1.1 - 1.5
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
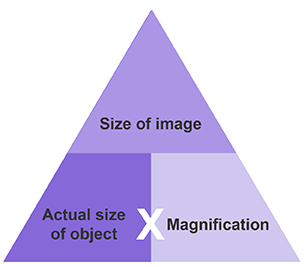
Magnification def
The number of times bigger the image looks compared to the real object
Real object def
The specimen you put under the microscope
Image def
What you see when you look through the microscope; the image of the real object appears magnified
Magnification formula triangle
Resolving power def
The measure of the ability to distinguish two separate points that are close together
How does a light microscope work?
It uses a beam of light to form an image
What is a light microscope’s maximum magnification?
2000x
What are the advantages of a light microscope?
Relatively cheap
Easy to use
Can be used almost anywhere
Can magnify live specimens
What is the disadvantage of light microscopes
Magnification isn’t very high: you can see cells and some structures but not the details of organelles
When was the electron microscope invented?
1930s
How does the electron microscope work?
Electron microscopes use a beam of electrons to from an image
What is the maximum magnification of an electron microscope?
2,000,000x
What are the advantages of the electron microscope?
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) can create dramatic 3D images
Transmission electron microscope (TEM) has very high magnification and resolution
What are some disadvantages of the electron microscope?
Very expensive
Hard to use
Has to be kept in temperature, pressure and humidity controlled rooms
Can’t magnify live specimens (specimen has to be kept in a vacuum)
How many metres is one micrometre
10^-6
How many metres is 1 nanometre
10^-9
What is the resolution of a TEM and SEM?
SEM = 10nm
TEM = 0.2nm
What is the resolution of a light microscope
200nm
What could an electron microscope be used for?
To examine sub cellular structures (eg chromosomes during cell division)
What can a light microscope be used for?
To look at cells dividing (eg stained onion cells)
Explain the importance of microscopes in the development of our understanding in cell biology (6)
Without light microscopes we cannot see most cells
Light microscopes
show cellular structures of living organisms and some subcellular structures (eg nucleus and chloroplasts)
Allows observation of living cells and staining to show features
Electron microscopes
Enable examination of cells in great detail
Help determine what goes on within individual body cells
Can only be used for dead specimens in a vacuum
When were the first light microscopes developed?
Mid 17th century
Why should you use the lowest magnification for the objective lens when you first use the microscope?
