OIA2007 CELL TYPES & INCLUSION
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Meristematic Cells
Small, isodiametric, thin-walled cells with large nuclei.
Actively divide (e.g., root & shoot tips, cambium).
Permanent Tissues
Derived from meristems; lose division ability.
Two types: Simple (e.g., parenchyma) and Complex (xylem, phloem).
Parenchyma
Living, thin-walled cells with air spaces; perform photosynthesis & storage.
Collenchyma
Living, thickened at corners (uneven cellulose); support in growing shoots & leaves.
Sclerenchyma
Dead cells with lignified walls; two types: fibres & sclereids.
Fibres
Long, slender cells.
Examples: Flax, jute, hemp, Cinchona bark (diagnostic features: large, funnel-shaped lumen).
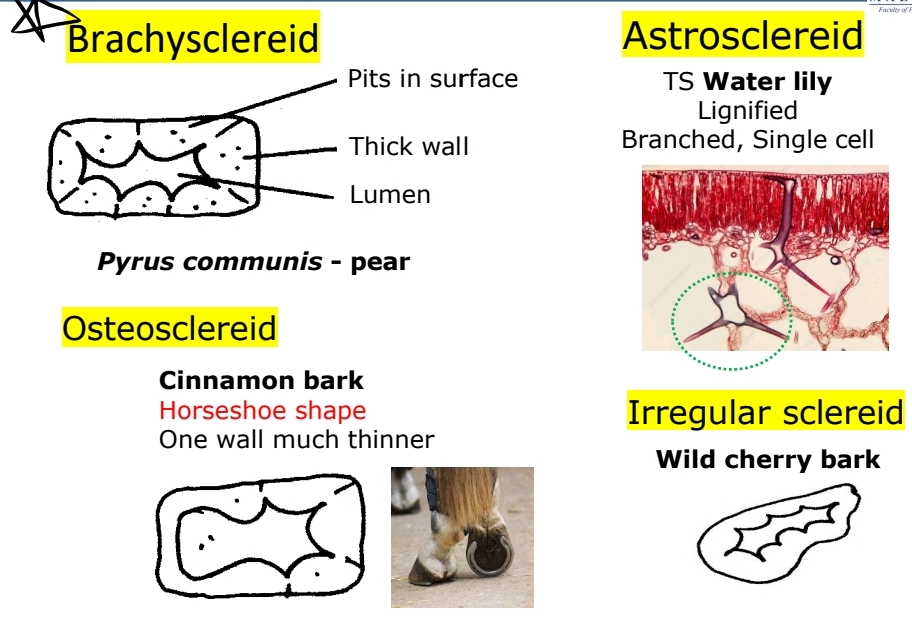
Sclereids (Stone Cells)
Short, thick-walled; e.g., in pear (Pyrus communis).
Types: Brachysclereids (Pyrus communis - pear), Astrosclereids (water lily), Osteosclereids (cinnamon bark) & irregular sclereid (wild cherry bark)
Xylem Components
Vessels, tracheids (water conduction), fibres (support), parenchyma (storage).
Xylem Lignin Patterns
Annular, Spiral, Scalariform (male fern rhizome), Reticulate (Gentian root, Rhubarb), Bordered Pitted (Liquorice root).
Phloem Components
Sieve-tube members (conduct), Companion cells (support, regulate).
Sieve Plates
Perforated ends connecting sieve tubes, enabling nutrient transport.
Epidermis
Protective, continuous outer layer; may contain crystals, papillae, trichomes.
Cuticle
Fatty cutin layer on epidermis; can be striated (diagnostic).
