MSK Physiology: Bones
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
support, muscles, organs, formation, mineral
Roles of the Bones
-Form the body
-________ tissue
-Permit movement by providing attachment points for _________
-Protect vital ________
-Site of blood cell ___________
-Role in _______ homeostasis
chondrocytes, cartilage, osteoblasts, long, most
Bone Formation: Endochondral Ossification
-Begins during embryonic development, much more common than intramembranous ossification
-Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) → ____________ → develops mineralized ________ scaffold → forms __________ → forms ____ bones and ____ other bone elements
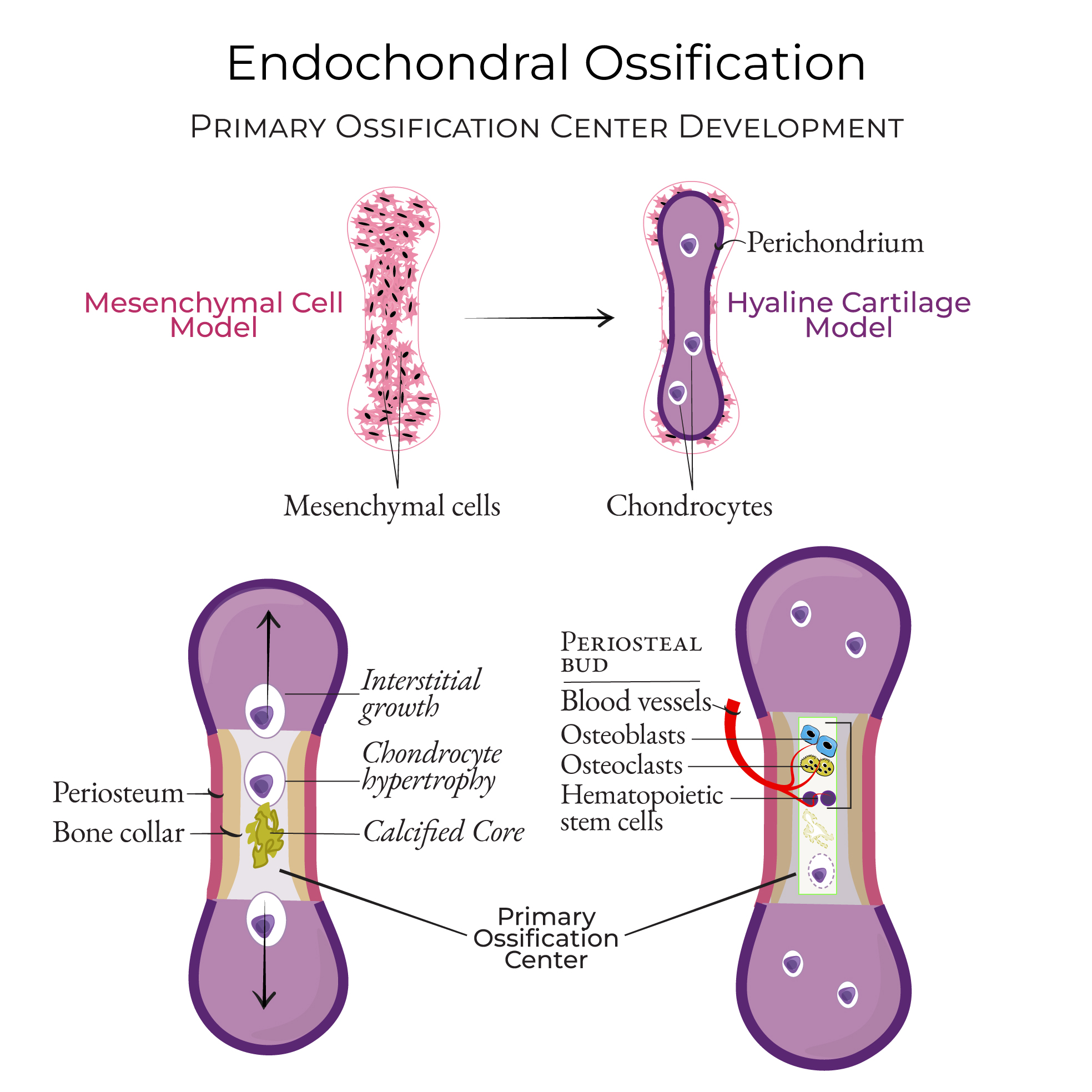
pre, cartilage, skull, flat
Bone Formation: Intramembranous Ossification
-Skip the cartilage formation stage and go straight to building bones
-MSC → ___osteoblasts → osteoblasts without ________ framework → forms _____ and ____ bones
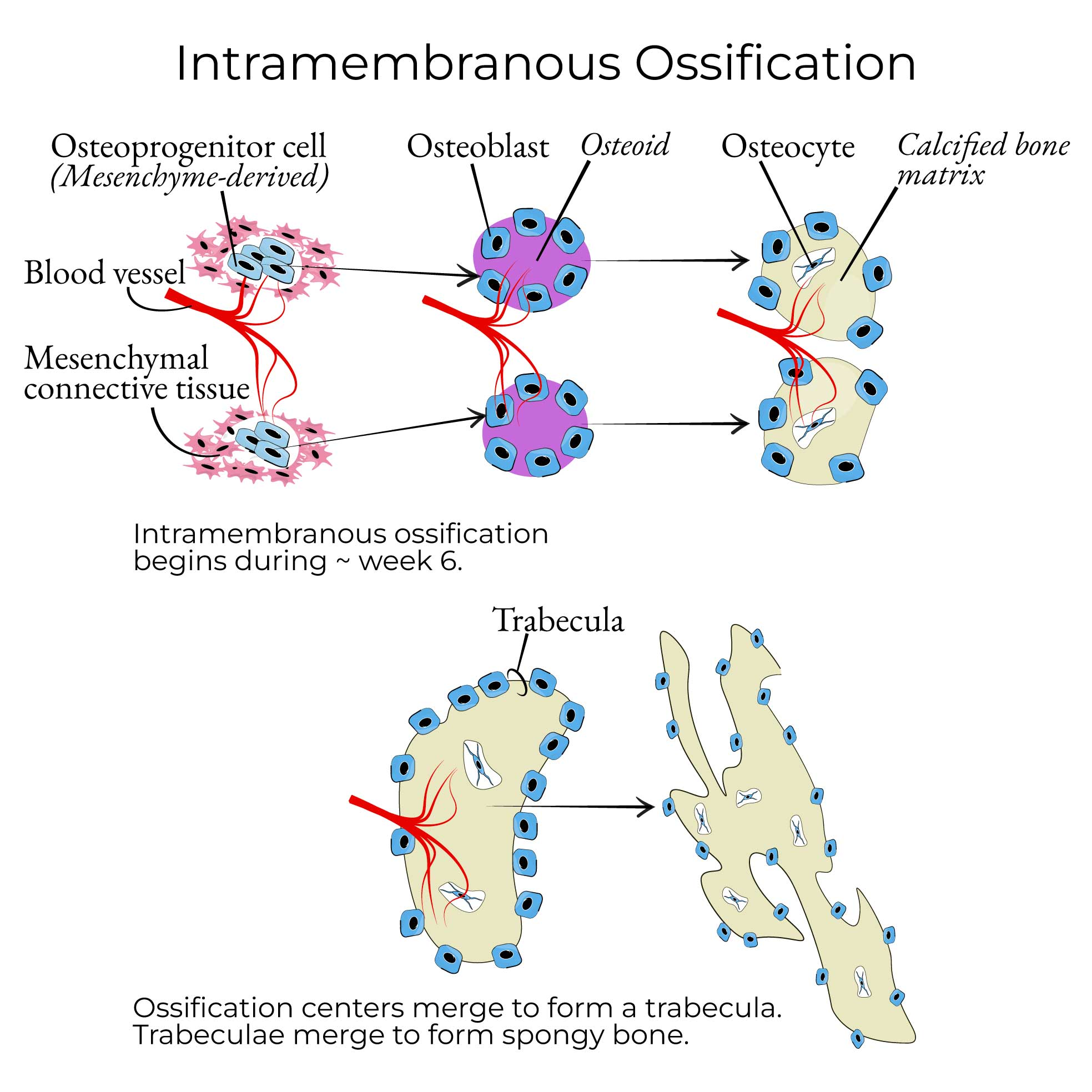
matrix, calcification
