Histology
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
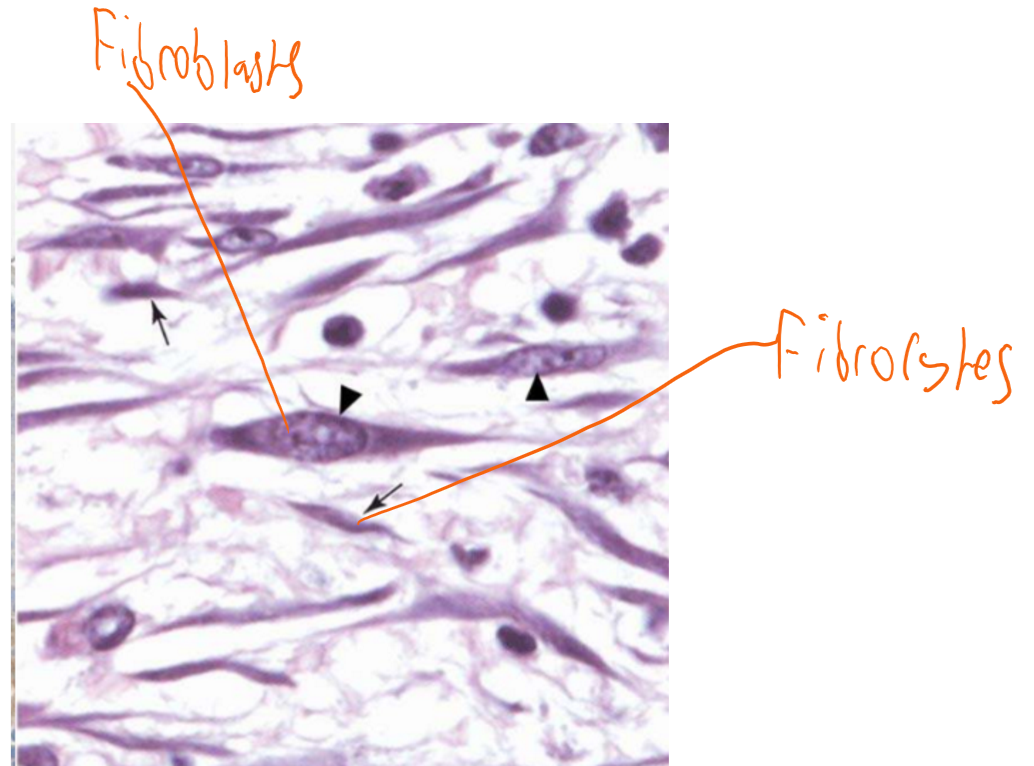
fibroblasts
synthesises extracellular matrix
simple squamous epithelium
endothelium, type 1 alveoli cells, peritoneum, form walls of lymphatic vessels
simple cuboidal
line tubules & ducts for excretory/ secretory/ absorptive processes, small bronchioles, exocrine glands
transitional epithelium
surface of bladder, ureters and part of urethra
simple columnar
bronchi (ciliated), digestive tract (intestine, stomach) and some glands; involved in absorption and secretion
pseudostratified
trachea- ciliated
stratified squamous
lining oesophagus, skin (keratinous), oral cavity
stratified cuboidal
common in ducts
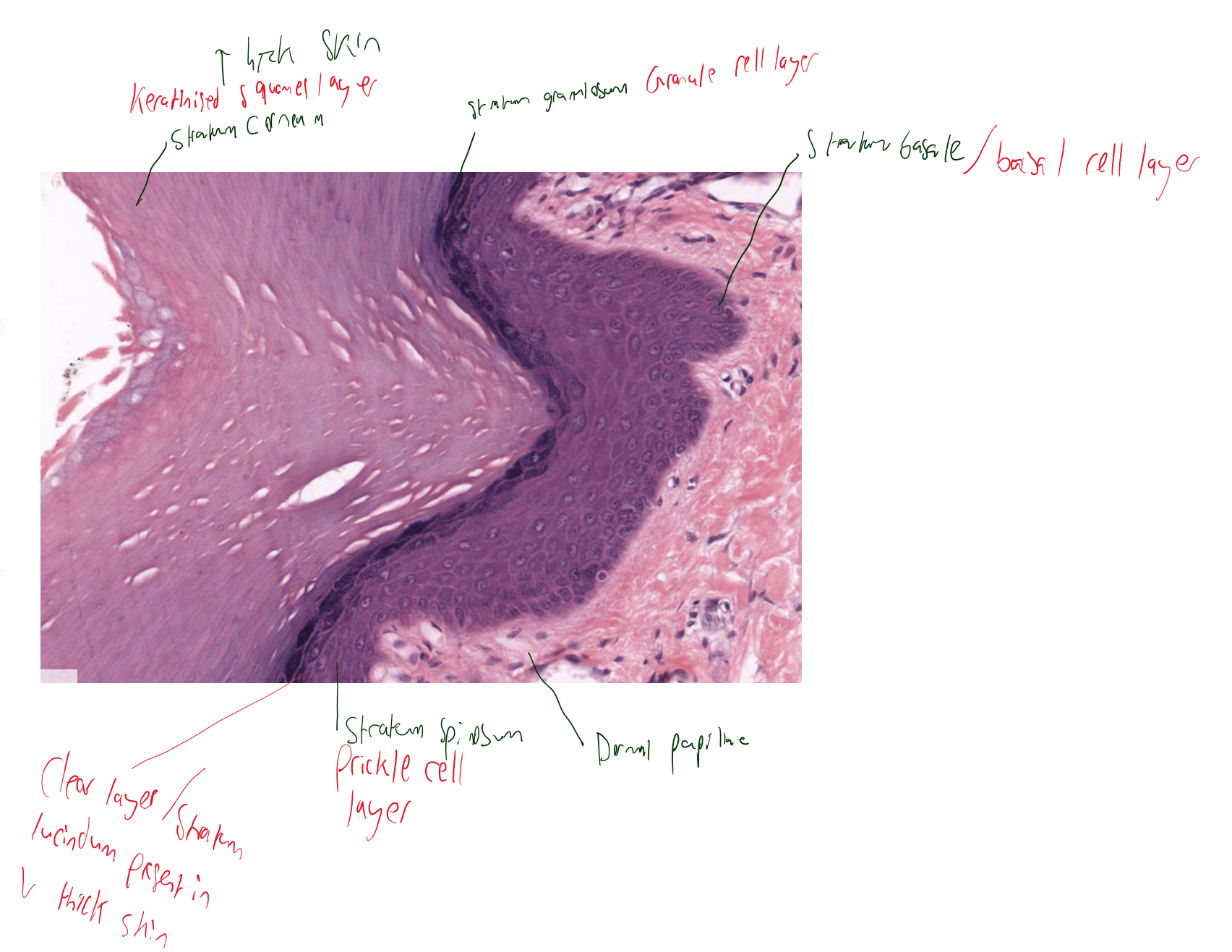
thick skin vs thin skin
thicker epidermis (clear zone), lack hair follicles & sebaceous glands
5 layers of skin
basal cell layer
prickle cell layer
granule cell layer
clear layer- only thick skin
keratinised squames layer- thicker in thick skin and thinner in thin skin.
apocrine vs merocrine (eccrine) glands
apocrine: secrete into hair follicle, secrete viscous milky substance
merocine (eccrine): produce sweat
epithelium type of merocrine gland
excretory part= stratified cuboidal
secretory part (earlier)= simple columnar
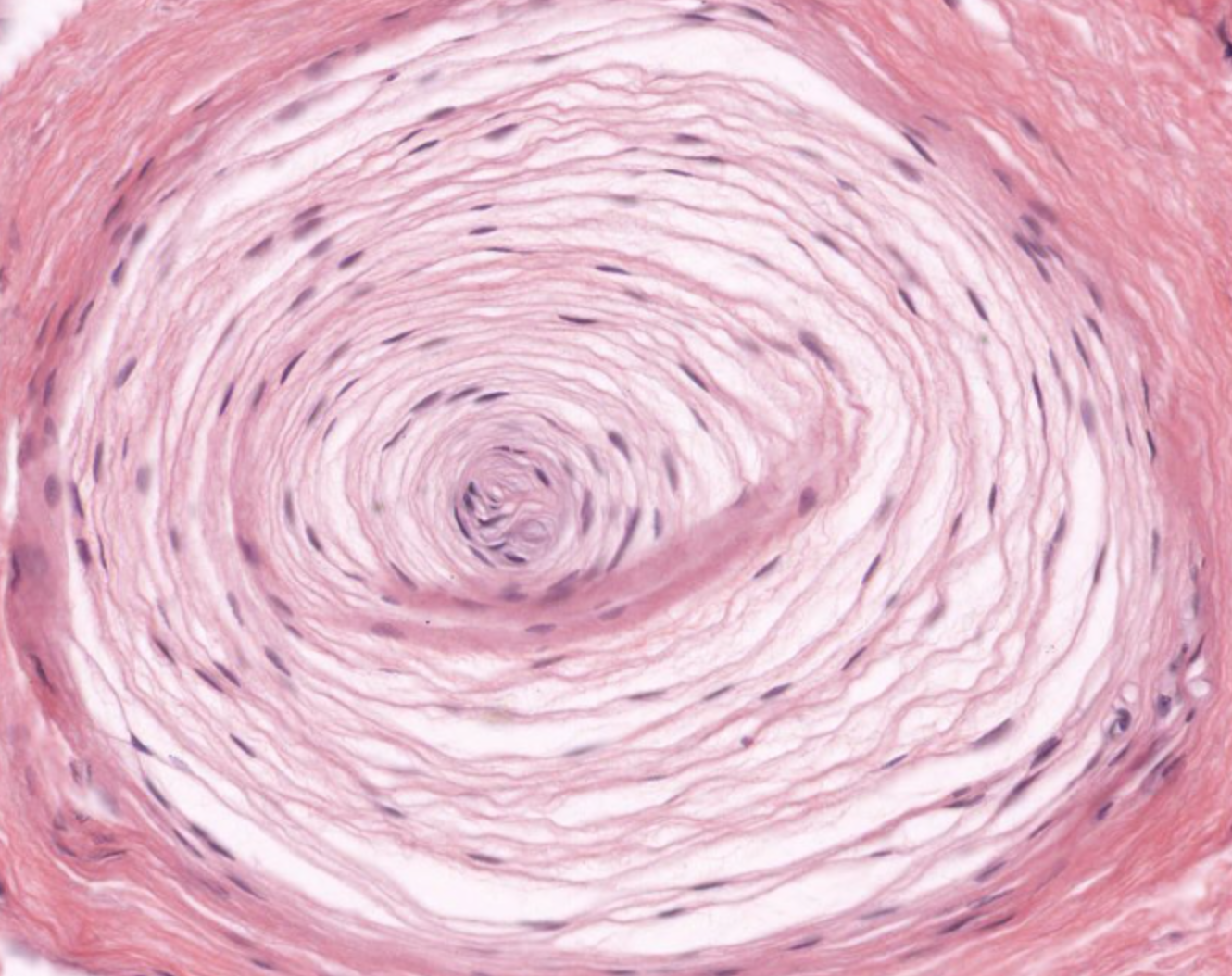
pacinian corpuscle- deep pressure and vibration (in dermis and hypodermis)
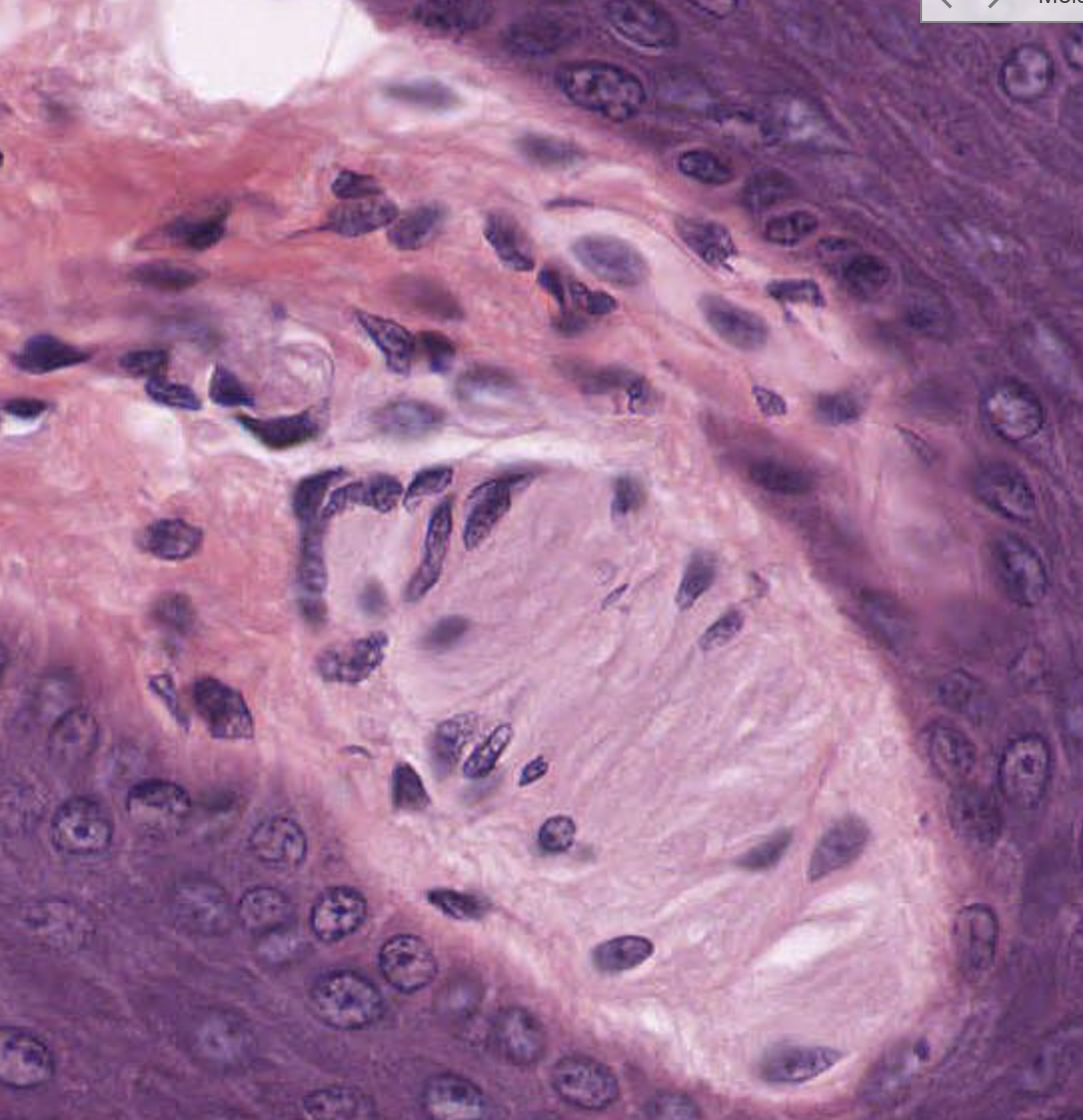
Meissner’s corpuscle: light touch- elliptical structures in dermal projections/ papillae
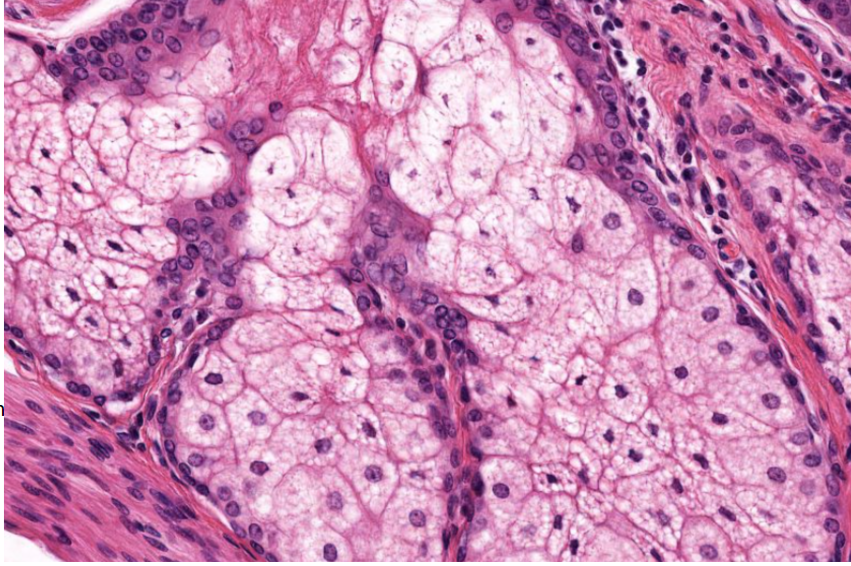
sebaceous gland- secrete sebum into hair follicles
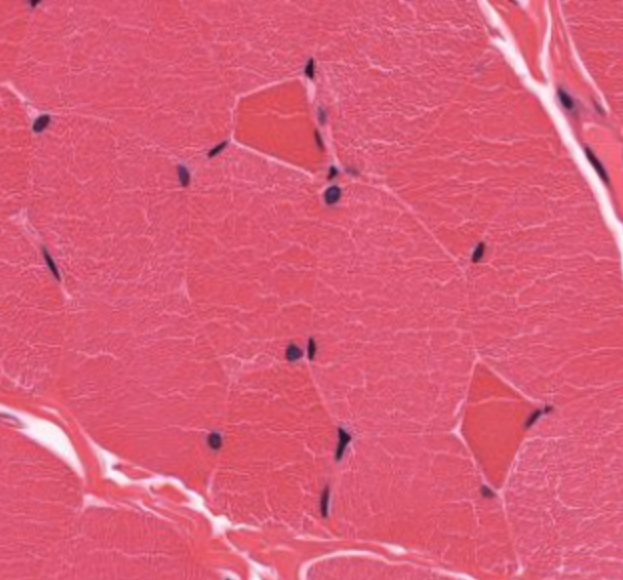
skeletal muscle- dark red= type 1 (slow twitch) and light red= type 2 (fast twitch) fibers.
