APHUG - Unit 5
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Earliest settlements
Near rivers due to enriched soil and resources.
Agricultural Surplus
When crop yields are sufficient to feed more people than just the farmer and their family. [ Agricultural Surplus and socioeconomic stratification necessary for development ]
Socioeconomic Stratification
Structuring of society into different groups, such as a leader, government, ruling class.
The First Urban Revolution
A period characterized by socioeconomic stratification and agricultural surplus that led to the emergence of early cities.
Urban Hearth Areas
Regions where the world's first cities evolved, such as Mesopotamia, the Nile River valley, the Indus River Valley, and the Yellow River Valley in China.
Site
The absolute location of a place on Earth, defined by specific coordinates.
Situation
The relative location of a place in relation to its surroundings.
Diffusion of Urbanization (Europe)
Began with the Greek and Roman empires, where cities grew as outposts using water transportation through aqueducts and a road and highway system.
Development of Cities in Spain, Chinatown, Americas
Various influences shaping cities: Spanish cities as centers of learning and commerce, Chinese cities around traditions and beliefs, and American cities marked by control and subjugation.
Capitalism
An economic and political system where a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners rather than the state.
Communism
An economic and political system in which all property is publicly owned and managed.
Rural to Urban Migration in China
Under communism, rural Chinese were forced to migrate to cities; after state policy reform, many abandoned poverty.
Transport Technologies for cities
Henry Fords Model T, Samual Morse telegraph, Alexander Ghrams Telephone
Streetcar Suburb
A settlement outside of a city connected by streetcar lines, allowing for easy transportation in and out of the city.
Second Urban Revolution
The period marked by industrial innovations in mining and manufacturing that led to urban growth [ result of industrialization and innovations in mining ]
Effects of Second Urban Revolution
Reshaped cities, capitalist cities(housing districts became segregated based on money), ancient urban hearth areas(little separation between ones home and workplace)
Government Policies
Ancient cities(leaders managed agriculture etc), Colonialism( euro. Colonial cities as administrative or commercial centers), Industrial Revolution(govt policies regulated transport, housing, cultural life)
Redevelopment
A set of activities intended to revitalize an area that has fallen on hard times; redevelopment around waterways, canals, and harbors has revitalized modern cities by bringing in buisnuss opportunities, creating cultural settlers
Common site feature to hearth cities in Africa and Asia
Rivers in the Nile, Mesopotamia, Indus and Huang Ho valleys
Connection between agriculture and urbanization
Why cities couldn’t support large populations in the first urban revolution
As cities grew agricultural production and transportation must develop to get products to the city
Agricultural production
Metropolis
Very large and densely populated city particularly the capital or major city of a country or region (New York)
Urban area
- any self governing place in teh unites states that contains at least 2500 people
Urban Area
Any self governing area in the US that contains at least at least 2500 people
Urbanized area
An urban area with 50,000 people or more
Urban cluster
An urban area with fewer than 50,000 inhabitants
Suburb
Populated areas on the outskirts of a city (small stores and businesses, residents may travel to the city for work)
Urbanization pattern
55% live in cities, 2050 rise to 68%
High Urbanization Rate Europe, Latin America, Caribbean (75% or more living in urban areas)
Low Urbanization Rate 40% or less
Increase in urbanization - unemployment for migrants, not enough housing, water and sewage systems cant handle influx
Urbanization rate
% of nations population living in towns and cities
Meta Cities & Megacities
Result of rapid urbanization
Top 5 meta - Tokyo, Delhi, Shanghai, San Paulo, Mexico
Top 5 Mega - Cairo, Mumbai, Beijing, Dhaka, Osaka, Kyoto
Classified by population only
Suburbanization
Sprawl
The movement of people from urban cores areas to area to the surrounding outskirts of a city (started 19th booming 20th cent.)
The tendency of cities to grow outward in an unchecked manner
Automobile Cities
Decentralize
Edge cities
Cities whose shape and size is dictated by and almost require individual automobile ownership; layout is oriented around cars ( Miami, Atlanta, Las Vegas, Phoenix)
To move operations from core city areas onto outlaying areas such as suburbs
A. Branch offices to suburbs to be closer to workforce and led to edge cities
Concentration of businesses, shopping, entertainment that developed in suburbs outside of city’s traditional downtown or central business district
Boomburbs/boomburg
Infill development
Exurb
More than 100,000 residents but not core cities in metropolitan areas; large suburbs w/ own govt; needs lots of land and sustained development
The building of new retail, business or residential spaces on vacant on underused parcels in already developed areas
An exurb is a small, less crowded community located beyond the suburbs, usually with more open space and a rural feel
Urban hierarchy
Way to rank cities and towns based on their size, population, power, and services. Generally larger cities are at the top of the hierarchy
Village, Town, City, Metropolis, Megalopolis
Urban System
Network of cities and towns connected through transportation, communication, trade, and social interaction.
Interdependence, Flow of goods, people and info, social and economic connections
Bay Area (tech and social hub)
Rank-Size Rule
Population of a city is inversely proportional to its rank in the urban hierarchy
Largest city have 1 million, Second largest city ½ of that, and third largest city has 1/3 of 1st
Primate City
Largest city in a country which is significantly larger and more influential than any other city in the region
Dominates country’s economy, politics, culture, and population
Paris, France. Bangkok, Thailand. Mexico City, Mexico (can leave other cities less urbanized)
Causes - economic factors, centralization of wealth and resources, colonial legacy
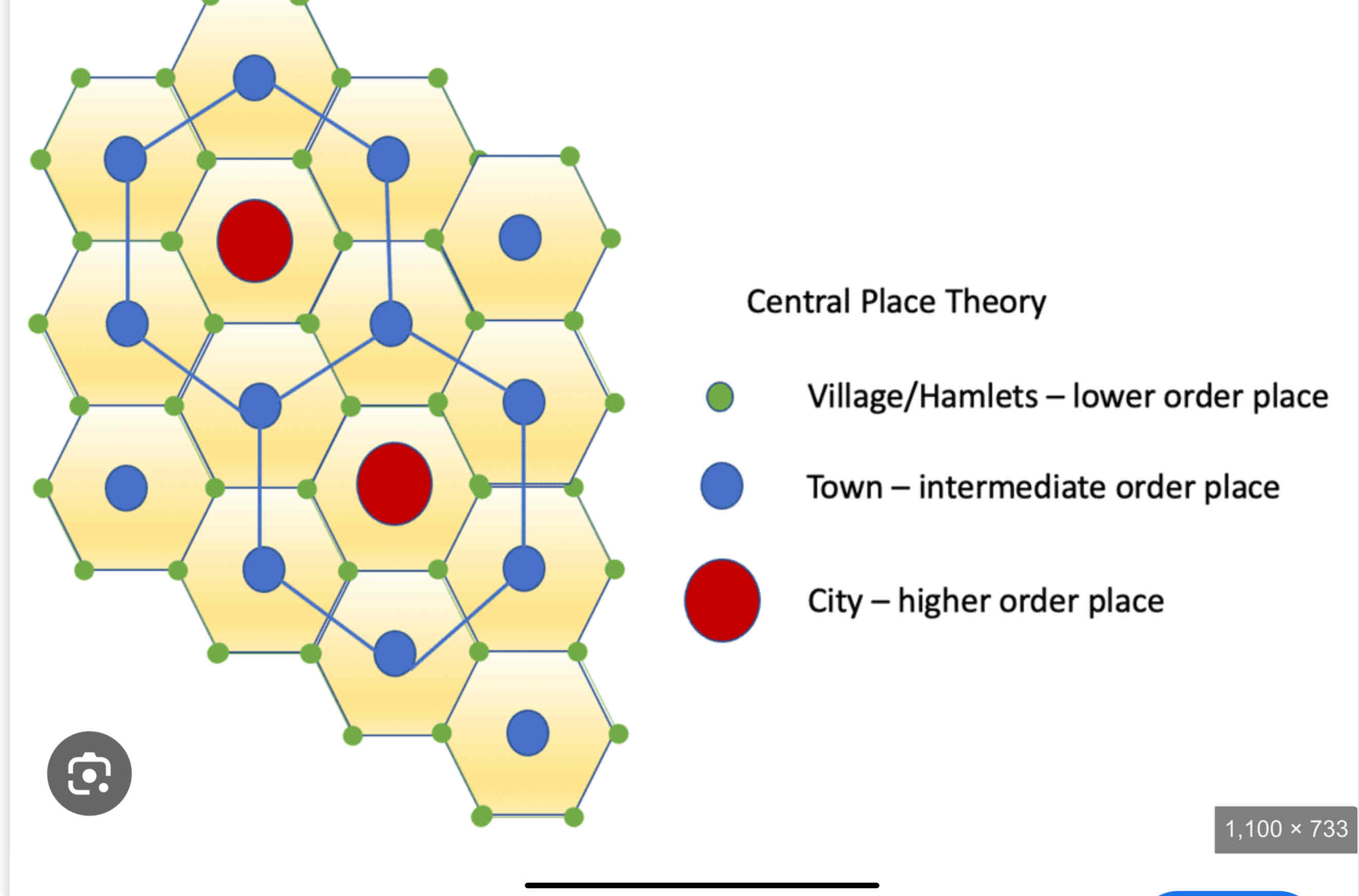
Walter Christaller’s central place theory
(Christallers’s ) Central Place Theory
Range
Threshold
explains how towns, cities, and villages are distributed in a region, based on their size and the services they provide. Larger cities (central places) offer specialized goods and services and are spaced farther apart, while smaller towns and villages provide basic services and are closer together. This creates a hierarchical pattern where people travel to the closest place that meets their needs.
In CPT the distance people are willing to travel to acquire a good
In CTP the number of people required to support a business (demand for good in comparison to where it is placed)
Types of Settlements FIX
Harbor
Island
Fall Line
Confluence
Access to board and trade (Istanbul,Turkey)
Defence and hard to reach (Paris,France)
Types of Settlement sites FIX
Hilltop/Acropolis
Oasis
River Narrowing
Religious Pllgramage
Commander of..
Trade Route
Borchert’s Epoch
Sail and Wagon Cities (1790 - 1830)
Steamboat - Iron Horse(1830-1870)
US new country , boats and ships, wagons (ex. Boston (harbor site) , New York, Philadelphia)
Early westward expansion, trains on iron tracks, steamboats, ppl settle along rivers for settlements
Borchert’s Epoch
Long Haul/ Steel Rail 1870-1920
Automobiles *1950’s after WW2
Wes
World City… Role in globalization?
…as nodes
A city that is a control central of the global economy in which major decisions abt financial morkets and commercial networks are made
A. Key characteristics : cultural diversity and institutions, headquarters of multinational companies, banks, stock exchanges…. New York, London, Tokyo
B.Wealthy people concentration in world cities
World cities as nodes at global scale exerting political power and connection to other big cities
Ex. Bergen Norway cod production led to trading and it having economic power (not world city rn)
Gated communities
Privately governed secured residential area with amenities for the wealth, cutting them off from the poor
In some ways urban wealthy have opted out of participation in world city
What are the networks and linkages that drive globalization with WORLD CITIES
Transport services - mostly built on waterways so have a harbor can handle cargo ships, railways connected to transport cargo, modern inter. & dom. Airports
Communications Systems- advanced comm systems access to immediate info, news to international powers
Large law firms, pools of job talents, high employment opportunities, powerful marketing companies affect consumer taste
City Structures in general
Most cities were unplanned driven by usefulness and accesebilty to transport
Early cities were compact as people walked but long distance travel was achieved by horse car, cable car, railroad, trolley, streetcar and land near here was expensive
New transport systems cause socieoeconomic divide (income inequality) wealthy ppl in suburbs and large houses low income in multi family housing and mass transit
Automotive effect on city landscape?
