Kins 304 Exam 2
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
linear distance
measured along the entire path of motion (scalar)
linear displacement
measured as the straight line between the initial and first position
-vector
linear speed
distance covered divided by time taken to cover
speed = l/change in time
linear pace
the taken to cover a specified distance
pace = time/distance
linear velocity
rate of change in location/position
linear acceleration
rate of change in linear velocity
-vector
a = V2-V1/change in time
SOHCAHTOA
SIN (Opposite/Hypotenuse) COS (Adjacent/Hypotenuse) TAN (Opposite/Adjacent)
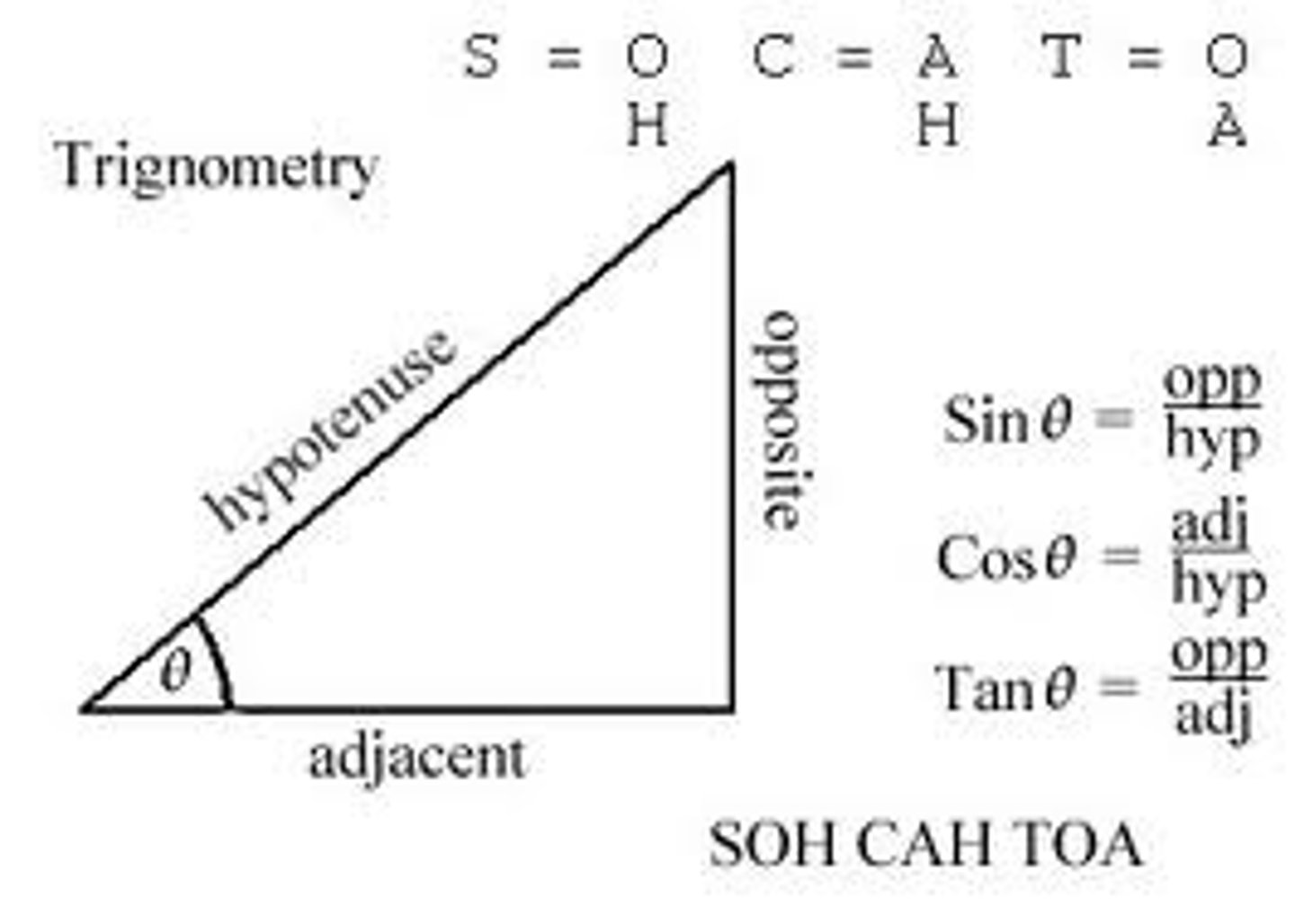
Pythagorean Theorem
a²+b²=c²
Law of Sines
sinA/a=sinB/b=sinC/c
Law of Cosines
a²=b²+c²-2bcCosA
b²=a²+c²-2acCosB
c²=a²+b²-2abCosC
vector composition
