PTE 743: exam 1
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
infant development, toddlerhood, early childhood, developmental testing, and historical overview
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
what is the definition of primitive reflexes?
automatic, involuntary movements that are present in newborns and young infants
T or F: development of reflexes parallel typical voluntary movement.
T
poor integration of which primitive reflexes indicate a moderate chance of developmental problems?
moro, galant, ATNR, STNR
what is the definition of postural reactions?
a series of responses that help maintain an upright position; righting reactions incorporate into equilibrium reactions
T or F: postural reactions appear to proceed functional control.
T
list the time frames of the first 4 quarters of life.
0-3 months
4-6 months
7-9 months
10-12 months
what are the main motor “goals” for each quarter of life?
first= head control
second= trunk control
third= horizontal movements
fourth= vertical movements
at what age does the integration of primitive reflexes occur?
4 months
rooting, galant, babinski, palmar grasp, crawling, primitive standing, and stepping
T or F: postural reactions usually appear in the first quarter of life.
T
TLR, landau, labyrinthine and optical righting, body-on-head, and body-on-body
during the first quarter of life, what angle of head control does an infant have in prone?
head unsustained at 45 degrees with forearm support
T or F: during the first quarter of life, an infant’s head remains in midline in supportive sitting and dependent standing.
T
“head in midline” and head “aligned with body”
play during the first quarter of life is termed “_______ play” because an infant is stimulating movement with his/her actions.
experimental
hands open consistently
brings hands to mouth
playing with fingers, hands, and toes
what is an infant’s acuity during the first quarter of life?
20/100
improving color, depth, and size perception
T or F: an infant during the first quarter of life lies within Piaget’s sensorimotor substage 1.
F; substage 2 (primary circular reaction)
what is a game that assists with the development of object permanence and causality during the first quarter of life?
peek-a-boo
when do infants begin to recognize universal sounds and imitate vowel sounds?
first quarter: 0-3 months
what emotions appear around the first quarter?
joy, sadness, disgust, and possibly anger
list the reflexes and postural reactions that occur around the second quarter of life (4-6 months).
landau
tilt and parachute in prone
body-on-body righting response with spinal rotation
what is a “big” motor milestone that occurs during the second quarter of life?
rolls from prone to supine
T or F: brief sitting can occur during the second quarter.
T
with upper extremity support tho
when do infants’ oral motor control improve to more active sucking with liquid loss from lip corners?
second quarter of life (4-6 months)
can infants have solid foods during the second quarter?
yes as long as they have up and down jaw movement
describe the fine motor control that an infant may have during the second quarter?
grabs toy, holds it, shakes it, and/or brings it to mouth
picks up toy in one hand and holds it in palm
reaches or grabs toy with both hands
T or F: an infant in the second quarter can reach and grab for objects as small as a Cheerio
F; they cannot grab the objects until the third quarter (often using the raking motion)
an infant during the second quarter lies within which of Piaget’s sensorimotor sub-stages?
sub-stage 3 (secondary circular reactions)
selective attention is developing
when does babbling using both consonants and vowels begin?
6 months old
when do the emotions of fear and surprise appear?
second quarter
list the postural reactions that occur during the third quarter of life (7-9 months).
tilt reaction response in supine, sitting, and maybe quadruped
protective extension forward and sideways
what is a “big” motor milestone that occurs during the third quarter of life?
sitting independently/without support
when does the radial digital grasp develop?
third quarter
when do teething and sucking on thumb usually begin?
third quarter
T or F: during the third quarter, infants have free use of tongue and can suck liquid from a cup but may still experience liquid loss.
T
describe the fine motor patterns of an infant in the third quarter of life.
grabs objects with one hand
holds toy with tips of fingers rather than in palm
able to place toy on surface without dropping it
when can a parent feed his or her baby spaghetti?
during the third quarter bc baby can now successfully grab at string-like objects
describe the perception-cognition of an infant in the third quarter.
coordination of vision and sense of touch is developing
behavior is intentional
evidence of combining of schema
when can an infant begin to understand words and gestures to communicate needs and wants?
