Genetic/Congenital Diseases of Sheep and Goats
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
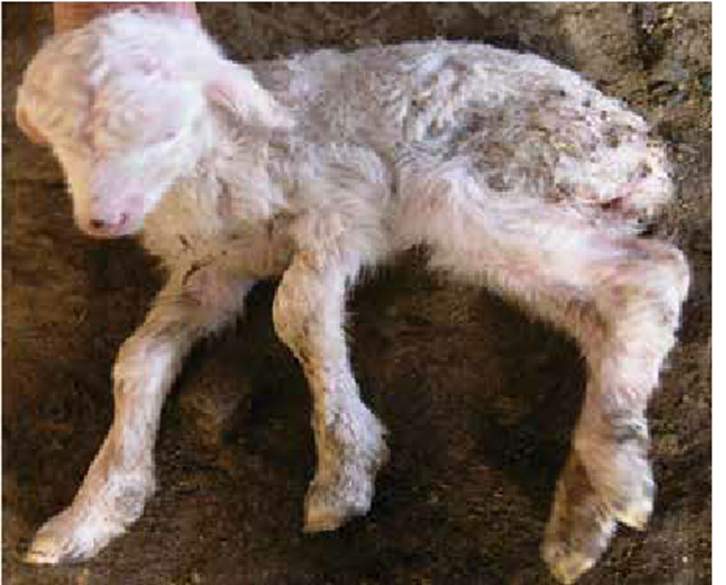
Border Disease (Hairy Shaker Lambs)
Togavirus
Congenital, Contagious & Infectious
Transmission: Border Disease
Vertical- transplcement
Horizontal- Direct contact
Clinical Signs: Border Disease
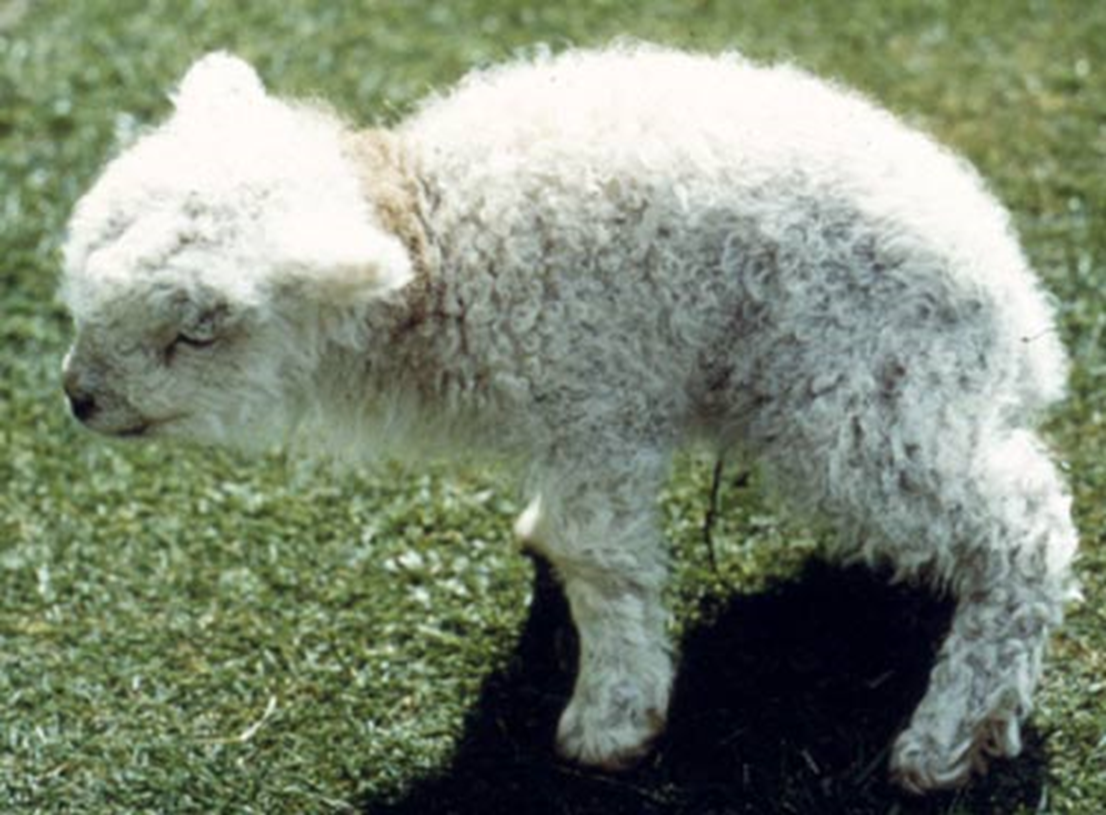