Because it is easier to focus and gives the largest field of view
How could you adjust a microscope to see an object more clearly?
Turn the fine focus knob
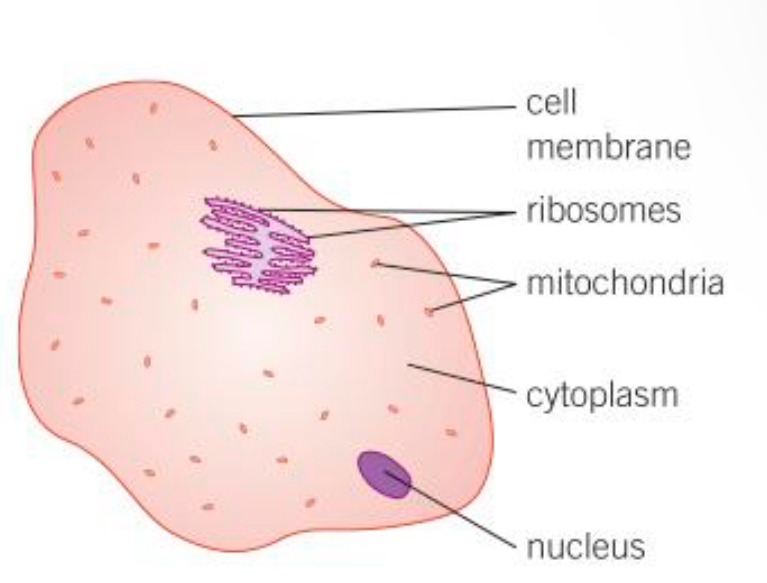
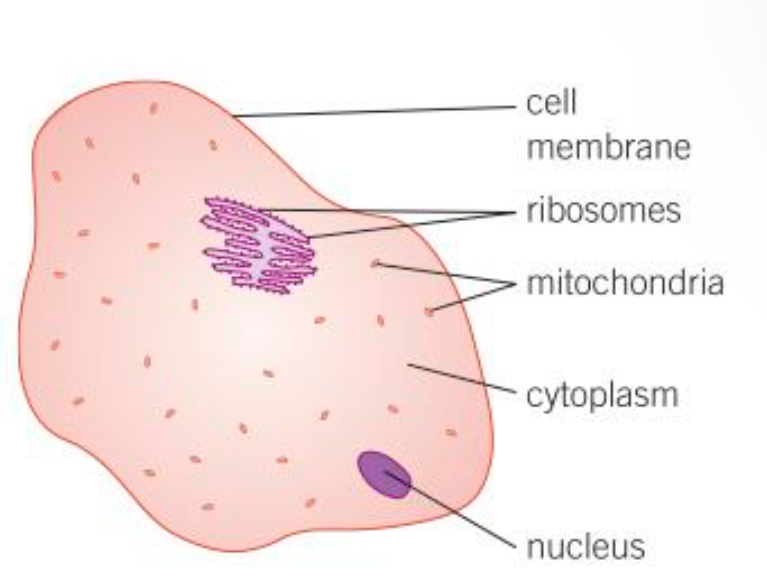
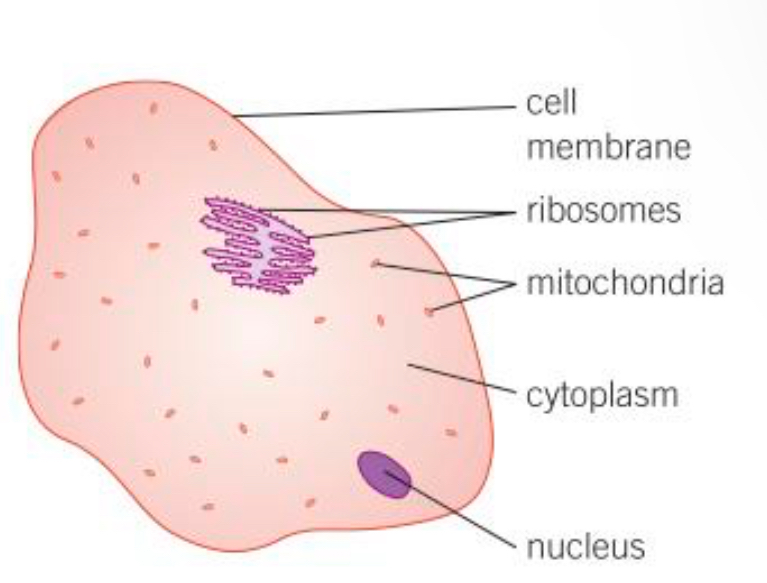
Ribosomes def
The area where protein synthesis takes place. All proteins needed in the cells are made here
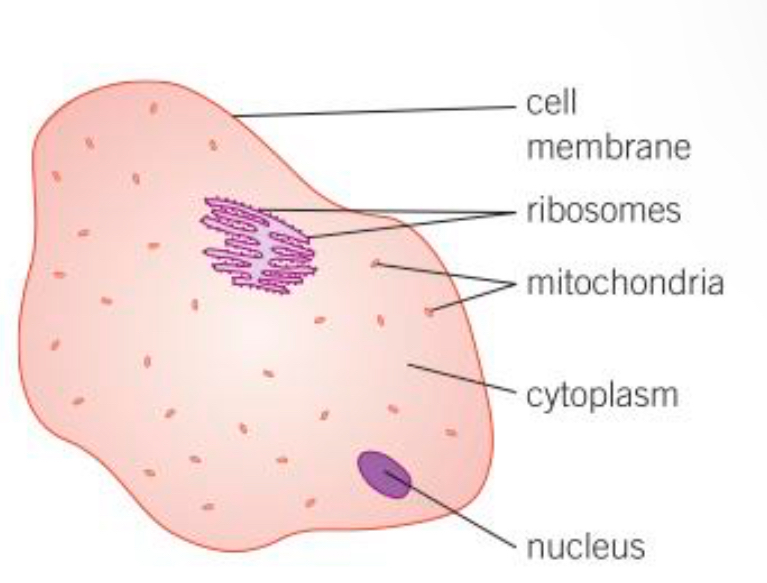
Mitochondria def
Organelles that release the most energy during respiration
Cytoplasm def
Liquid gel where chemical reactions occur
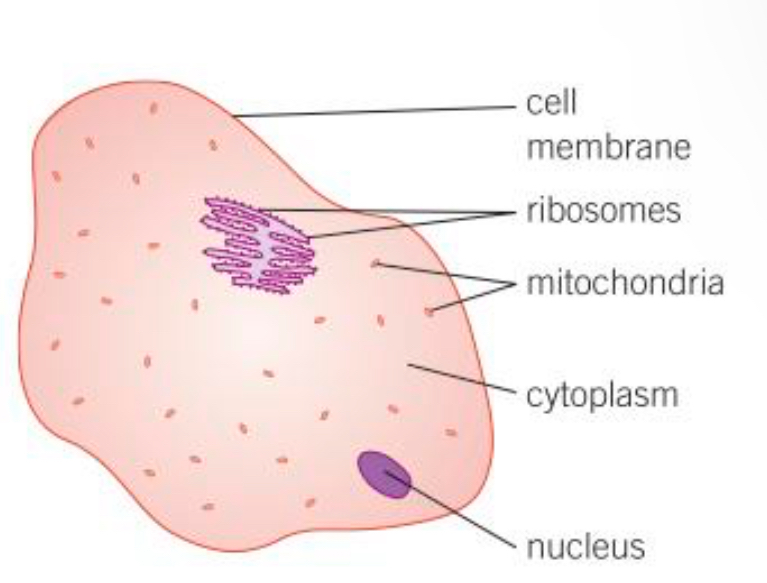
Nucleus def
Controls the functions of a cell, contains genetic information to build new cells or organisms
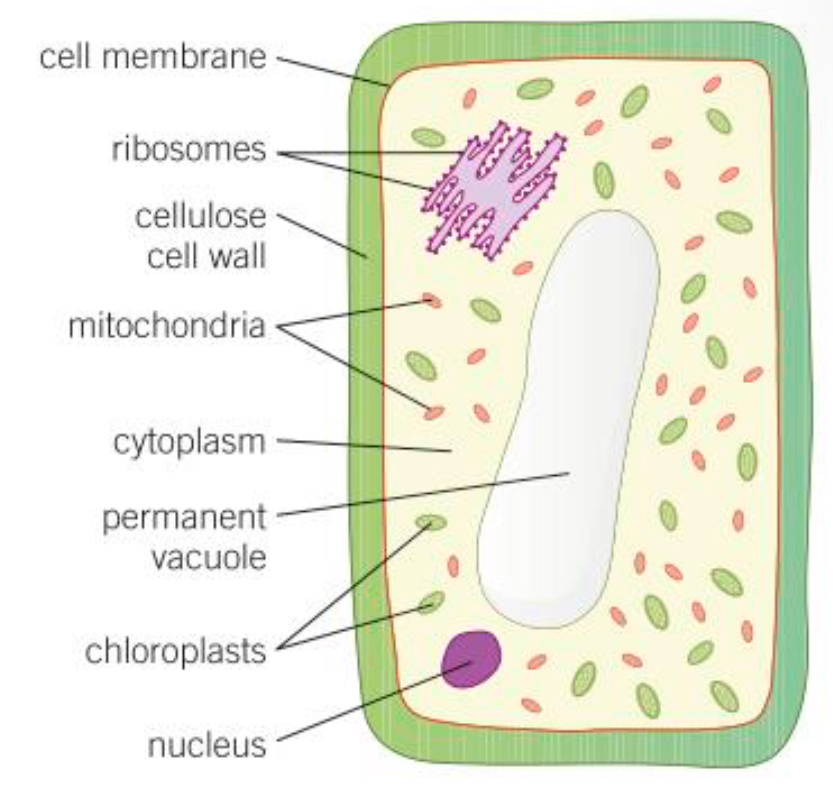
Cell wall def
Made of cellulose for strength and support
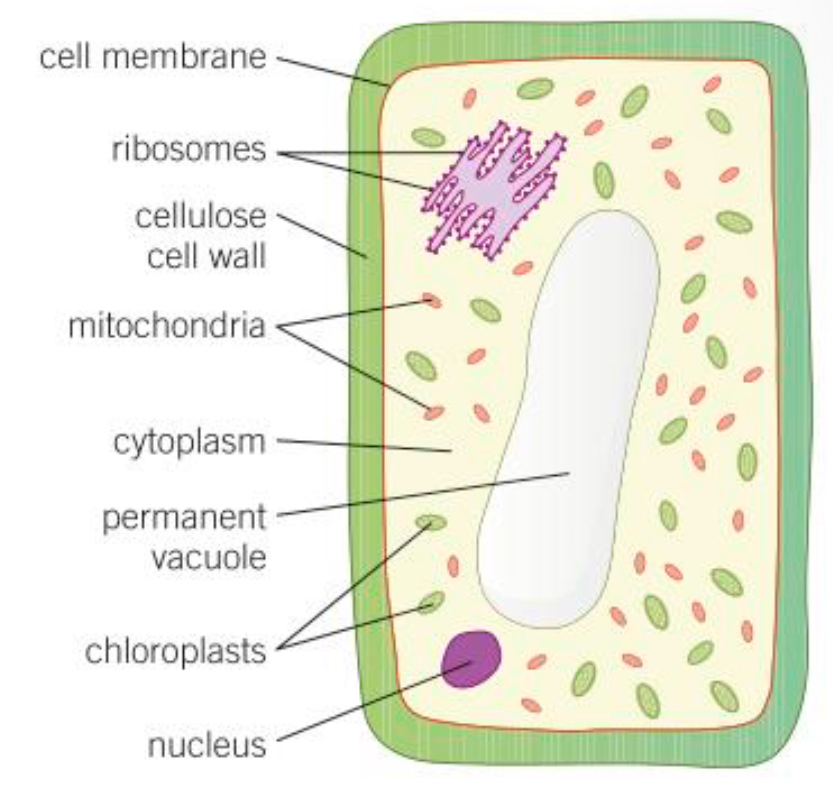
Chloroplast def
Contains chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight so the plant can create food via photosynthesis
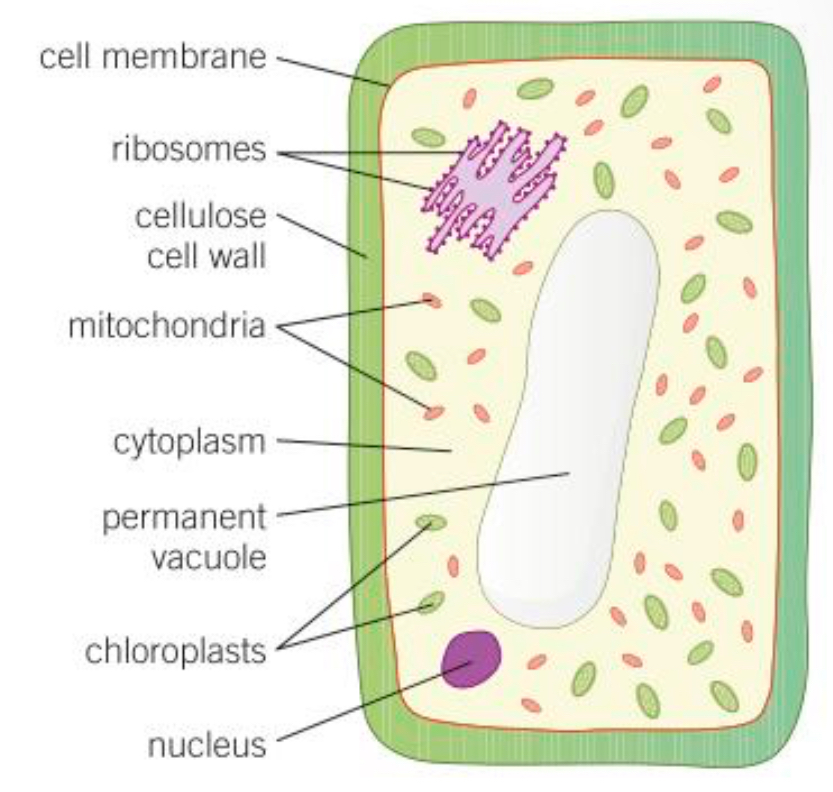
Cell membrane def
Controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell
Vacuole def
Space in the vacuole filled with sap (sugar and salt solution) which keeps cells rigid
Suggest two cells that are unlikely to have chloroplasts and why they don’t have any
root cells - no exposure to light
