osteology
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Mastoid process
A bony prominence located behind the ear, part of the temporal bone.

Styloid process
A slender, pointed piece of bone that serves as an attachment point for ligaments and tendons.

External auditory meatus
The ear canal that leads to the eardrum.
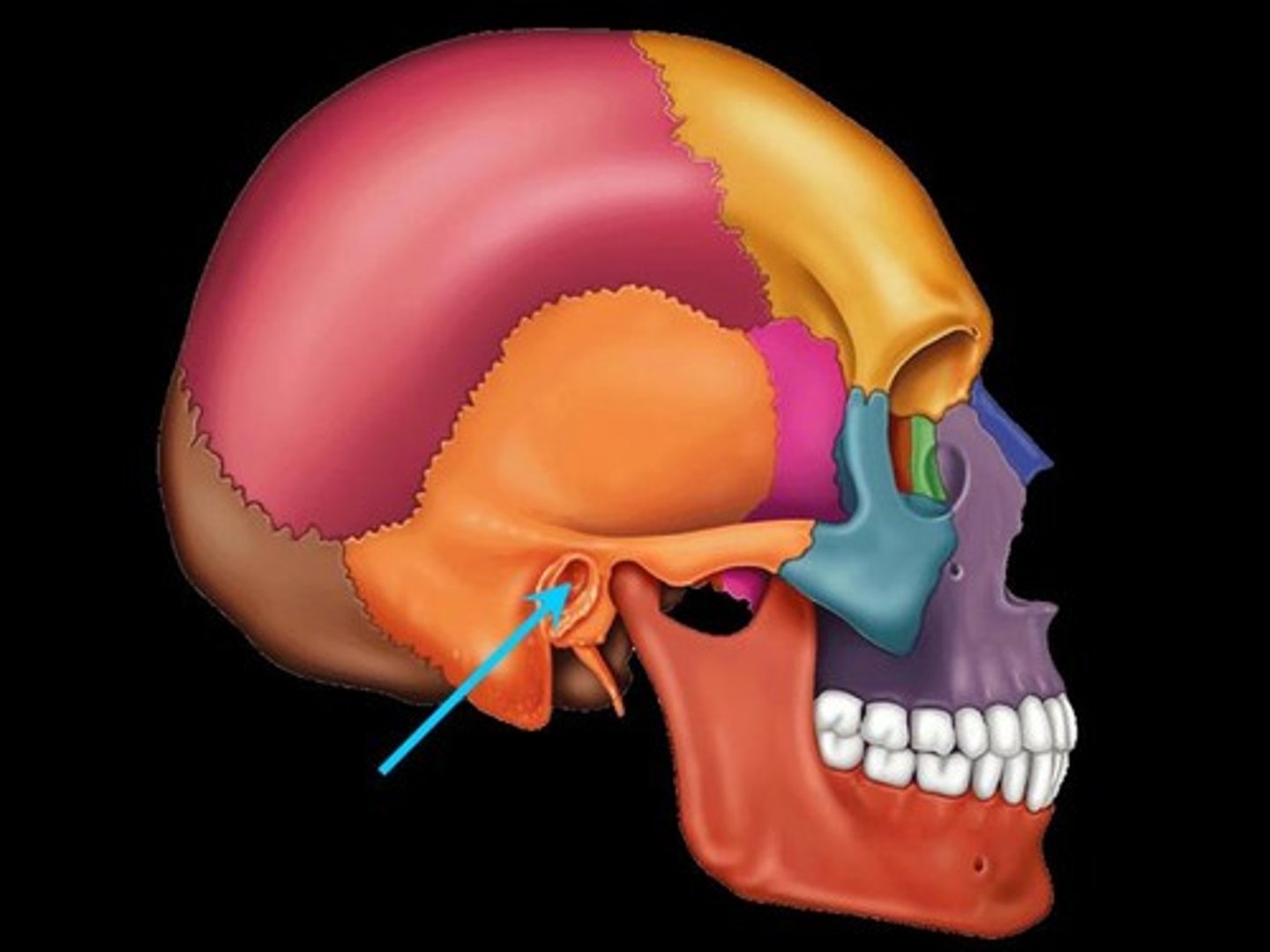
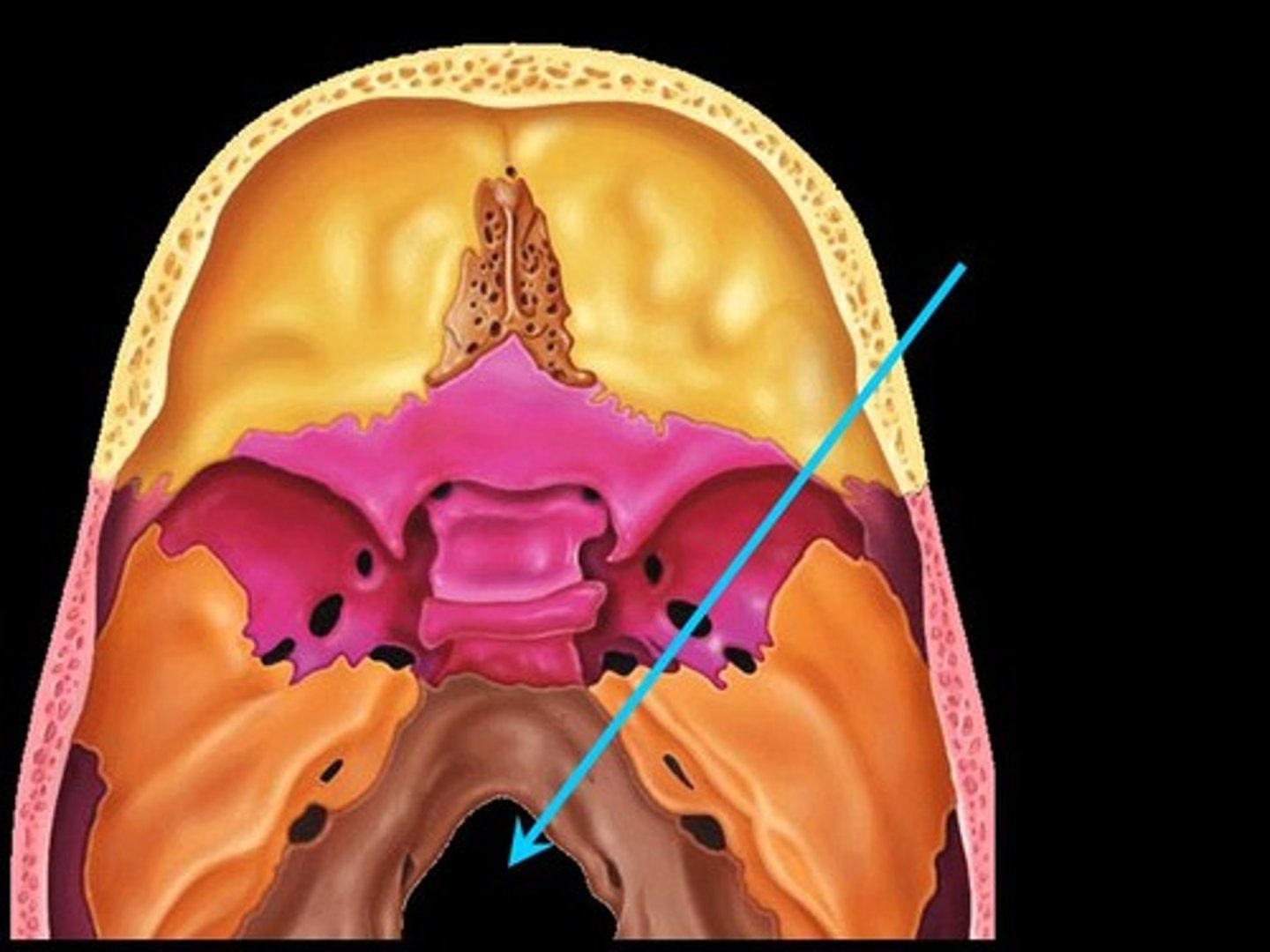
Foramen magnum
The large opening at the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes.
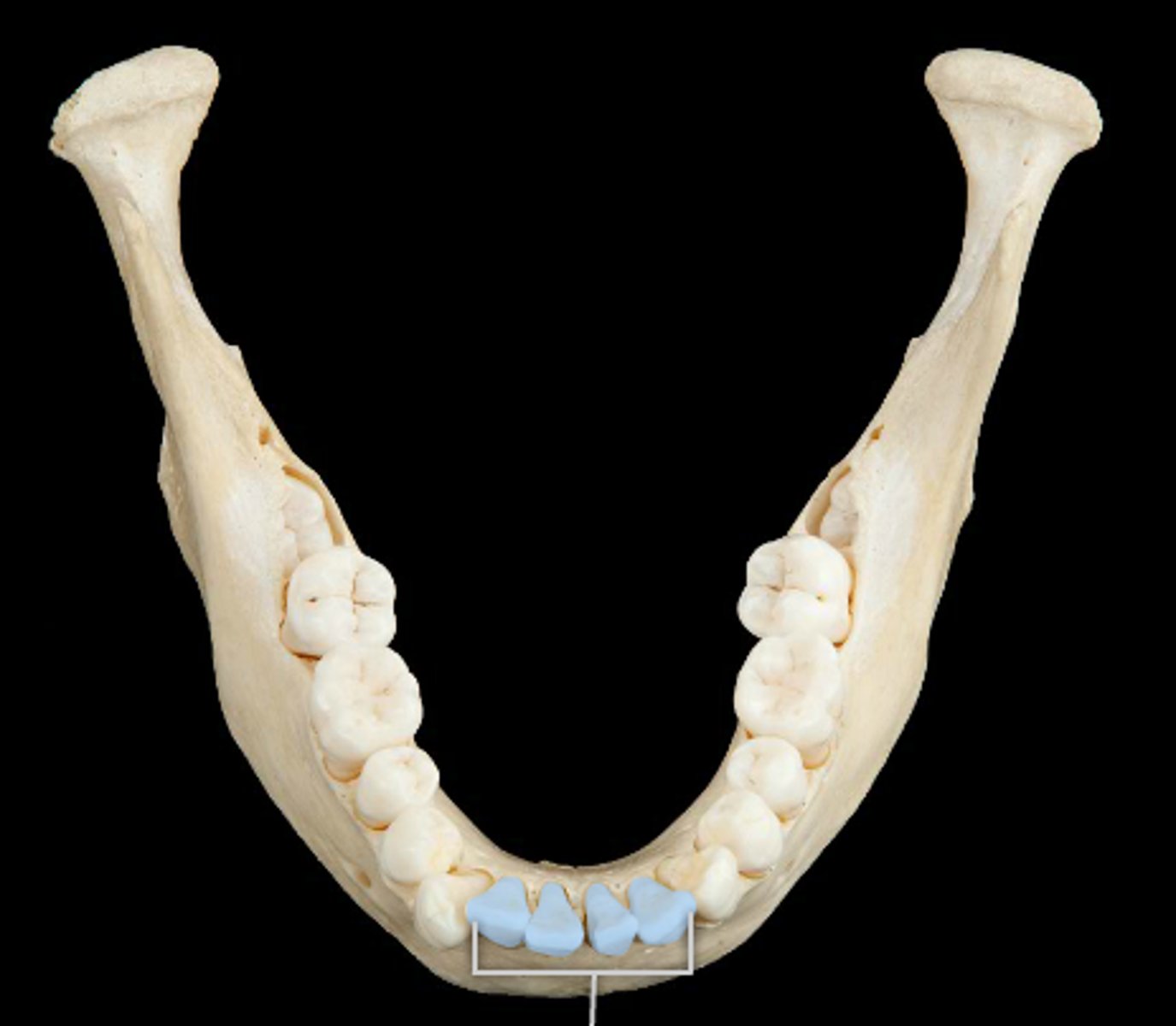
Incisors
The front teeth used for cutting food.
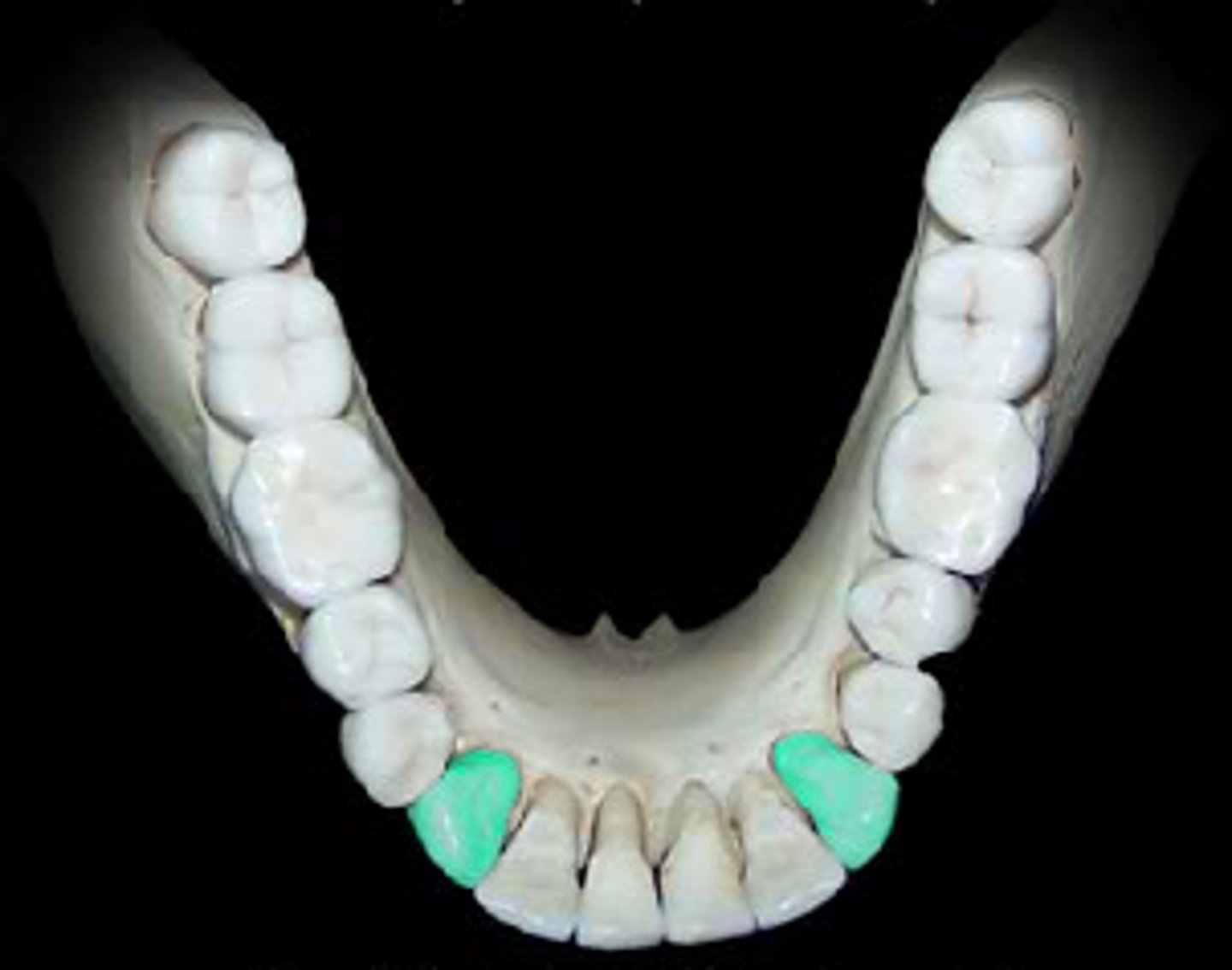
Canines
The pointed teeth located next to the incisors, used for tearing food.
Premolars
The teeth located between canines and molars, used for crushing and grinding food.
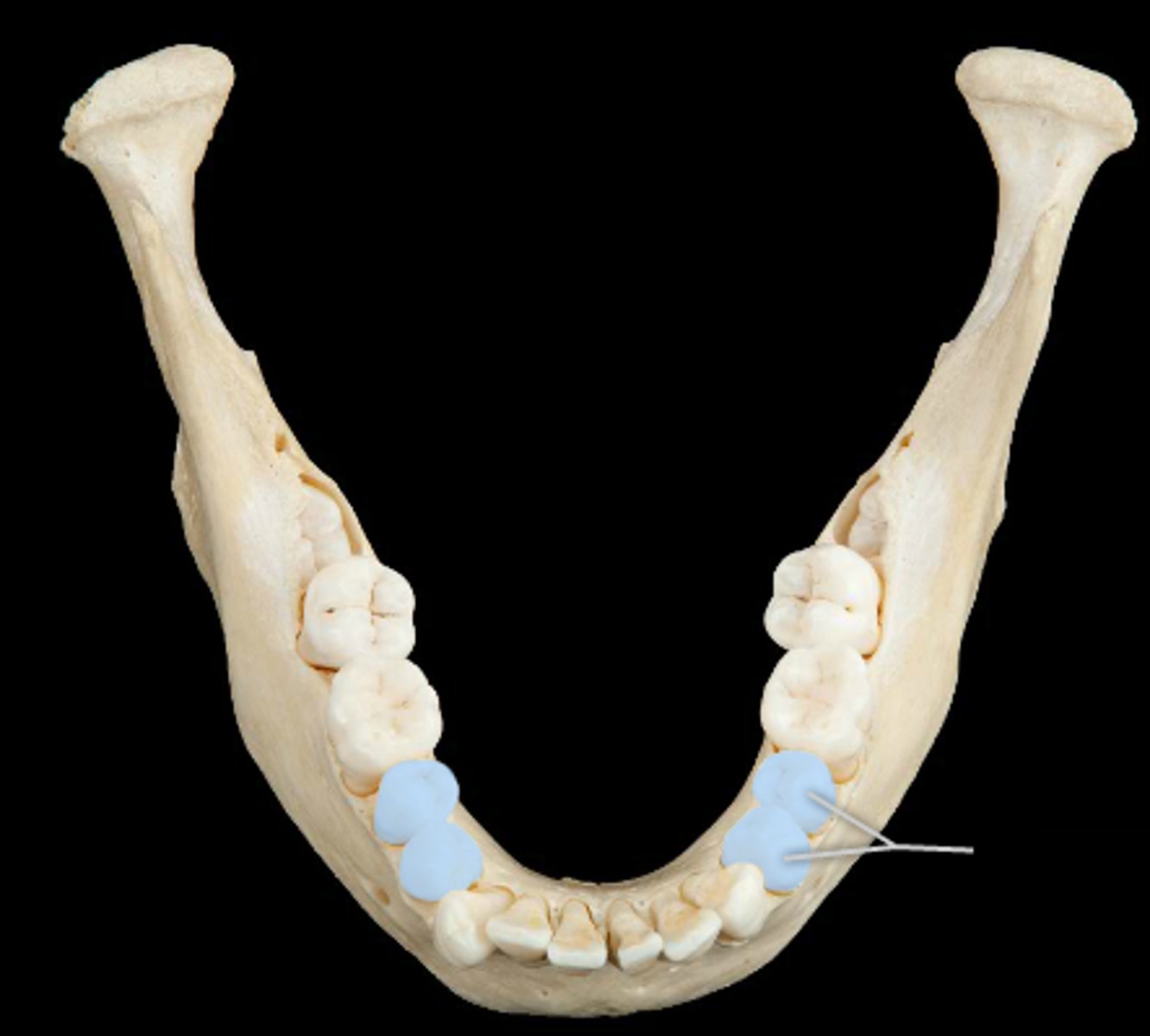
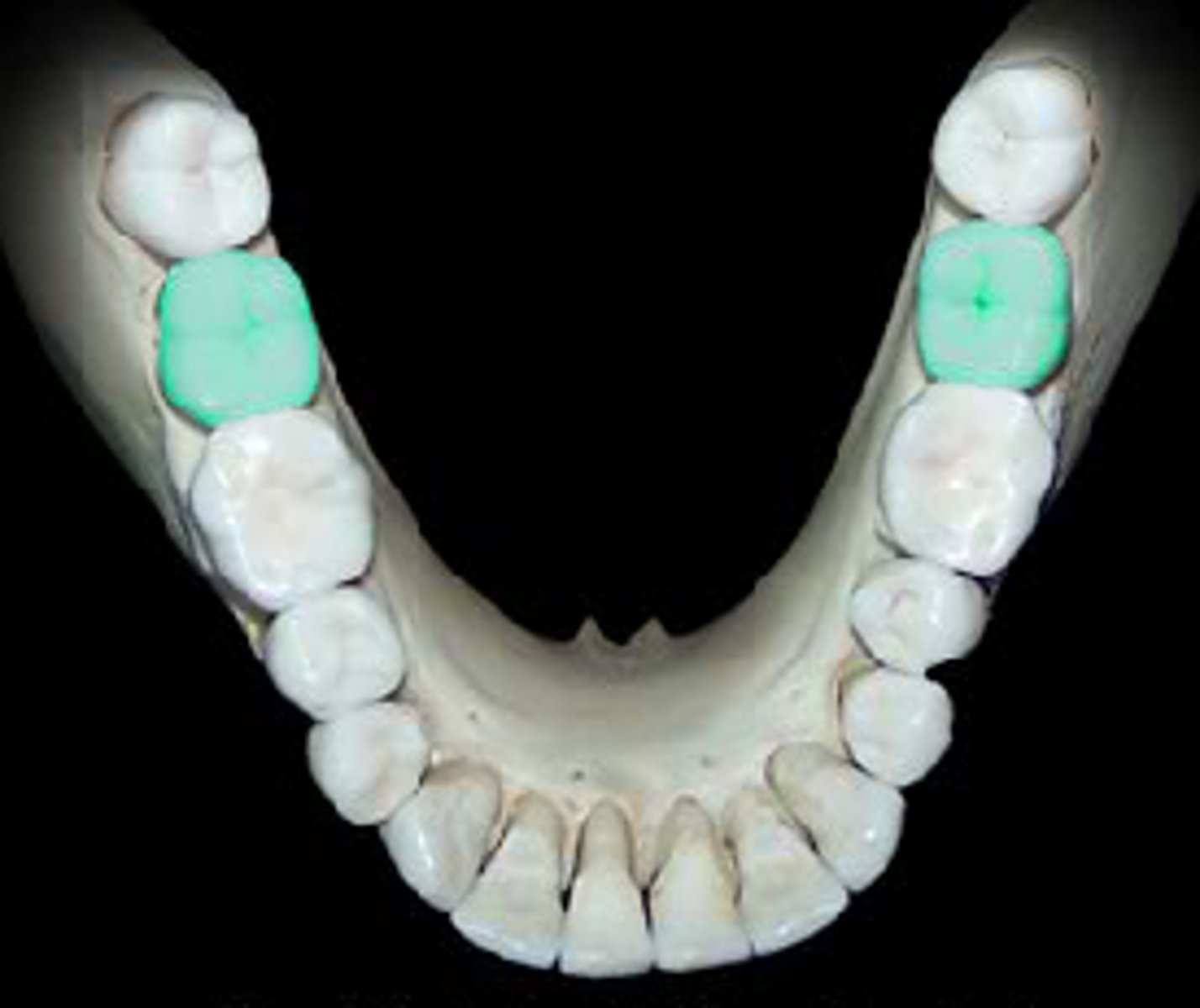
Molars
The large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth used for grinding food.
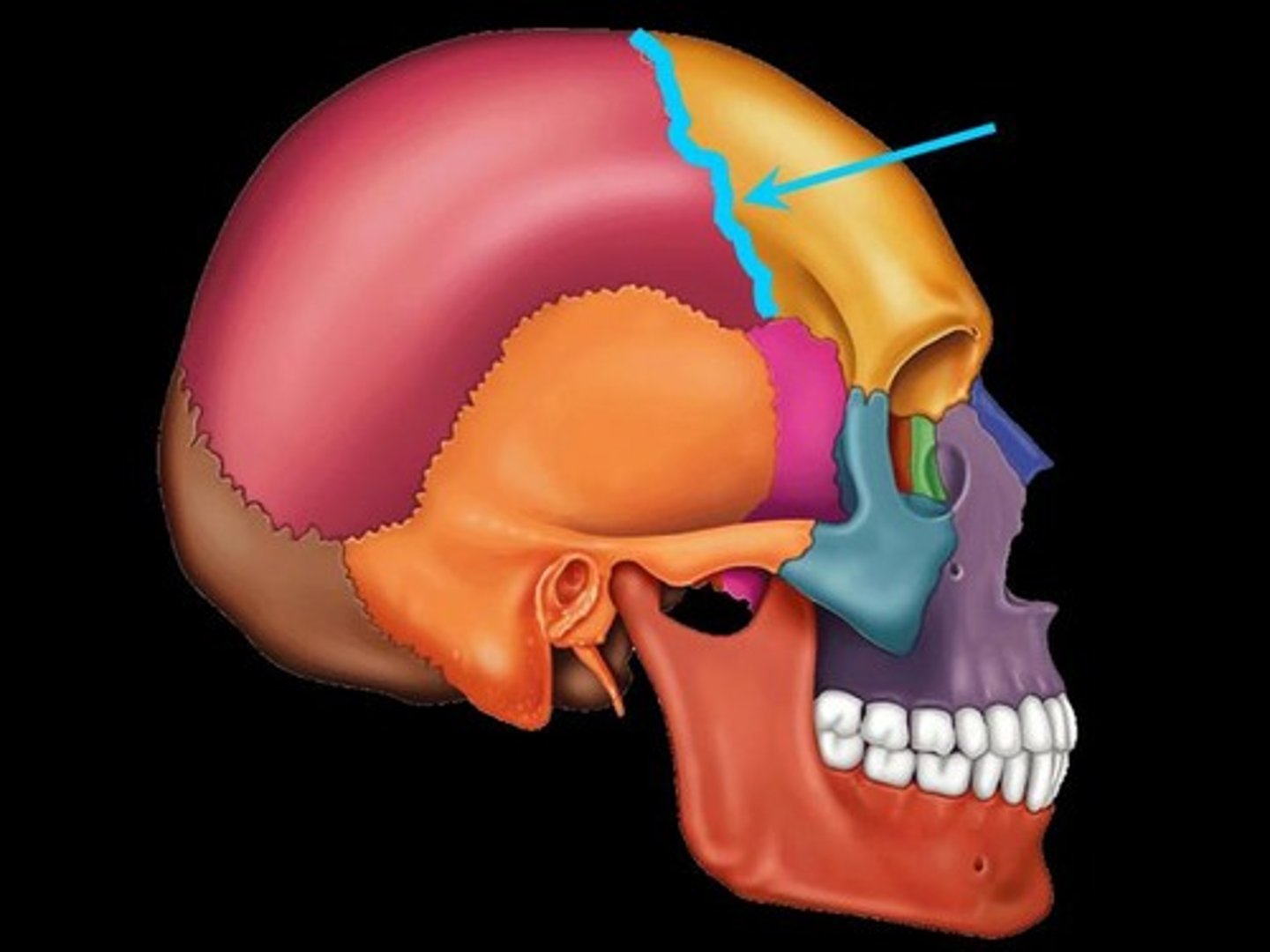
Coronal suture
The fibrous joint that connects the frontal bone to the parietal bones.
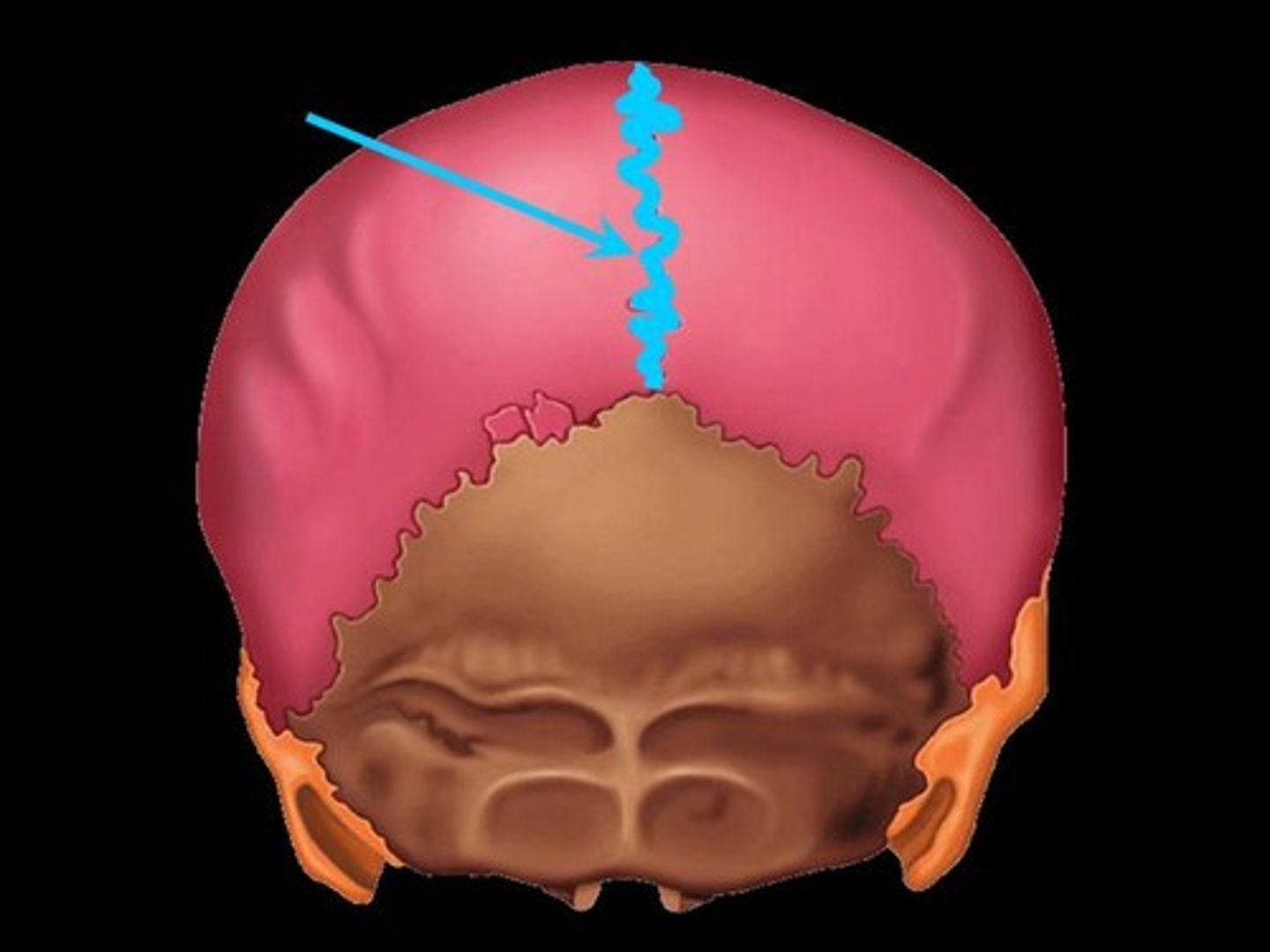
Sagittal suture
The fibrous joint that connects the two parietal bones along the top of the skull.
Lambdoid suture
The fibrous joint that connects the parietal bones to the occipital bone.

Squamous suture
The fibrous joint that connects the temporal bone to the parietal bone.
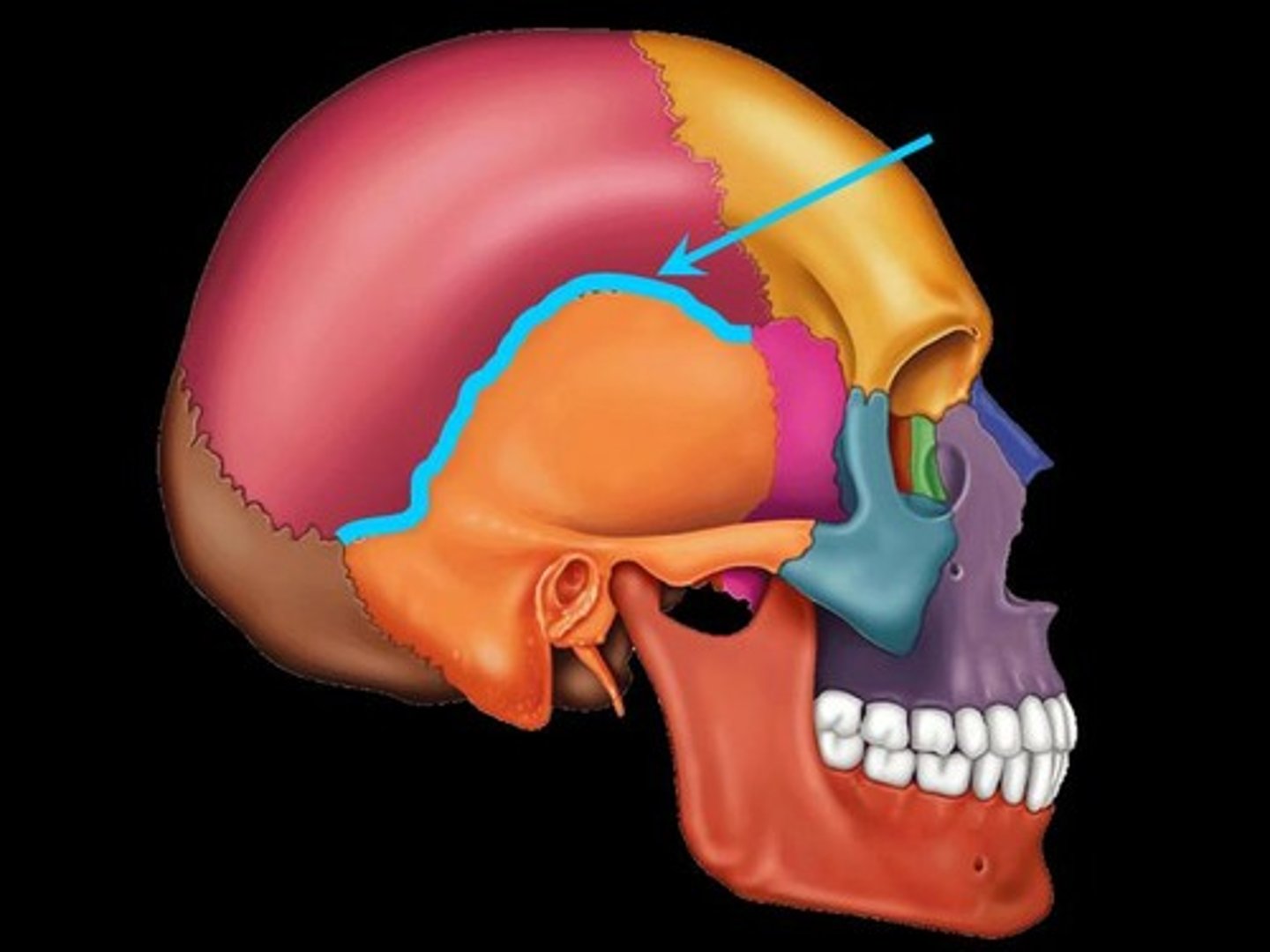
Frontal bone
The bone that forms the forehead and the upper part of the eye sockets.
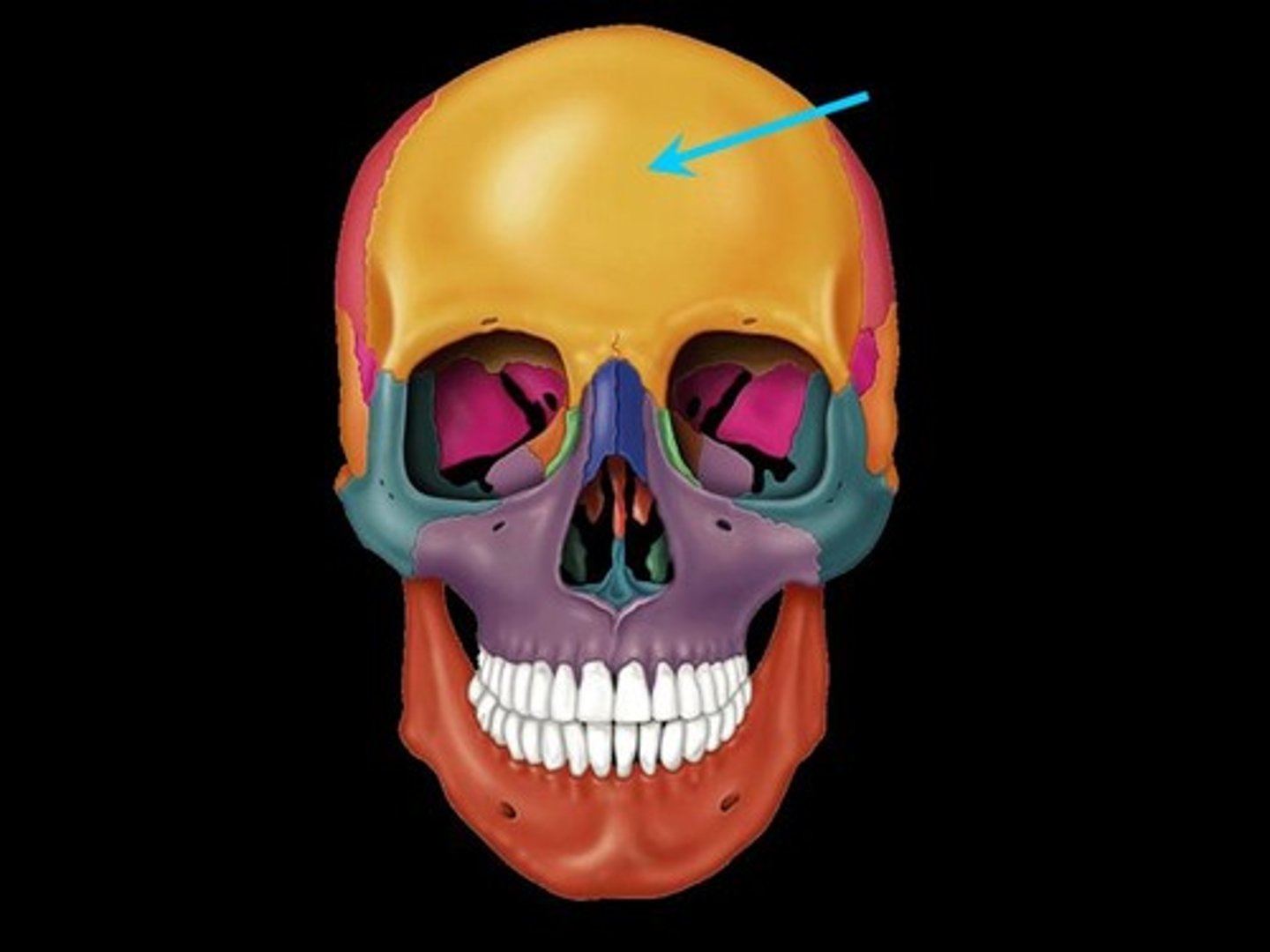
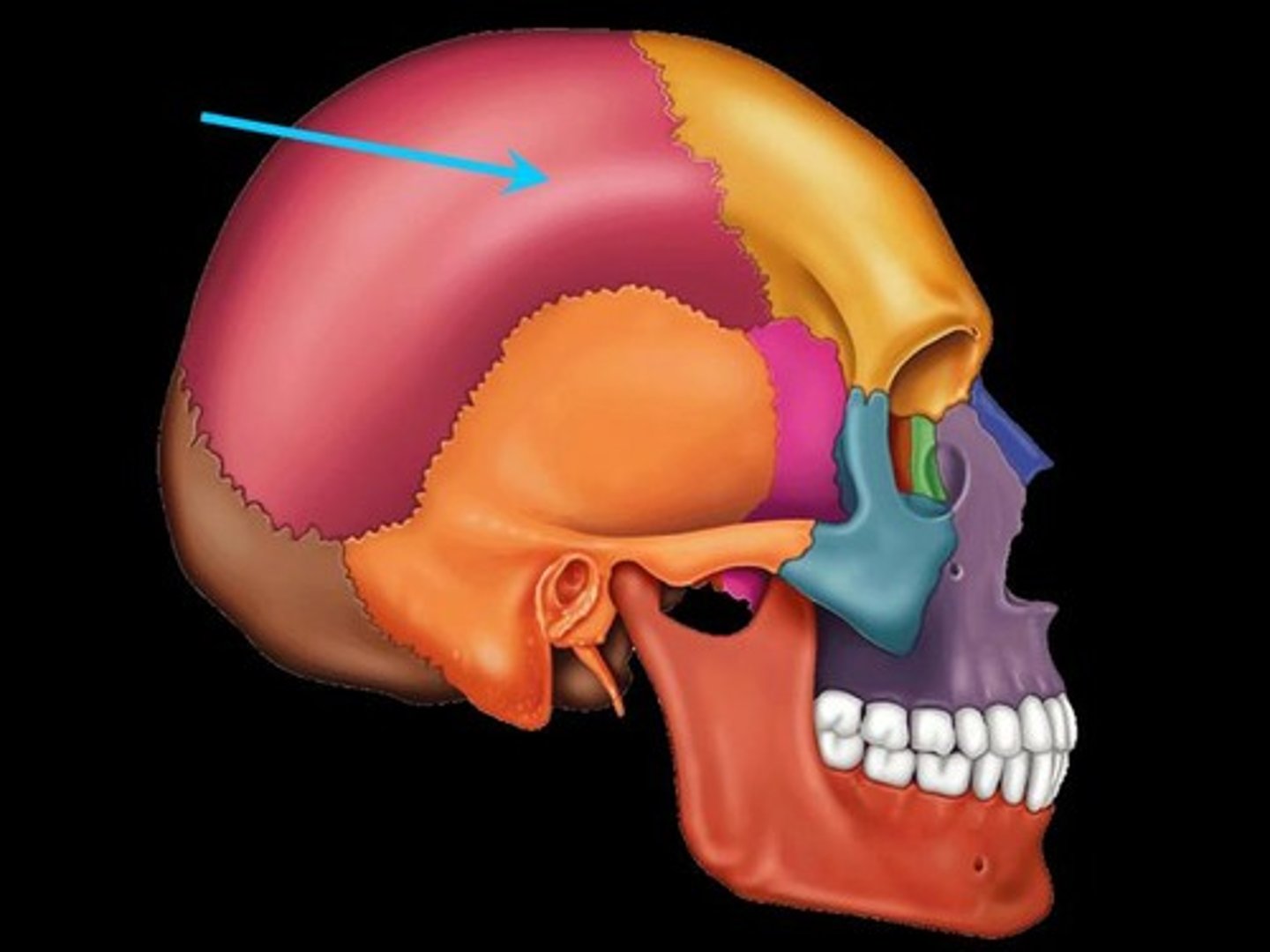
Parietal bones
The two bones that form the sides and roof of the skull.
