Economics 1.5
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Examples of goods not (completely!) distributed by the free market mechanism in the UK…
Education (places at schools)
Guns
Public transport (busses, trains, cars)
Illegal drugs
Healthcare, treatment for illness/disease
Roads
National security
Market Failure
Market failure occurs when the free market mechanism fails to allocate resources efficiently.
Efficiently meaning in the context of market failure
For resources to be allocated ‘efficiently’ would mean that everyone’s welfare is maximised - everyone is as well off as they can be.
What are externalities
production or consumption of a good may actually impact other people - not just those buying or selling the good
Why might the free market fail
The free market acknowledges private benefits to consumers and costs to firms, and bases prices on these. External costs and benefits to third parties are ignored. This can lead to market failure!
External costs
- costs which impact third parties
External benefits
- gains which impact third parties.
Private costs
- the costs paid by a supplier of a good/service
Private benefit
a buyer’s gains from consumption of a good/service.
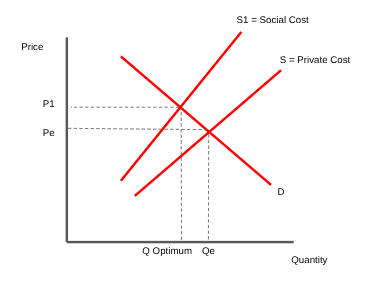
Social cost
the total cost to individuals and third parties associated with supply of a good
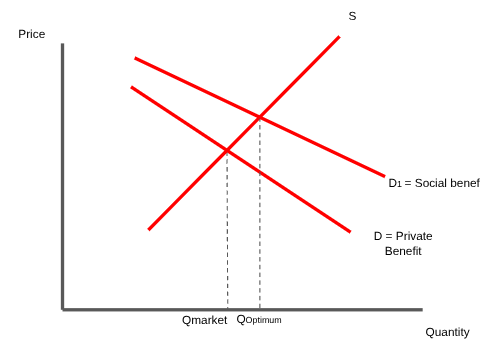
Social benefit
-the total benefit to consumers and third parties associated with supply of a good.
How does a good with a high social cost look
How does a graph with a high social benefit look
How do we draw externalities on the demand and supply graph
we always reflect costs in the supply curve and benefits in the demand curve
Advantages of the free market
greater efficiency, driven by competition and the profit motive; increased consumer choice as businesses create goods and services to meet demand; higher innovation as firms compete to develop new and better products; and potential for economic growth as resources are allocated efficiently and investment is encouraged
Disadvantages of the free market
wealth inequality,market failure
Whats government provision
when a government directly provides goods and services, often to correct market failures like under-provision of public goods and merit goods
what are merit goods
goods and services that are under-consumed in a free market, despite being beneficial for individuals and society
What are public goods
a commodity or service that is provided without profit to all members of a society, either by the government or by a private individual or organization
Why are private goods, goods which cant be sold by a private firm
they are non-excludable-cant be bought without others benefiting
non rivalrous-it cant be used up by an individual consumer
Types of government intervention
Legislation
Regulation
Indirect taxation
Grants & subsidies
Tax breaks
voluntary agreements
How do taxes and subsidies affect graphs
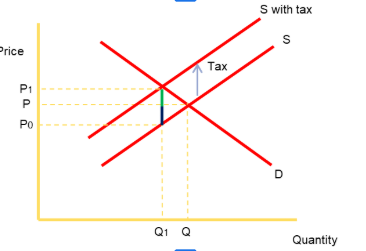
taxes-shift left in the supply curve
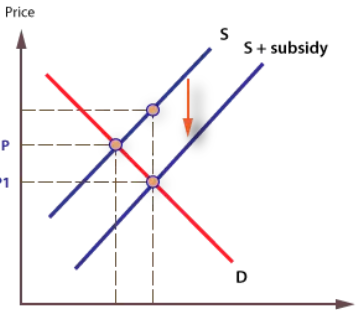
subsidies-shift right in the suply curve
Graph of indirect taxes
Graph of subsidies
How does direct provision work +disadvantages
the government provides as much of the good as people need and sets a fair price or provides it for free, funded by taxation.
Government management can be less efficient due to lack of profit incentive
Funding from taxation mean it is difficult to provide enough of a service without raising taxes which people dislike
How does Bans work +disadvantages
Prevents harmful products reaching consumers
Some may argue that the government shouldn’t be able to decide if people want to consume harmful goods
How does regulation work +disadvantages
Government sets rules or targets that businesses must comply with
unnecessarily restrictive and compromise personal freedom
Complying with regulation may increase legal or production costs for firms, which they will pass onto consumers leading to higher prices.
How do indirect taxes work +disadvantages
Prices are increased which is tantamount to an additional ‘cost’ for suppliers
Some taxes may punish certain groups unfairly
High taxes could lead to an increase in illegal imports and black market activity
Voters may dislike high taxes and punish governments who introduce them, making it harder for governments to place taxes on certain goods
How do subsidies work +disadvantages
Reduces effective costs of production for firms and shifts supply curve downwards, leading to lower prices and high quantities produced
Subsidies may be difficult to sustain in long run and firms may not be able to keep up production when subsidy is removed
Can encourage firms to become less efficient as they have less reason to reduce costs since government is giving them money to cover a portion of their costs
How do voluntary agreements work +disadvantages
Encourages firms to sign up to rules they are able to keep and monitor themselves,
Firms may set the bar low for quality or word agreements vaguely to avoid firm commitments
Reason for government failure and examples
Government failure occurs when a public sector activity or government intervention, intended to correct a market failure, makes the situation worse instead.
High administrative costs
The law of unintended consequences
Information gaps
Distorting market signals