Respiratory radiology
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms

What is the radiological diagnosis in pneumothorax?
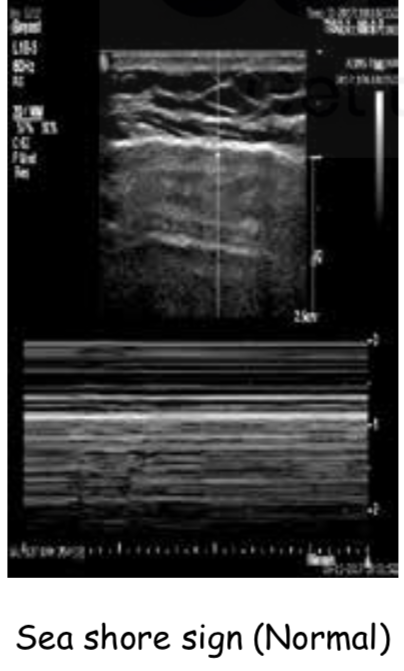
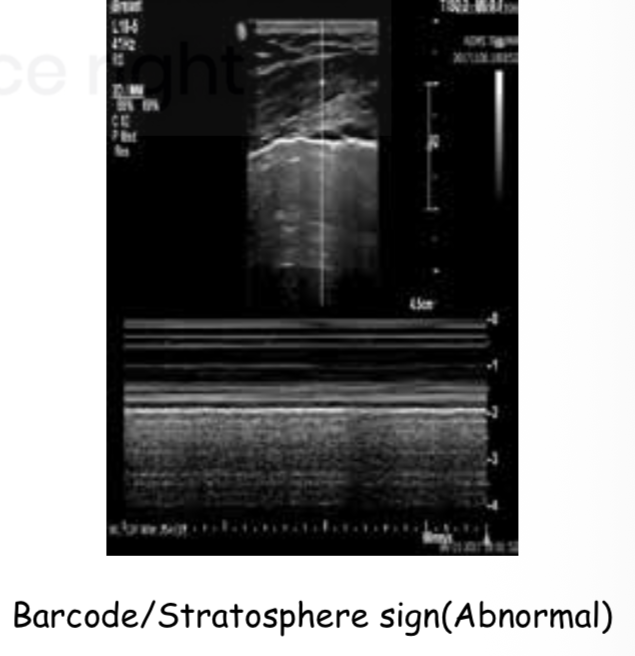
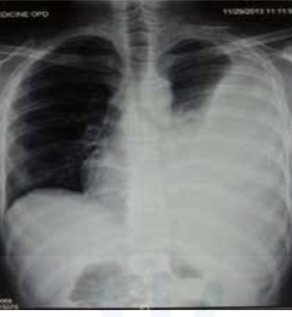
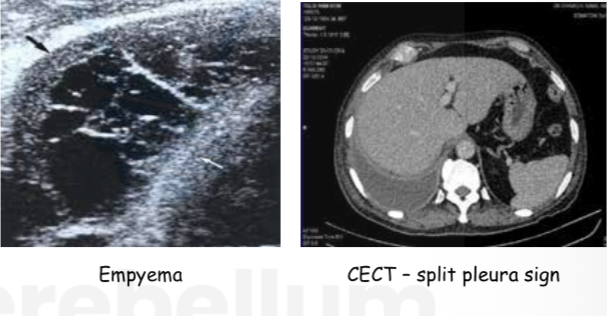
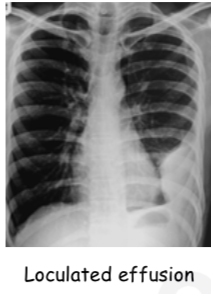
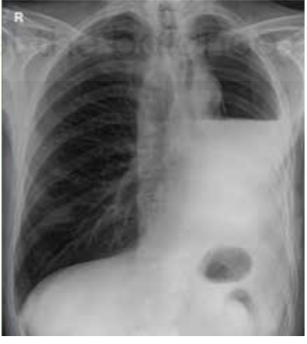
Radiological diagnosis of pleural effusion
Meniscus sign / Ellis S curve
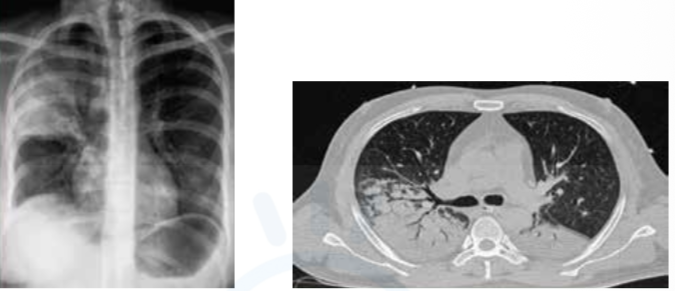
Pathological basis of consolidation
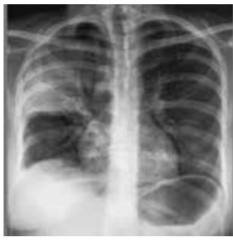
Klebsiella pneumonia ( red current jelly sputum )
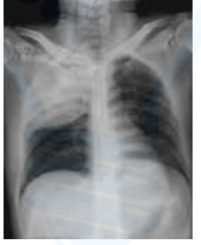
Definition of silhouette sign