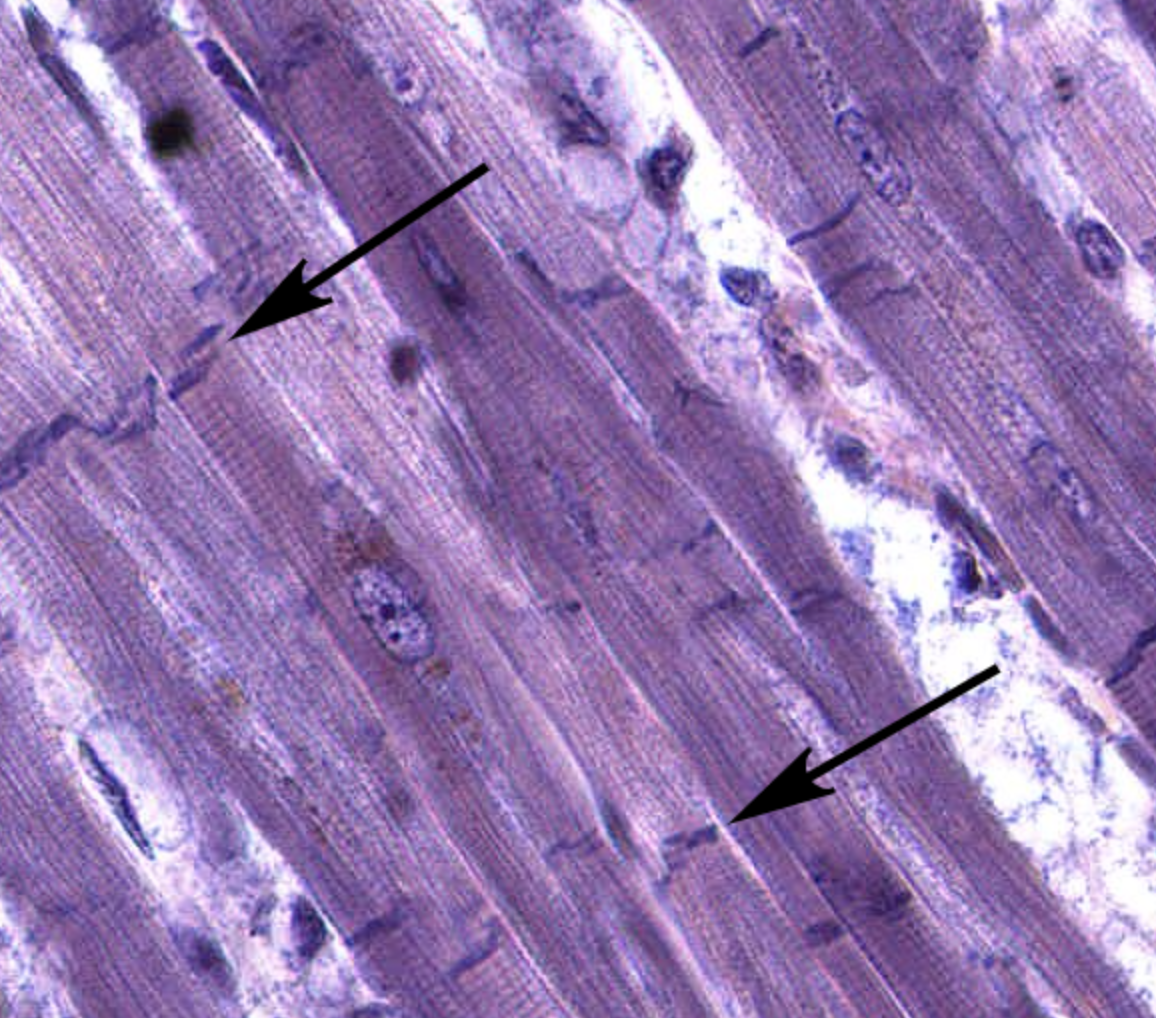
cardiac muscle with visible intercalated discs
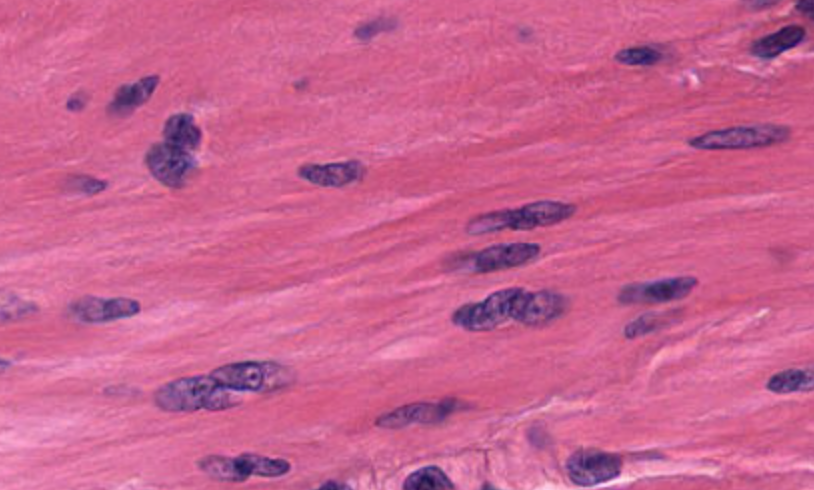
smooth muscle
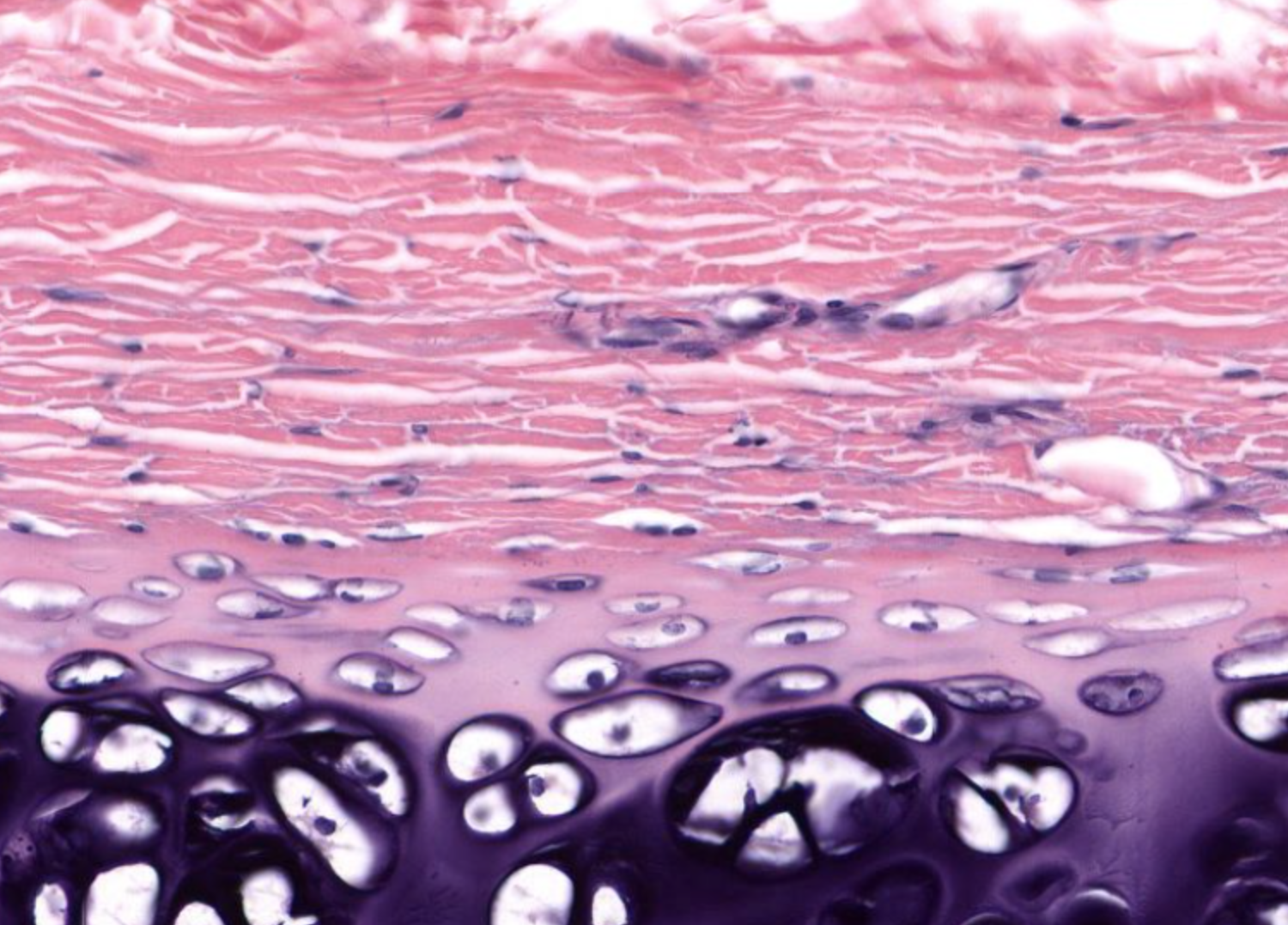
hyaline cartilage
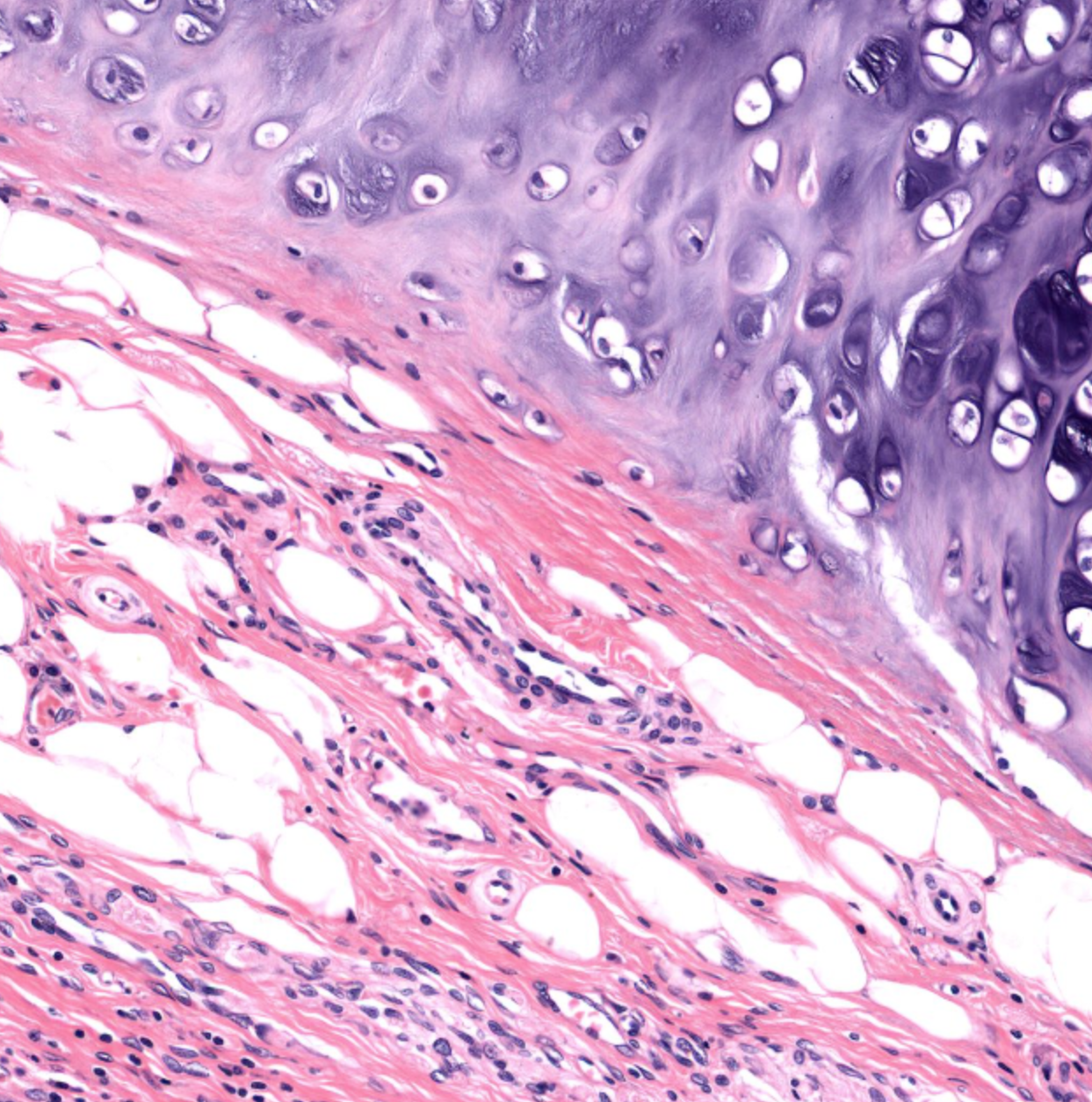
elastic cartilage- pink in purple from elastin fibres (easier to see when stained)
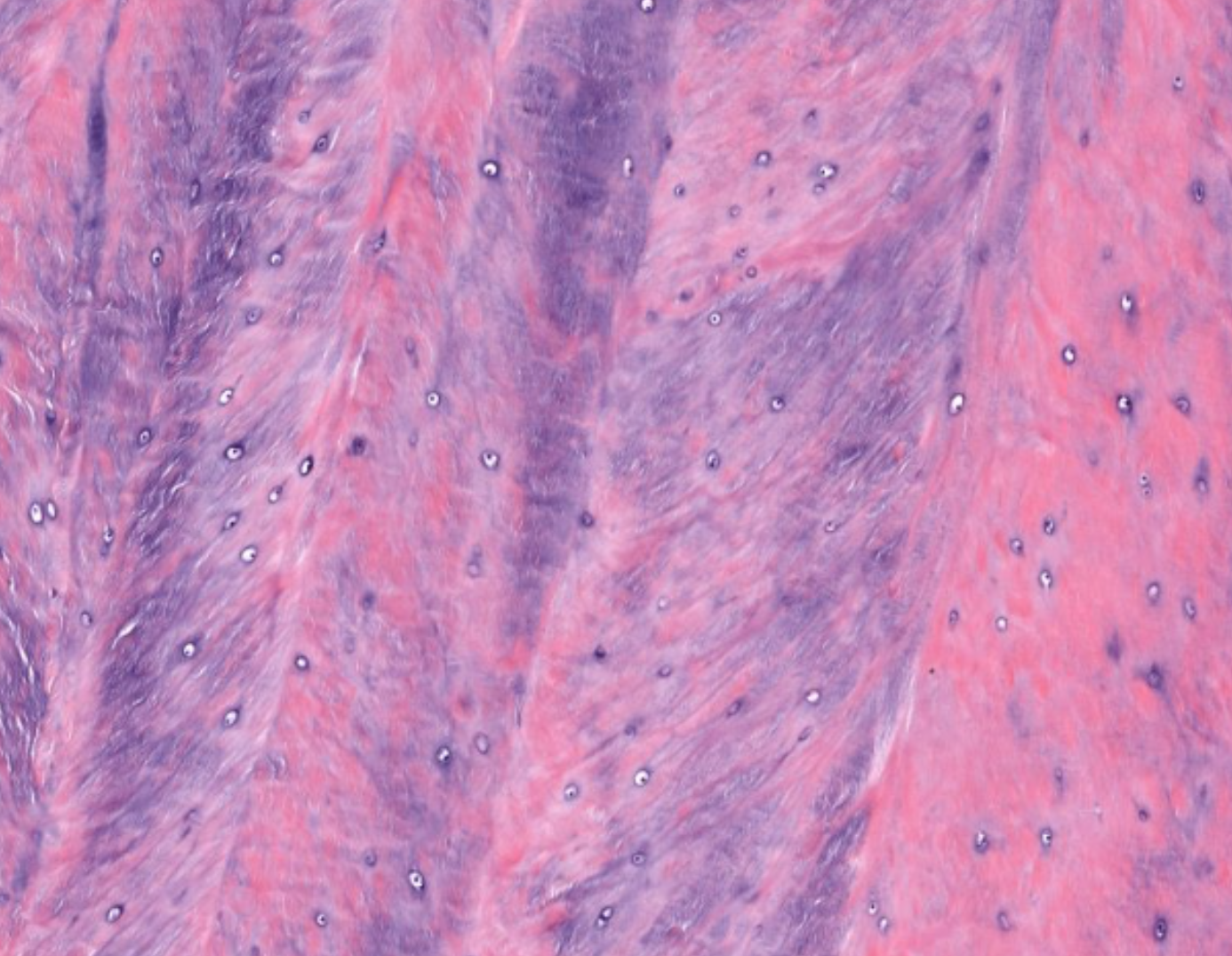
fibrocartilage- no perichondrium
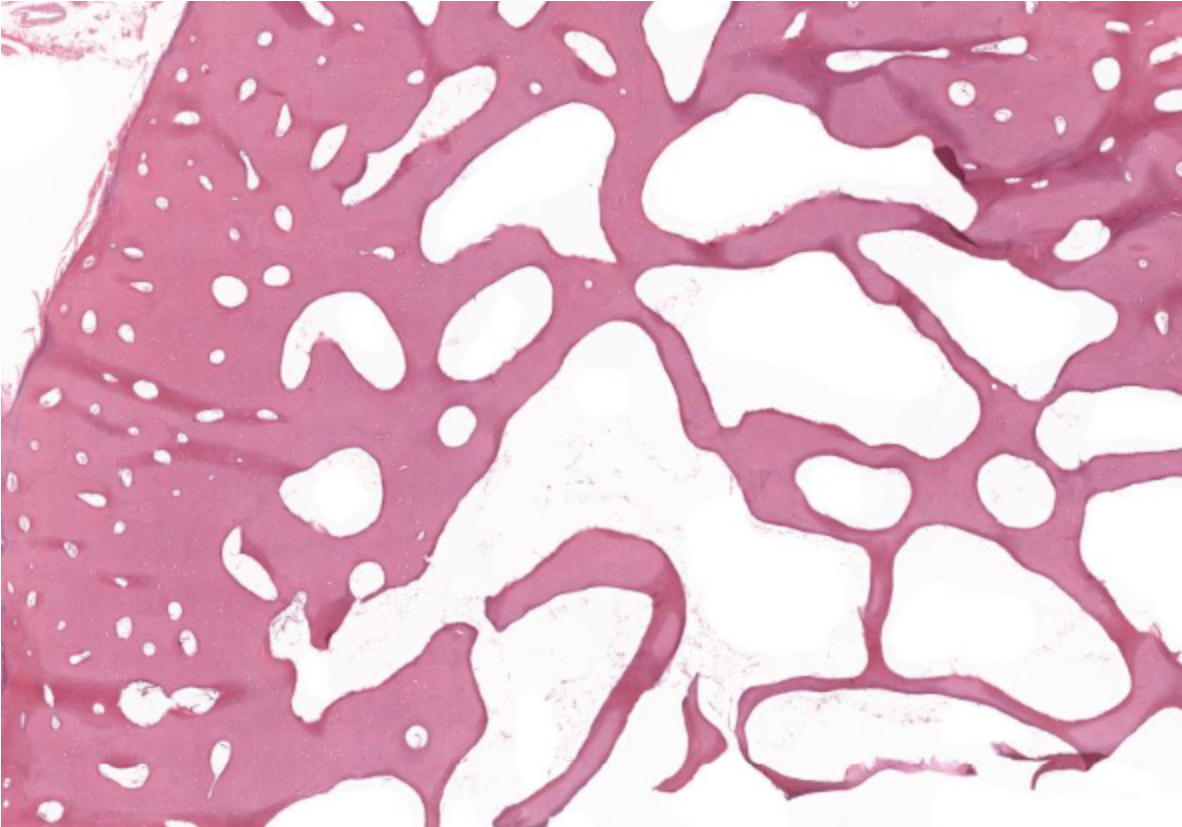
compact (left) and spongy/ cancellous/ trabecular bone (right)
zones of growth at epiphyseal plate

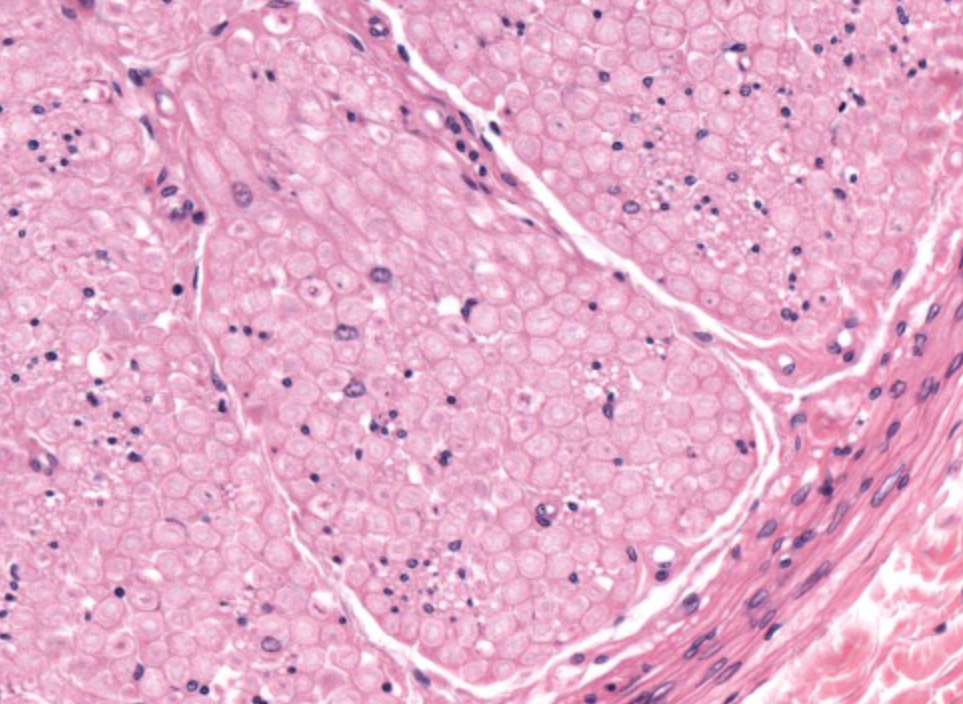
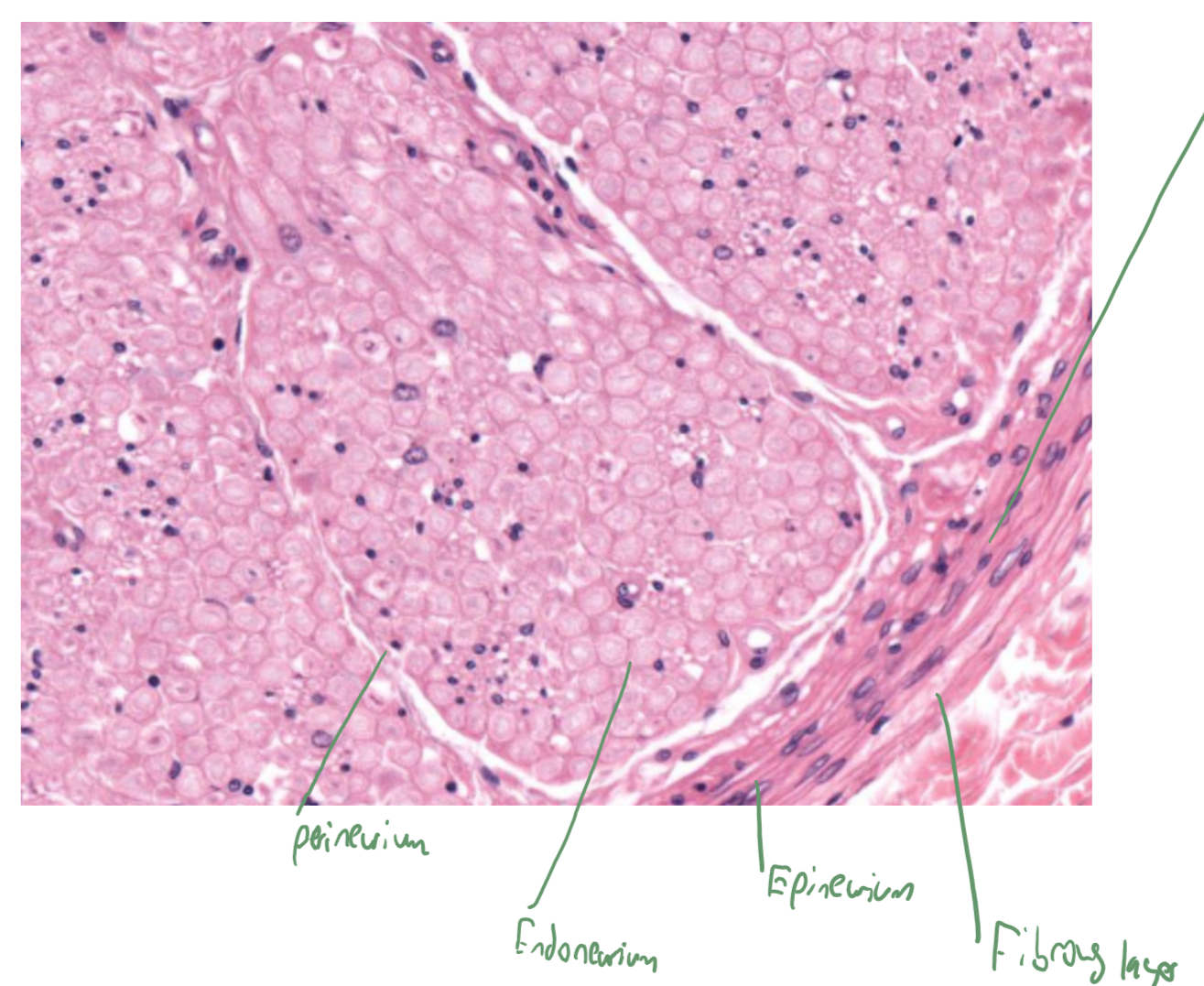
nerve
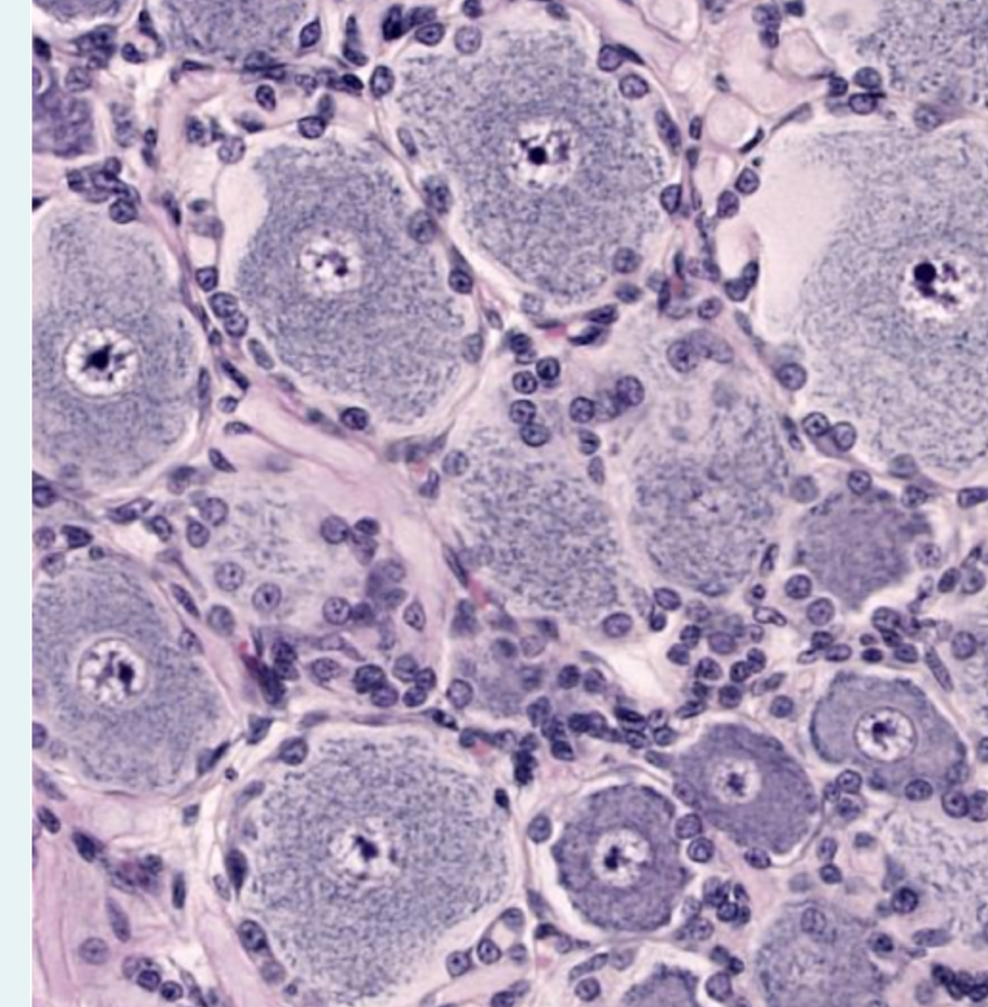
which ganglion
dorsal root ganglion- variable body size, neat circle of satellite cells,
