4.5- Energy Changes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the conservation of energy principle?
Energy is conserved in chemical reactions. The amount of energy in the universe at the end of a chemical reaction is the same as before the reaction takes place
What is an exothermic reaction? Give examples
An exothermic reaction is one that transfers energy to the surroundings so the temperature of the surroundings increases.
Examples include:
Combustion,
Oxidation reactions
Neutralisation (acid + alkali) reactions.
Negative sign of energy change.
Everyday uses of exothermic reactions include self-heating cans and hand warmers.
What is an endothermic reaction? Give examples
An endothermic reaction is one that takes in energy from the surroundings so the temperature of the surroundings decreases.
Examples include:
Thermal decomposition
Reaction of citric acid and sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Positive sign of energy change.
Some sports injury packs are based on endothermic reactions.
What is needed for chemicals to react
Chemical reactions can occur only when reacting particles collide with each other and with sufficient energy.
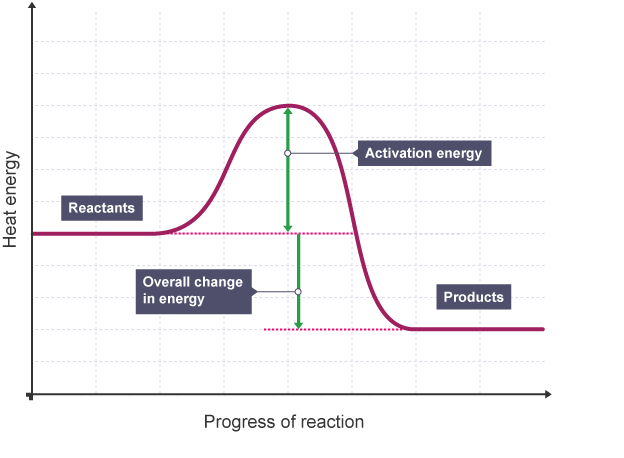
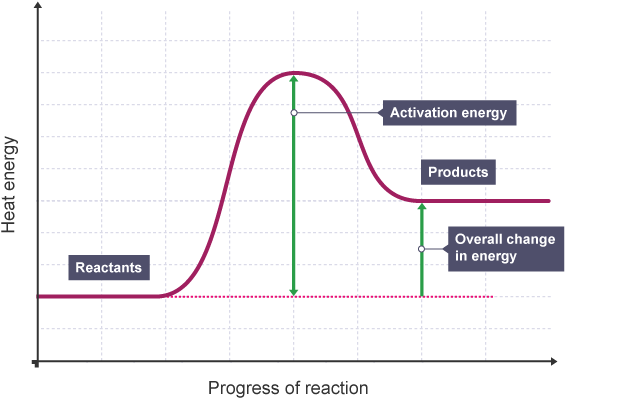
The minimum amount of energy that particles must have to react is called the activation energy.
What is activation energy?
Minimum amount of energy that particles need to react
What is a reaction profile?
Reaction profile is a graph which shows the relative energies of reactants and product, as well as activation energy of the reaction.
Draw and annotate the reaction profile diagram for an exothermic reaction
Draw and annotate the reaction profile diagram for an endothermic reaction
What occurs in a chemical reaction in terms of bond energies? Describe exothermic and endothermic reactions in terms of bond breaking/forming.
Energy is supplied to break bonds
Energy is released when bonds are made;
In an exothermic reaction, the energy released from forming new bonds is greater than the energy needed to break existing bonds.
In an endothermic reaction, the energy needed to break existing bonds is greater than the energy released from forming new bonds.
What is the equation to find enthalpy change in terms of bond energies?