2+ vectors to create single vector
-tip to tail vector comp -> resultant vector
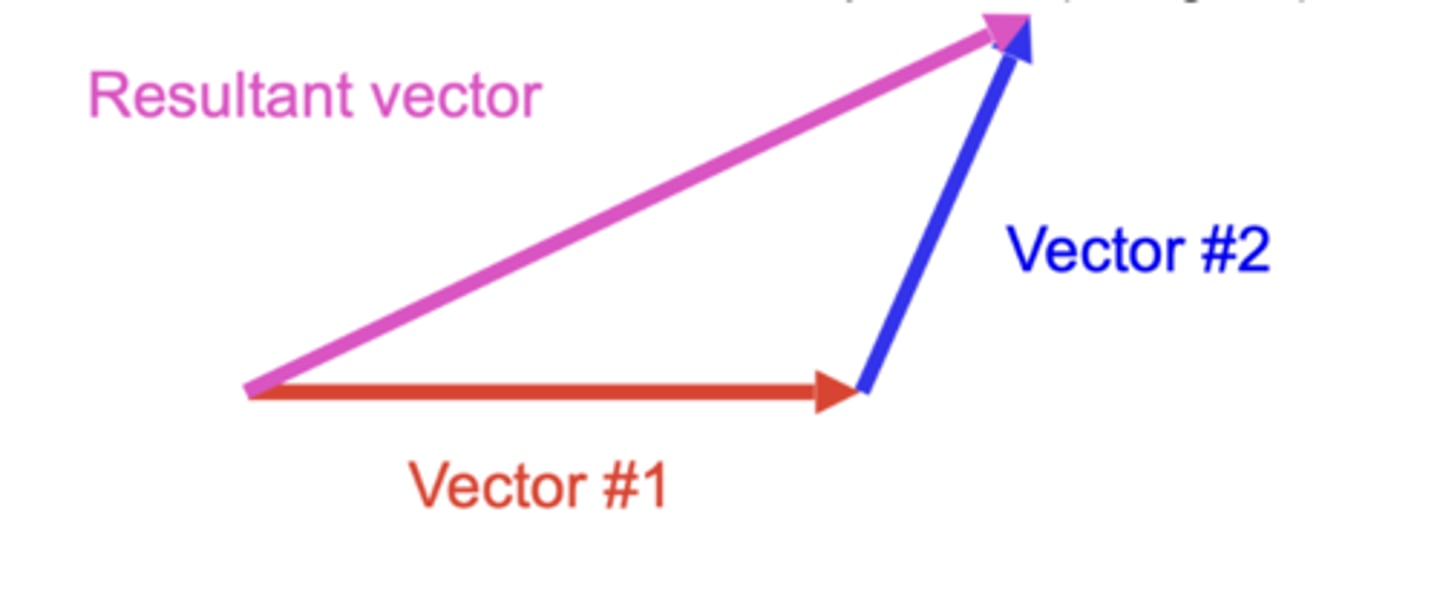
same direction vector
sum
opposite direction vector
difference
different orientation vectors
tip to tail
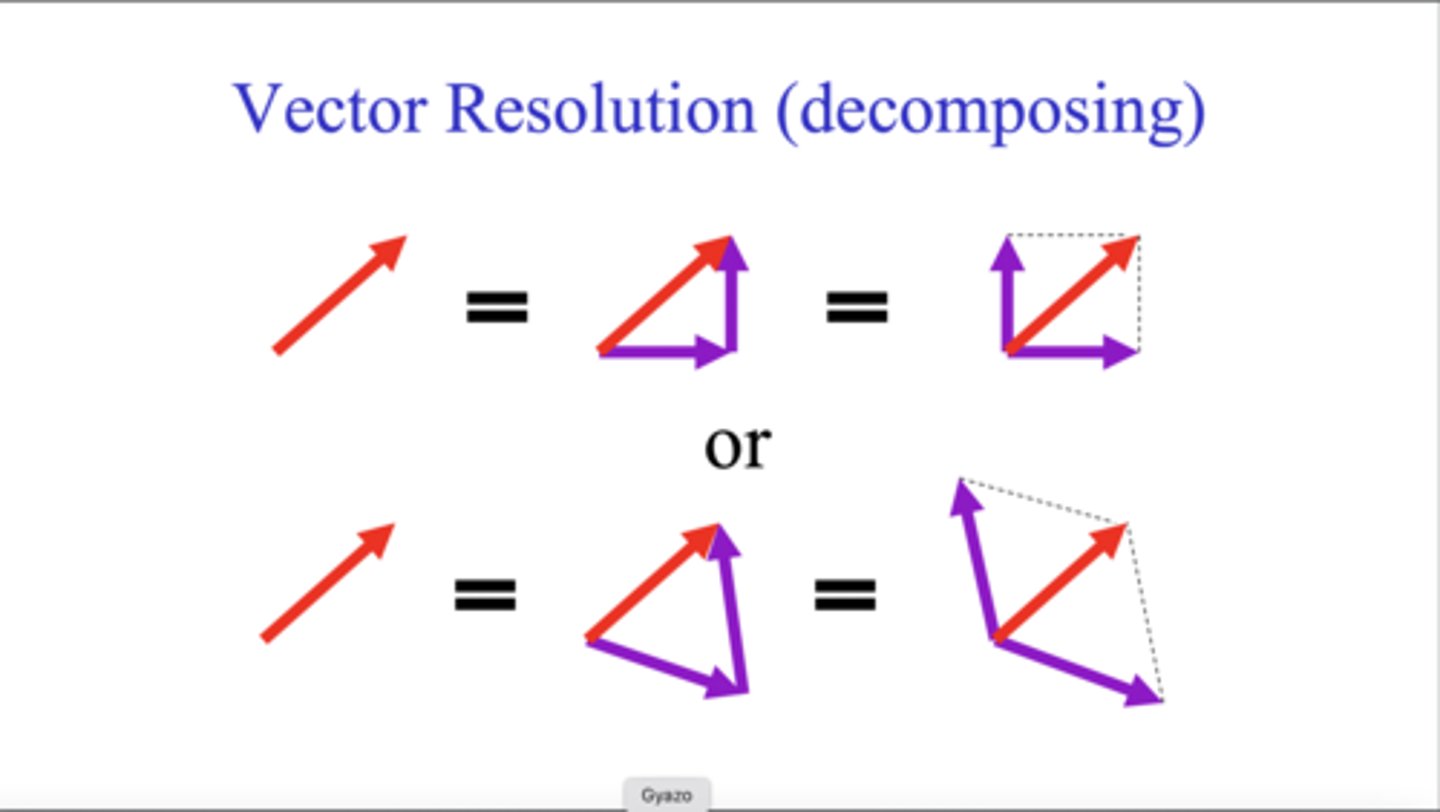
vector resolution
break down into horizontal and vector components
difference between average and instantaneous quantities?