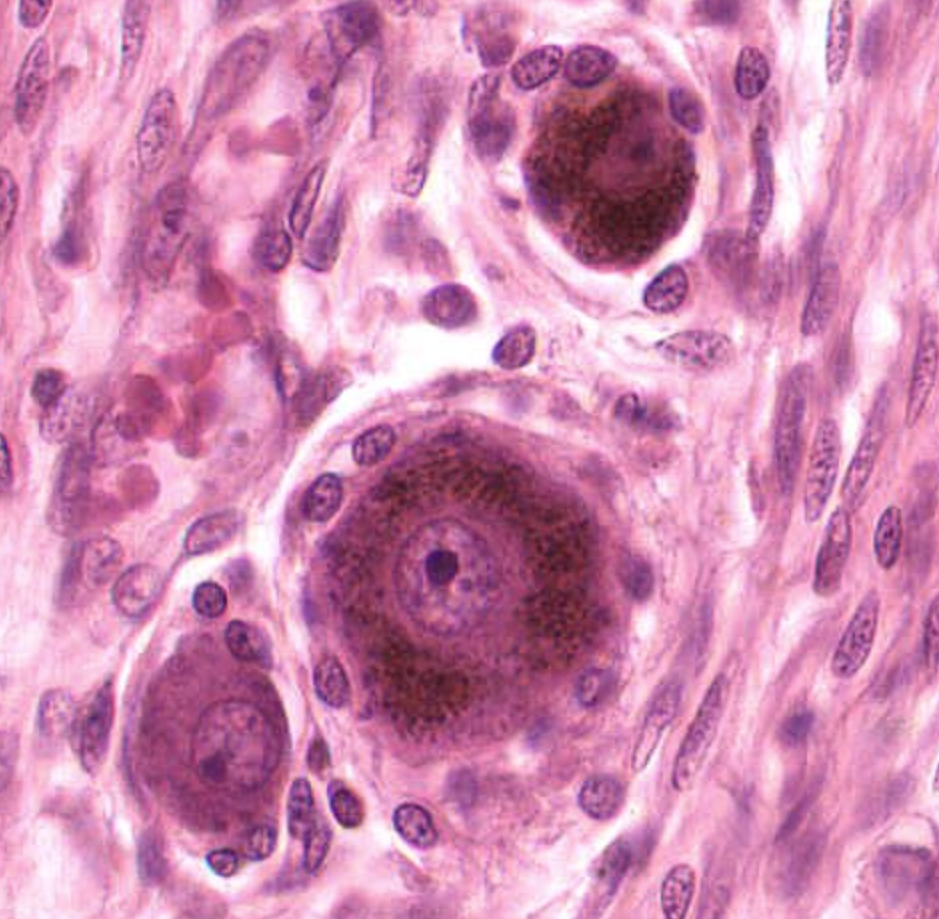
which ganglion
sympathetic, smaller and more uniform body size- no clear ring of satellite cells (scattered)
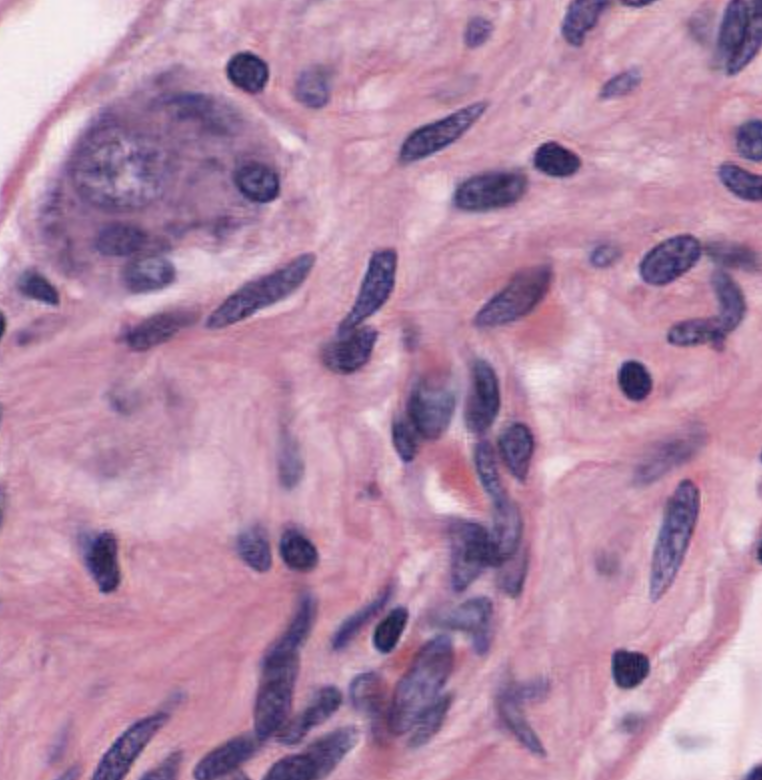
which ganglion
parasympathetic nucleus not centrally located & no neat ring of satellite cells
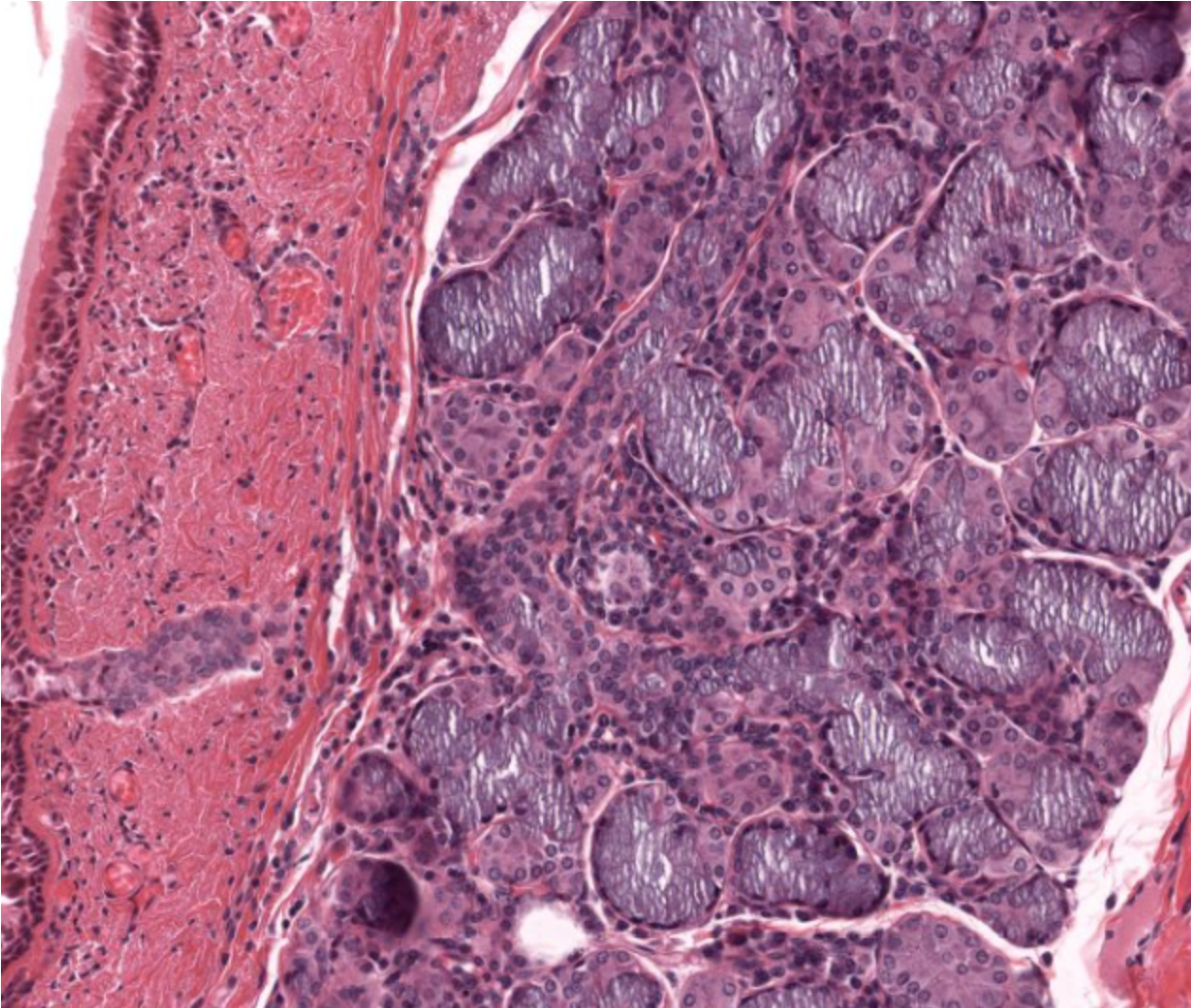
trachea- sero-mucous glands on right
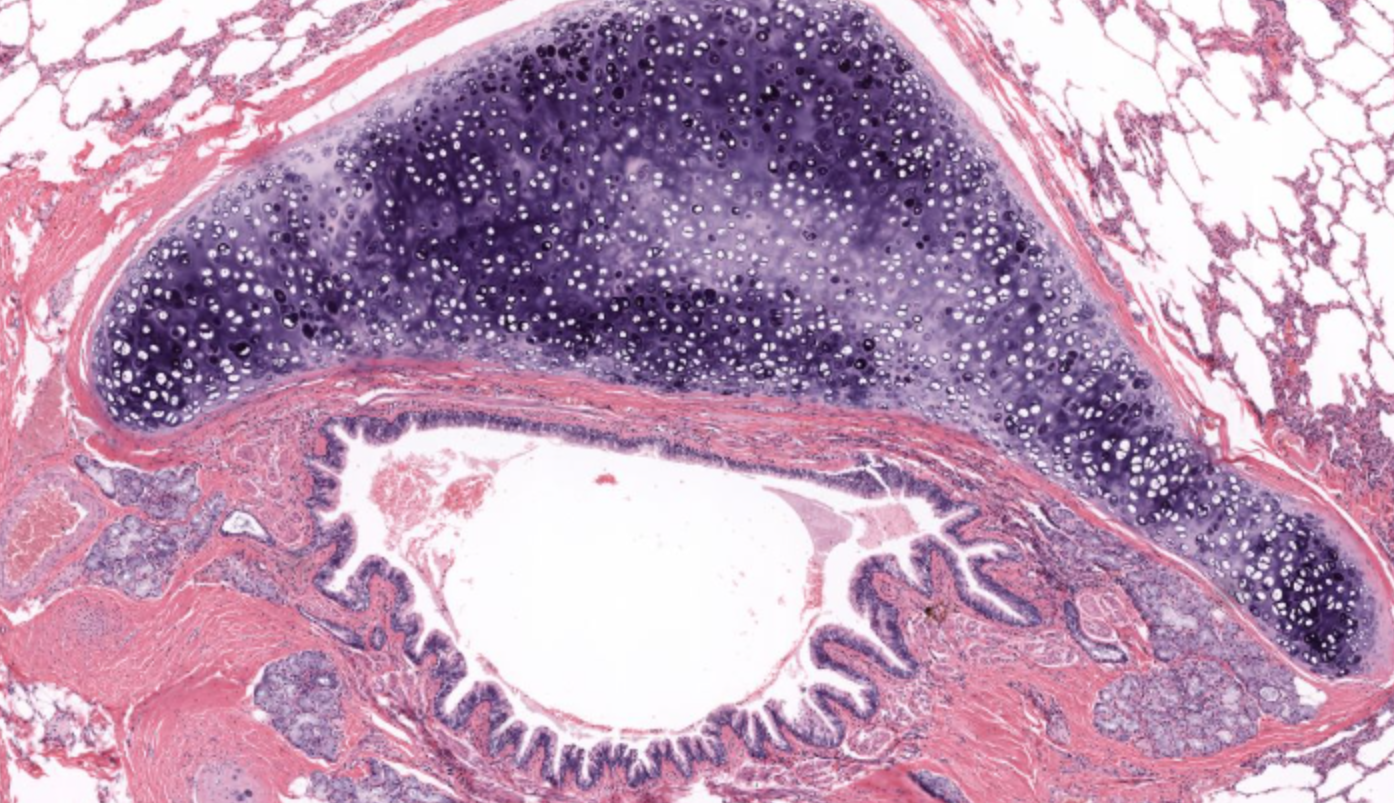
bronchi
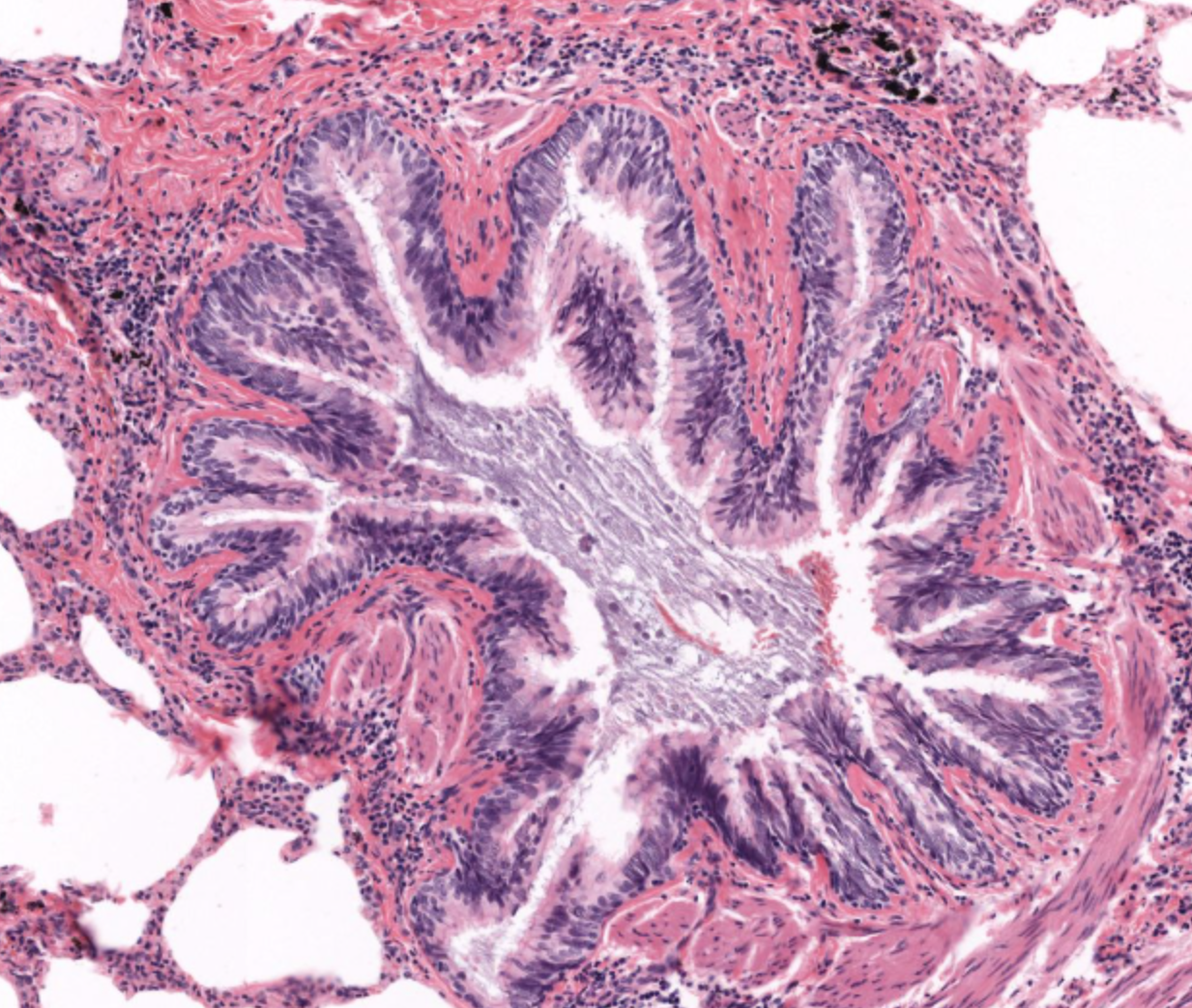
primary bronchi- contain club (clara) cells
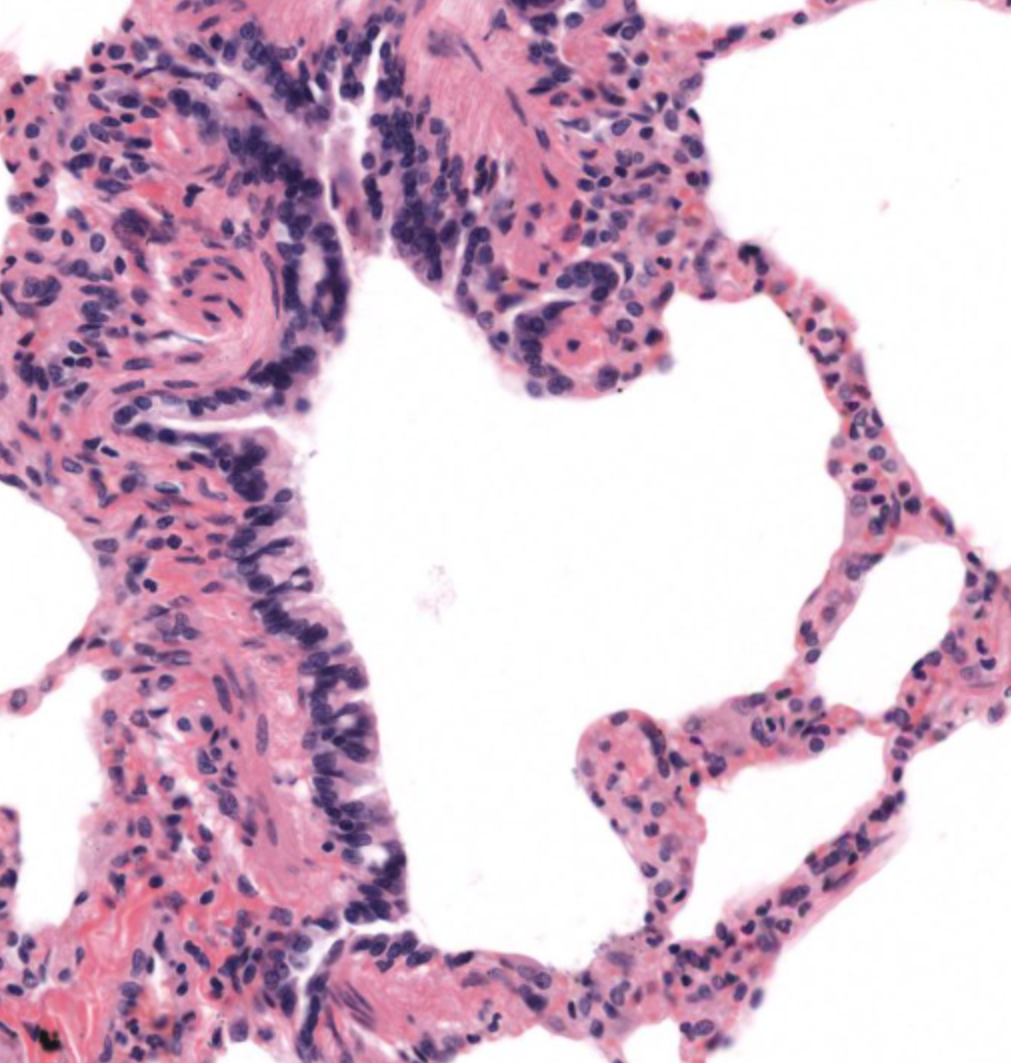
respiratory bronchioles
type 1 pneumocytes vs type 2 pneumocytes
type 1 (40%) make up 90% of SA of alveoli
3 layers of blood vessels