8 months
T or F: at 0-6 months, infants become familiar with individuals and will respond to them, but at the third quarter of life, infants may demonstrate stranger anxiety.
T
list the motor controls that occur during the fourth quarter of life (10-12 months).
abdominal-thoracic breathing pattern is developing
protective extension backwards
what is a “big” motor milestone that occurs during the fourth quarter of life?
baby can pull to stand and cruise along furniture
when does baby’s first steps usually occur?
anytime between 12-17 months of age
when does chewing with a mixture of up, down, and diagonal patterns occur?
fourth quarter
describe the fine motor patterns of a baby in the fourth quarter of life.
develops bimanual dexterity
demonstrates early hand preference
throws a ball with forward arm motion
assists with turning pages
during the fourth quarter, the _____ grasp develops which is described as grabbing a small object with isolated control of thumb and index finger.
pincer
what is an infant’s acuity during the fourth quarter of life?
20/20
according to some sources, but others say acuity reaches 20/20 at 2 years of age (Dr. Williamson’s slides say both)
T or F: infants slow to habituate to stimulus have better memories than infants who habituate to stimulus more quickly
F; they have poorer memories
when can you expect a baby to say his or her first word?
fourth quarter
what word is important to include into a baby’s receptive language?
“no” —> set limits and expectations of baby
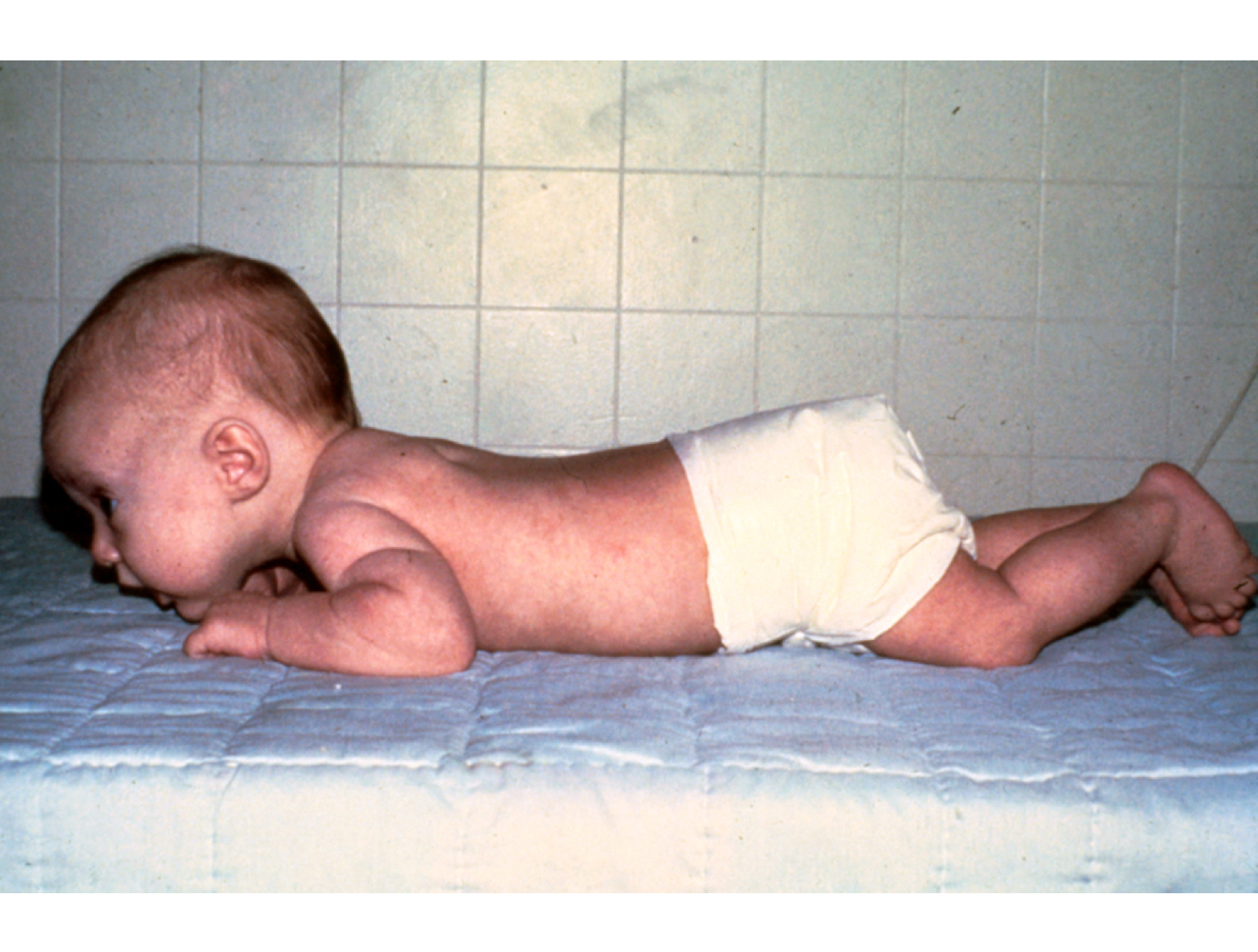
what quarter of life is this infant demonstrating?