Bone Formation
-First Step → develop bone _______ (collagen/fiber formation)
-Final Step → ____________ or mineralization
flexible, osteocytes, new, collagen, diffusion, calcium
Elements of Bone: Rigid Yet _________ Connective Tissue
-Cells
Osteoblasts, ___________, and osteoclasts
Help with bone growth, bone repair, to change shape, make ___ bone, and resorb old tissue
-Fibers
__________
Gives tensile strength and ability to hold itself together
-Ground Substance
Gelatinous material (proteoglycans/hyaluronic acid)
Medium for _________ between bone and blood vessels
-Crystalized Materials
Mostly _________
Provides rigidity
forming, mesenchymal, calcium, osteoid, outer, PTH, osteocalcin, inorganic
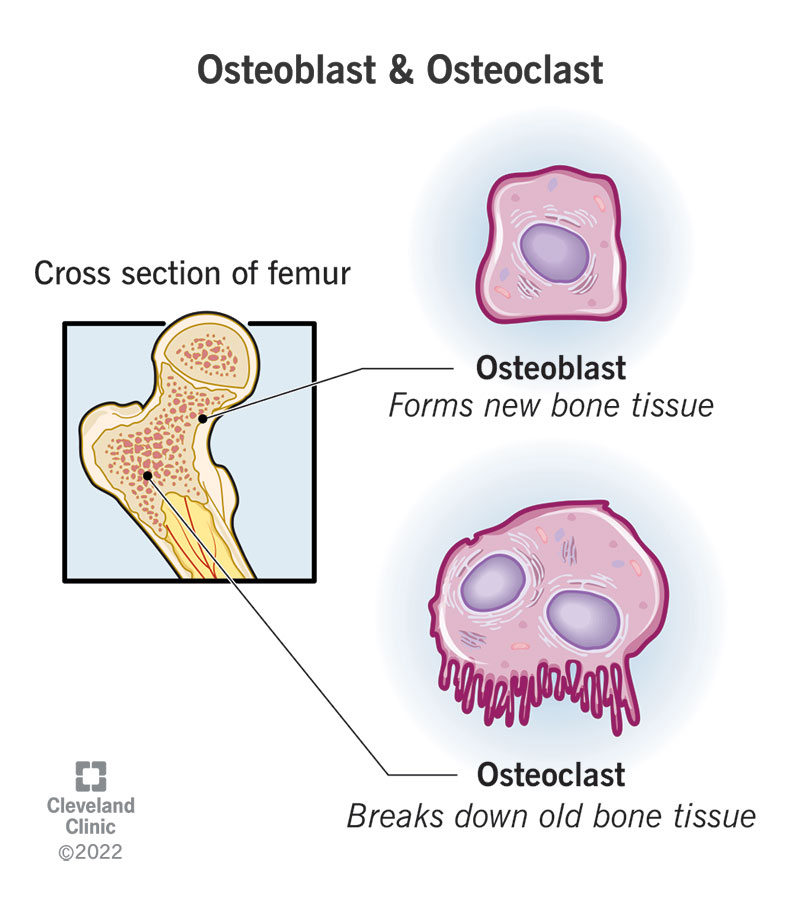
Bone Cells: Osteoblasts
-Responsible for bone __________
-Derived from ____________ stem cells (MSC)
-Form new bone → deposition of _________ and synthesis of ________ (nonmineralized bone matrix)
-Found on the _______ layer of bone and respond to ___ → produce __________ in response to Vitamin D → produce _________ calcium phosphate
