BIOL 2 Invertebrates
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
What is the current debate?
What are the early branching order of animals (Metazoa)
Why are porifera considered the most basic animals?
No tissues, no organ systems, no hox genes (control body plan)
What did the evolution of hox genes do?
New and complex body plans
What also lack hox genes?
Ctenophores
What are sponges?
Porifera
What had complex multicellularity, were filter feeders, and and sexual & asexual reproduction (hermaphrodites)?
Porifera (sponges)
develop two embryonic germ layers: an ectoderm and an endoderm or mesendoderm
Diploblasts
develop a third layer—the mesoderm—which arises from mesendoderm and resides between the endoderm and ectoderm.
Triploblasts
the outermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early development, or the parts derived from this, which include the epidermis and nerve tissue.
ectoderm
the innermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early development, or the parts derived from this, which include the lining of the gut and associated structures.
endoderm
a transient, bipotential layer of cells in early embryonic development that differentiates into both the mesoderm and endoderm, the two germ layers that give rise to various tissues and organs. (arises from mesendoderm)
mesendoderm
the middle developmental layer between the ectoderm and endoderm, which gives rise to the skeleton, muscle, heart and bones.
mesendoderm
Cnidaria is:
Diploblast
Endoderm
Inner Derm (skin) Layer
Mesoderm
Middle Derm (skin) Layer
Ectoderm
Outer Derm (skin) Layer
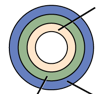
What are the three layers here?
Diploblast
Yellow: Endoderm
Green: Non-living tissue
Blue: Ectoderm
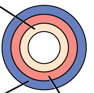
What are the three layers here?
Mesoderm
Yellow: Endoderm
Orange: Mesoderm
Blue: Ectoderm
Do porifera have symmetry?
No
Does Cnidaria have radial symmetry?
Yes
All diploblastic animals have radial symmetry
True

What type of symmetry?
No symmetry

What type of symmetry?
Radial

What type of symmetry?
Bilaterial
the process involving the concentration of sensory and feeding organs such as nerve cells, mouth, and jaws at the anterior end and the development of the brain.
Cephalization
All of what animals are triploblastic?
Bilaterally symmetry animals
Most of what animals have a clear head (cephalization)?
Bilaterians
What are jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, and hydra?
Cnidaria
What have specialized stinging cells (nematocysts) for feeding?
Jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, hydra (Cnidaria)
Corals form symbioses with
dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium)
Calcium carbonate skeleton in 'reef building' coral critical to
marine ecosystems
What is "first mouth"?
Protostoma
What is 'second mouth'?
Deuterostoma
What are the two groups of protostomes?
LOPHOTROCHOZOA & ECDYSOZOA
This group had organisms with lorphophore or trochophore larvae
LOPHOTROCHOZOA
This group had organisms that would shed their exoskeleton
Ecdysozoa
"shedding"
Ecdysis
What group are flatworms, tape worms, and flukes a part of?
Platyhelminthes
What are able to reproduce by fragmentation?
Triploblast, Aceolomate
Some flatworms and flukes are human parasites and a global health concern; particularly in areas without _____________________________
adequate food and water sanitation
"not" is also known as
A
body cavity, fluid filled space with organs
Coelom
contained completely within the mesoderm
True Coelom
"false" is also known as
Pseudo
What does the distribution of coelom types across molecular phylogeny suggest?
Coelom is not homologous (i.e. evolved in multiple lineages)
What are the only acoelomates?
Platyhelminthes
______________________ are the only bilateral, triploplastic organism that does not have a body cavity
Platyhelminthes
Which are the only pseudocoelomates?
Rotifers & Nematodes
What are across Protostomes/Deuterostomes?
Platyhelminthes and Rotifers & Nematodes
What group are Octopus, Cuttlefish, Clams, Snails, Slugs, Squid in?
Mollusca
"soft body"
Mollusca
What are the earliest coelomates?
Mollusca
What group has many organisms excrete calcareous shell to protect soft body?
Mollusca
What group has the 2nd most species of any animal phylum?
Mollusca
Which group has about 100K species living and about 80K species extinct?
Mollusca
What group has Earthworms, leeches, many marine forms?
Annedlia
"ringed"
Annelida
Which group has organisms with the earliest segmented body plan?
Annelida
Segmentation is found in which three phyla?
Annelids, Arthropods, and Chordates
Most evidence points towards __________________________________ evolution of the segmented body plan and the segmentation process in these three phyla.
independent (convergent)
What is the first advantage of segementation?
Robust development of repeating units of different organ systems along the body axis.
What is the second advantage of segmentation?
Improved locomotion
What is the third advantage of segmentation?
Developmental modularity - can modify sub parts of the body without affecting others
What group is Nemerteans a part of?
Lophotrochozoa
Ribbon words are
Nemerteans
What are similar to flatworms and can reproduce by fragmentation, has separate males and females, and eversible (turn inside out) proboscis for feeding)
ribbon worms (Nemerteans)
Rotifers are a part of?
Lophotrochozoa
What are the oldest asexual animals?
Rotifers
Pseudocoelomate are a part of?
Rotifers (Lophotrochozoa)
Pseudocoelomate and Bedelloids rotifers are a part of?
Rotifers (Lophotrochozoa)
Round worms are also known as
Nematoda
What group are Nematoda a part of?
Ecdysozoa
What is a pseudocoelomate?
Round worm (dematoda)
What causes trichinosis mainly from undercooked meat?
Trichinella
What are many mammal parasites a part of?
Nematoda (round worms)
'joint footed'
Arthropoda
Which phylum is the most diverse animal phyla?
Arthropoda (Ecdysozoa)
What are the four major groups of Arthropoda?
Crustaceans, Arachnids, Myriapoda, Hexapoda
What is present in all Arthrpods?
exoskeletons
What does exoskeletons provide?
protection, mechanical support, prevents desiccation
Do exoskeletons grow with the animal?
No
What must be molted (shed) for animals to grow?
Exoskeleton
What is the similarity between Arthropods and Fungi?
both have chitin (fungi have a cell wall made of chitin)
a strong, flexible, and naturally occurring polymer that makes up the exoskeletons of arthropods
chitin
Complete metamorphosis
Holometabolous (egg, larva, pupa, adult)
Incomplete metamorphosis
Hemimetabolous (egg, nymph, adult)
What comprise of approximately 22% of ALL known living species (not just animals)?
Coleoptera (beetles)
Tardigrades (water bears) are a part of what grpup?
Ecdysozoa
'spiny skin'
Echinoderms
What are echinoderms a part of?
Deuterostoma
Sea stars, sea cucumbers, sea urchins, and sand dollars a part of?
echinoderms (deuterostoma)
What has re-evolved radial symmetry (many larvae are bilaterial, but become radially symmetric adults)
echinoderms
What defines the Chordata?
nerve cord, tunicates, lancelets, vertebrates
What are the major evolutionary transitions?
• Multicellular/specialized cells
• Tissues
• Radial symmetry
• Bilateral/Triploplastic
• Body cavity
• Protostome vs. Deuterostome