tunica intimia- thin layer with endothelium, basement membrane & subendothelial connective tissue & internal elastic laminae
Tunica media- smooth muscle cells, elastic laminae & collagen fibres
Tunica adventitia- external elastic lamina, lots of connective tissue with many collagen fibres (vasa vasorum & nerves)
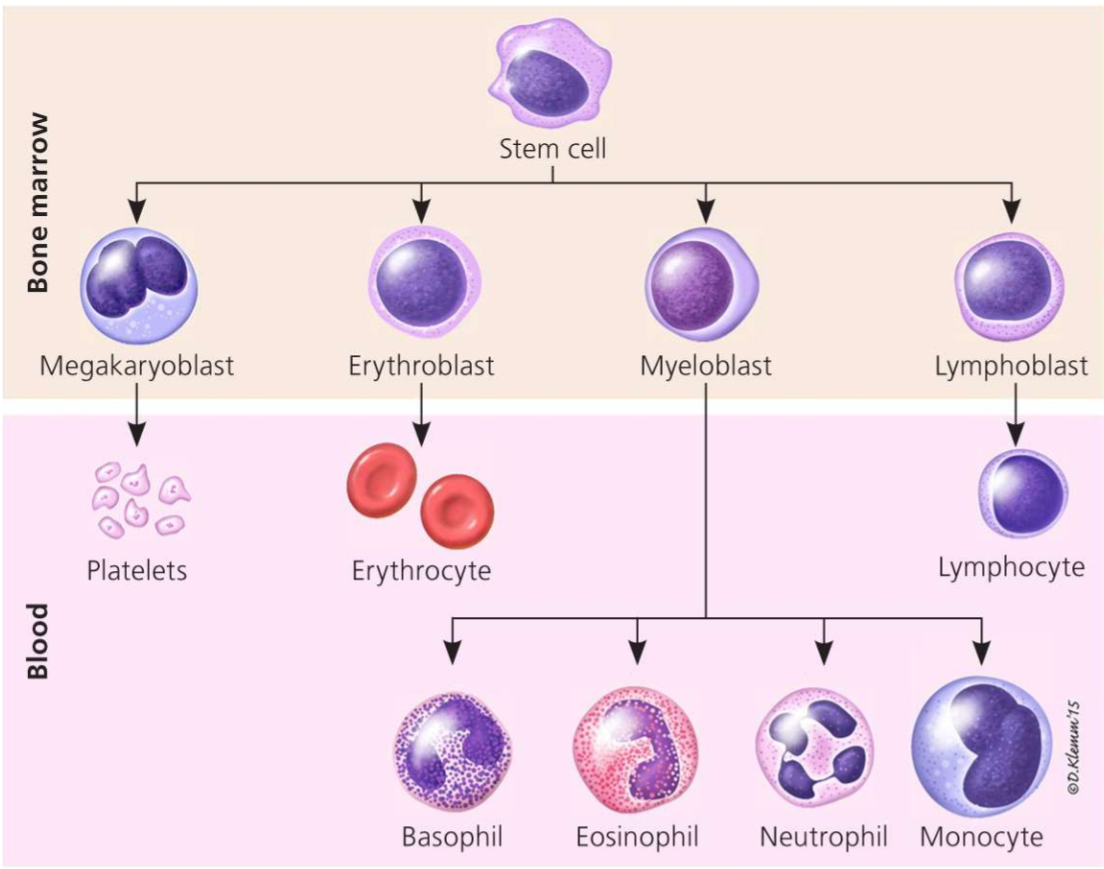
staining of WBCs
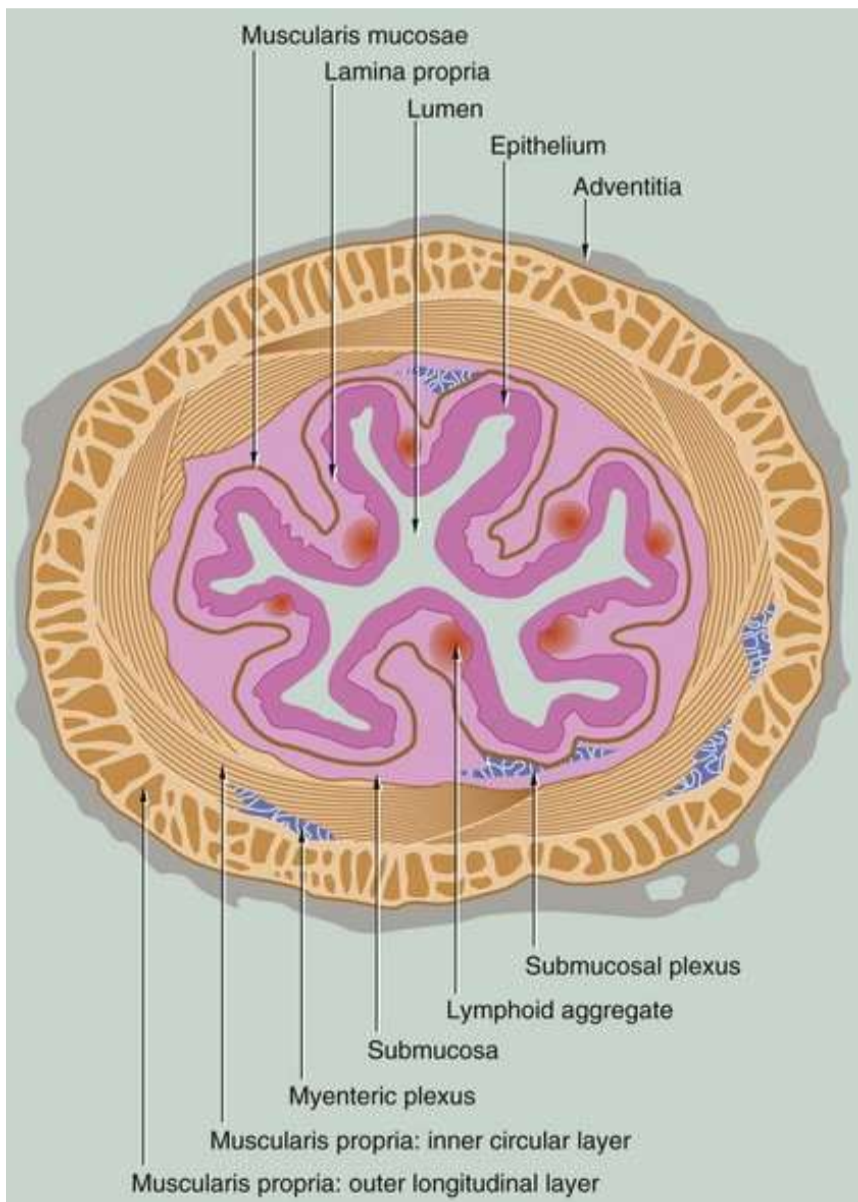
digestive system general layers
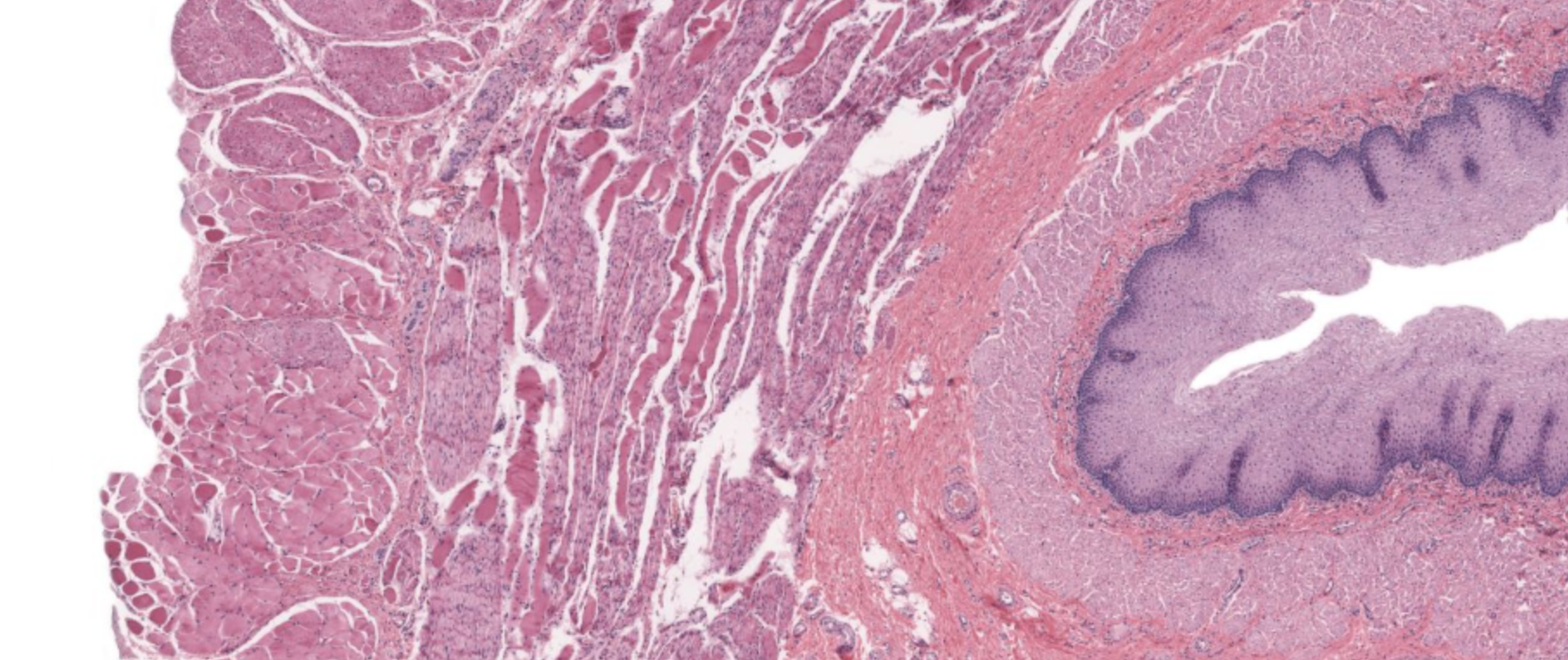
oesophagus, stratified squamous epithelium
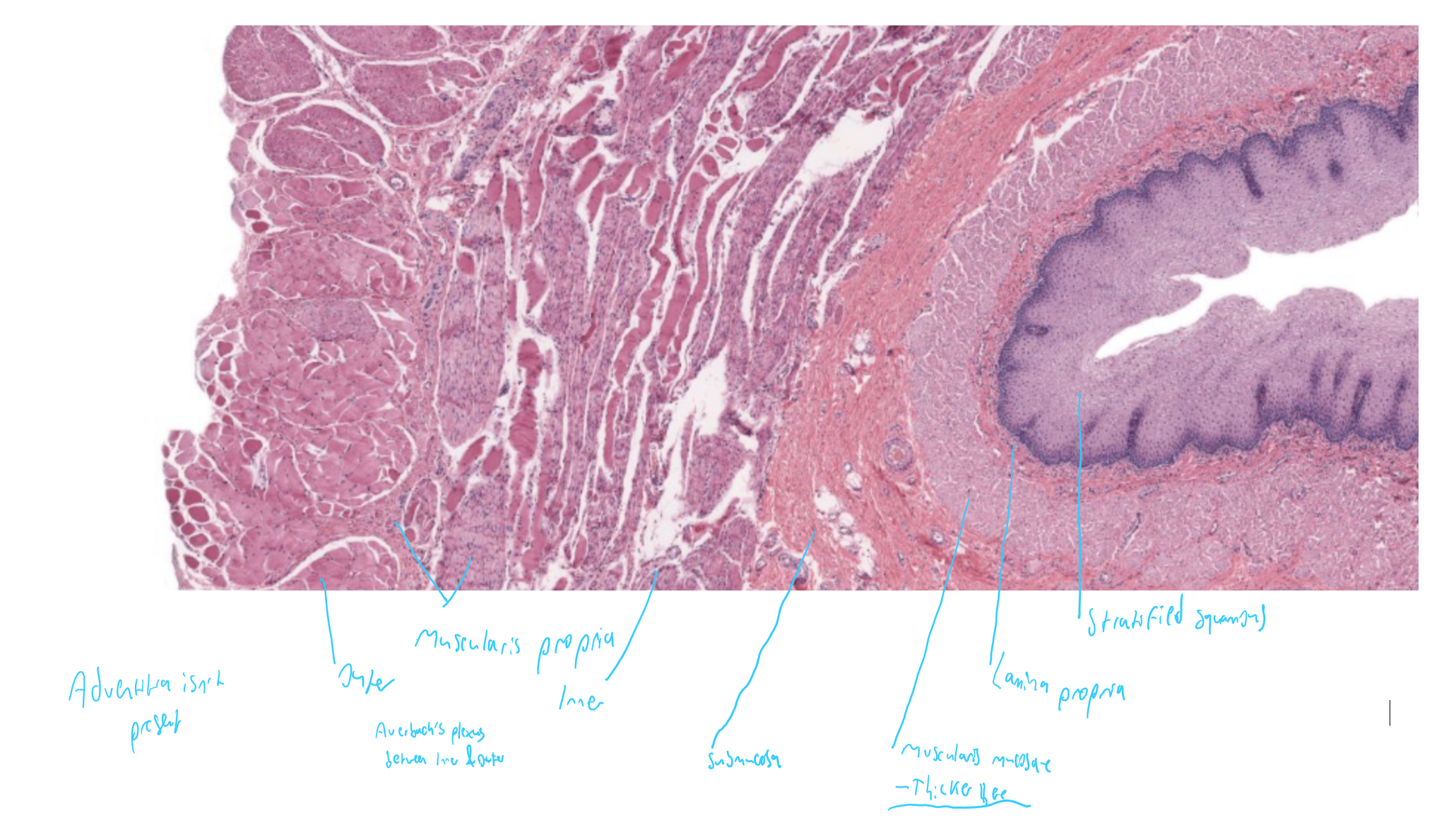
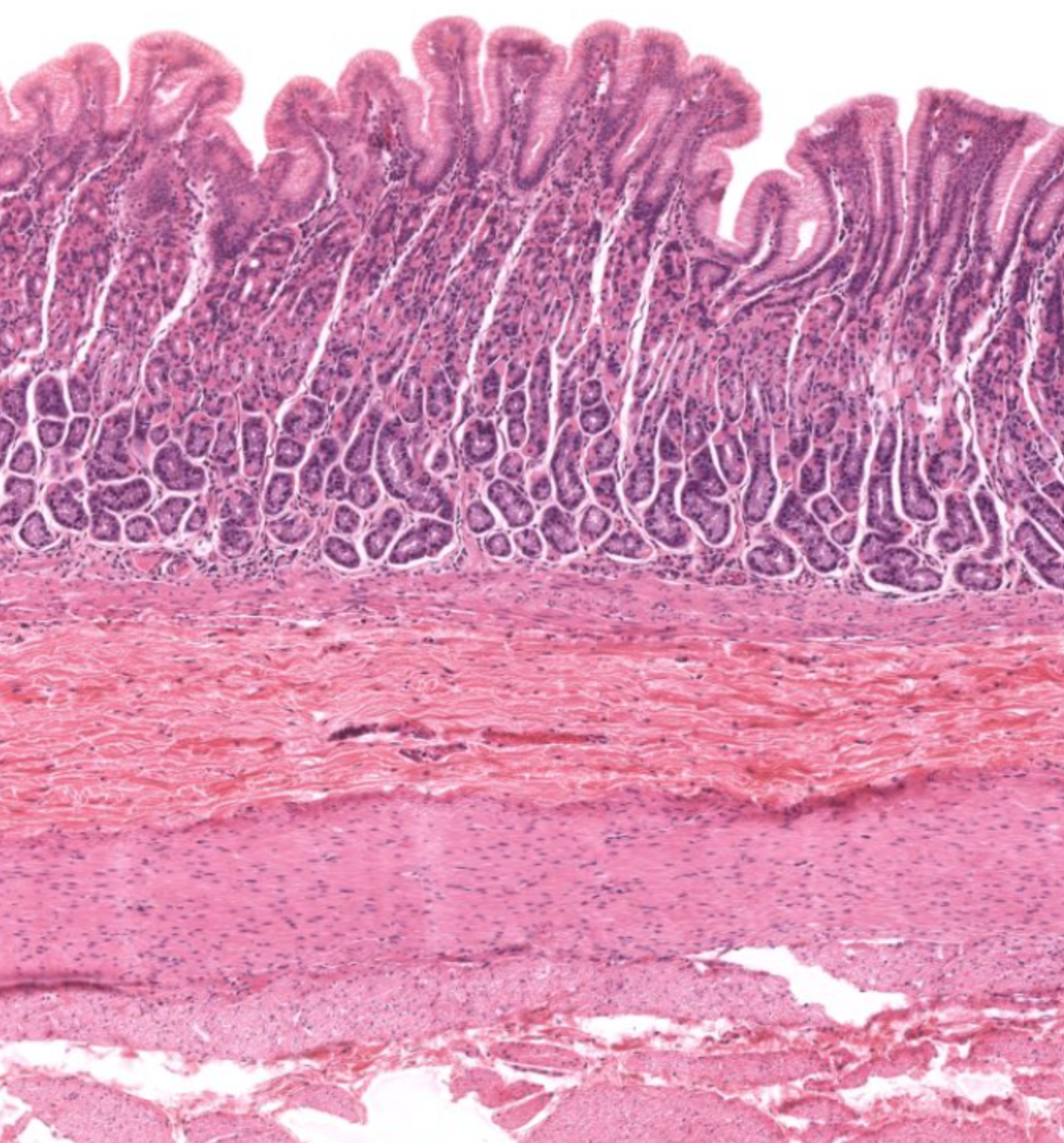
fundus/ body of stomach- simple columnar epithelium
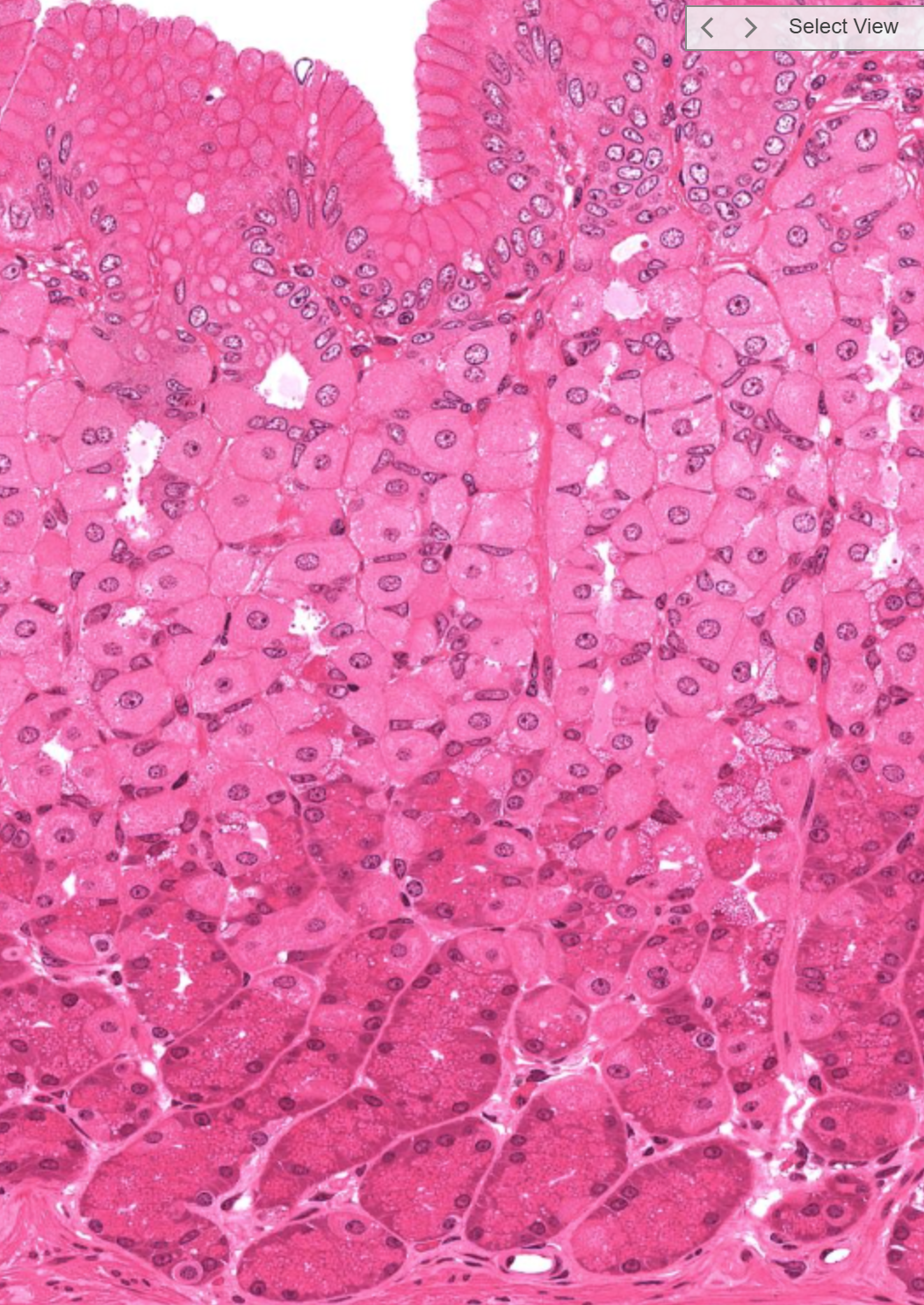
body of stomach, what are the two groups of cells
