PSY3301-lecture content
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
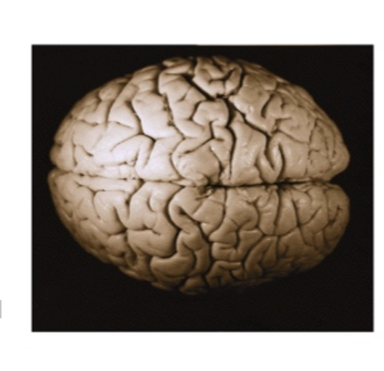
What view of the brain is this
Dorsal
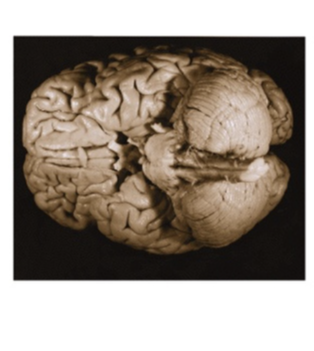
What view of the brain is this
Ventral
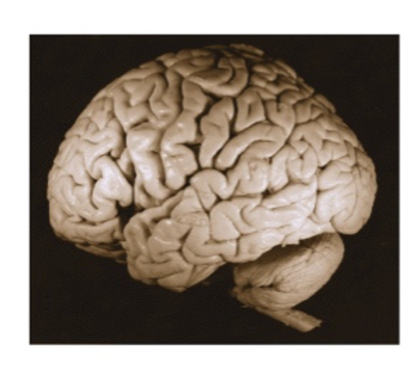
What view of the brain is this
Lateral
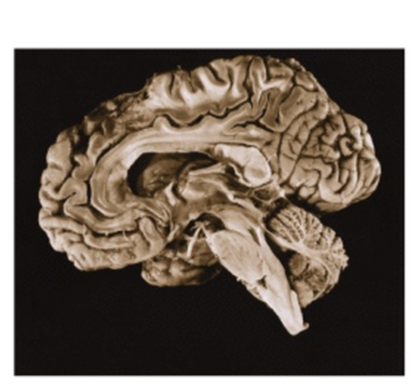
What view of the brain is this
Medial
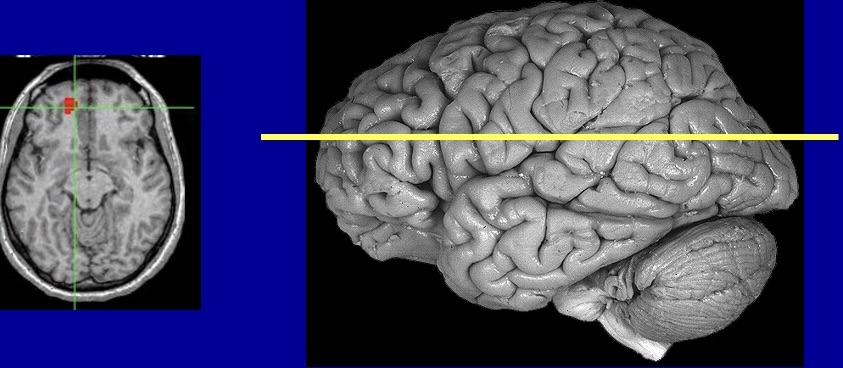
What type of plane/slice of the brain is this
axial / horizontal / transverse
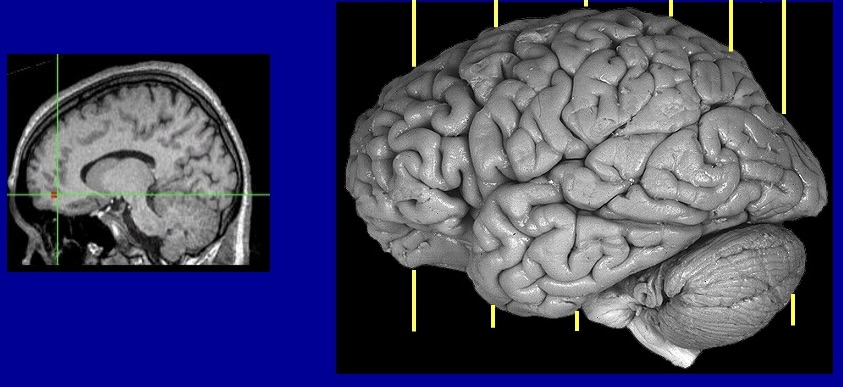
What type of plane/slice of the brain is this
sagittal
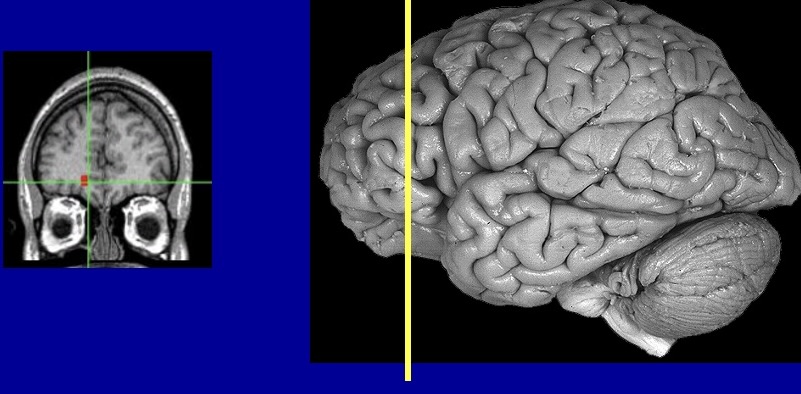
What type of plane/slice of the brain is this
coronal or frontal section
to and from the brain
To the brain: afferent
From the brain: efferent
Meninges: what are the 3 layers
1. Dura: hard
2. Arachnoid: thin sheet of delicate connective tissue
3. Pia matter: soft
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): does what
serves as a cushion so the brain can move or expand slightly
explain meningitis, cause, result, side effects
Caused by infections in the meninges
Can result in brain swelling
Side effects: headaches, cervical rigidity, drowsiness, coma
what is the difference between meningitis and encephalitis
encephalitis is an infection in the brain
what are the gyri
outer part of the folds
what are the sulci
inner part of folds
What is the cerebral cortex
the outer layer of the brain
What are the major cortical divisions
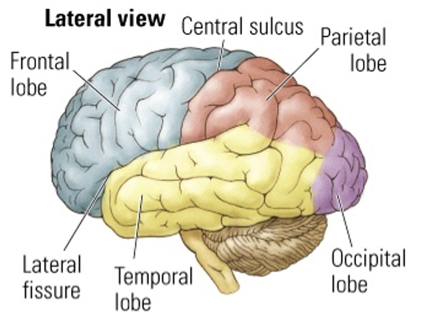
the central sulcus is the only lateral sulcus in the brain what does it allows us to find
the primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus)
And the primary somatosensory (postcentral gyrus)
What are Cytoarchitectonic (Brodmann) Maps, and describe
Brodmann defined areas by the organization and characteristics of the cells
Layer IV is thicker in the sensory cortex vs in the motor cortex
Explain the afferents vs efferents of Cytoarchitectonic (Brodmann) Maps
Afferents go to layer IV (from the thalamus) as well as to layers II and III
Efferents go to other parts of the cortex and to the motor structures
Hemorrhagic stroke
bleed, leaks into brain tissue
Ischemic stroke
block, clot stops blood supply to an area of the brain (more common, easier to treat)
appearance of gray vs white matter
White matter: areas rich with axons (myelin=white appearance)
Gray matter: composed of cell bodies
What do the ventricles do
secrete CSF, which suspends the brain in the skull, protecting it (shock absorber), they also provide a route for chemical messengers
3 main points about then venticular system
