Epithelial Tissue pt II
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
types of cell junctions
tight/occluding junctions
zonular adherens
desmosome
hemidesmosome
communication junctions
function of tight junctions
tightly adhere cells together along apical/luminal border
forms selective barrier
controls paracellular diffusion
enables epithelium to protect proteins underlying tissues
prevents diffusion of membrane proteins/lipids between apical and basolateral membrane necessary for polarity
what is the effect of fluorescein
will wash away in healthy ocular surface
will stain in damaged ocular surface since tight junctions are leaky
what is the function of adherens and adhering belt
connect epithelial cells to each other to create another barrier below tight junctions
connects cell-cell junction to actin cytoskeleton
multiple zonula adherens for continuous belt around cell
epithelial cells with high content of adheren junctions form strong cohesive epithelium
strong mechanical adhesion between neighboring cells
function of desmosomes
desmosomes connect neighboring epithelial cells to each other forming plaques between cells
anchor epithelial cells to intermediate filamentous cytoskeleton
function of hemidesmosomes
anchor epithelia to basal lamina of basement membrane
linked to intermediate filaments (keratin) within the cytoplasm
function of communicating junctions
gap junctions are made of connexins form a channel between adjacent cells
cell-cell communication, permit the passage of small molecules between cells
location of tight junctions
more superior region between cells
anchor/cytoskeleton of tight junctions
actin filaments
function of tight junctions
prevent/limit leakage between epithelial cells
maintains polarity of epithelial cells by limiting apicobasal diffusion
location of zonular adherens
inferior to tight junctions
anchor/cytoskeleton of zonular adherens
actin cytoskeleton
function of zonular adherens
form cell-cell and cell-basement membrane adhesion complexes
can form bands encircling the cell
allows for a cohesive epithelium
location of desmosomes
more inferior region between cells
anchor/cytoskeleton for desmosomes
keratin intermediate filaments
function of desmosomes
strong cell-to-basement membrane adhesion
resistance to intense mechanical stress
location of hemidesmosomes
basal side of cell
anchor/cytoskeleton
keratin intermediate filaments
function of hemidesmosomes
strong cell-to-basement membrane adhesion
resistance to intense mechanical stress
location of gap junctions
between epithelial cells
function of gap junctions
directly connects the cytoplasm of cells allowing the exchange of small molecules, ion, and electrical impulses
what does the loss of cell-cell adhesion lead to
sloughing off of epithelial cells
what is epithelial basement membrane dystrophy
defective corneal epithelial basement membrane
redundant basement membrane
leads to poor epithelial adhesion and epithelial inclusion cysts
what is recurrent corneal erosion
condition caused by abnormal epithelial adhesion to underlying basal lamina leading to repeated breaks in the corneal epithelium
symptoms of recurrent corneal erosion
ocular pain, blurred vision, tearing, and photophobia
etiology of recurrent corneal erosion
trauma around 60% of the time
genetics around 20-30% of the time
epithelial basement membrane dystrophies, fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy, previous cornel infections, dry eye disease, diabetes mellitus
treatment objectives for recurrent corneal erosion
relief of symptoms
epithelial integrity
prevent infection
reduce recurrence by lubricating epithelium
treatment options for recurrent corneal erosions
hyperosmotics
lubricants
bandage contact lens
anterior stromal micropuncture
photoablation
debridement
what are microvilli
small finger like projections on the luminal side of epithelia
not typically visible on light microscope
shorter and narrower than cilia
core contains actin filaments
what is the function of microvilli
increase surface area by 30x
increase absorption like in the brush border of the small intestine
function of microvilli in the corneal epithelium
increases surface area for anchoring of the tear film via rich mucin glycocalyx
corneal hydration
barrier protection from pathogens and friction
what are cilia
long motile structures
visible by light microscope
beat in rhythmic pattern allowing them to propel surface mucus and fluids for unidirectional movement
where are cilia found
respiratory tract
female reproductive tract
how do glands form
from epithelial cells after invagination into the underlying tissue
characteristics of endocrine glands
no duct system
secretions are released into the bloodstream
may have multiple types of secretion
act on distant targets
what type of gland are the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pituitary, gonads, and pancreas
endocrine
how does exocrine secretion work
release their secretions into a duct and then onto an epithelial surface
what are the three types of exocrine secretion
merocrine
apocrine
holocrine
characteristics of merocrine secretion
most common
involves exocytosis
only secretory component is released
mostly protein products
characteristics of apocrine secretion
membrane bound vesicles released (apical)
usually lipid products
breast and some sweat glands

what type of secretion is this
merocrine
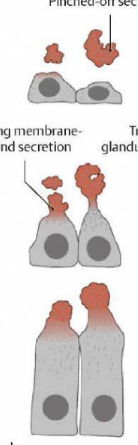
what type of secretion is this
apocrine
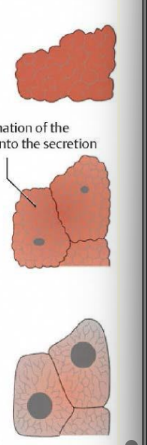
what type of secretion is this
holocrine
characteristics of holocrine secretion
disintegration of cells to release lipid products
sebaceous glands mainly
classification of merocrine/eccrine sweat glands
secretory or acinar cells
ductal cells
myoepithelial cells
what type of glands are sweat, salivary, and lacrimal glands
merocrine/eccrine
classification of apocrine glands
secretory or acinar cells
ductal cells
myoepithelial cells
what are merocrine glands associated with
thermoregulation
what are apocrine glands associated with
thermoregulation (sweat surface tension)
scent production
territory marking
sexual attractant
what are axillary/groin regions and mammary glands an example of
apocrine glands
what are meibomian glands, aerola, labia, and vulva examples of
holocrine sebaceous glands
characteristics of holocrine sebaceous glands
usually associated with hair follicle (at about 1/3 depth)
sebum - waterproofing and lubrication
may be independent of follicle
characteristics of goblet cells
modified columnar epithelial cells
unicellular
synthesize and secrete mucous
scattered throughout many epithelial tissue linings
protective function
where can goblet cells be found
epithelial lining of
respiratory tract
ocular conjunctiva
digestive tract