Cells in flowers of plants - their function is not to photosynthesise
What types of substances does the cell membrane control the passage of in and out of the cell?
Glucose, mineral ions, hormones and urea
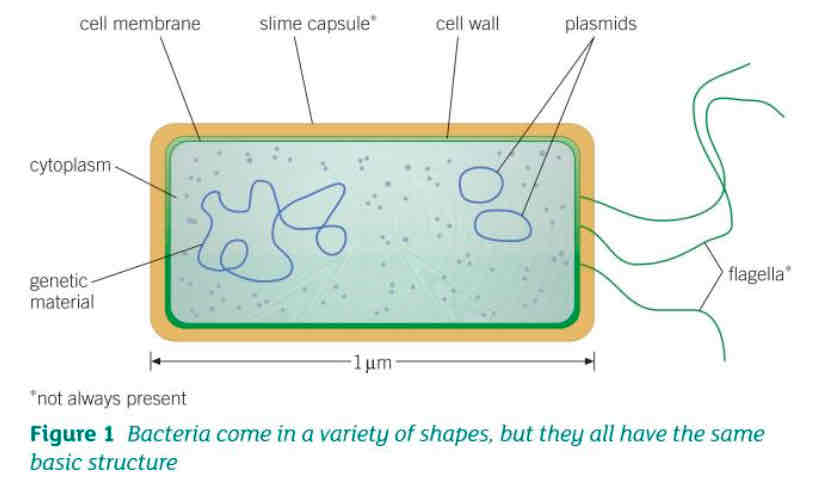
Describe the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells
Found in bacteria and archaea
No nucleus
Found in unicellular organisms
No membrane bound organelles
Smaller
No membrane bound organelles
Reproduction is asexual
DNA is circular. Can have one or more small rings (plasmids)
Has cell wall
Eukaryotic cells
Found in animals and plants
Has nucleus
Found in multicellular organisms
Have membrane bound organelles
Reproduction is sexual
DNA is linear
Cell wall is for plants only
How big is a eukaryotic cell?
10-100 micrometres
How big is a prokaryotic cell?
1 micrometre
How big is a virus?
100 nm (nanometres)
How big is DNA?
10 nanometres (nm)
How big an atom?
1 nanometre (nm)
Put the following in size order: (smallest to largest)
Eukaryotic cell
Virus
Atom
DNA
Prokaryotic
Atom
DNA
Virus
Prokaryotic cell
Eukaryotic cell
What are flagella?
Long protein strand that lashes out
State one use of a flagella in a prokaryote
Movement
Describe the similarities and differences between the features found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic plant and animal cells.