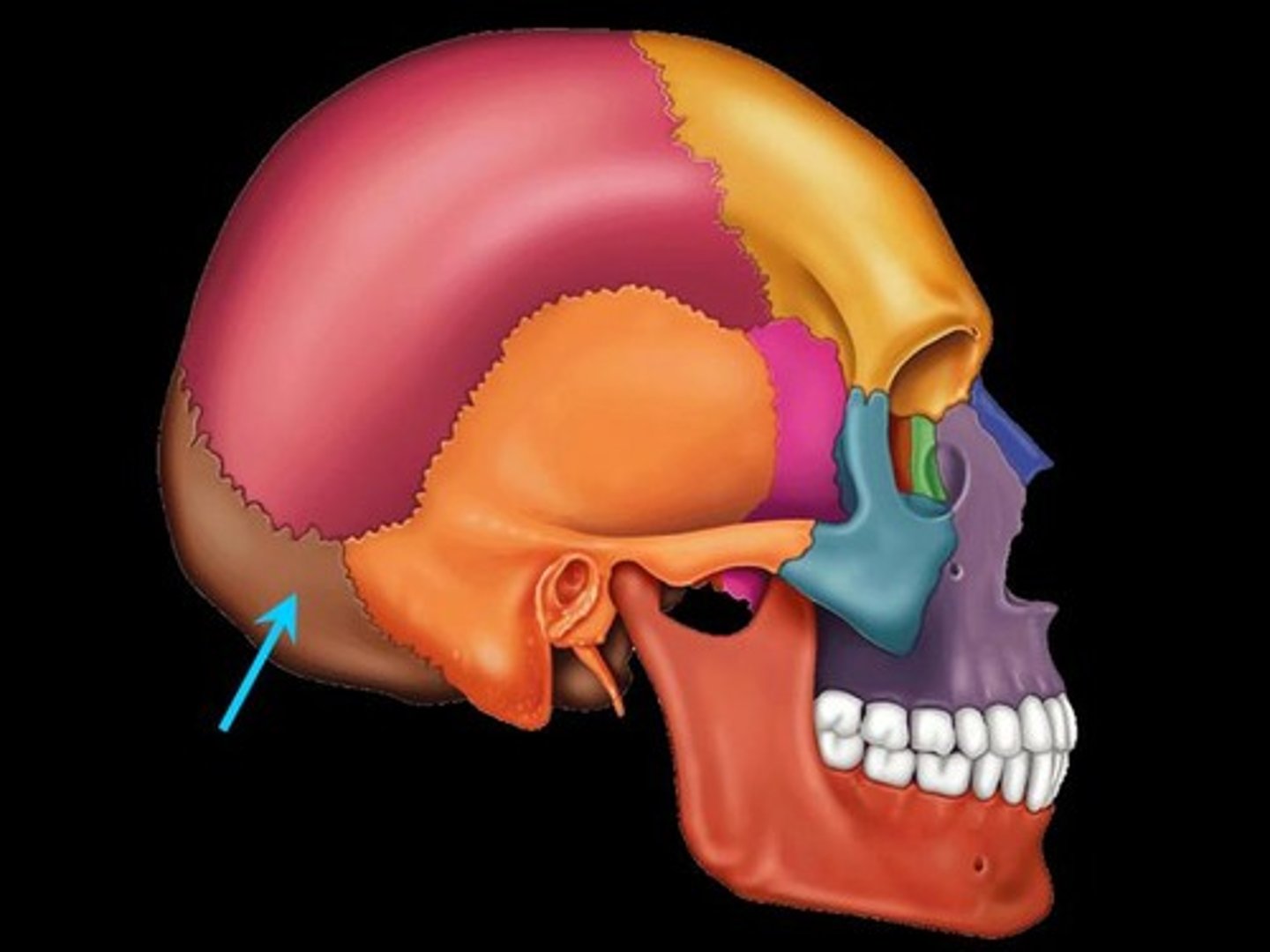
Occipital bone
The bone that forms the back and base of the skull.
Nasal bone
The two small bones that form the bridge of the nose.

Lacrimal bone
The small bone forming part of the eye socket, located at the inner corner of the eye.
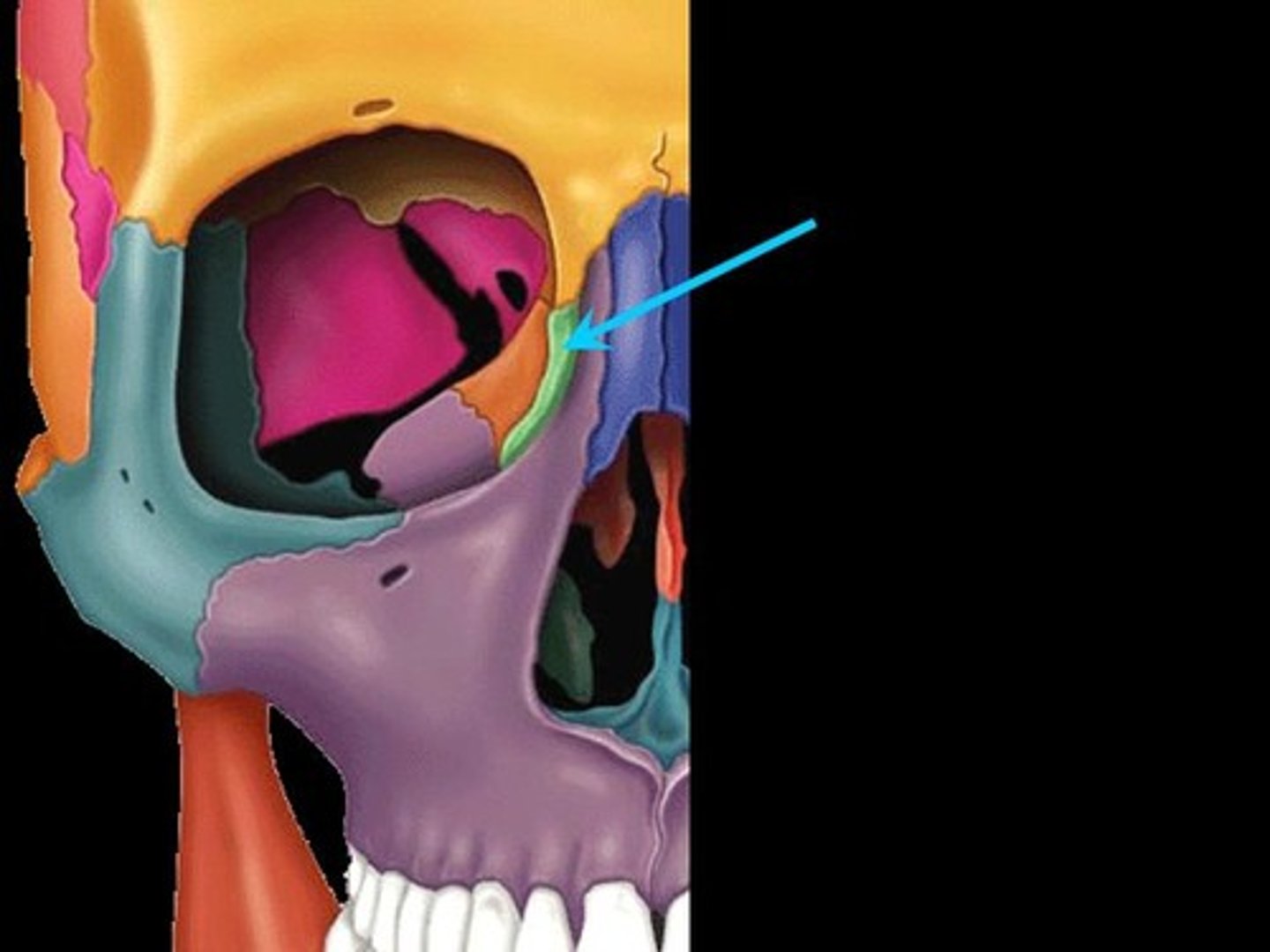
Zygomatic bone
The bone that forms the cheek and part of the eye socket.
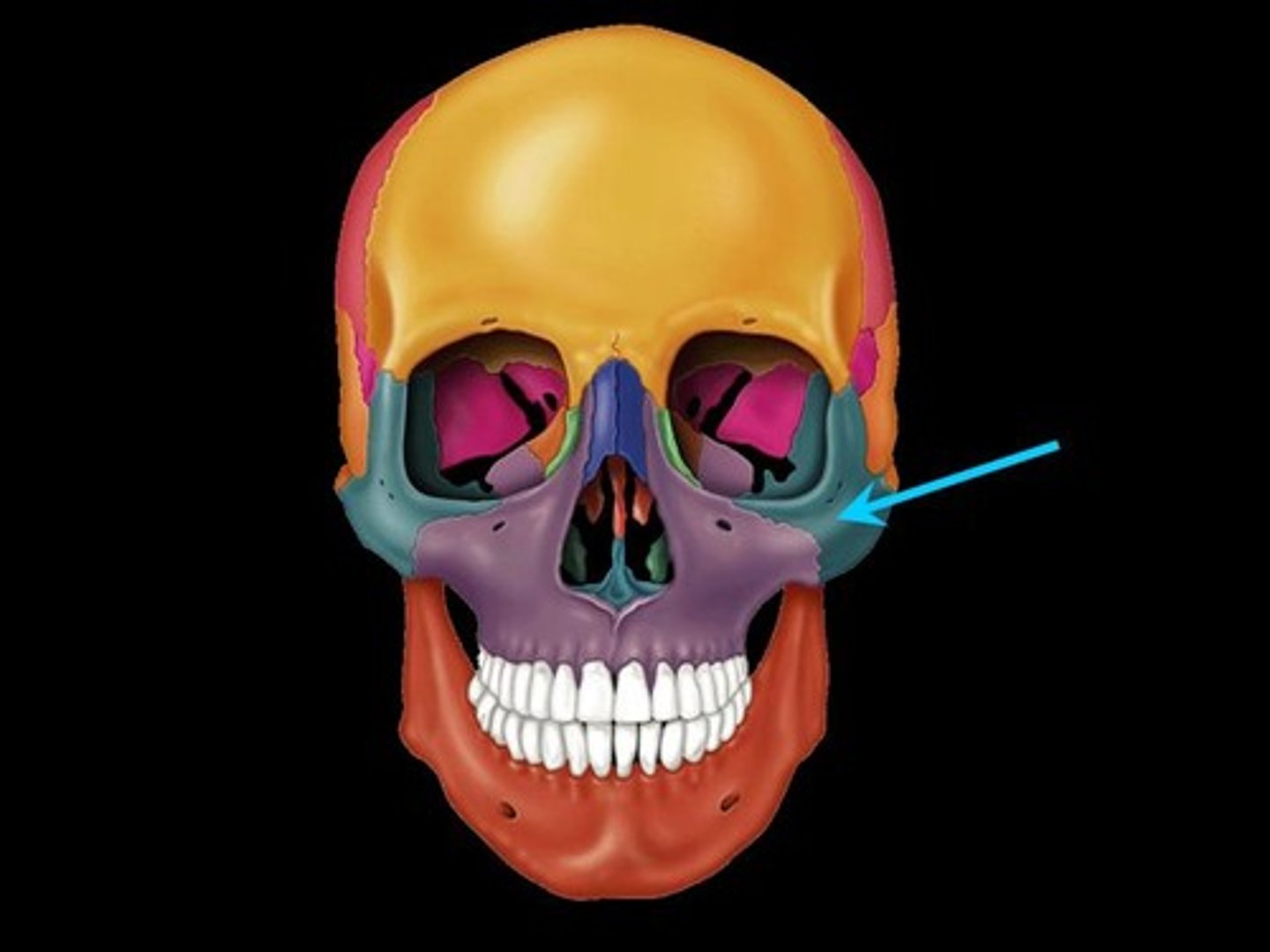
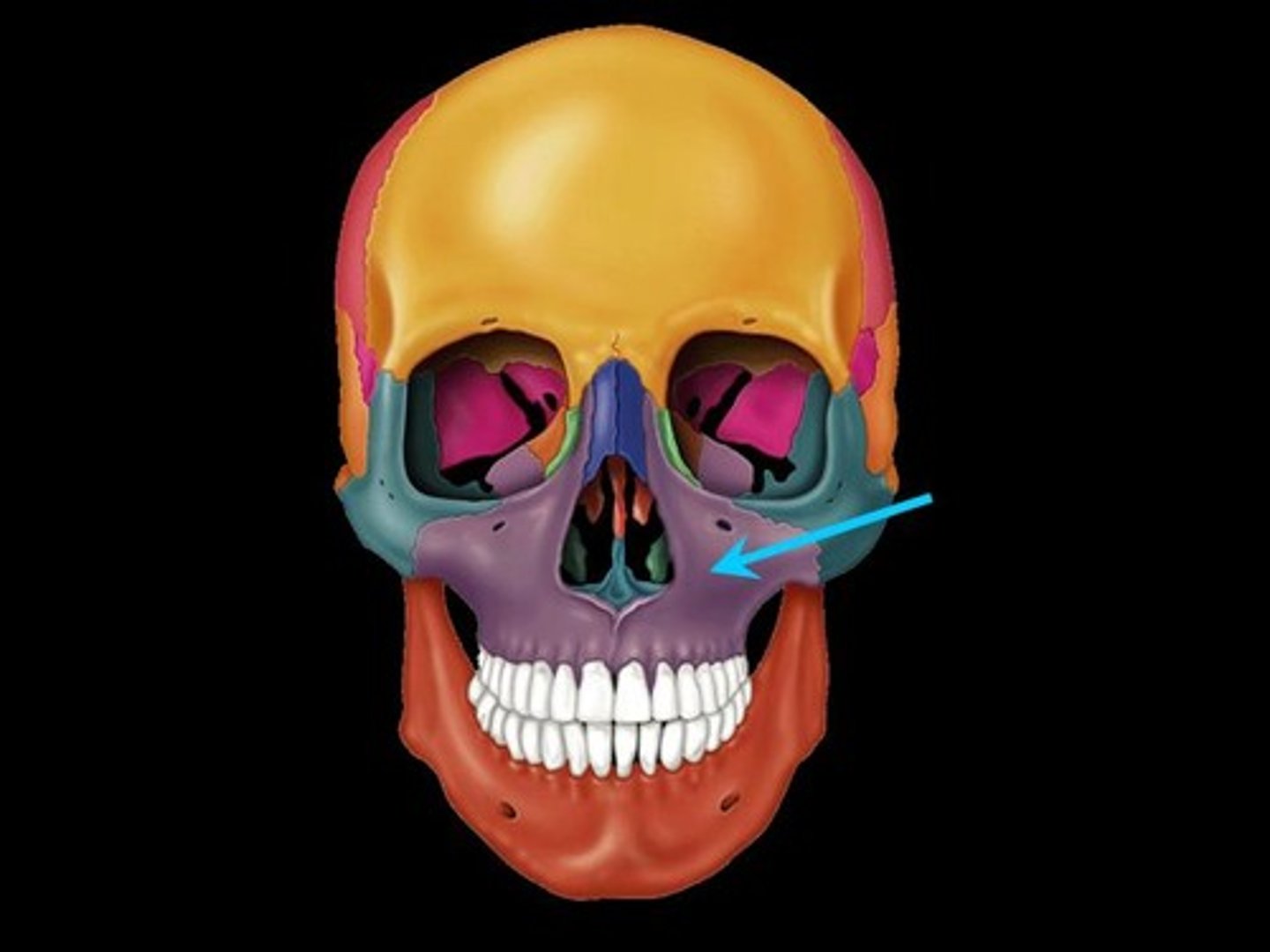
Maxilla
The upper jawbone that holds the upper teeth.
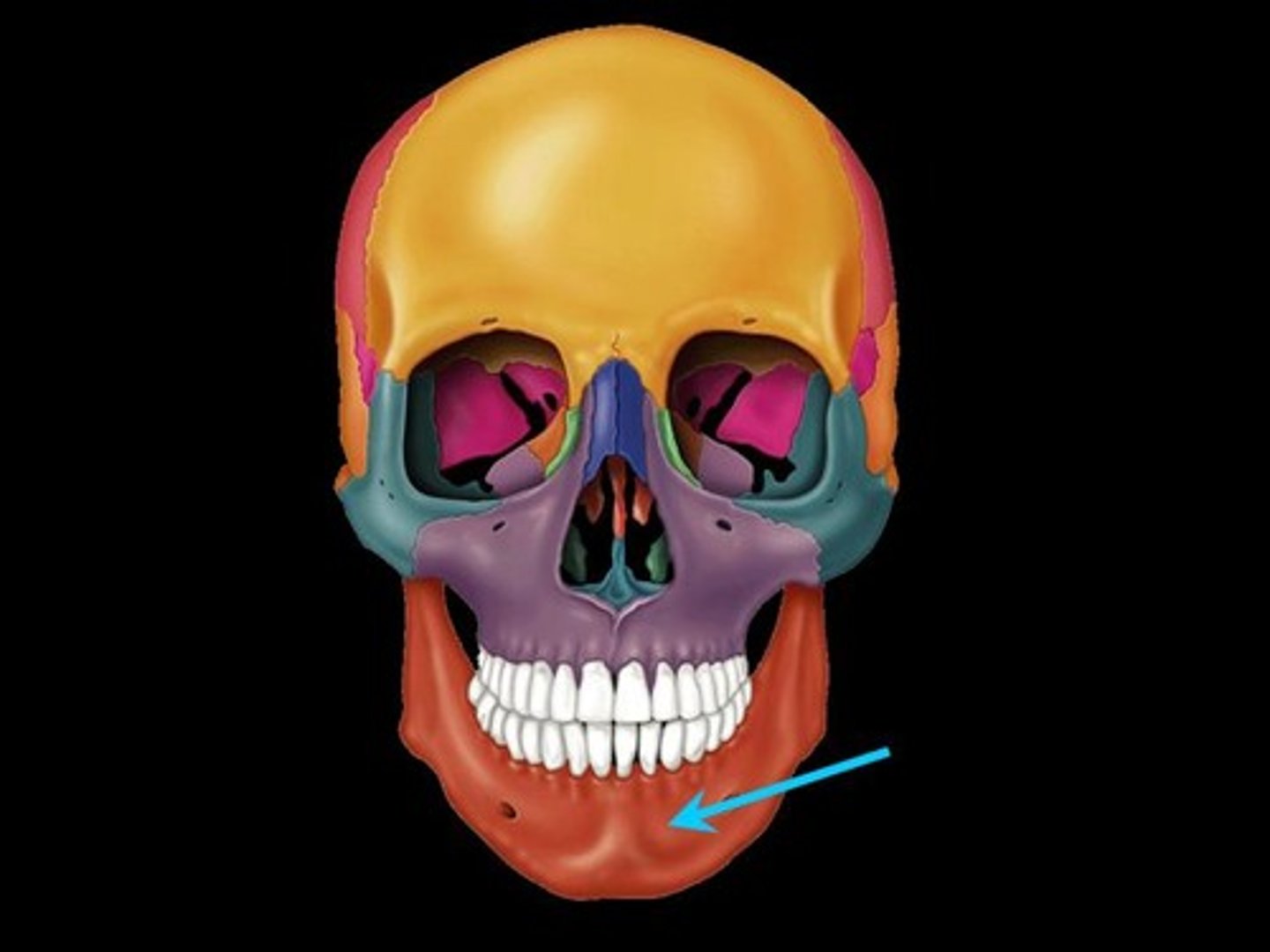
Mandible
The lower jawbone, the only movable bone of the skull.
Temporal bone
The bone that forms the sides and base of the skull.
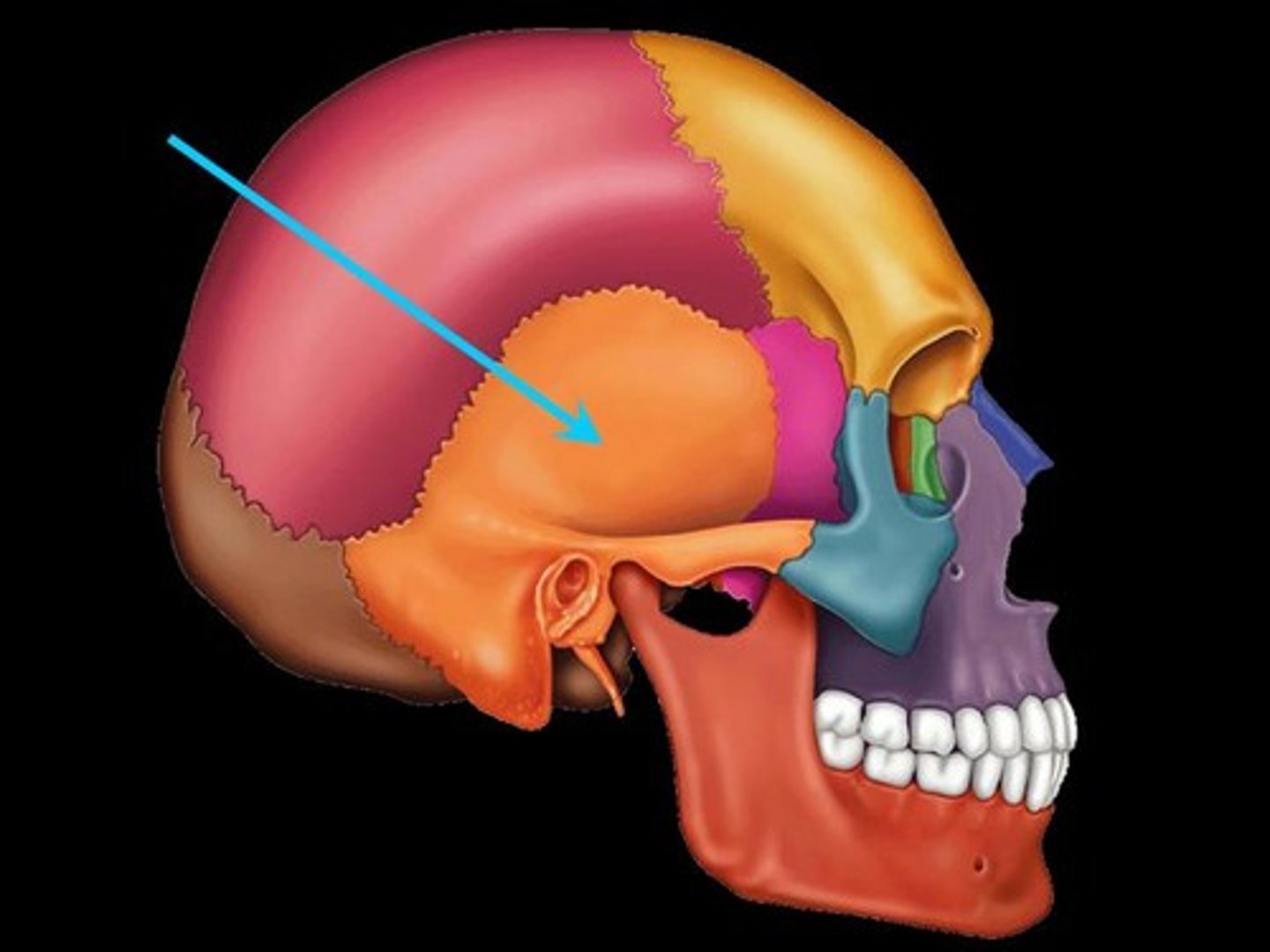
Sphenoid bone
A complex bone located at the base of the skull, contributing to the eye socket.
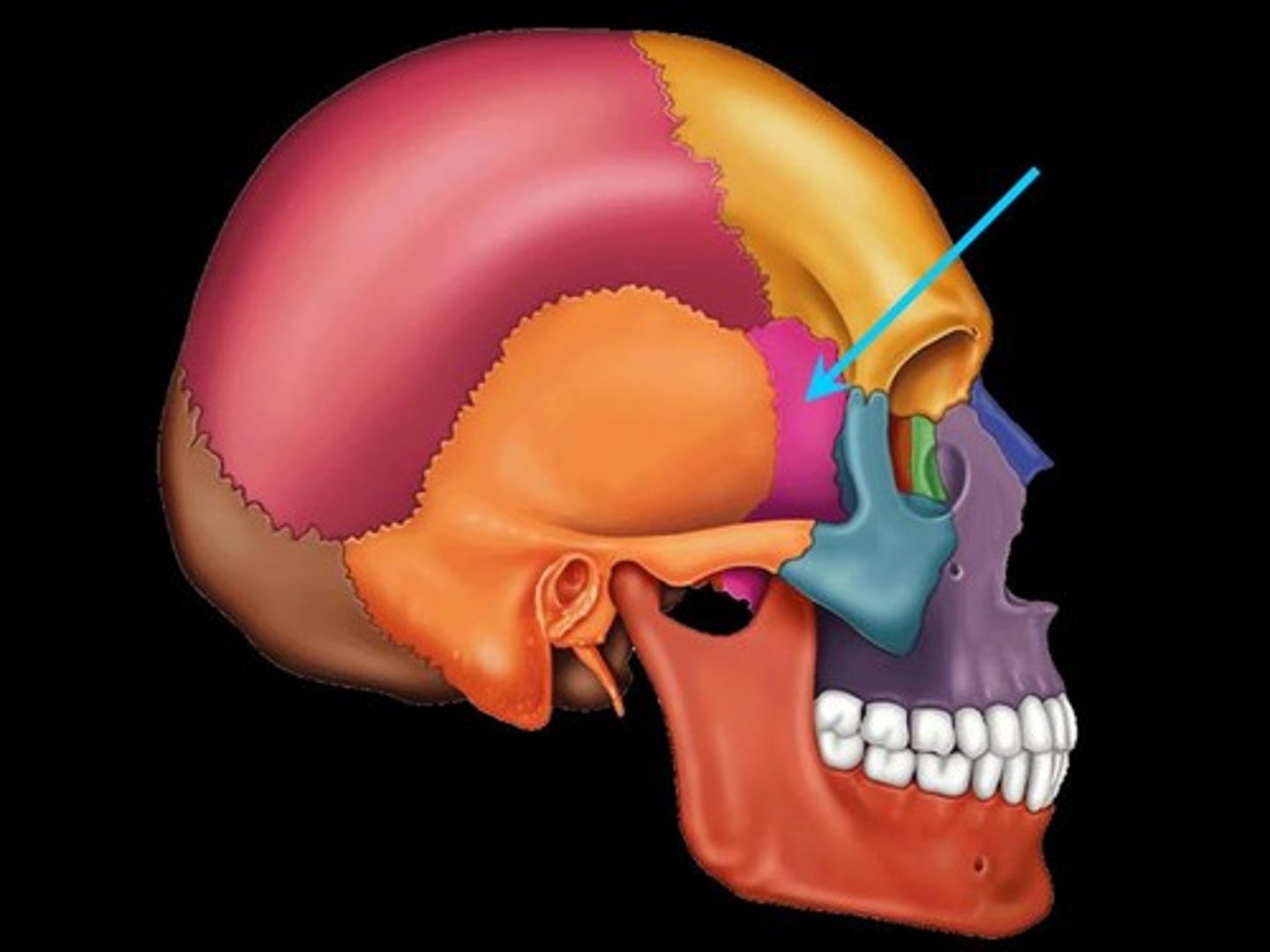
Ethmoid bone
A light and spongy bone located between the eyes, forming part of the nasal cavity.
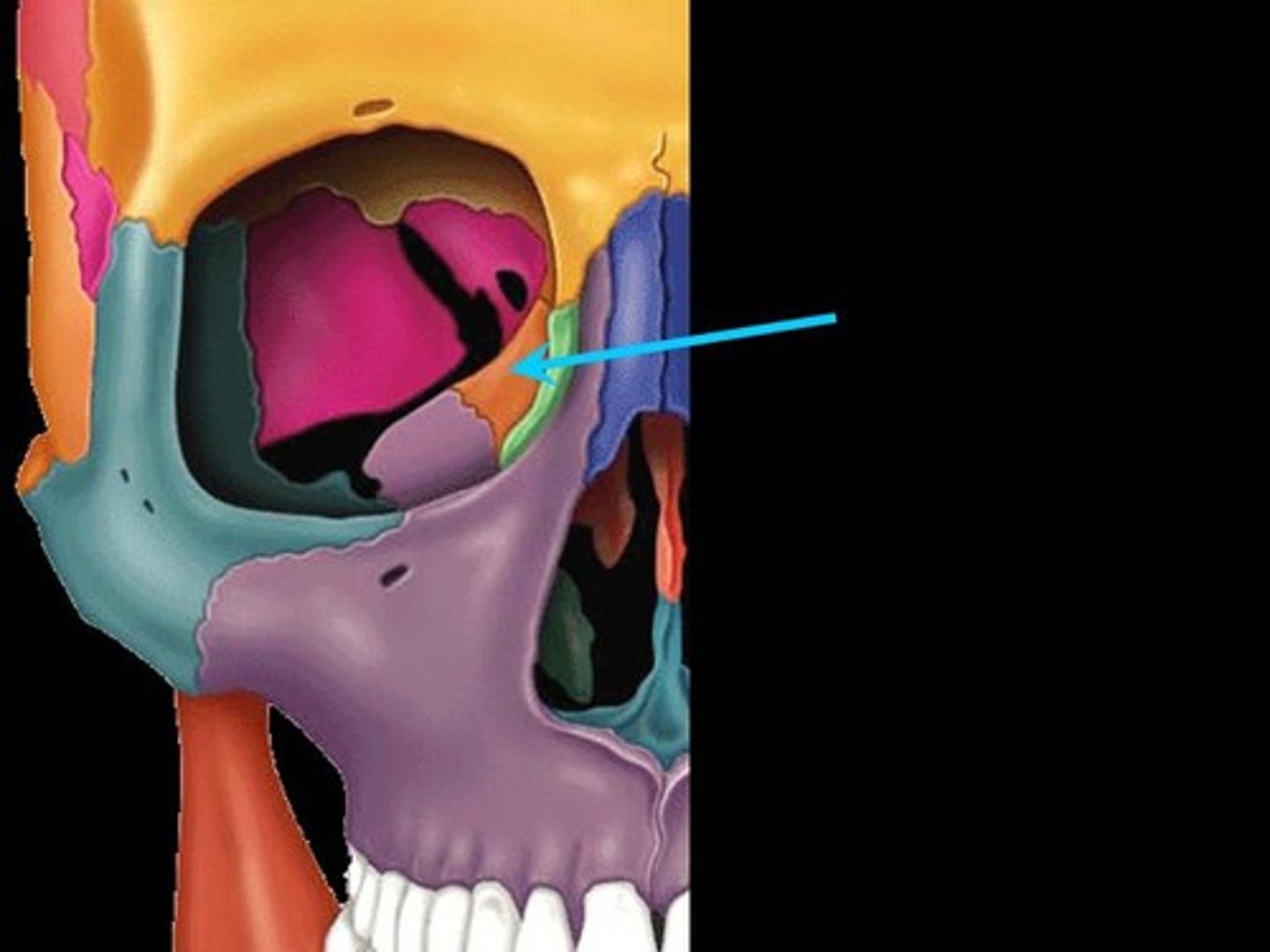
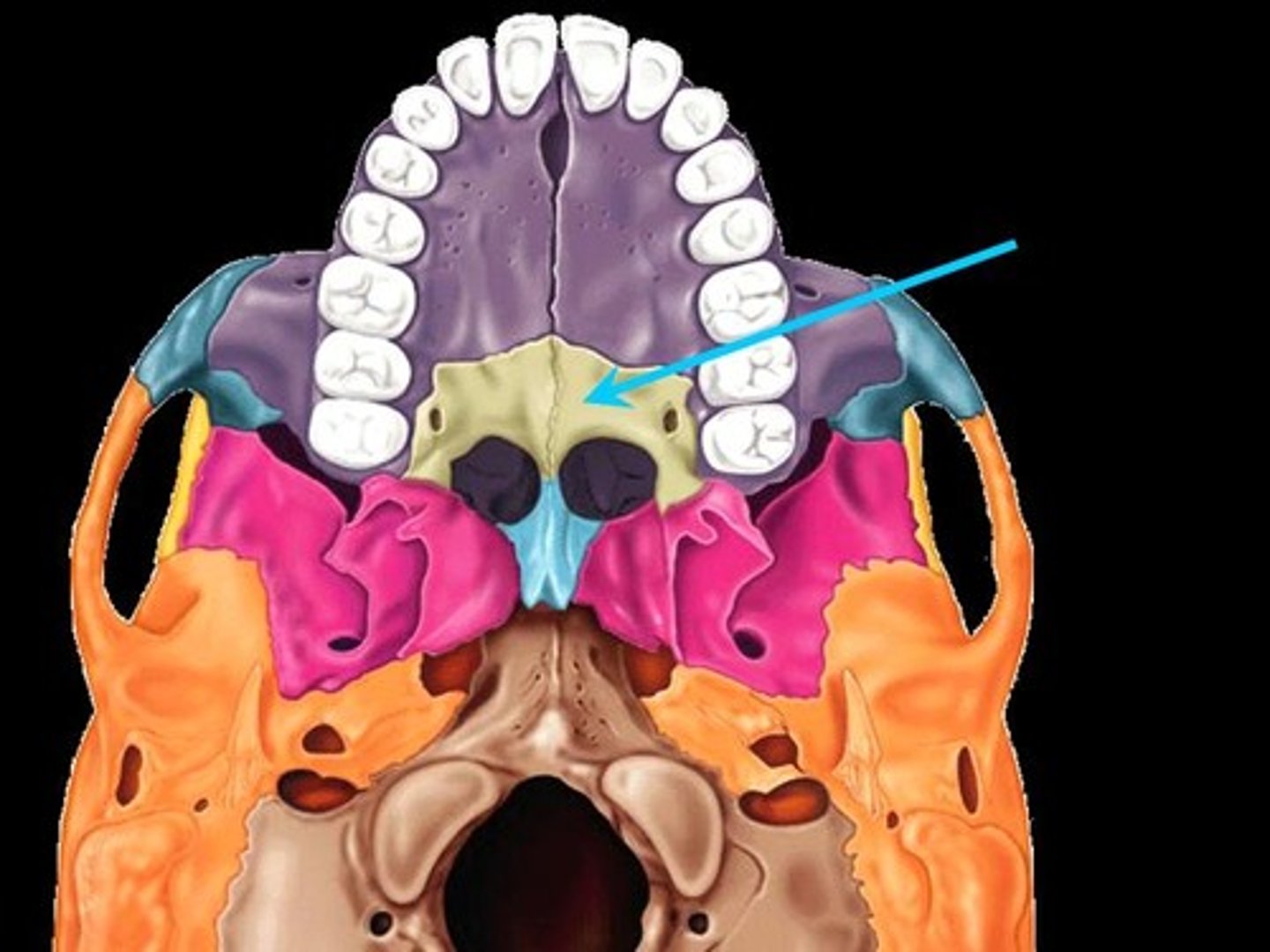
Palatine bone
The bone that forms the back part of the hard palate of the mouth.
Vertebrae
The individual bones that make up the vertebral column (spine).