Big cities contained housing units for all economic class as automobiles became more ubiquitous people began to sprawl from the suburbs with bigger housing leading to the movement of jobs and commercial properties to follow
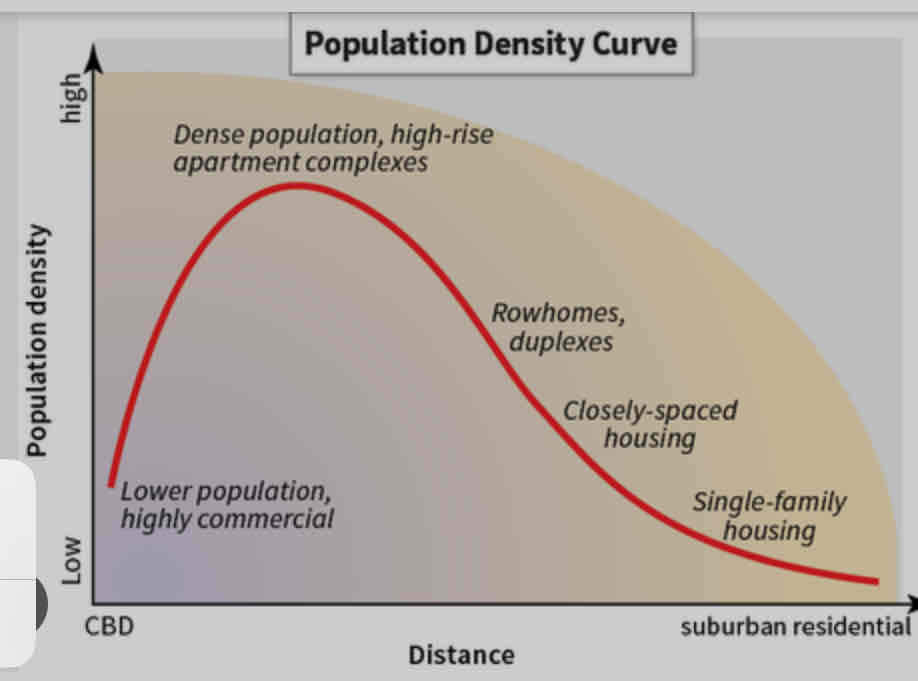
Population density gradient
Perceived density
Zoning regulations
