Topic 2 - Electricity (without static)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is electrical current?
The flow of electric charge round the circuit
When will current flow across a circuit?
Will only flow around a closed circuit if there’s a p.d .
What is p.d? (what is it measured in)
The driving force that pushes the charge around, measured in volts
What does rhe current flowing through a component depend on?
The p.d across it and the resistance of the component.
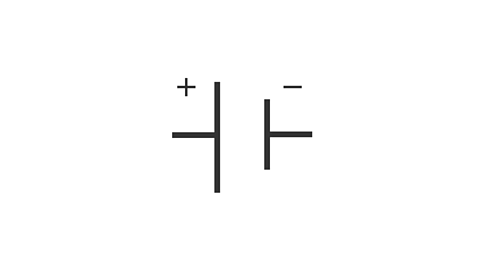
What is this circuit symbol?
Cell
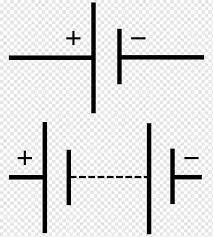
What is this circuit symbol?
Battery
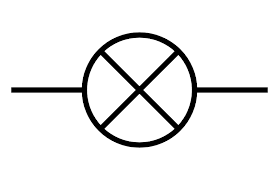
What is this circuit symbol?
Filament lamp (bulb)
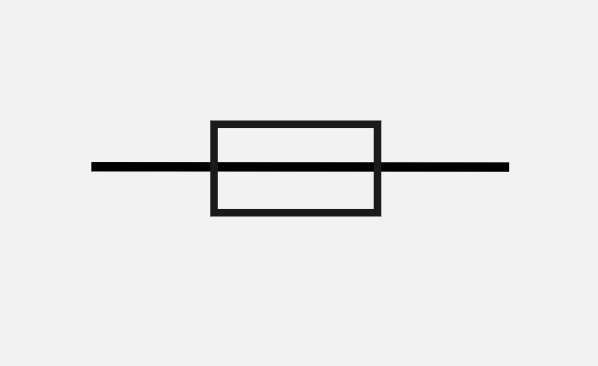
What is this circuit symbol?
Fuse
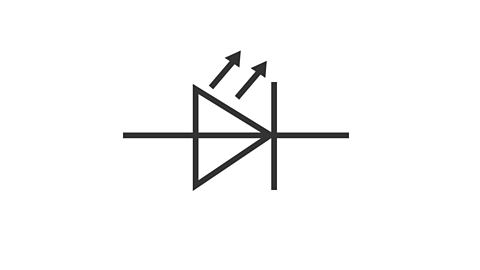
What is this circuit symbol?
LED
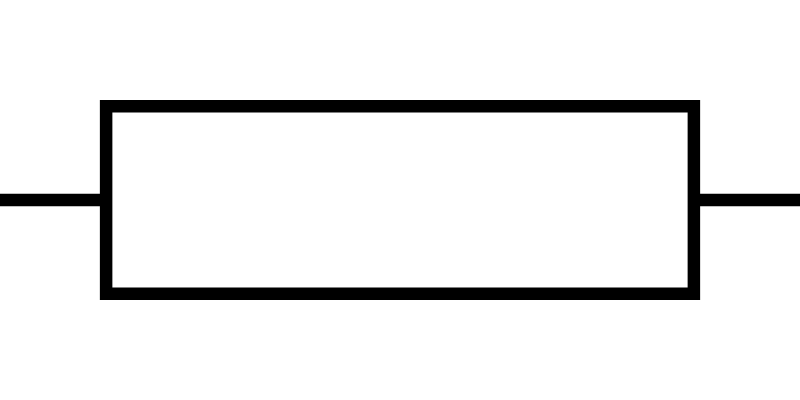
What is this circuit symbol?
Fixed Resistor
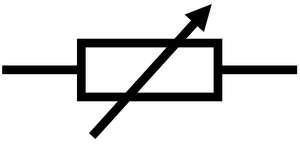
What is this circuit symbol?
