles
CN7
facial
facial muscles and taste
CN8
vestibular/auditory
balance
CN9
glossopharyngeal
taste, throat and tounge muscles
CN10
vagus
sensation from trunk, internal organs
CN11
Accessory
neck muscles
CN12
hypoglossal
tounge
somatic NS
has motor neurons- carry signals from CNS to skeletal muscles
sensory neurons- infro from sensory organs to CNS
autonomic NS
regulates body’s general activity level
controls smooth muscle, heart, glands
sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic ns
speeds up bodily processes such as heartbear, respiration, blood pressure and sweat glands
originate from middle of spinal cord
passes through synpathetic ganglion chain
parasympathetic ns
slows bodily processes back down
originates from ends of spinal cord
development of NS
1. Proliferation
Neurons divide and multiply at extreme rate
Occurs on lining of ventricular zone
2. Migration
Neurons migrate to final location by climbing radial glial cells
3. Circuit formation
Neurons send developing axons to make synapses with target cells
Growth cone develops at tips of developing axons and move towards final targets using chemical/molecular signals
4. Circuit pruning
Extra neurons that have developed die
Eliminates large numbers of extra synapses-> refines the organization
5. Plasticity
Ability of synapses to be modified by experience-> learning
Dec with age- cortical association areas are more likely to retain their plasticity
proliferation step of development of ns
1st step
neuron divide and multiply at extreme rate
occurs on lining of ventricular zone
migration step of development of ns
2nd step
neurons migrate to final location by climbing radial glial cells
circuit formation step of development of ns
3rd step
neurons send developing axons to make synapses with target cells
growth cone develops at tips of developing axons and moves towards final targets
circuit pruning step of development of ns
4th step
extra neurons that have developed die
refines organization by eliminating large #s of extra synapses
plasticity step of development of ns
last step
ability of synapses to be modified by experience→ learning
dec with age- cortical association areas more likely to retain plasticity
drug
chemical substance theat changes the body or its fxning
psychoactive drugs
have psychological effects
anxiety, relief, hallucinations
agonist
mimics of enhances the effect of a NT
having same effect on receptor or inc effect of NT on receptor
blocking reuptake or degradation of nt
morphine - agonist of endorphins
antagonist
blocks or reduces effect of NT
binding to receptor and not activating it
addiction
preoccupation with obtaining drug
compulsive use of drug
high tendency to relapse after quitting
withdrawal
negative reaction when drug use is stopped
symptoms often are the opposite of effects of the drugs (withdrawal from elation drug → depression during withdrawal)
dependence
need to keep using drug to avoid withdrawal
tolerance
inc amts of drug are required to produce the same results
mostly due to reduction in # and/or sensitivity of receptor to the drug
opiates
derived from opium poppy
opium-5700 bc
morphine- early 1800→ effective treatment of intense pain (most powerful)
heroin- late 1800s- initially sold OTC, highly soluable in lipids (BBB)
codeine- cough suppressant
analgesic
hypnotic (sleep inducing)
produce euphoria
addictive
agonist of endogenous opioids , bind to opiate receptors
depressants
ethanol, barbituates, benzodiazapines
ethanol
produced from fermented fruits and grains
complex action
high doses- sedative
low doses- stimulant
addictive- withdrawal involves tremors, anxiety, mood and sleep, delirium tremens - hallucinations, seizures, death
antagonist of glutamate, agonist of GABA (binding to GABA r)
binding of GABA and ethanol stretches channel to allow entry of ethanol
facilitates opening of Cl- channels→ hyperpolarization of mem
barbituates
high doses- sedative and hypnotic
low doses- inhibits cortical centers that inhibit behavior → talkativeness
antagonist of glutamate
agonist of GABA- in high doses can open Cl- channels even without GABA
benzodiazepines
created to be safe alternatives to barbituates for anxiety treatment
cannot open Cl- channels on own
produce anxiolytic (anxiety reducing), sedative, antiseizure, and muscle relaxing properties
addictive
stimulants
inc activity of CNS
produces euphoria, inc alertness
used to be legal OTC and in coca cola
agonist of dopamine and serotonin→ block reuptake
addictive
