eye and visual stimulus
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
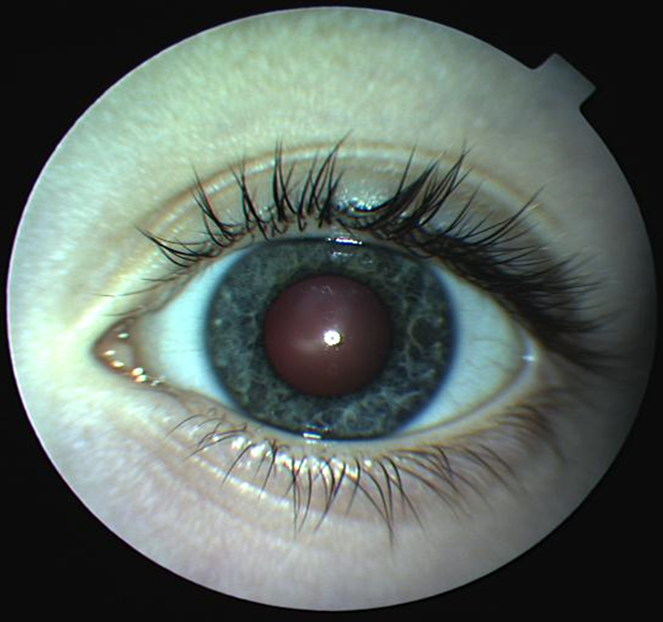
name the anatomical features of the ANTERIOR eye (9)
•Iris
•Pupil
•Cornea
•Conjunctiva/Sclera
•Limbus
•Cilia (eyelashes)
•Palpebrum (eye lid)
•Punctum lacrimalis (puncta)
•Lacrimal caruncle
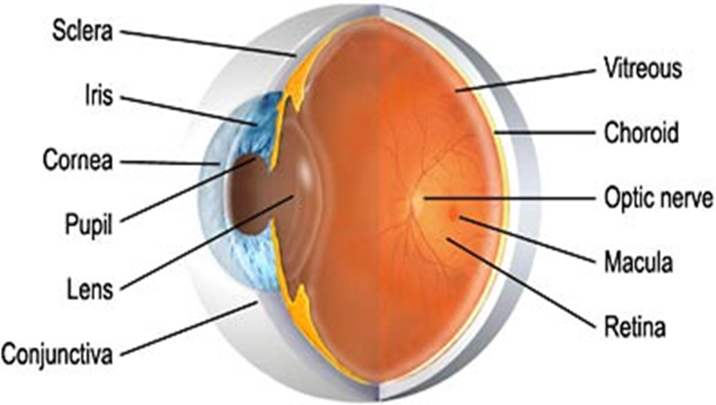
•Describe the main anatomical features of the human eye and some of their functions.
•Define radiometry and photometry.
•Describe the characteristics of both radiometric and photometric quantities.
•Describe a variety of sources of radiation.
describe the iris
•the loose open muscular membrane that is perforated in the center forming the pupil
describe the pupil
the central opening of the iris that allows light to enter the eye
Pupil size varies with the amount of light - constricts and dilates
describe the cornea
transparent, domelike optical structure covering the pupil and iris
Together with the lens, comprises the refracting elements of the eye
describe the conjunctiva/sclera
sclera is the tough fibrous outer coat that provides structural strength to the eye. It is covered by the conjunctiva - white part of eyeball
The conjunctiva extends over the eyelids (palpebral) - thin clear layer
describe the tear film
•not seen on image, but covers the cornea and conjunctiva
describe the limbus
this is the region where the cornea and conjunctiva/sclera meet - a ring around the cornea
describe the Punctum lacrimalis
tiny hole at inner corner of eyelids (upper and lower)
the opening to the tear drainage system (the canaliculus)
describe the Lacrimal caruncle
small pink/whitish raised area/lump in the medial/very inner corner of the eye (near the nose)
describe the aqueous humor
•occupies the anterior chamber of the eye comprising a clear fluid (mostly water)
describe the lens
crystalline, transparent structure suspended by thin fibrils attached to the ciliary body
Its shape changes by the action of the ciliary muscle (accommodation)
describe the vitreous
sits behind the lens, comprises a clear jelly-like structure
describe the choroid
•vascular layer that sits between the retina and sclera and provides nutrients to the eye
describe the retina
light sensitive organ containing neural elements including the photoreceptors (rods and cones)
describe the fovea
Vision is best developed at the fovea - shown as a small depression in the retina that contains only cones
It is about 1.5-2.0 degrees in size
Note the central fovea is avascular.