Variable resistor
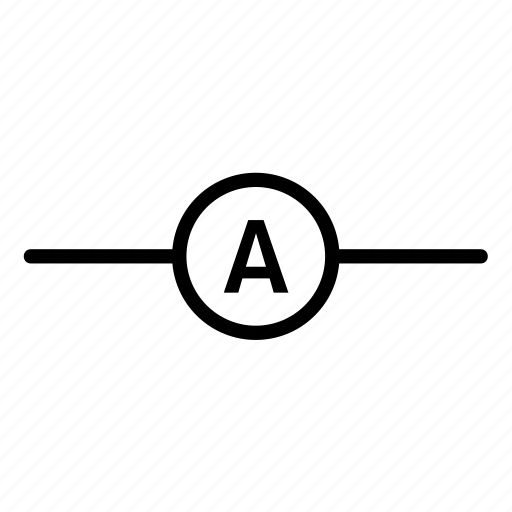
What is this circuit symbol?
Ammeter
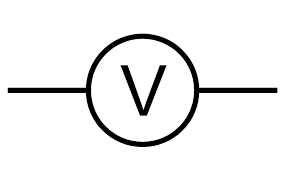
What is this circuit symbol?
Voltmeter
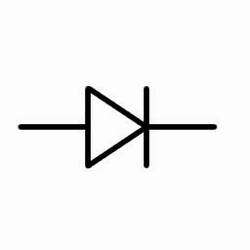
What is this circuit symbol?
Diode
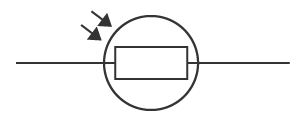
What is this circuit symbol?
LDR
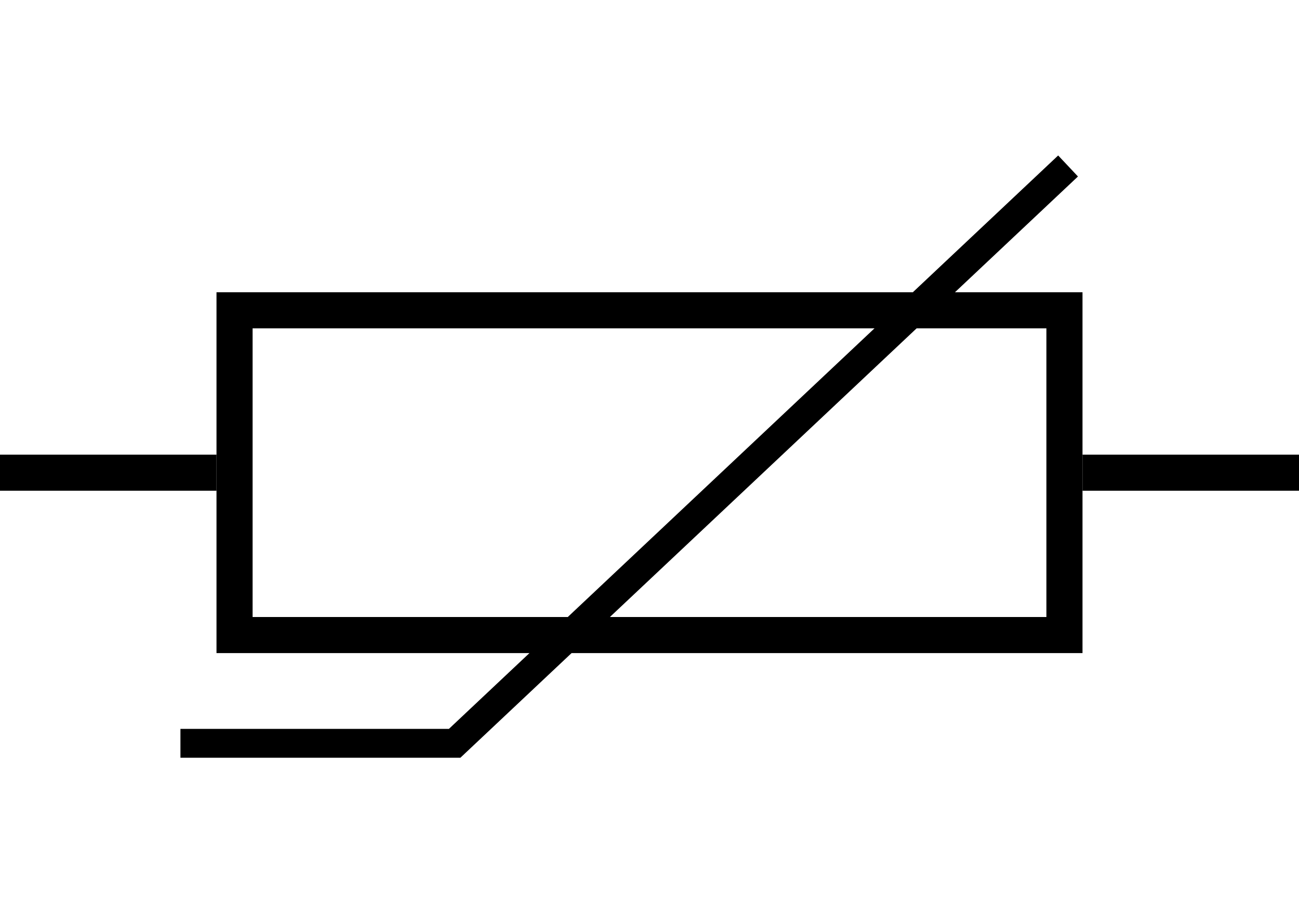
What is this circuit symbol?
Thermistor
What is an ohmic conductor?
At a constant temperature, the current flowing through an ohmic conductor is directly proportional to the p.d across it, and the resistance remains constant.
Examples of ohmic conductors?
Wire
Resistor
Examples of non-ohmic ocnductors
Filament bulb
Diode
What happens to the resistance when the temperature increases.
Resistance increases as the temperature increases
What happens in a diode when the direction of current is reversed?
Will have a very high resistance