average - occurring over designated time interval
instantaneous - occurring during small interval of time
what happens to vertical velocity of a ball being tossed up in the air?
velocity decreases prior to reach max height
projectile motion
bodies that move through the air unassisted
examples of projectile motion
baseball, shot put/ high/long jumper
vertical components of projectile
max height achieved
- influenced by gravity (-9.81m/s2)
horizontal components of projectile
distance the projectile travels
-no forces affect
vertical vs horizontal projectile example:
dropping a baseball vs bunting
Vertical = same
horizontal = different
3 factors that influence projectile trajectory
angle of projection, projection speed, relative projection height
change in projection angle
determines projectile trajectory
- vertical
-oblique
-horizontal
change in projection speed
magnitude of projection velocity
-affect range and height when other factors are constant
change in relative projection height
increase RPH -> increases flight time and horizontal displacement
your students are goofing around in gym class. they bet you that they can throw the ball hard enough to hit the ceiling. the students throw the ball velocity of 13m/s. if the ceiling is 10m tall, will the ball hit the ceiling?
V1 = 13/ms , ag = -9.81m/s2. height = 10m
0 = v1^2 + 2ad
0 = (13m/s)^2 + 2(-9.81m/s2)d
0 = 169m2/s2 + (-19.62m/s2)d
19.62m/s2(d)=169m2/s2 / 19.62m2/s2
= 8.61 m
you are trying to kick a soccer ball across the entire width of the field (50m). If the ball is kicked with a horizontal velocity of 14m/s with a flight time of 3.7s, how far was the kick?
Vh - 14m/s , t = 3.7s
d = Vh x t
d = 14m/s x 3.7 s
d = 51.8 m
a projectile is launched from the ground at an angle of 68 degrees with an initial velocity of 17m/s.
A) horizontal and vertical components?
B) how high does projectile go?
C) how far does projectile go
V1 = 17m/s ag= -9.81m/s2
A) horizontal: Cos = adj/hyp
cos 68 = vh/ 17m/s -> 0.375 = vh/ 17m/s -> vh = 6.37 m/s
veritcal: sin = opp/hyp
sin 68 = vv/17m/s -> 0.927 = vv/17m/s -> vv = 15.76 m/s
B) how high?
0 = v1^2 + 2ad
0 = (15.76m/s)^2 + 2(-9.81m/s2)d
0 = 248.38m2/s2 + (-19.62m/s2)d
19.62m/s2 (d) = 248.38m2/s2 / 19.62m/s2
= 12.66 m
C) how far?
0 = V1 + at
0 = 15.76m/s + (-9.81m/s2)t
9.81m/s2 = 15.76m/s / 9.81 -> t = 1.61 s
1.61s x 2 = 3.22s
dh = vh x t -> dh = 6.37m/s(3.22s)
dh = 20.51m
a swimmer orients himself perpendicular to the parallel banks of a river. If his velocity is 2m/s and the velocity of the current is 0.5m/s.
A) what is resultant velocity?
B)) how far will he actually have to swim to get to the other side of the bank if 50 m apart
a2+b2=c2
A) R2 = (2m/s)^2 + (0.5m/s)^2
R2 = 4.25
R = 2.06m/s
B) direction:
cos a = 2m/s / R
cos a = 2m/s / 2.06m/s -> 0.970
cos -1 (0.970) = 14 degrees
displacement:
cos a = 50m/D
cos 14 = 50m/D -> D(cos 14) = 50m -> D(0.970) = 50m / 0.970
D= 51.5m
soccer ball rolling down at t = 0, instantaneous velocity of 4m/s. If acceleration of ball is CONSTANT at 0.3m/s, how long will it take for a complete stop?
V1 = 4m/s V2 = 0 t1 = 0 a = -0.3m/s2
a = v2-v1/ change in time
-0.3m/s2 = 0-4m/s / t
-0.3m/s2 (t) = -4m/s / -0.3m/s2
t = 13.3 s
dennis decided to run 4 laps around a 400m track, ending in the same location as he began.