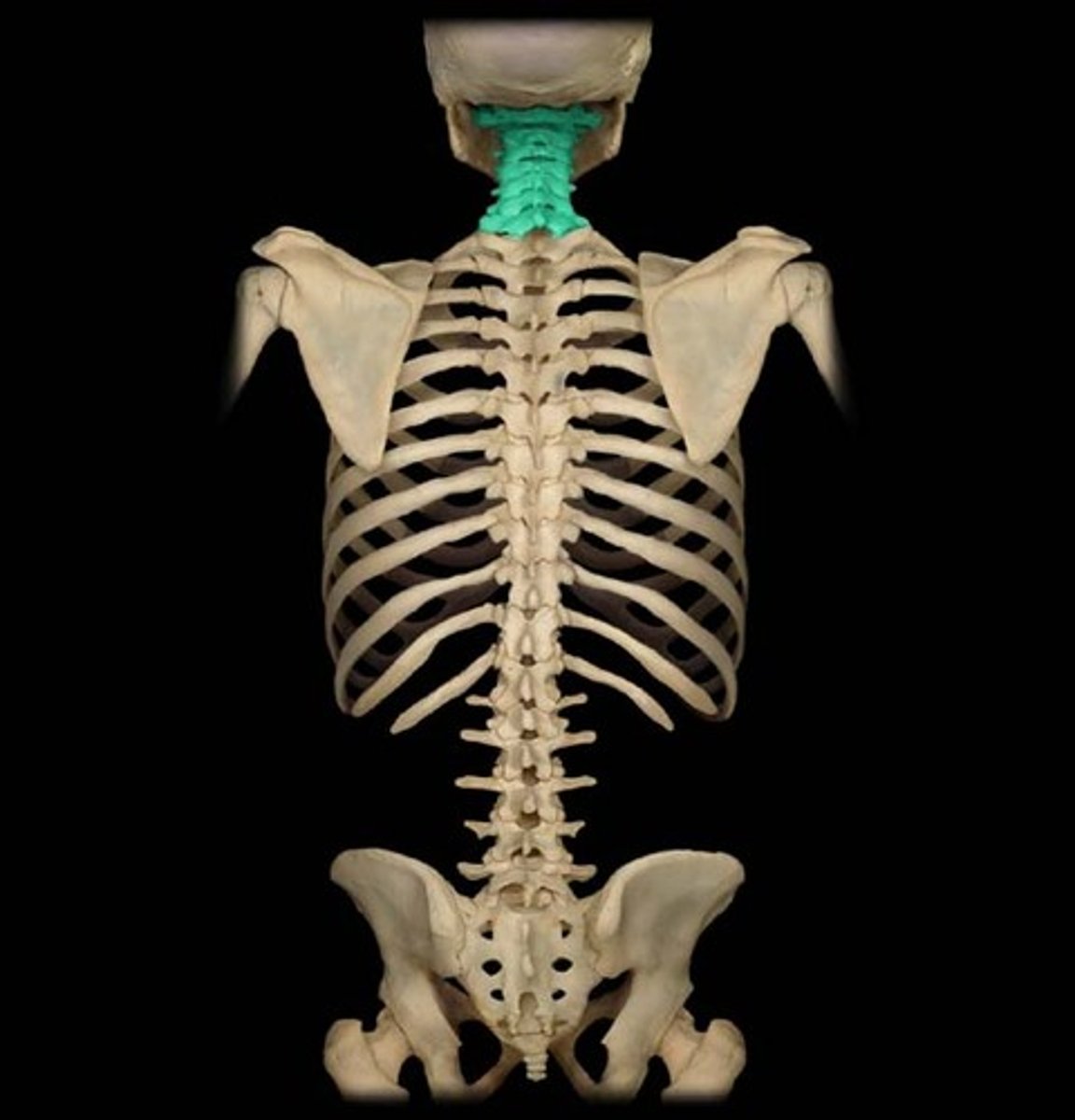
Cervical vertebrae
The seven vertebrae in the neck region, labeled C1 to C7.
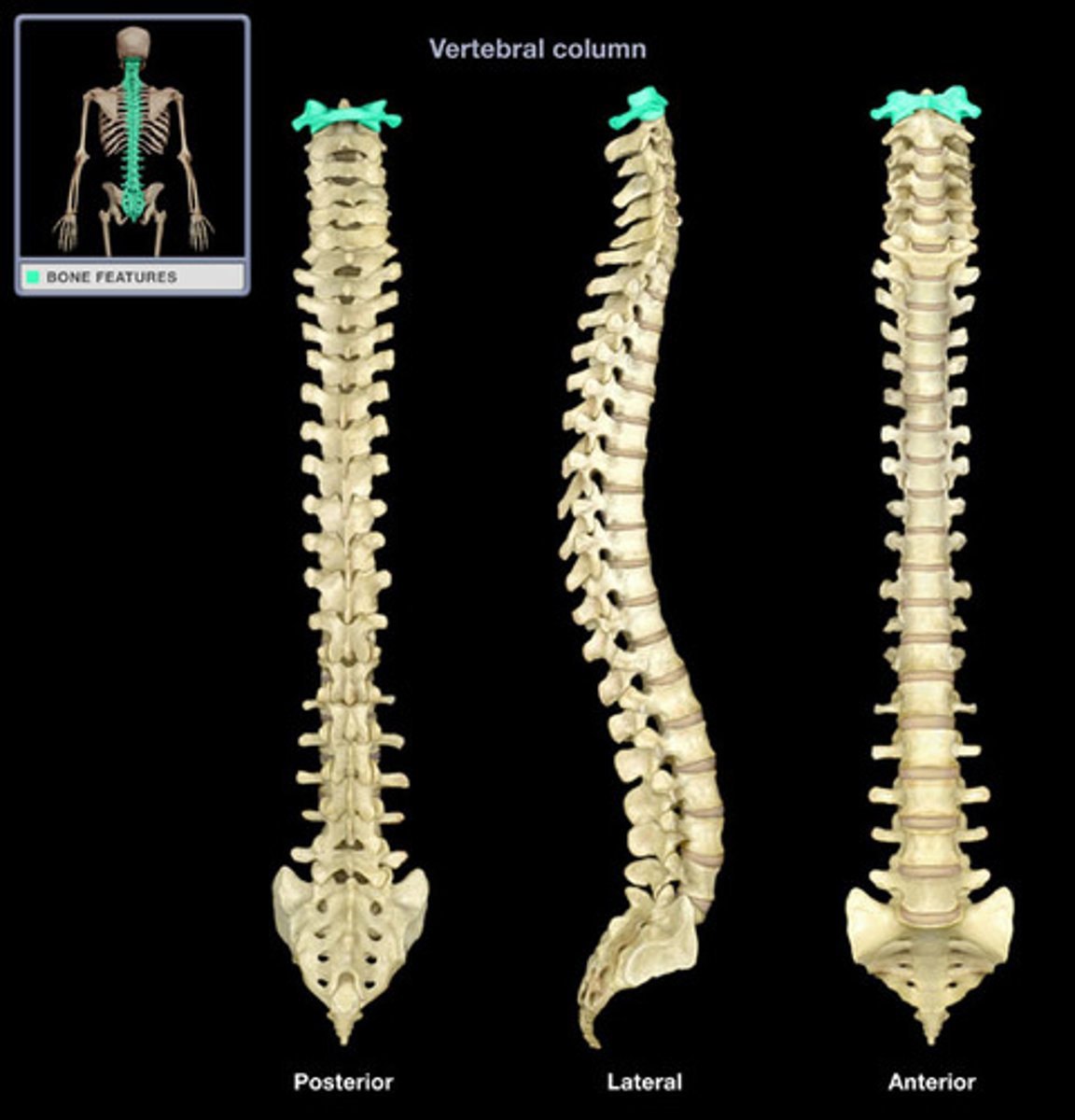
Atlas
The first cervical vertebra that supports the skull.
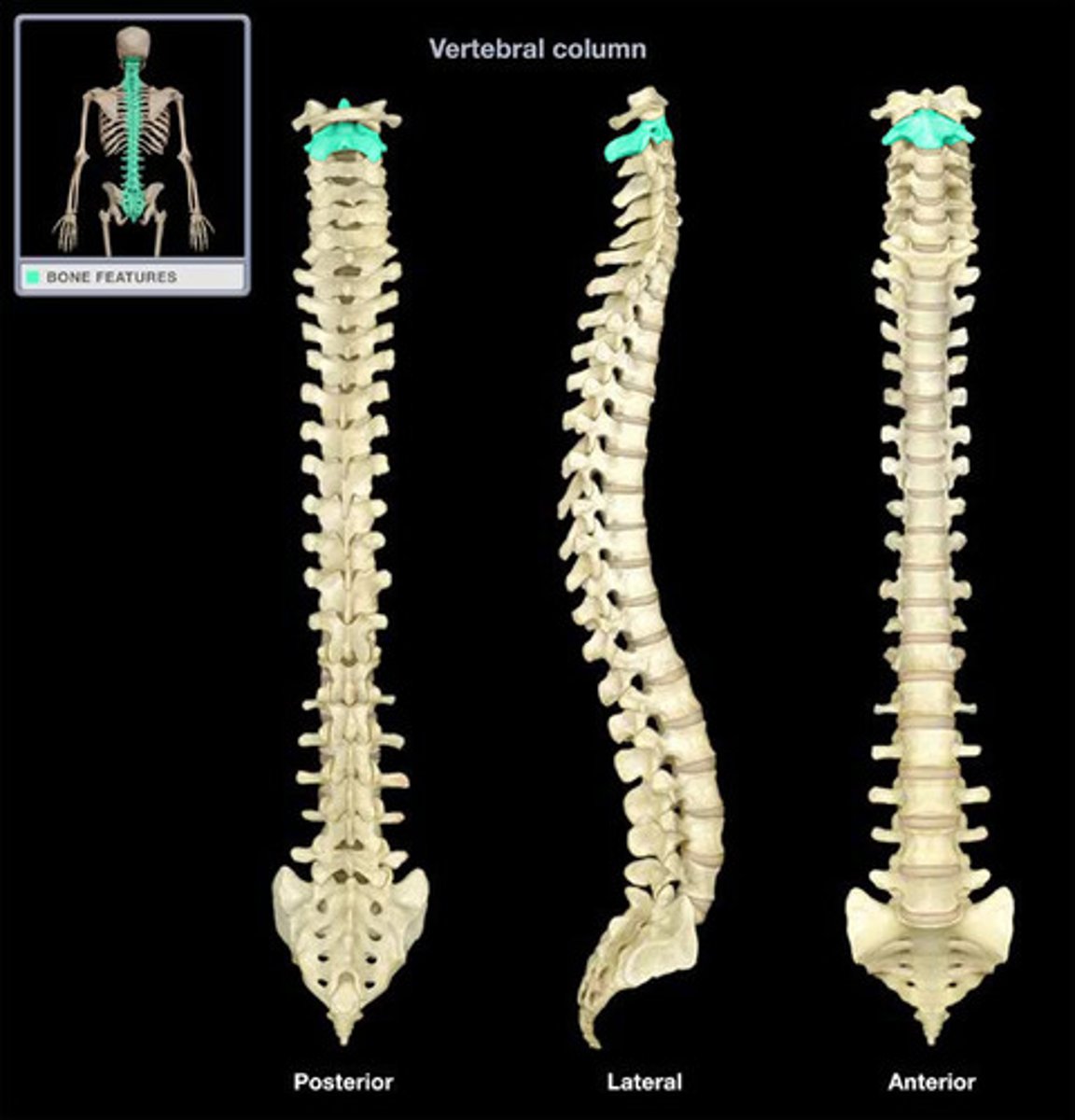
Axis
The second cervical vertebra that allows for the rotation of the head.
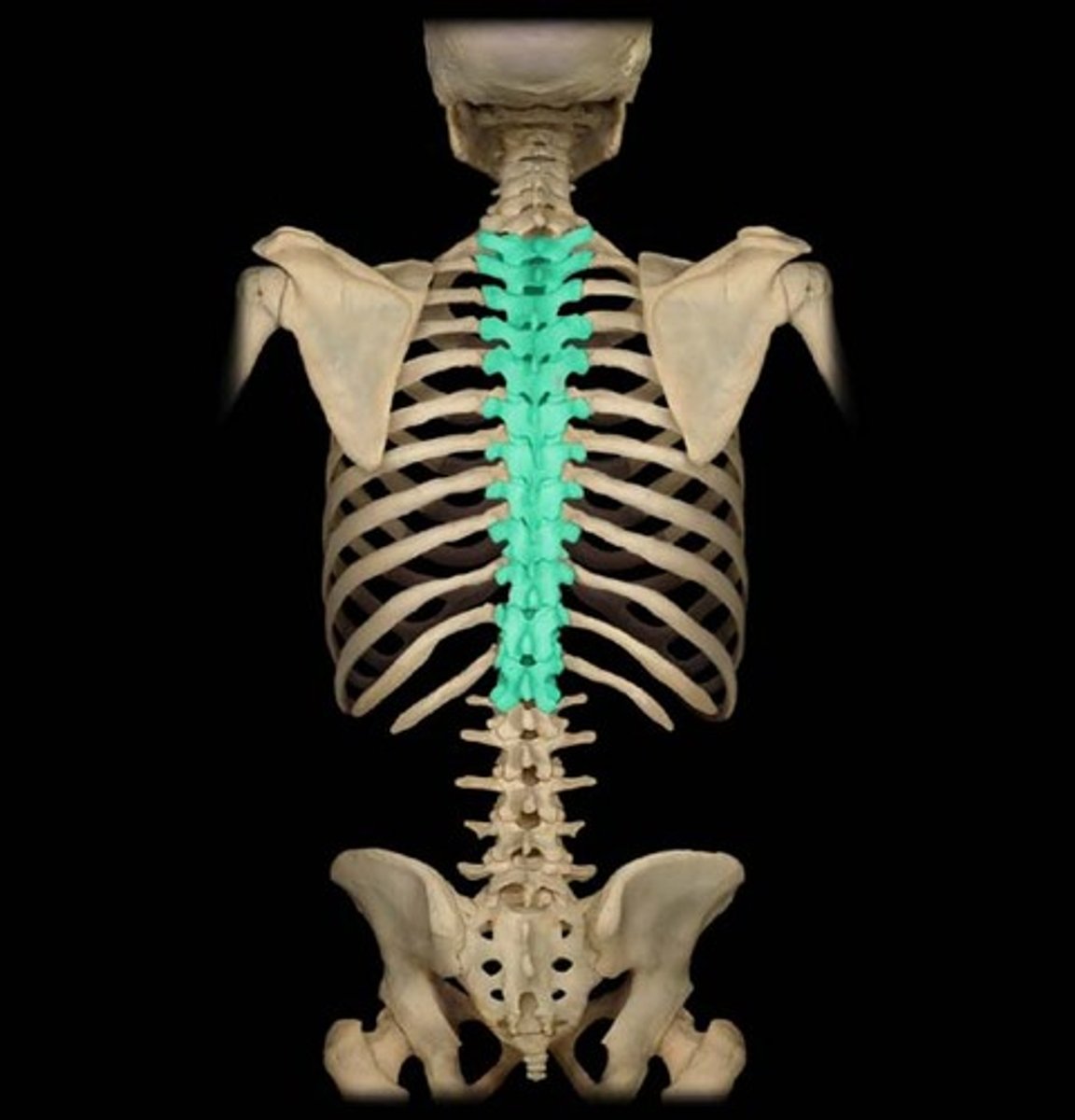
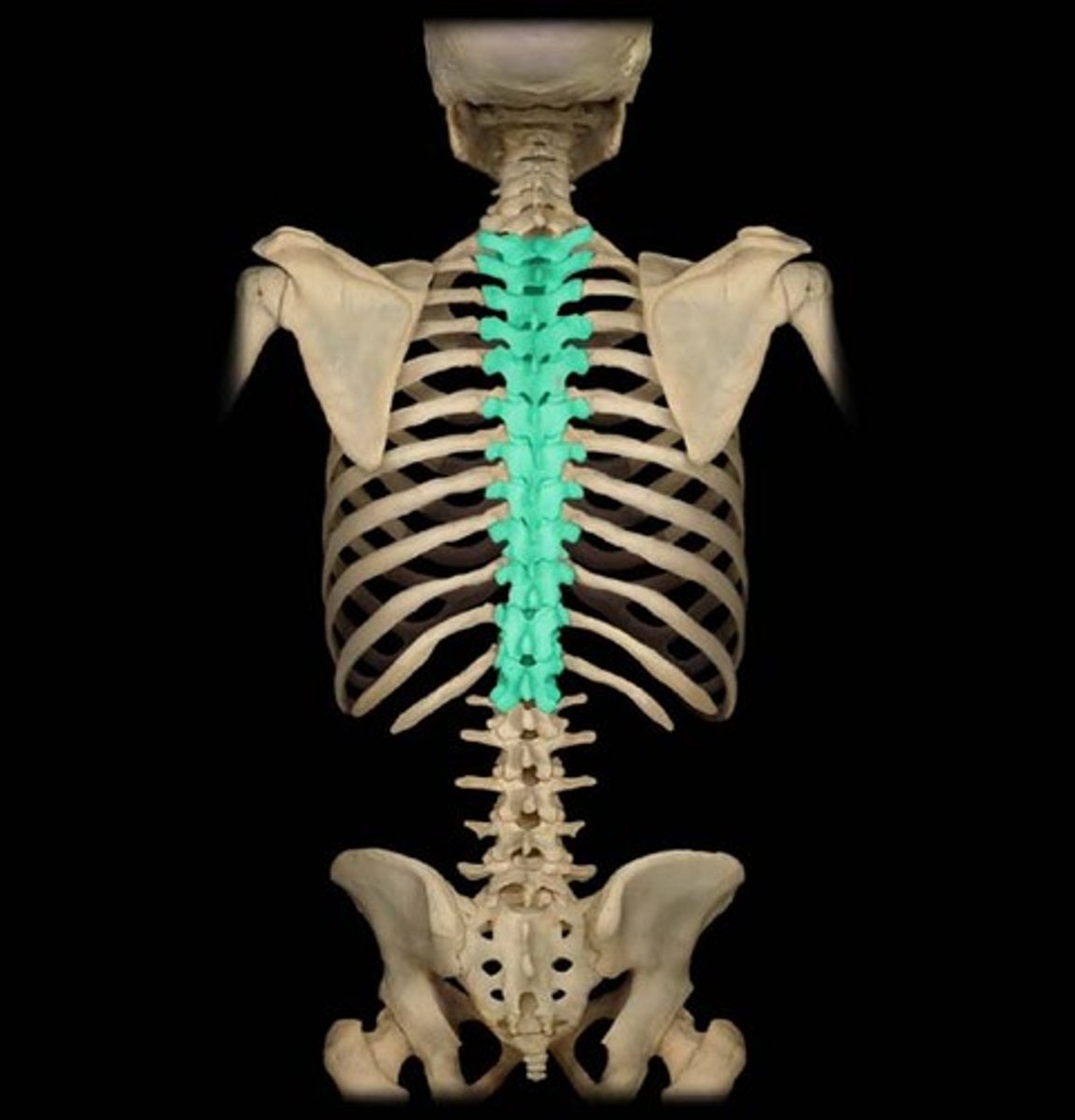
Thoracic vertebrae
The twelve vertebrae in the upper and mid-back region, labeled T1 to T12.
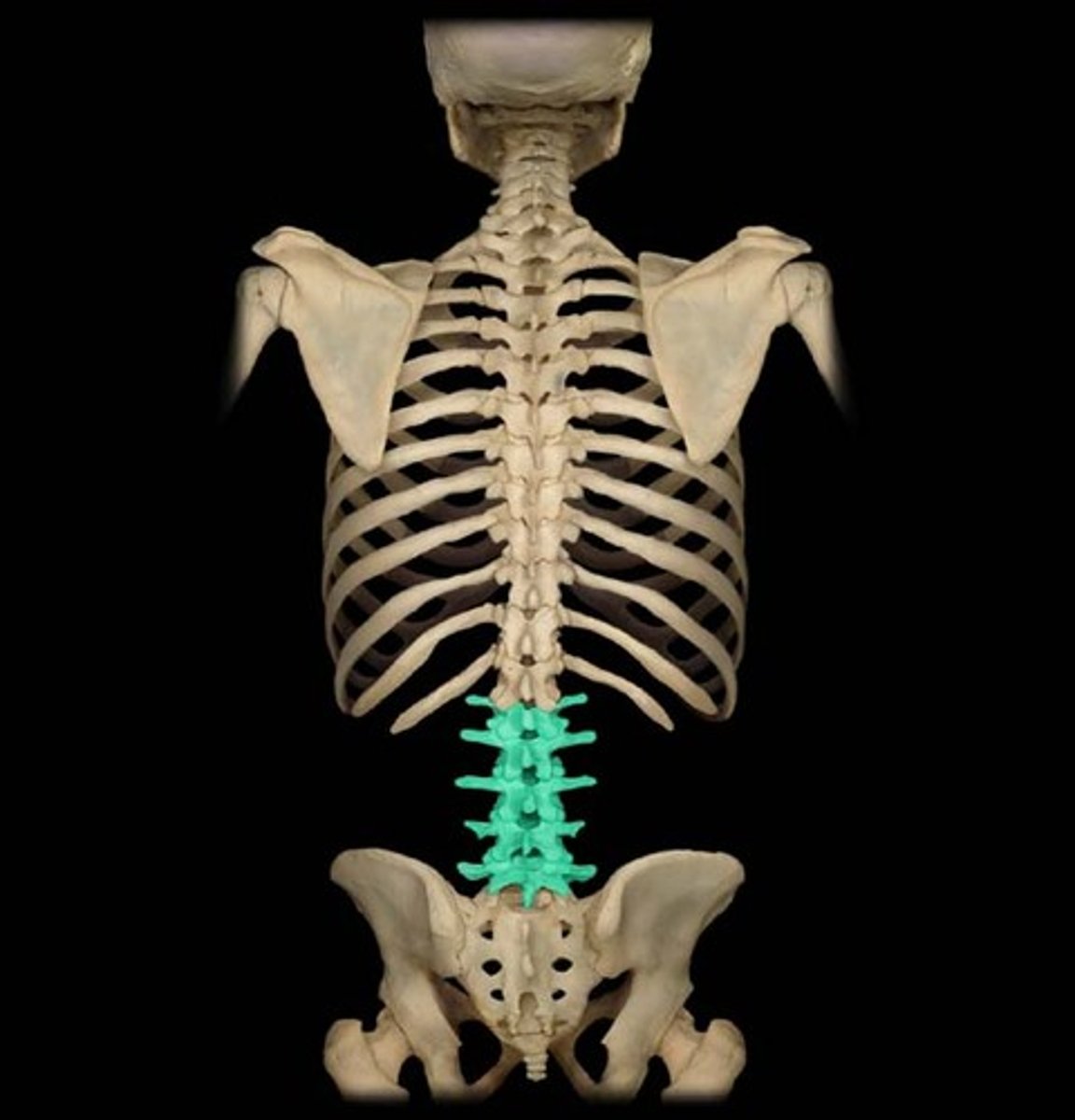
Lumbar vertebrae
The five vertebrae in the lower back, labeled L1 to L5.
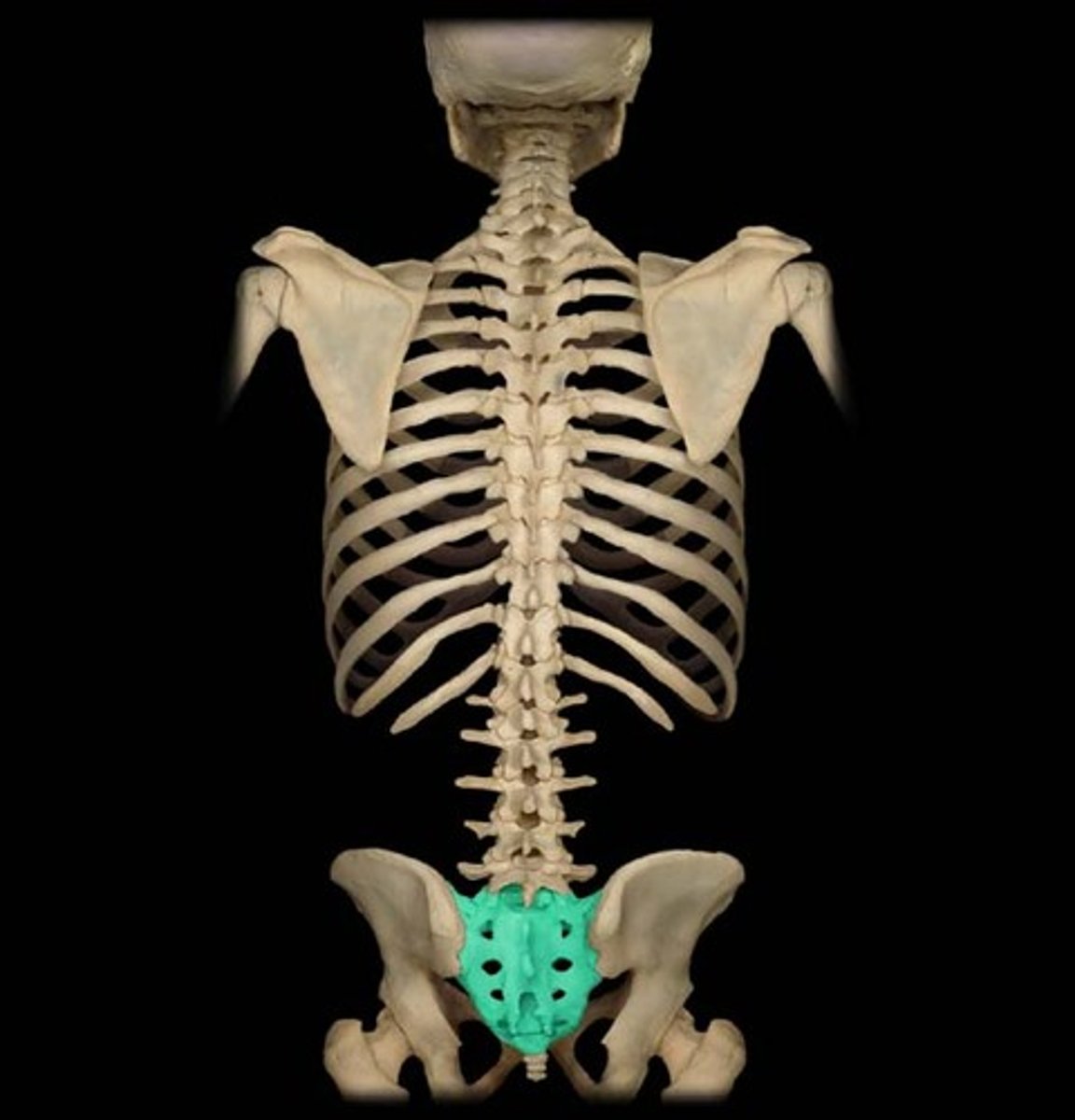
Sacrum
The triangular bone at the base of the spine, formed by the fusion of five vertebrae.
Coccyx
The small bone at the very end of the vertebral column, commonly known as the tailbone.

Pedicle
The short, thick bony process that connects the vertebral body to the vertebral arch.
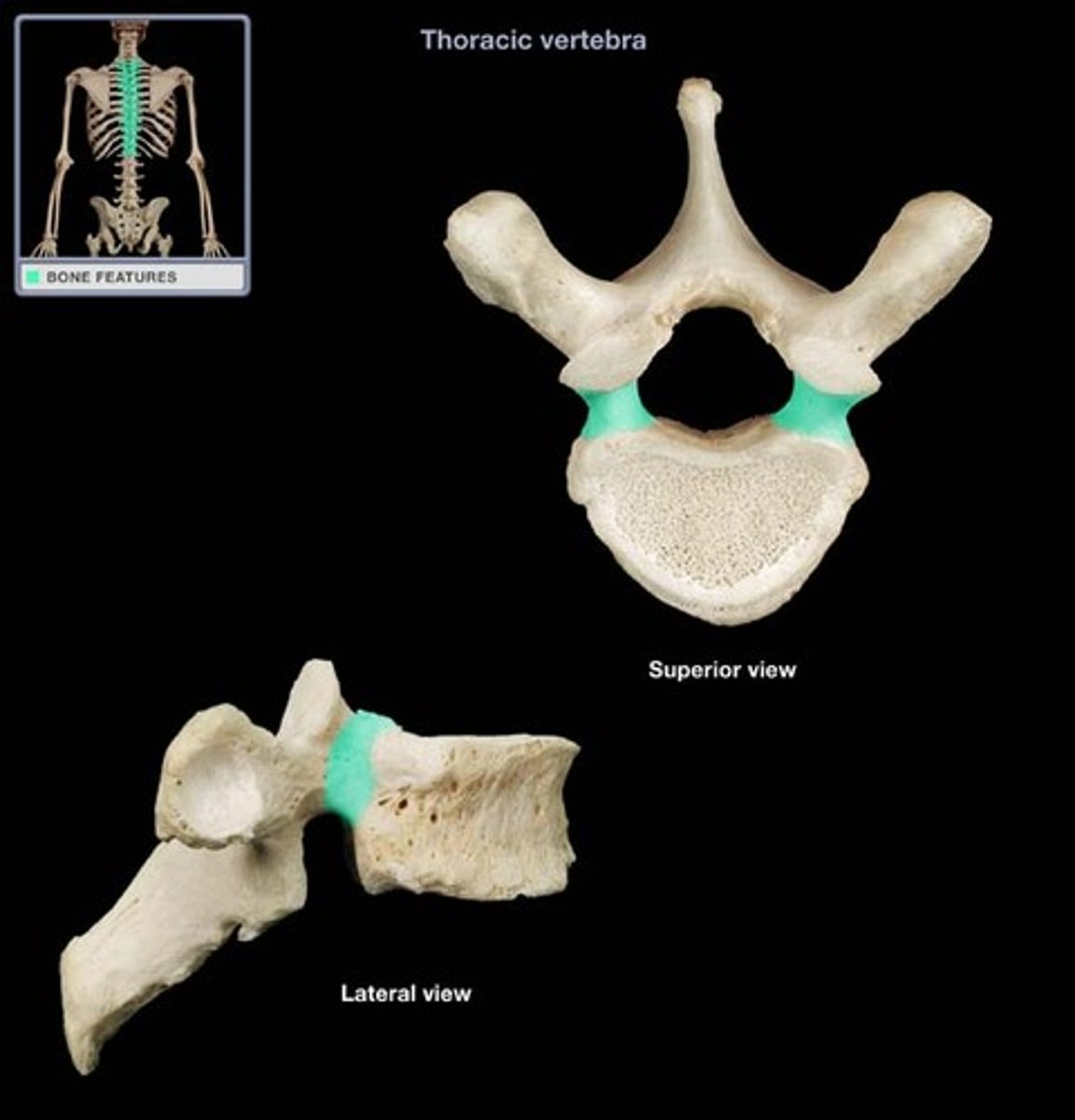
Transverse process
The bony projections on either side of a vertebra.

Lamina
The part of the vertebral arch that connects the spinous process to the transverse processes.
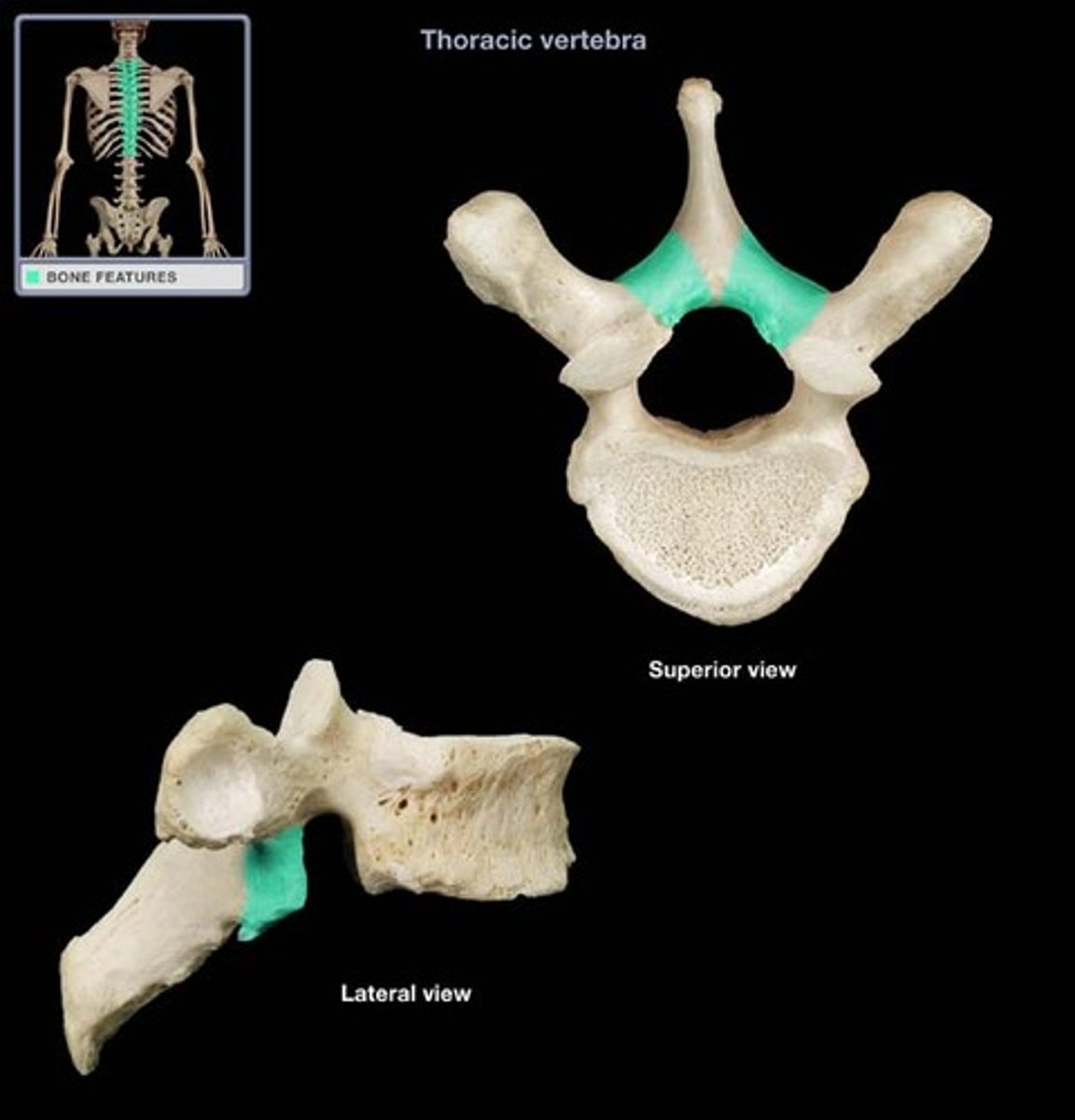
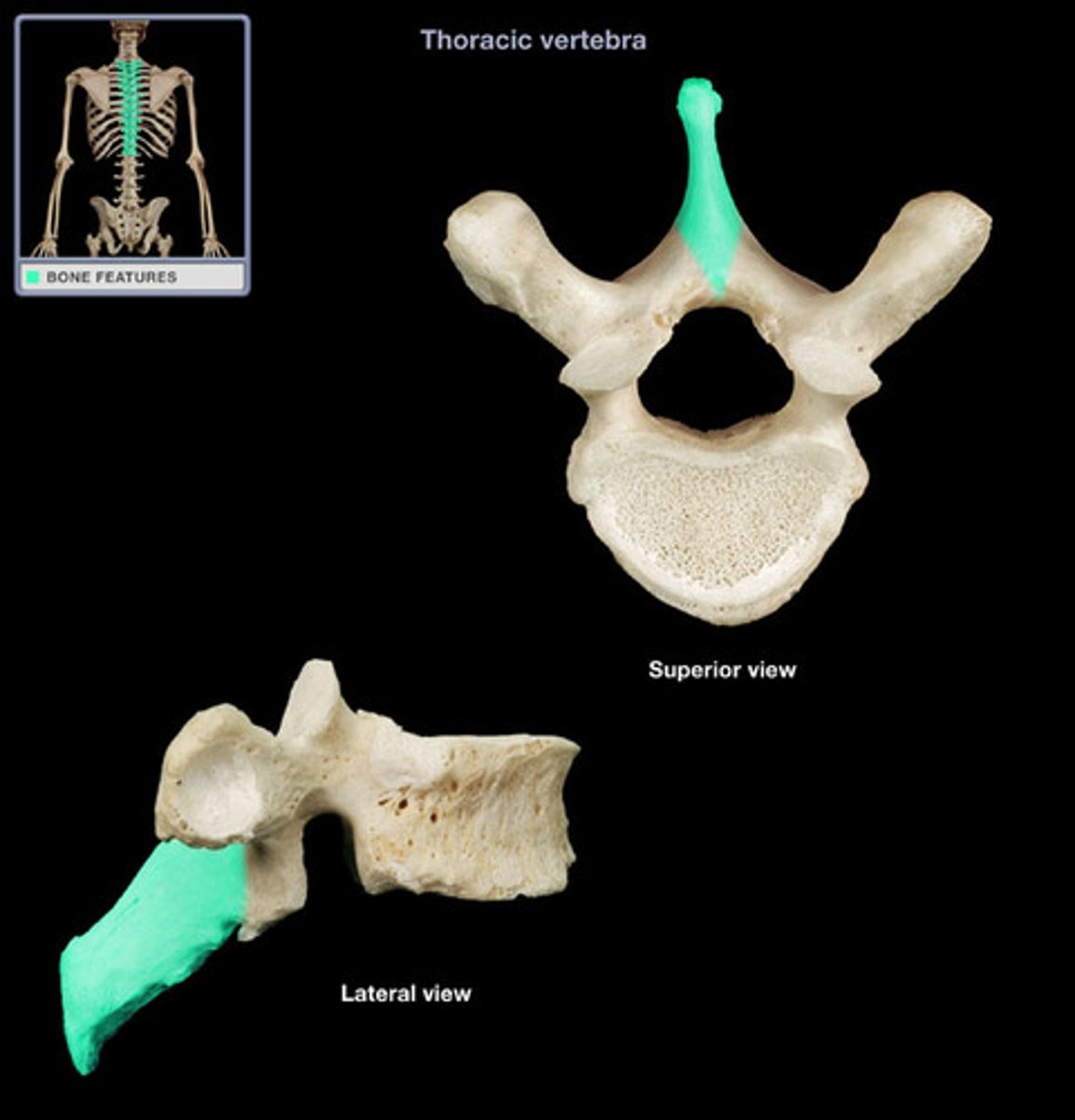
Spinous process
The bony projection on the back of a vertebra.
