resp. failure - obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
what is OSA?
repeated episodes of airway obstruction during sleep
due to muscle relaxation
how is happens?
Muscles relax during sleep
including those in the pharynx
This relaxation causes airway collapse in some ppl
Muscle tone decreases lots
collapse obstructs airflow
pressure decreases
trachea closes
⇓ O2
⇑ CO2
compensate
body wakes up from deep sleep
takes a deep breath
reopen airways
closes again
repeats multiple times per night
Diagnosis
A sleep study monitors
Cessation of breathing (apnea)
Respiratory effort
Oxygen levels
The Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) is used to classify severity:
measures how many times breathing partially (hypopnea) or completely (apnea) stops per hour during sleep.
<5 = Normal
5–15 = Mild
15–30 = Moderate
>30 = Severe
How OSA Affects Sleep, symptoms
Normally, sleep happens in cycles:
Non-REM Sleep (N1, N2, N3)
N3 (Deep Sleep) is restorative for the body.
REM Sleep (dreaming, memory processing)
in OSA:
Less REM sleep → Poor memory, focus, and mood.
Symptoms:
Loud snoring (caused by airway blockage and turbulent airflow).
Poor sleep quality → Waking up often, feeling unrested.
Insomnia (difficulty staying asleep).
Frequent urination at night (nocturia)
→ Due to changes in chest pressure
stimulating the Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
which increases urine production.
Swings of intrathoracic pressure
The heart releases Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
tells the kidneys to increase urine production and reduce blood volume.
frequent nighttime urination
contributes to disrupted sleep and daytime fatigue
risk factors for OSA
obesity
extra weight narrows the airways
age
Men over 40
Muscle tone decreases with age
easier for airway to collapse
gender
Men are more at risk
menopause
⇓ Estrogen levels = ⇓ in muscle tone
Alcohol and Sedative Use
Alcohol and sedatives
relax the muscles of the throat
easier for the airway to collapse during sleep.
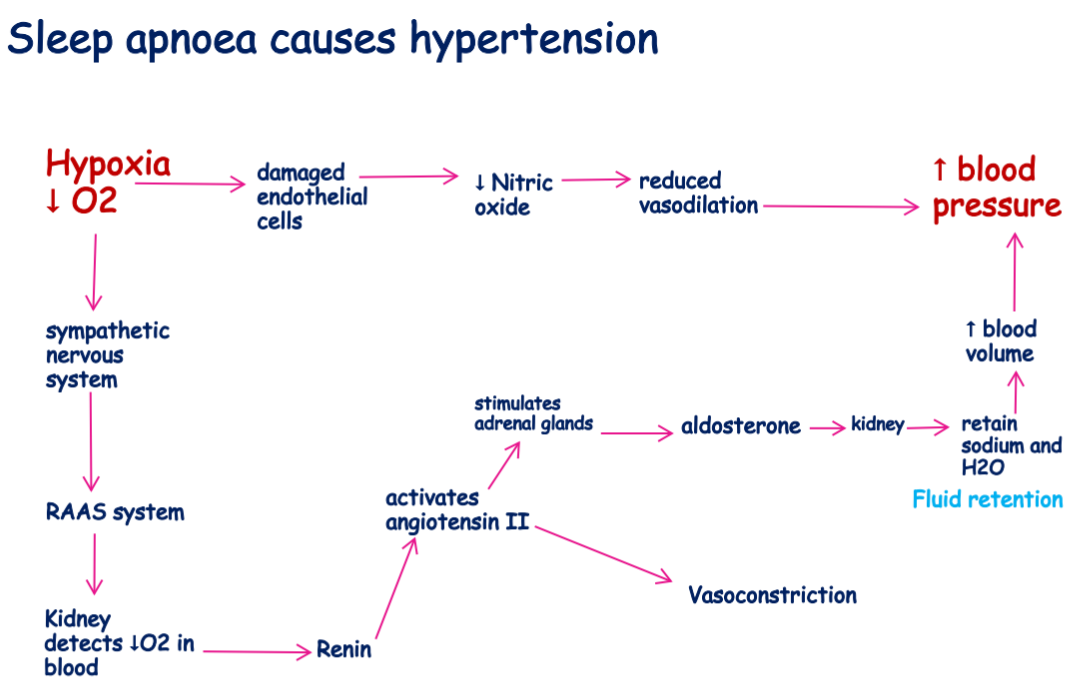
how does OSA cause hypertension?