top: parietal cells, fried egg appearance, then bottom: chief/ peptic cells: zymogen granules visible
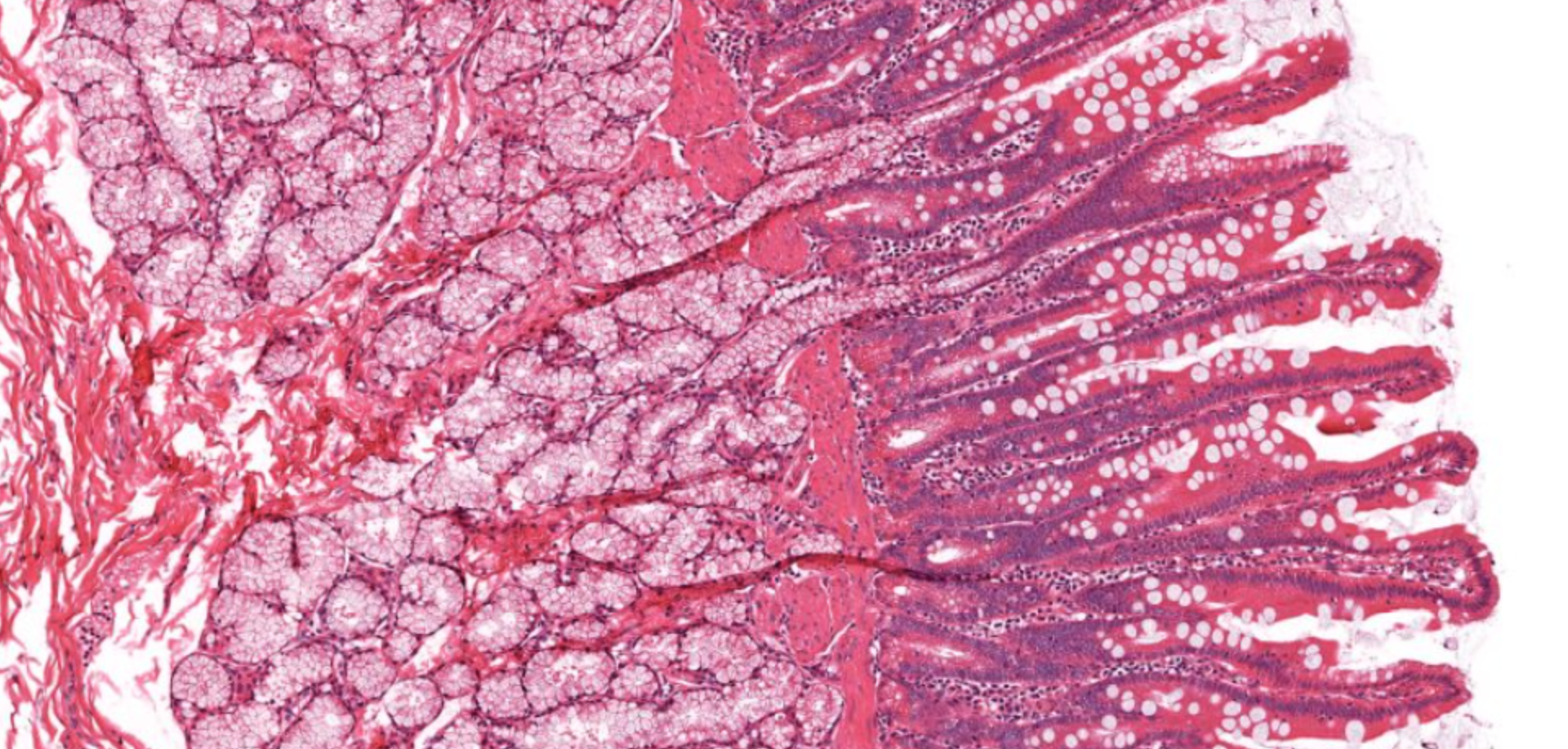
which part of SI?
duodenum due to the Brunner’s glands in the submucosa
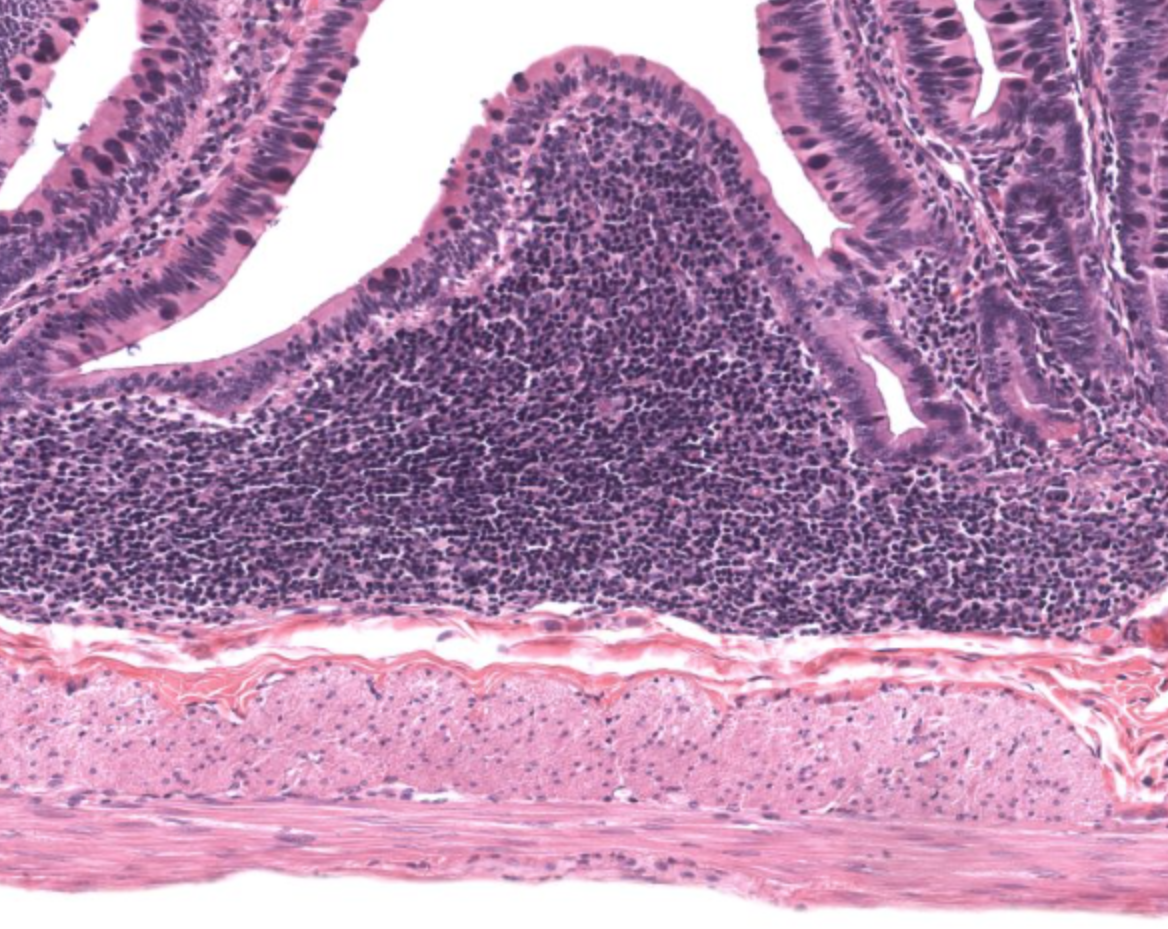
what is the mound in the middle
Peyer’s patch of ileum
defining feature of SI compared to stomach & colon
villi also they have columnar epithelial cells called enterocytes (not distinguishing)
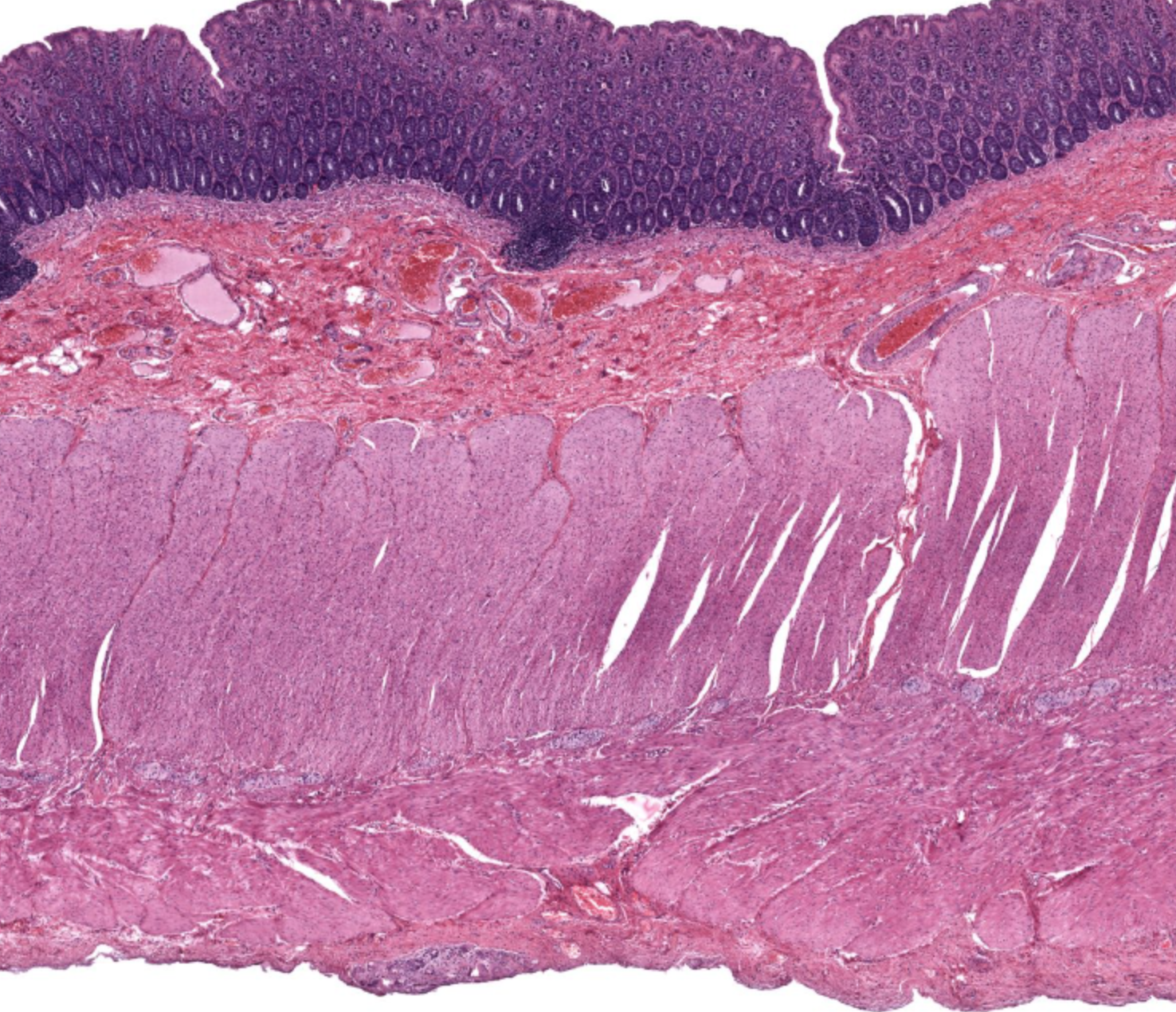
large intestine, no villi, extensive invaginations- colonic crypts, simple columnar
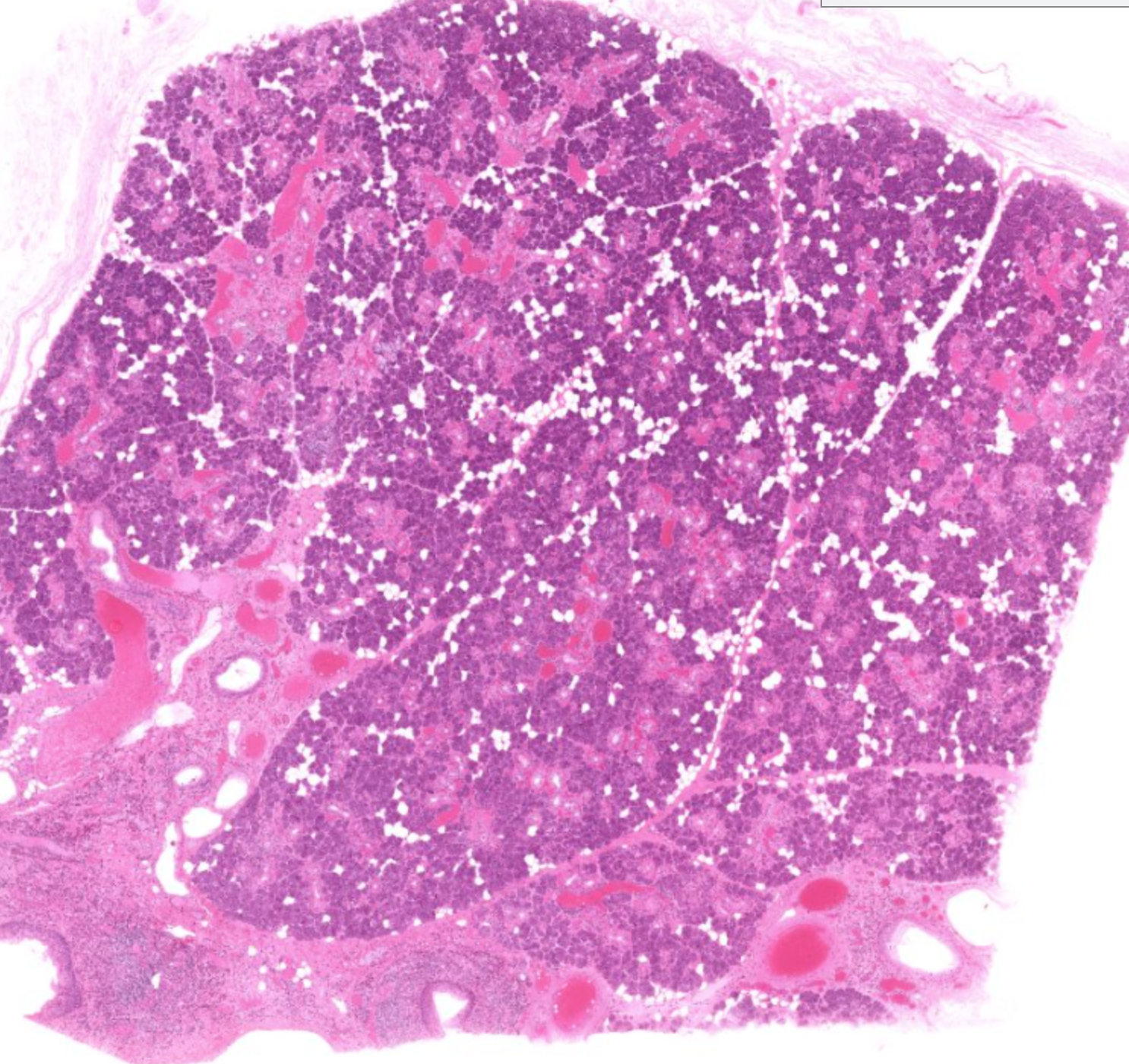
parotid gland (one of salivary glands), mostly serous cells visible
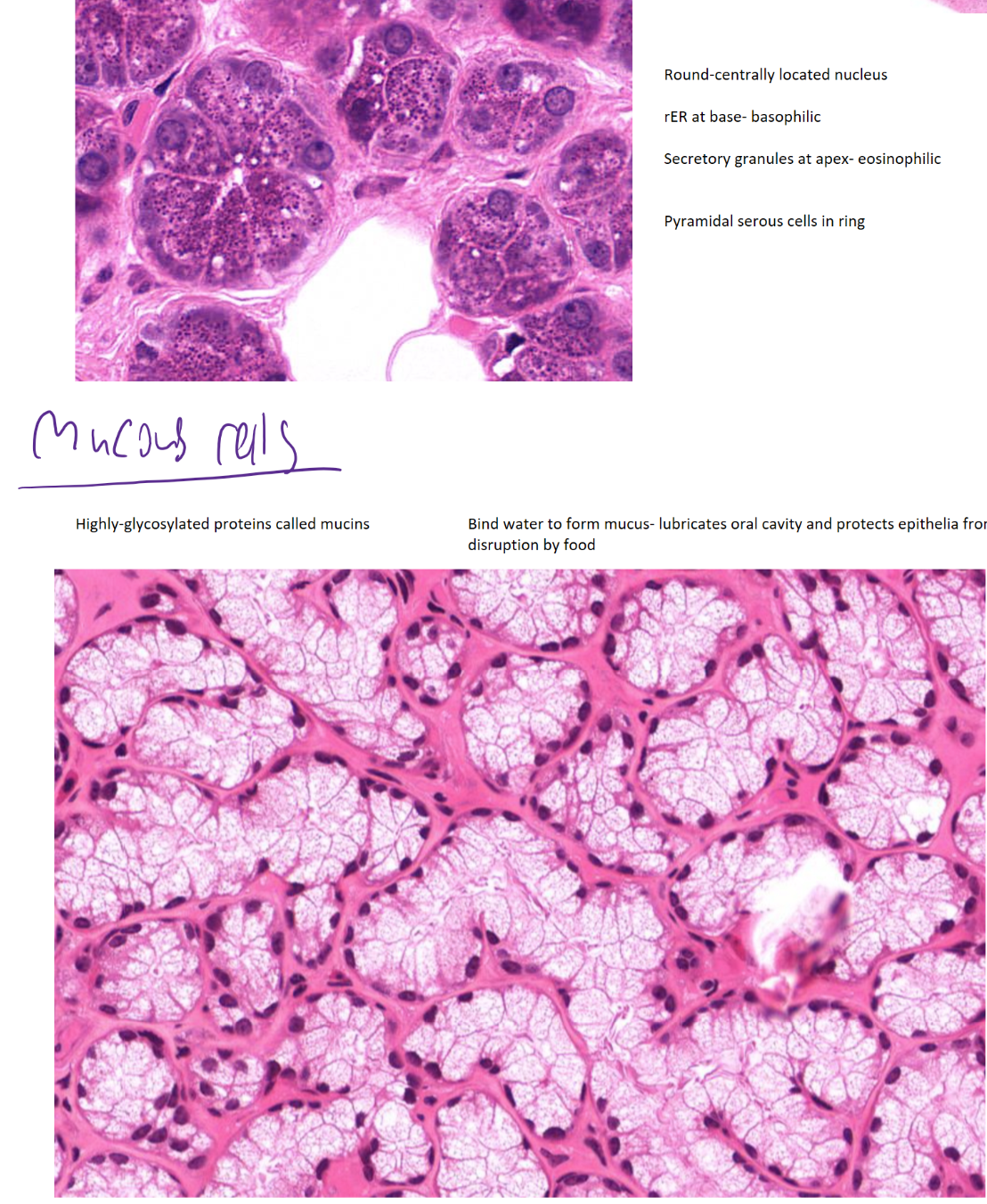
serous vs mucous cells
