Principles of Paleontology
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final Exam Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Microfossils
any evidence of past life you need to magnify to study
Foraminifera
Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Rhizaria
Phylum: ___
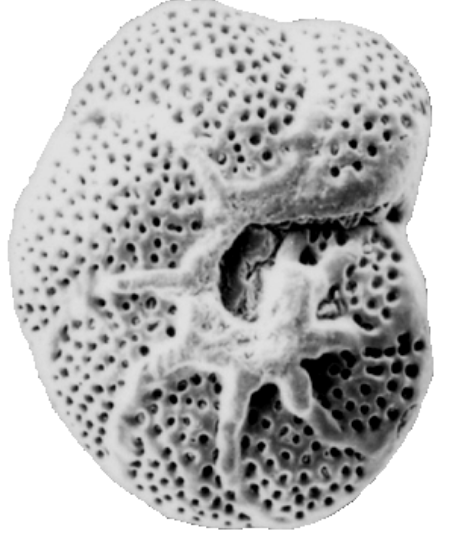
Radiolaria
Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Rhizaria
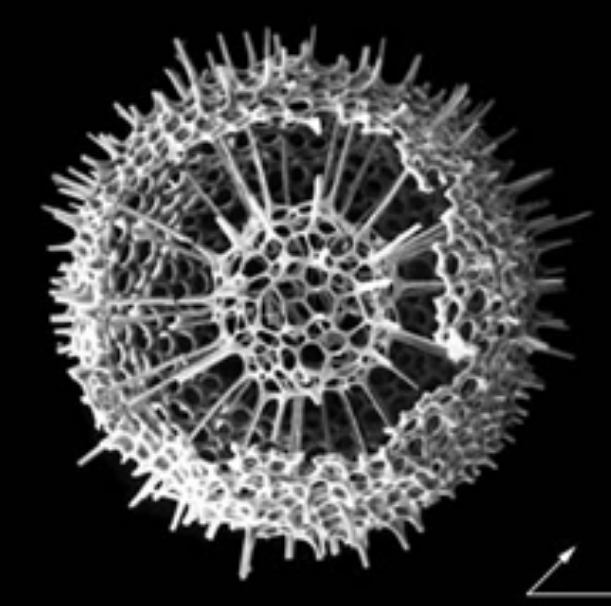
Diatom
😩 Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Chomalveolata
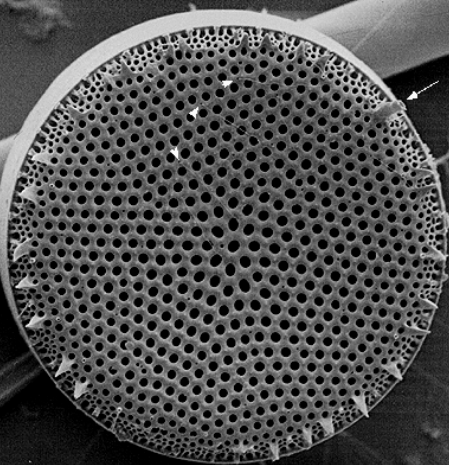
Coccolithophore
Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Chomralveolata (Algae like)

Porifera
Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Animalia
sponge spicules
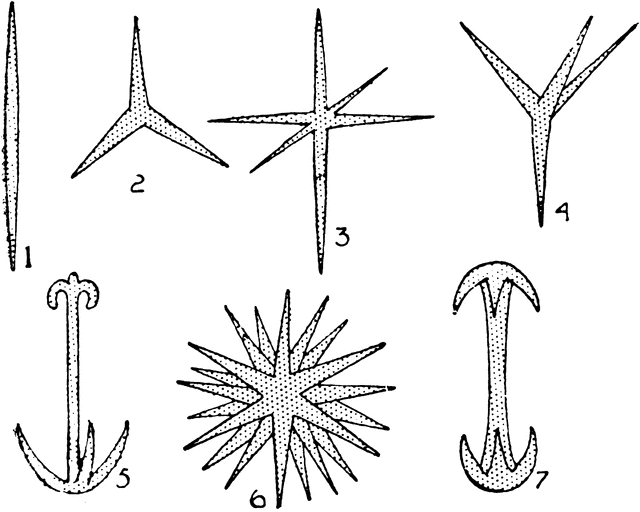
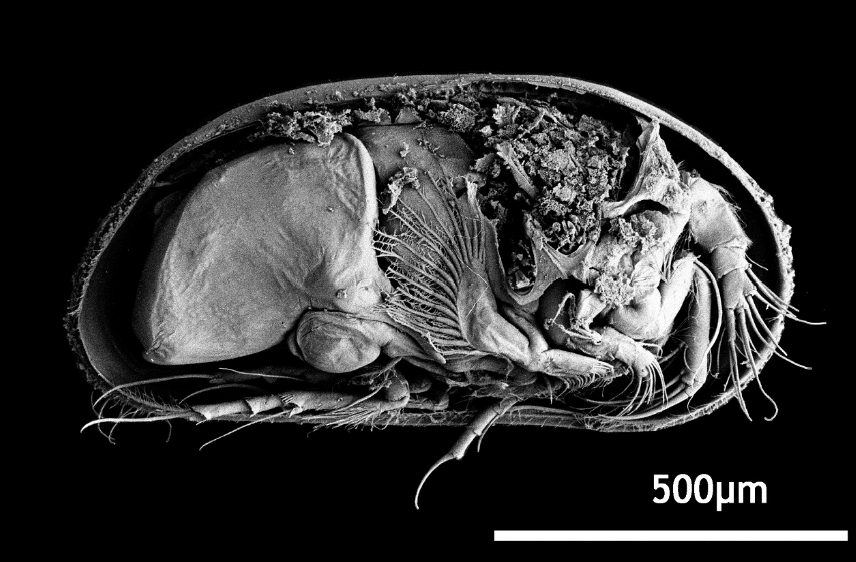
Ostracoda
Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Crustacea
Class: “seed shrimp”
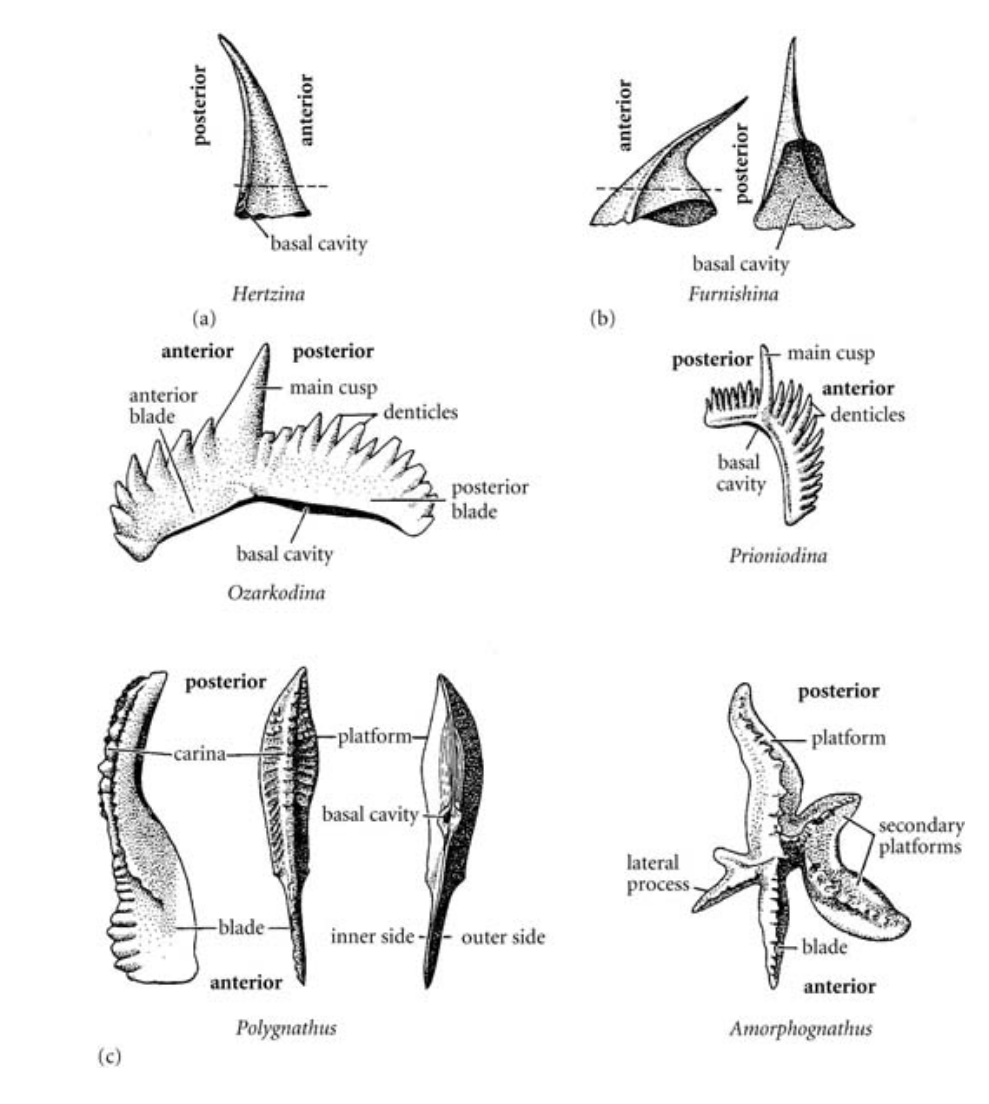
Conodonta
Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: ___
Conoform (cone); Ramiform (blade); Pectiform (platform)
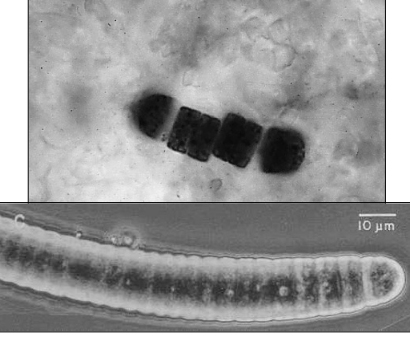