withdrawal- depression and anxiety
can cause brain damage- > loss of grey matter in prefrontal and temporal areas
impairment in executive fxns and memory
amphetamines, nicotine, caffiene
amphetamines
meth, speed, crank, crystal
produce euphoria, inc in confidence, alertness and concentration
agonist of dopamine and norepinephrine by inc in release in synaptic cleft
high doses- hallucinations, psychotic symptoms
chronic use- loss of grey matter in many regions
nicotine
primary psychoactive and addictive agent in tobacco
short puffs- stimulating
long puffs- relaxing
agonist of Ach and dopamine
addictive
withdrawal- nervousness,anxiety, drowsiness, headaches
caffiene
inc arousal, alertness and dec sleepiness
acts as agonist of dopamine and ACH→ inc release
block adenosine receptors→ have sedative effects
withdrawal- headaches, fatigue, anxiety, craving
psychedelics
cause perceptual distortions
LSD
ecstasy
angel dust
LSD
produces sensory distortions, hallucinations
binds to serotonin receptors
Ecstasy
MDMA
low doses- inc energy, sociability and sexual arousal
high doses- like LSD
blocks dopamine, norepi, and serotonin reuptake
high doses- kills serotonin neurons, hippocampus damage
angel dust
PCP, ketamine
dissociative effects→ schizo like symptoms
inhibit NMDA glutamate receptors m
marijuana
THC major psychoactive ingrediant→ concentrated in dried resin of plant→ hashish
THC → agonist of NT anandamide and 2-AG by binding to R
anandamide and 2-AG play impt role in regulation of mood, memory appetite and pain perceptions
withdrawal- anxiety, irritability, stomach cramps
withdrawal avoidance hypothesis
addiction is caused by desire to avoid withdrawal symptoms
considered correct to a certain point
does not explain use of drug before dependence develops, return to drug use after withdrawal has subsided, poor correlation btwn addictiveness of drug and severity of withdrawal symptoms
paraventricular/periaquductal gray
region of midbrain
may be key region of withdrawal
inject morphine into that part of brain→ rats did not press lever after morphine stopped being given
ventral tegmental area
involved in addiction in brain
pleasure center of brain
medial forebrain bundle
pathway from ventral tegmental area to nucleus accumbens
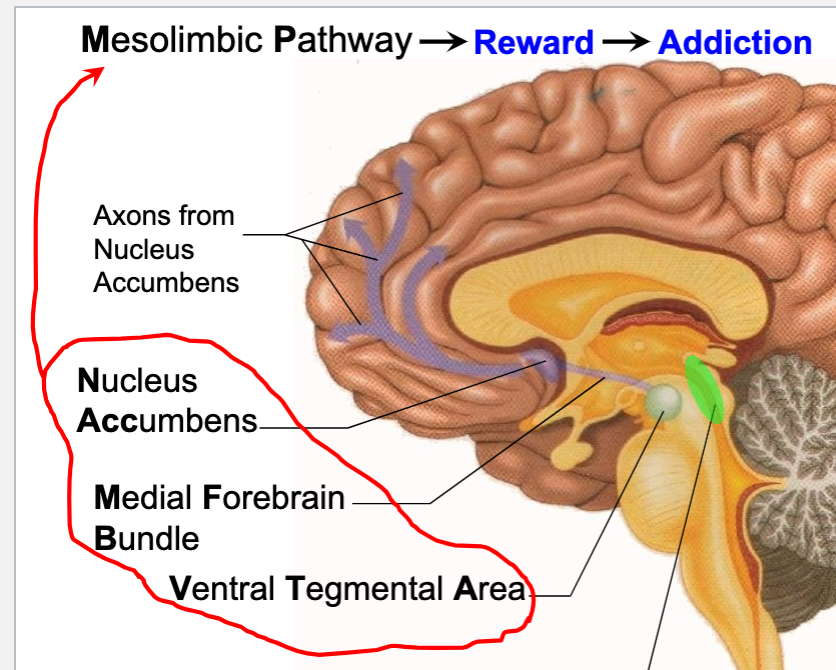
mesolimbic pathway
composed of:
nucleus accumbens
medial forebrain bundle
ventral tegmental area
general reward system
reward certain behaviors for survival purposes
electrical stimulation of medial forebrain bundle is rewarding in rats→ inc dopamine levels in NAcc
nucleus accumbens
rich in dopamine receptors
all drugs inc dopamine levels in NAcc
reducing dopamine levels in NAcc dec rewarding effects of drug
mesocorticolimbic dopamine system
changes in synaptic connections/signaling
inc for drugs, dec for normal stimuli
hypofrontality- reduced activity in frontal regions→ impulsivity→ inc chance of relapsing
pharmacological treatments of dependence
agonist treatments (nicotine gum, methadone)
antagonist treatments (blocker)
aversive treatments (antabuse)
antidrug vaccines (stim immune syst)
agonist treatments for drug dependence
replace addicting drug with another with similar effect
nicotine gum, methadone for heroin treament
antagonist treatments for drug dependence
involve drugs that block effects of addicting drug
GABAa receptor blocker limits alcohol effects
aversive treatments for drug dependence
cause negative reaction when person take affictive drug
antabuse prevents breakdown of alcohol byproducts, makes you ill when you drink
antidrug vaccine treatments for drug dependence
stimulates immune system to produce antibodies that break down drug
long term action, avoid side effects of other medicines
motivation
set of factors that initiate, sustain and direct behavior
organizes sources of behavior
inability to explain behavior solely in terms of external stimuli
theoretical approaches to motivation
instinct
drive theory
incentive theory
arousal theory
drive theory revised
instinct theory of motivation
complex behavior
automatic, unlearned
occurs in all members of a species
nest building, web building
reflex is too simple
drive theory of motivation
body actively maintains homeostasis for basic tissue needs
departure from homeostasis→ aroused condition→ drive
lack of nutrients, drop in temp
motivates org to engage in appropriate behavior to restore homeostasis
incentive theory of motivation
individuals are motivated by external stimuli
money, grades