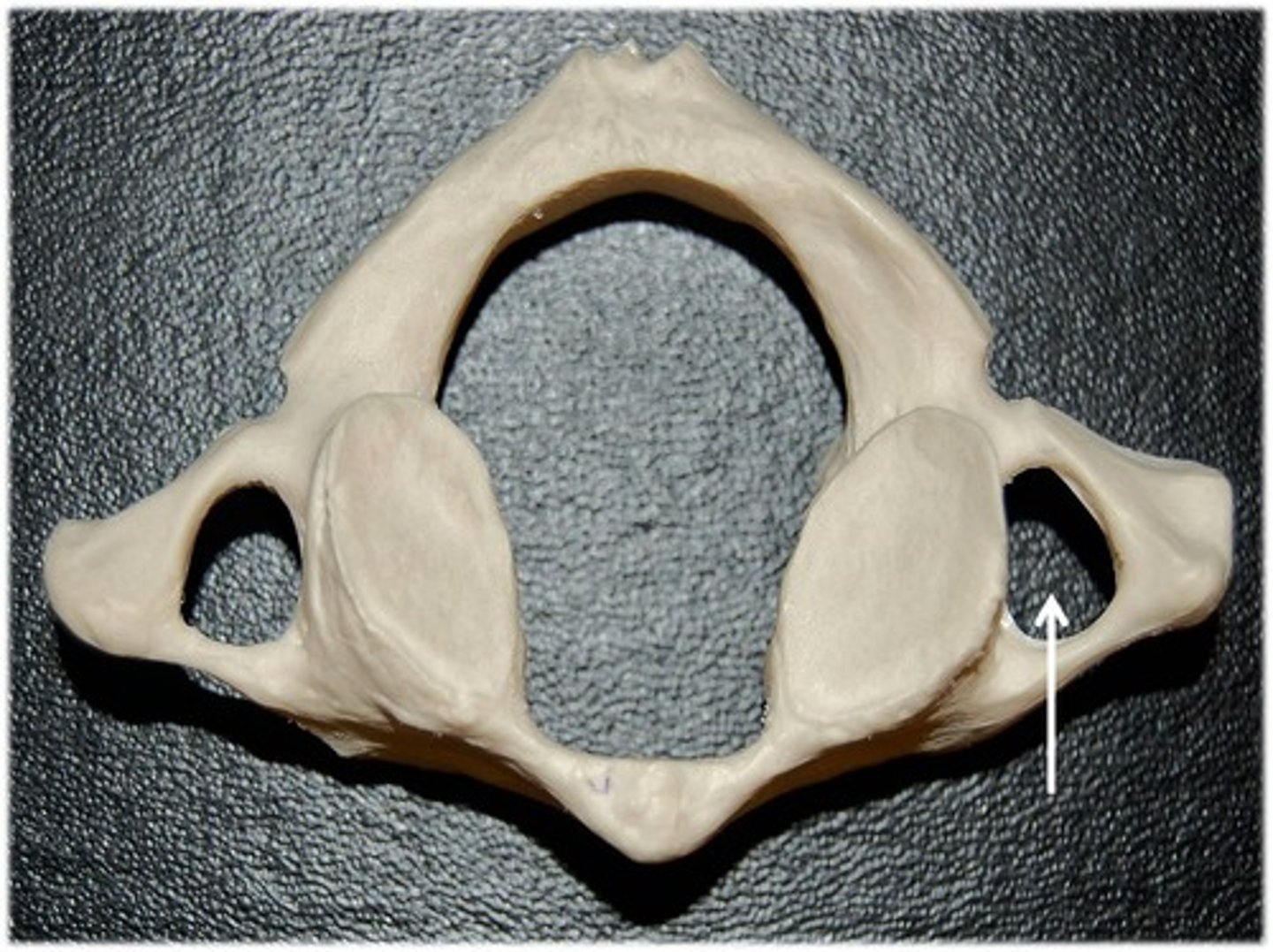
Transverse foramen
The openings in the transverse processes of cervical vertebrae for the passage of blood vessels.
Vertebral body
The large, cylindrical part of a vertebra that bears weight.

Vertebral foramen
The opening in a vertebra through which the spinal cord passes.

Odontoid (dens)
The peg-like projection on the axis vertebra that allows for head rotation.
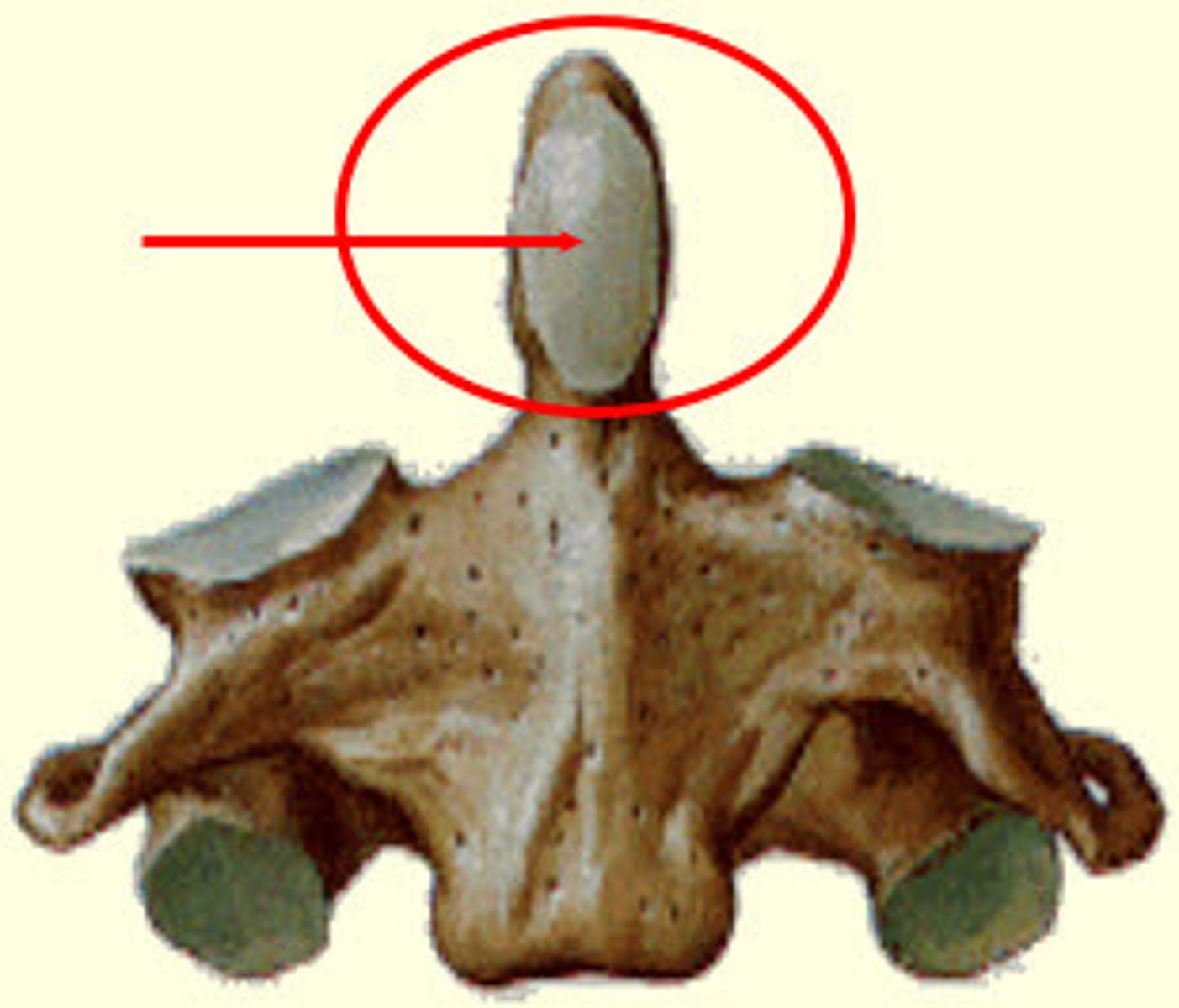
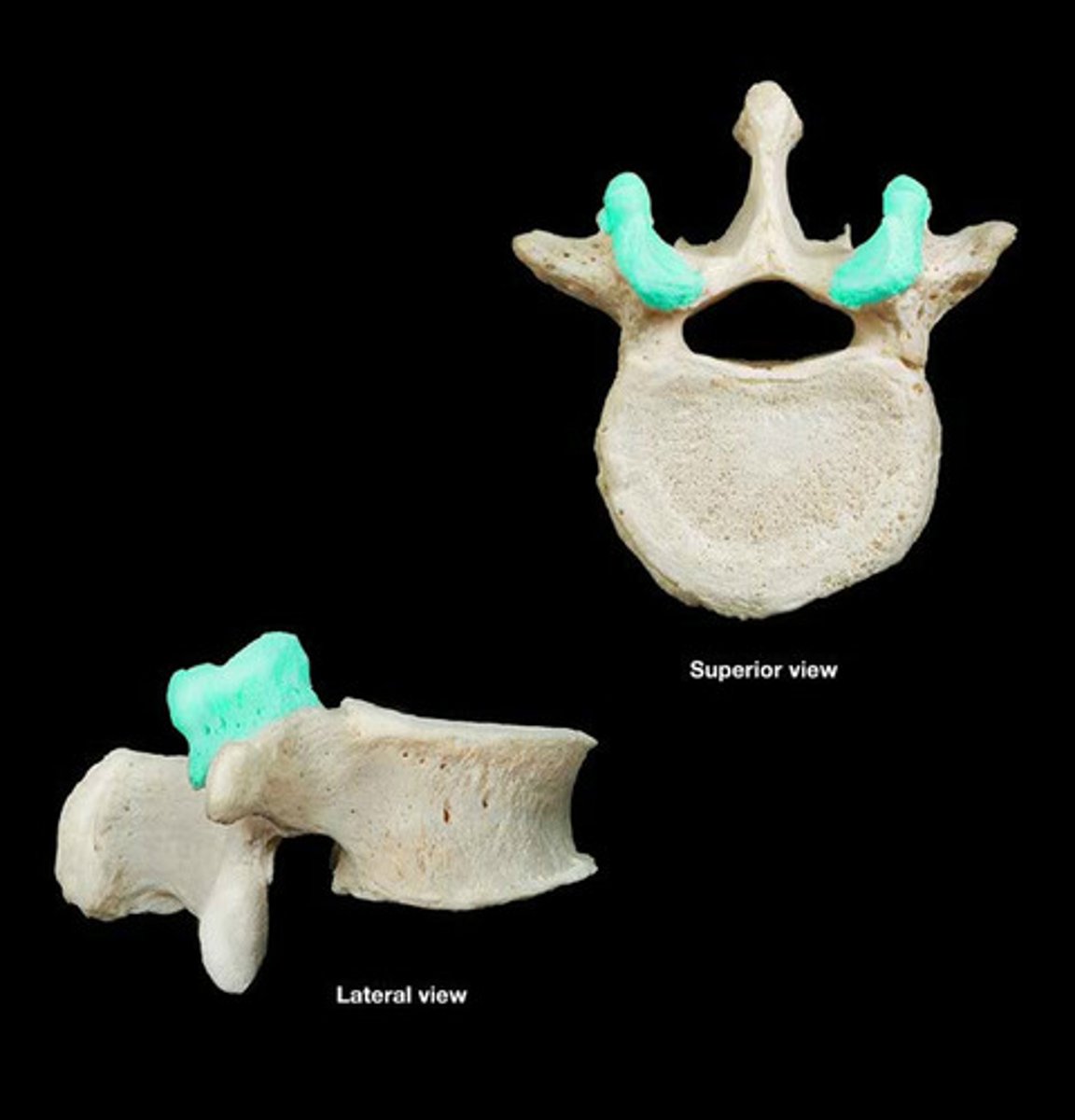
Superior articular process
The bony projections that form joints with the vertebrae above.
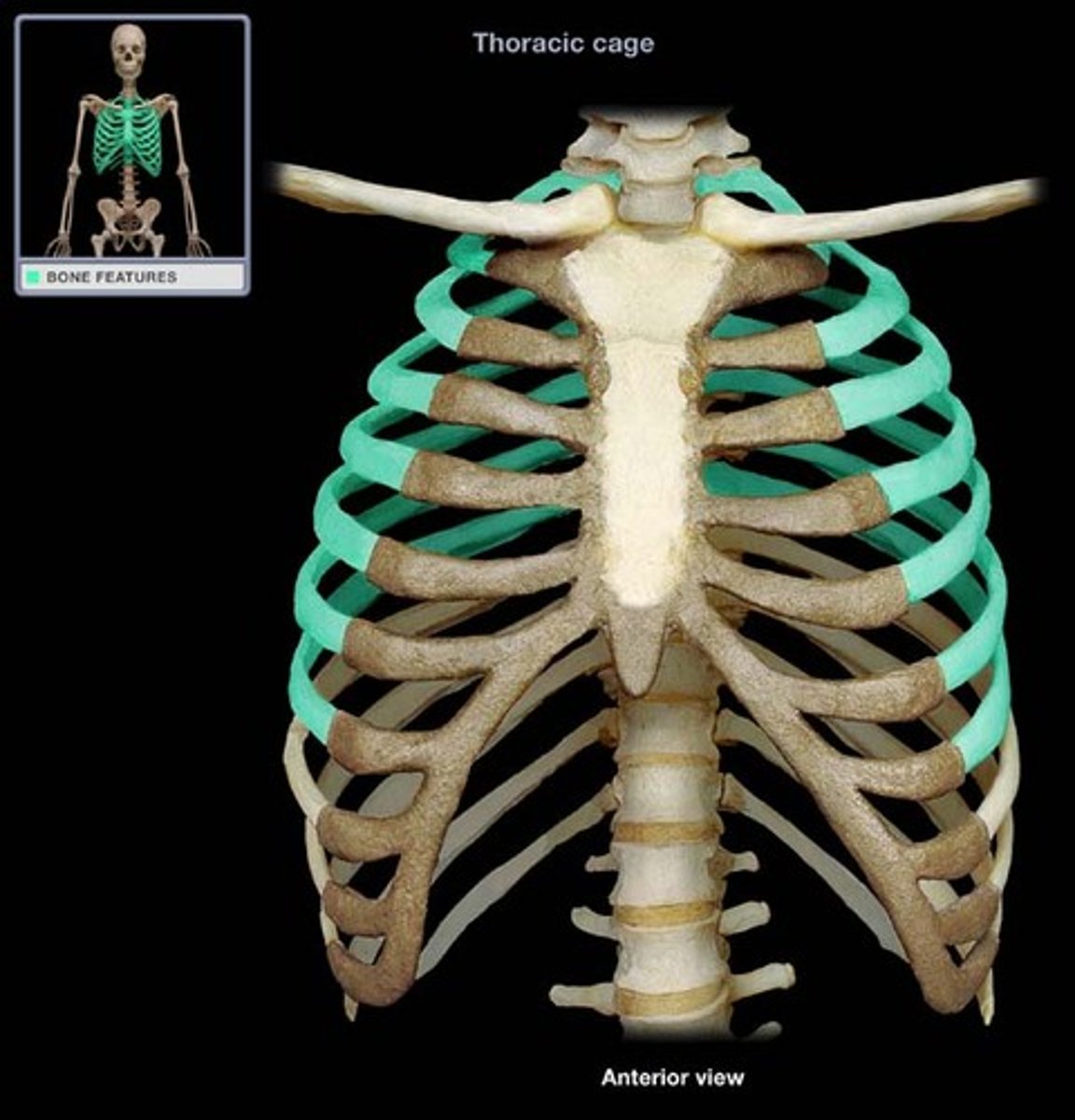
Ribs
The curved bones that form the rib cage, protecting the thoracic cavity.
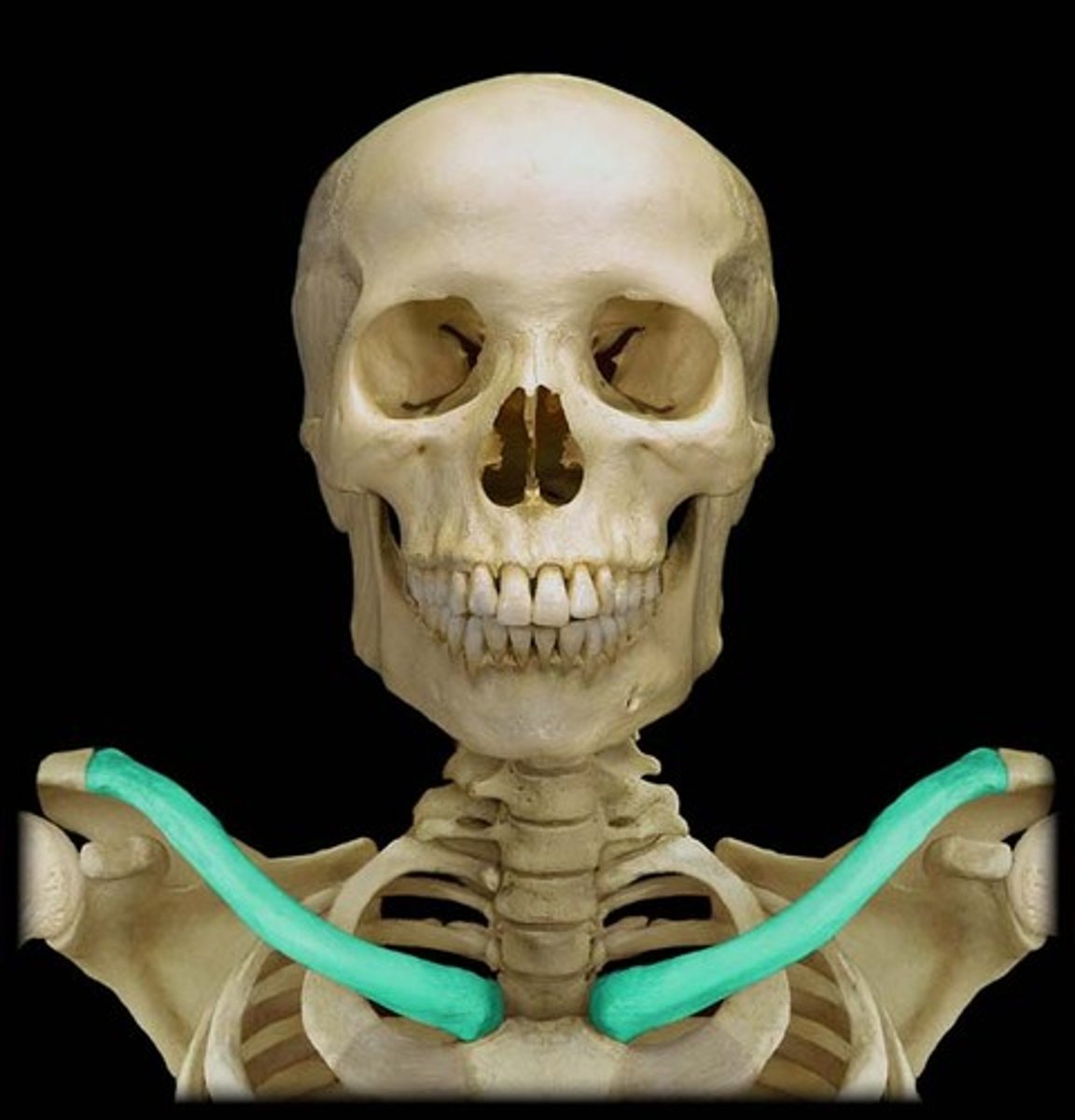
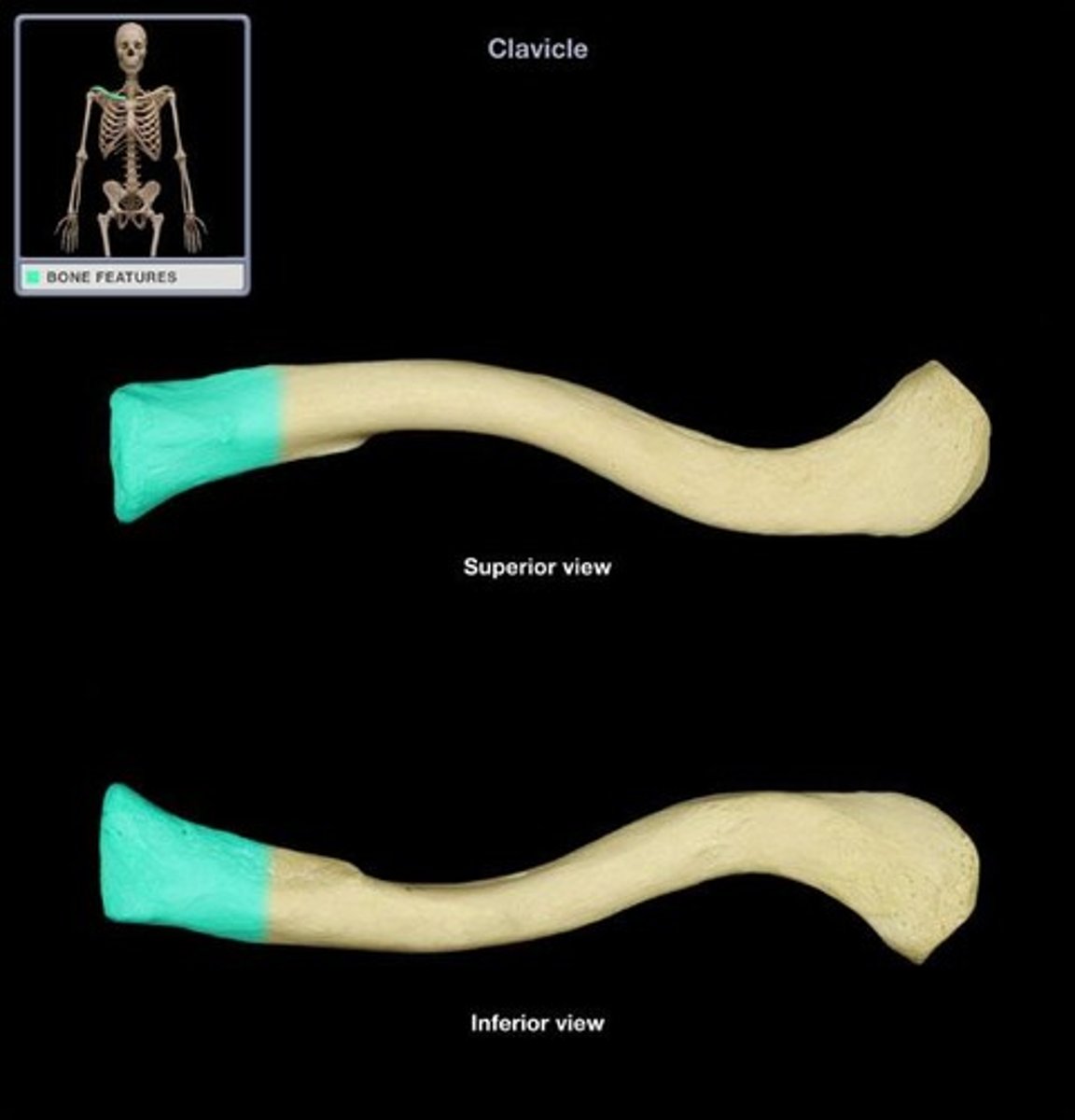
Clavicle
The collarbone, connecting the arm to the body.
Acromial extremity
The end of the clavicle that articulates with the acromion of the scapula.
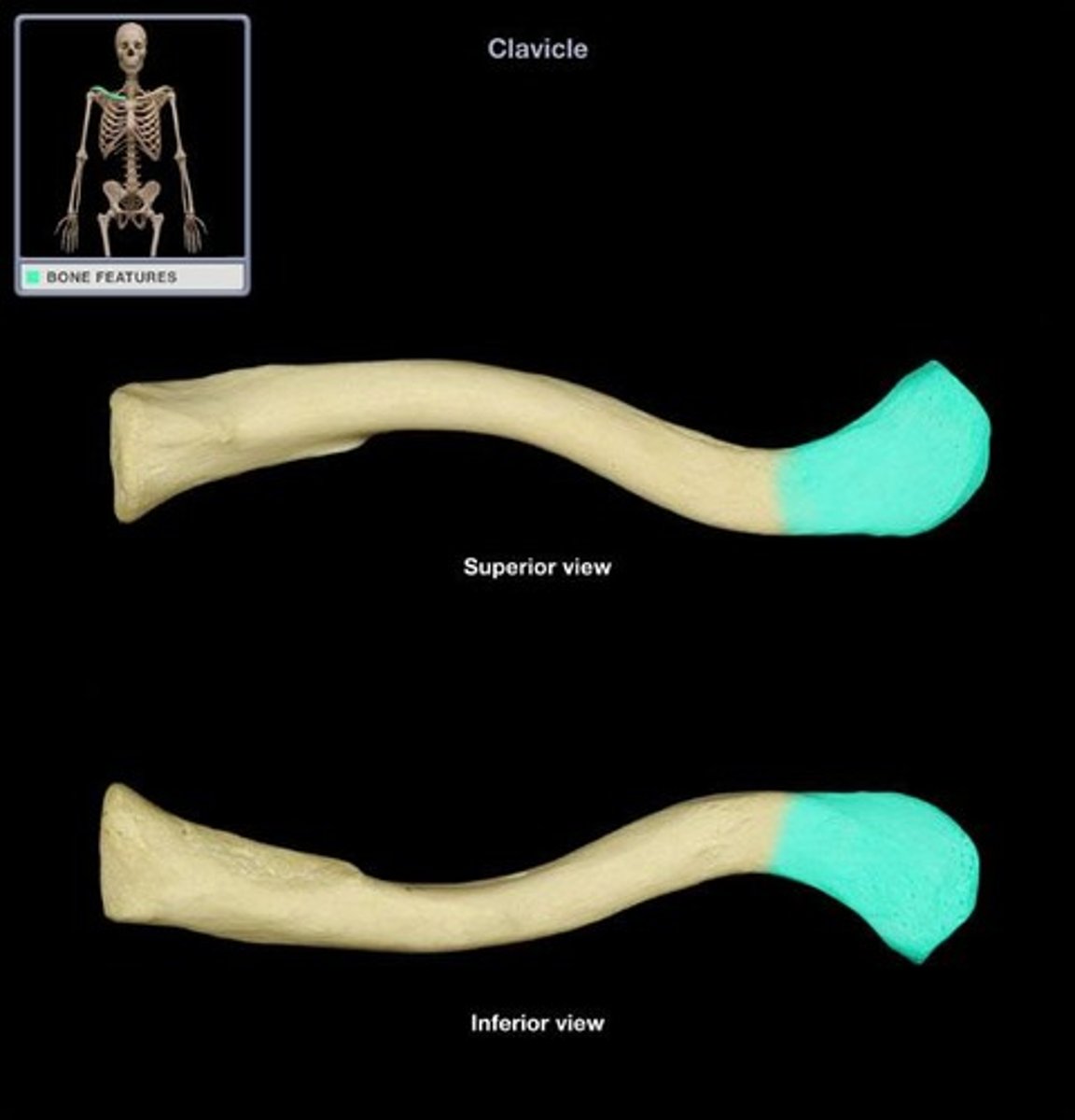
Sternal extremity
The end of the clavicle that articulates with the sternum.
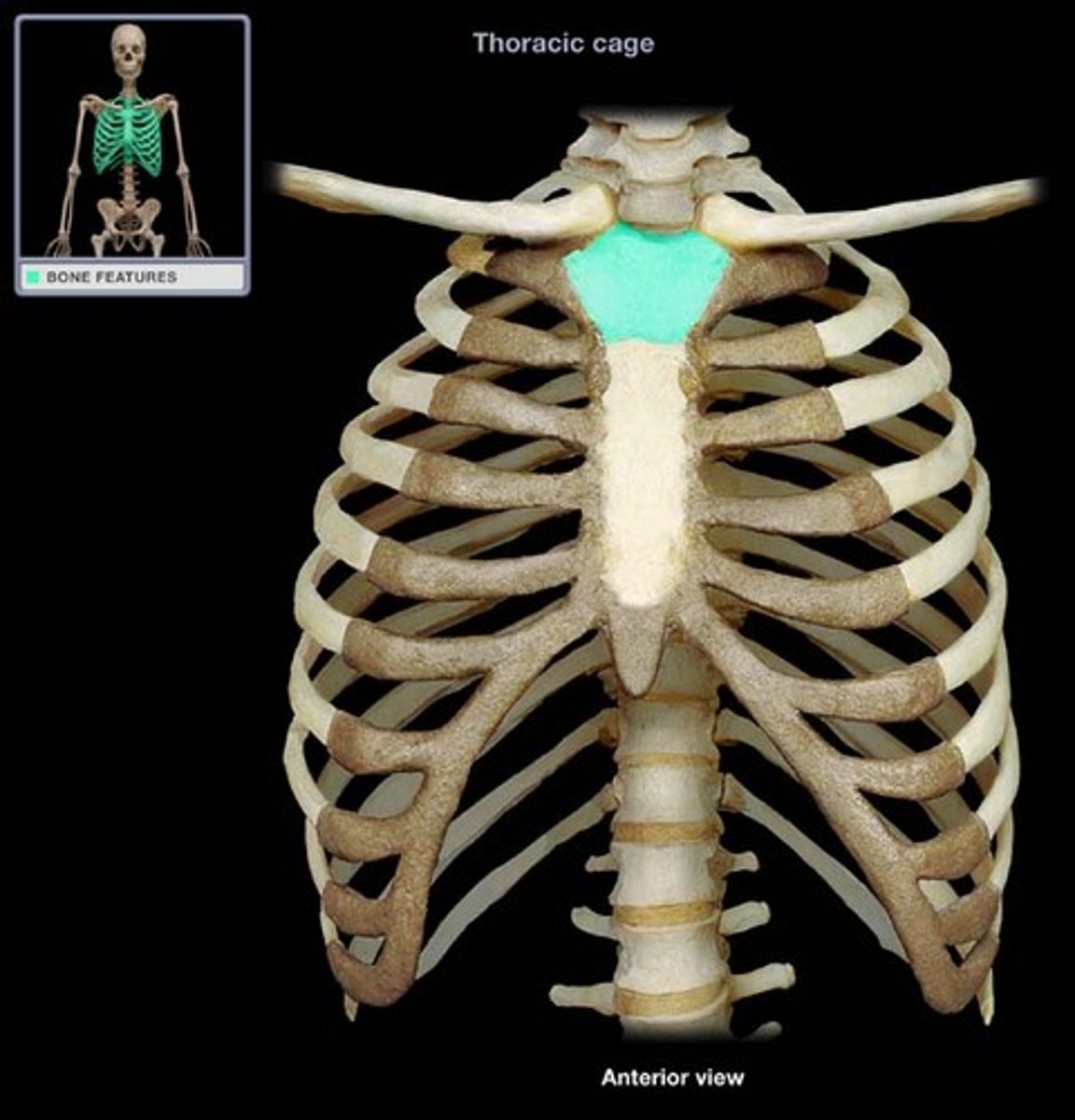
Sternum
The breastbone located in the center of the chest.

Manubrium
The upper part of the sternum.
Body of sternum
The central part of the sternum.
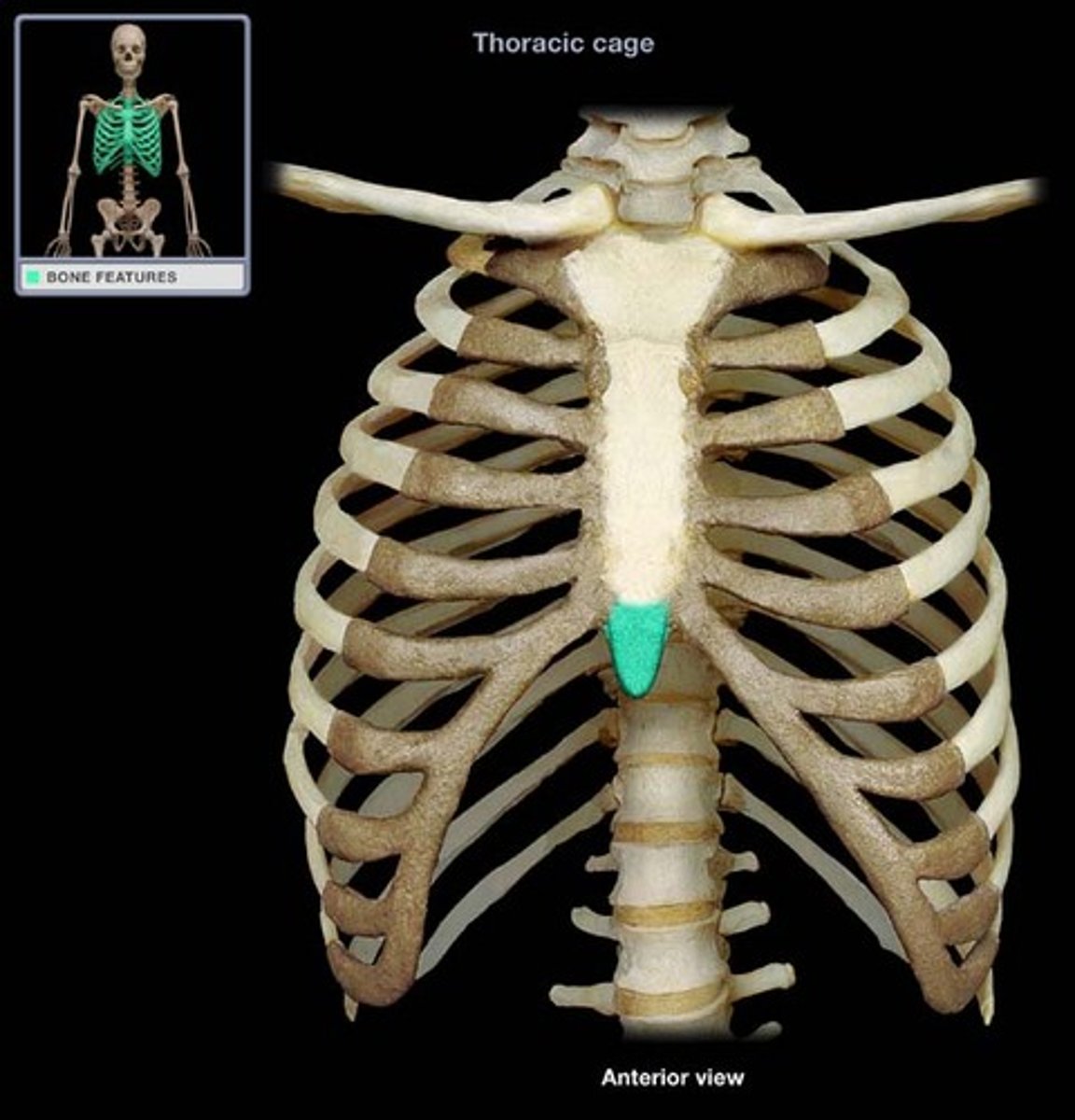
Xiphoid process
The small, cartilaginous extension at the lower end of the sternum.
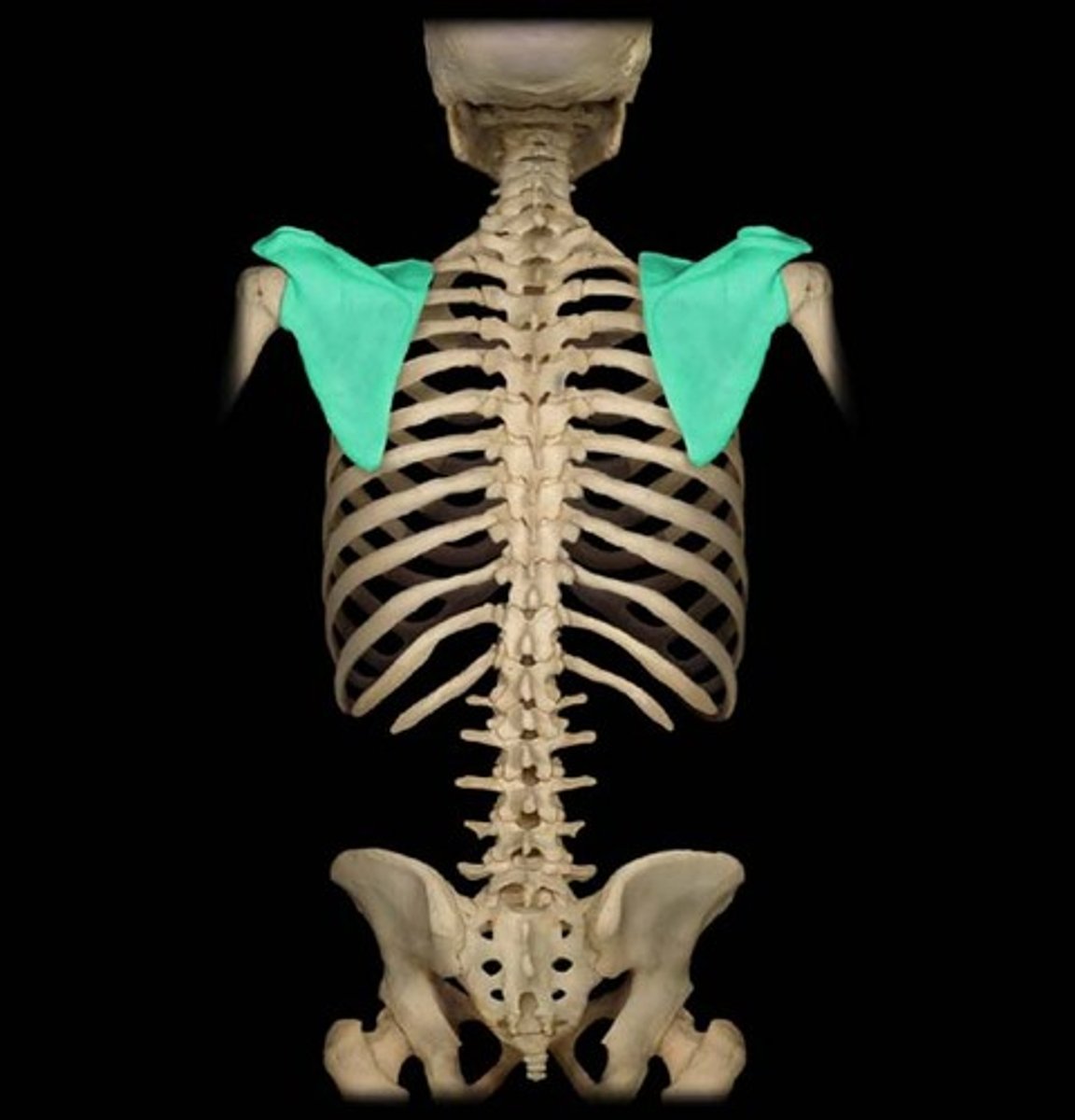
Scapula
The shoulder blade, a flat bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle.