Embryos
juveniles of all animals ex. microfossils
Micro-vertebrates
teeth
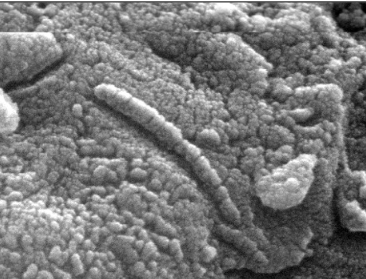
Modern Cyanobacteria
Domain: Eubacteria
Occasionally preserved in chert
Stromatolite

Psuedofossil
A
Architarchs
Archaea, bacteria, or eukaryotes
Morphology
the study of form (size, shape, structure) of organisms and the relationship of their constituent parts
What constrains size?
metabolism/feeding
reproduction
locomotion
What do size constrains predict?
an organisms life mode
Biological Shape
dimensionless ratio of size parameters
Ratios
Can still be inadequate in defining shape
How to communicate measurement
Table of data
numerical analysis
graphs and plots
Drawing
removes noise
difficult subjects like bones
reconstructions
photographs
are purely objective (if unaltered)
Models
Mathematical Equation (coiling model to build the shape
Landmark analysis - eliminates size and distortion, only looks at shape
Harmonic analysis
Variables in similar groups
more characters, more detail
features will only be applicable to a few groups
Variables in higher taxa
fewer characters, less detail
applicable to more groups
