Unit 3 personal and business finance
1/395
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
396 Terms
internal finances
internal sources of finance are those available from within a business. these include:
Sale of assets
selling an item worth owned by a business in order to achieve an immediate cash injection.
Retained profit
this is the profit kept in the company rather than being paid out by shareholders as a dividend sales revenue - total cots
Net current assets
current assets - current liabilities shows the money available in the business to fund day-to-day expenditure
Mortgages
is a legal agreement that is made by you and the bank/building society to lend money at interest in order to buy a house
Owner's capital
is where the owner puts his/hers own money to invest into the business
Loans
is money that is borrowed, especially a sum of money that is expected to be paid.
Hire purchase
way a buying goods gradually. You make regular payment until you have paid the full price and the goods belong to you
Crowdfunding
practice funding a project or venture by raising money from a large number of people who contributes a relatively small amount
Debt factoring
This involves the selling of a business’s debt to a third party in order to receive cash quickly.
Peer to peer lending-
matches up people who are looking for to invest their money who want to borrowing it, paying higher interest to savers to savers and lower rates for borrowers. Find out how it works
Invoice discounting
a way for businesses to borrow money based on amount due for customers
Leasing
its a contract on paper that states that you own the property
Grants
is an amount of money given by the government to a person or organization for a special purpose
Straight line depreciation
Formula= asset purchase price-estimated salvage value/ Estimated useful life of an asset
Sstraight line deprecation is most commonly used due to…
its simplicity and consists of allocating depreciation evenly over the useful life of the asset
External sources of finances:
external sources of finance are those available from outside the business. this includes:
Advantage of sales of assets
A good way of raising funds from assets that are not needed any longer.
Disadvantage of Sales of assets
Not all businesses have surplus assets that they can sell. May be a slow method of raising funds as some assets may take time to sell.
Advantage of retained profits
Does not have to be repaid and has no interest payable.
disadvantage of retained profits
Not available to new businesses and many
advantage of net current assets
A quick way of raising money. Selling off inventory reduces the costs related to holding it.
disadvantage of net current assets
May have to accept a lower price for its inventory.
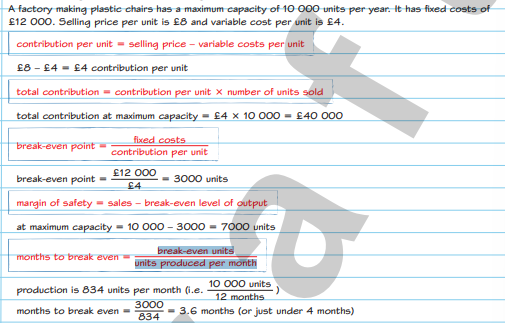
Gross profit =
GR
contribution per unit =
selling price – variable costs per unit
total contribution =
contribution per unit × number of units sold
break-even point =
fixed costs/contribution per unit
margin of safety =
sales – break-even level of output
months to break even =
break-even units/units produced per month
example of one
Break- Even chart
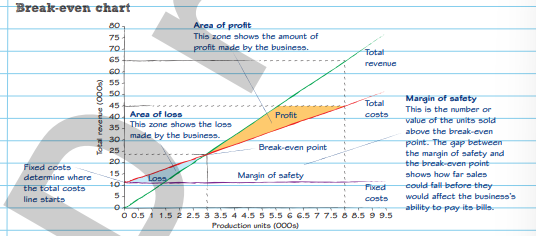
Area of profit
This zone shows the amount of profit made by the business
Margin of safety
This is the number or value of the units sold above the break-even point. The gap between the margin of safety and the break-even point shows how far sales could fall before they would affect the business’s ability to pay its bills.
Area of loss
This zone shows the loss made by the business
Fixed costs
Determine where the total costs line starts
Using Break-Even
Break-even is a valuable management tool used by businesses to plan, monitor, control and set targets. As part of break-even, contribution per unit has both limitations and benefits.
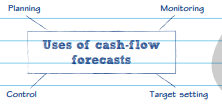
Planning
break-even helps the business to work out how many items it needs to sell over a certain period to cover its costs and to use this information to set a price that will enable it to make a profit
Monitoring
break-even alerts the business to potential problems, e.g. increased fixed or variable costs or a fall in sales, allowing it to take steps to fix them in good time
Control
break-even can be used to identify where costs are increasing, allowing the business to take action to control this.
Target -Setting
Break-even helps a business to set targets for sales, unit costs, contribution, and profit.
Contribution benefits
A business is able to see whether the products it produces actually cover its own variable costs.
This is used to set the price of the product in relation to direct production costs.
Contribution per unit may be very low, so the business will need to sell a large number to cover the fixed costs.
Contribution limitations
Contribution per unit on certain products may be extremely high.
In each case the contribution per unit is distorted and may not be valuable.