A) what is distance ran?
B) displacement?
C) dennis finished 4 laps in 7 minutes. what was his speed?
A) 4 x 400 m =1600m
B) displacement = 0
- not a straight line
C) speed:
7minutes = 60s/1min = 420s
speed = 1600m/420s
= 3.81m/s
angular distance
sum of all changes undergone by a rotating body
-total motion of path
angular displacement
change in angular position or orientation of a line segment
-difference of initial and final position
-vector, counter clockwise (+) vs clockwise (-)
angular speed
angular distance divided by the time that the motion occued
-scalar
- angular speed = angular distance change in time
angular velocity
angular displacement covered in time given
- vectori, direction +/- or counterclockwise vs clockwise
angular acceleration
rate of change in angular velocity
a = w2-w1/t2-t1
positive angular acceleration
increase angular velocity in positive direction
OR
decrease angular velocity in negative direction
negative angular acceleration
decrease angular velocity in positive direction
OR
increase angular velocity in negative direction
linear positive acceleration
increase velocity in positive direction
or
decrease velocity in negative direction
linear negative acceleration
decrease velocity in positive direction
or
increase velocity in negative direction
apex
highhest point in trajectory of projectile
trajectory
flight path of a projectile
range
horizontal displacement of projectile landung
flight time influenced
initial vertical velocity and relative projection height
horizontal displacement influenced
horizontal velocity and relative projection height
vertical displacement influenced
initial vertical velocity and relative projection height
trajectory influenced
angle of projection, projection speed, and relative projection height
OPH
optimal projection angles
RPH = 0
best angle = 45 defrees
linear vs angular distance
linear - measured along a path
angular - sum of all changes in a rotating body
linear vs angular displacement
linear - straight line (first->second)
angular - change in angular position (different from initial and final)
-counterclockwise/clockwise
linear vs angular spped
linear - distance covered
angular - angular distance/time
linear vs angular velocity
linear - rate of change in location
angular - displacement covered in time
- clockwise/counterclockwise
Linear vs Angular Acceleration
linear: change in velocity in straight line
angular: change in rate of rotation
difference in joint angles and body segment orientation
joint angle - angle between anatomical position (0 degrees)
-relative angle
body segment- angular orientation of a body segment with a fixed line reference
-absolute angle
relationship between linear and angular distance
during angular motion, greater the radius between a given point on a rotating body and axis of rotation, greater linear distance undergone by point of interest
relationship between linear and angular velocity
all other factors held constant, the greater radius of a rotating body = greater linear velocity
tangential acceleration
represents the change in linear speed for a body traveling on a curved path
at = v2-v1/t
at = tangential acceleration
v1 = initial linear velocity
v2 = second linear velocity
t = time interval velocities assessed
Radial accerleration
represents change in direction of a body in angular motion
ar = v2/r
ar = radial acceleration
v = linear velocity of moving body
r = radius rotation
tangential and angular acceleration relationship
at = ar
at - linear acceleration (tang accel)
a = angular acceleration
r = radius of rotation
during a bicep curl, the elbow joint flexes 120 degrees. If you performed 15 reps, what is the total angular distance completed?
120 degrees x 2 = 240 degrees
240 degrees x 15 reps = 3600 degrees
you do 5 bicep curls at 90 degrees (anatomical position)
A)distance?
B)isplacement?
C)form change?
A) 90 x 10 = 900
5 bicep curls = up , + 5 more for down
B) displacement = 0 degrees
C) when form changes, angles, displacement and distance all change
a golf ball is struck with an angular velocity of 20rad/s. If the length of the club is 1.1m...
what is the linear velocity at the point of contact?
r1 = 1.1m
w1=20rad/s
v=rw
v= (1.1m)(20rad/s)
= 22 m/s
two baseballs are consecutively hit by a bat. The first ball is hit 0.2m from the bats axis of rotation and the SECOND ball is hit 0.4m from the bats axis of rotation. If the angular velocity of the bat is 30 rad/s at the instant both balls were contracted....
what was the linear velocity of bat at the two contact points?