All cells have cell membranes and cytoplasm
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes can have a cell wall
Prokaryotes have no nucleus and no chloroplast
Eukaryotes have no plasmids
Evaluate the possibility that chloroplasts and mitochondria may have originally been free-living bacteria
bacteria are 1-2 orders of magnitude smaller than eukaryotic cells
Bacteria contain free genetic material
Bacteria can reproduce
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are similar in size to bacteria
Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain free genetic material so they can reproduce independently of the cell dividing
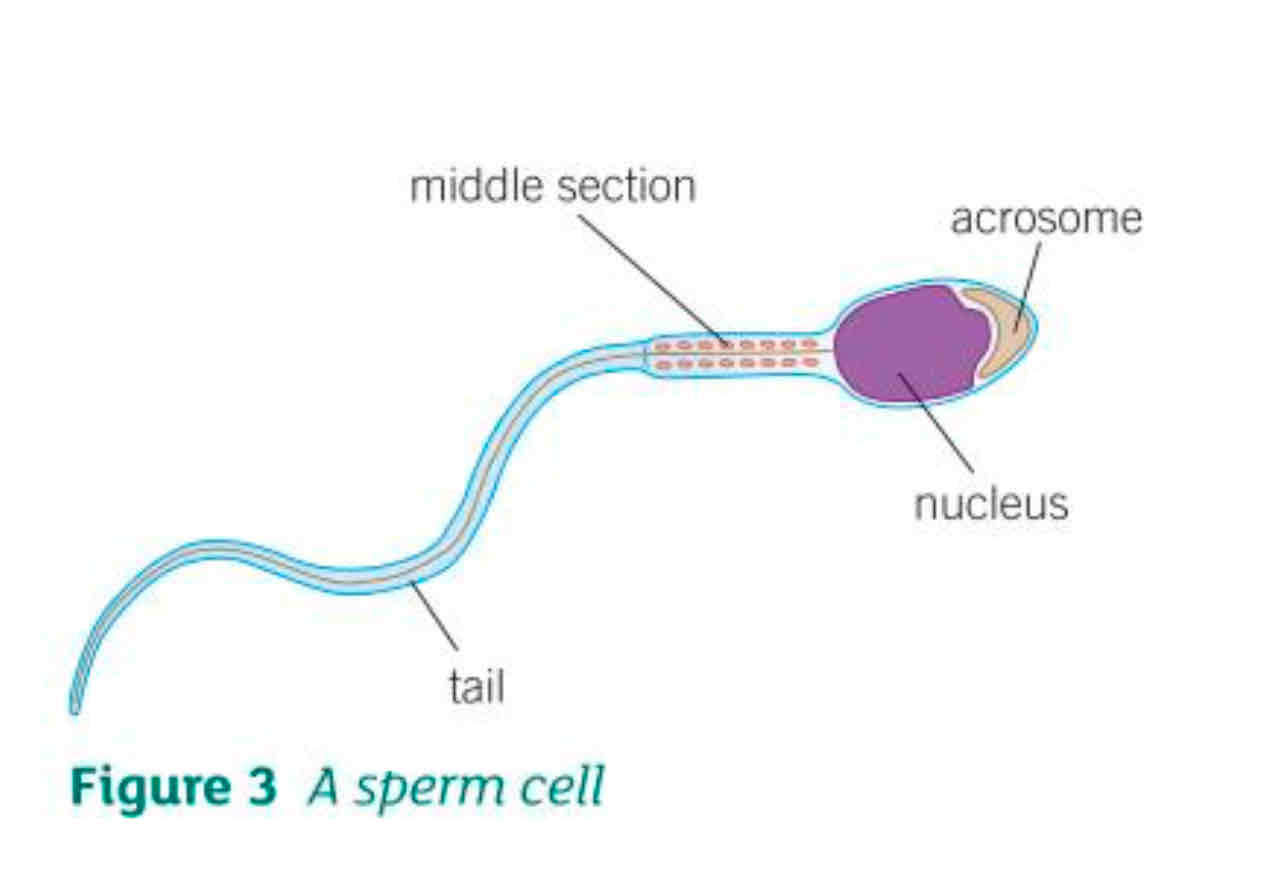
What is the function of a sperm cell?
To transport the male DNA to the egg
Where are sperm cells found?
In the testes
What are the 3 adaptations of the sperm cells?
A long tail to swim to the egg
Lots of mitochondria to provide energy from respiration for the sperm to swim long distances
An acrosome at the front of the head which stores digestive enzymes to break down the outer layer of the egg
Where are muscle cells found?
In the muscles
What is the function of muscle cells?