first quarter (0-3 months)
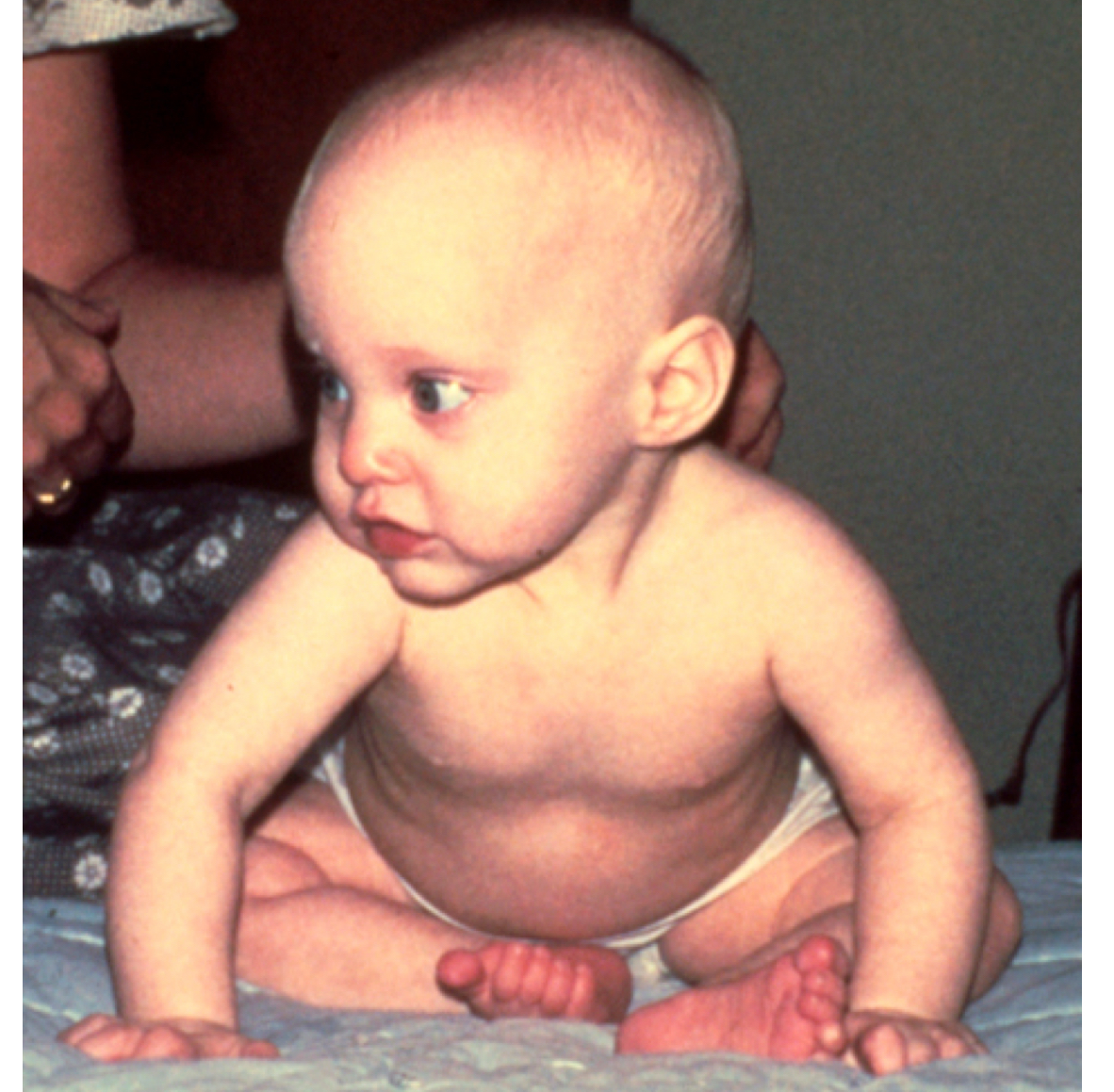
what quarter of life is this infant demonstrating?