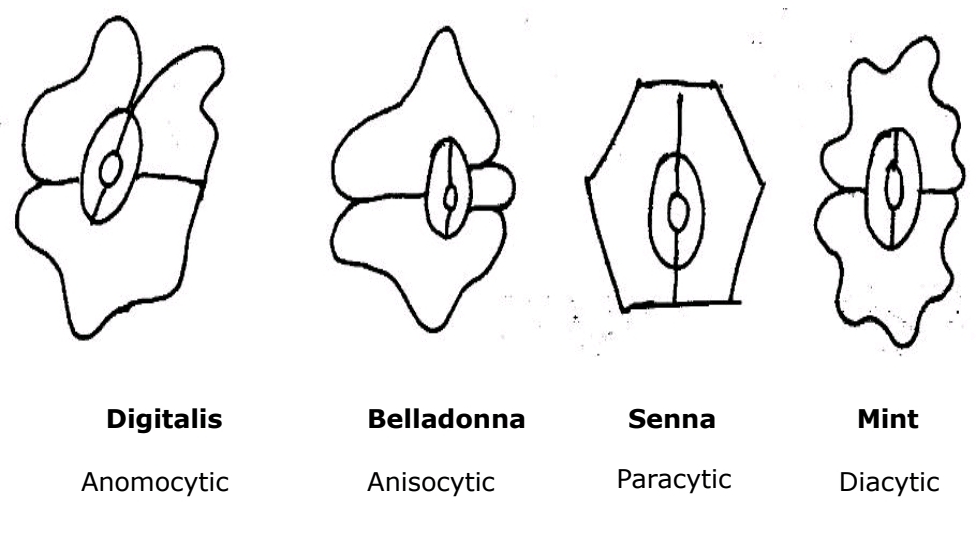
Stomata Types
Anomocytic (Digitalis), Anisocytic (Belladonna), Paracytic (Senna), Diacytic (Vasaka).
Guard Cells
Regulate stomatal opening via turgor pressure.
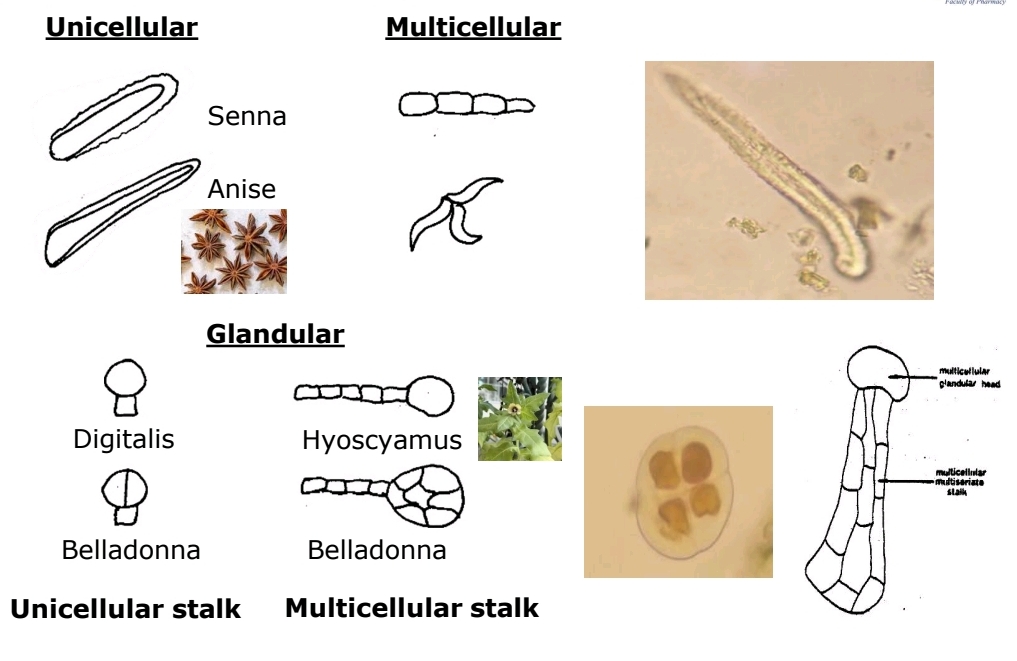
Trichomes Definition
Epidermal outgrowths; can be unicellular or multicellular, glandular or non-glandular.
Glandular Trichomes
Found in Hyoscyamus, Belladonna, Digitalis.
Non-Glandular Trichomes
Protective, reduce water loss; found in Senna, Anise.
Cicatrix
Scar left behind when trichome detaches—diagnostic marker.
Ground Tissues Functions
Photosynthesis, storage, support, secondary growth.
Ground Tissues Found In
Pith, cortex, mesophyll, endosperm.
Ergastic Substances
Non-living cell products: reserve, excretory, and secretory.
Reserve Carbohydrates
Starch (potato, rice), inulin (Dahlia), cellulose.
Starch Grain Shapes
Maize: polyhedral, Potato: ovoid, Ginger: sac-like.
Multicompound Starch
Seen in Ipecacuanha.
Starch Staining
Blue-violet with iodine, shows hilum, concentric rings
Proteins
In amorphous (Maize) or crystalline (Castor) forms (e.g., aleurone grains).