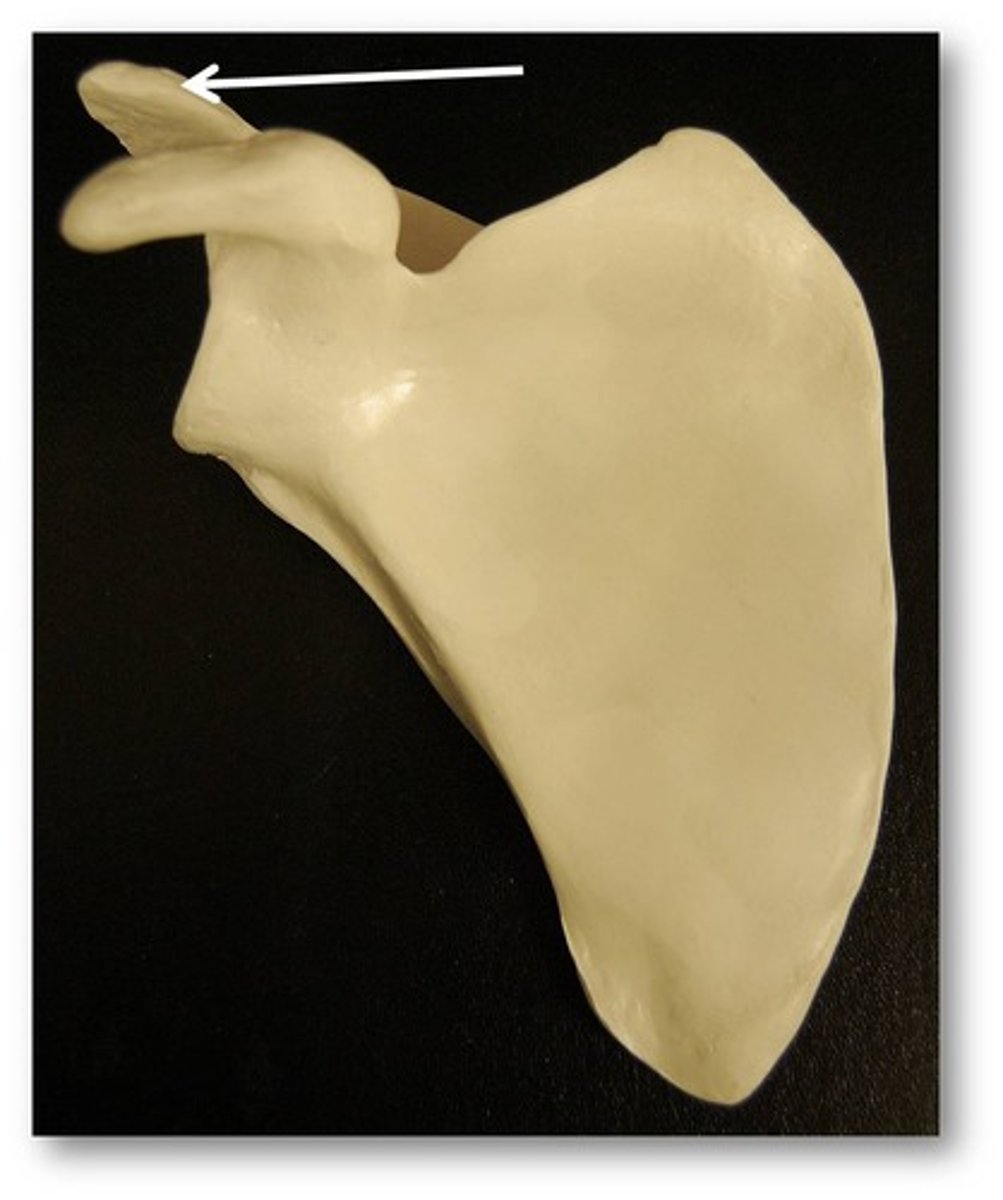
Coracoid process
A small hook-like structure on the scapula for muscle attachment.
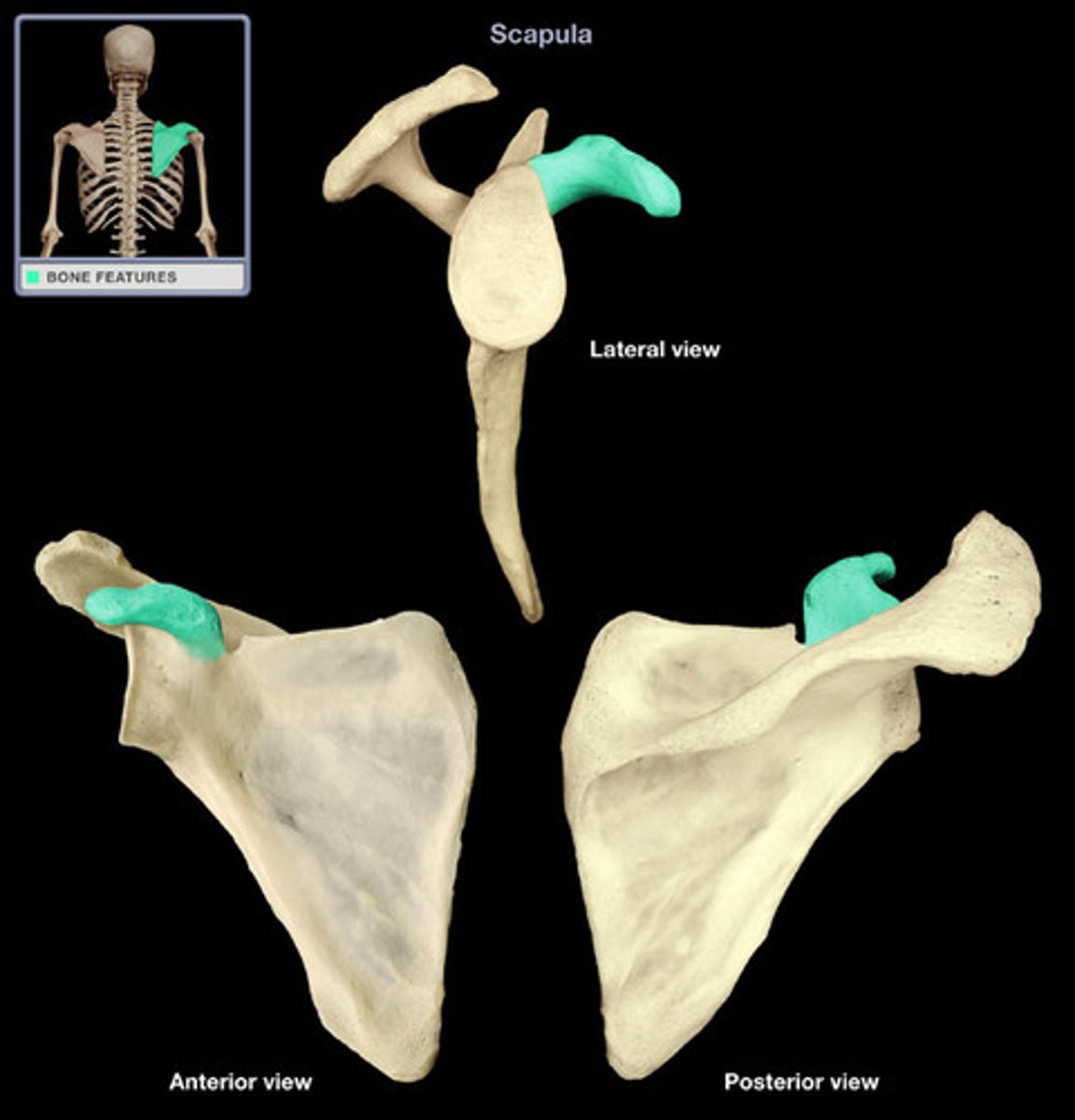
Acromion process
The bony process on the scapula that forms the highest point of the shoulder.
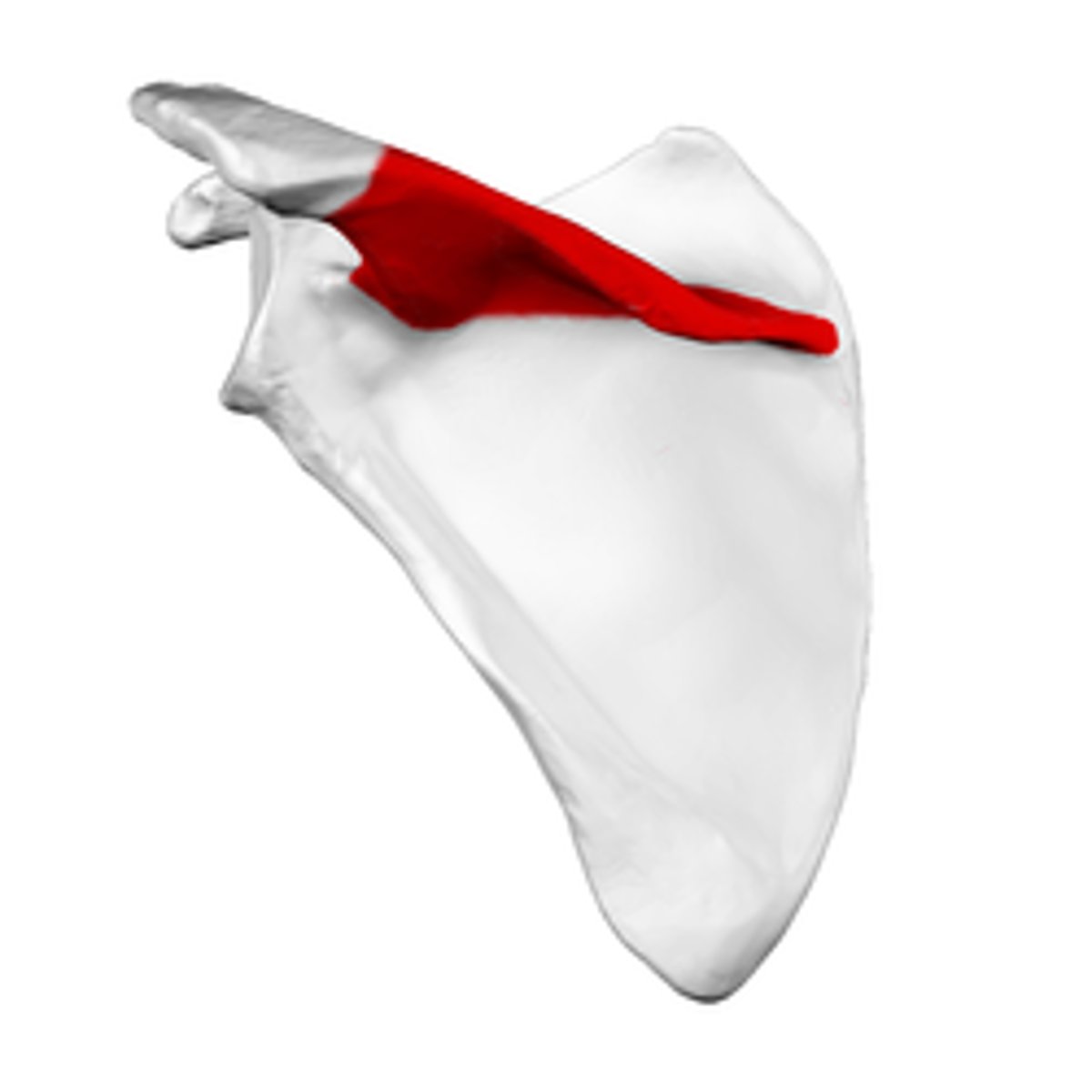
Spine of scapula
The prominent ridge on the posterior surface of the scapula.
Glenoid cavity
The shallow socket in the scapula that articulates with the head of the humerus.

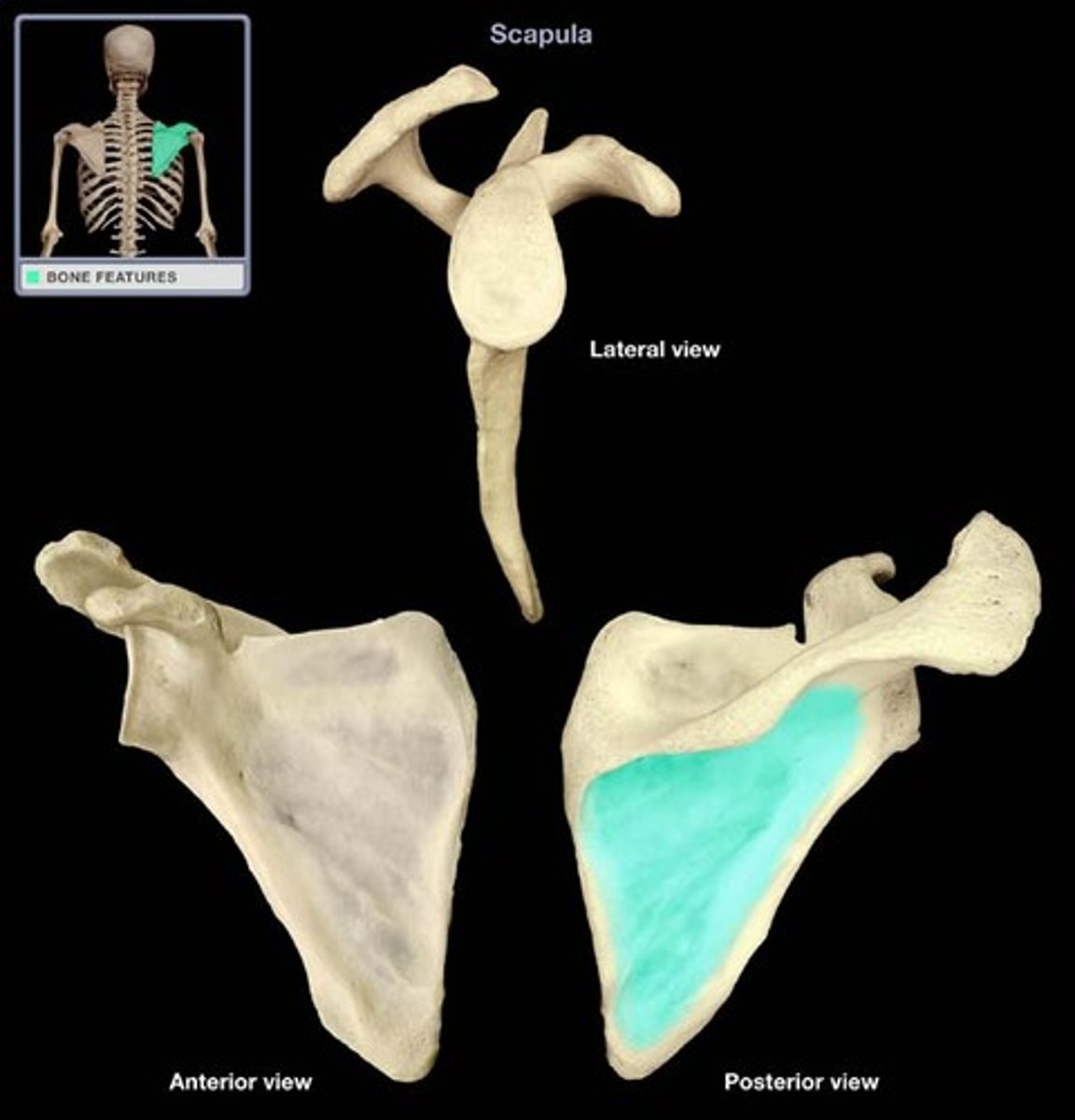
Infraspinous fossa
The depression below the spine of the scapula.
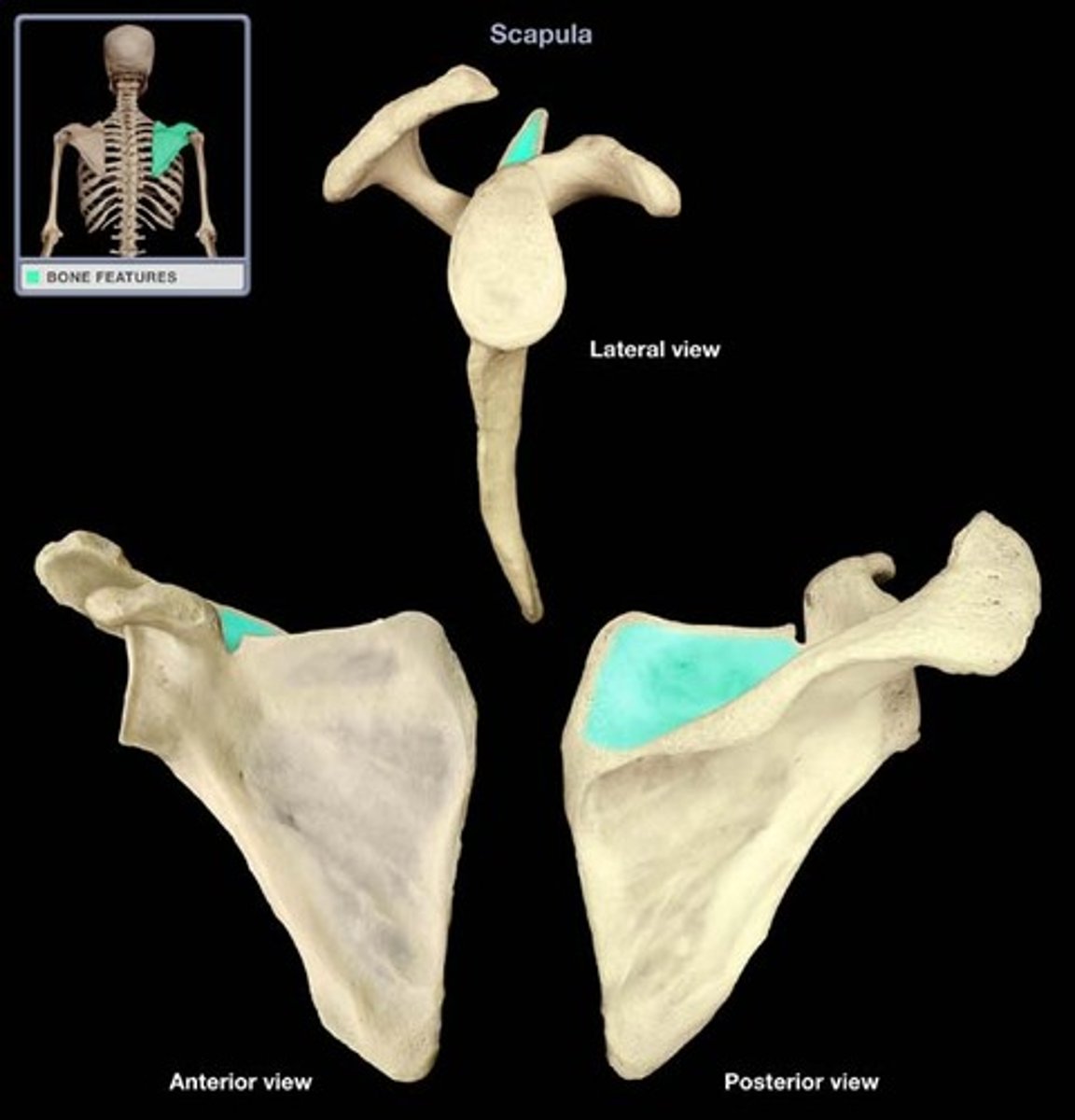
Supraspinous fossa
The depression above the spine of the scapula.
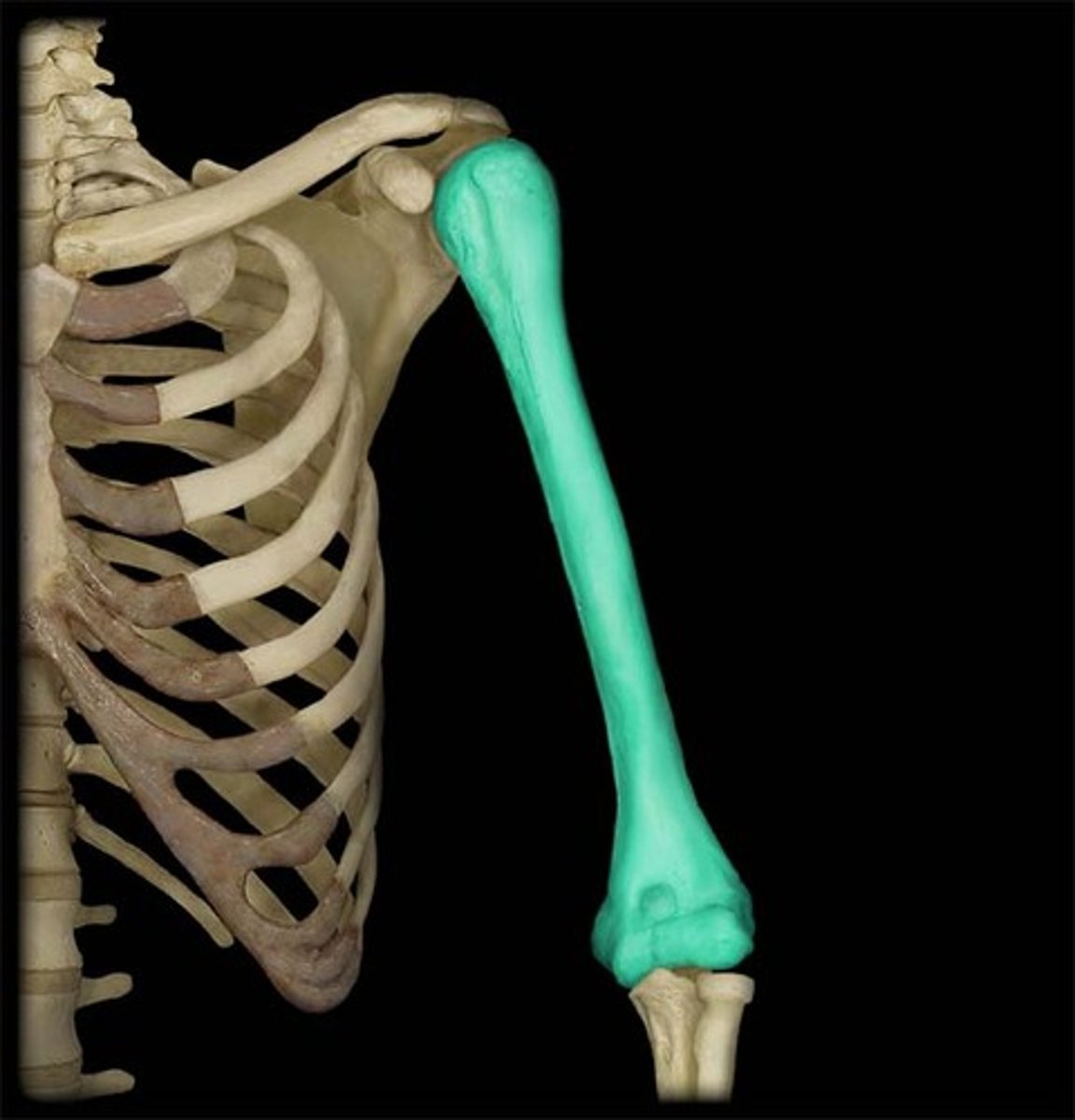
Humerus
The long bone of the upper arm.
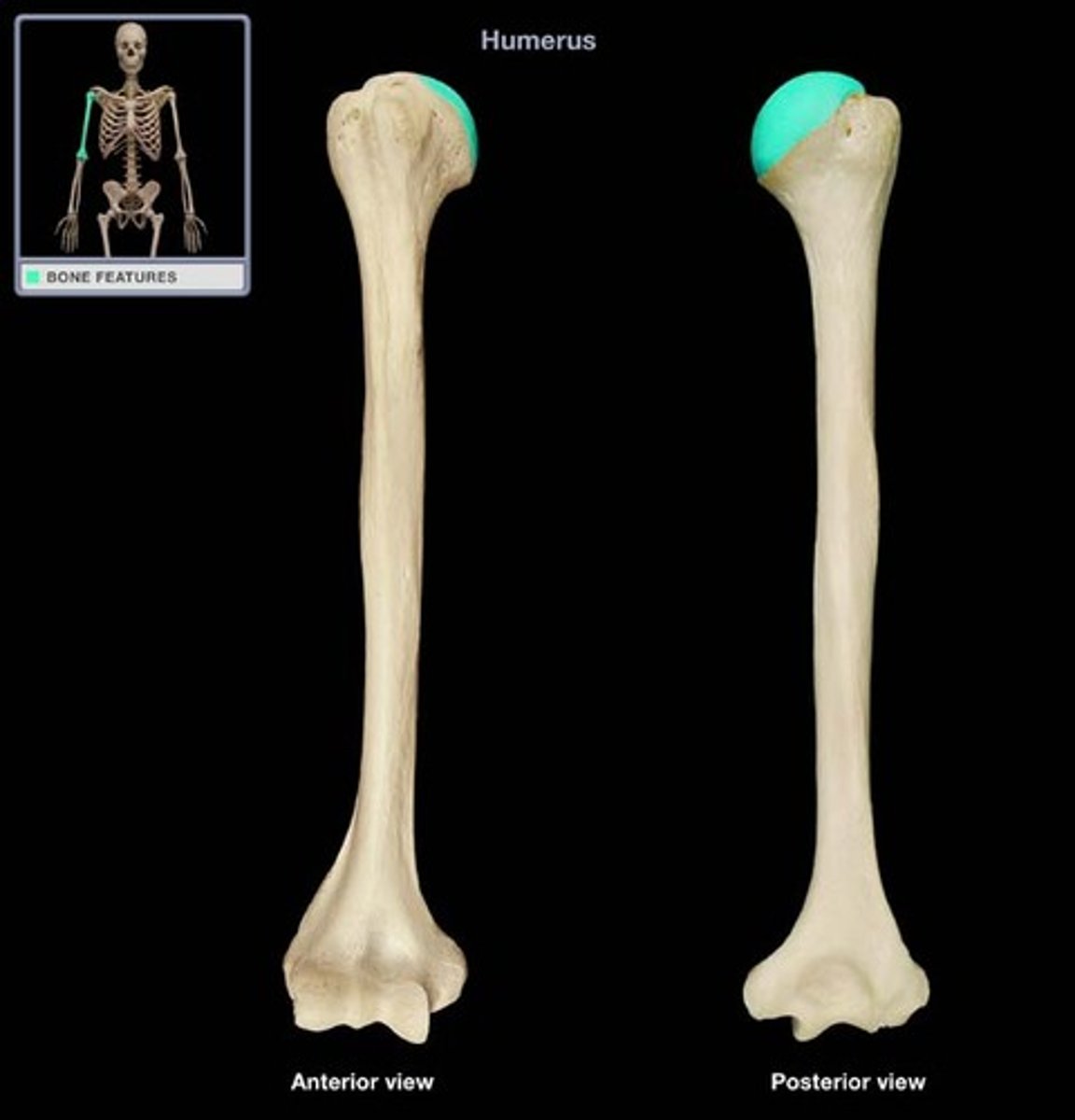
Head of humerus
The rounded proximal end of the humerus that fits into the glenoid cavity.
Olecranon fossa
The depression on the posterior side of the humerus that accommodates the olecranon of the ulna.
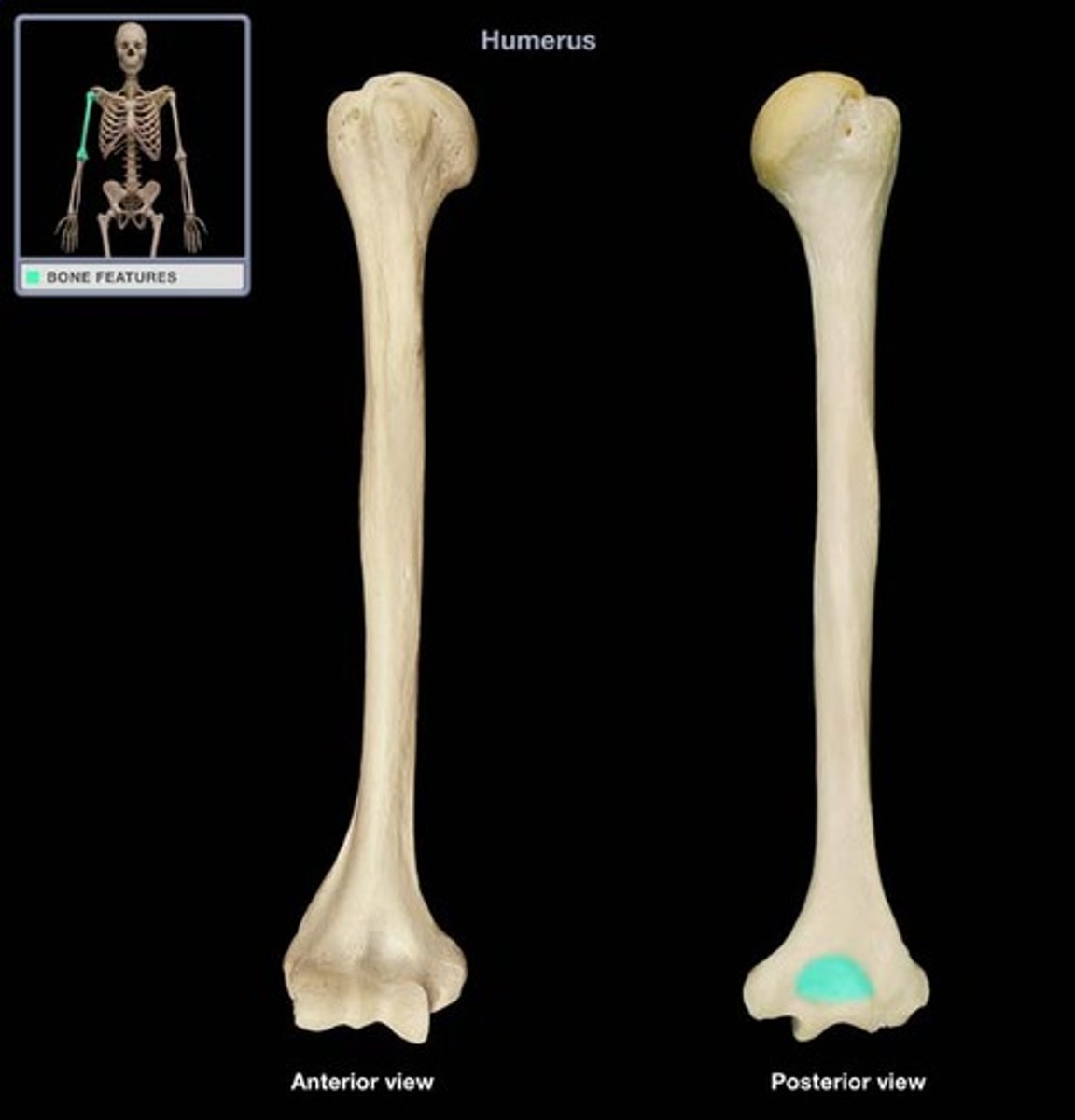
Lateral epicondyle
The bony prominence on the outer side of the distal humerus.
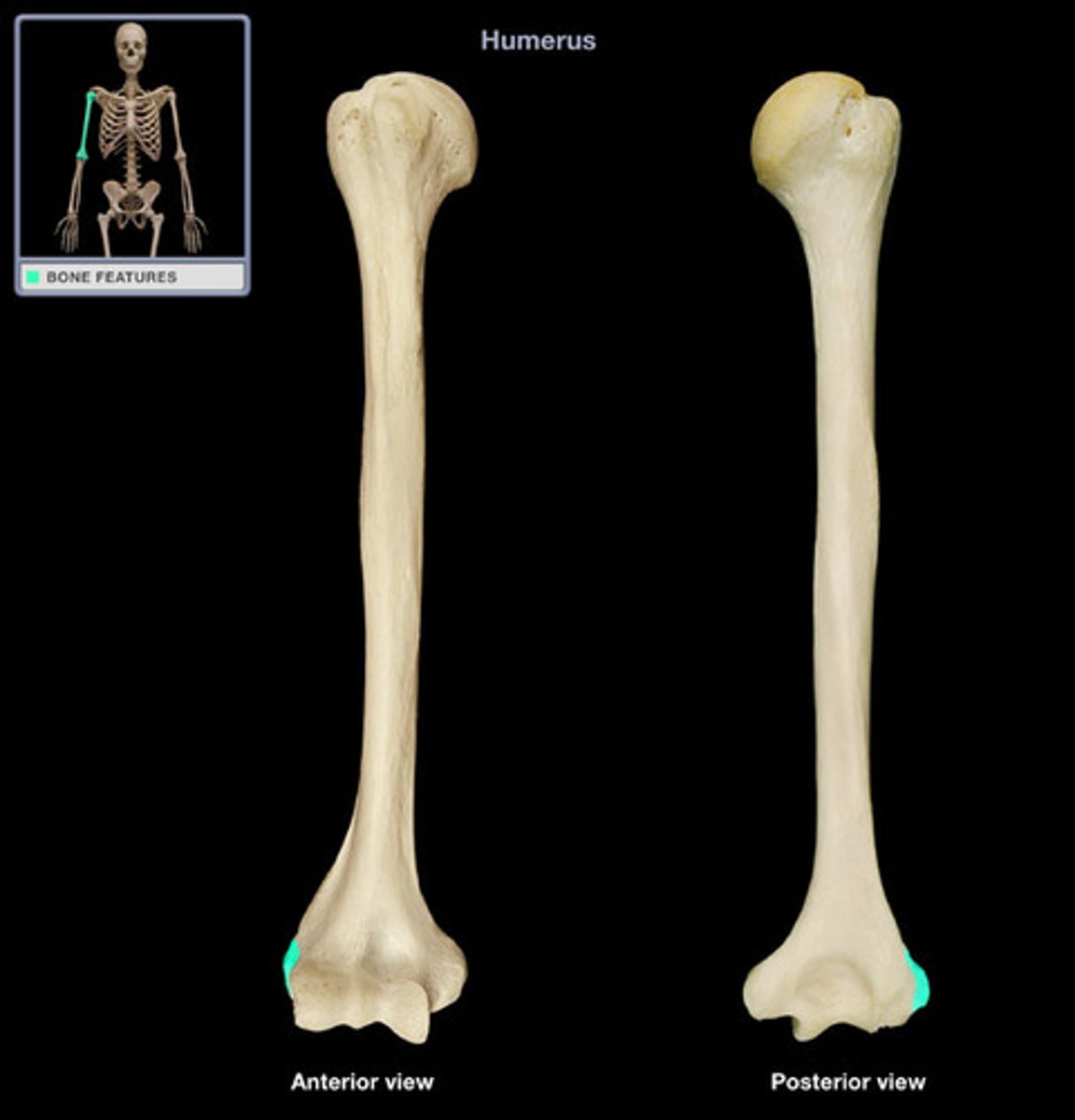
Medial epicondyle
The bony prominence on the inner side of the distal humerus.
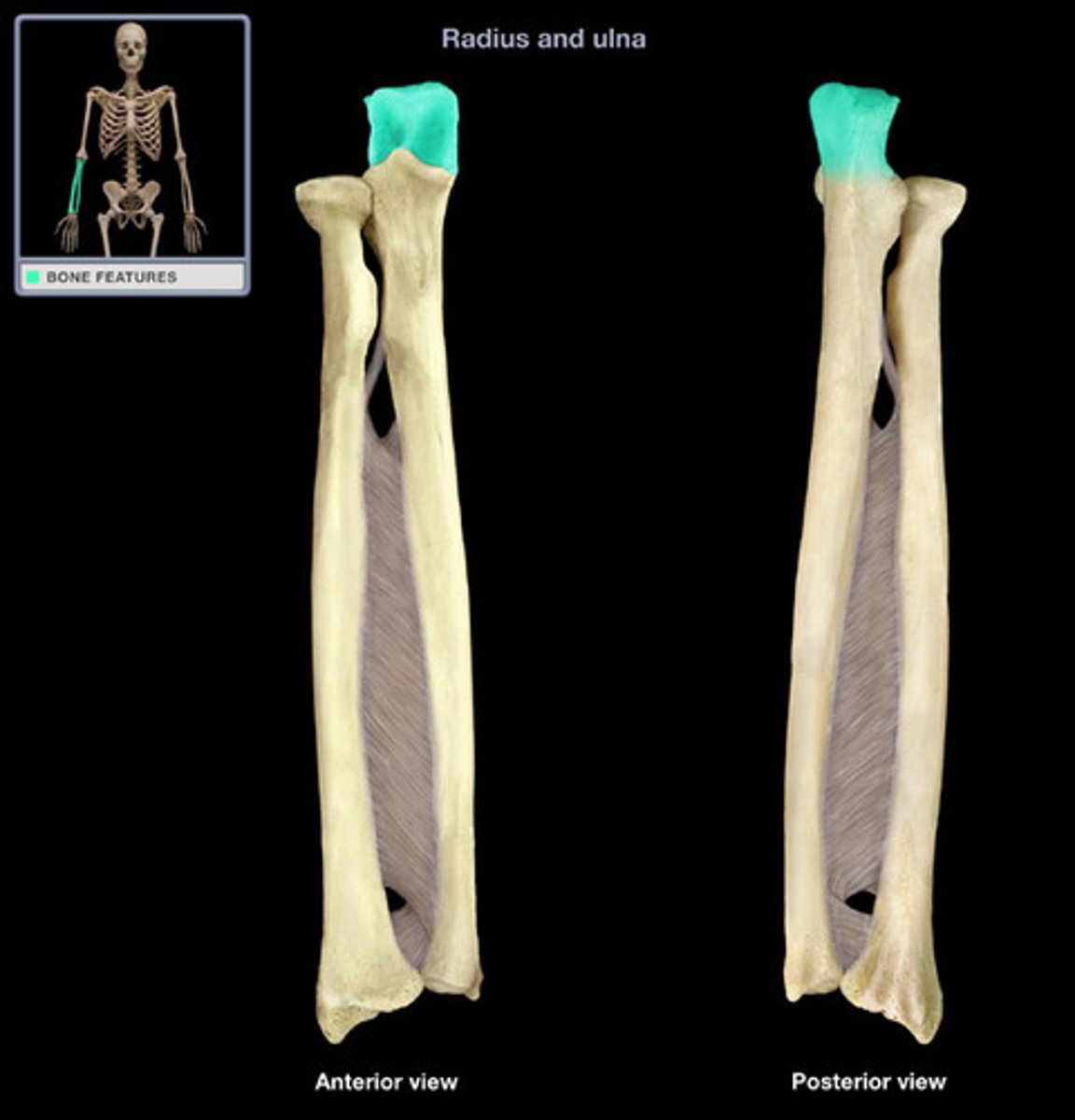
Ulna
The inner and larger bone of the forearm.