The general impression of the estimated people present in a given area (lots of multistory apartments = high population)
Laws that dictate how land can be used
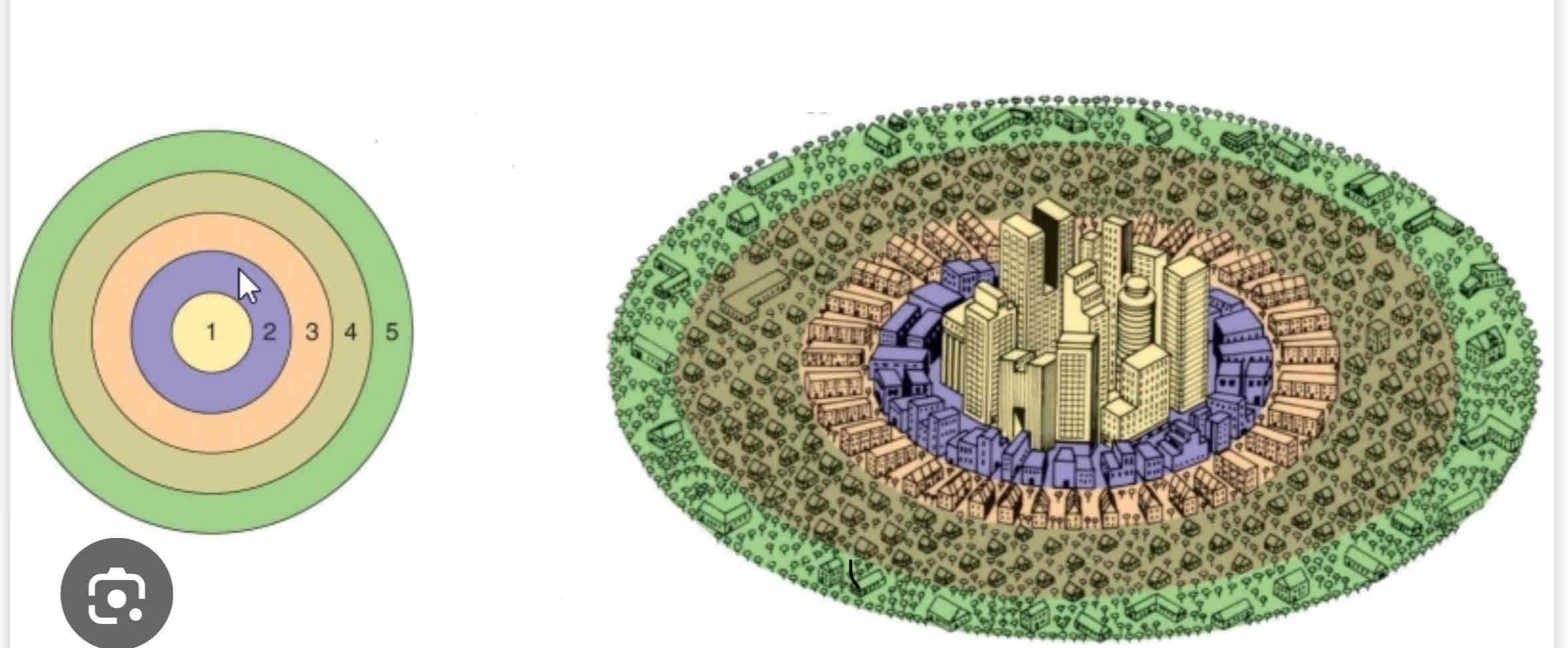
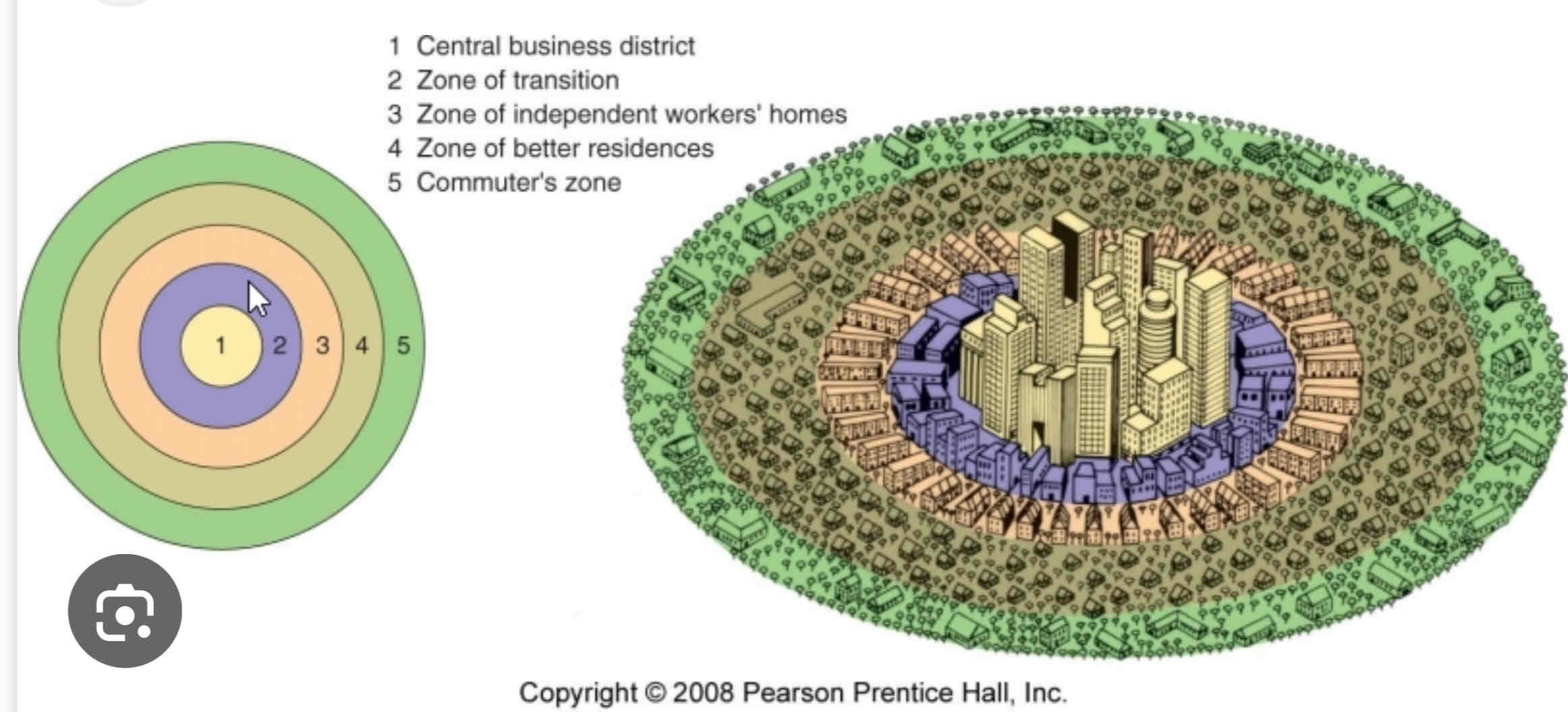
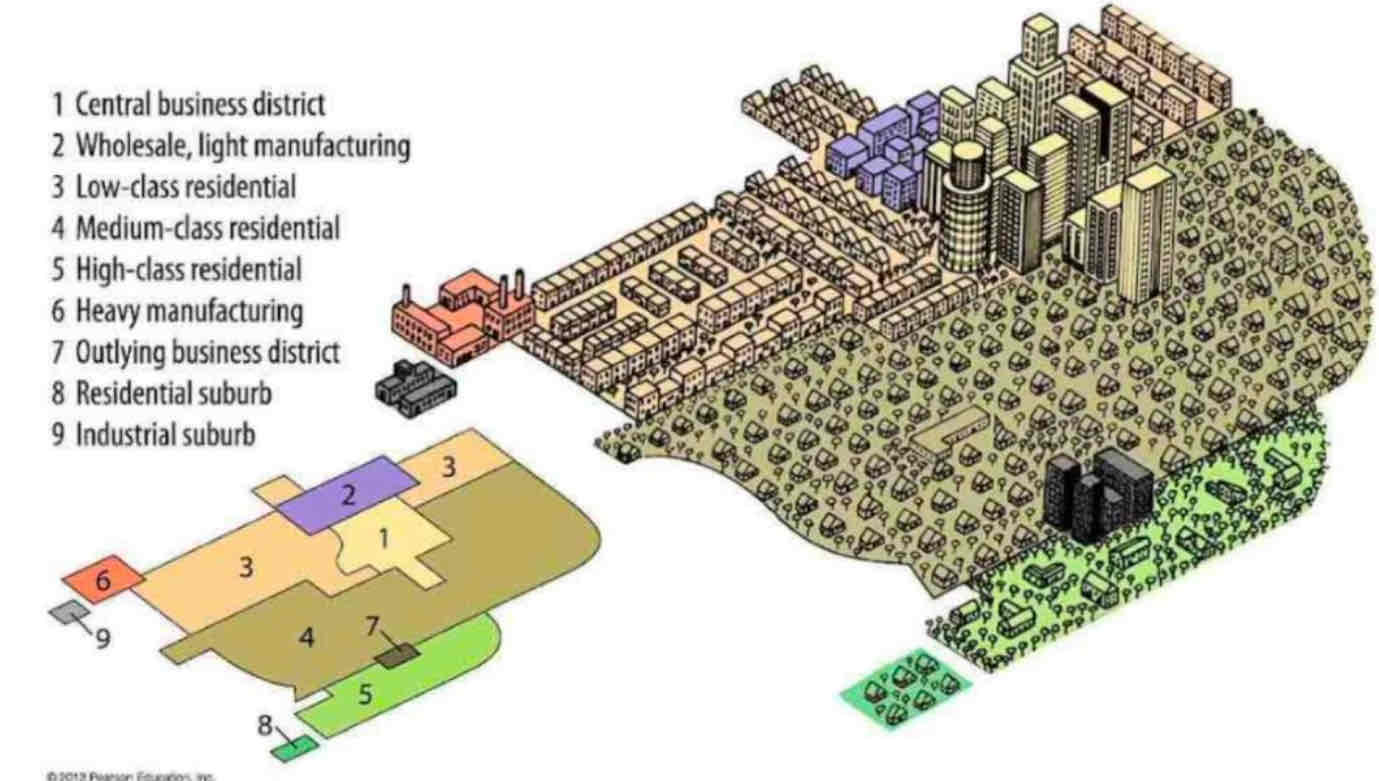
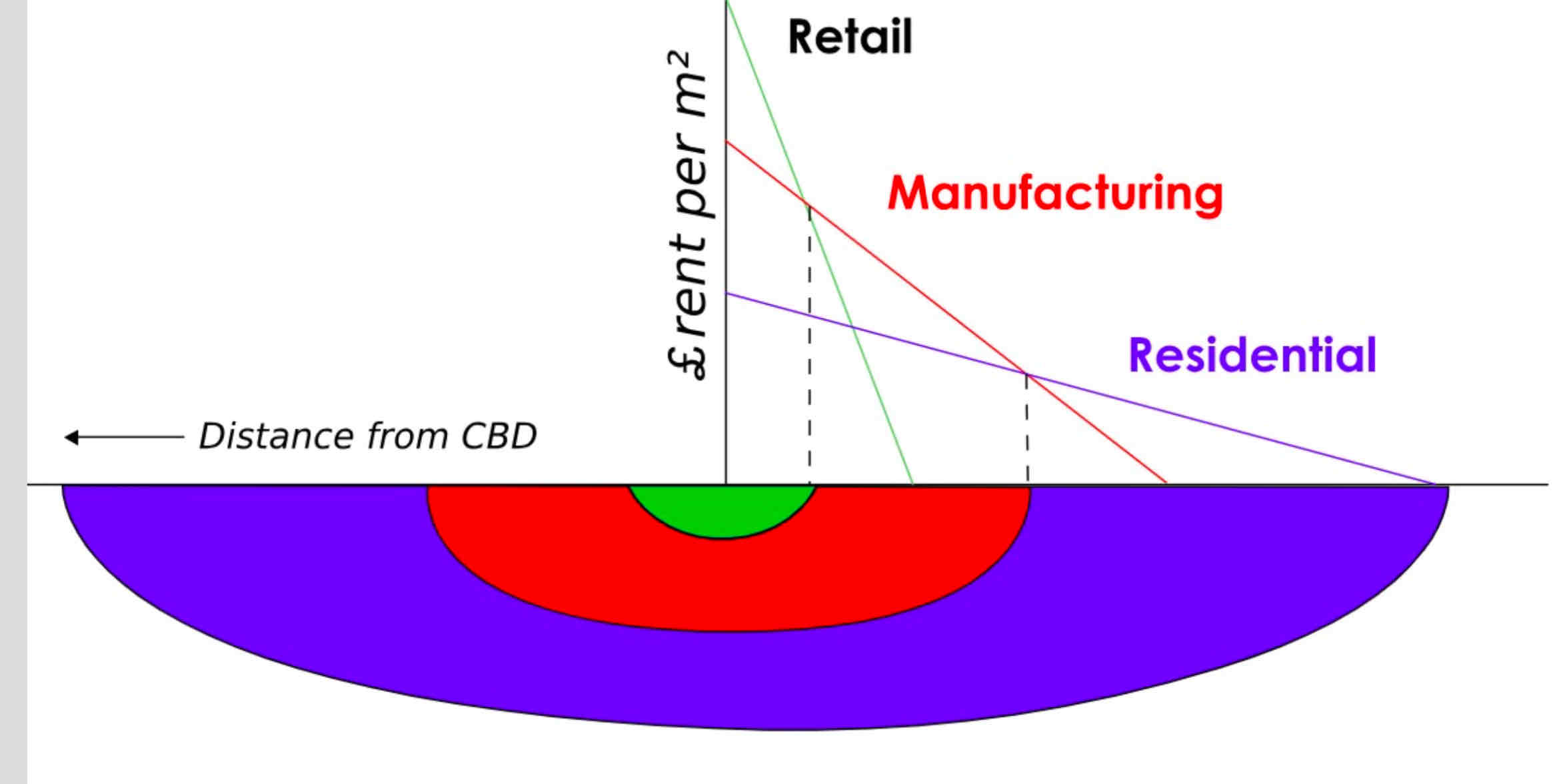
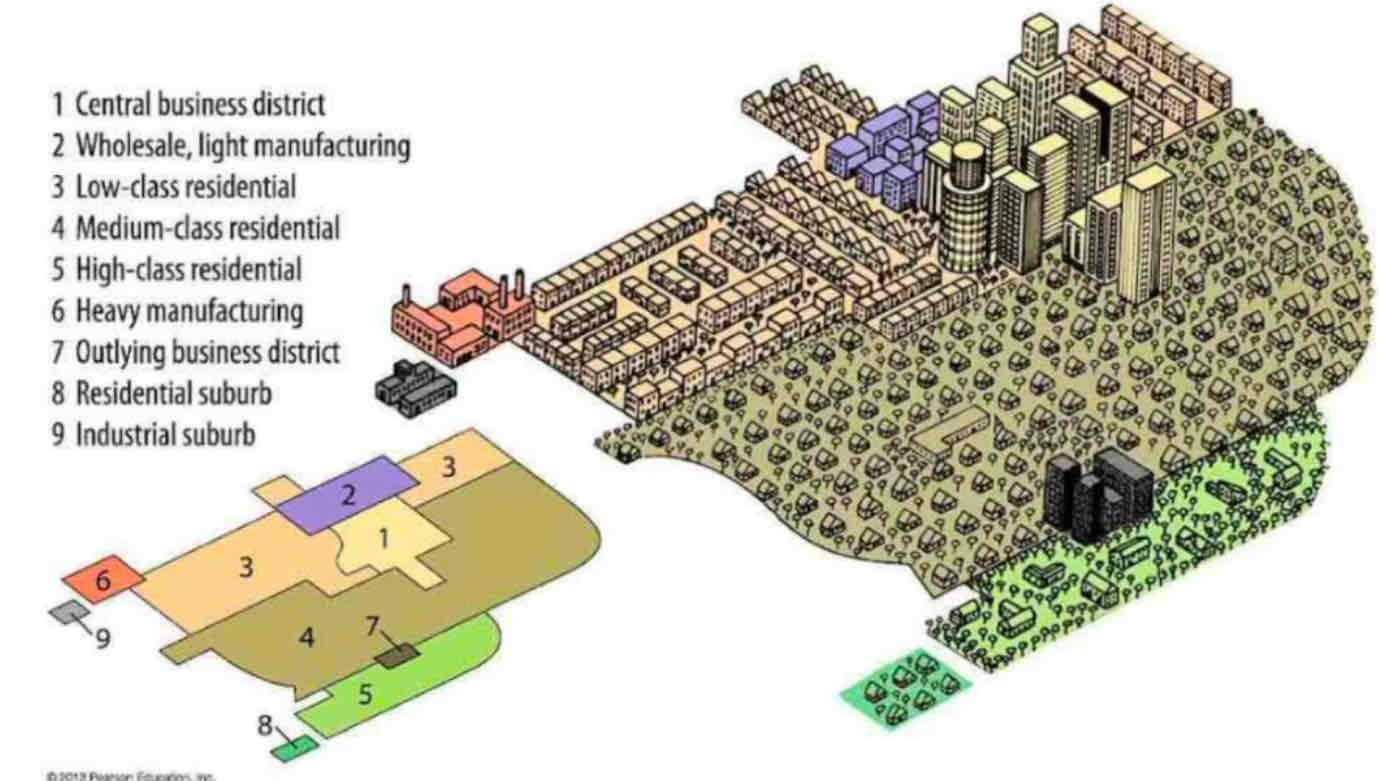
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