To contract and relax to move bones in the skeleton
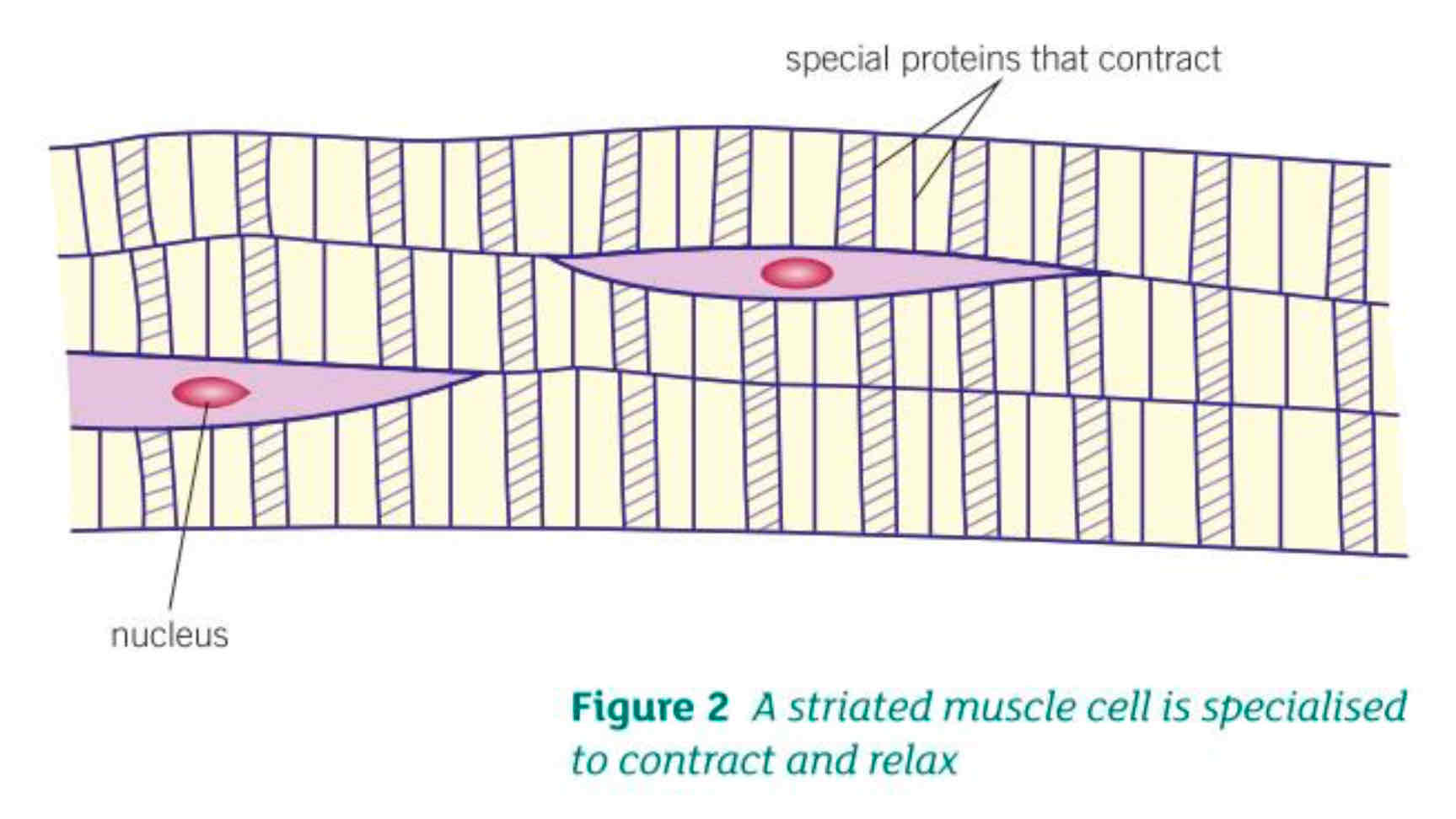
What are the 3 adaptations of muscle cells?
Special proteins slide over each other making the fibres contract
There are many mitochondria to transfer energy
Contain a store of glycogen which can be broken down and used in cellular respiration to transfer energy needed for fibres to contract
What is the function of nerve cells?
The function of nerve cells is to carry nerve impulses around your body
Where are nerve cells found?
In the nervous system
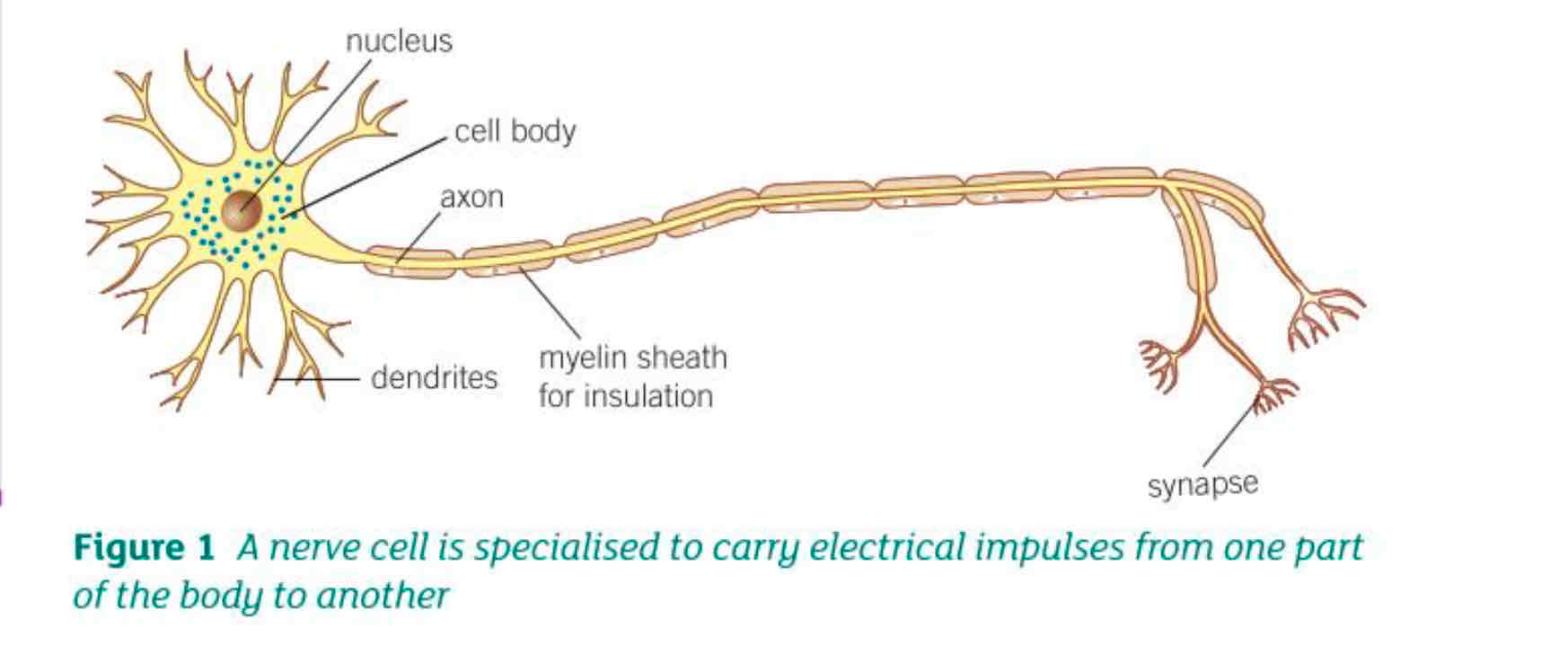
What are the 4 adaptations of nerve cells?
Nerve endings (synapses) pass impulses
Contains lots of mitochondria to make transmitter chemicals
Long axon carries nerve impulses
Dendrites make connections to other nerve cells