1) cells that line the ventricles make the CSF that fills them
2) flows from the 2 lateral ventricles to the 3rd and 4th ventricles (midline ventricles)
3) then flows between the layers of the meninges/spinal cord canal
what happens to CSF with hydrochephalus
there will be an increase in CSF
Describe the corpus callosum
band of white matter which connects the 2 hemispheres
what are the main structures of the forebrain
Cerebral cortex (neocortex)
Basal ganglia
Limbic system
what is the cerebral cortex
forms the outer layers and is made of 6 layers of grey matter
what does the cerebral cortex do
Regulates mental activity such as planning and perception, higher-order processing
describe neocortex vs limbic cortices
Neo: 6 layers of gray matter, more advanced, higher-order processing
Limbic: 3 to 4 layers of gray matter on top of 1 layer of white matter, more primitive, controls motivational states
what is the basial ganglia made of
Collection of nuclei deep to white matter of cerebral cortex
What structures are included in the basal ganglia (3)
Striatum = caudate + putamen (large structure) + nucleus accumbens
Corpus striatum = striatum + globus pallidus
Lenticular nucleus = putamen + globus pallidus
What does the brainstem do and where does it start
Controls the basic functions of life: breathing, HR, swallowing, BP, sleep, balance
Begins where spinal cord enters the skull
what are the inputs and outputs of the brain (brainstem)
Afferent inputs (to brain): from all of the body's senses
Efferent Outputs (from brain): to control all of the body's movements
what are the 3 regions of the brain
Hindbrain, Midbrain , Diencephalon
^^these 3 regions have both sensory and motor functions
what is the diencephalon composed of
the thalamus, the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland
why is the diencephalon hypothalamus important
important in almost all aspects of behaviour: feeding, sexual behaviour, sleeping, temperature control, emotion, hormone function, movement
what is the tectum and what is it made of (in the midbrain)
receives a large amount of information from the eyes and ears. Consists of 2 major parts: superior colliculus, inferior colliculus
what is the tegmentum
Composed of many nuclei
Mainly involved in movement.
What does the VTA do
ventral tegmental area = nuclei for dopamine pathway and reward
what are the 4 main parts of the hindbrain
Reticular formation: responsible for wakefulness and alertness
Pons, medulla, cerebellum
how do different regions in the brain communicate
Fiber system of the cerebral hemispheres
1. commissures (ex. Corpus callosum, anterior commissure)
2. association tracts
3. projection fibers