Ontogeny
life history of an organism
Direct Development
zygote - adult through gradual change
Indirect development
zygote - larval stage - adult
abrupt metamorphosis
95% of marine invertebrates
Marine invertebrate Larvae
Planktic
Marine invertebrate Adults
Benthic
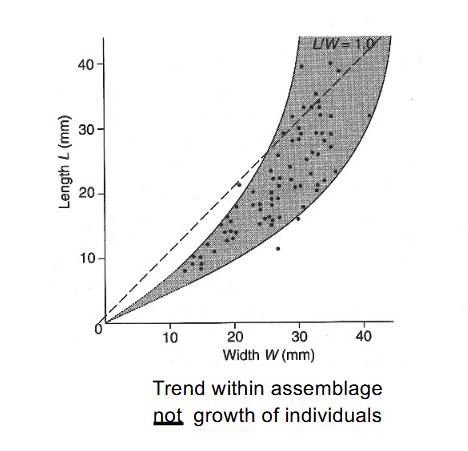
Cross Section analysis
plotting variation in assemblage presumed to present various growth stages (multiple specimens)
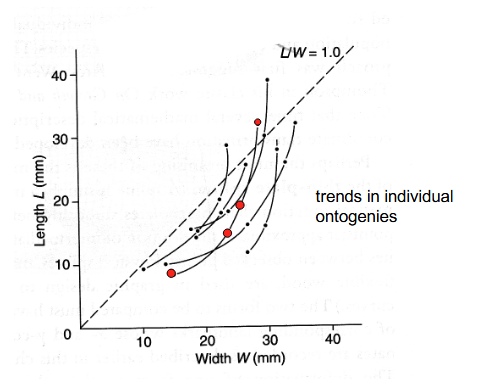
Longitudinal analysis
One individual
plotting growth in single individuals
requires growth lines
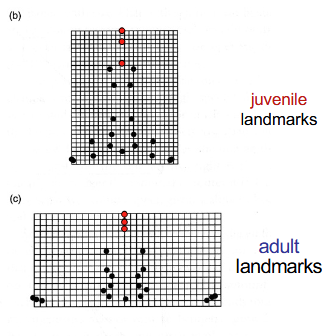
Coordinate Transformation
compares landmarks between 2 growth stages
juvenile vs adult
Determinate Growth
rapid early growth, flattens toward adult hoot
more common
Indeterminate growth
many invertebrates continue to grow as long as they live and eat
problem: population comparisons
Isometric growth
ratio between any 2 measurements does not change
ie. shape does not change from juvenile to adult
Anisometric growth
ratio between 2 measurements does change throughout ontogeny
What does Surface Area/Volume ration effect?