What is an I-V characteristic?
Refers to a graph that shows how the current flowing through a component changes as the potential difference is increased.
What are linear components?
have an I-V characteristic that’s a straight line
What are non-linear components?
Have a curved I-V characteristic?
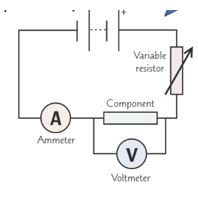
What is the circuit to find out the I-V characteristic of a component?
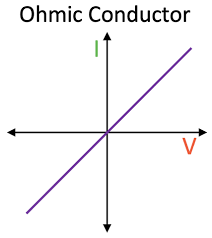
What is the I-V characteristics for an ohmic conductor and why?
The current through an ohmic conductor is directly proportional to the p.d, so there is a linear line
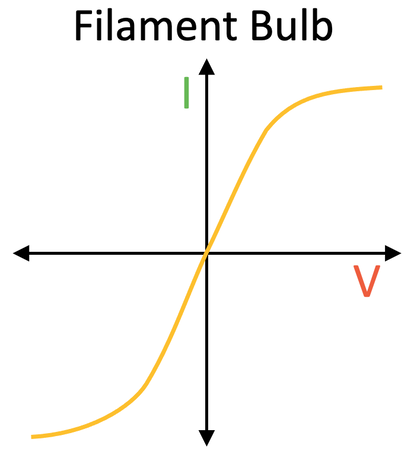
What is the I-V characteristic of a Filament lamp and why?
As the current increases the temp of the filament increases, so the resistance increases, this means that less current can flow per unit pd, hence the graph gets shallow and is curved.