Treatment/Control:
Identify carriers
Segregate pregnant, non-infected sheep
NO treatment
NO vaccine
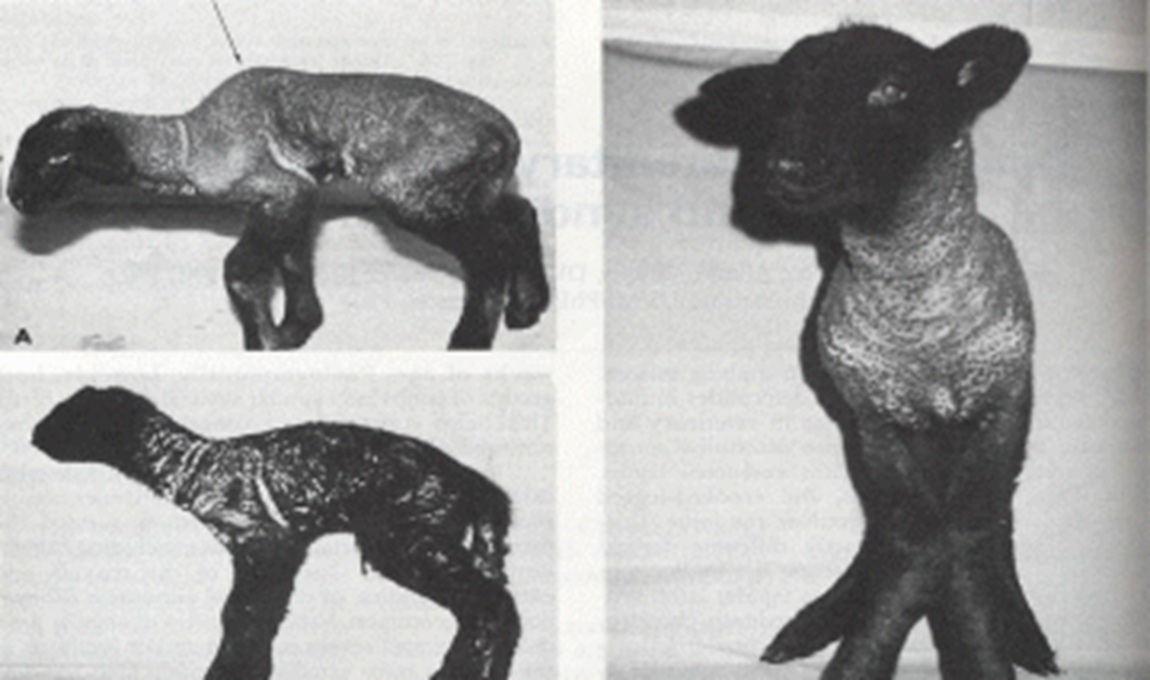
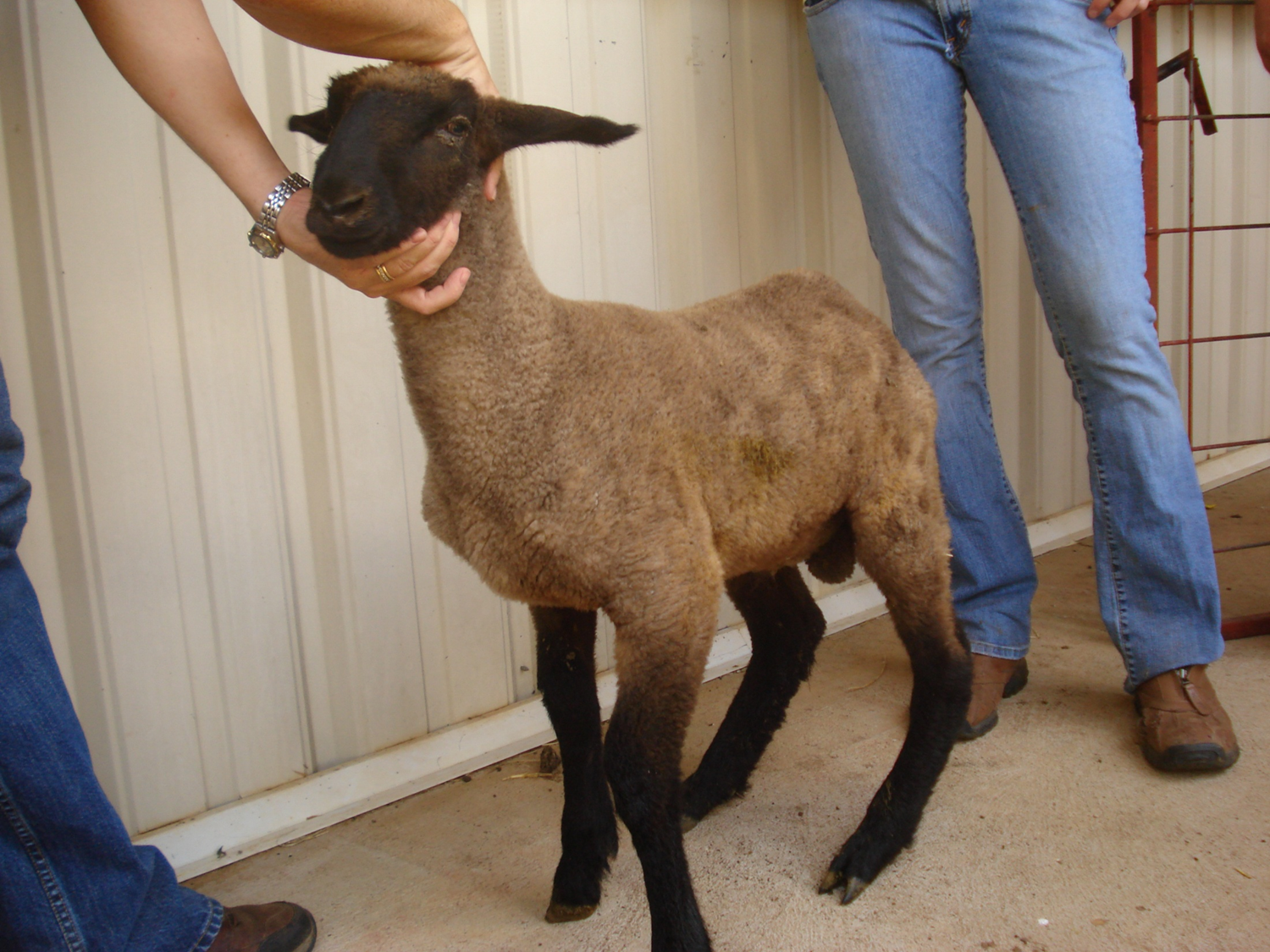
Spider lamb Syndrome (Ovine hereditary chondrodysplasia)
Suffolk, Suffolk X, Hampshire
Congenital & Genetic
2 types of lambs
Abnormal at birth
Develop abnormalities at 3-8 weeks
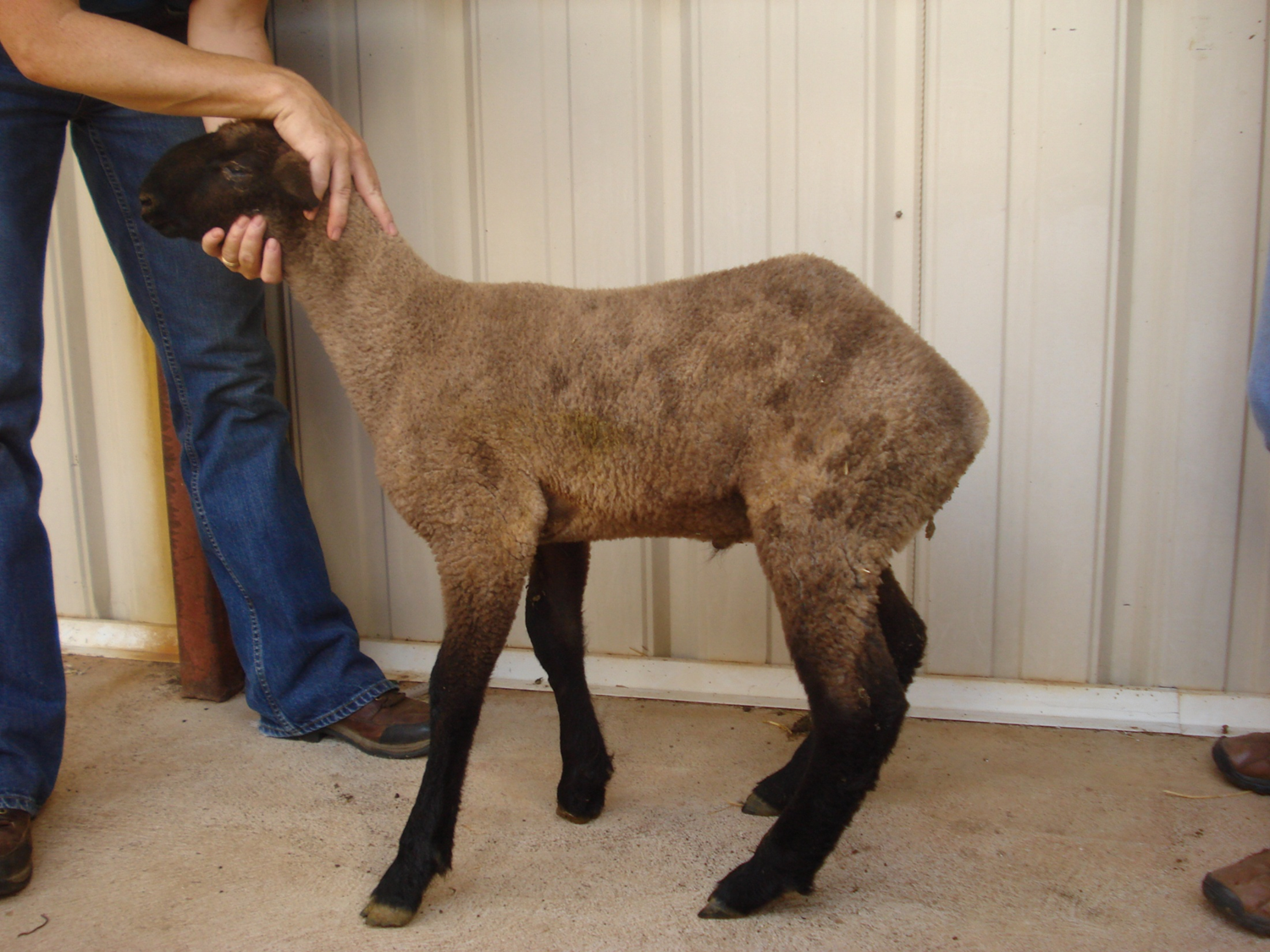