-Differentiate into osteocytes imbedded in bone
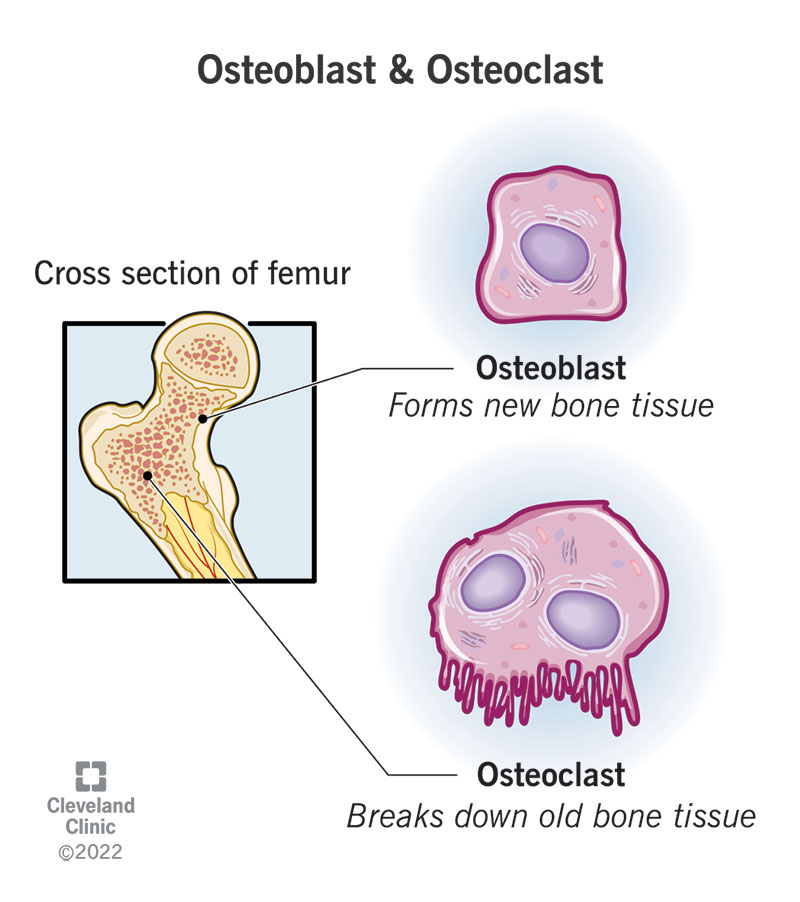
maintaining, lacuna, mechanical, stress, PTH, form, resorb
Bone Cells: Osteocytes
-Bone ___________
-Located in the _______, which are depressions found in the bone. They develop dendritic processes that extend to either bone surface or bone’s vascular space.
-Can detect ___________ force and respond to changes in ______, also responds to ___
-Signals osteoblasts and osteoclasts to _____ and ______ bone
hematopoietic, Howship, hydrochloric, dissolve, degenerates
Bone Cells: Osteoclasts
-Large, multinucleated cells that resorb bone
-Derived from _____________ stem cells located in ________/resorption lacunae, which are scalloped cavities in the bone.
-Secrete ____________ acid, acid proteases, and matrix metalloproteinases → _________ bone minerals and collagen
-Once resportion is complete → __________ or becomes inactive
osteoblast, osteoclast, loss, cytokines
OPG/RANKL/RANK System
-Helps regulate ________ and _________ activity/function, which is essential for homeostasis
-Balance between RANKL and OPG determines amount of bone ____
-Regulated by different __________ and hormones, which are balanced under normal circumstances
glycoprotein, inhibits, resportion, formation
OPG (Osteoprotegerin)
-____________ (TNF family) from osteoblasts and osteocytes
-_______ osteoclast formation → inhibits bone ___________ → promotes bone _________
-Binds to RANK, which is a receptor on osteoclast precursor cells
cytokine, T, osteoclasts
RANKL
-_________ from osteoblasts and _ cells
-Formation and activation of __________ → increases bone loss
-Binds to RANK
injuries, remodeling, apoptosis, osteoclast, digest, osteoid, calcium
Bone Remodeling: Repair Microscopic ________ and Maintenance of Bone Integrity
Phases
-Activation of __________ cycle
Osteocyte cell death (_________) → signals _________ activity. Injured or old tissue needs to be resorbed somewhere.