second quarter (4-6 months)
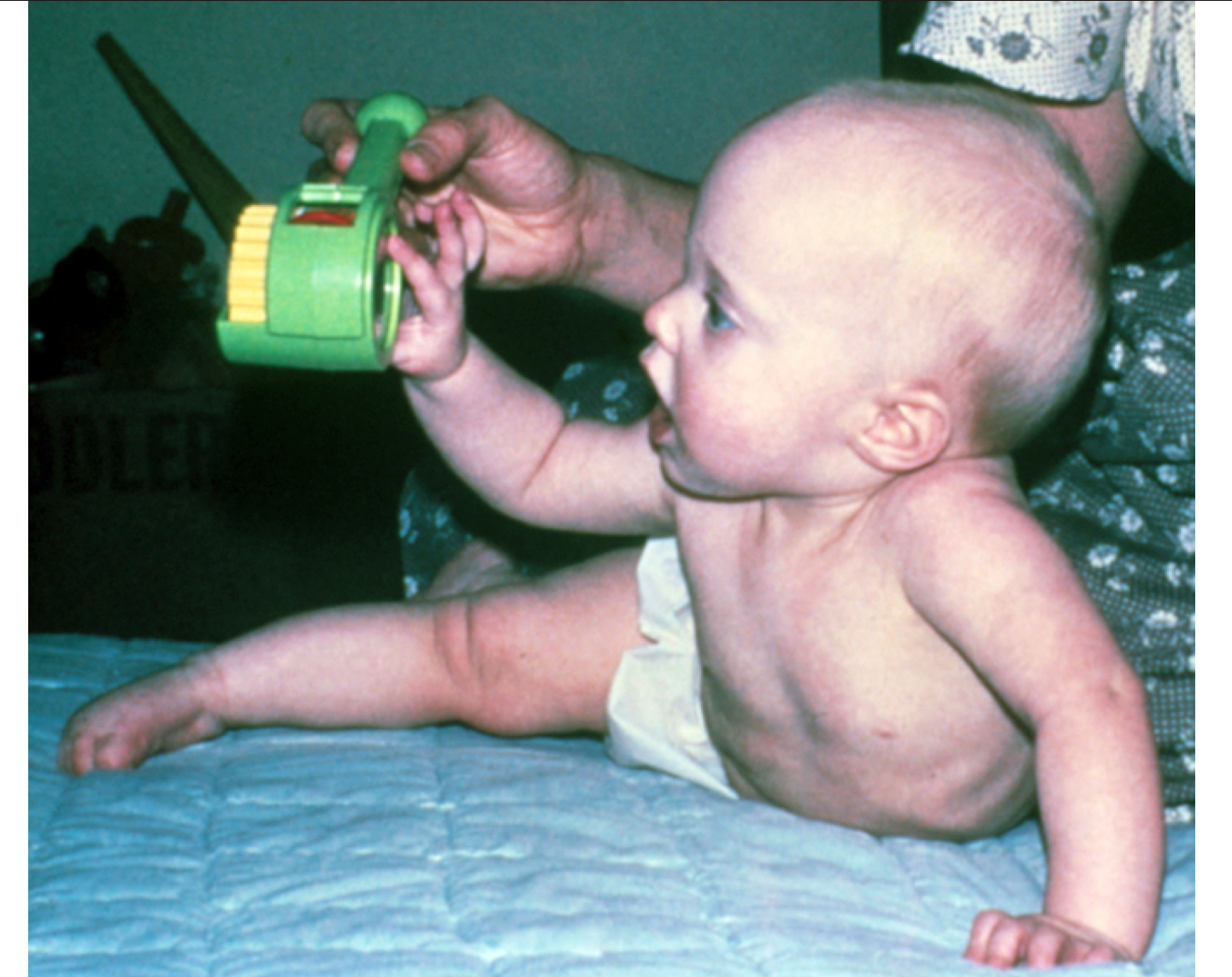
what quarter of life is this infant demonstrating?