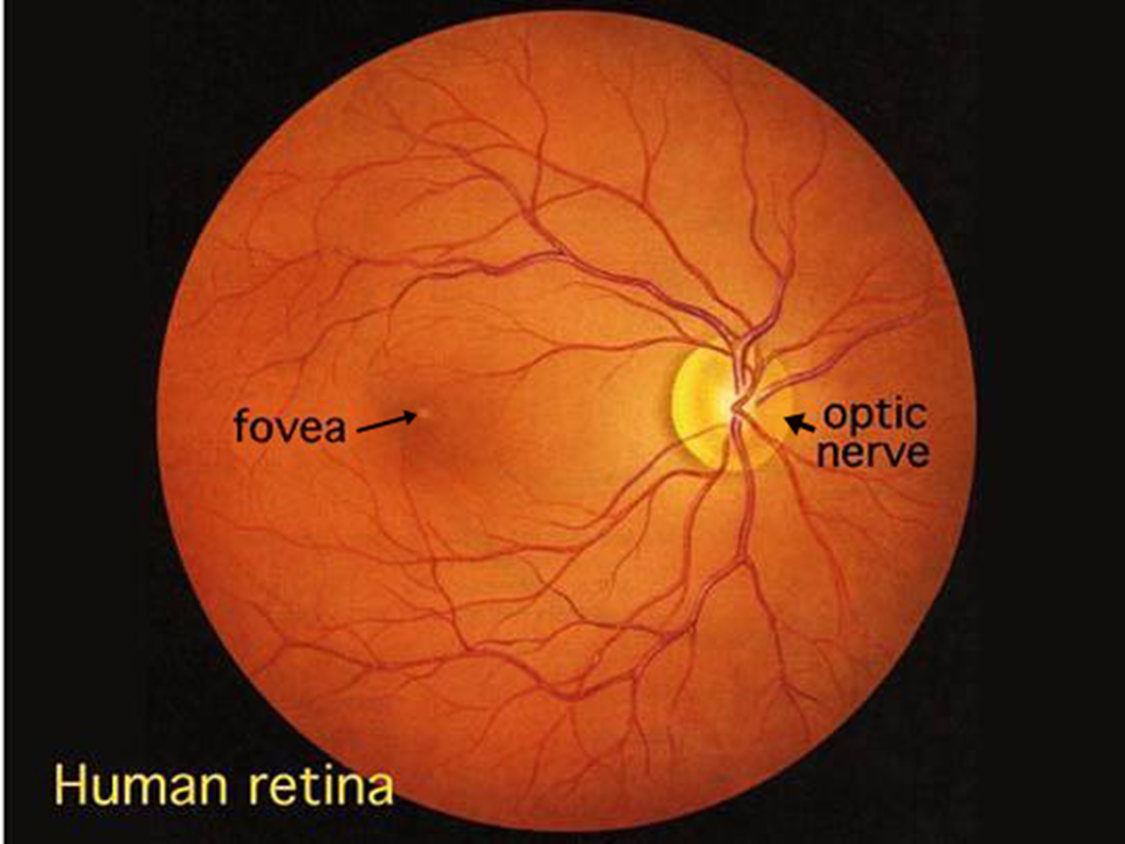
describe the macula
•surrounds the fovea and appears yellow in colour due to the presence of pigment
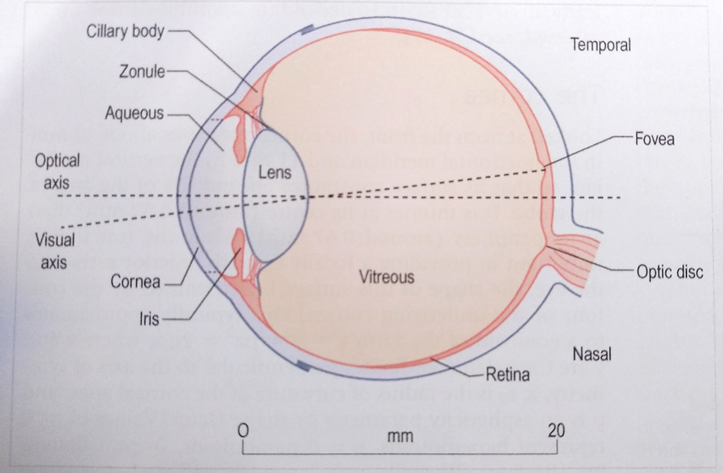
what is the visual and optical axis
visual axis or line of fixation = that line drawn from the fovea to a point that the eye is gazing at
optical axis = the line through the optical centre of the eye – note that it differs from the visual axis
explain what frequency of a wave/wavelength is
refers to the number of cycles passing a particular point per second (measured in cycles per second or Hertz)
Lower frequency – longer wavelength - lower so slower
Higher frequency – shorter wavelength
when frequency is high energy is also high and vice versa
therefore short wavelength light has higher energy
describe the visible spectrum/visible light
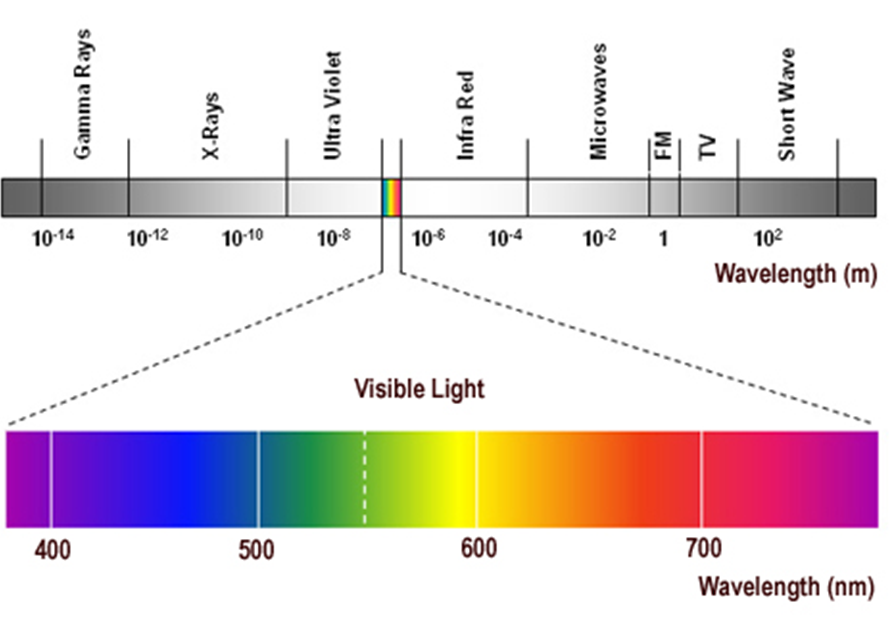
Generally speaking, we can see light of wavelengths between 370 nm and 730 nm
380 nm-Violet - shorter wavelengths…
460 nm-Blue
480 nm-Cyan
520 nm-Green
580 nm-Yellow
600 nm-Orange
620 nm-Red - longer wavelengths…
define radiometry
Radiometry is concerned with measurements and specification of the quantity/energy of the electromagnetic radiation using physical energy units and radiometric devices
across the full range of electromagnetic radiation - ACROSS ENTIRE SPECTRUM
define photometry
Photometry is concerned with measurements of visible radiation / visible light - this is what we are interested in as this is what is sensitive to the eye
i.e. the ability to produce a sensation for the human eye taking into account human sensitivity to different wavelengths at different light levels.
Typically wavelengths of light between 380 and 750nm
