Theme 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is working capital?
The capital used by a business in it's day-to-day operations --> calculated as current assets - current liabilities
What does limited liability mean?
Business owners are only responsible for the debts up to their initial investment
What does unlimited liability mean?
Finances of the business are treated inseparable from the owner's finances. If the business goes into debt the owner needs to sell their own personal assets
Name 3 sources of external finance
Bank loans
Share capital
Venture capital
Government grants
Overdrafts
Name 3 sources of internal finance
Retained profit
Selling assets
Owner's capital
What is a monthly balance?
Cash inflow for a month - cash outflow
What are the advantages and disadvantages of cash flow forecasts?
Advantages:
Improves financial planning
Ensures liquidity (cash in the business)
Ensures budget control
Disadvantages:
Based on estimates (overoptimistic)
Unpredictable for external factors
What are fixed costs? Give examples
Any costs that do not vary directly with the level of output e.g. rent, salaries, insurance
What are variable costs? Give examples
Costs that directly vary due to the level of output e.g. raw materials, fuel, wages
What is a break even point?
The level of output when revenue equals total costs
What is a budget?
A target set for costs or revenue in a given time - income budgets set a minimum target, expenditure budgets set a maximum costs
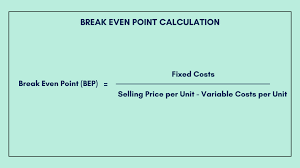
What is the formula for break even points?
Explain the types of budgeting
Historical budget - based on historical data
Zero-based budget - budget set on zero and each cost is justified and added to total (very time consuming)
What is variance in budgeting?
The amount the actual result differs from the budgeted figure
How are positive and negative variances referred to as?
Favourable and adverse
What are the reasons for using a budget?
Controlling finance
Spending power delegated to managers
Motivate staff
What are the factors affecting sales forecasts?
Consumer trends
Economic variables
Actions of competitors
What required document do plcs have to publish containing annual profits?
Statement of comprehensive income
What are the 3 types of profit and how do you calculate each?
Gross profit = revenue - costs of sales
Operating profit = gross profit - fixed costs
Net profit = operating profit - taxing and financing
What is liquidity?
The ability of a firm to find the cash to pay bills
What does the statement of financial position contain?
Company's assets and liabilites at the end of the year
What are the 2 types of calculating liquidity, how do you calculate each?
Current ratio = current assets/current liabilities
Acid test ratio = (current assets - stock)/current liabilities
How can you improve liquidity?
Selling under used assets
Raising more share capital
Increasing long term borrowing
What are some internal causes of business failure?
Marketing failure (low market share and no new products)
Poor management of cash flow
Systems failure (IT)
What are some external causes of business failure?
Changes in technology
New competitor
Economic change
Bank’s behaviour
What does production and productivity measure?
Production = quantity of output
Productivity = efficiency --> dividing output by time period
Describe the different methods of production
Job production - producing a one off product for a one time customer
Batch production - producing a set number of identical items
Flow production - continuous production of a single item
Cell production - small group processes so that items can be made flexibly
What is labour-intensive production?
Labour costs are highest percentage of total costs
Low financial barriers to entry
Highly flexible
What is capital-intensive production?
Large percentage of total costs is machinery costs
High financial barriers to entry
Inflexible
What is capacity utilisation?
A measure of a firm's current output level as a percentage of their maximum output level.
What is the consequence of under-utilisation of capacity?
Fixed costs are spread over the fewer products outputted.
What is the consequence of over-utilisation of capacity?
You cannot fulfil orders if demand increases
Struggle to train staff/service machinery
What are 2 ways to improve capacity utilisation?
Increase demand
Cut capacity
What is the objective of stock control?
Minimising the costs of holding stock
What are the different stock levels?
Maximum stock level - largest amount of stock a firm can hold
Reorder level - when stock falls to this level new stock is ordered
Minimum stock level (buffer stock) - minimum stock in case supply chain is affected
What are the consequences of poor stock control?
Cash flow problems
Higher storage costs
Increased wastage of stock
What is JIT production?
Ensures that inputs are only added to the production process when needed.
Reduces waste and storage costs
Inflation
The rate at which the general prices of goods and services rises, reducing the purchasing power of money
Effects of inflation on businesses
Reduces profitability as costs increase
Higher repayments on loans
Reduced consumer demand
Uncertainty
Exchange rates
Value at which one currency can be exchanged for another
Appreciation
When the value of a currency rises and strengthens
Depreciation
When the value of a currency decreases and weakens
SPICED
Stronger
Pound
Imports
Cheaper
Exports
Dearer
WPIDEC
Weaker
Pound
Imports
Dearer
Exports
Cheaper
Interest rates
The cost of borrowing money or the return on savings
Effects of high interest rates
Encourage savings
Reduced borrowing
Lower disposable income
Effects of low interest rates
Encourage borrowing
Reduced savings
Increased disposable income
Taxation
Money collected by the government from businesses and individuals to fund public services and infrastructure
Gross domestic product (GDP)
Total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a specific time period
Stages of the business cycle
Boom - highest levels of consumer spending and low unemployment
Recession - economy declines
Trough - low consumer spending and high unemployment
Recovery - economy begins to grow again
Types of business legislation
Consumer protection
Employee protection
Environmental protection
Competition policy
Health and safety
Impact of consumer protection legislation
Increases costs (compliance)
Improves quality
Improves customer satisfaction/reputation
Impact of employee protection legislation
Increased costs (e.g. minimum wage)
Penalties for non-compliance
Improved motivation among staff
Impact of competition policies
Prevents monopolies (dominating markets)
Reduces barriers to entry
More competitive pricing for smaller firms
Impact of health and safety regulations
Increased costs
Potential fines/penalties
Safe environment —> motivation (Maslow)
Margin of safety formula

Lean production
Manufacturing approach maximising efficiency and minimising waste
Kaizen
A continious improvement approach where small, ongoing changes are made to improve the efficiency and quality of the process