What is the function of root hair cells?
To absorb minerals and water from the soil
Where are root hair cells found?
In the roots of plants
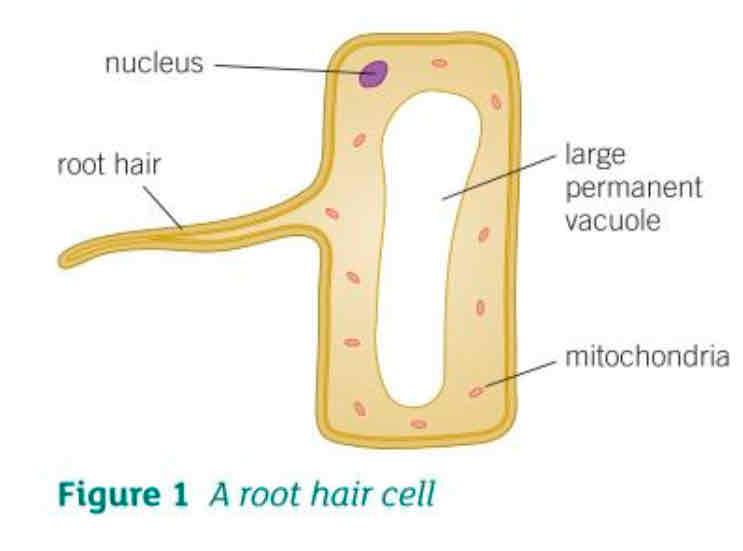
What are the 3 adaptations of root hair cells?
Increase surface area available for water to move into the cell
Large permanent vacuole that speeds up the movement of water by osmosis from the soil across the root hair cell
They have many mitochondria that transfer energy needed for the active transport of mineral ions into the root hair cells
What is the function of photosynthetic (palisade) cells?
Make food for the plant via photosynthesis
Where are palisade cells found?
In the top of the leaf
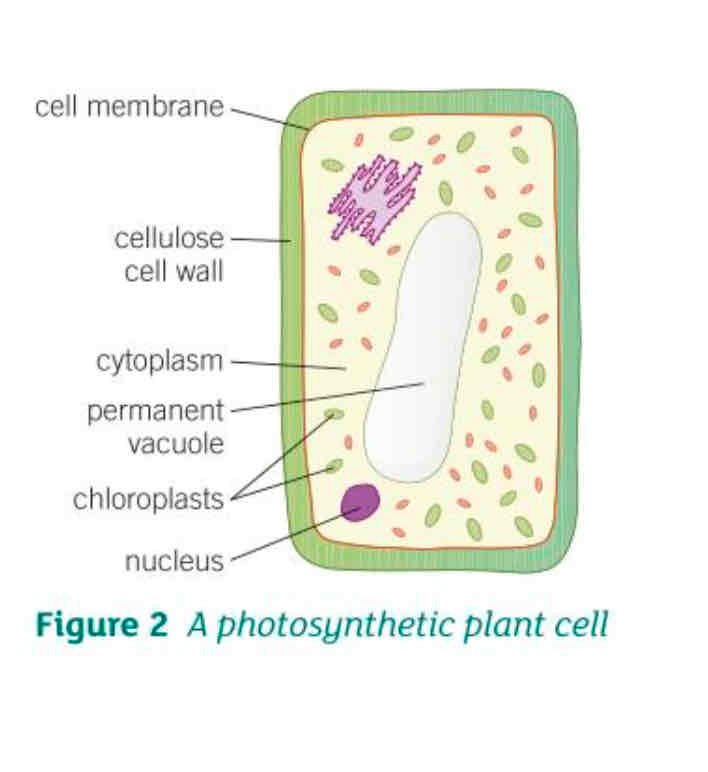
What are the 3 adaptations of palisade cells?