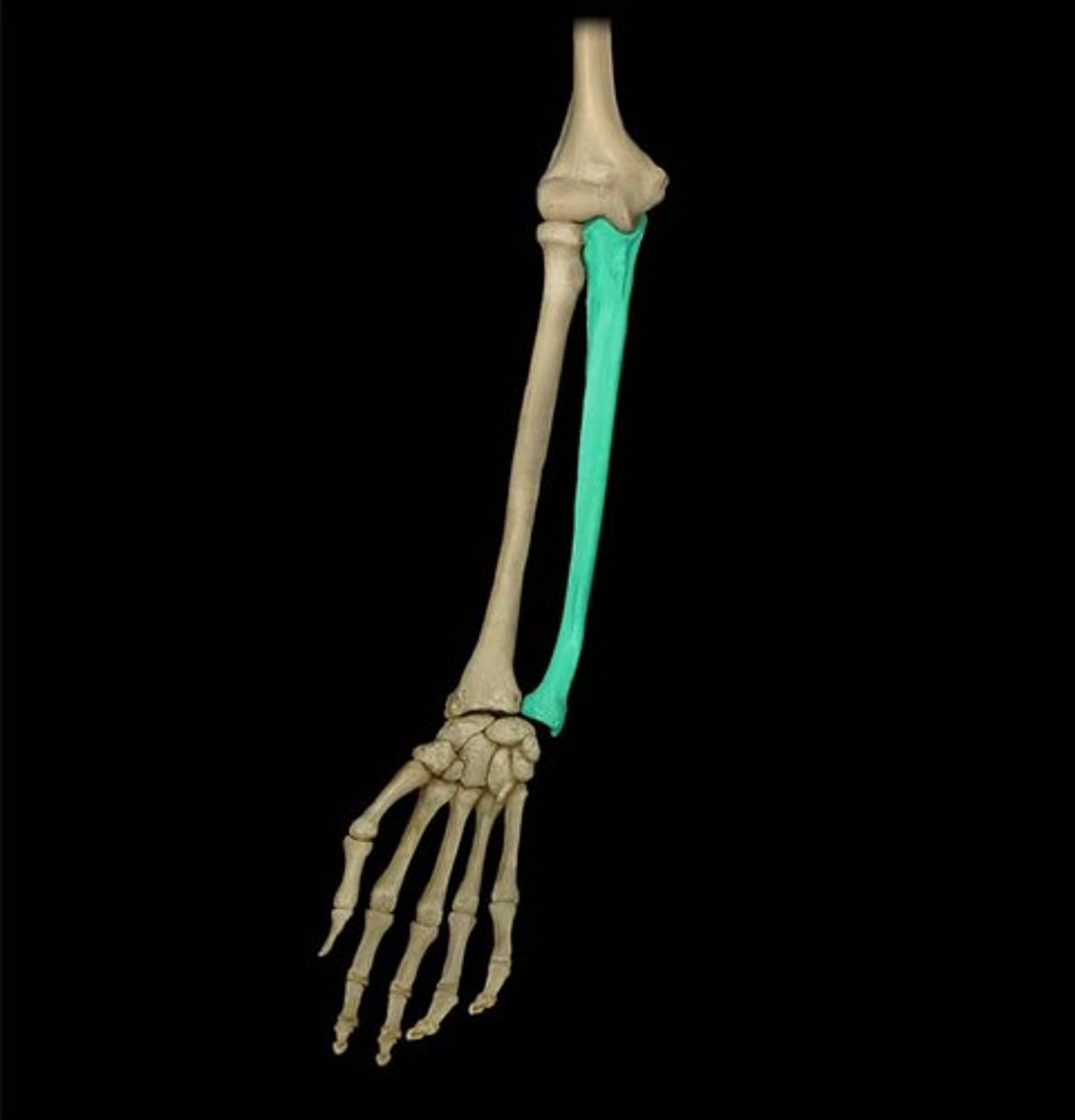
Olecranon process
The bony prominence of the ulna that forms the elbow.
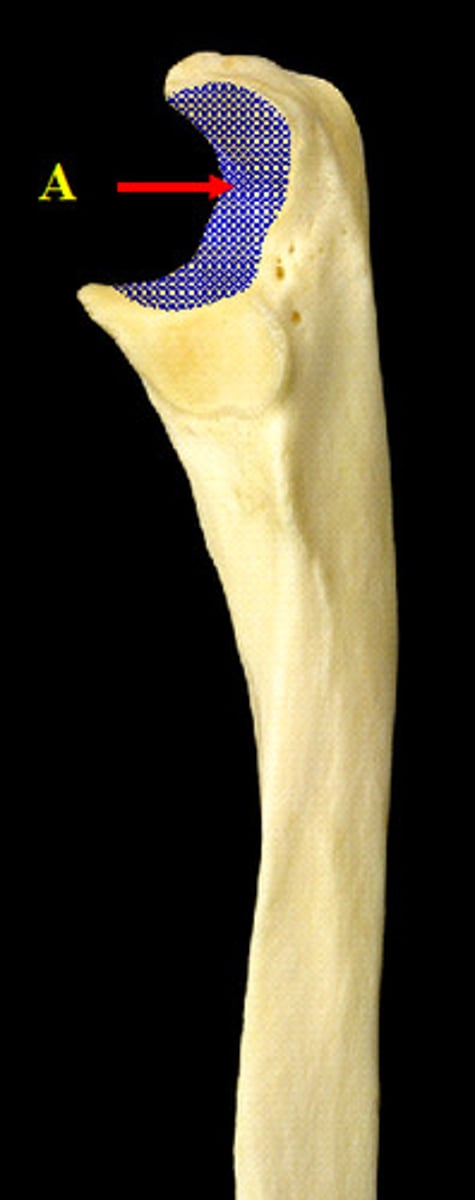
Trochlear notch
The curved area of the ulna that articulates with the humerus.
Coronoid process
The projection on the ulna that fits into the coronoid fossa of the humerus.

Styloid process of ulna
The pointed projection at the distal end of the ulna.
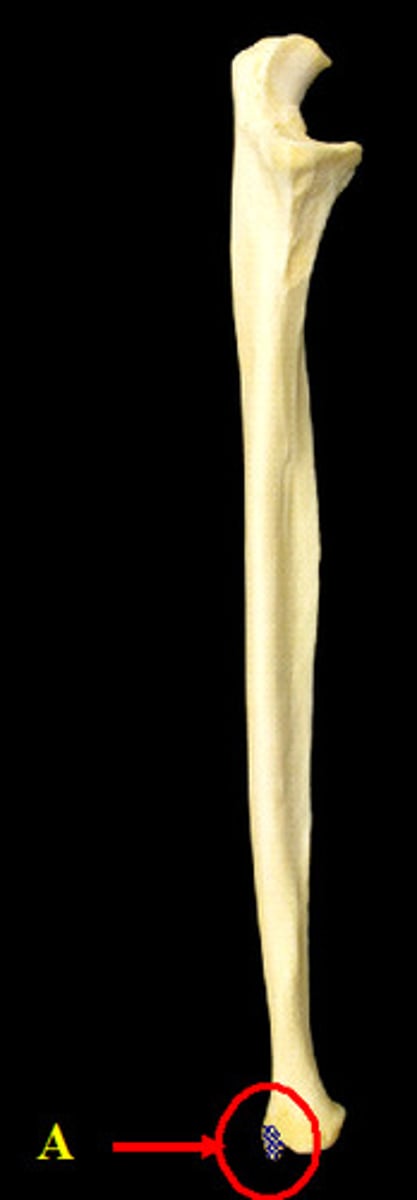
Radial tuberosity
The bony prominence on the radius for muscle attachment.
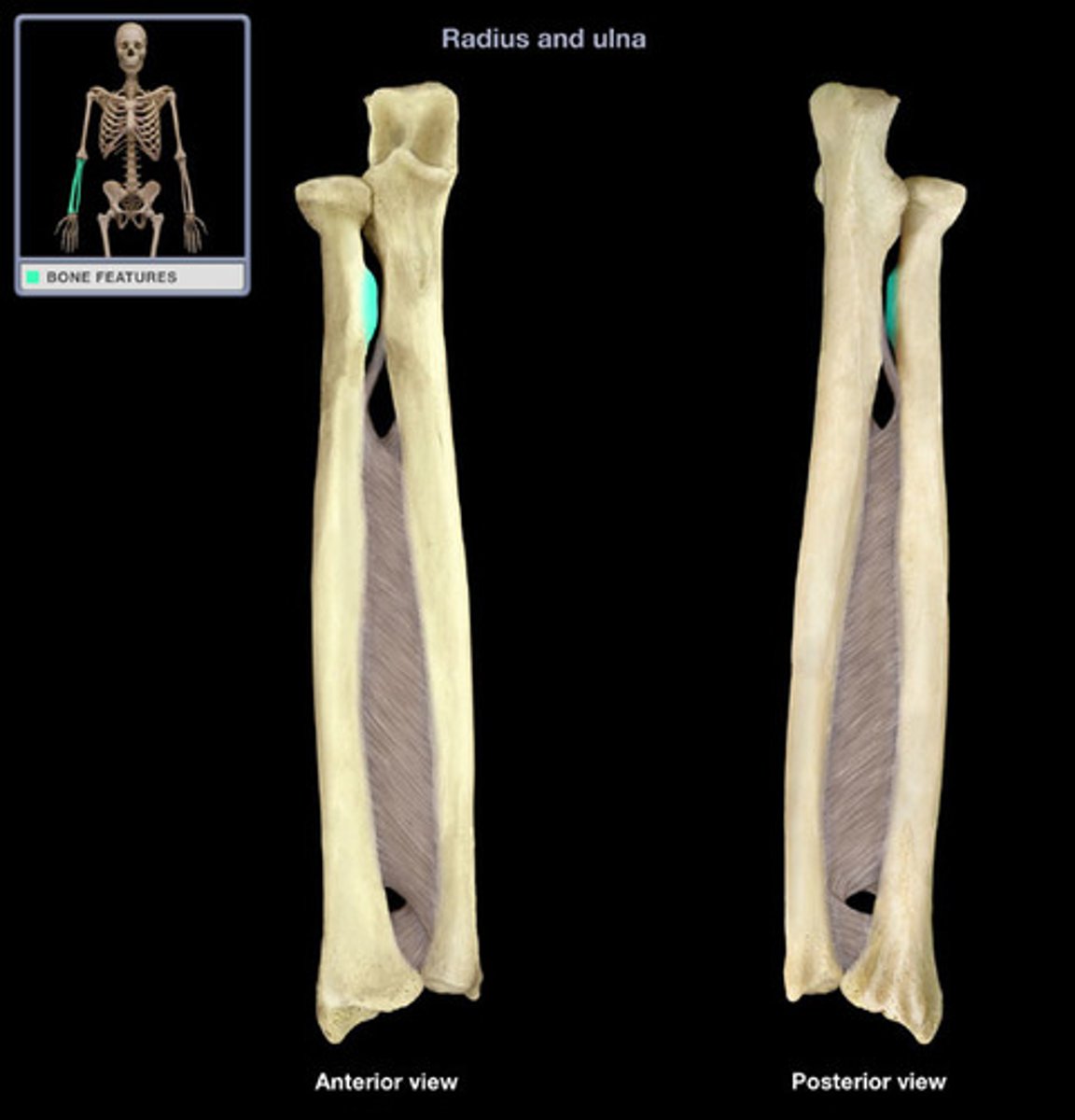
Radius
The outer and shorter bone of the forearm.
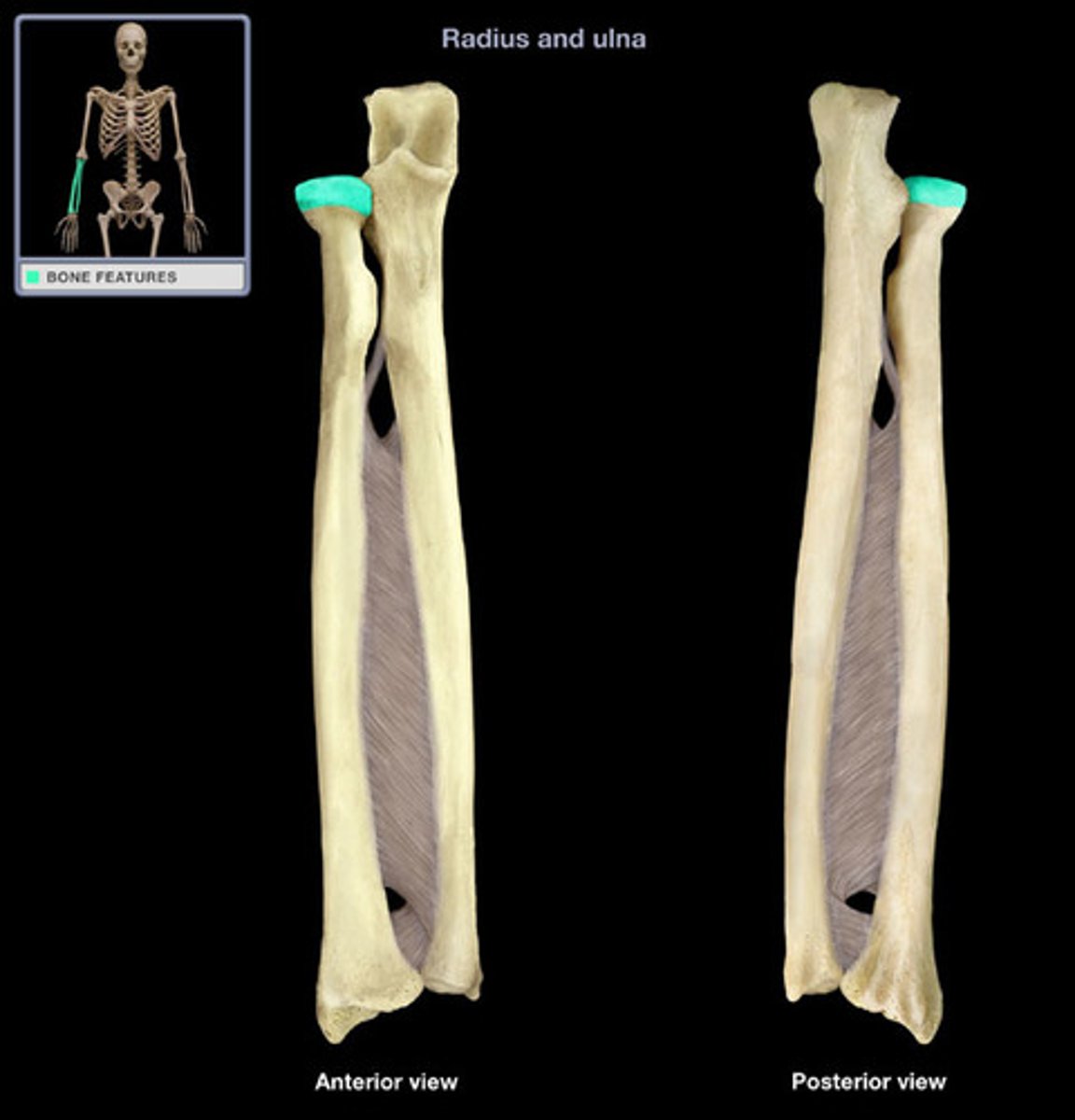
Head of radius
The rounded proximal end of the radius that articulates with the humerus.
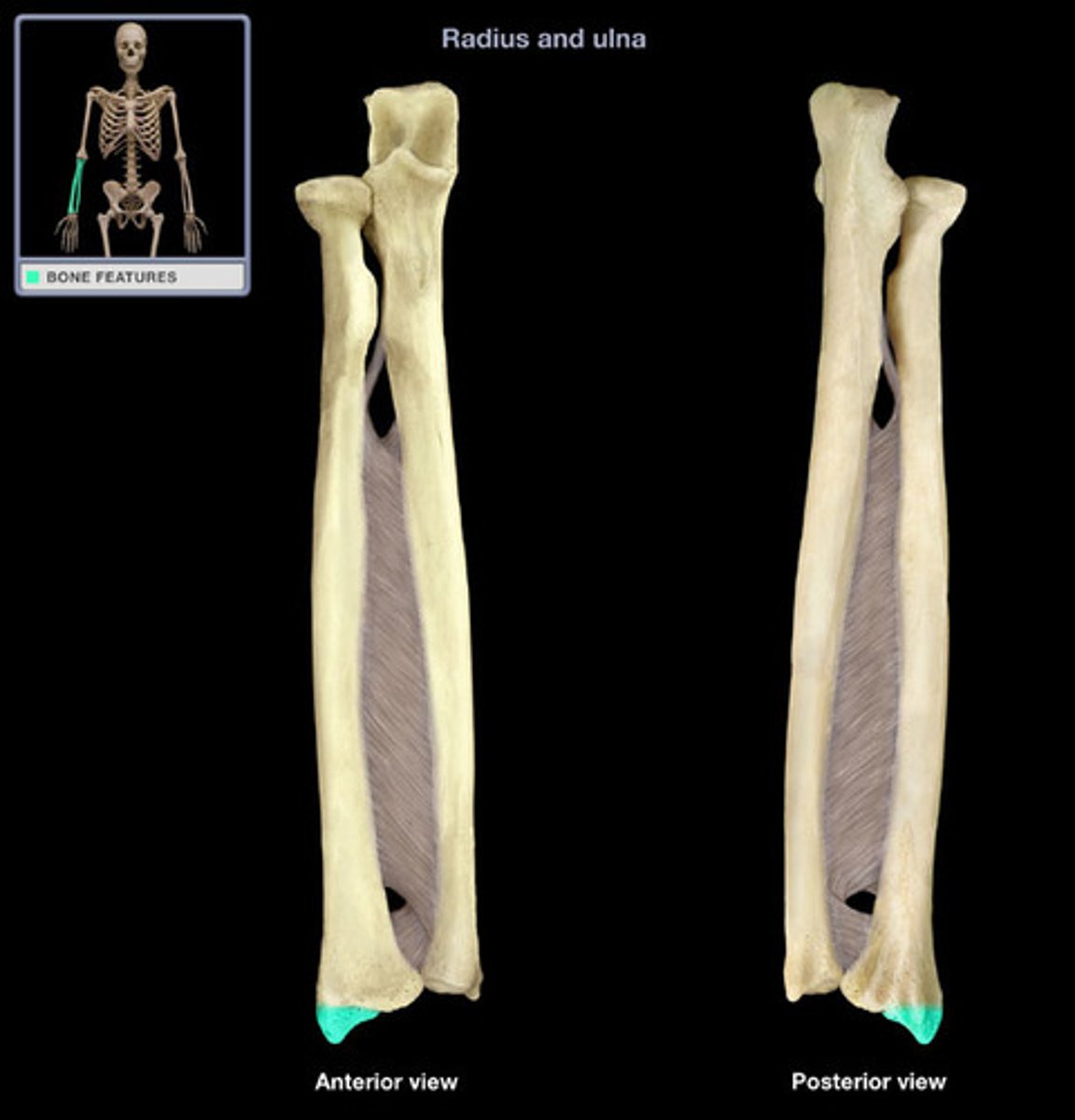
Styloid process of radius
The pointed projection at the distal end of the radius.
Hand bones
The bones of the hand, including carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges.
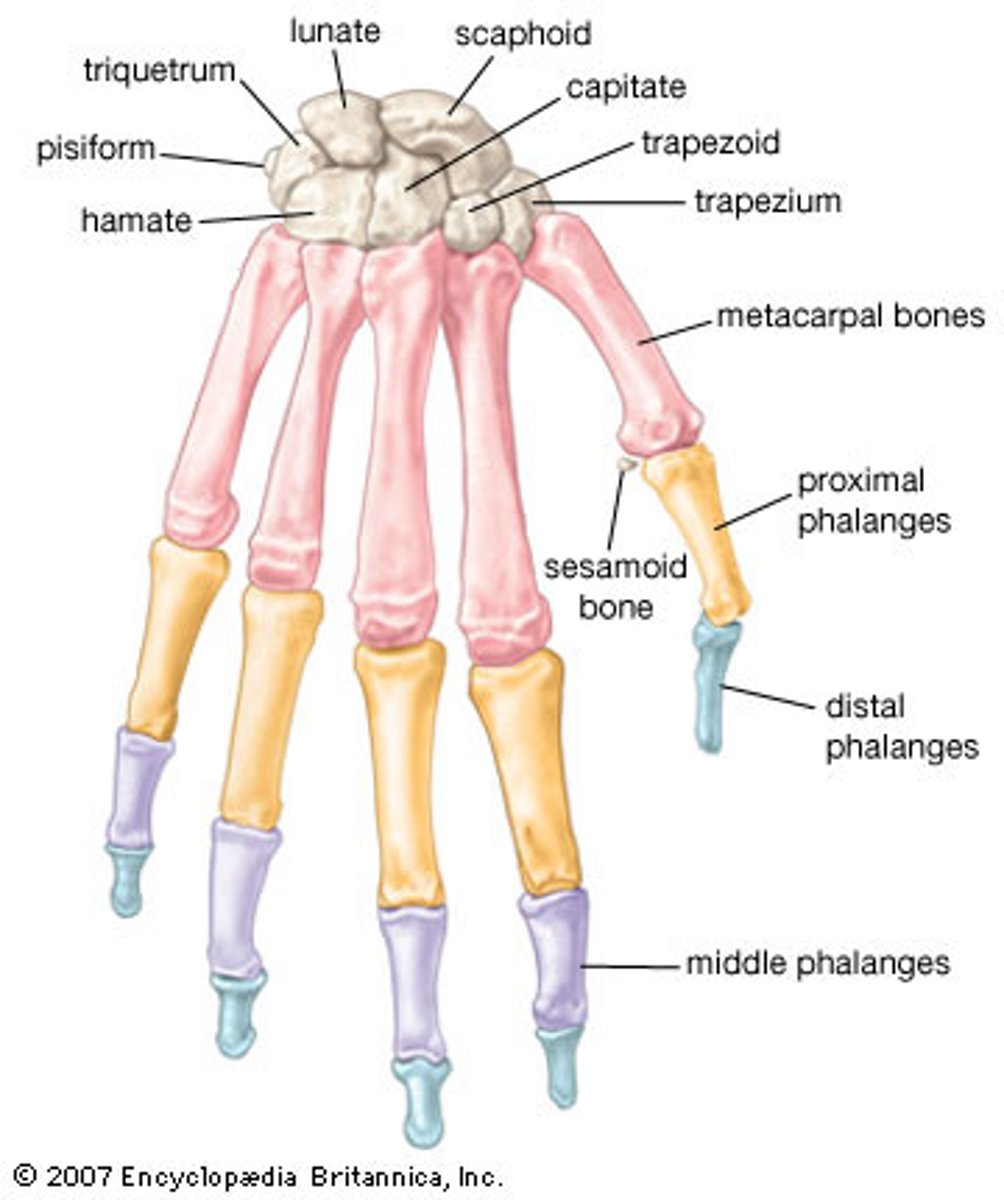
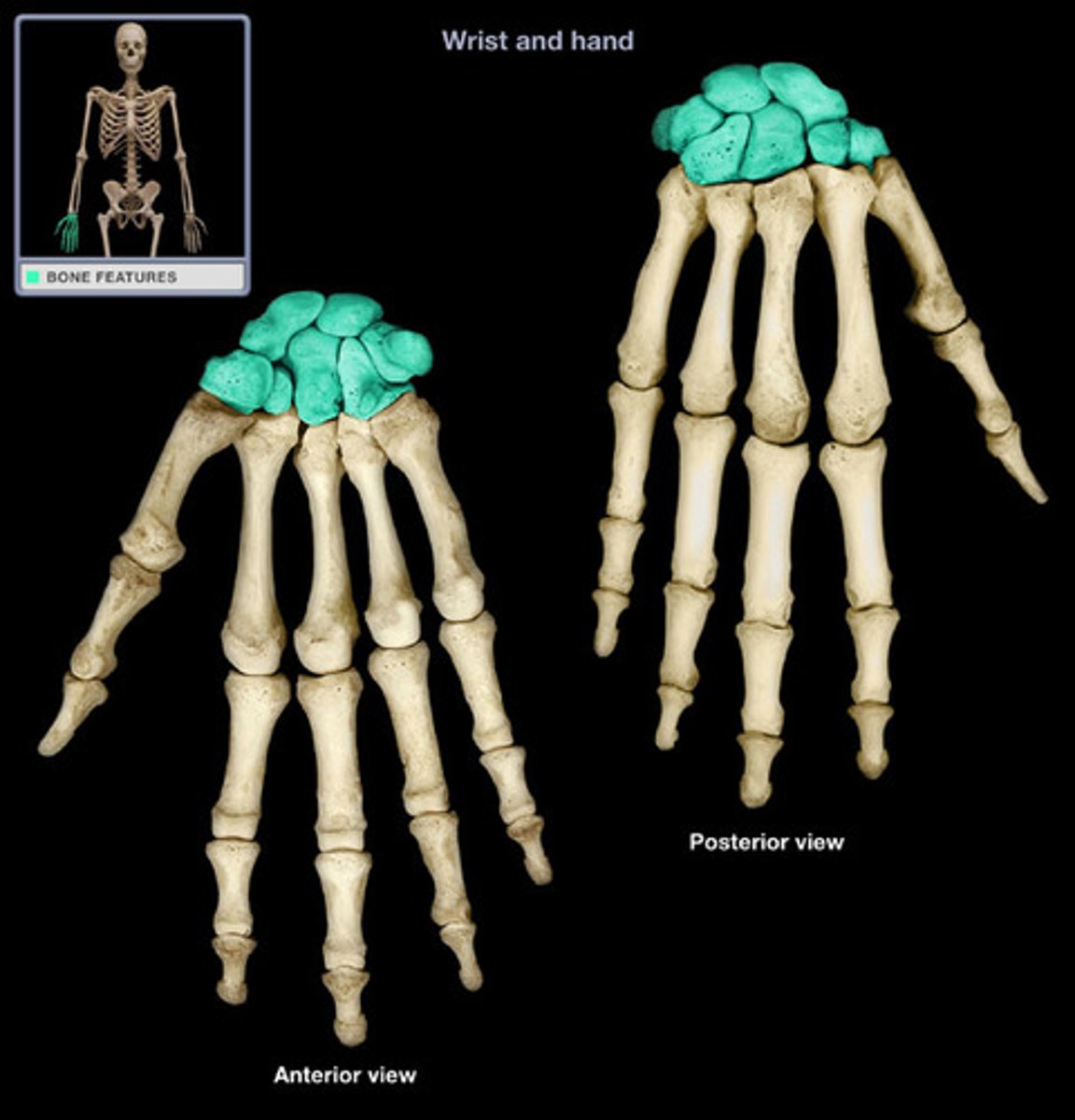
Carpals
The eight small bones that make up the wrist.
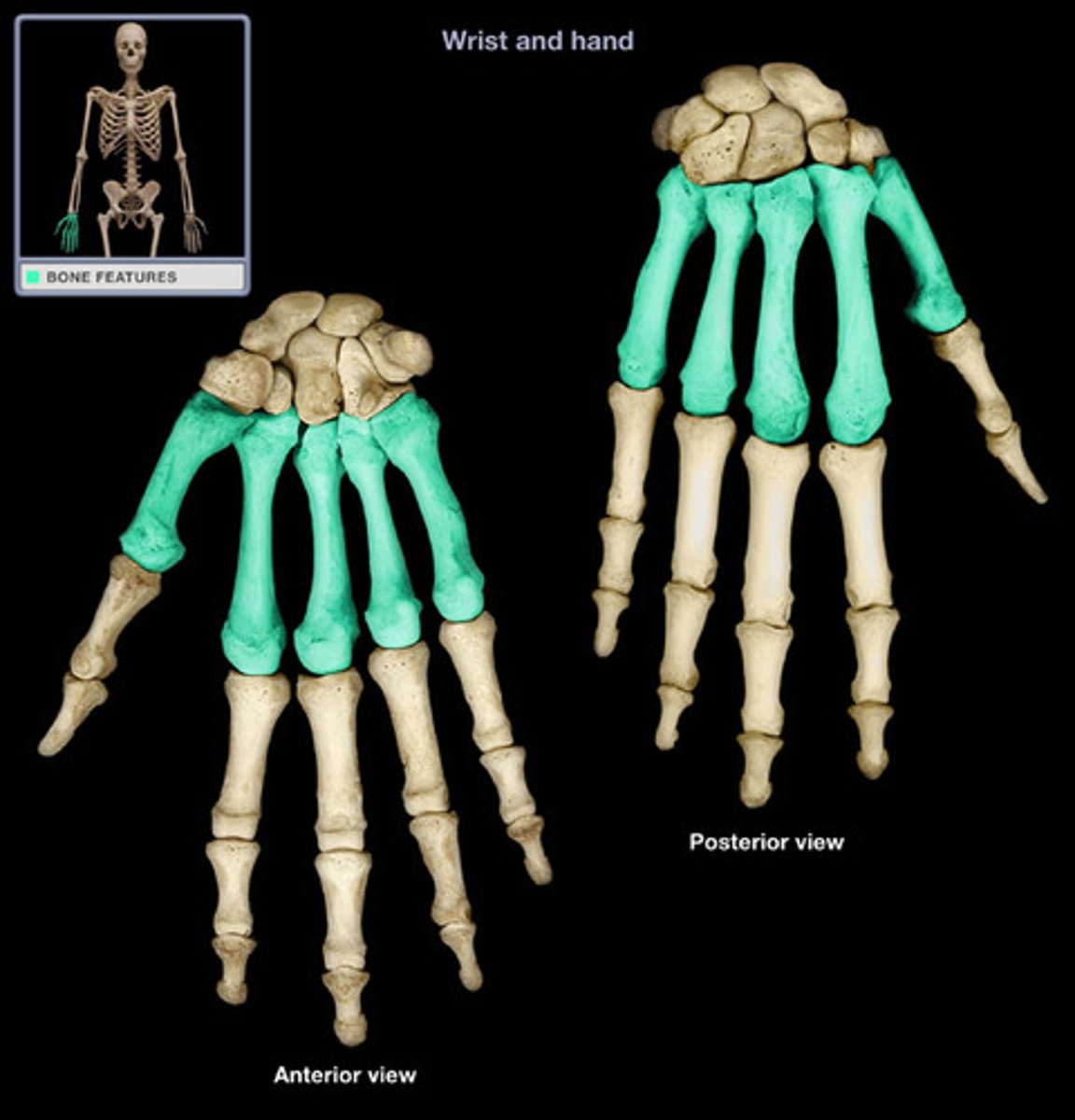
Metacarpals
The five bones that make up the middle part of the hand.
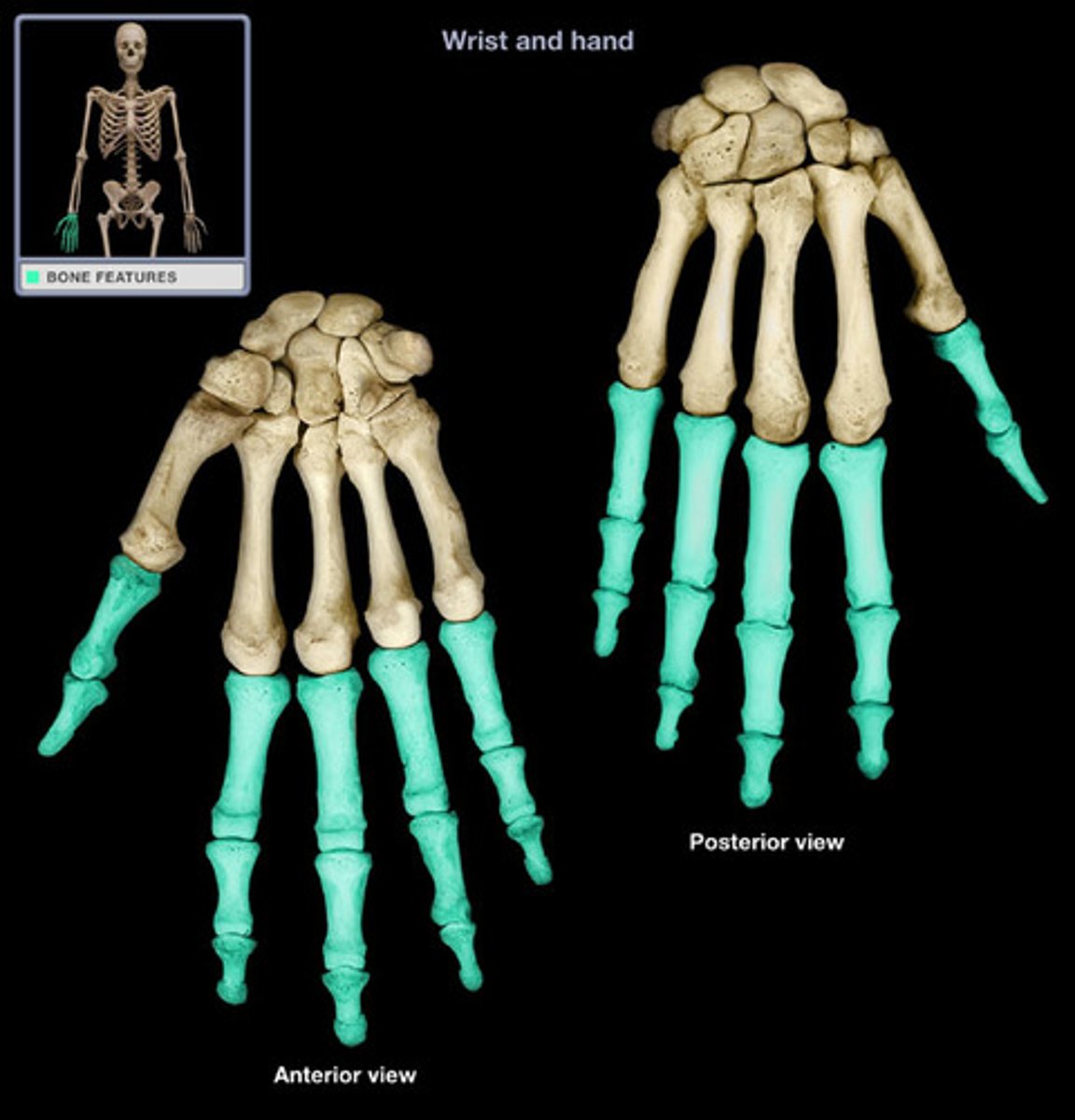
Phalanges
The bones of the fingers and toes.
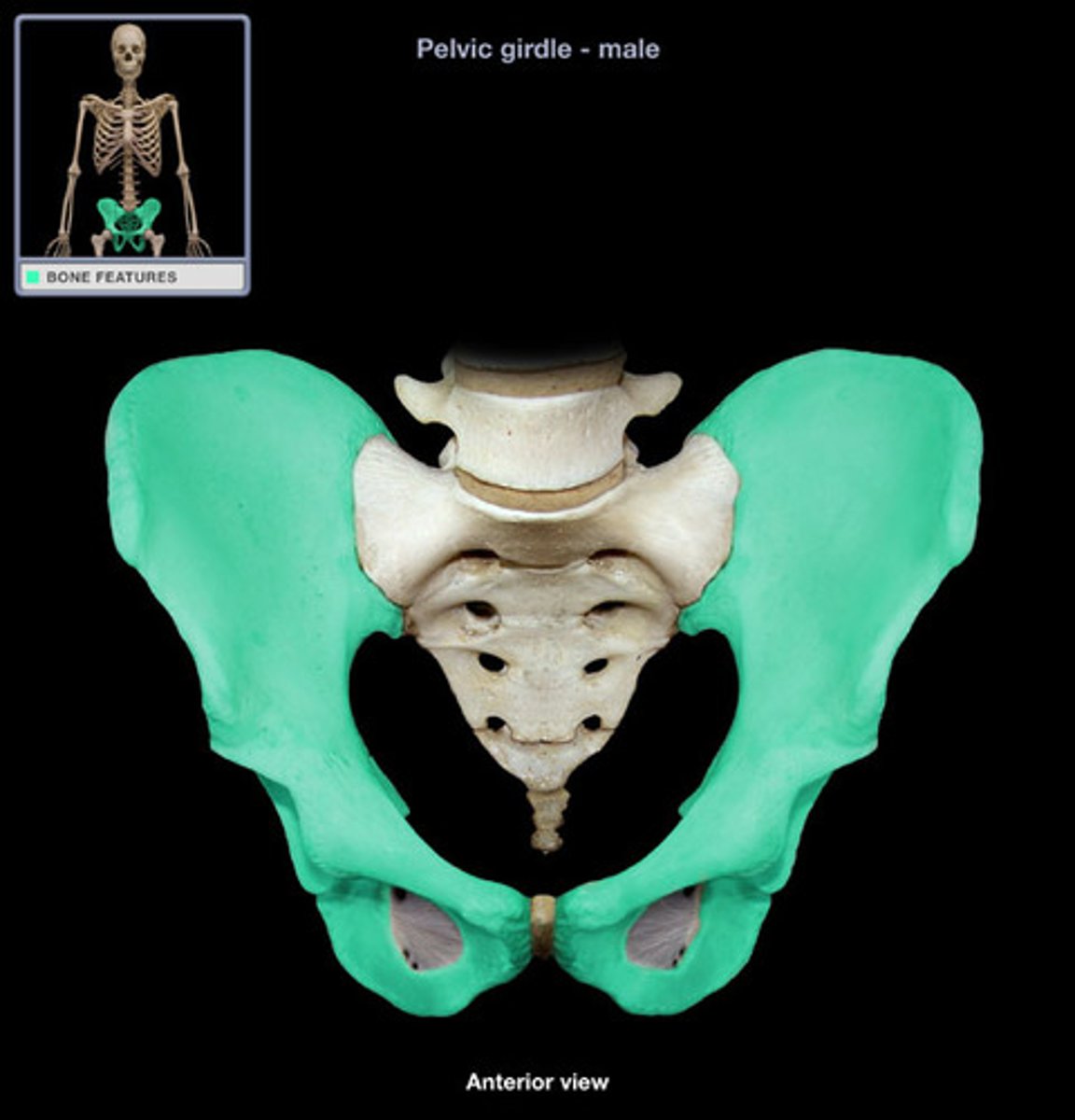
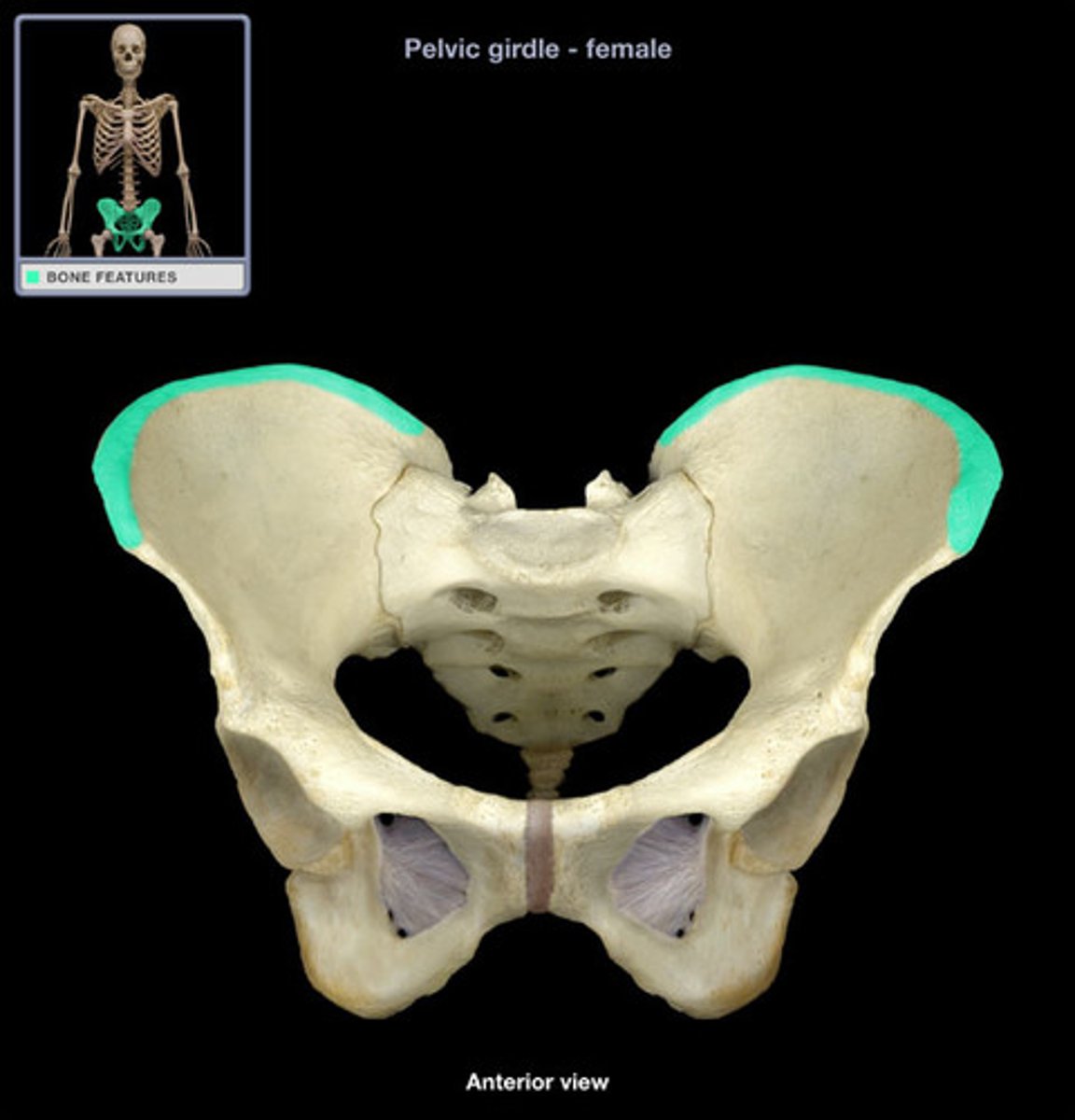
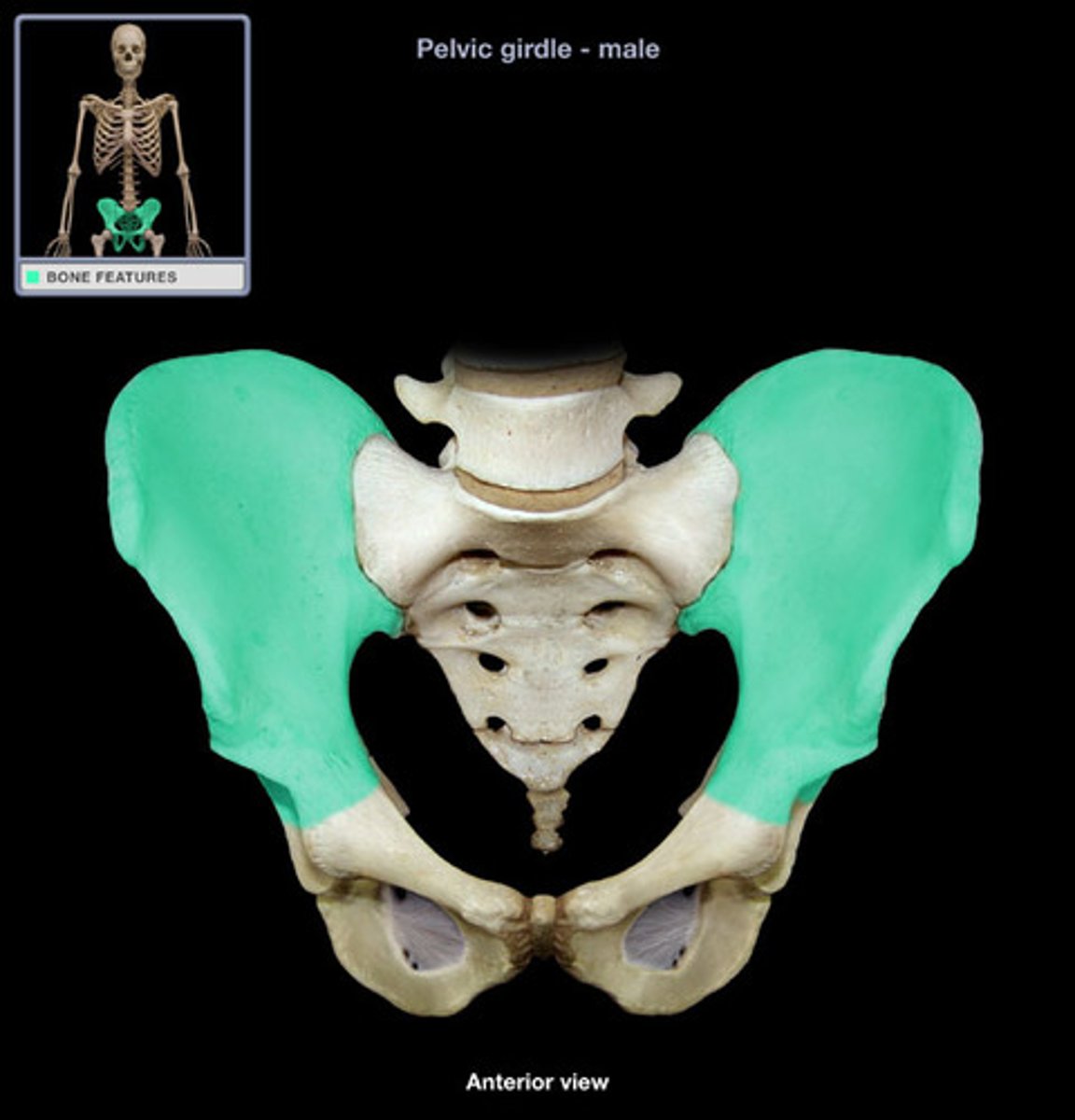
Os Coxa
The hip bone, formed by the fusion of the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
Iliac crest
The upper curved edge of the ilium.