serous- produce protein rich fluid (amylase, lysozyme)- visible secretory granules, centrally located nuclei
mucous- produce mucin (glycosylated protein)- poorly staining cytoplasm, peripheral nuclei
levels of ducts in salivary gland
intralobular (intercalated & striated ducts) to the interlobular ducts (PNS innervation, ganglia present)
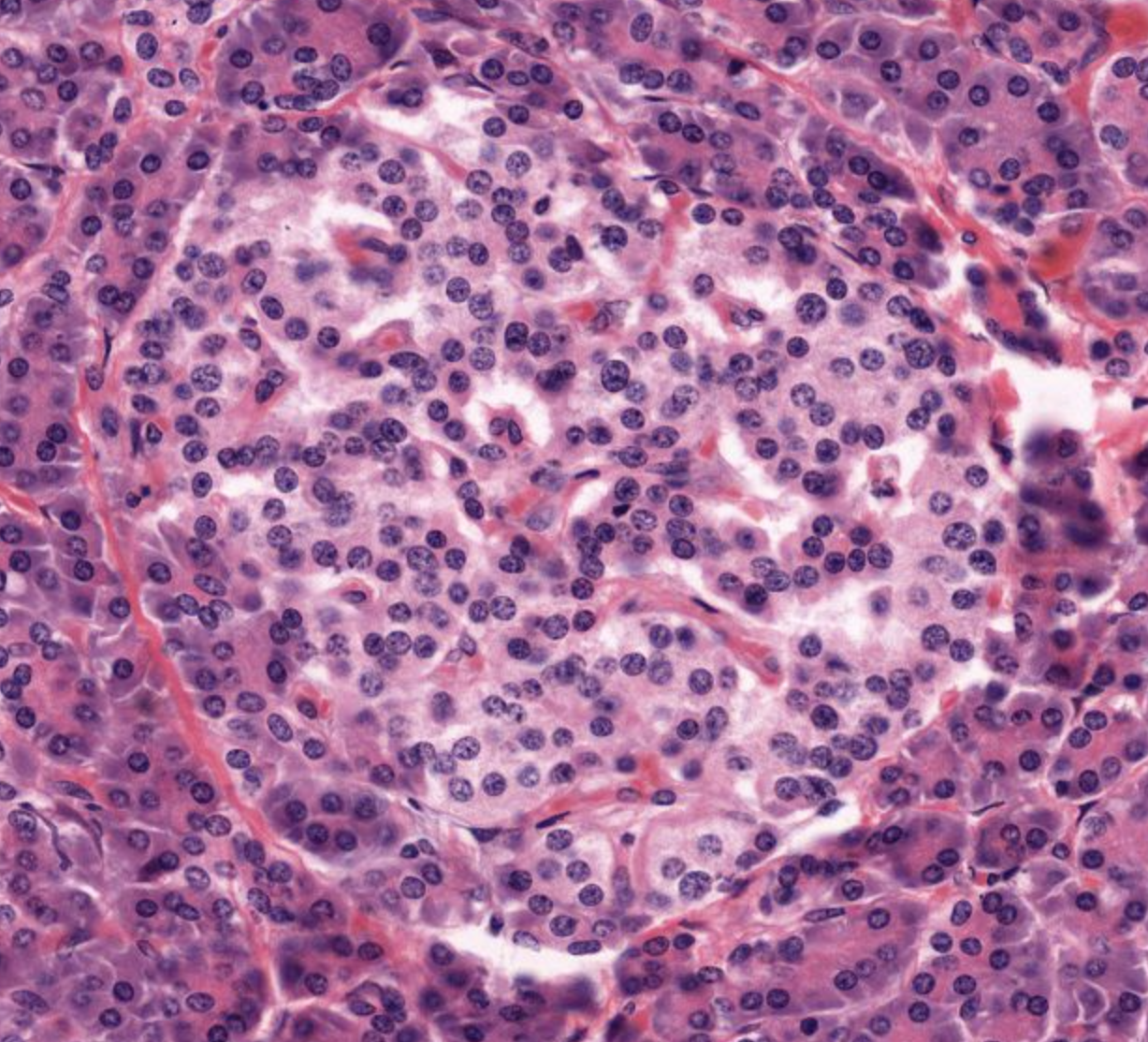
islet of langerhans- only 1-2% of pancreas volume

pancreas
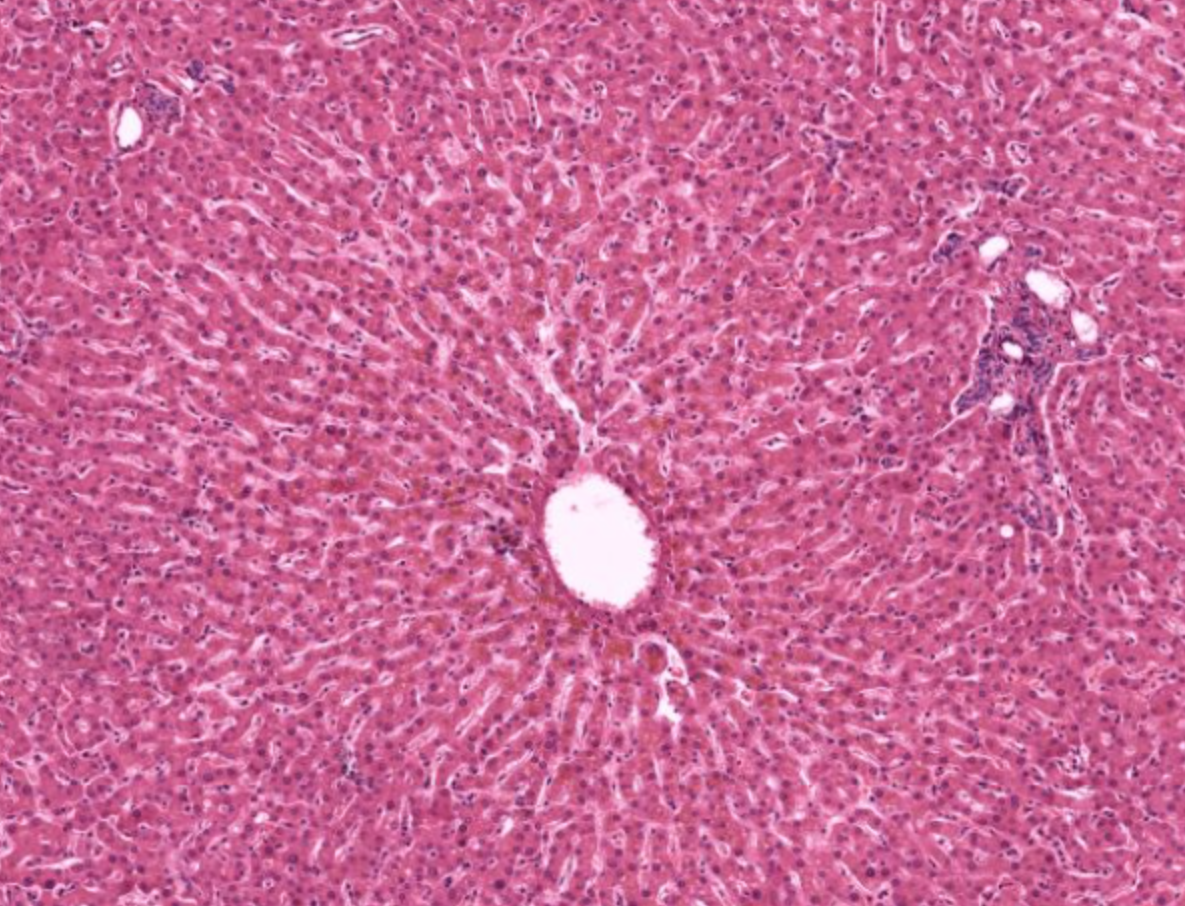
liver lobule- functional unit of liver
space of disse
perisinusoidal space- between sinusoidal capillary and hepatocytes
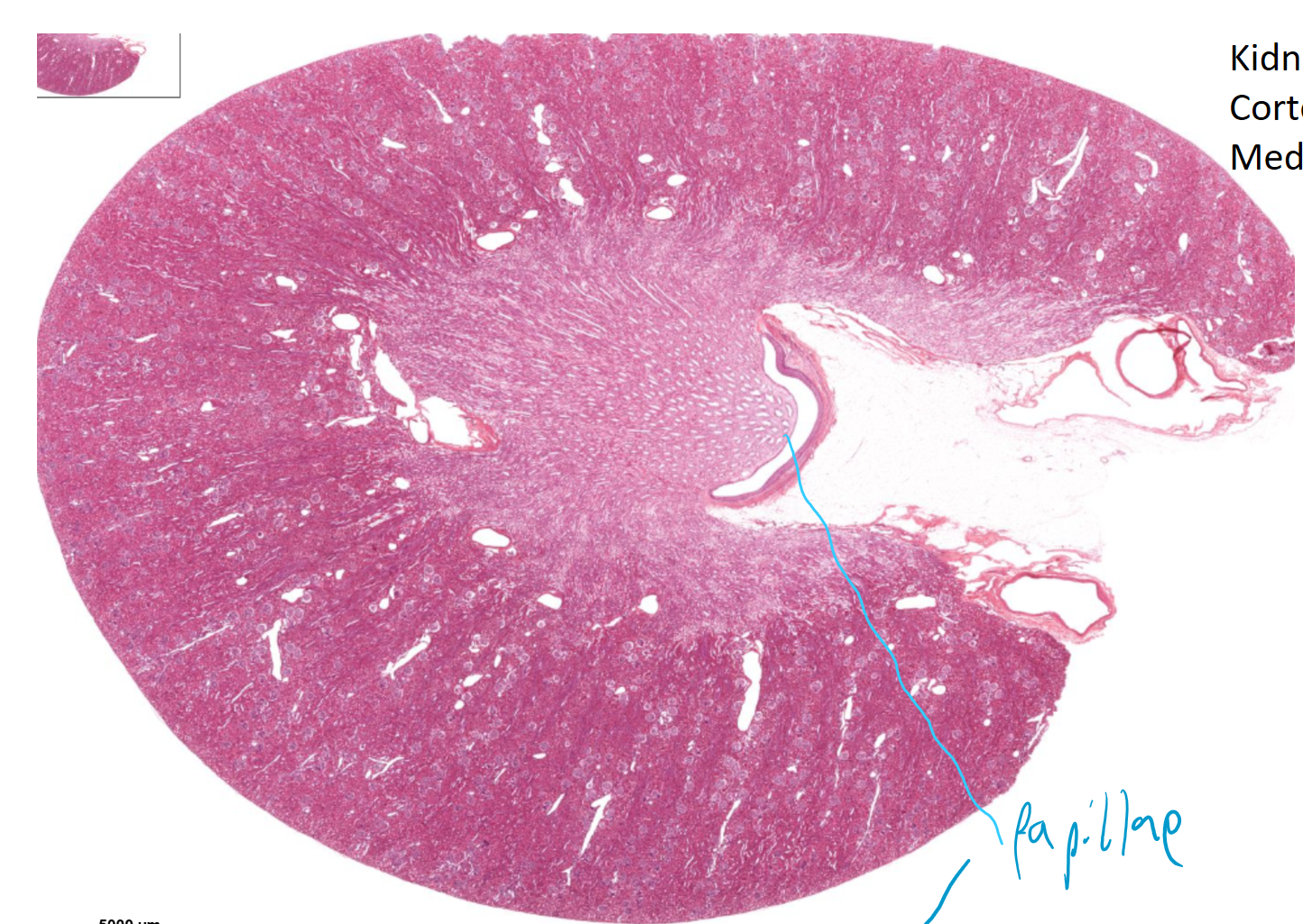
kidney, renal papilla and minor calyx visible
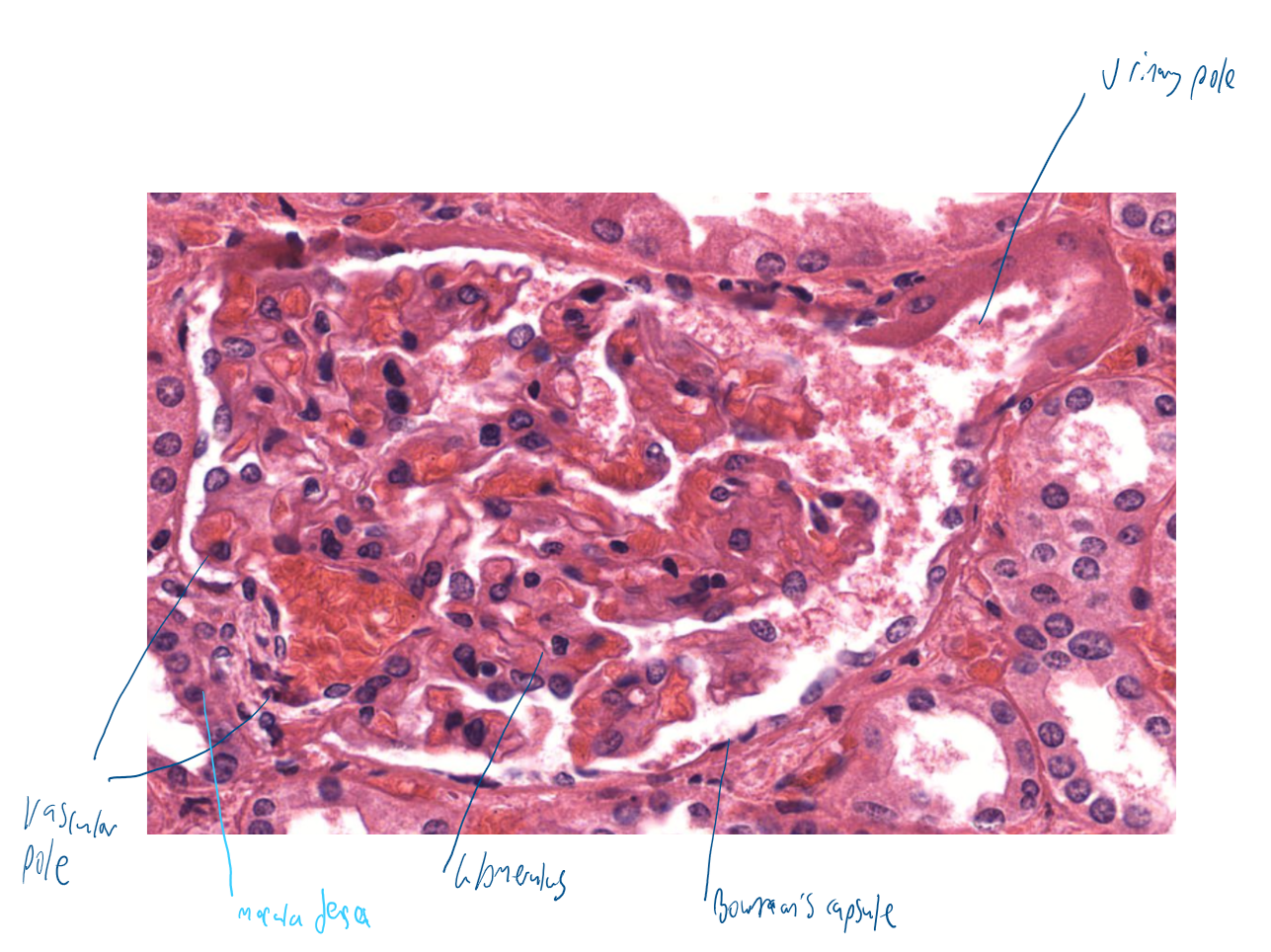
renal corpuscle structure
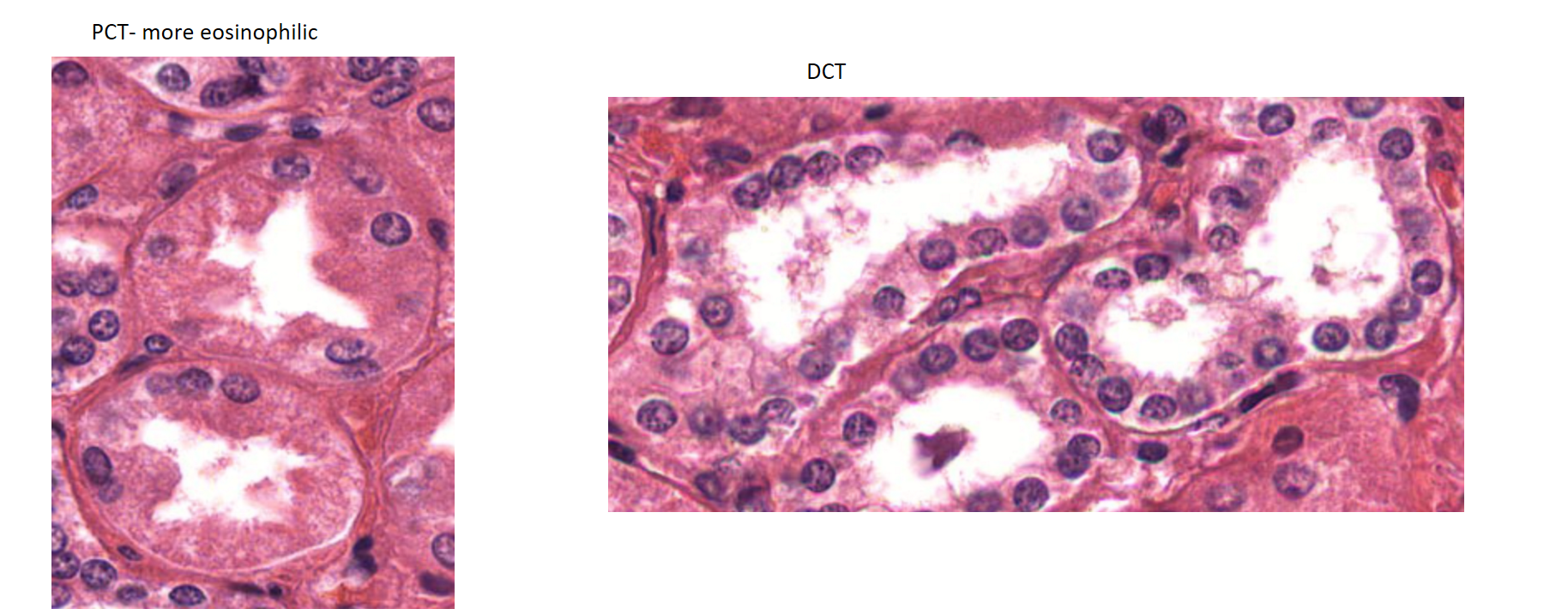