Hoyt Sector Model
Harris & Ullman multiple nuclei model
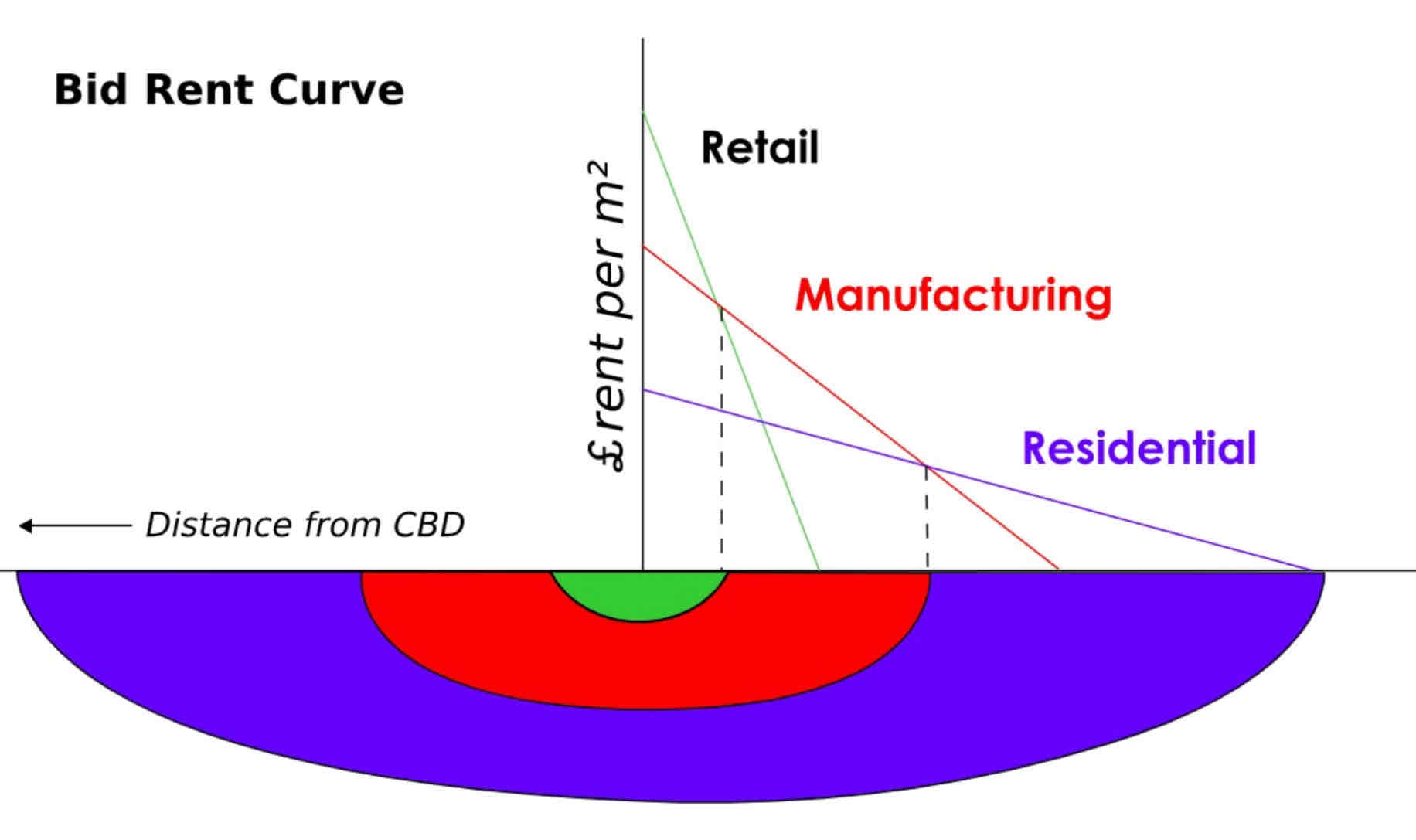
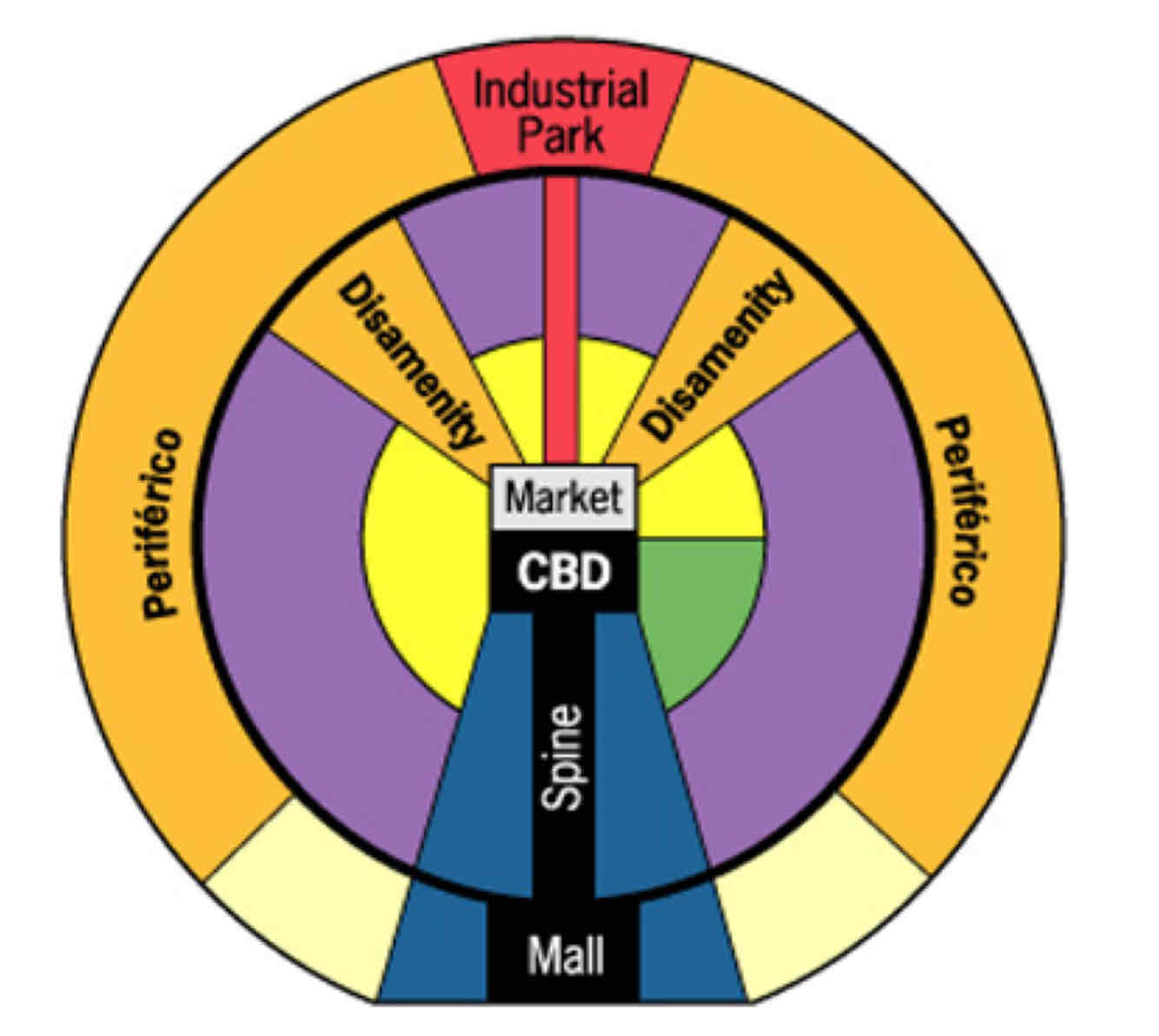
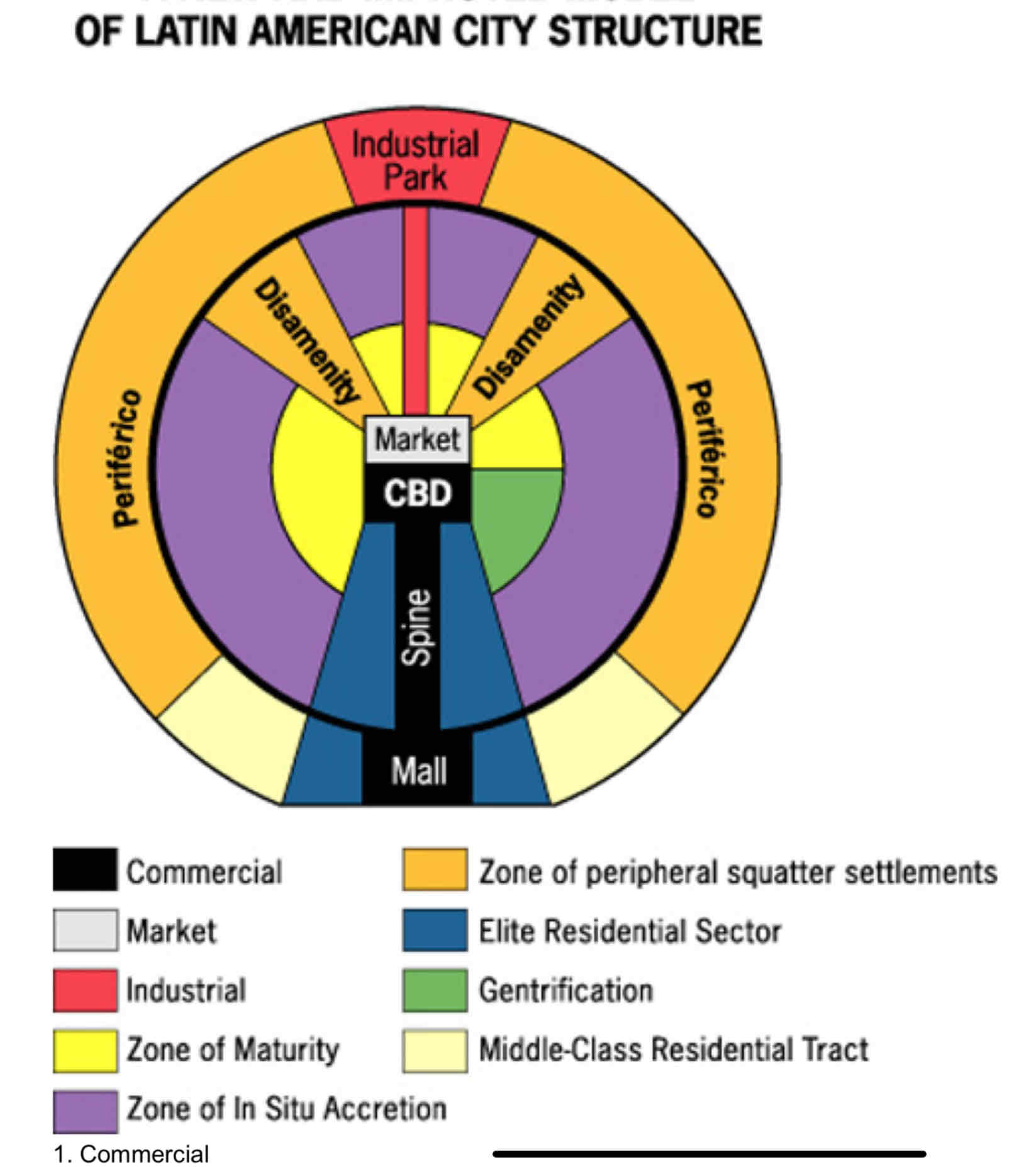
Latin American City Model
South Asian City Model
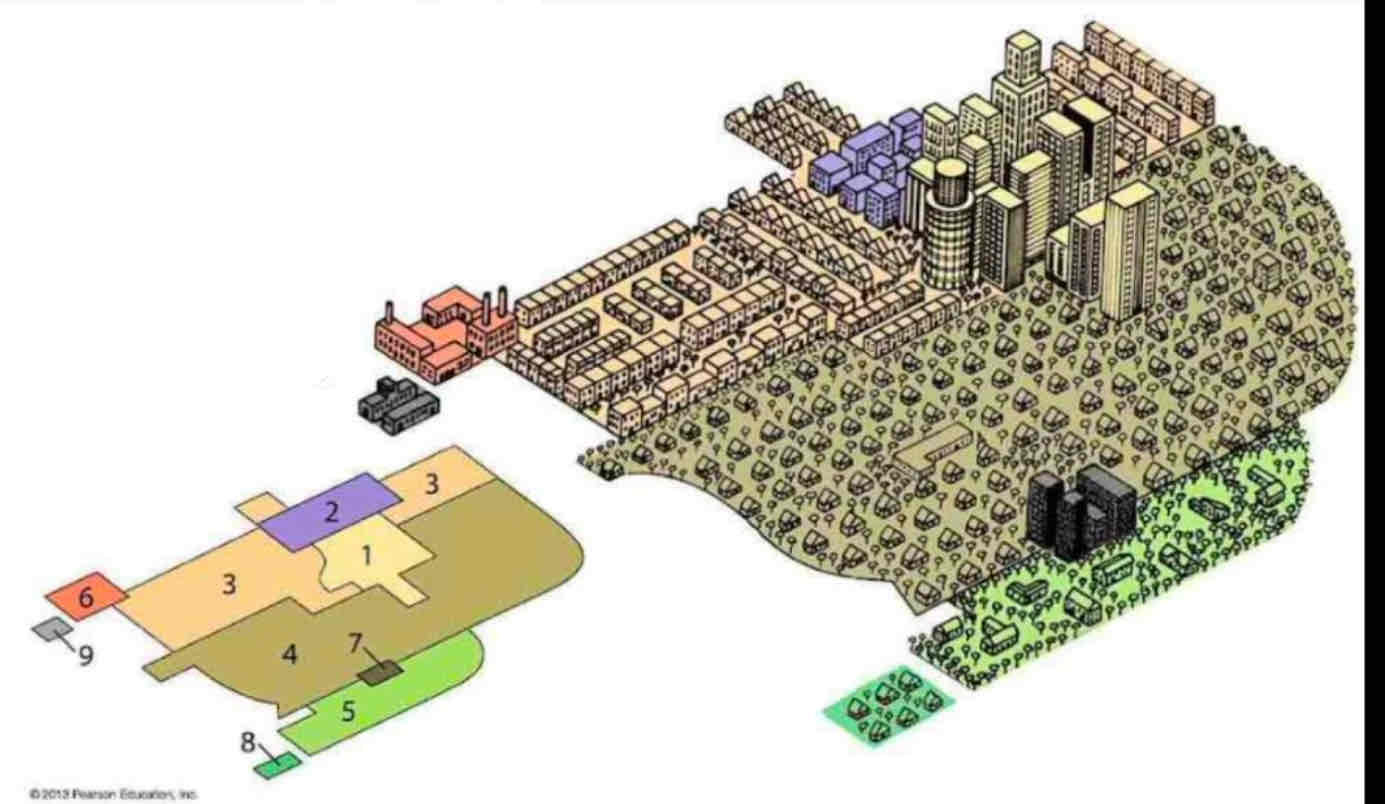
Multiple Nuclei Model
- Created in 1945 to explain cities with decentralized growth and multiple activity hubs.