PNEUMATOCELE (Consolidation with pneumatocele) suggests
Tree-in-bud appearance indicates

Cavitation
fibrosis
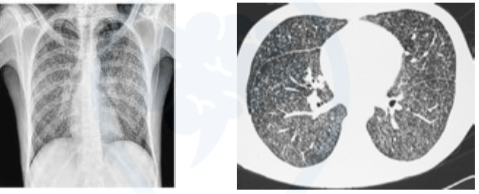
Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia / Loeffler’s syndrome
Patient profile commonly associated with lung abscess
Necrotic thick-walled cavity with air-fluid level
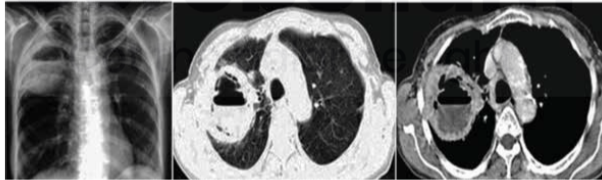
Water lily sign indicates
Multiple nodules with central solid part ( ground glass opacity )
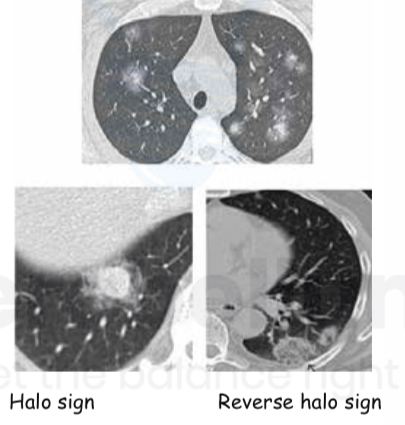
Immunocompromised with febrile neutropenia
Aspergilloma described as
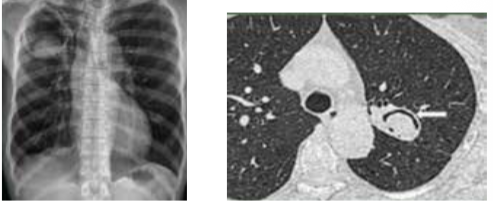
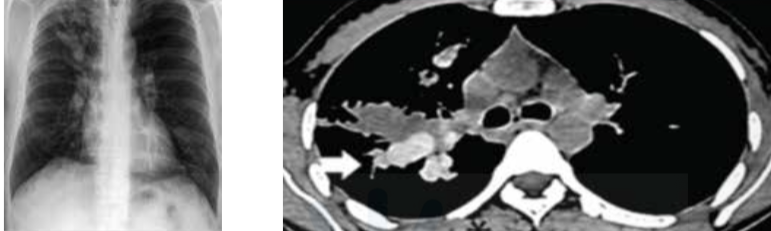
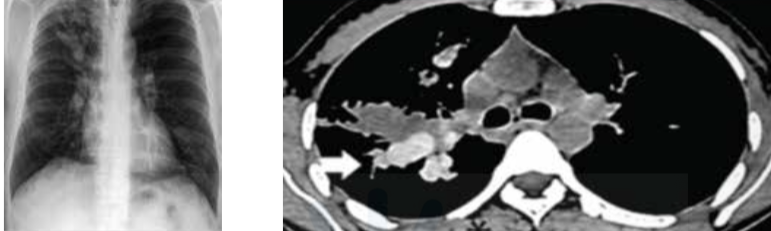
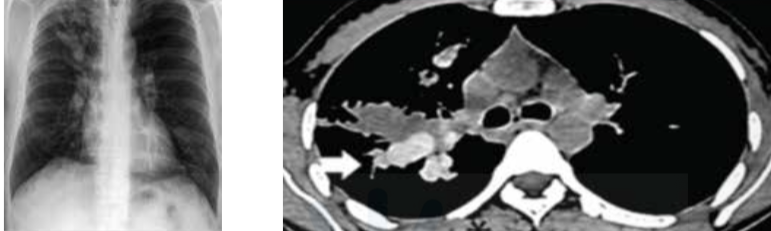
High attenuation mucus inn aspergiiiosis is called
Typical CT findings in COVID-19
Multifocal Peripheral and basal ground glass opacities
Chart of CORAD

Normal or non-infectious findings ( mas/emphysema)
Equivocal findings ( perihilar ground glass opacity, pleural; effusion )
High suspicion for COVID-19 ( multiple consolidation, preexisting lung disease )
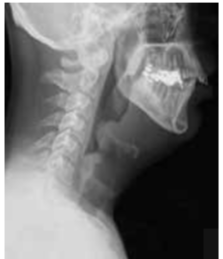
Thumb sign seen in
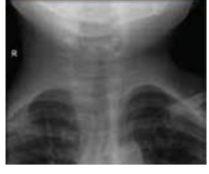
Definition of bronchiectasis
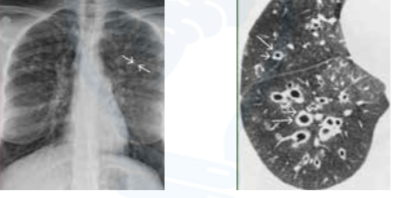
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (Kartager’s syndrome)
Sarcoidosis presents with
Non-caseating / non necrotic
Raised ACE levels, Hypercalcemia