third quarter (7-9 months)

what quarter of life is this infant demonstrating?
fourth quarter (10-12 months)
what age is considered toddlerhood?
13-36 months
at what age is the landau postural reaction integrated?
13-24 months
at what age is equilibrium in standing (with some staggering) present?
15-18 months
when does a toddler’s adult binocular vision develop?
around 2 years old
T or F: self-produced movement in the right environment facilitates depth perception.
T
describe the spatial perception a young toddler experiences when walking/cruising.
at 13 months: ability to detour around a barrier
at 14 months: can take shortest route
play during toddlerhood is termed “_______ play” bc babies are understanding functional relationships and basic conceptual categories.
pretend/symbolic
if a toddler presents with a long attention span, what might that be indicative of?
autism
toddlers usually have short attention spans
T or F: expressive language makes up > 50 words of vocabulary by 18 months and 200-300 words by 24 months.
T
with two-word phrases by 24 months
what’s the difference between holophrastic speech and telegraphic speech?
holophrastic speech: a stage of language development when children use single words or short phrases to express ideas
telegraphic speech: a stage of language development where children speak in short, simple phrases that convey the main idea
at what age does separation protest peak?
at 15 months
appearance of which “self-conscious” emotions begin to develop during toddlerhood?
empathy, jealousy, and embarrassment
T or F: social referencing, gender typing, and beginning of self-regulation develop during toddlerhood.
T
describe the gross motor patterns of a toddler aged 25-36 months.
jumping from 12 inches with both feet
running
ascending stairs with railings
underhand throwing of a ball
open doors
what is an example of a toy that toddlers would enjoy and further their gross motor development?
tricycle
or any feet-propelled wheeled riding toys
describe the fine motor patterns of a toddler aged 25-36 months.
hold handled cup in one hand
unbutton large buttons and unzip large zippers
pouring and filling containers
stack 4-6 blocks
toddlers can assist with basic hygiene. what are some examples of basic hygiene skills?
washing hands, washing face, and brushing hair
T or F: with a toddler’s improved hand-eye coordination, they can place objects together and complete simple classification tasks.
T
when can a baby recognize and express pain and its location?
toddlerhood (specifically aged 25-36 months)
what are the three mental states of metacognition that babies begin to understand in toddlerhood?
perceptions
desire
emotions
at what age do children begin to transition to adult communications?
by 36 months when children demonstrate functional grammar and can use plurals
when do temper tantrums peak?
toddlerhood (specifically around 25-36 months)
describe the social development a child experiences at the end of toddlerhood.
talk about their own and others’ emotions
cause and consequences of feelings
beginning to control behavior
difficulty with delay-gratification
what age range is considered early childhood?