Clinical Signs: Spider lamb syndrome
Appendicular
Axial


Prevention/Control: Spider Lamb Syndrome
Carrier rams should be destroyed
Carrier ewes can be used to produce market lambs
Barber Pole Worm
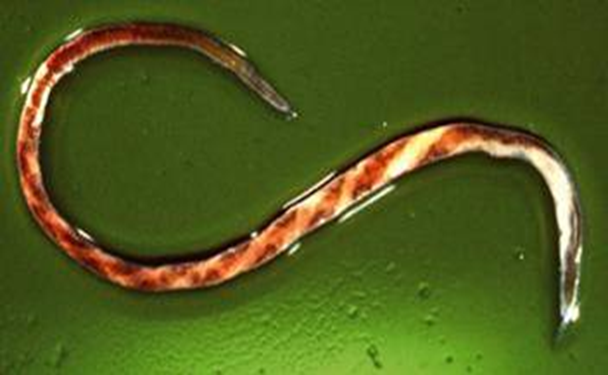
Haemonchus contortus
Common in goats
Southeastern region of US
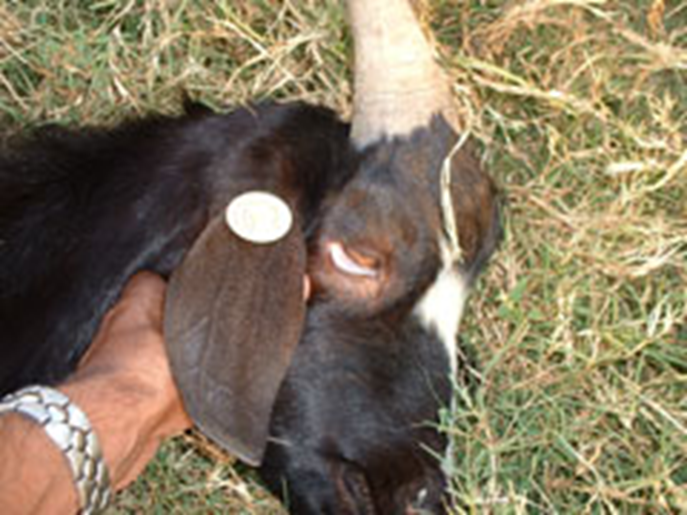
Clinical Signs: Barber Pole Worm