Variable costs
The variable costs relate to the additional costs incurred per unit
Total Costs
Total costs are the total of these two figures.
Total Revenue
is calculated by multiplying the number of units sold by the price the business received for them.
selling price
if the selling price is increased total revenue will be greater and rise more quickly. If it falls then total revenue will drop
Fixed costs
total costs will increase if fixed costs increase
Variable costs
these will affect the total costs line, shifting it up if unit costs increase and down if they fall.
Break-even may have to be recalculated when there is a change in…
Selling price, fixed costs, variable costs.
Stages necessary to work out break-even
The variable costs, to Total costs, to Total Revenue.
Cash inflows/receipts
-The money coming into the business
-Money flows into the business when income is received.
Cash outflows/payments
-The money going out of the business
-Money flows out of a business when payments are made.
Cash sales
when customers paid for it at the time of the purchase
Credit sales
paid for the products however it takes time for it to be paid for
Value added tax
Value Added Tax is charged on most goods and services. A business must be registered for VAT if its sales go over the VAT threshold (£82 000 in 2015). The business adds VAT to the cost of its goods and services.
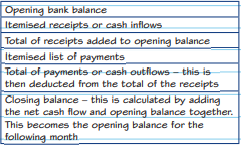
Cash flow forecast
a prediction of the expected cash balance at the end of each month in the future
Opening balance
the amount of cash the business has the start of the month
Total cash inflow
the total cash the business expect to receive during the month
Total cash outflow
the amount of cash the business expects to spend during the month
Inflow-outflow
the difference between the cash coming in and out of the business
Closing balance
the opening balance + the difference between the cash coming in and the cash coming out.
Purchase of assets
These are small and large expenditures on items, from computer printers and telephones to vehicles and expensive machinery and buildings
Rent, rates, salaries, wages and utilities
These are all regular outflows. The business must have the cash to cover these.
Cash and credit purchases
Anything a business buys is an outflow whether it is for use by the business or resale, e.g. raw materials, stationery.
loan outflow
Money borrowed by the business from an external source
capital introduced
Funds invested in the business by the owner or shareholders
sales of assets
Money received from selling an asset, e.g. machinery
bank interest received
the business may store money in a savings account on which the bank will pay interest
four profitability ratios
gross profit margin mark up net profit margin return on capital employed
ratio: gross profit margin
gross profit/revenue x 100
ratio: markup
gross profit/cost of sales x 100
ratio net profit margin
net profit/ revenue x 100
interfirm
between different firms, for example, comparing the performance of two different house builders
intrafirm
within the firm, for example, comparing this year's results with last year's, or the performance of the Leicester branch of a retail store.
Stakeholder
anyone with an interest in the activities of a business, whether directly or indirectly involved.
return on capital employed ROCE
net profit before interest and tax/ capital employed x 100
measuring liquidity
liquidity ratio measures how solvent a business is
Types of liquidity ratio
current ratio acid test ratio/ liquidity ratio (liquid cap)
current ratio
current assets/ current liabilities
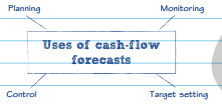
Cash flow forecasts
Cash flow forecasts are used by businesses to identify potential problems with cash flow. This will enable them to plan, monitor and control spending more effectively.
format of forecast
entering data

Use of cash flow forecast
The flow of cash into and out of a business has to be carefully managed. Having too little cash means that suppliers, and even employees, may not be paid on time.
profit and cash
Businesses selling lots of products and services may have major cash flow problems. If the business is selling products and services and recording them as being sold they may be short of cash if they have sold them on credit as they will not have yet received the money. They will need to replace the inventory but as they have not been paid for items they have already sold, they may not have funds to do this.
Benefits and limitations
Cash flow forecasts should help the business predict when they might have cash flow problems. If the business has predicted and planned for its financial needs, then banks may extend overdrafts or offer loans. Cash flows fail to consider that a business can delay payments to increase its net cash inflows and that it can buy using a leasing arrangement to avoid using cash.
ways to improve cash flow
what does break-even analysis identify?
it identifies the point at which a business’s costs are matched by the money it receives from sales.
Types of costs are?
Fixed, variable and semi-variable
Fixed costs
These are incurred by the business regardless of how well it is doing, e.g. business rates.
Variable costs
These increase when the business increases its activity or output, e.g. raw materials. total variable costs = variable cost per unit × quantity
Semi-variable costs
These are a combination of fixed costs and costs which become variable once a certain level of activity or output is reached, e.g. fixed phone line rental plus a variable charge based on the number of calls made.
Total costs (TC) =
fixed costs + variable costs + semi - variable costs
Types of sales are?
Selling price per unit, Sales in units, Sales in value.
Selling price per unit
Amount paid by each customer for each item bought
Sales in units
Quantity of sales, i.e. number of items sold