3-5 years old
describe the gross motor patterns of a child.
walking backwards
ascending and descending stairs foot over foot
developing advanced motor skills
list the six advanced motor skills of a child.
running
jumping
throwing
hopping
catching
galloping
children should be able to self-dress (shoes, socks, pants, front zippers, snaps, and belt buckles) by age 3 but what two dressing skills are not developed until 5 years of age or older?
back fasteners
tie shoes
at what age should a child be potty trained?
by 3 years old
at what age should a child brush and floss teeth thoroughly?
by 5 years old
when does primitive reasoning begin to develop?
around 4-7 years old
a child should develop syntax and pragmatic language during early childhood. what do syntax and pragmatic language mean?
syntax: the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language
pragmatic language: the ability to use language in a way that is appropriate for social situations
at what age should a child improve self-control and be able to distinguish themselves from others in concrete, physical descriptions?
by 5 years old
T or F: a child aged 3-5 is egocentric and unable to understand cause and effect but is beginning to consider other’s viewpoints.
T
describe the main social development points of early childhood.
3 years old: play with others
4 years old: strong emotion relationships
5 years old: cooperative play
IFC model
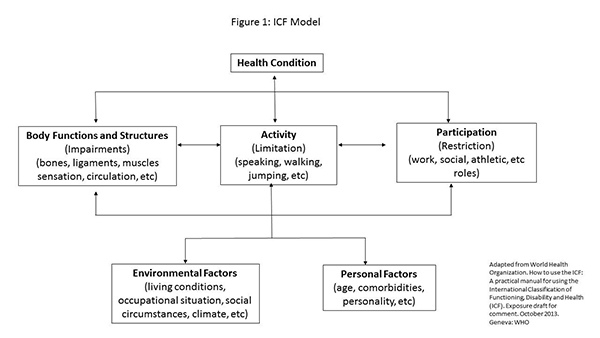
IFC model case example: an older woman presents with L LE weakness after suffering a MCA stroke. she lives with her husband and currently gets around via wheelchair. her goal for therapy is to stand for longer periods of time to do house work.
health condition: MCA stroke
body structure/function: L LE weakness
activities: cannot stand for long periods of time
participation: uses wheelchair
environmental factors: lives with husband
personal factors: older
what are the three models of motor control?
reflex
hierarchical
systems
reflex theory model of motor control
reflexes are the basis of all movement
coordinated movement is the accumulation or compounding of reflexes
motor control comes from peripheral parts of the nervous system- “peripheralist view”
hierarchical model of motor control
higher center selects and delegates motor programs to subordinate centers for execution
basis of traditional neurologic physical therapy
normal movements driven by motor programs (muscle activation patterns) issued from within the nervous system- “centralist view”
systems model of motor control
movements are not driven but emerge as result of interaction among many systems, each contributing to different aspects of control
control of movement includes the neurological system, environment, the musculoskeletal system, etc.
control is over abstract aspects of motor behavior
what are the three neurologic rehab (therapeutic) approaches?
muscle re-education approach
facilitation approach
task-orientated approach
muscle re-education approach
patient is an active participant in rehab
approach is based upon knowledge of gross muscle anatomy and on human willpower
goal of approach is to strengthen motor units in weak muscles by activating individual muscles and individual motor units
facilitation approach
assumes nervous system can be modified to control movements more effectively if it experiences “normal” movement patterns guided by “skilled” therapists
primary neurophysiological aim: inhibit abnormal tone and primitive reflexes and facilitate normal movement patterns
task-oriented approach
assumes control of movement is organized around goal-directed, functional behaviors
therapists do not limit training to one “normal” movement pattern but allows patients to learn alternative movement strategies to coordinate motor behaviors as efficiently as possible
list a few ideas on how someone could learn to move to perform functional tasks with somatosensory loss.
compensate with vision
proprioceptive training
practice/develop motor learning and coordination
assistive devices
postural control and balance training
feedforward and feedback systems work throughout our body. which theory of motor control has limitations due to these systems?
reflex model
what is the overall order of what a therapist should test during the neurological exam?
impairments
strategies
functional tasks
what is Phase 1 of differential diagnosis?
overview of initial assessment
comprehensive history taking
physical exam
initial diagnosis
basic diagnostic tests
(from chatgpt)
what is Phase 2 of differential diagnosis?
further investigation and refinement of diagnosis
targeted diagnostic tests
referral to specialists
monitoring disease progression
(from chatgpt)