- Cities develop around functional nodes (e.g., industrial, residential) based on specific needs and land use.
- Explains diverse urban patterns but struggles with unique layouts and assumes independent node development.
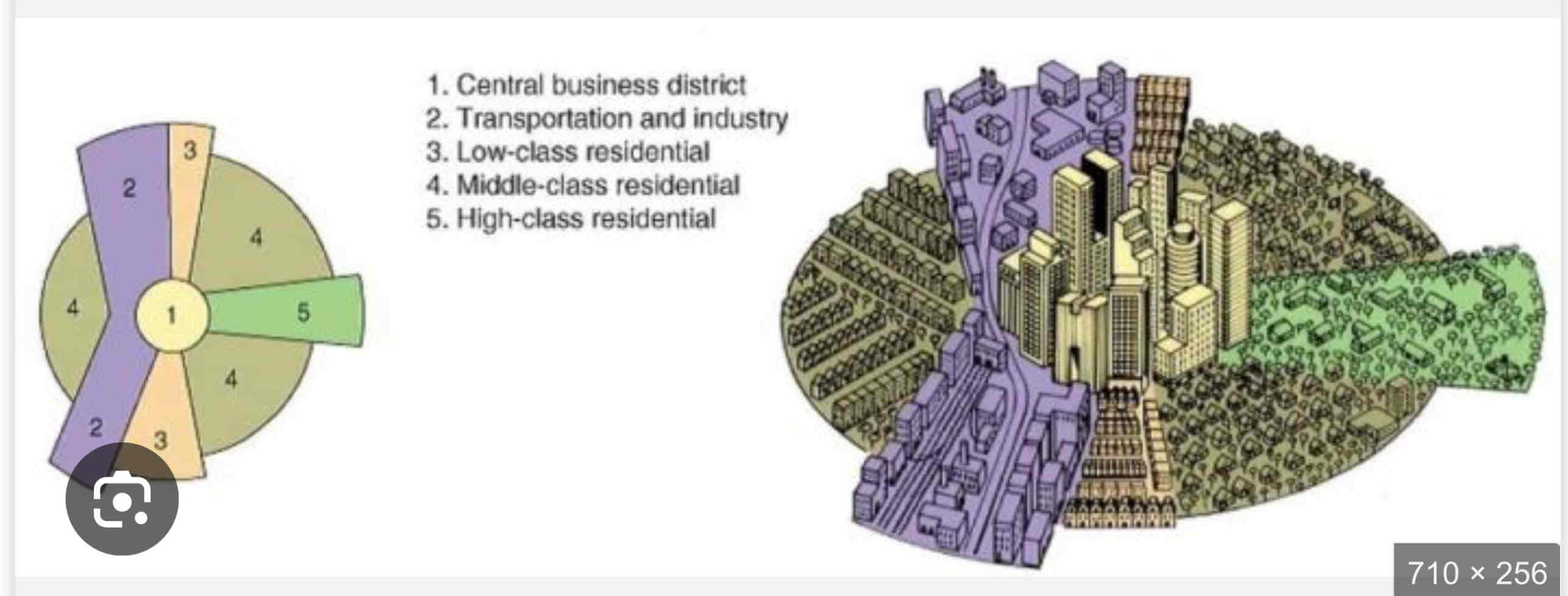
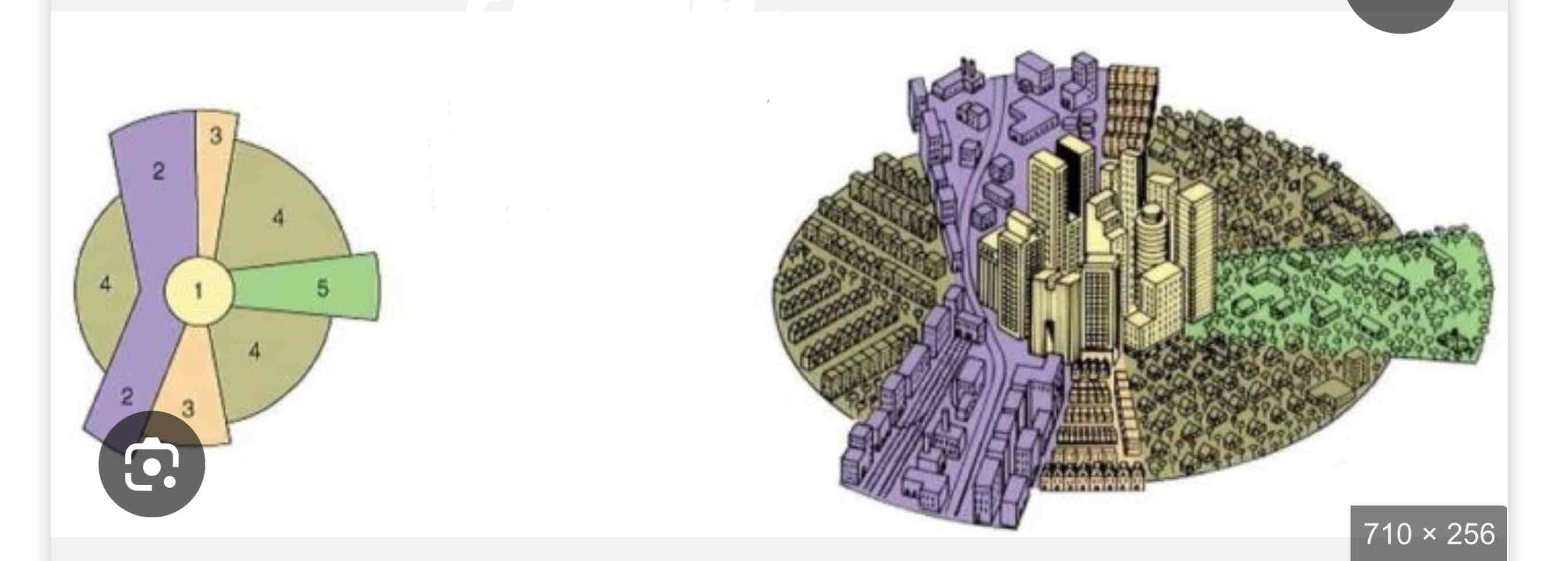
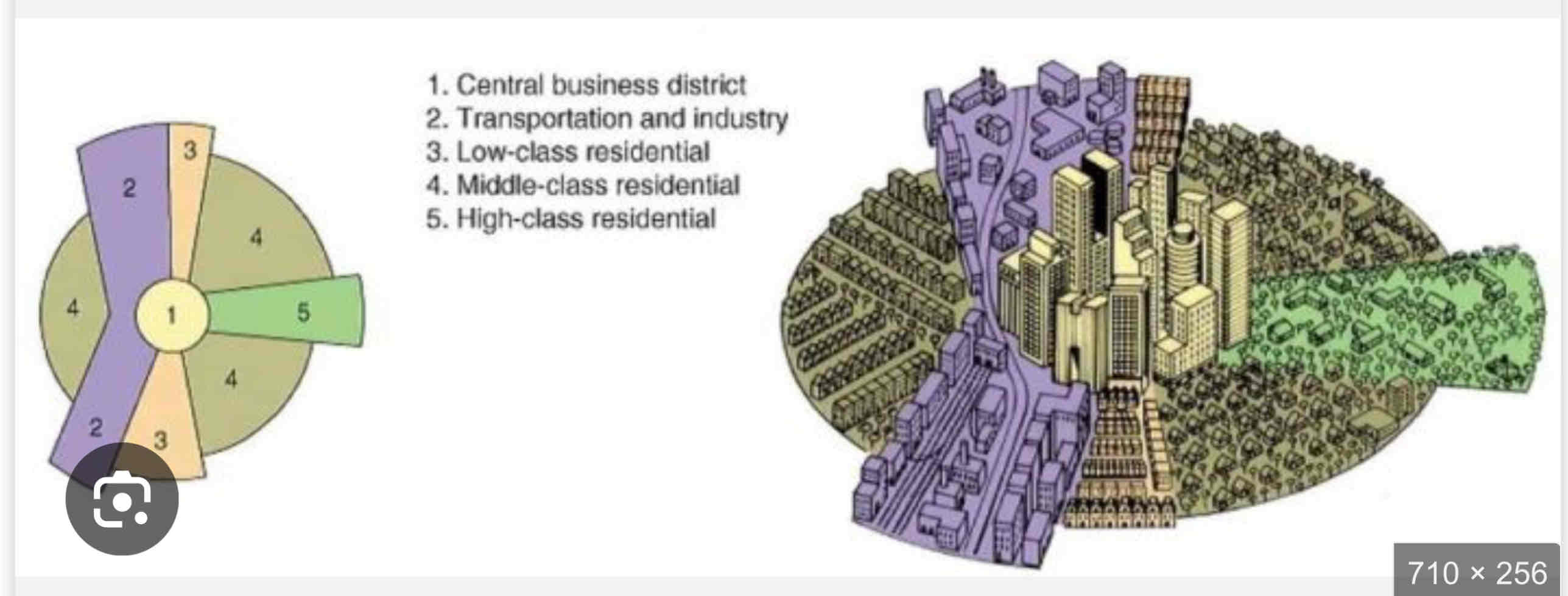
Hoyt Sector Model
• Developed by Homer Hoyt in 1939 to improve upon Burgess’s model.
• Cities grow in wedges or sectors, not rings, based on transportation routes and accessibility.
• High-income housing expands along desirable areas, like major roads, while industry follows railways or waterways.