Respiration/absorption
Strength
metabolism/heat
adhesion vs. Gravity
How to adjust for surface area/volume problems
Anisometric growth
Complex structures (convolutions)
Large organisms need to increase girth of their bones proportionally more to support themselves
Unused material in volume (inert material)
Allometry
the growth of body parts at different rates, resulting in a change of body proportions
study the relationship of body and size
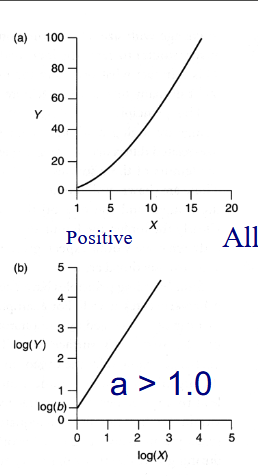
Y = bXa
Log (Y) = aLog(X) + Log(b)
Positive Allometry
Y increases at a faster rate than X
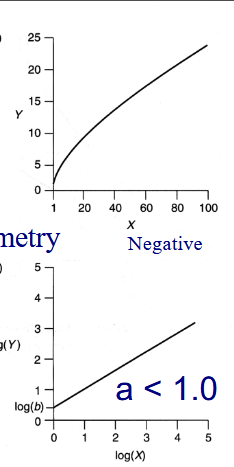
Negative Allometry
Y increases at a slower rate than X
Brain mass vs. Body Mass
Human Ontogeny
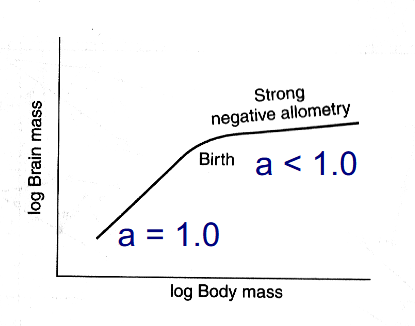
Encephalization
enlarged brain relative to an allometric trend
Examples of Allometry
Brain mass vs Body mass
Metabolic Rate vs Body mass
Muscle characteristics vs fiber number/weight
Heterochrony
Evolutionary changes in the timing of development
Paedomorphosis
descendant adults resemble ancestor juveniles
Hypermorphosis
process can either end later or extends development
aka adult descendant looks older than adult ancestor
Classification
arrangement of objects according to a system or principle
Classification in paleontology
an outline of evolutionary history
Monophyletic Classification
a group contains an ancestor and all of its descendant members
Paraphyletic classification
a group contains an ancestor and only some of its descendants
Polyphyletic classification
a group of unrelated members
Orthodox Classification
organisms are grouped on the basis of features that seem to reflect their common ancestry
Disadvantages of Orthodox classification
subjective
difficult to reproduce
untestable
Phenetic Classification
Organisms grouped on overall similarity
Steps for phenetic classification
identify as many features as possible
record features in a data matrix; code matrix
derive similarity table
sort into groups (phenogram)
produce formal classification
evaluate plausibility
Advantages of Phenetic Classification
objective
all characters/features hold equal weight
lots of features
can group anything
Disadvantages of phenetic classification
convergence isn’t considered as a factor for similar features
can group anything
Cladistics
Organisms are grouped on features that all members possess
Cladogram
branching diagram with taxa at the ends, relative position reflects evolutionary sequence
There is no ancestor
No depiction of time
Apomorphy
derived character/feature
Synamorphy
shared derived character/feature
Pleisiomorphy
primitive character
Synpleisiomorphy
shared primitive character
Node
represents hypothetical common ancestor at the branch tops and is defined by synamorphies that unite those taxa
Outgroup
primitive relative of the clade used to “root” the tree
Advantages of Cladistics
objective
reproducible
testable
Disadvantages of cladistics
Does not produce convenient nomenclature higher taxonomic groups; New naming system proposed - Phylogenetic systematics
Parsimony
Shortest number of steps
calculate every possible arrangement and go with the simplest/least steps
Bayesian
Probability based on prior observation