Energy of reaction = sum of bonds broken – sum of bonds made
Describe a method to investigate temperature changes in the reaction between sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid
Measure 30cm3 of 0.1 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid using a measuring cylinder, and pour into a polystyrene cup. Place the polystyrene cup into a beaker for stability
Use a thermometer to measure the temperature of the solution
Measure 5cm3 of 0.1 mol/dm3 sodium hydroxide using a measuring cylinder, and pour into the cup
Quickly place a lid with a hole in on the cup, and place a thermometer on in the hole
Record the maximum temperature reached with the thermometer
Repeat 3 more times and calculate a mean
Repeat with volumes 10cm3, 15cm3, 20cm3, 25cm3, 30cm3, 35cm3, and 40cm3
Plot the results on a graph, and draw 2 lines of best fit- one for the increasing values, and one for the decreasing- the point where they cross is the maximum temperature reached
The reason the temperature decreases is because there is no longer any hydrochloric acid to react, it has become the limiting reactant, so no more particles can react than before, but because the volume is still increasing, the energy is less concentrated
What is a cell?
A cell is composed of two electrodes dipped in an electrolyte solution. It produces electricity from a chemical reaction.
What is a battery?
A battery consists of two or more cells connected in series.
What determines the voltage obtained from a cell?
Identities of metals (difference in reactivity) used as electrodes and the identity and concentration of an electrolyte.
What would be the half equations for a zinc copper cell
Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
What happens in a non-rechargeable cell
In non-rechargeable cells and batteries the chemical reactions stop when one of the reactants has been used up.
Alkaline batteries are non-rechargeable.
What happens in a rechargeable cell
Rechargeable cells and batteries can be recharged because the chemical reactions are reversed when an external electrical current is supplied.
State the advantages and disadvantages of using cells and batteries.
(+) more or less cheap, some are rechargeable, a convenient source of electrical energy
(-) harmful chemicals
What is a fuel cell?
Fuel cells are supplied by an external source of fuel and oxygen.
The fuel is oxidised electrochemically within the fuel cell to produce a potential difference
What is the overall reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell? What are the half equations?
Cathode: H2 + 2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
Anode: O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
Overall: → 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
The overall reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell involves the oxidation of hydrogen to produce water.
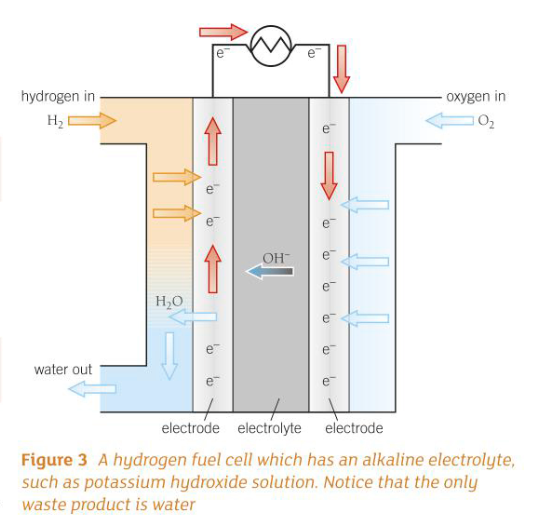
What are the advantages of hydrogen fuel cells over lithium ion batteries?
time for refuelling a fuel cell is faster than recharging
a fuel cell does not need to be recharged
a fuel cell has a greater range
hydrogen can be renewable if made by electrolysis using renewable energy
lithium-ion batteries can catch fire
produces only water (no pollutants produced)
lithium-ion batteries may release toxic chemicals on disposal
lithium-ion batteries (eventually cannot be recharged so) have a finite life
What are the advantages of lithium ion batteries over hydrogen fuel cells
lithium-ion uses energy more efficiently
cost of lithium-ion car much less
cost of recharging much less than refuelling with hydrogen
hydrogen is often made from fossil fuels so is not renewable
charging points are more widely available than hydrogen filling stations
hydrogen takes up a lot of space and is difficult to store
hydrogen can be highly flammable and explosive
no emissions produced
catalyst in the hydrogen fuel-cell eventually becomes poisoned so have a finite life