IB DT: Topic 2.6: Eco Design
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1E2rY-DzYgeaXJMUWr8JnCg2rcSZhLXNajbv436j_k0I/pub?start=false&loop=false&delayms=3000&slide=id.g13f1151ba5_3_422
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
what is eco design?
a more comprehensive approach than green design because it attempts to focus on all three broad environmental categories (materials, energy and pollution/waste), whereas green design only focuses on one or two. this makes eco-design more complex and difficult to achieve than green design.
what are the internal and external drivers for eco-design?
internal: managers’ sense of responsibility, need for increase product quality, need for a better product/company image, need to reduce costs
external: gov., market demand, social environment, competitors, trade organisations, suppliers
what are the two eco design philosophies?
cradle to grave: a design philosophy that considers the environmental effects of a product from manufacture to disposal
cradle to cradle: a design philosophy that aims to eliminate waste from the production, use and disposal of a product. it centres on products which are made to be made again
how can LCAs help to avoid a narrow outlook on environmental concerns?
compiling an inventory of relevant energy and material inputs and environmental releases
evaluating the potential impacts associated with identified inputs and releases
interpreting the results to help make a more informed decision
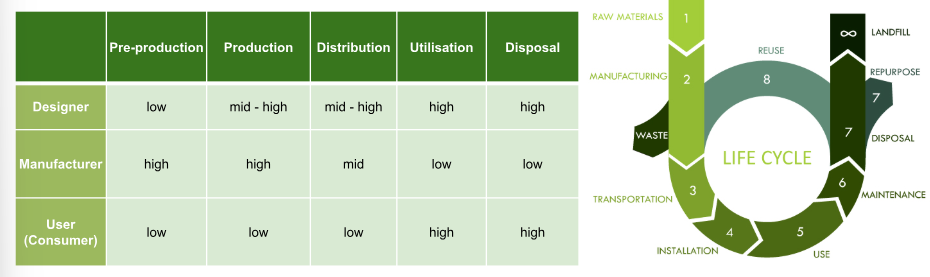
how does the role of the designer, manufacturer and user change throughout the production process in ensuring eco-design?
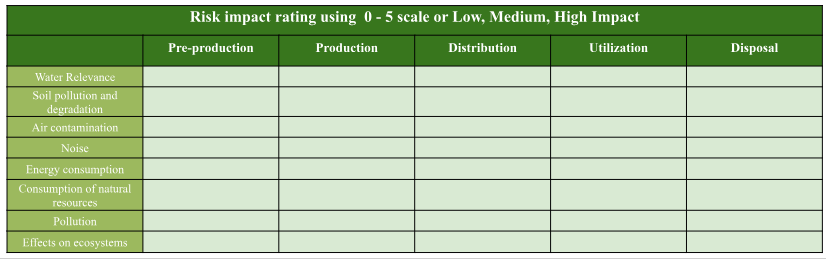
what is an environmental impact assessment matrix?
what are the different stages an LCA should consider?
pre-production: obtaining natural resources
production: processing of the resources and shaping to make the product
distribution: taking the product from the factory to the warehouse
utilisation: the product’s use
disposal: recycling, biodegrading or landfill
diagram breaking down environmental problems products can cause and their scale

what is the unep ecodesign manual?
1996 un eco-design manual also known as design for sustainability (d4s)
aimed to increase recyclability, reduce energy requirements, maximise use of renewable resources, reduce creation and use of toxic materials, reduce material requirements of goods and services, increase product durability, reduce planned obsolescence
what is design for the environment software?
software products that assist designers in designing for the environment. CAD software like solid works allows designers to examine the environment consequences of various decisions and optimise their designs to obtain a cost effective environmentally sensitive outcome.
what is converging technology?
the amalgamating or merging of existing technologies into new forms that create innovative products and systems that may offer greater convenience or efficiency
what are examples of converging technologies?
telecommunications: when one device can perform multiple functions
wearable technology
medicine: wearable implants for example