define luminance power or flux AND luminance intensity, give the photometric unit and the radiometric equivalent and unit
Definition | Photometric Unit | Radiometric equivalent and units | |
Luminous power or flux (F). | The total amount of light emitted by a source (in all directions). | Unit of lumen (lm). | Radiant power or flux (Fe) (joules/sec = watts). |
Luminous intensity (l) | Measure of light (luminous flux, F) delivered in a solid angle from a point source particular direction. | Unit of lumen/steradian = candela (cd). 1lumen/steradian = 1 candela. | Radiant intensity (le) (watts/steradian) |
define luminance AND illuminance intensity, give the photometric unit and the radiometric equivalent and unit
Definition | Photometric Units | Radiometric equivalent and units | |
Luminance (L) the light coming OFF the chart and into the eye | The amount of light coming off an extended surface in a particular direction. | Unit of Candelas/m2 (cd/m2). Commonly used unit in optometry. Typical visual acuity test chart has luminance of between 100 and 300 cd/m2 | Radiance (Le). The amount of radiation coming off an extended surface in a particular direction. watts/steradian/m2 |
Illuminance (E) This is the light that falls ONTO the chart | The amount of luminous power falling onto a unit area of a certain surface. | Unit of lumens/m2 also called ‘lux’. Standards are available describing proper levels of light required for different settings. Retinal illuminance units (trolands). | Irradiance (Ee) The amount of radiant flux per unit area falling onto a certain surface. Unit of watts/m2 |
what does retinal illuminance depend on/the amount of light that falls onto the retina (3)
•Luminance of the stimulus.