Nematode that lives in the abomasum and intestines
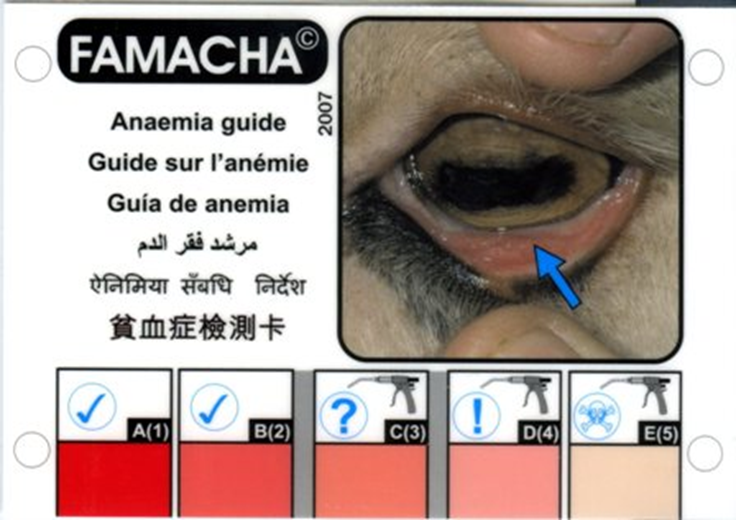
Anemia
Bottle jaw (edema under the jaw)
Diarrhea is rare; hard, dry feces
Weakness
Death


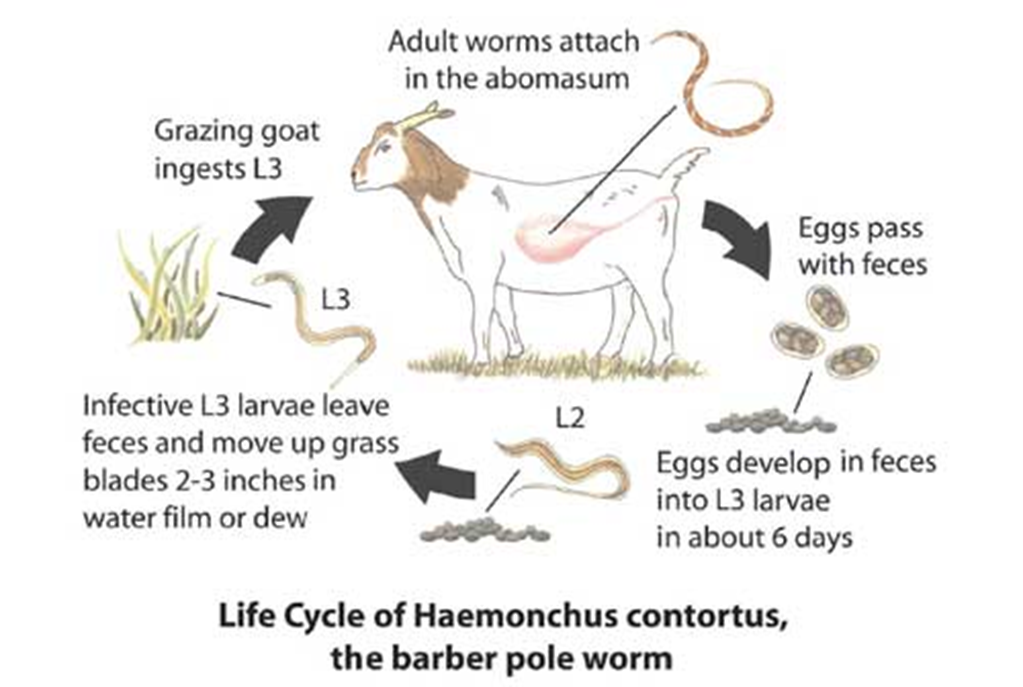
Life cycle: Barber Pole Worm
Treatment: Barber Pole Worm
Increased resistance to parasiticides
Fenbendazole (Panacur/Safeguard)
Morantel tartrate (Rumatel)
Control: Barber Pole Worms
Improve herd, pasture management practices
Keep stocking rates low
Provide clean water and mineral
Keep hay off the ground
Use gravel/concrete in the feedlot area to break the worm life cycle
Incorporate browse plant species when possible
Use clean feeders and practice good hygiene in pens and pasture
Use FAMACHA system and fecal exam for monitoring