Body of ilium
The large, flat part of the ilium.
Body of ischium
The lower part of the hip bone.
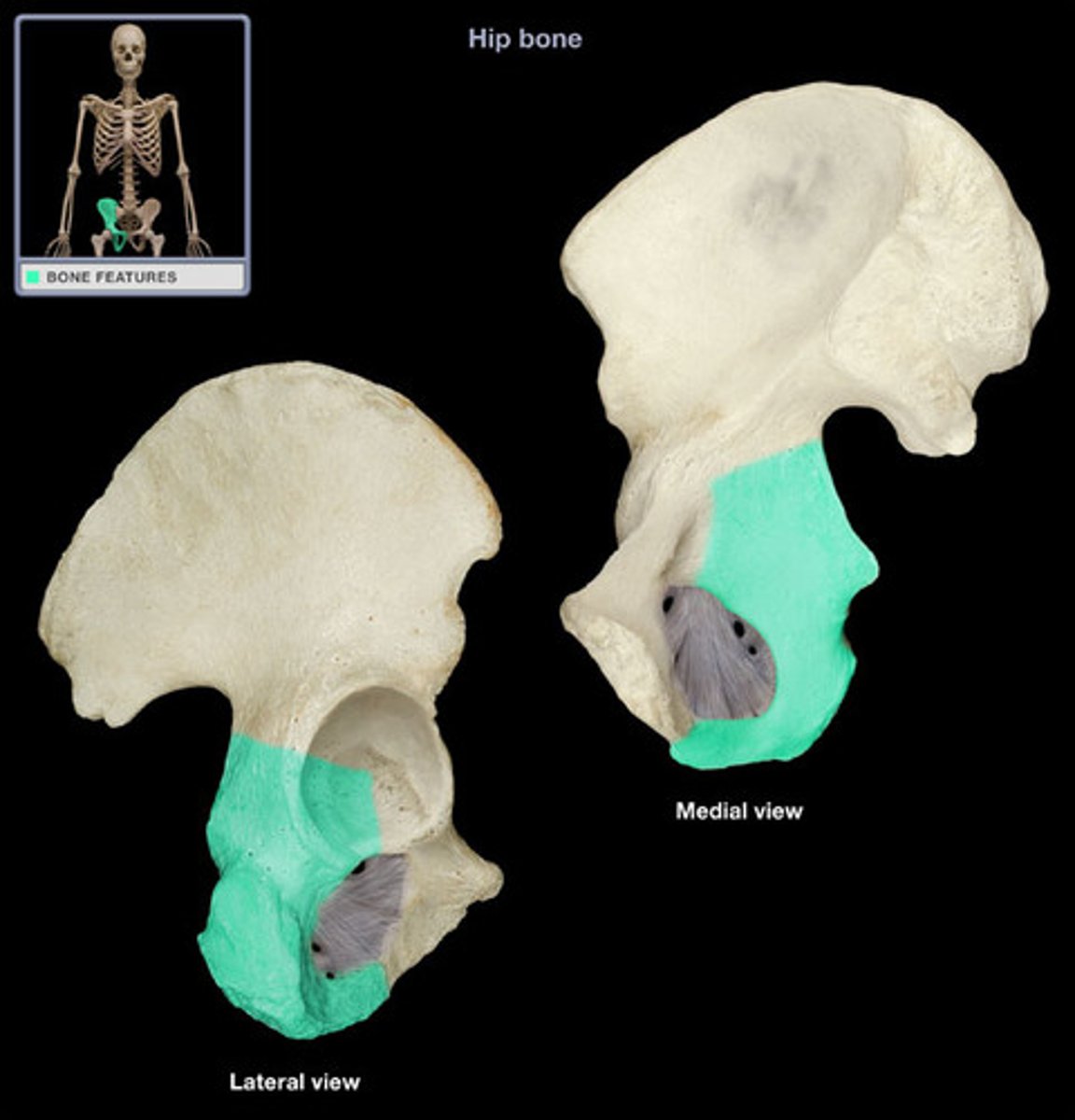
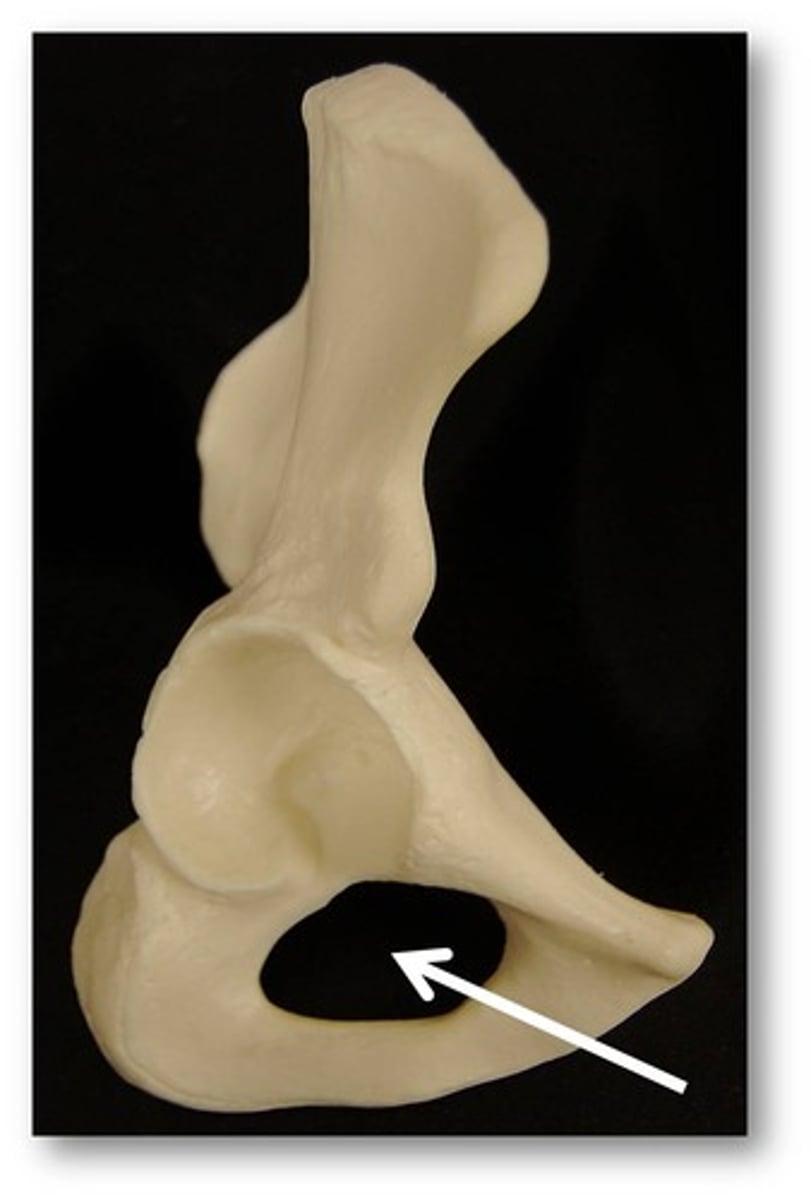
Obturator foramen
The large opening in the hip bone formed by the ischium and pubis.
Acetabulum
The socket in the hip bone that receives the head of the femur.
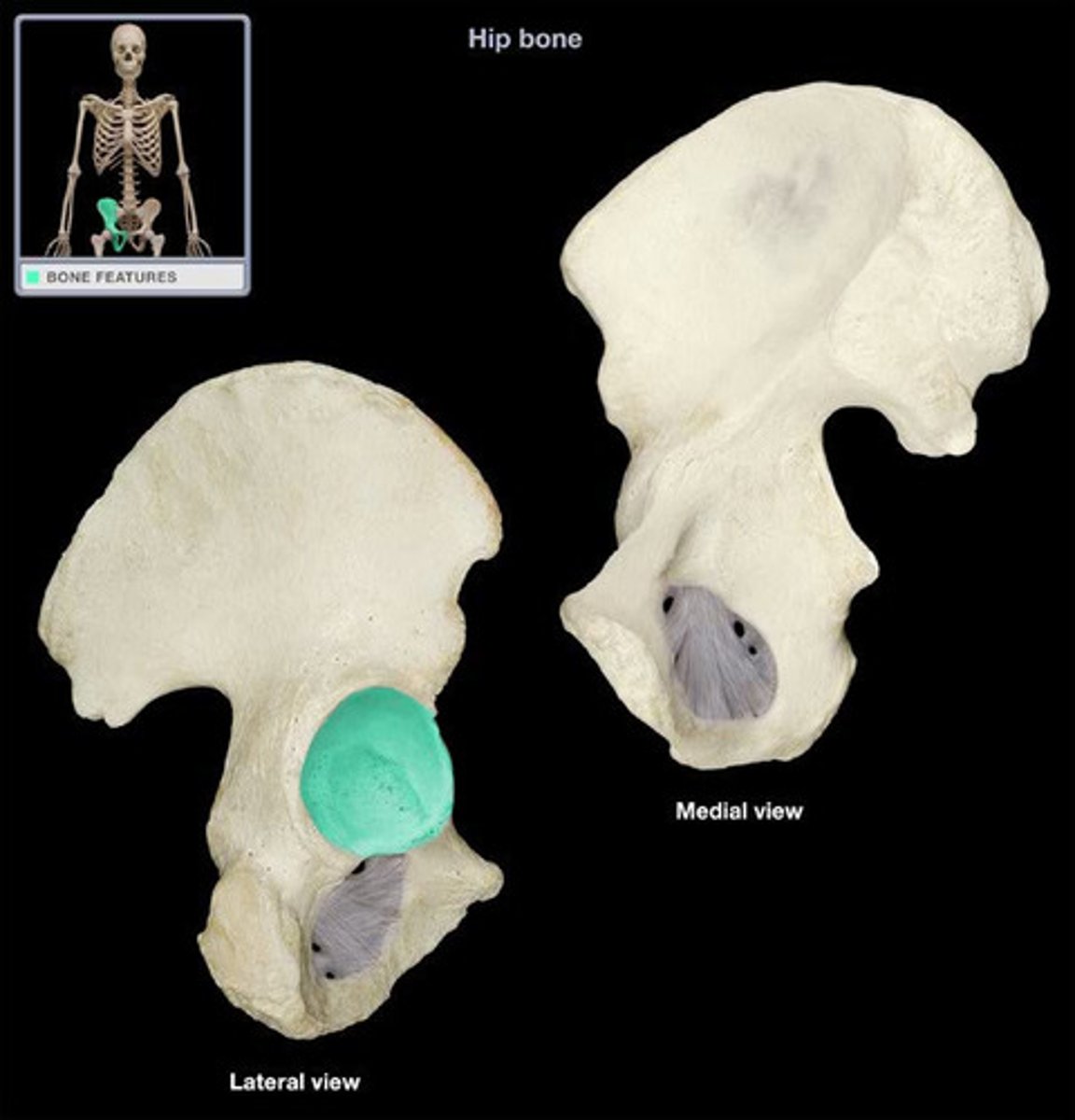
Pubis
The front part of the hip bone.
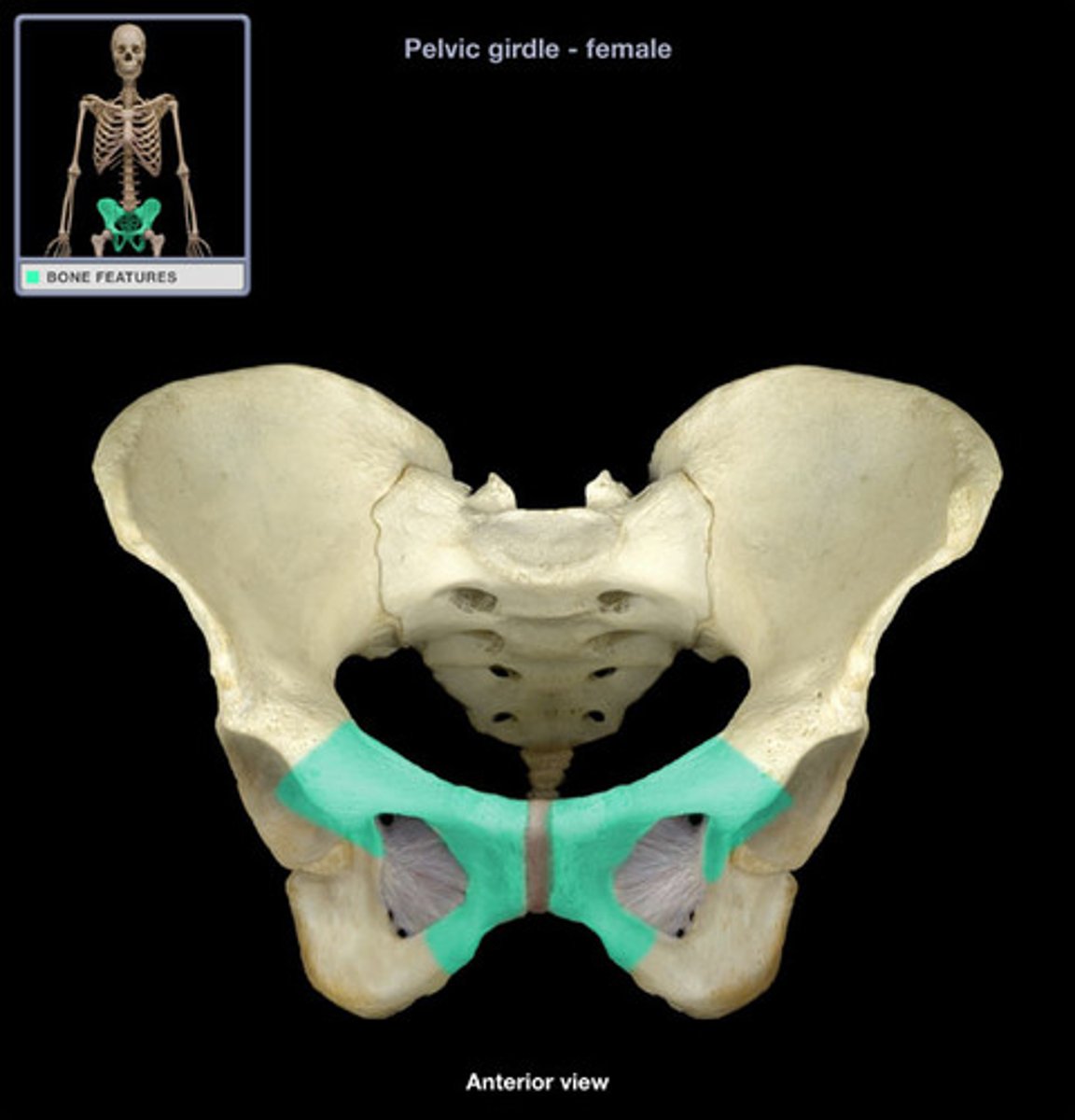
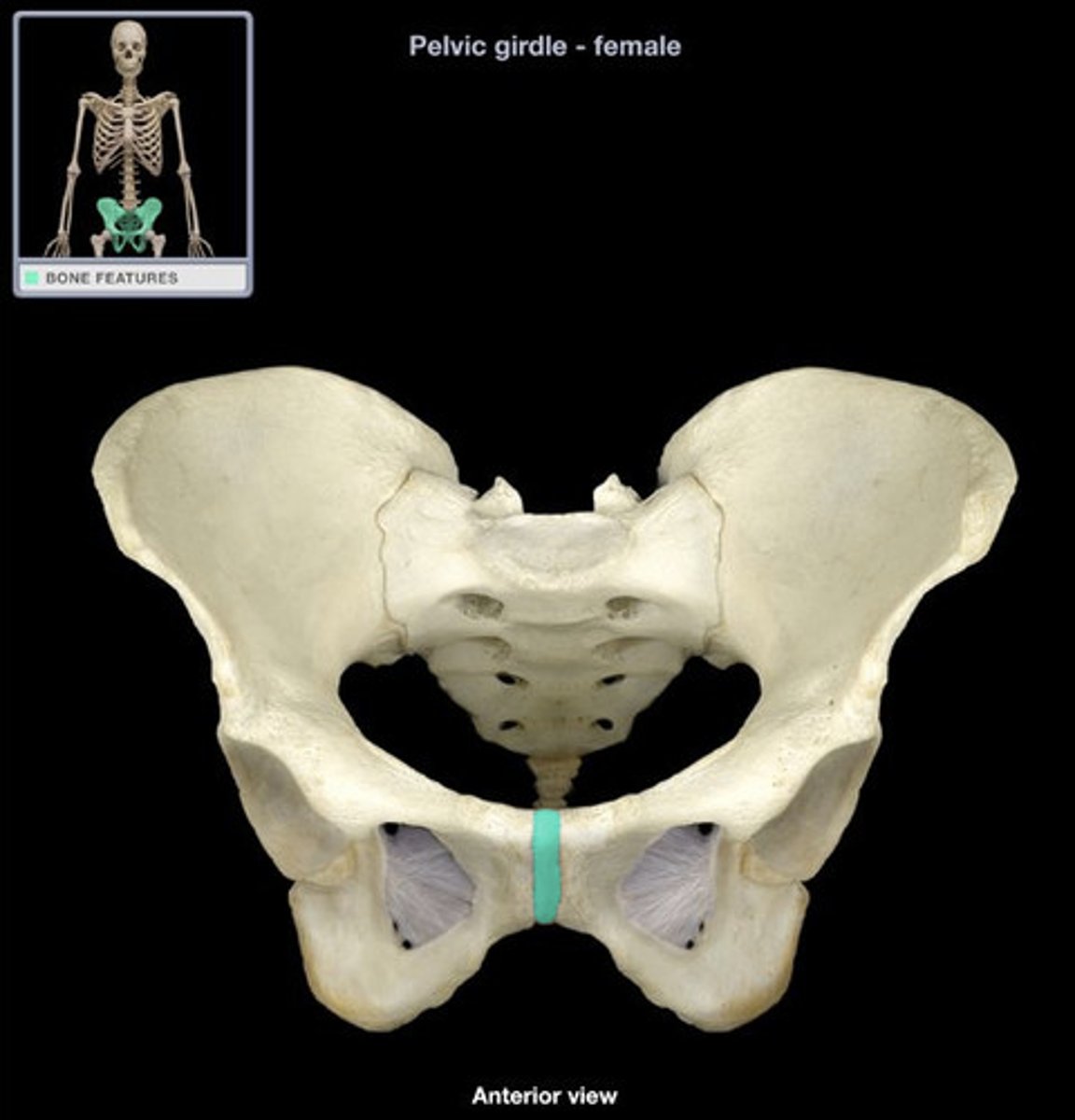
Pubis symphysis
The cartilaginous joint where the two pubic bones meet.
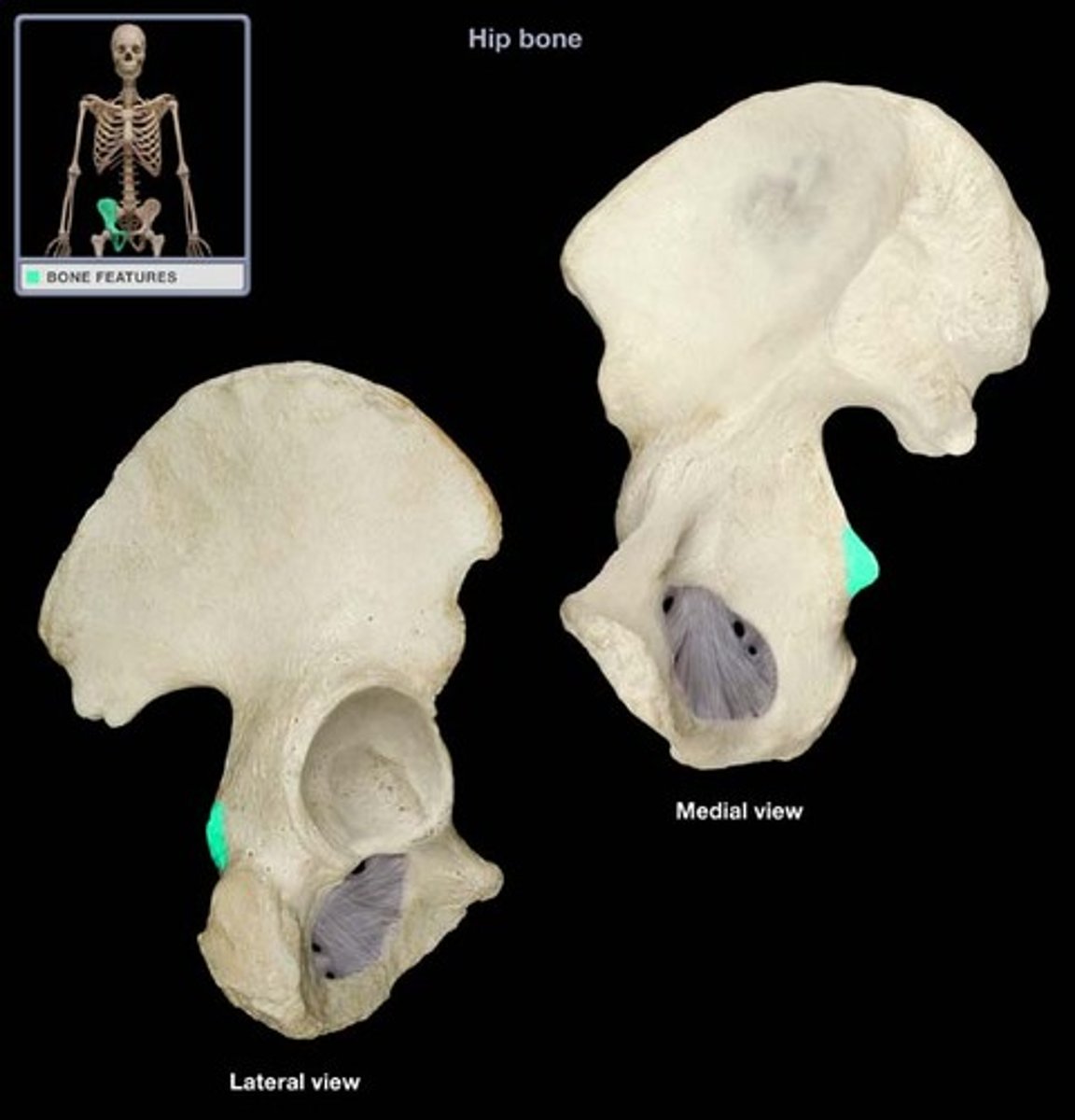
Ischial spine
The bony projection on the ischium.
Femur
The thigh bone, the longest bone in the body.
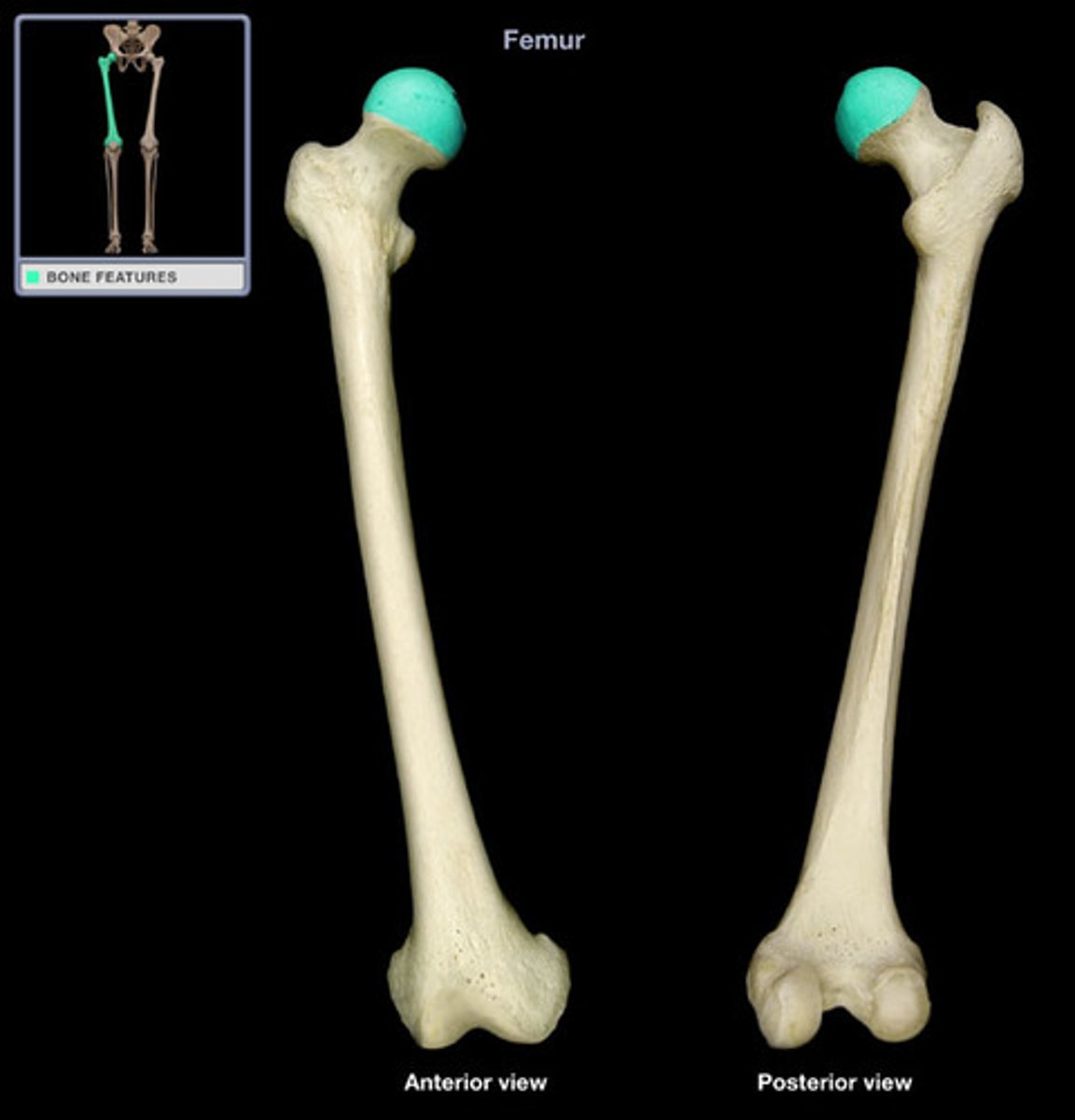
Head of femur
The rounded proximal end of the femur that fits into the acetabulum.
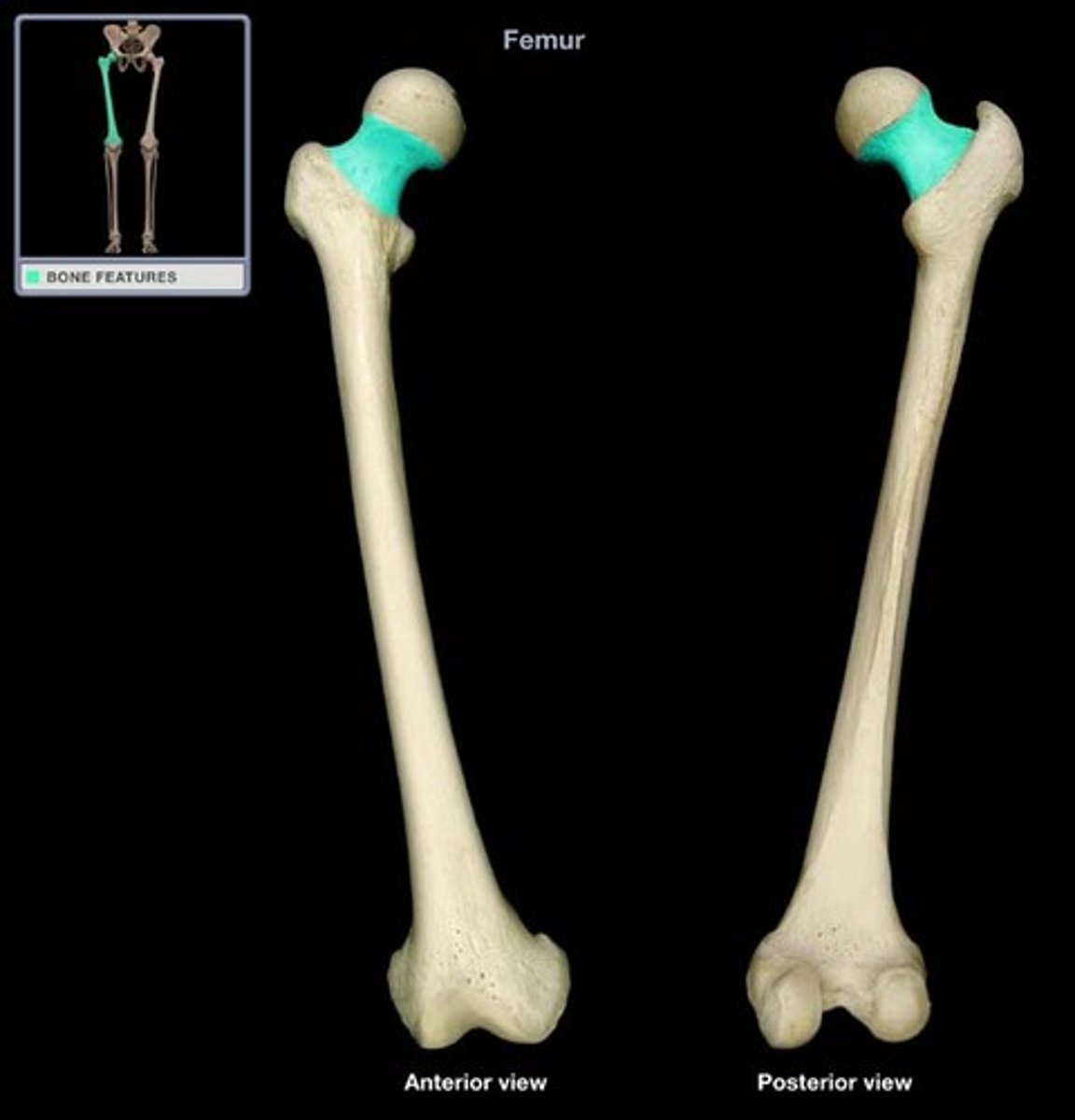
Neck of femur
The narrowed region just below the head of the femur.
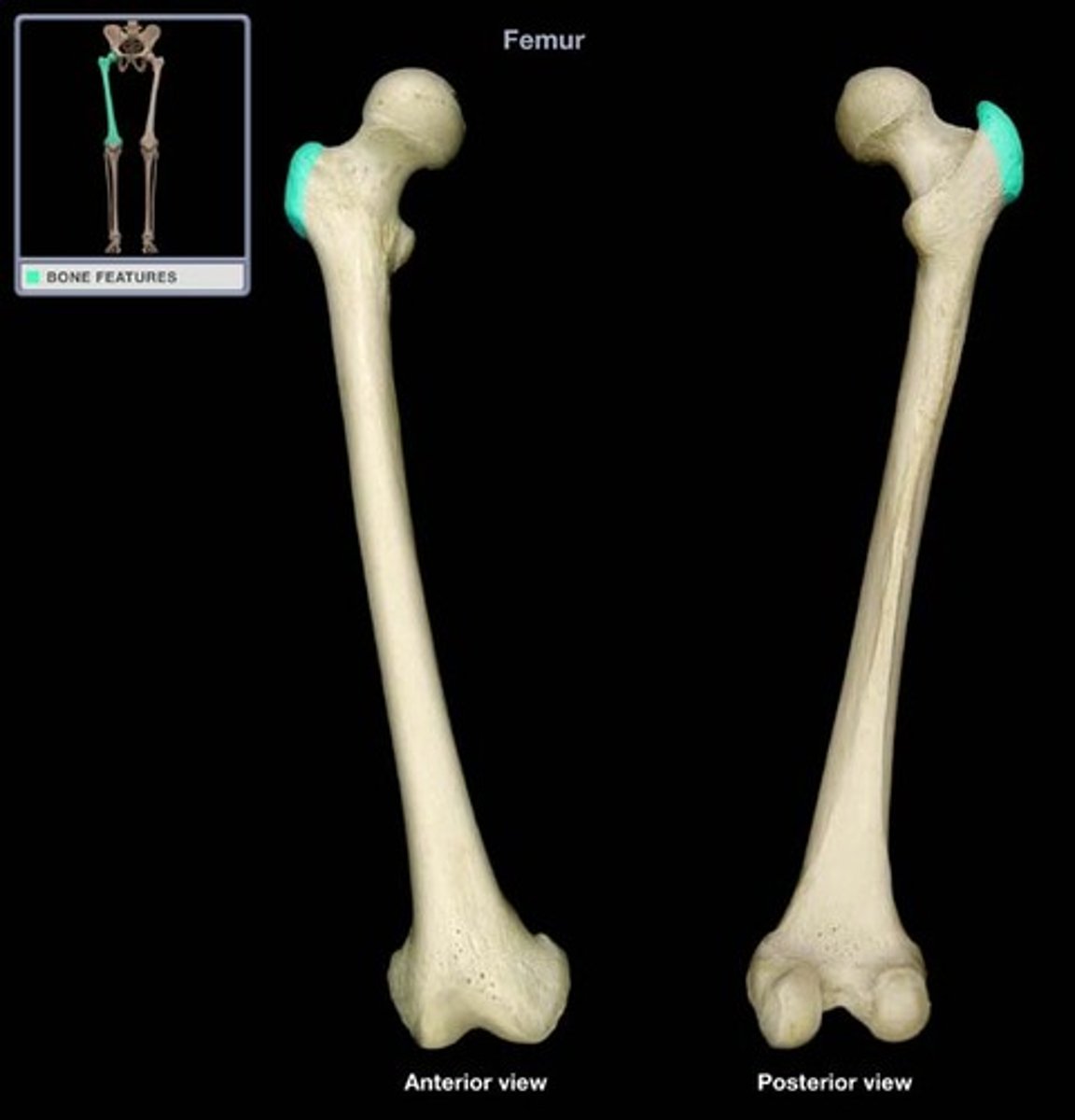
Greater trochanter
The large bony prominence on the femur for muscle attachment.