•The optical transmittance of the eye (i.e. how much of the light gets to the retina).
-The area of the pupil
what is the retinal illuminance units - referring how to much light falls onto the retina
•This unit is the Troland.
•One (1) Troland is the amount of retinal illuminance (Eret) arising from a light source emitting a luminance (L) of 1 cd/m2 through a pupil area (a) of 1mm2.
•Eret = L x a
visual stimulus - units summary
Radiometric quantities:
•Radiant power Fe = Watts (joules/sec)
•Radiant intensity Ie = watts/steradian
•Irradiance Ee = watts/m2
•Radiance Le = watts/steradian/m2
Photometric quantities:
•Luminous power F = lumen
•Luminous intensity I =candela
•Illuminance E = Lumens/m2 or lux = Trolands (Retinal E)
Luminance L = cd/m2
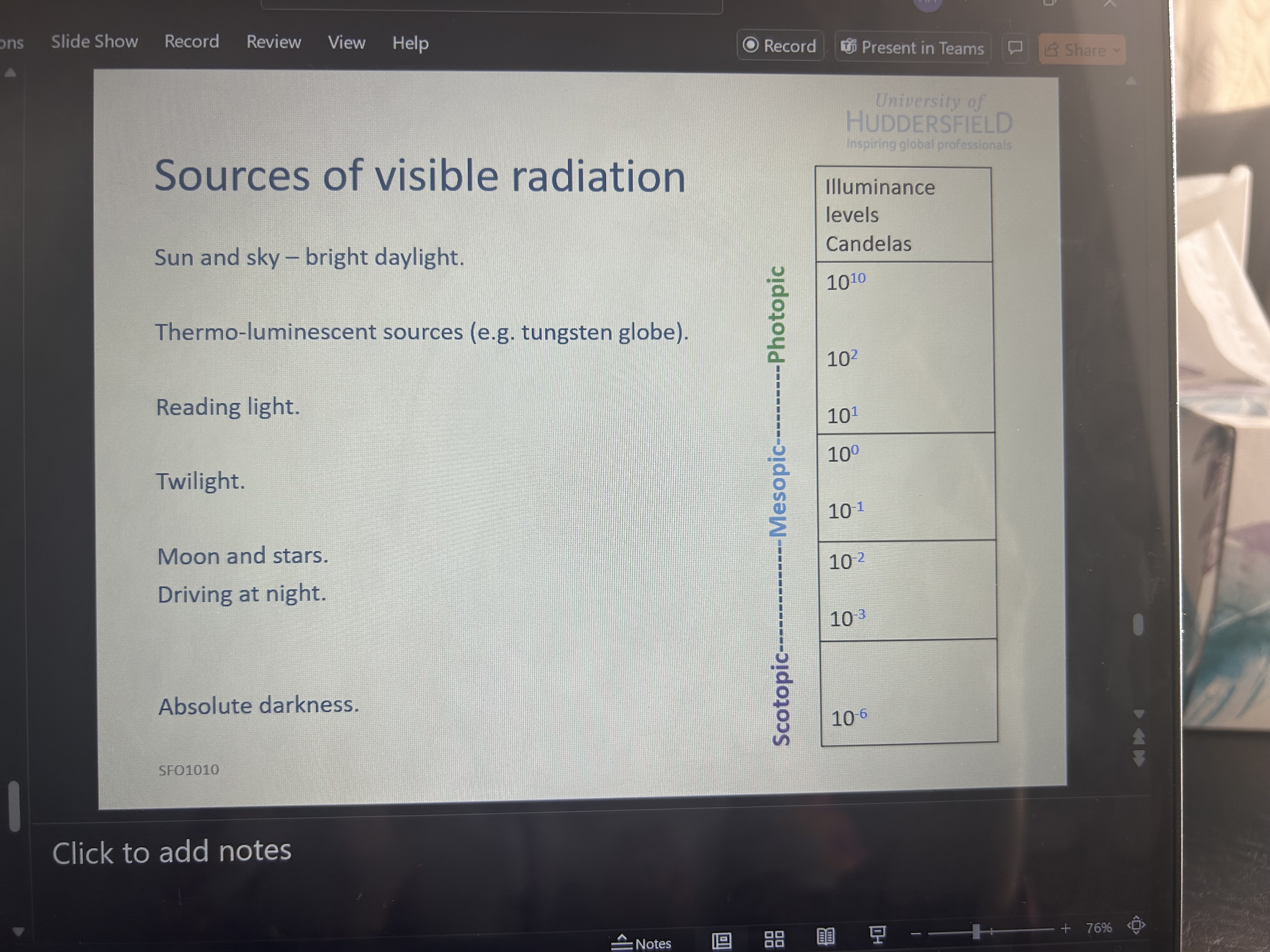
name sources of visible radiation - and their illuminance levels - candelas
define luminance
is the measured light from a surface (adjusted for the differential sensitivity of the eye)
define brightness
is the perception of the amount of light and depends not only on the luminance but also on the surround
define lightness
is the perception of the surface colour in reference to black, white and shades of grey
REMEMBER
equal luminance does not necessarily mean equal brightness
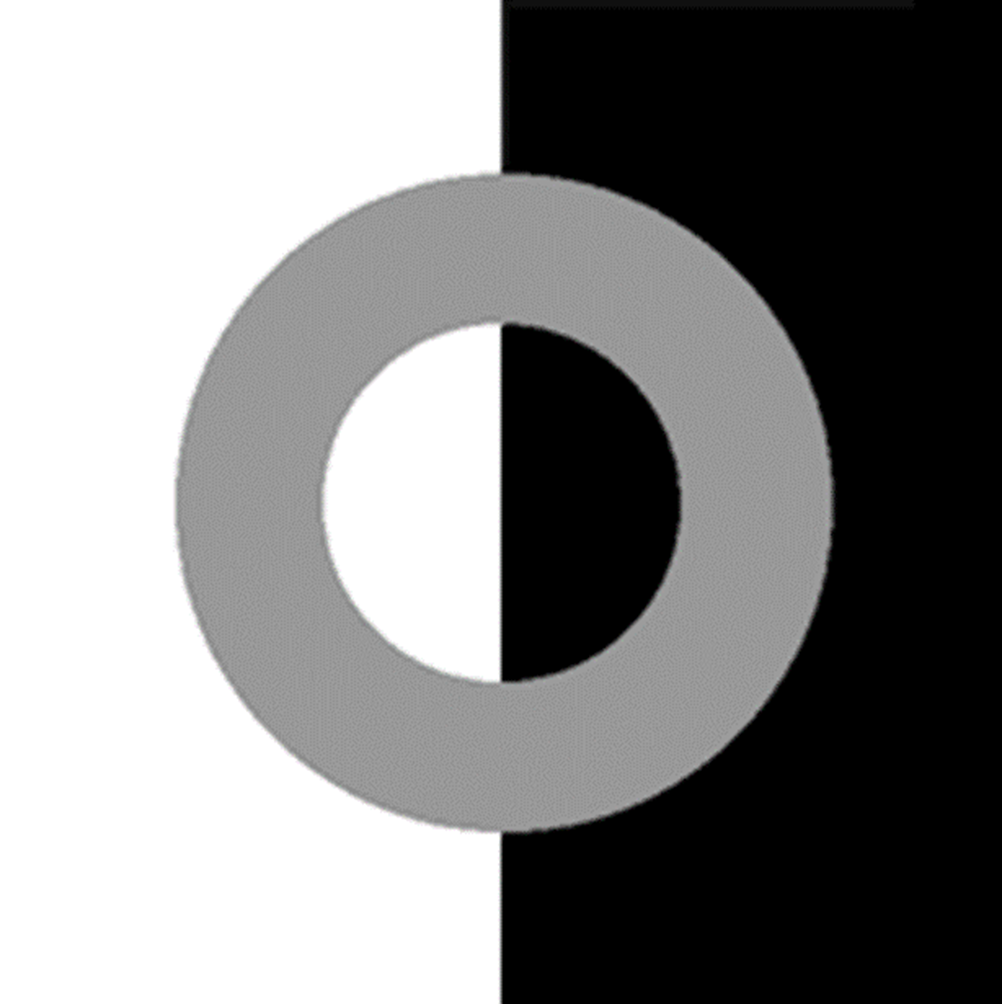

this is a visual illusion