A) r1 = 0.2m w1=30rad/s
v=rw
v =(0.2m)(30rad/s)
= 6m/s
B) r2 = 0.4m w2= 30 rad/s
v=rw
v=(0.4m)(30rad/s)
=12m/s
a windmill-style softball pitcher executes a pitch of 0.65s. If her pitching arm is 0.7m long....
A) what are the magnitudes of the TANGENTIAL and RADIAL acceleration on the ball just before ball release when the ball velocity is 20m/s
B) what is the magnitude of the total acceleration on the ball at the point of release?
t = 0.65s r = 0.7m v2 = 20m/s
A) at = v2-v1/change in t
at= 20m/s - 0m/s / 0.65s
at=30.8m/s2
ar= v2/r
ar=(20m/s)2 / 0.7m
ar= 571.4m/s2
B) a2 = at2 + ar2
a2 = (571.4m/s2)2 + (30.8m/s2)2
a=572.2m/s2
a discus thrower executes the throw in 2.5 seconds. If the throwing arm is 0.83m long..
A) what are the magnitudes of the TANGENTIAL and RADIAL acceleration of the disc just before the release when the tangential velocity is 22m/s
B) what is the magnitude of the total accerleration?
t = 2.5 s r = 0.83m v2 = 22m/s
A)
at=v2-v1/change in t
at = 22m/s- 0m/s / 2.5s
at = 8.8m/s2
ar=v2/r
ar=(22m/s)^2 / 0.83
ar= 583.13m/s2
B) a2= at2 + ar2
a2 = (8.8m/s2)2 + (583.13m/s2)2
a2 =340118.0369m2/s4
a=583.20m/s2
swimmer crosses lake 0.9km wide for 30minutes.
a) velocity?
b) average speed?
a) v = d/t
t= 30min d=0.9km
30 min = .5 hour
v = 0.9 km / 0.5 hr
= 1.8 km/hr
b) cant do speed, no distance
the score was tied 20-20 between Vikings and Packers. At the end of the game, the Vikings had an opportunity to kick the winning field goal. The ball was placed 42m from goalpost. If the ball was kicked horizontal component of initial velocity of 19m/s and flight time of 2.4s...
was the kick long enough to make field goal?
vh = 19m/s t = 2.4 s d = 42m
d=vh x t
d = 19m/s x 2.4s
= 45.6 m
yes it was long enough!
a volleyball is deflected vertically by a player during a block. The high school gym has a ceiling clearance of 10.5m. If the initial velocity of the ball is 14m/s...
will the ball hit the ceiling?
v1 = 14m/s ag= -9.81m/s2 height = 10.5m
0 = v12 + 2ad
0 = (14m/s)2 + 2(-9.81m/s2) x d
19.62 m/s2 x d = 196m2/s2
d=9.99 m
will not hit the ceiling
a soccer ball is kicked at a 40 degree angle with an initial velocity of 10m/s
a) how high does the ball go?
b) how far does the ball go?
v1 = 15m/s ag = -9.81m/s
horizontal:
cos 40 = vh/10m/s
10m/s x 0.766 = vh
vh = 7.66m/s
vertical:
sin 40 = vv/10m/s
10m/s x 0.643 = vv
vv = 6.43m/s
a) 0 = v12 + 2ad
0 = (6.43m/s)2 + 2(-9.81m/s2) x d
19.62m/s x d = 41.34m2/s2
d= 2.11 m high
b) 0 = v1 + at
0 = 6.43m/s + -9.81m/s2 x t
9.81m/s2 x t = 6.43m/s
t = 0.655 x 2
t = 1.31
dh=vht
dh= 7.66m/s x 1.31 s
= 10.03m far