Lesser trochanter
The smaller bony prominence on the femur for muscle attachment.
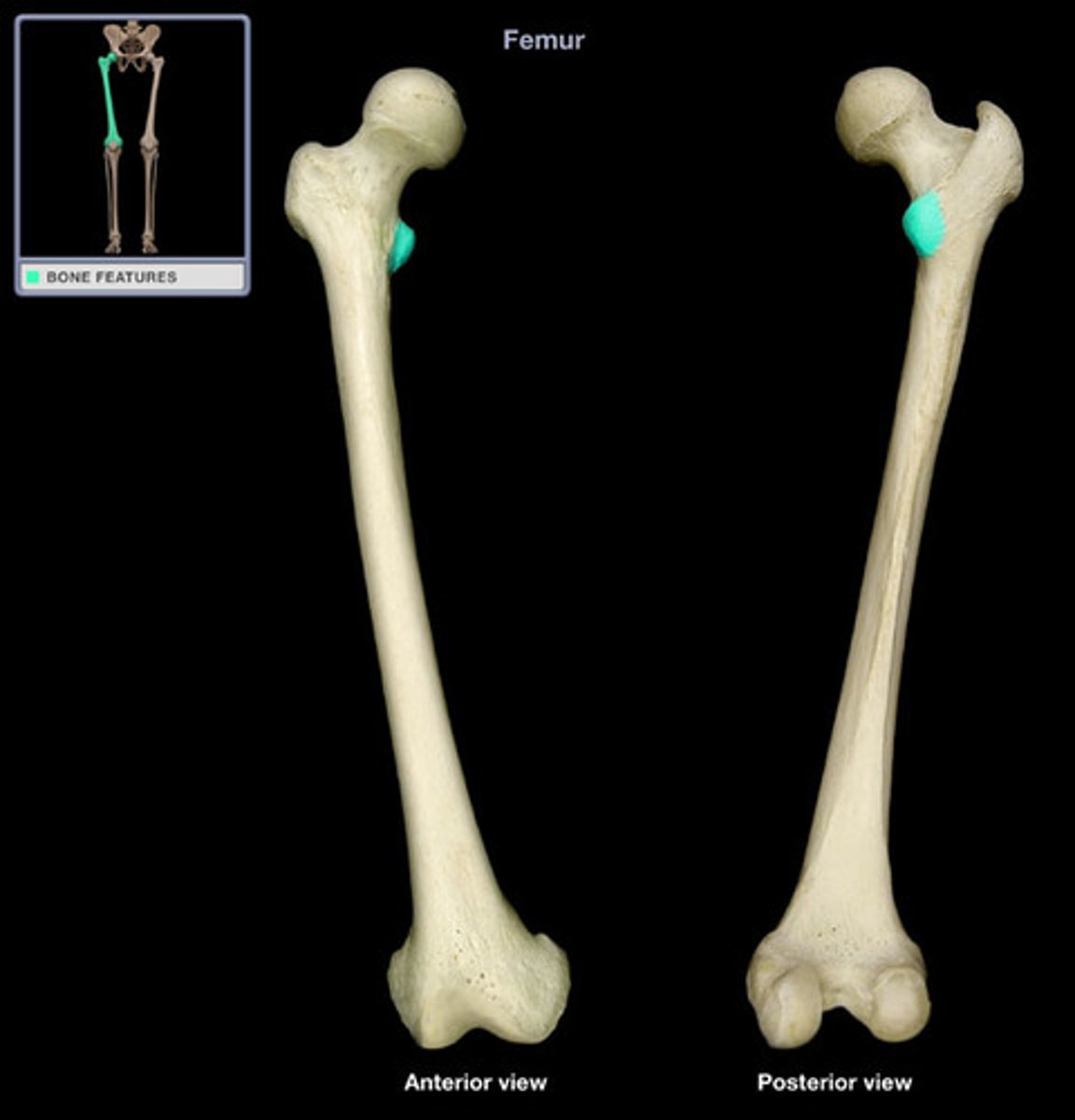
Lateral epicondyle of femur
The bony prominence on the outer side of the distal femur.
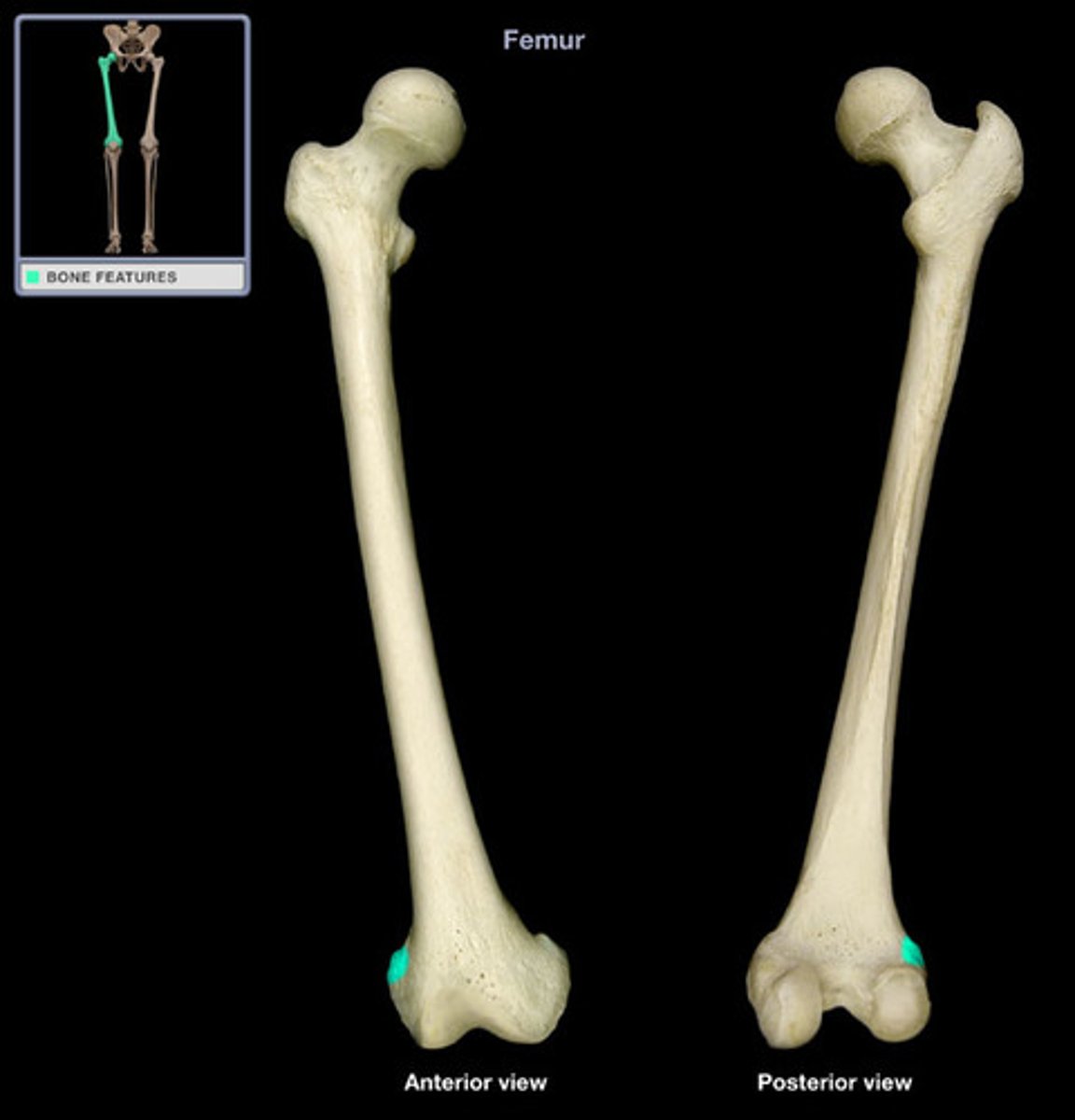
Medial epicondyle of femur
The bony prominence on the inner side of the distal femur.
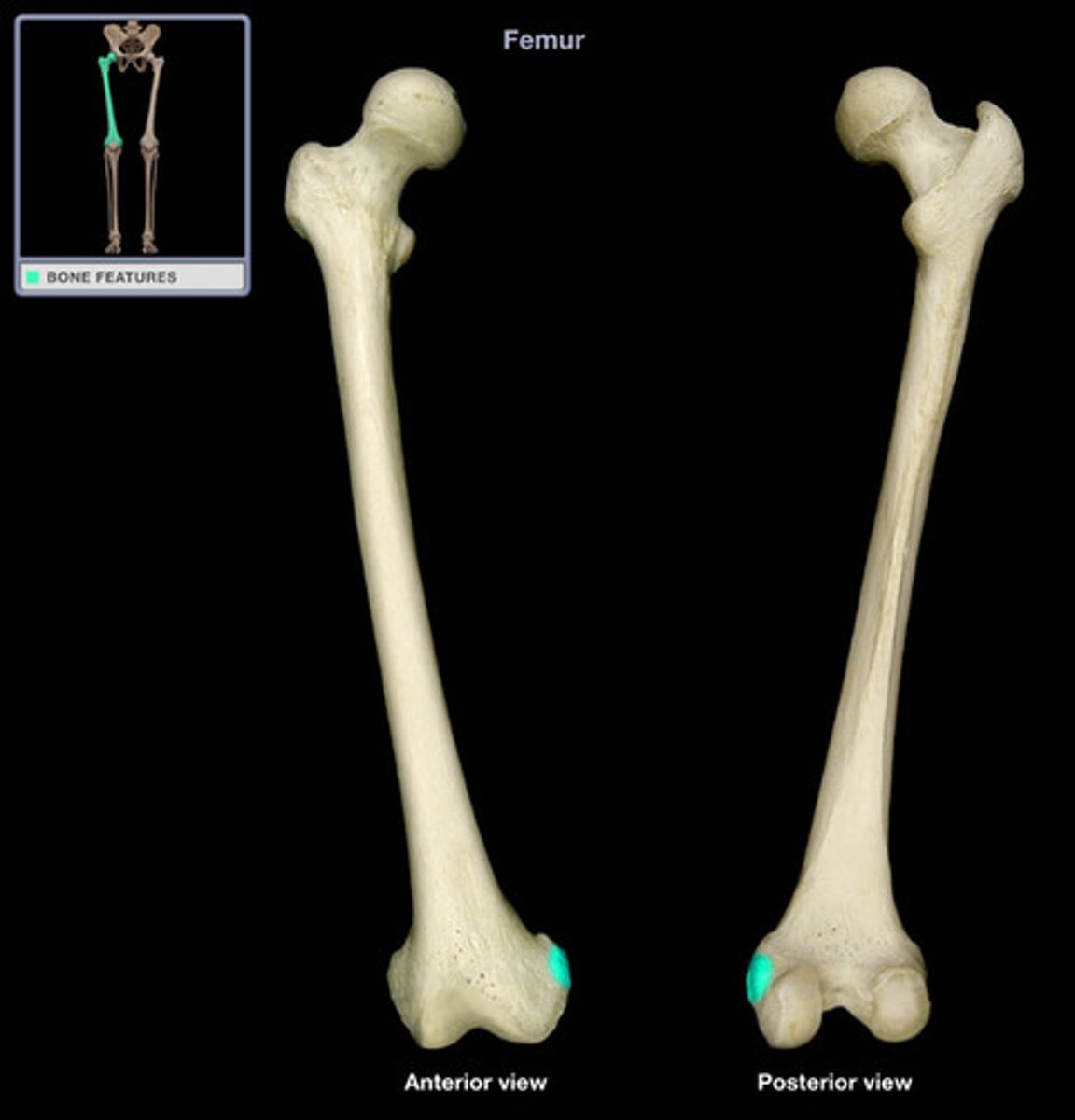
Patellar surface
The smooth area on the femur where the patella (kneecap) articulates.
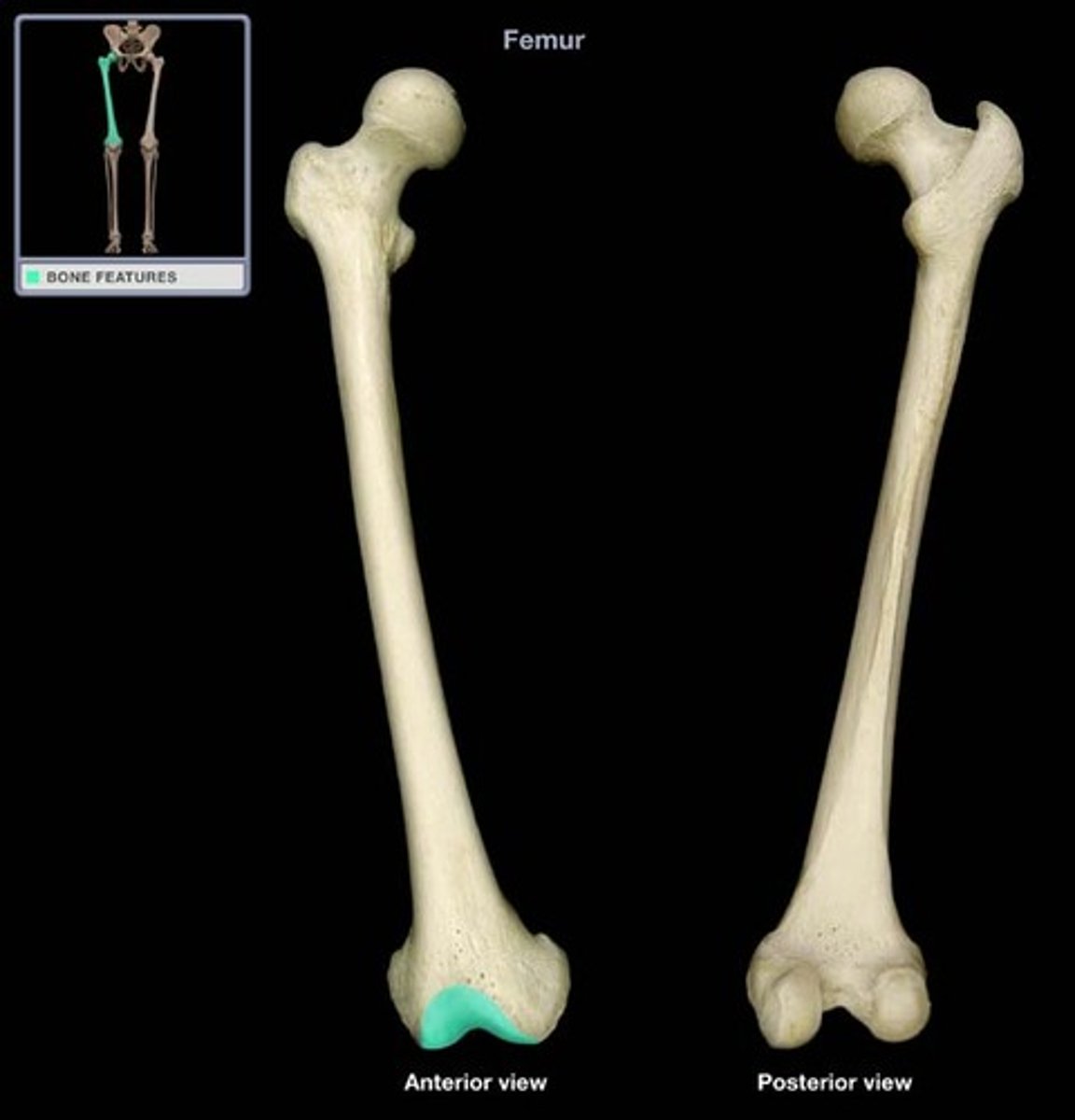
Lateral condyle
The rounded outer part of the distal femur that articulates with the tibia.
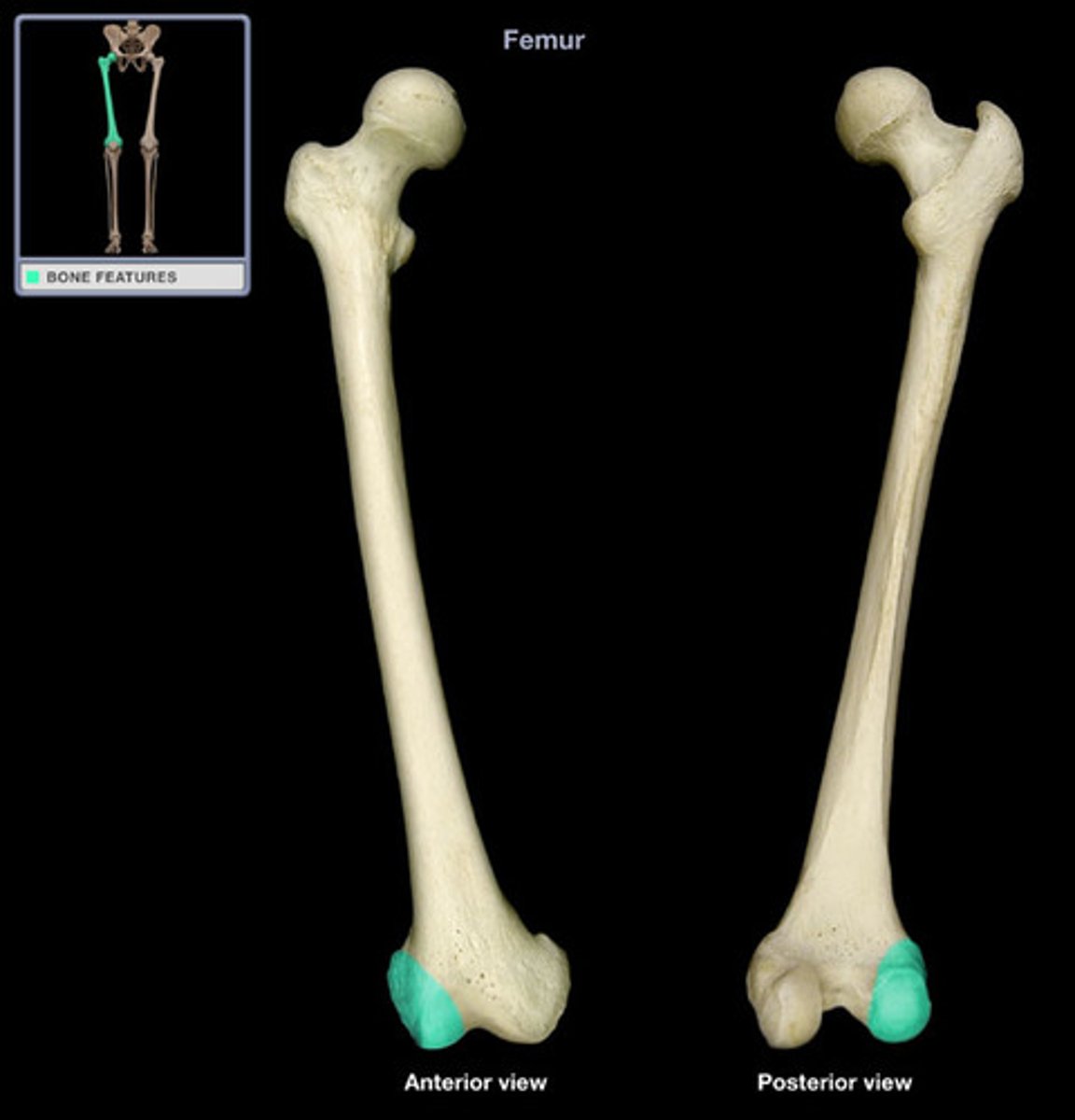
Medial condyle
The rounded inner part of the distal femur that articulates with the tibia.
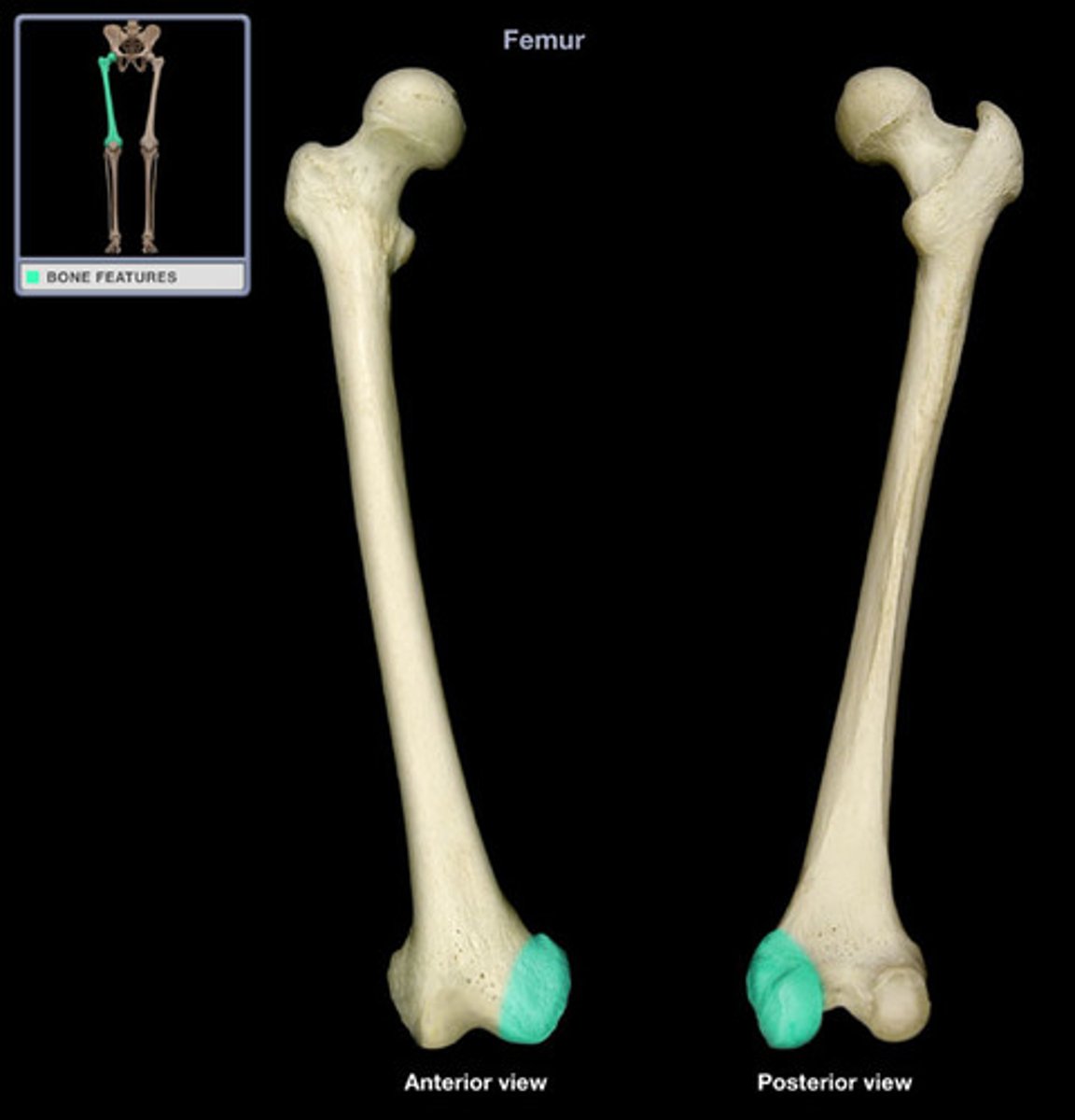
Patella
The kneecap, a small bone that protects the knee joint.
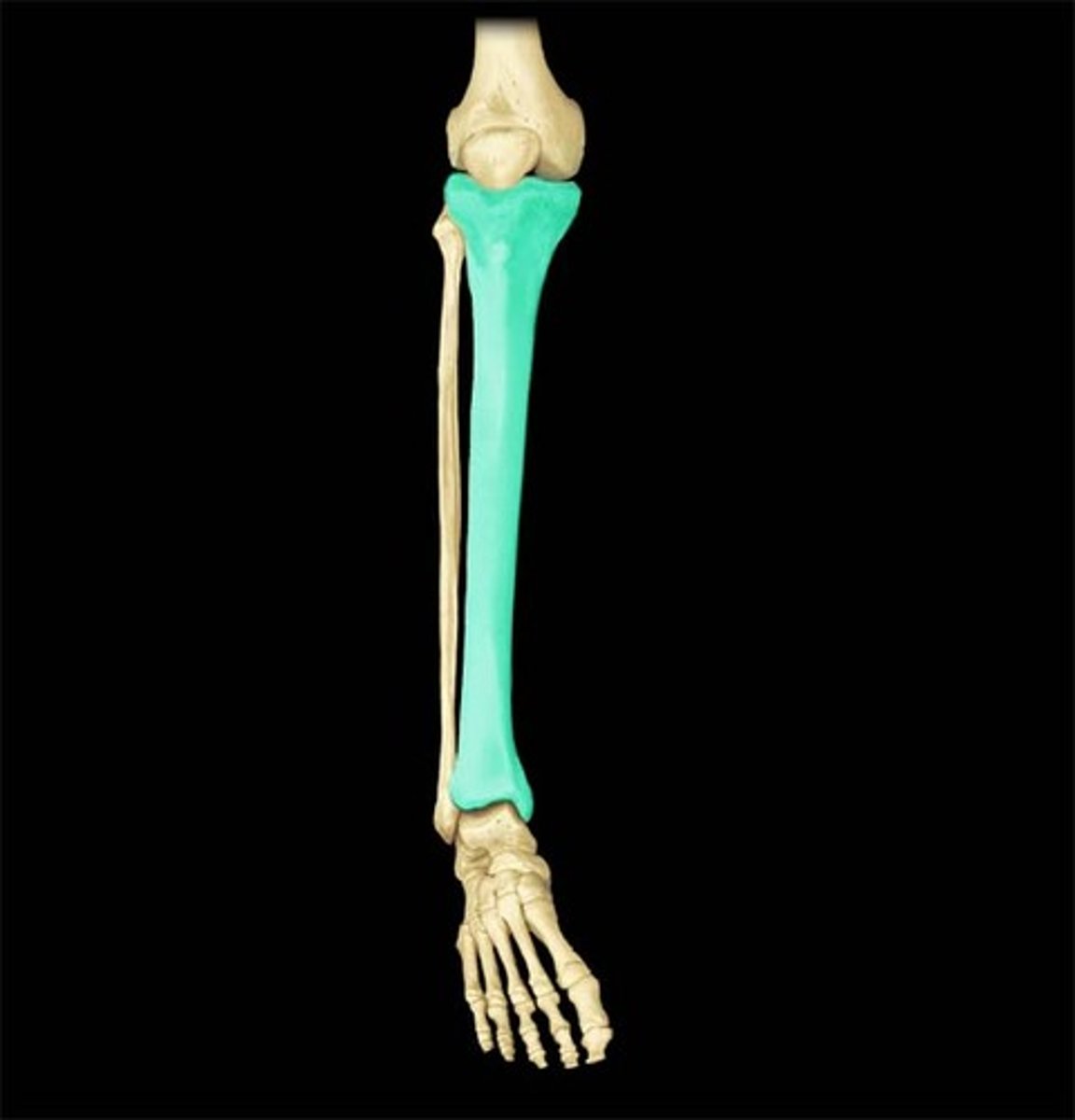
Tibia
The larger bone of the lower leg, commonly known as the shinbone.
Medial malleolus
The bony prominence on the inner side of the ankle, part of the tibia.
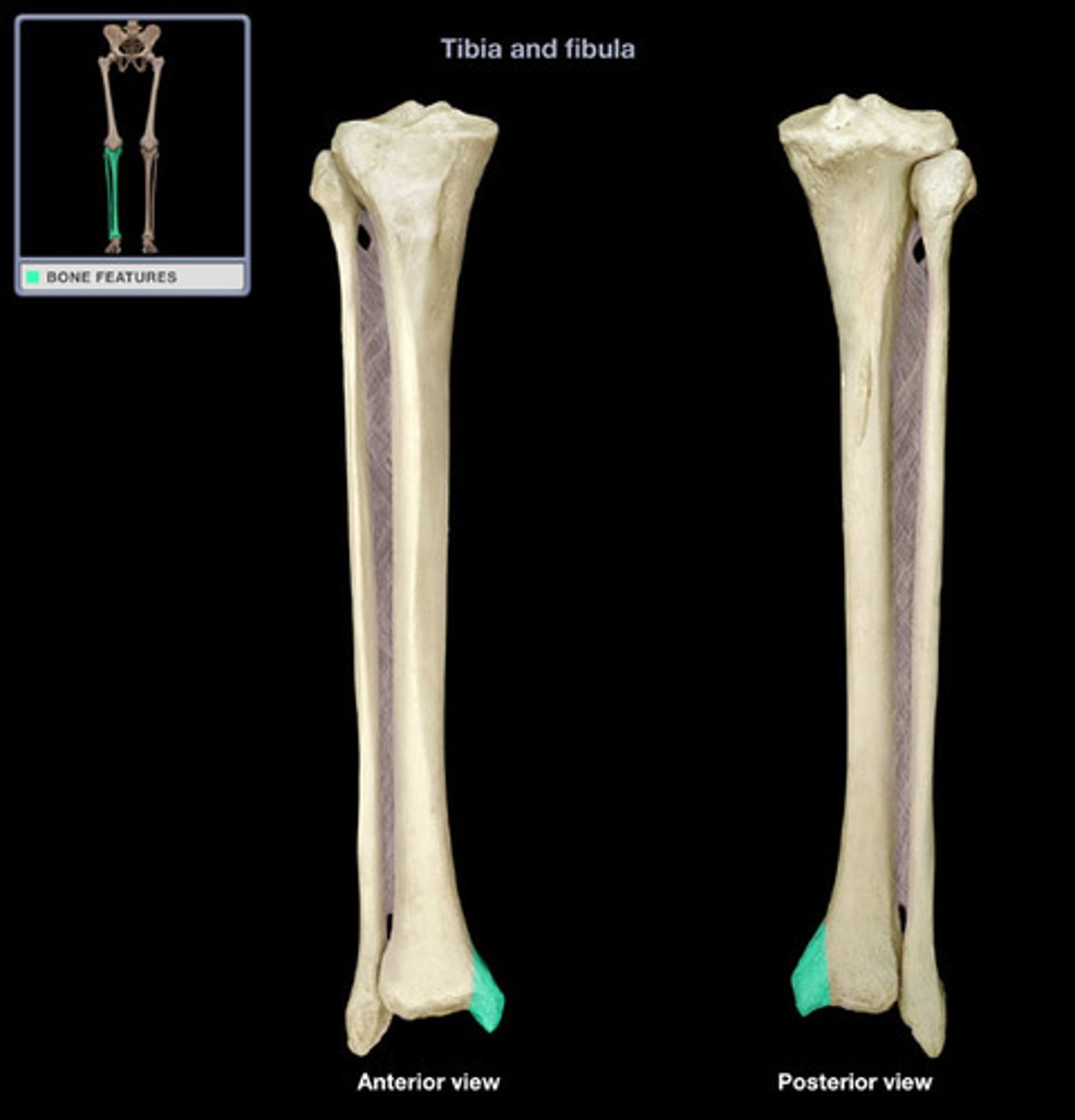
Lateral condyle of tibia
The rounded outer part of the proximal tibia that articulates with the femur.
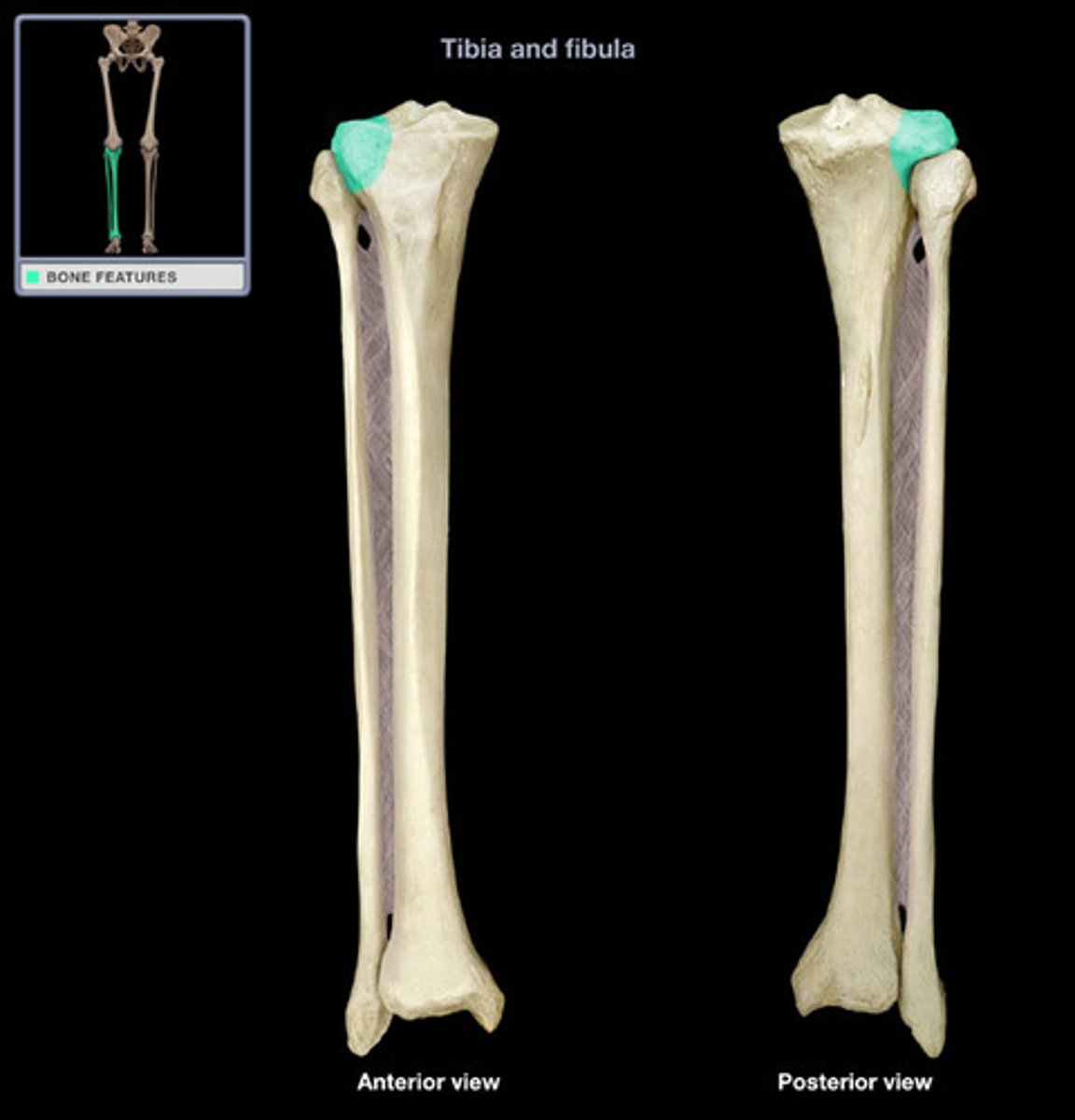
Medial condyle of tibia
The rounded inner part of the proximal tibia that articulates with the femur.
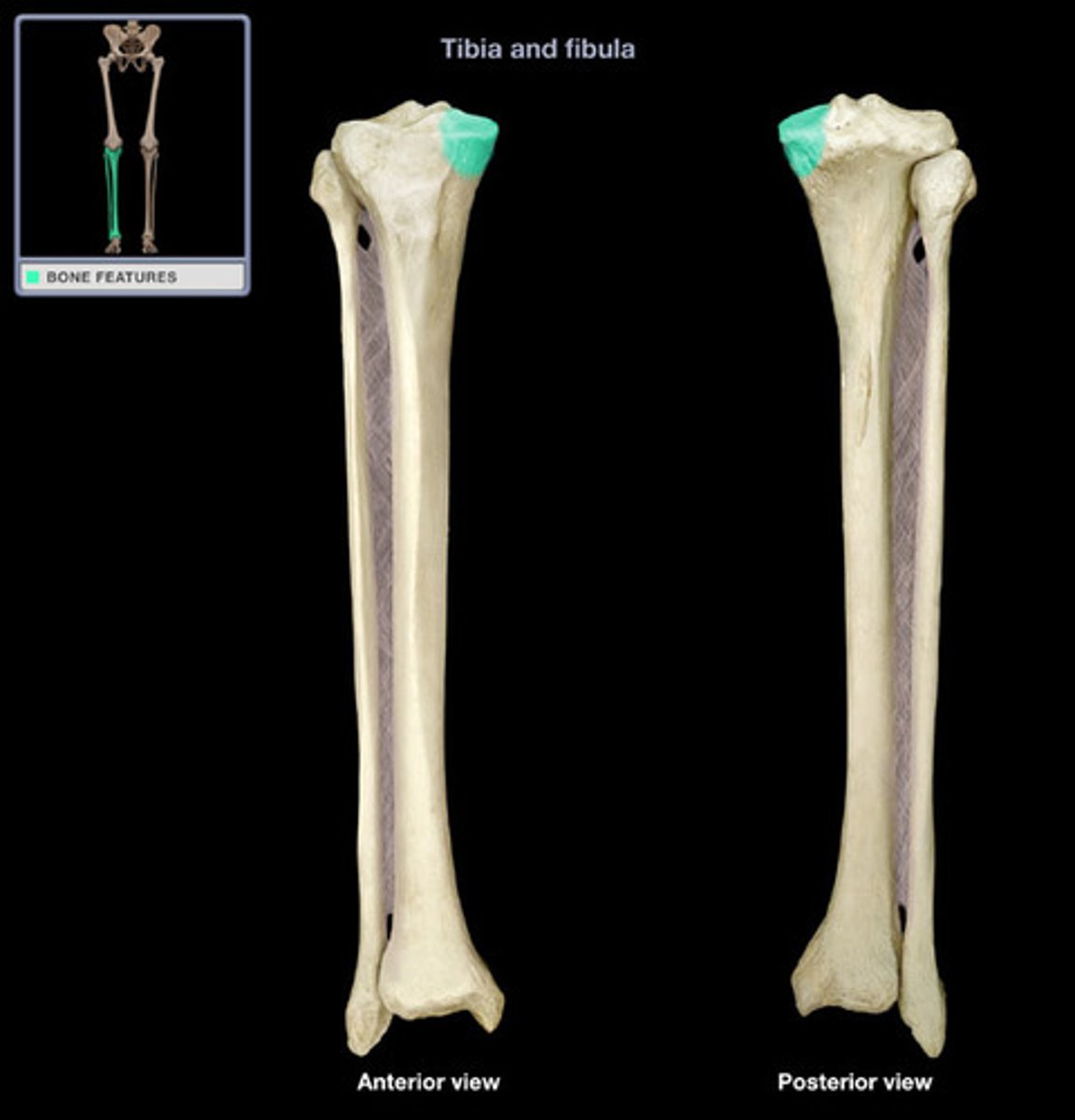
Fibula
The smaller bone of the lower leg, located alongside the tibia.

Lateral malleolus
The bony prominence on the outer side of the ankle, part of the fibula.
