U of U PA School Calcium and Phosphorus
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Where is phosphorus stored? What does it do?
Stored in bones as hydroxyapatite
Phosphorylates enzymes
Major intracellular cation in skeletal system
What amount of phosphorus is found in serum?
<1% of total amount
10% of that is bound to albumin
Why are phosphorus deficiencies less common?
Easily absorbed in GI tract from bood
Unbound form freely filtered at glomerulus and PCT
-Able to reabsorb high levels based on need
What can cause a phosphorus deficiency? (5)
Low vitamin D
Extreme starvation
Improper TPN
Refeeding syndrome
Respiratory alkalosis shifts phosphorus intracellularly
What does mild hypophosphatemia cause? Severe?
Mild - well tolerated, mostly asymptomatic
Severe
-Weakness
-Respiratory muscle weakness
-Hemolytic anemia
What are the normal serum levels of phosphourus?
3-4.5 mg/dl
What is the treatment for mild hypophosphatemia? What should be monitored with this?
Oral elemental phosphorus
-Often paired with sodium or potassium
Monitor BMP to avoid hypernatremia or hyperkalemia
What is the treatment for severe hypophosphatemia? What should be monitored with this?
IV dosing of phosphorus
Can cause hypocalcemia
Recheck levels after 6 hours of administration
When is hyperphosphatemia seen? What causes it?
Seen in CKD when GFR <25
Caused by decreased excretion of phosphorus within kidney
-Decreased GFR leads to decreased excretion
What does hyperphosphatemia cause?
Increased mortality and CV events
-Regardless of CKD status
Secondary hyperparathyroidism - renal atrophy in CKD
Phosphorus deposits -> calcification of vasculature
What is secondary hyperparathyroidism?
High phosphate and PTH
Low calcium
Low vitamin D
How does secondary hyperparathyroidism present?
Secondary chronic hypocalcemia
-Elevated phosphorus binds calcium causing decreased serum levels
Presents similarly to CKD
What can hyperparathyroidism cause?
Renal osteodystrophy
Calciphylaxis in CKD
What is the treatment for hyperphosphatemia?
Calcium carbonate to bind excess phosphate and mitigate hypocalcemia
-Give even if normal calcium levels
Sevelamer - PO4 binder
Vitamin D supplementation
What are normal serum total calcium levels?
8.4-10.2 mg/dl
How does hypocalcemia present?
Muscle tetany and neuronal hyperexcitability
-Paresthesias
-Chvostek sign - facial muscle twitch
-Trousseaus sign - wrist flexion with BP cuff
What is the treatment for hypocalcemia? How should it be monitored?
If symptomatic and severe
-IV calcium chloride or calcium gluconate
Reevaluate levels every 6 hours
Monitor electrolyte levels
-Potassium
-Phosphorus
-Magnesium
-Vitamin D
What can treatment for hypocalcemia cause?
Nausea
Hypertension
What is the treatment for asymptomatic or mild hypocalcemia? How should it be monitored?
Oral calcium and vitamin D
If acutely low reevaluate in 24 hours
If chronically low reevaluate weekly
Replace magnesium and potassium as needed
How does hypercalcemia present?
Bones (osteopenia, fractures)
Stones (kidney stones)
Abdominal groans (anorexia, constipation)
psychiatric overtones (weakness, fatigue, altered mental status)
What is the treatment for mild hypercalcemia?
Discontinue meds that can cause it
-Supplements
-Thiazides
-Lithium
What is the treatment for severe hypercalcemia?
NS to expand volume - 1st line
-Give lasix if volume overload
SQ calcitonin
IV bisphosphonates
Glucocorticoids
Why are glucocorticoids used in hypercalcemia?
Decrease intestinal calcium absorption and vitamin D synthesis
What is calciphylaxis? When is it seen most commonly?
Calcific uremic arteriopathy
-Calcium deposits on medial layer of small arteriaes causing small vessel stenosis
Seen in ESRD
What does calciphylaxis cause?