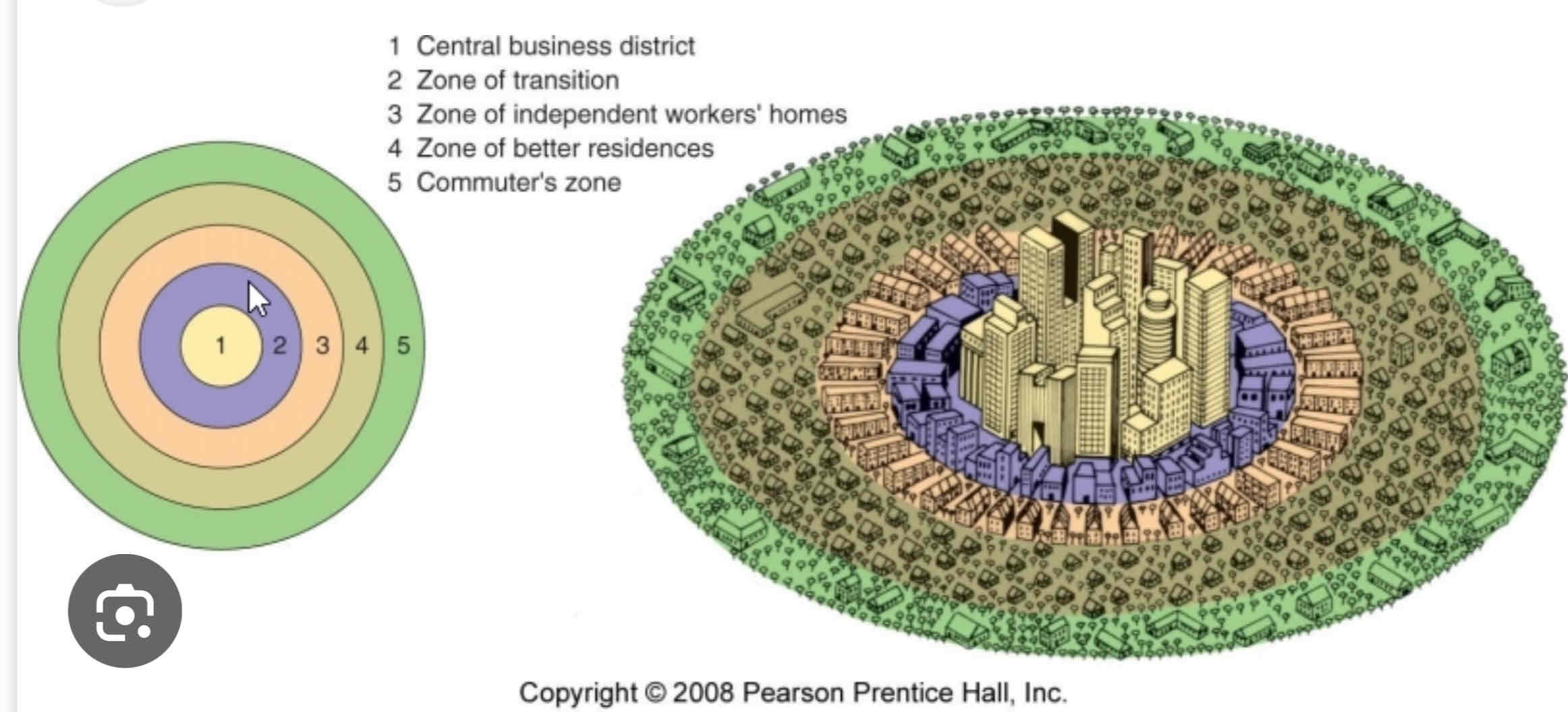
Concentric Zone Model
- Chicago during rapid industrializationÂ
- migrants move in to low quality homes is sector pushing long terms residents move to better housing in zones 4 and 5 (automobile access)Â
- Buisinesses in CBD can generate enough to stay in centerÂ
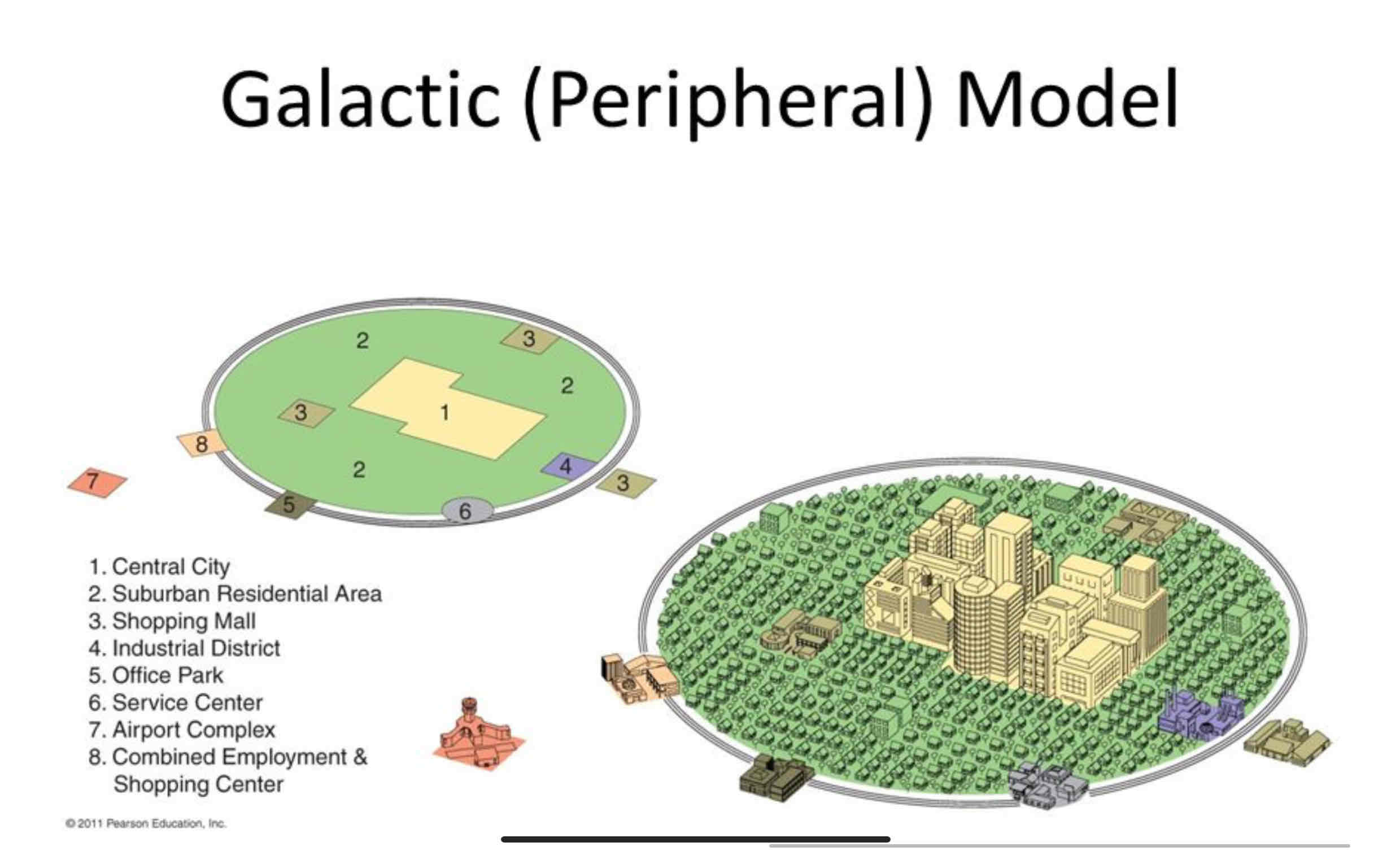
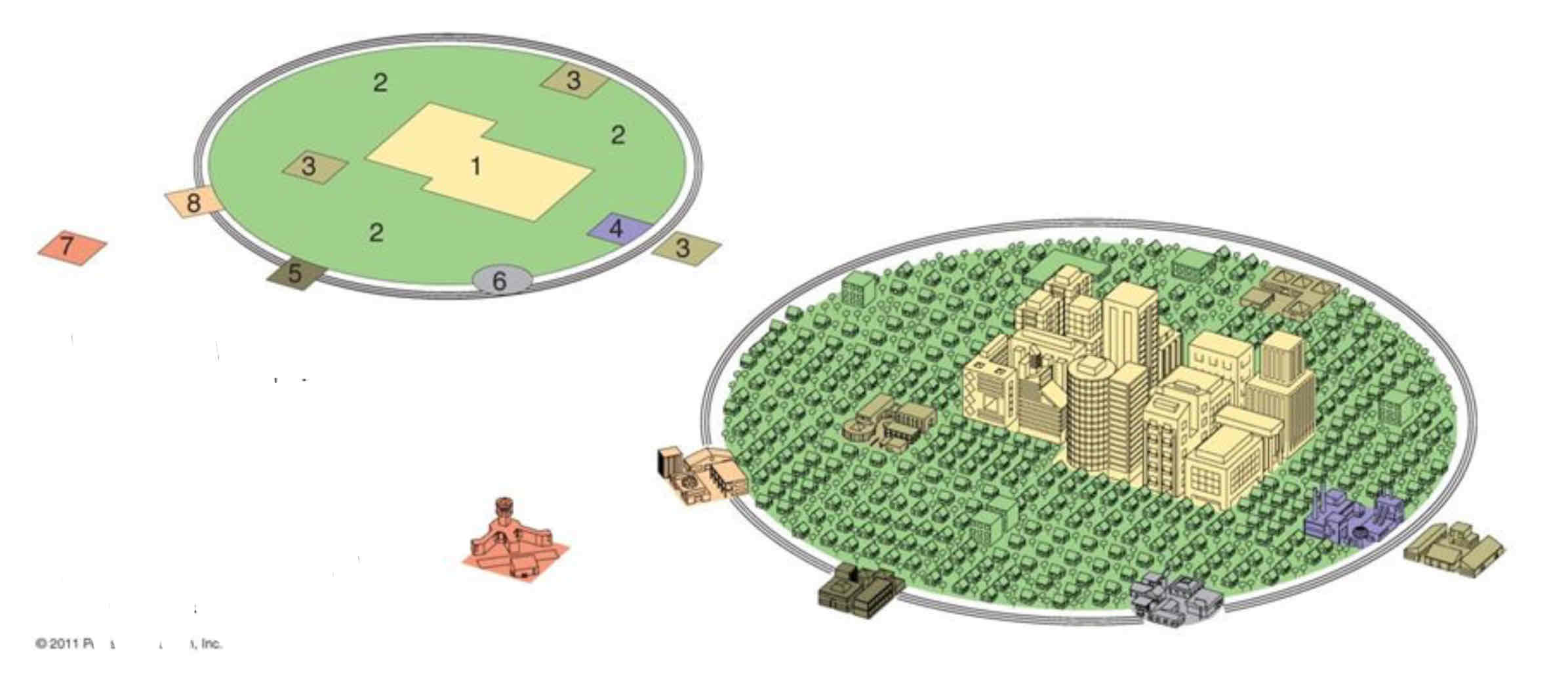
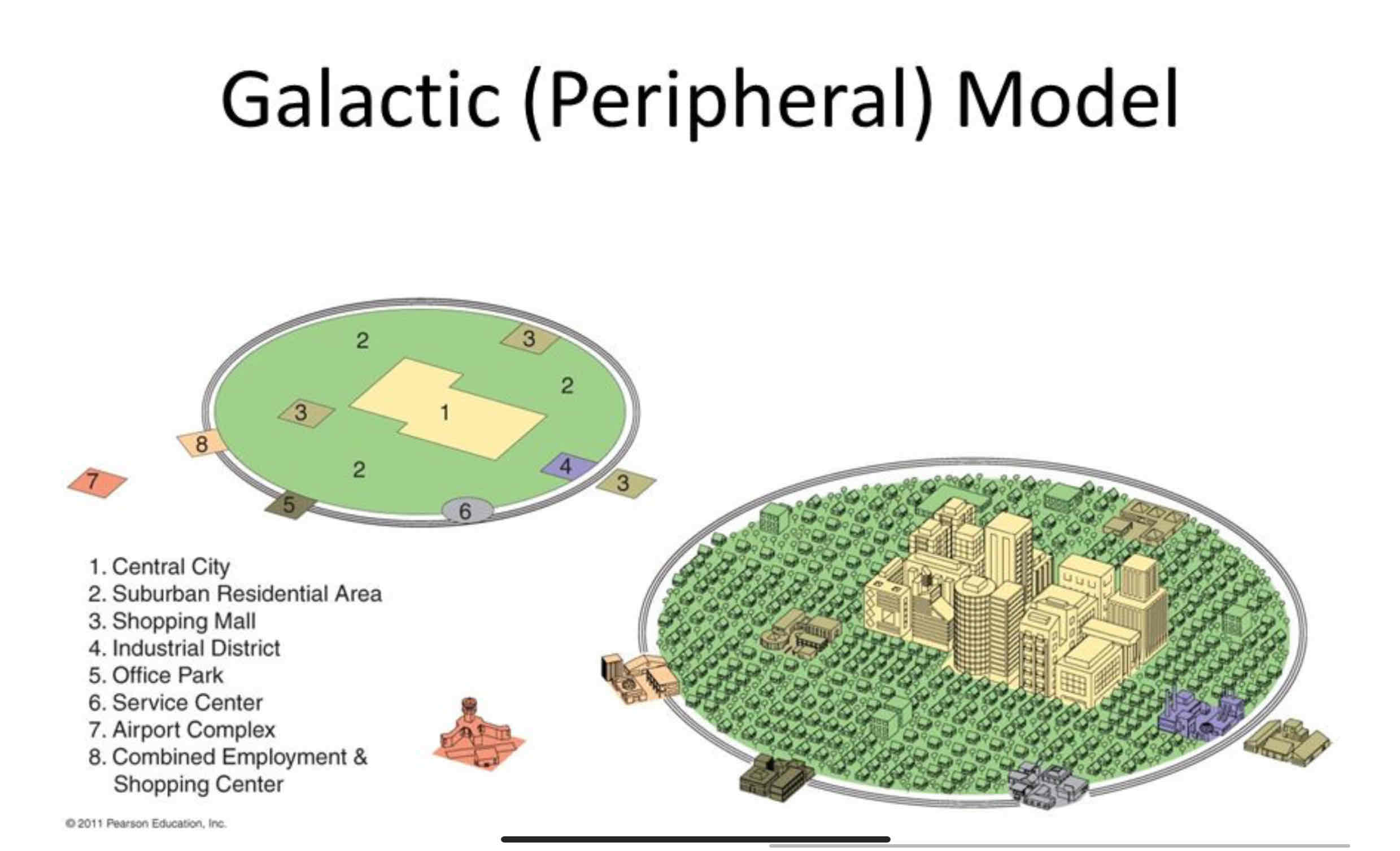
Galactic City Model
• Developed in the 1960s to describe post-industrial cities shaped by suburbanization and car dependence.