PCT vs DCT
PCT has brush border, stains more intensely than DCT
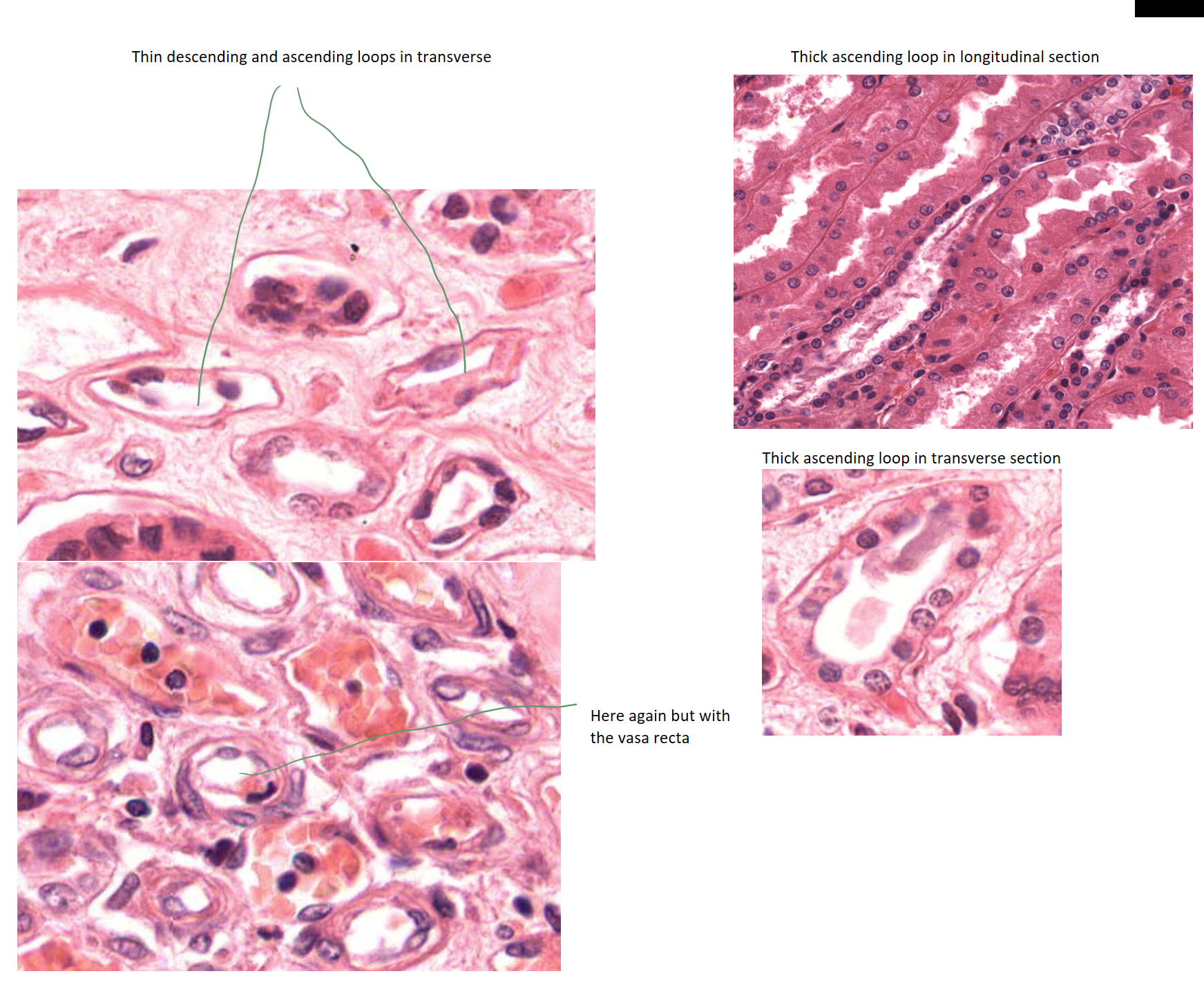
thin descending/ ascending vs thick ascending
simple squamous vs simple cuboidal
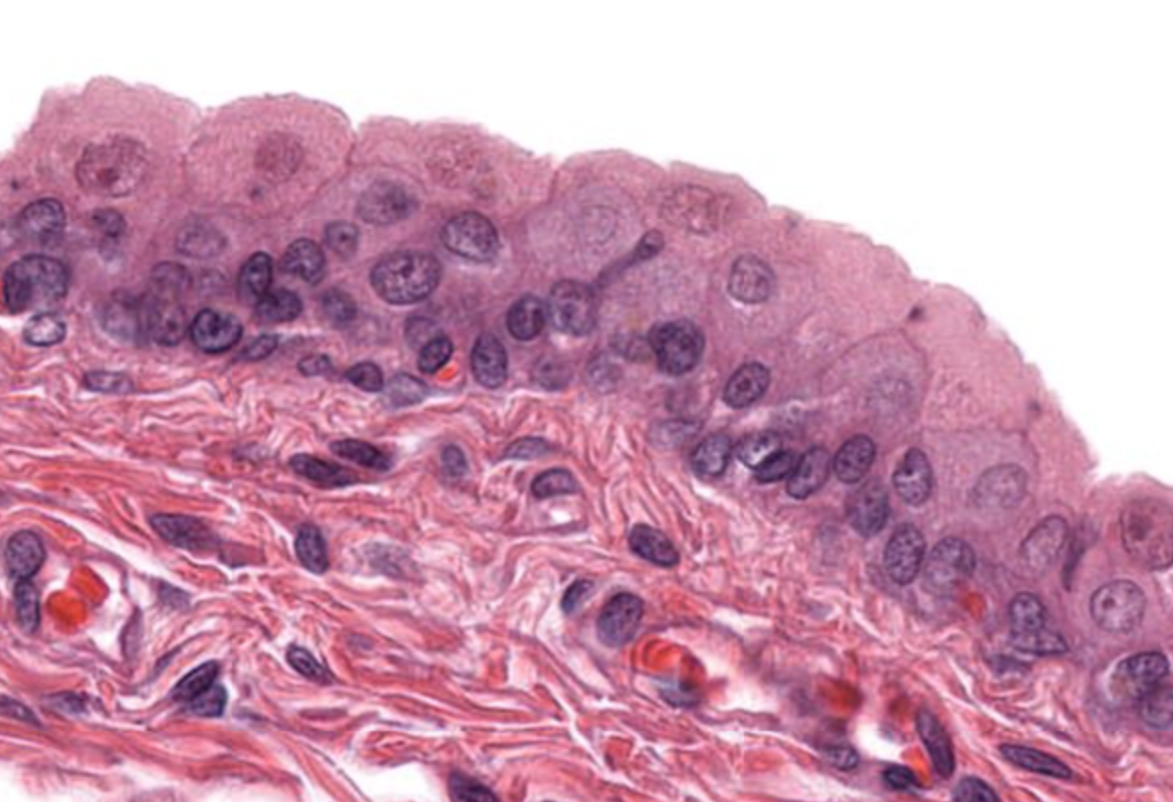
transitional epithelium- bladder, ureter and upper urethra, umbrella cells on top
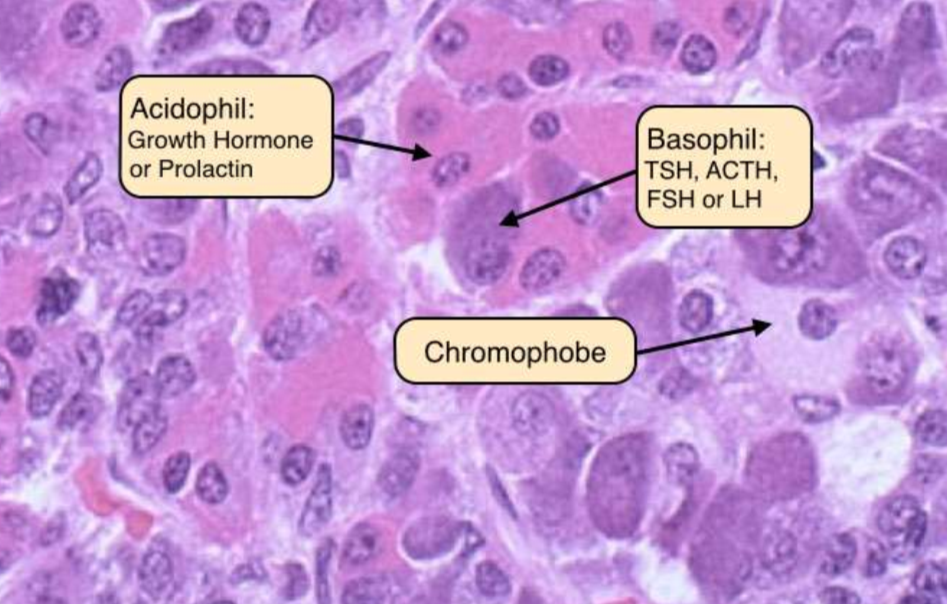
cells in anterior pituitary
are cuboidal to columnar epithelial cells that secrete various hormones such as GH, ACTH, TSH, FSH, and LH.
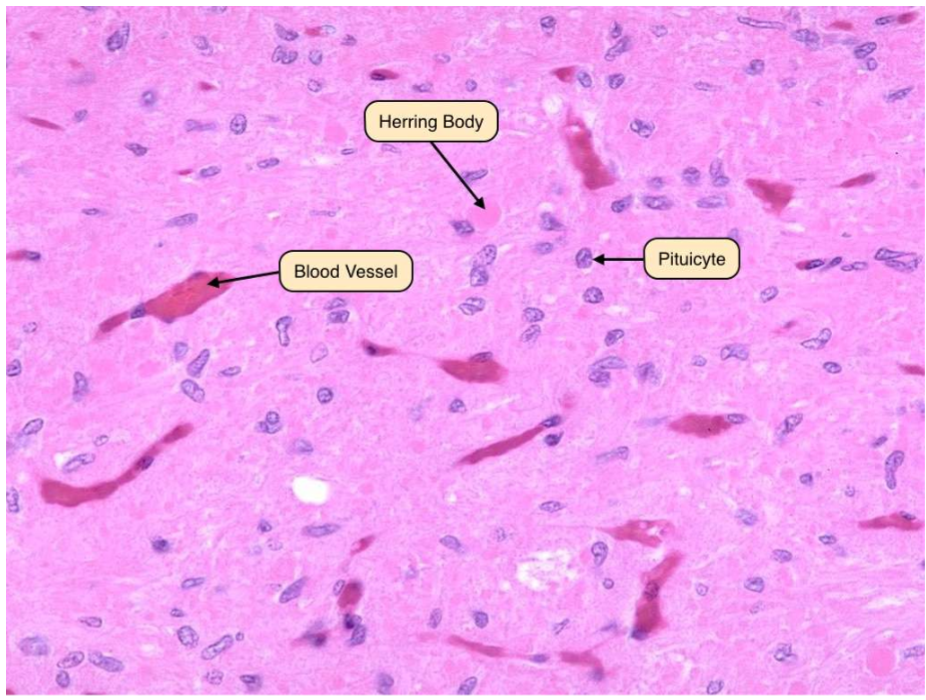
cells in posterior pituitary
most nuclei= pituicyte cells, herring bodies= axonal swellings full of secretory granules that store and release hormones like oxytocin and vasopressin, produced in the hypothalamus.