Painful cutaneous lesions due to tissue ischemia and infarct
Can lead to ulcers and infection
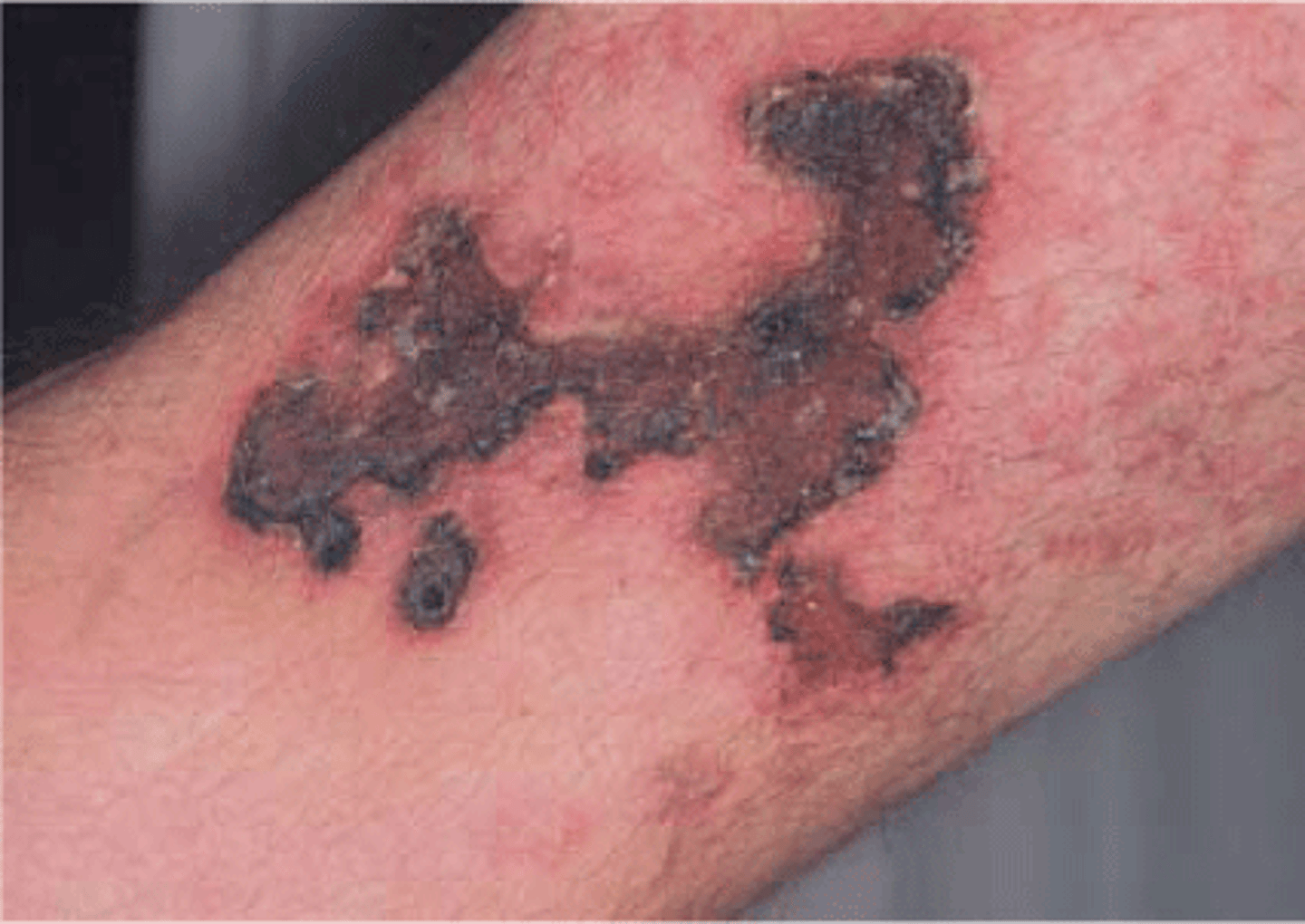
How is calciphylaxis diagnosed?
Vessel biopsy
Where does calciphylaxis most commonly affect?
Core adipose reguions
How is calciphylaxis treated?
Discontinue calcium supplements
Supportive wound care
How do loop diuretics affect calcium?
Block NKCC2 leading to increased renal calcium and sodium excretion
Can help in hypercalcemia
How do thiazide diuretics affect calcium?
Block NCC causing increased calcium reabsorption
Can help in hypocalcemia and prevent calcific kidney stones