Contain chloroplasts containing chlorophyll that trap the light needed for photosynthesis
Positioned in continuous layers in the leaves and outer layers of the stem so that they absorb as much light as possible
Large permanent vacuole that keeps the cell rigid as a result of osmosis
Why is a large permanent vacuole useful for palisade cells?
they keep the cell rigid as a result of osmosis
When these rigid cells are arranged together to form photosynthetic tissue, they help to support the stem
They keep the leaf spread out to capture as much light as possible
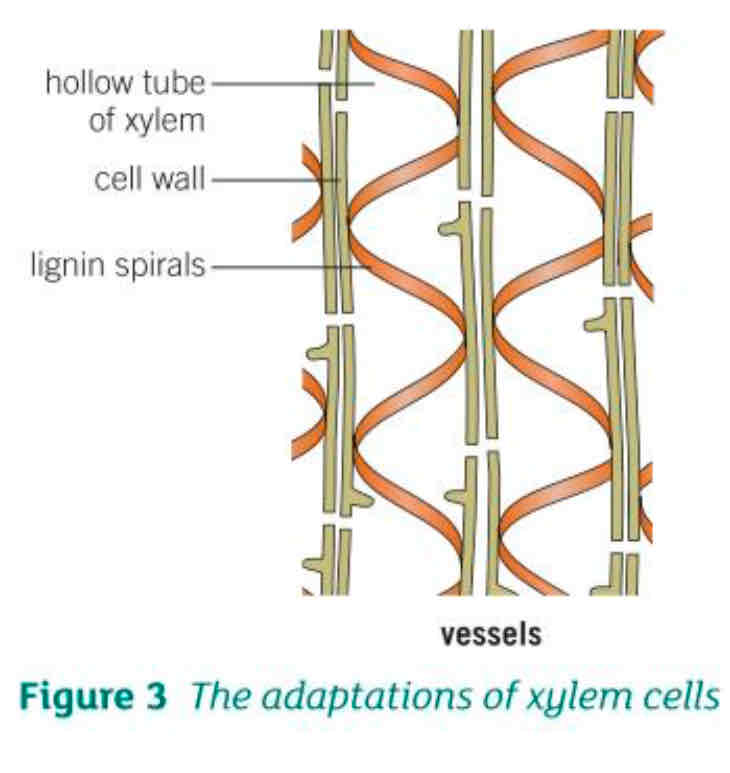
What is the xylem?
It is the transport tissue in plants that carries water and mineral ions from the roots to the leaves and shoots
It also helps to support the plant
In which 2 ways are xylem cells adapted to their function?
Xylem cells are alive when first formed but a chemical called lignin builds up spirals in the cell walls. The cells die and form long hollow tubes that allow water and mineral ions to move easily through them
Spirals and rings of lignin make the cells very strong to withstand the pressure of water moving up the plant. They also help to support the plant stem
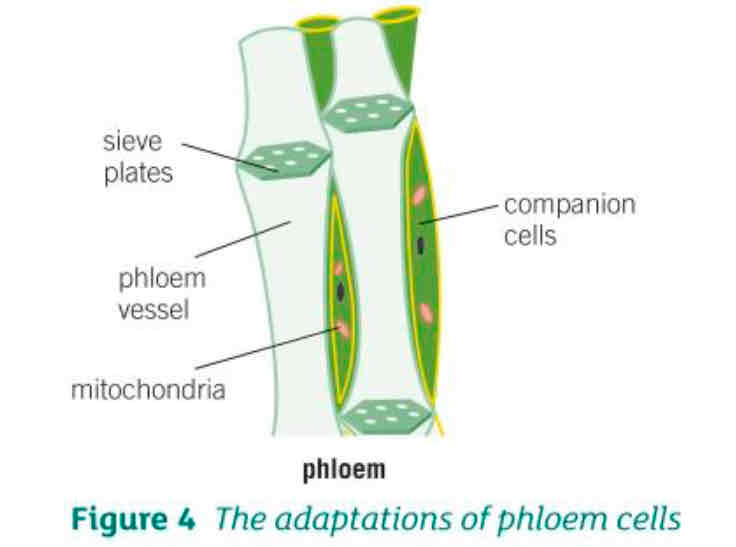
What is phloem?
The specialised transport tissue that carries food made by photosynthesis around the body of the plant
Made up of phloem cells that form tubes
What are the 2 adaptations of phloem cells?
Cell walls between cells break down to form sieve plates. These allow water carrying dissolved food to move freely up and down the tubes
Phloem cells lose a lot of internal structures but they are supported by companion cells that help to keep them alive. Mitochondria from companion cells transfer the energy needed to move dissolved food around the plant