-Resorption of bone
Osteoclasts attach to bone and release lysosomal enzymes to ______ bone
-Formation of new bone
Osteoblasts form _______ and alkaline phosphate → sites for _______ and phosphorous deposition
Takes 4-6 months
osteoid, I, calcium, phosphate
Bone Matrix: Composition
-35% organic → _______
Mostly type _ collagen
Small amounts of glycosaminoglycans and other proteins
-65% inorganic → _________ and _____________ minerals
-5-8% water
-Proteoglycans
-Glycoproteins
osteoblasts, fibrils, twist, strength
Bone Matrix: Collagen Fibers
-Make up the bulk of bone matrix
-Synthesized and secreted by ___________ → form ______ → fibrils form staggered pattern creating gaps for mineral deposition → fibrils ______ to form ropelike fibers → gives bone tensile and support _________
-Over 20 types → all with a specific function
ground, compression, collagen, strengthen, transport, deposition
Proteoglycans
-Make up some of _______ substance
-Forms ____________ resistant network between ________ fibrils → helps ___________ bone
-Controls particle __________ (mostly calcium) through bone matrix
-Role in bone calcium ___________ and calcification
calcification, inhibits, resorption, binds, stabilizes, osmotic
Glycoproteins
-Sialoprotein
Promotes __________, a calcium binding protein
-Osteocalcin
_______ calcium phosphate precipitation
Promotes bone __________
-Osteonectin
_____ calcium in bone
-Laminin
__________ bone basement membrane
-Albumin
Transports essential elements to bone cells
Maintains ______ pressure of bone fluid
formation, osteoblast, proliferation, collagen
Bone Minerals: Mineralization
-Final step in bone ___________
-Phases:
Formation of hydroxyapatite crystals
Buds from chondrocyte, ___________, and odontoblast surface
___________ of hydroxyapatite into extracellular matrix and deposition between _________ fibrils
solid, Haversian, osteocytes, lack, red, trabeculae
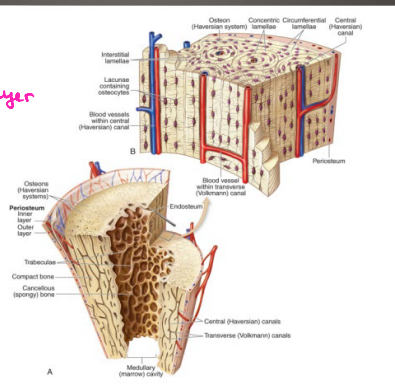
Types of Bone Tissue
-Compact (Cortical) Bone
85% of skeleton
______ and extremely strong
________ system (basic structural unit) → Haversian canal, lamellae, lacunae, ___________, and canaliculi
-Spongy (Cancellous) Bone
15% of skeleton
____ Haversian system, less organized
Filled with ___ bone marrow