• Cities have a central CBD surrounded by specialized edge cities connected by highways. (Highway Belt)
• Explains modern sprawl and decentralized growth but assumes car-based cities and may not fit older urban areas.
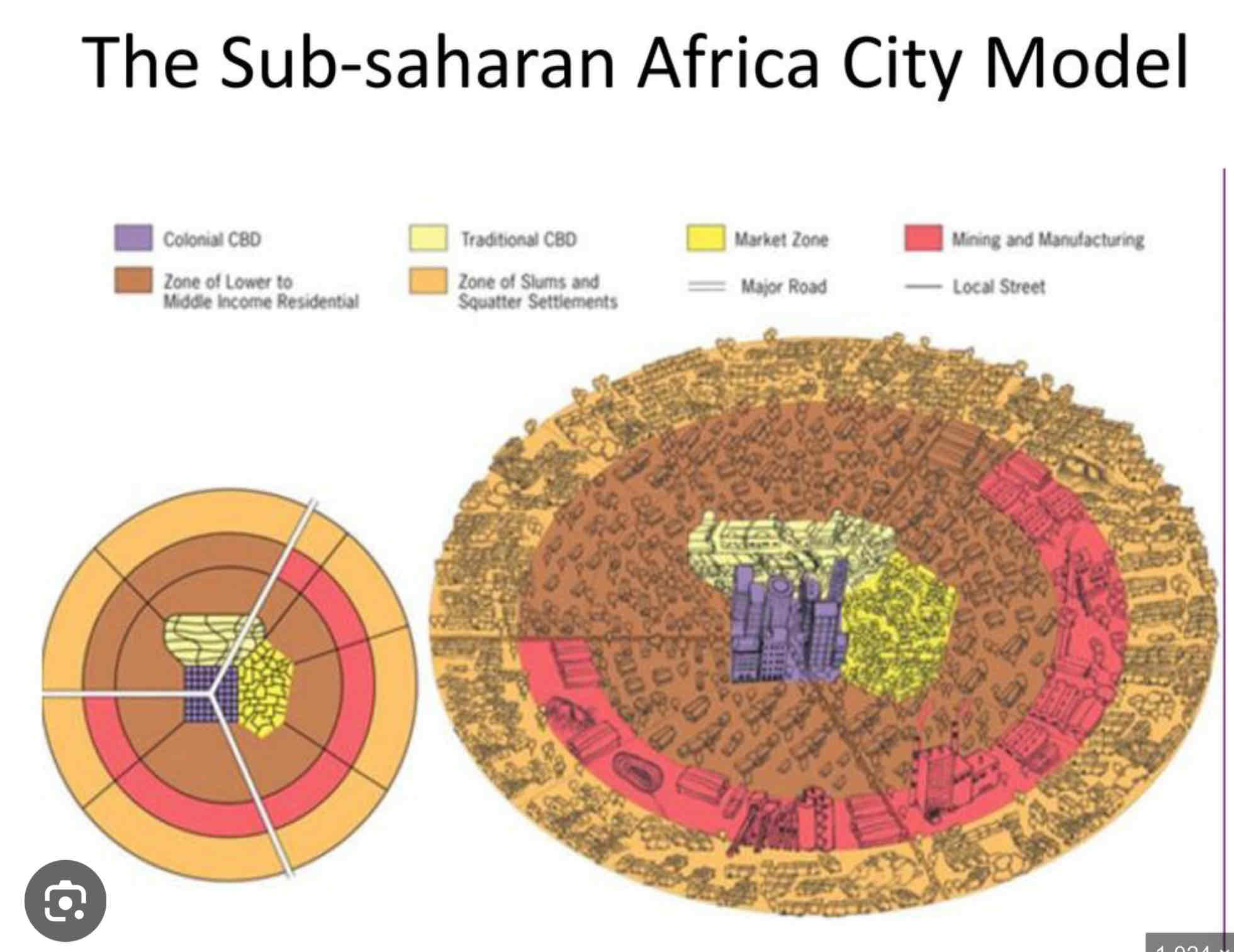
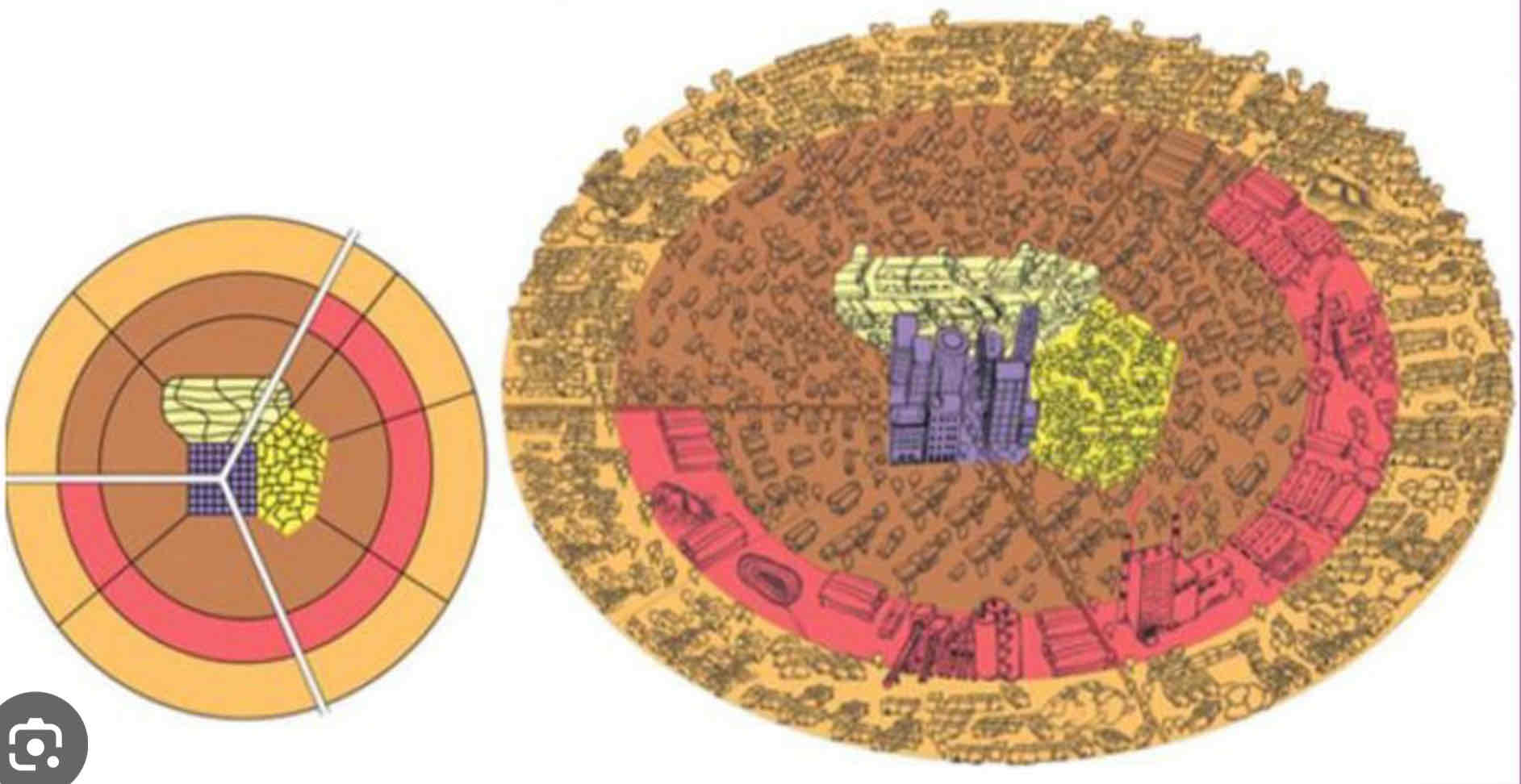
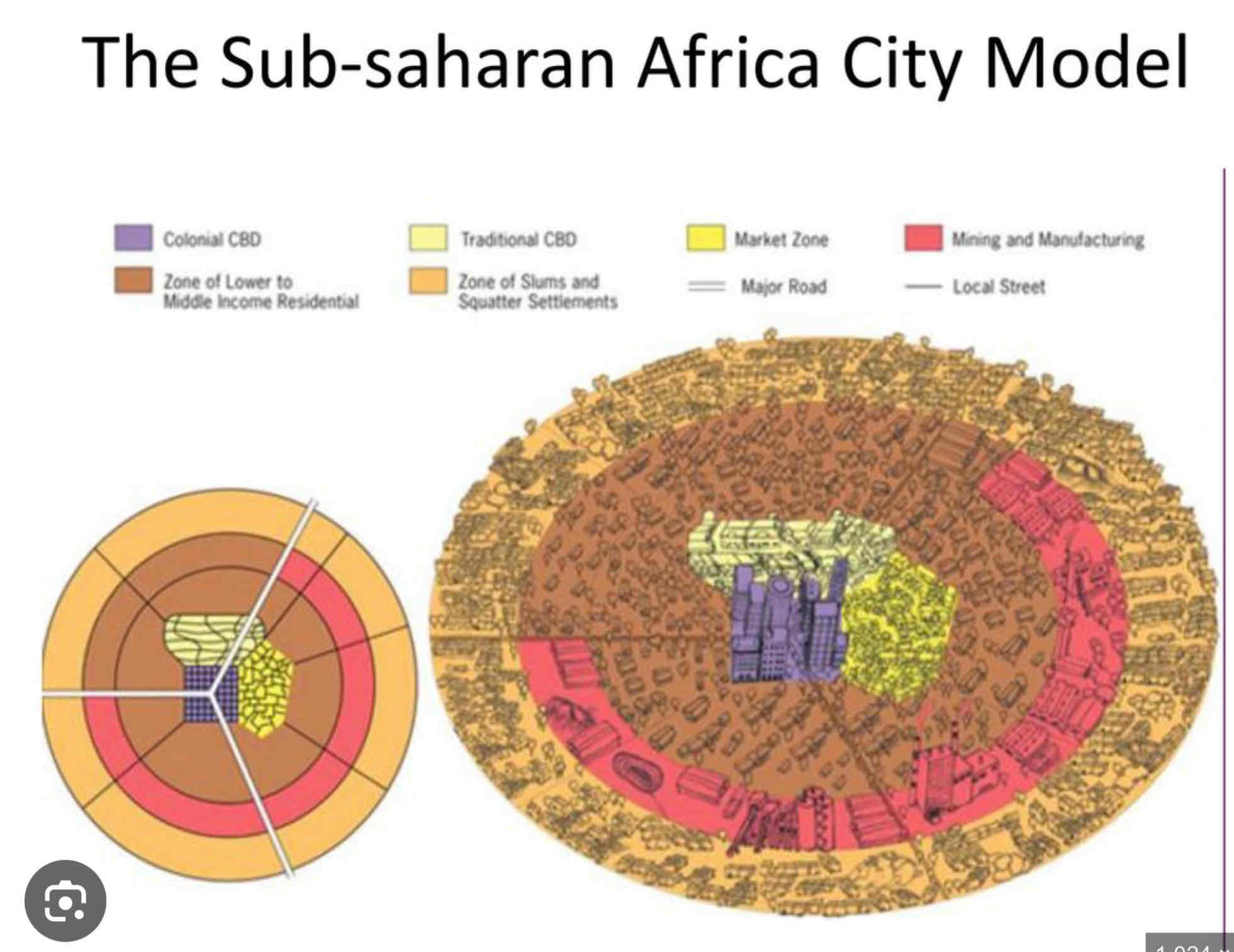
African City Model ??