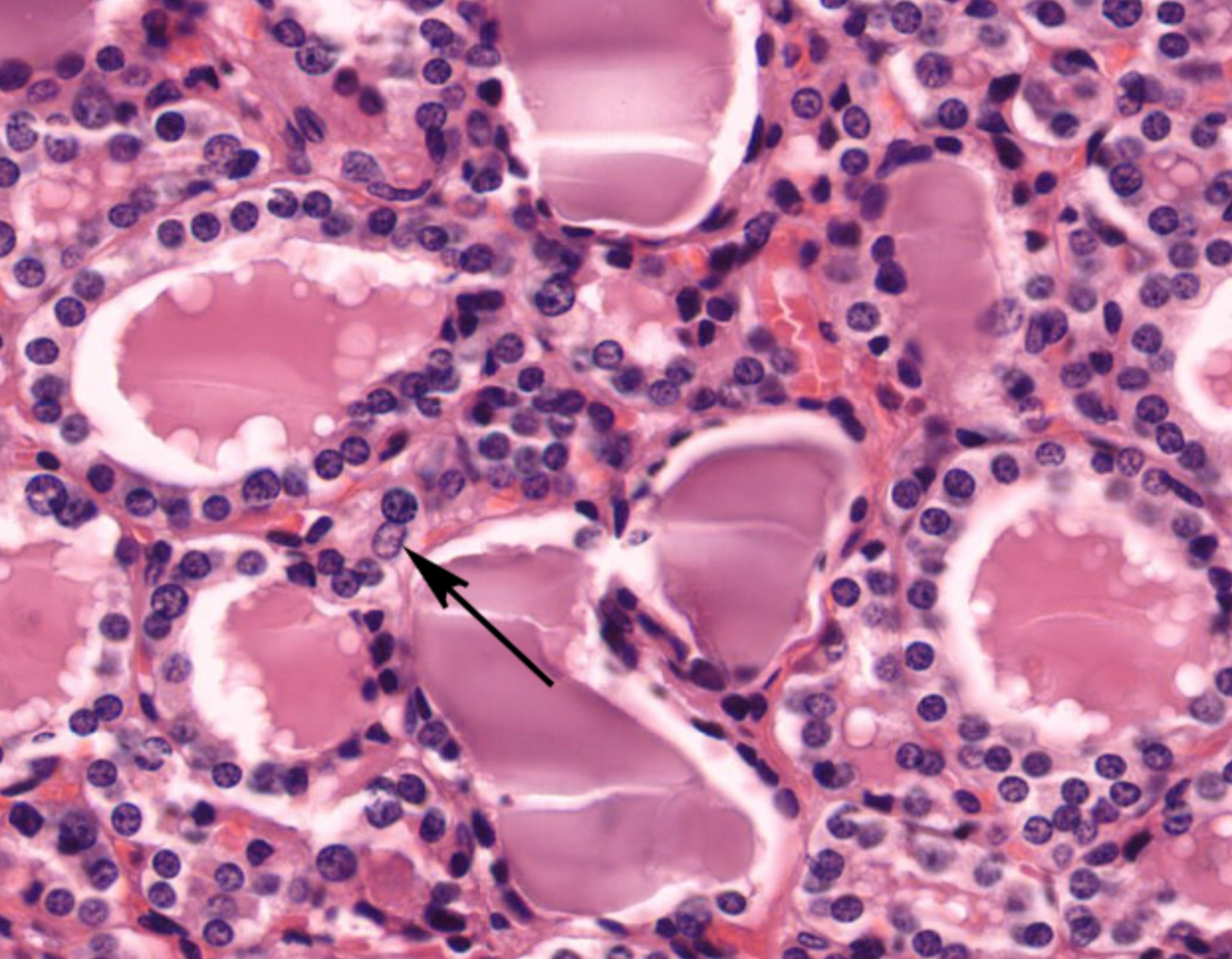
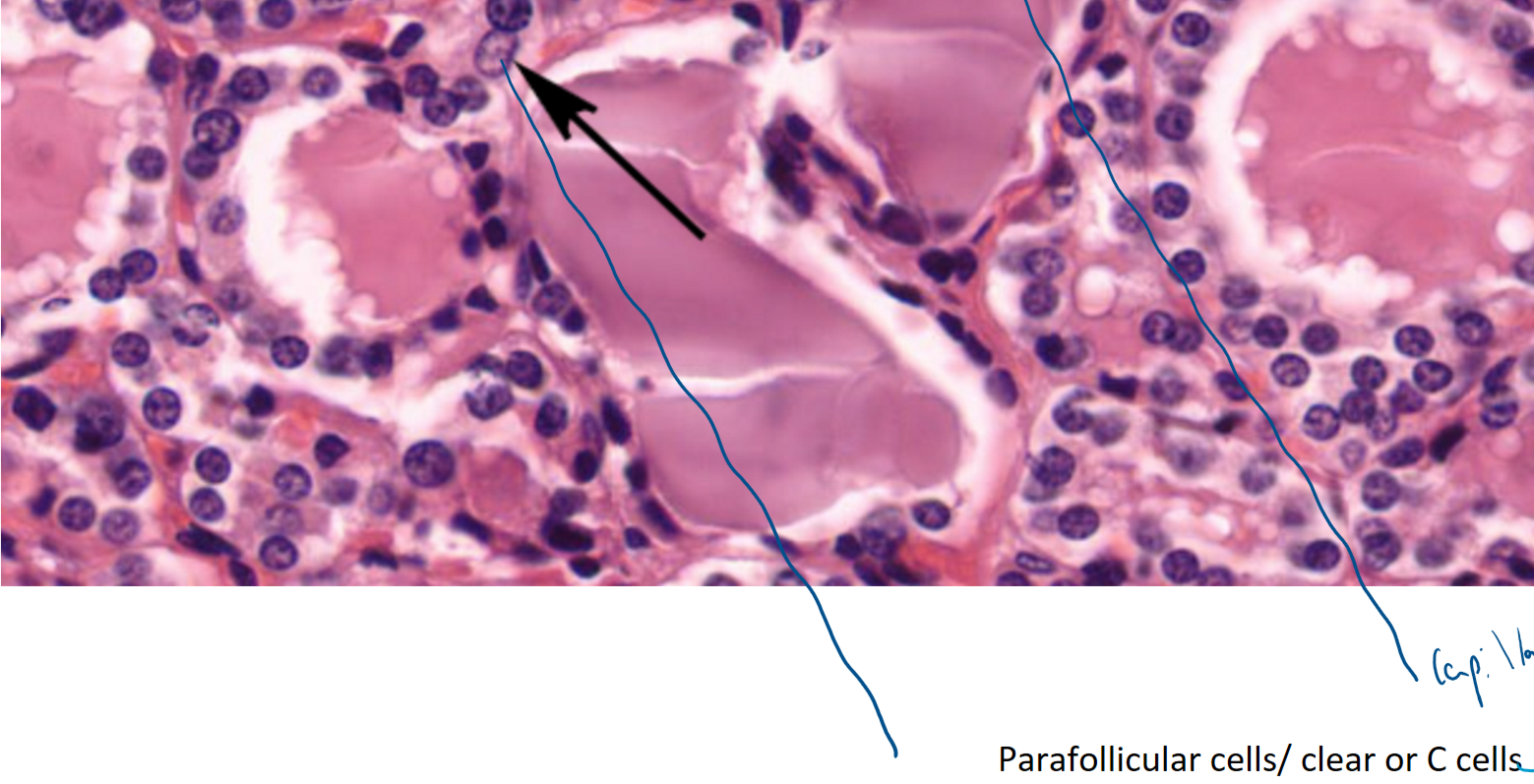
zoomed in on the thyroid gland- distinctive follicles with colloid in the lumen- gaps are artefact
parafollicular cells/ C cells/ Clear cells?
produce calcitonin (inhibits bone resorption), in periphery of follicles, stain poorly with H&E
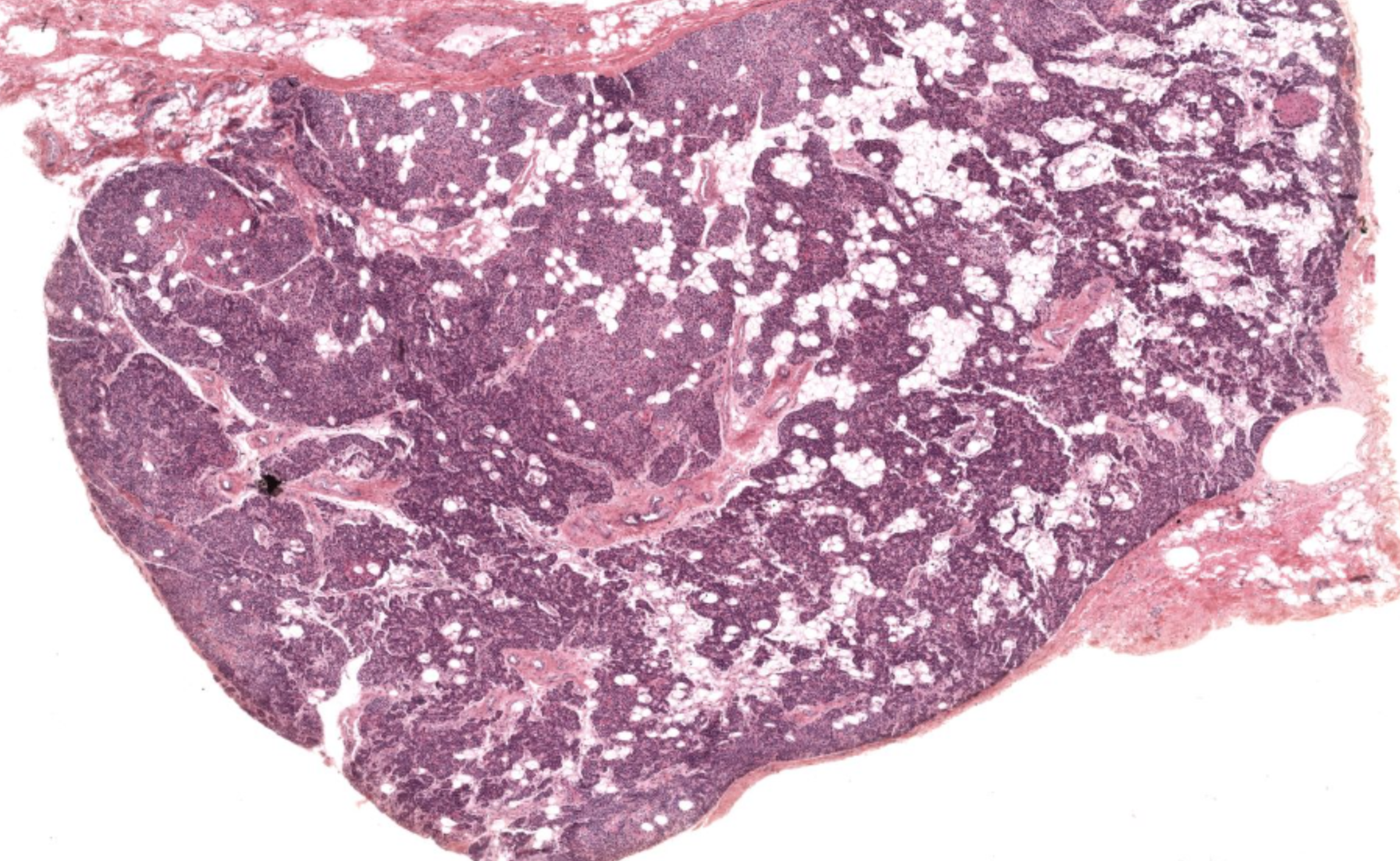
parathyroid gland
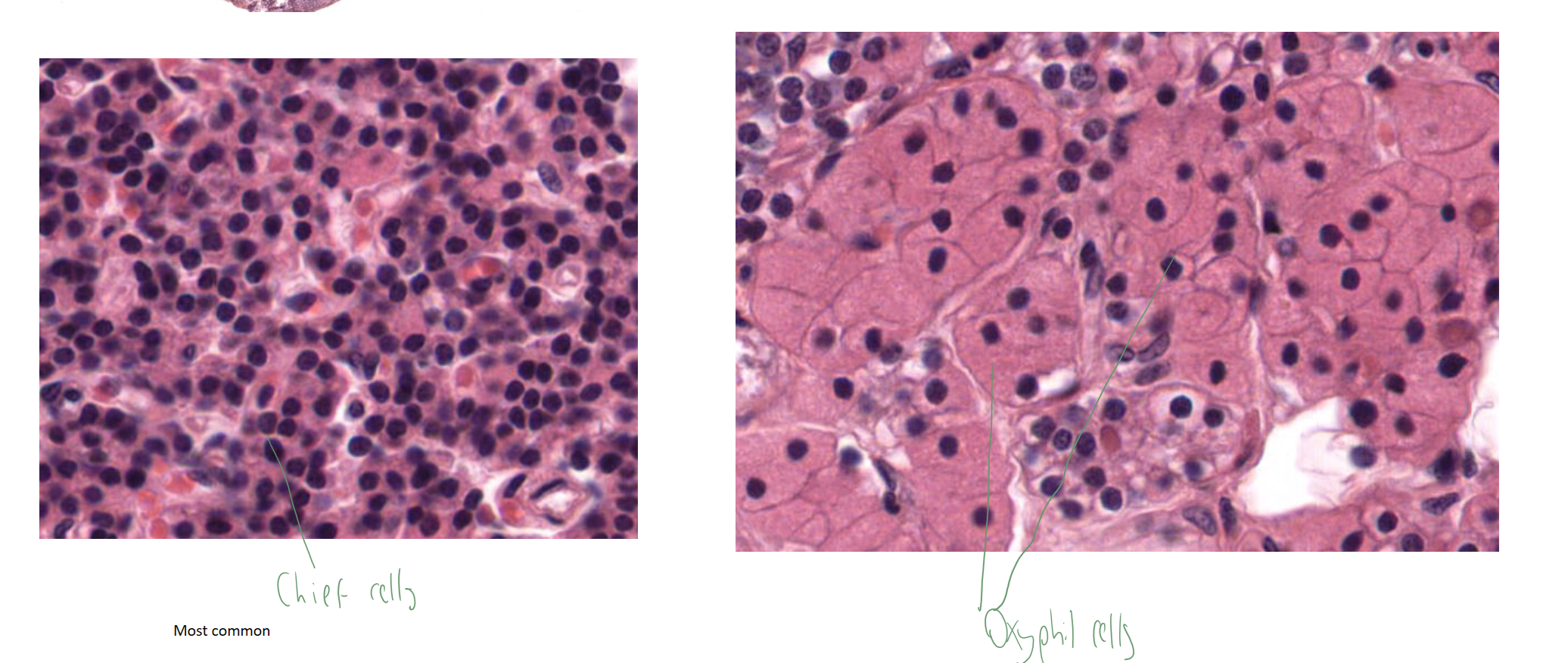
cells in the parathyroid gland?
oxyphil cells & chief cells (produce PTH)
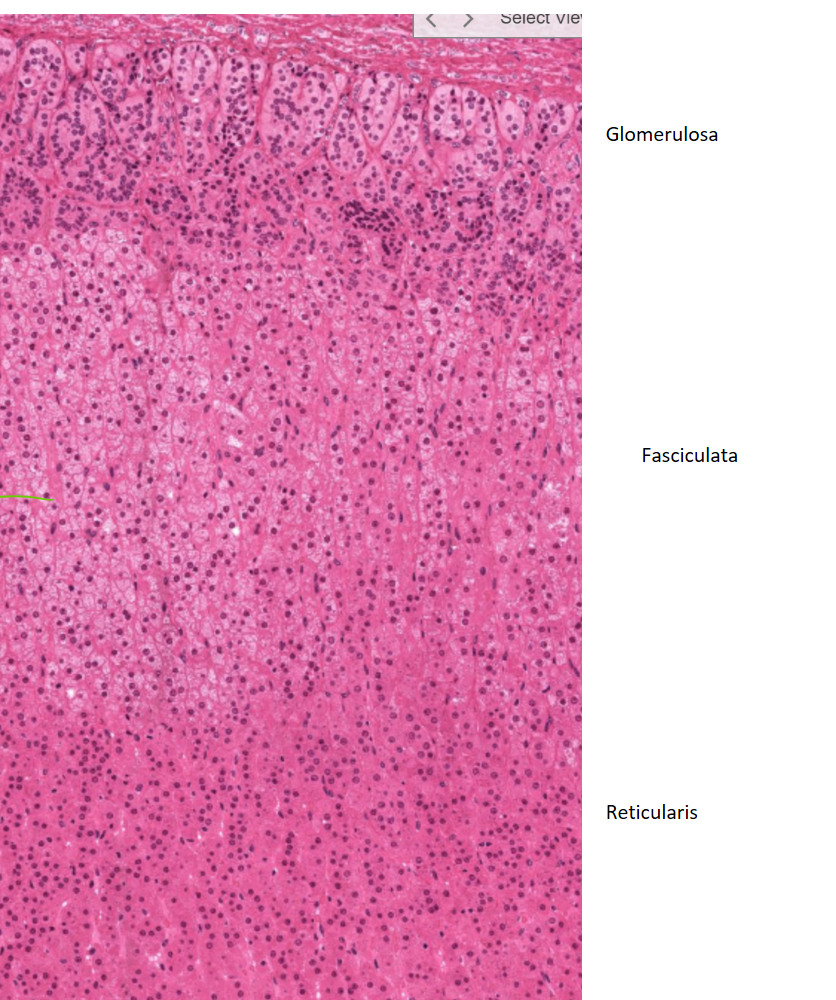
zones of the adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa on outside (produces aldosterone), zona fasciculata (makes up most of cortex) (produces cortisol), and zona reticularis (produces androgens).
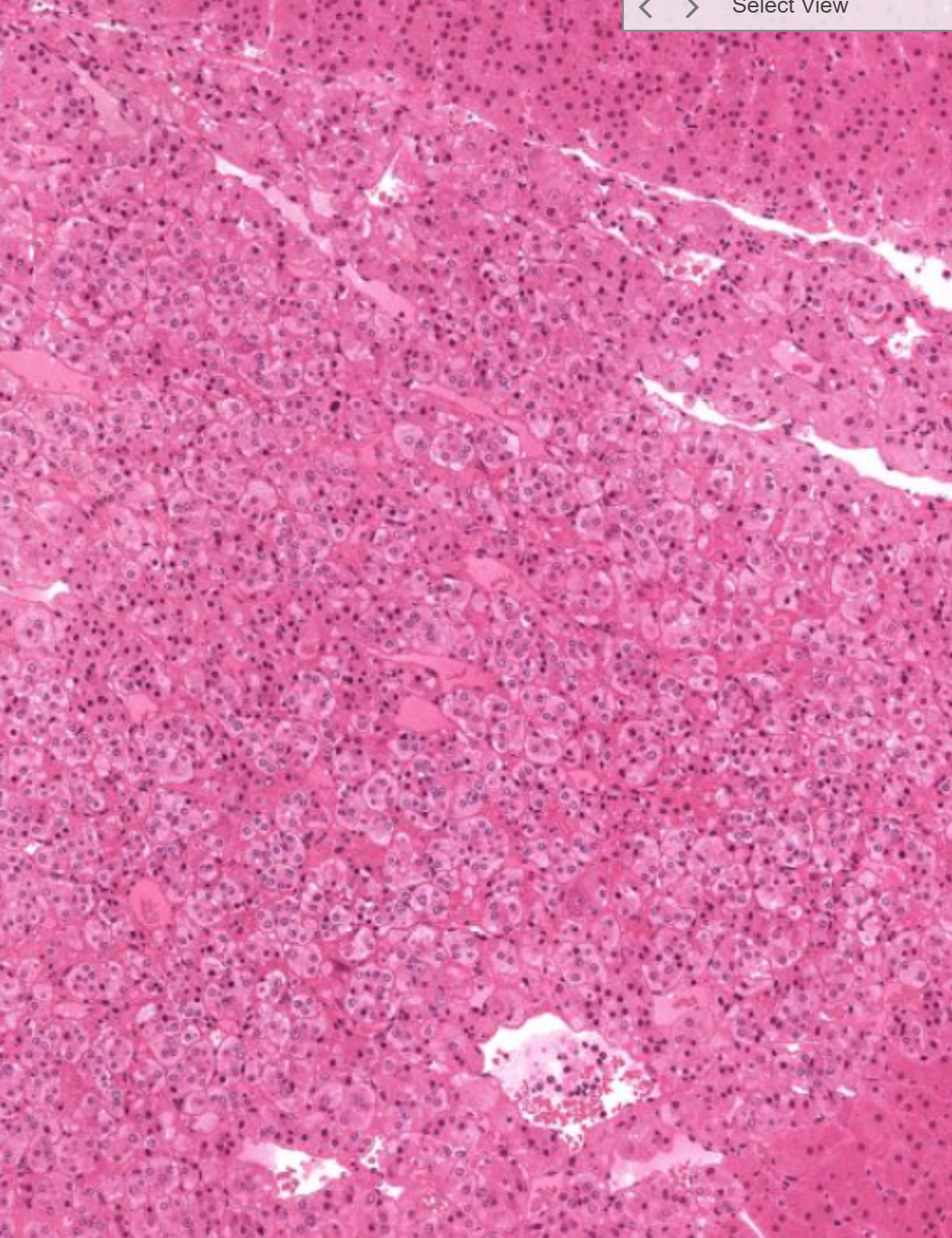
Adrenal medulla containing ganglion cells and chromaffin cells that produce catecholamines like adrenaline or noradrenaline (or dopamine)