__________: plates or bars
blood, nerve, transports, osteocytes, lamellae, lacunae, canaliculi, connect, transport
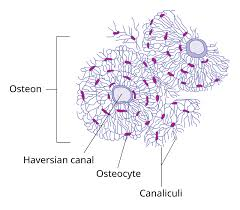
Haversian System
-Central Canal (haversian canal)
Contains ______ vessels and _____ fibers
________ nutrients and wastes to and from ___________
-Concentric layers of bone (________), which surround the canal
-Tiny spaces between lamellae (_______), where the osteocytes sit
-Small channels or canals (_________)
_______ lacunae to each other and to the haversian canal
_________ nutrients and molecular signals to lacunae
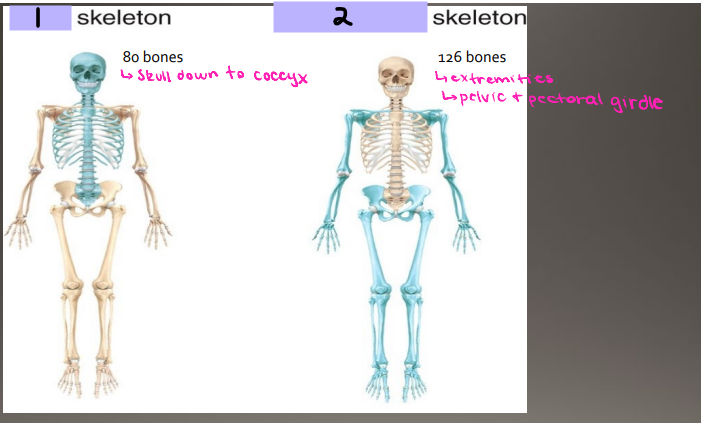
Axial, appendicular
List #1 and #2 in order
long, flat, short, irregular
Characteristics of Bone
-____ → diaphysis, metaphysis, epiphysis, epiphyseal plate (children). Examples of femur and humerus
-____ → examples of ribs and scapula
-______ (cuboidal) → example of bones of the wrist or ankle
-_________ → example of vertebrae, mandible, and facial bones
anchored, vessels, growth, diaphysis, yellow, spongy, red, spongy, red
Characteristics of Bone
-Periosteum
Connective tissue _________ to bone
Contains _______ and nerves
Aids in bone _______ and healing
-Endosteum
Connective tissue lining surface of both marrow cavities
-__________ (shaft)
Mostly compact bone
Medullary cavity containing fatty tissue: _______ marrow
-Metaphysis (neck)
Mostly _______ bone containing ___ marrow
-Epiphysis
Mostly _______ bone containing ___ marrow
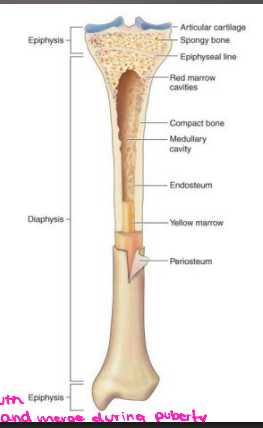
Epiphysis
#1
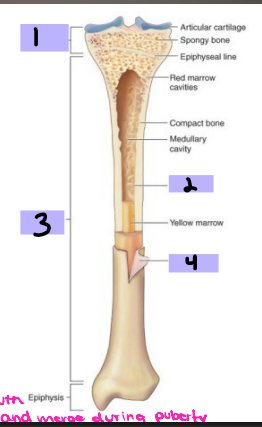
Endosteum
#2
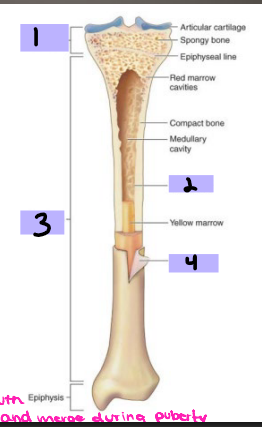
Diaphysis
#3
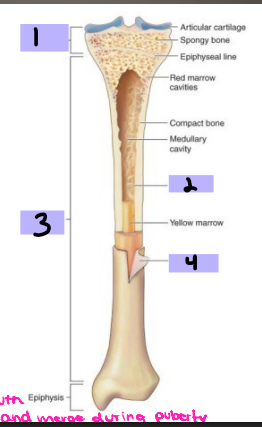
Periosteum
#4
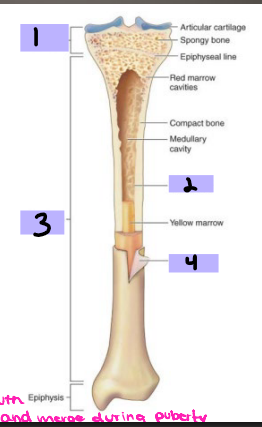
hematoma, procallus, granulation, callus, calcium, lamellar, trabecular, periosteal, remodeled, before
Bone Repair
-________ formation (within hours)
Clot forms → vessels break/tear, fibrin and platelets form framework
-_________ formation (within days)
Produces __________ tissue
-_____ formation (within weeks)
Forms membranous or woven bone → enzymes allow phosphate to join with ________ to harden the callus
-Replacement (within years)
Callus replaced with ________ bone or ________ bone
-Remodeling (within years)
__________ and endosteal surfaces of bone __________ to the size and shape of the bone _______ injury