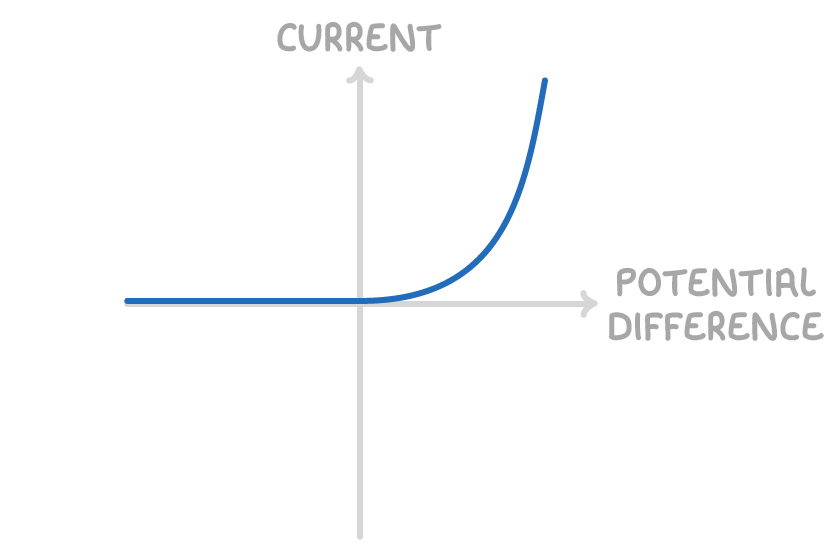
What are the I-V characteristics of a Diode and why?
Currency will only flow through a diode in one direction, the diode has very high resistance in the reverse direction as shown.
What is an Ammeter?What is its rule?
Measures the current flowing through a wire. Must be placed in series with whatever you’re investigating.
What is a voltmeter? What is the rule with voltmeter?
Measures the potential difference across a wire. They must be placed in parallel around whatever you’re measuring.
What is an LDR?
A resistor that is dependent on the intensity of light
In low levels of light what happens to the resistance of a LDR?
Increases
3 applications of a LDR?
Automatic night lights
Outdoor lighting
Burglar detectors
What is a thermistor?
A temperature dependent resistor
What happens to the resistance of a Thermistor in cool conditions?
Increases
What is a thermistor used for?
Temperature detectors
What type of circuit are sensing circuits?
Series circuits
What are sensing circuits?
Can be used to turn on or increase the power to components depending on what conditions they are in - typically use thermistors or LDRs
What happens when one component in a series circuit is broken?
All other components stop and the circuit is broken.
Rules of series circuits?
Cell p.d adds up
Total p.d is shared (V = V1 + V2)
Current is the same everywhere (I2 = I1 = I3)
Resistance adds up (R = R1 + R2)
What happens when one component doesn’t work in a parallel circuit?
Hardly affects the other components
Rules of parallel circuits?
p.d is the same across all components (V1 = V2 = V3 )
Current is shared between branches (I = I1 + I2 + …)
IF there are 2 resistors in parallel - their total resistance is smallest of the two resistors
2 types of electricity supplies?
DC and AC
What uses AC?
The UK mains supply
What is the volts and hertz that the UK/AC mains supply uses
230V and 50 Hertz
What is alternating current?
Current is constantly changing direction - produced by alternating p.d in which the positive and negative ends keep alternating
What uses direct current?
Cells and batteries
What is direct current?
Current that is always flowing in the same direction - created by a direct p.d
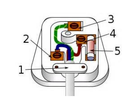
What is 1 in this image?
Cable grip - prevents wires inside the the cable from being pulled loose from their terminals
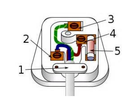
What is 2 in this image? What is its voltage?
Neutral wire - completes the circuit - 0V
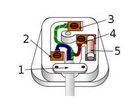
What is 3 in this image? What is its voltage?
Earth wire - stops the appliance casing from becoming live - 0V
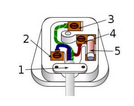
What is 4 in this image?
Fuse - breaks the circuit if too much current is flowing through it
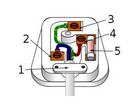
What is 5 in this image?
The live wire - provides alternate p.d from the mains supply - 230 V
What is a power rating on appliances?
Maximum safe power that they can operate at
What is the national grid?
Giant system of cables and transformers that covers the UK and connects power stations to consumers
The national grid uses….
A high p.d and low current
What is the problem with using a high current in the national grid?
It is not efficient as some energy when there is high current is transferred to the thermal energy store of the surroundings.
What is a step-up transformer?
For efficient transmission the p.d is increased using a step-up transformer
What is a step-down transformer?
P.d is reduced for domestic use using a step-down transformer