• Reflects cities in sub-Saharan Africa, influenced by colonial history and rapid urbanization.
• Features three CBDs: traditional, colonial, and informal markets, with residential zones extending outward.
• Explains fragmented city structure but oversimplifies diverse urban forms across Africa.
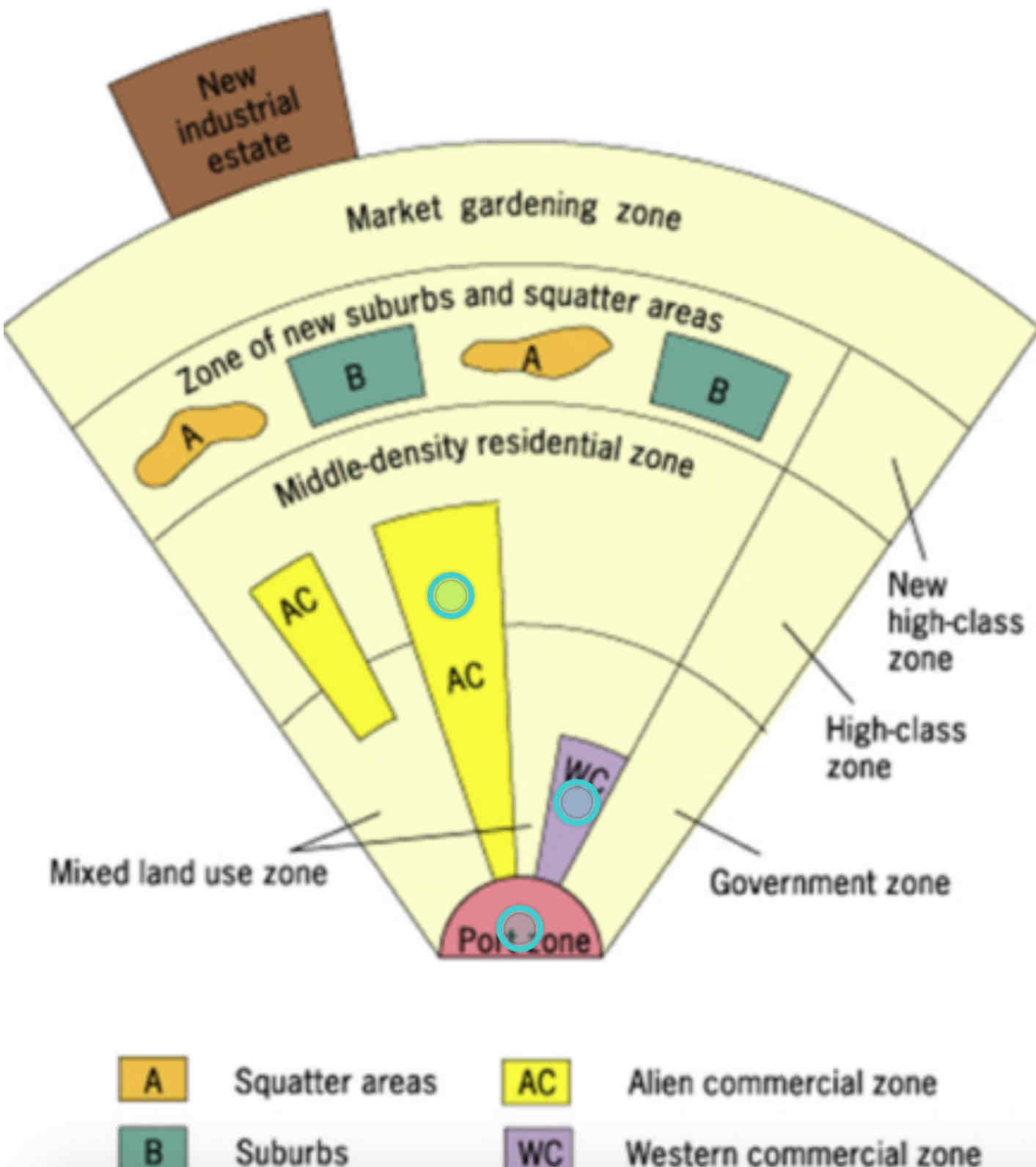
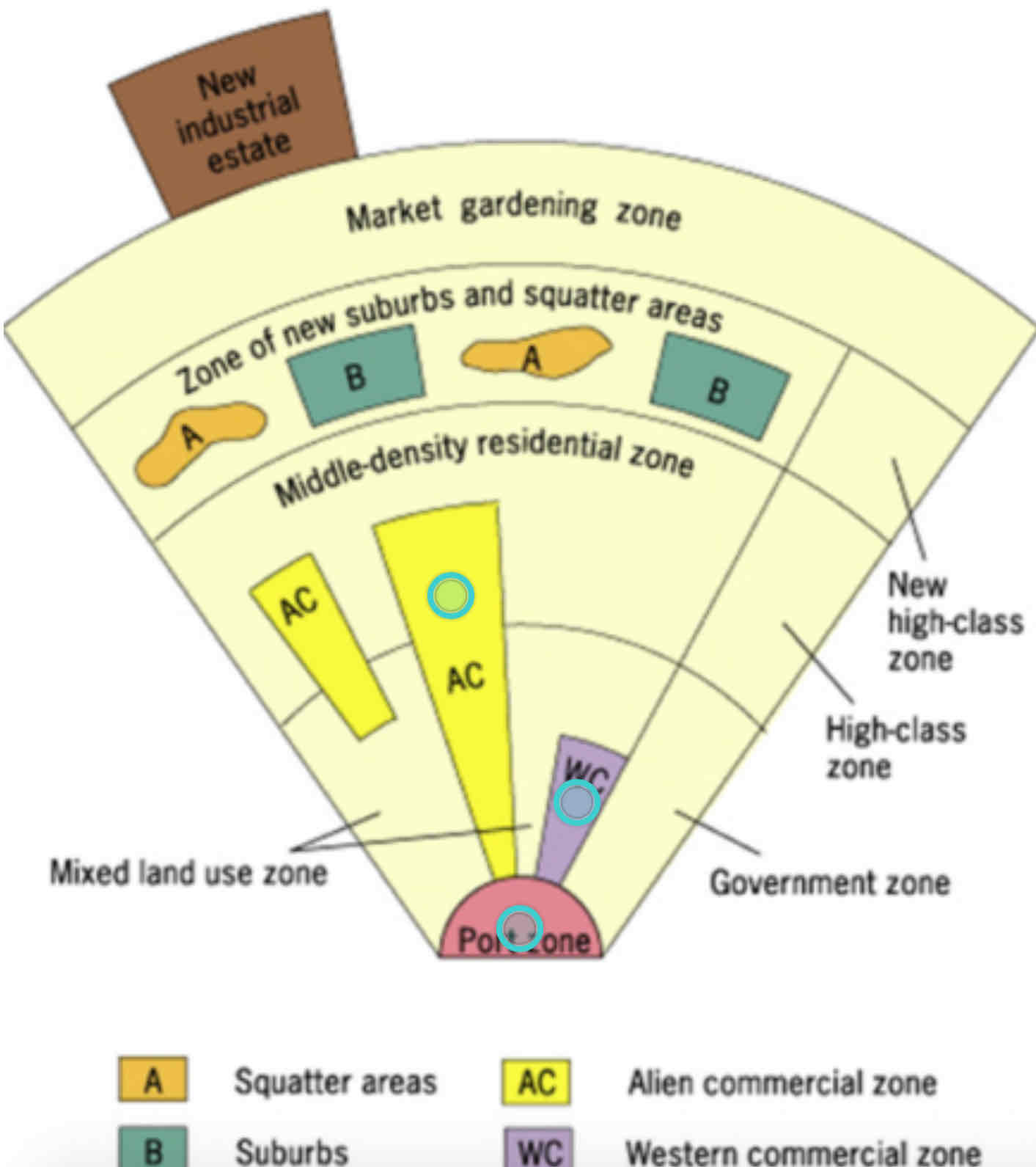
Southeast Asian City Model??
• Based on cities in Southeast Asia, shaped by colonial history and coastal trade.
• Features a port at the center with surrounding zones for commerce, housing, and industry.
• Explains growth around ports but doesn’t fit inland or non-colonial cities.
Latin American City Model??
• Developed to describe cities in Latin America, influenced by colonial history and rapid urbanization.
• Features a central plaza (CBD), with zones for elite housing along main roads and squatter settlements on the outskirts.
• Explains the sharp contrast between wealth and poverty but oversimplifies diverse urban patterns.
Gentrification
The displacement of lower income resident by higher income residents as an area or neighborhood improves
City patterns general (land,population)
land value and population density decrease farther from the city
As residential housing in cities increases so does population density
Wealthier people in suburbs as they have transport to the city and want bigger housing
Red lining
Practice of identifying high risk neighborhoods on a city map and refusing to lend money to people who want to buy in those neighborhoods > poorer neighborhoods become more run down
Block Busting
White Flight
Realtors persuade white home owner in a neighborhood to sell their homes by convincing them that the neighborhood is declining due to black people moving in but then they sell properties to the black people which causes
The mass movement of white people from the city to the suburbs
Which both affect affordability of the housing
Housing choice voucher program
A federal govt program to assist very low income families, the elderly, and the disabled with affordable, decent, safe, and sanitary housing
Squatter settlements (favela)
An area of degraded, seemingly temporary inadequate and often illegal housing (dont have right to hold or own property (land tenure))
Inclusionary Zoning
Exclusionary zoning
NIMBY’s
Below market rate housing
Municipal and county planning in ordinances that require a given share of new construction that has to be affordable for people with low to medium incomes
Zoning that attempts to keep low to moderate income people out of a zone
“Not in my backyard” people who try to prevent affordable housing in their area
Housing that costs much less then going rate
Fiscal imbalance
Fiscal zoning
Occurs when a govt must spend more that in receives in taxes
The practice of using local land use regulation to preserve and possibly enhance the local property tax base