Lipids
Reserve oils (liquid/solid); e.g., Castor oil.
Mucilage
Present in epidermis, stains pink with ruthenium red (e.g., Senna, Isapgol).
Examples of Excretory Products
Alkaloids, tannins, glycosides, resins, volatile oils, calcium salts.
Calcium Oxalate Crystals
Types: prisms, clusters, needles, crystal sand (microsphenoids).
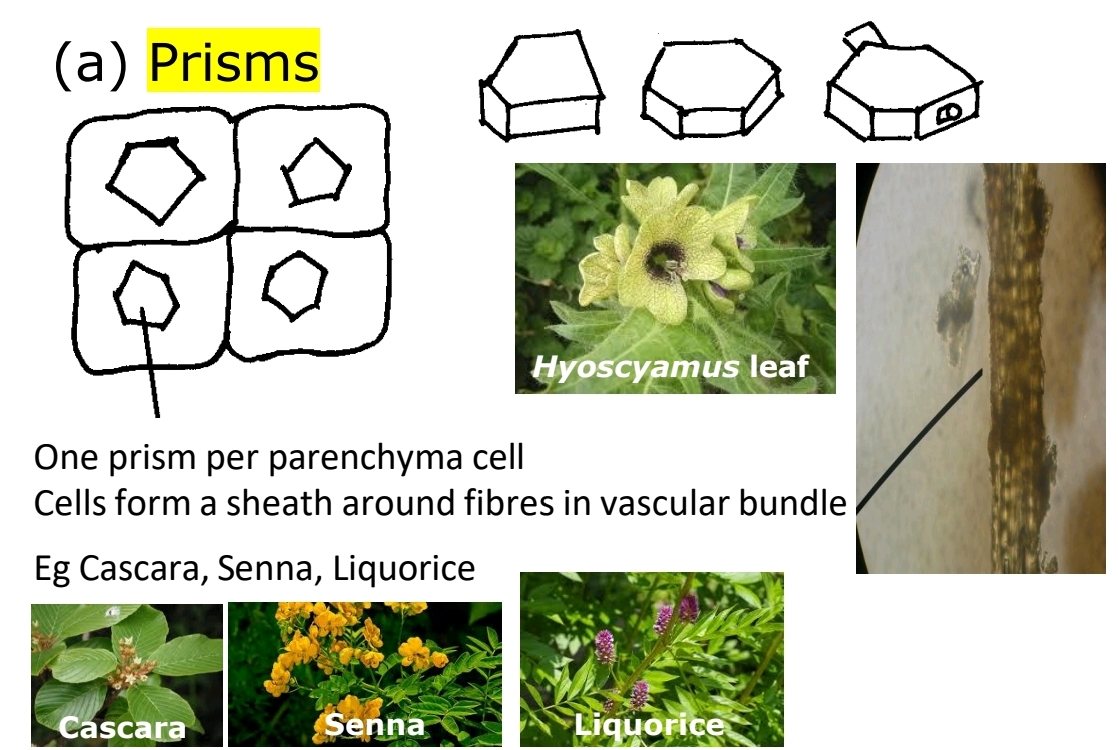
Prisms
One prism per Parenchyma cell (form sheath around fibres), found in Cascara, Senna, Liquorice
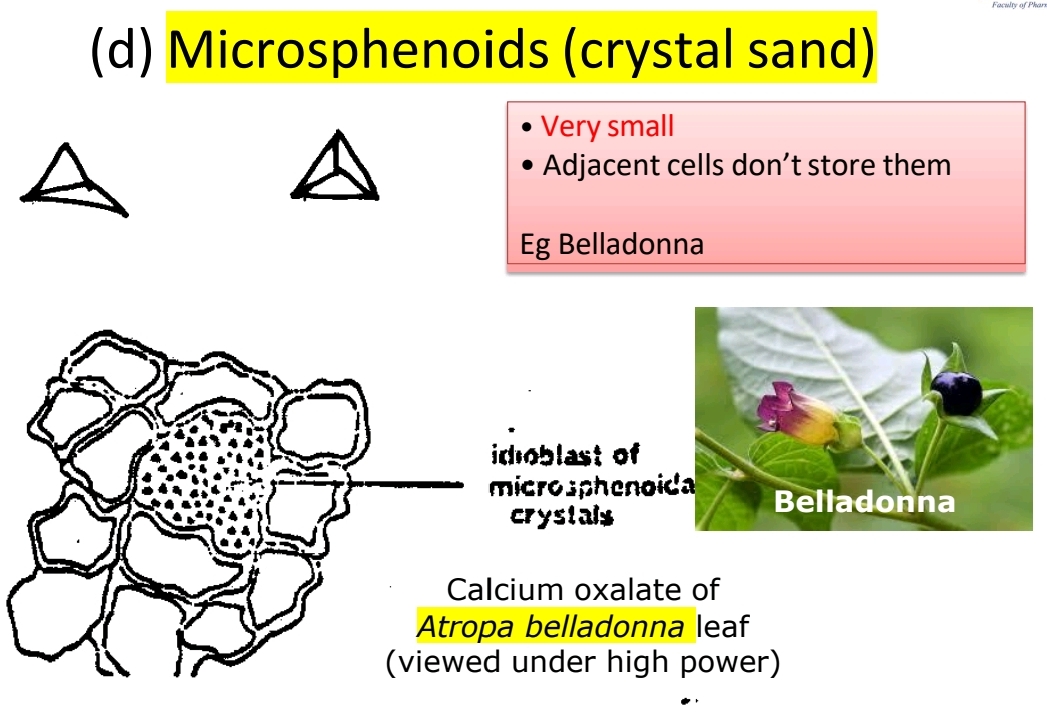
Crystal Sand (Microsphenoids)
Tiny crystals found in Atropa belladonna.
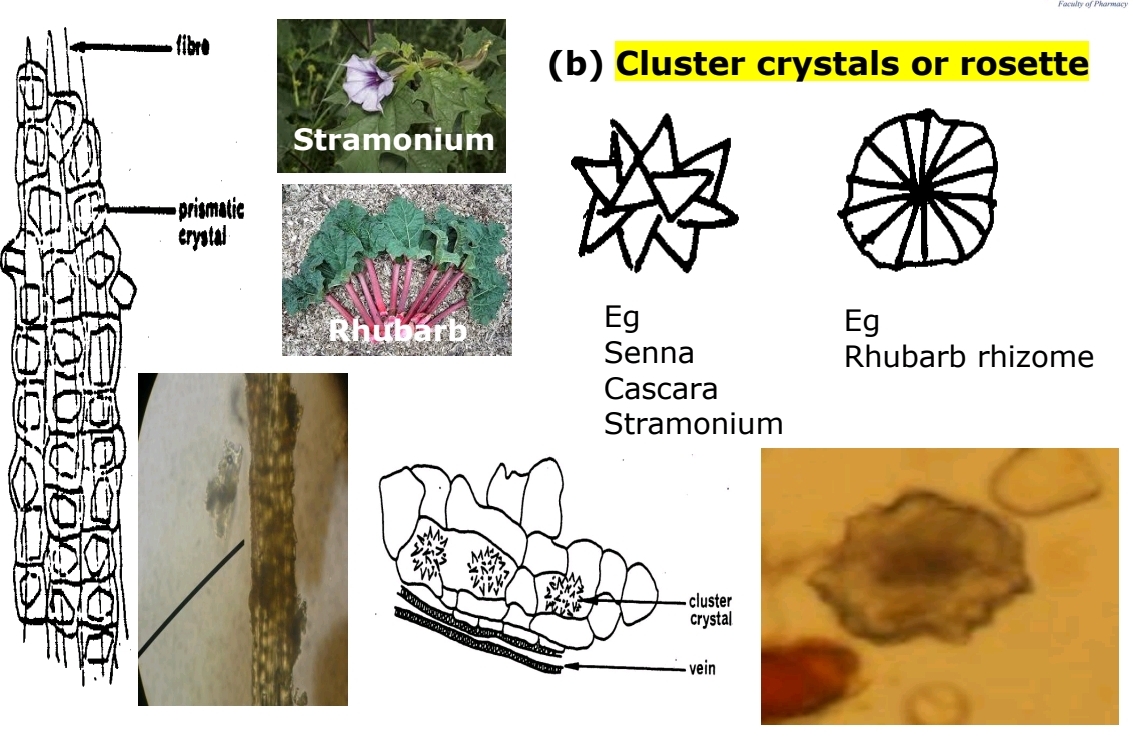
Rosette/Cluster Crystals
Found in Stramonium, Rhubarb, Senna.
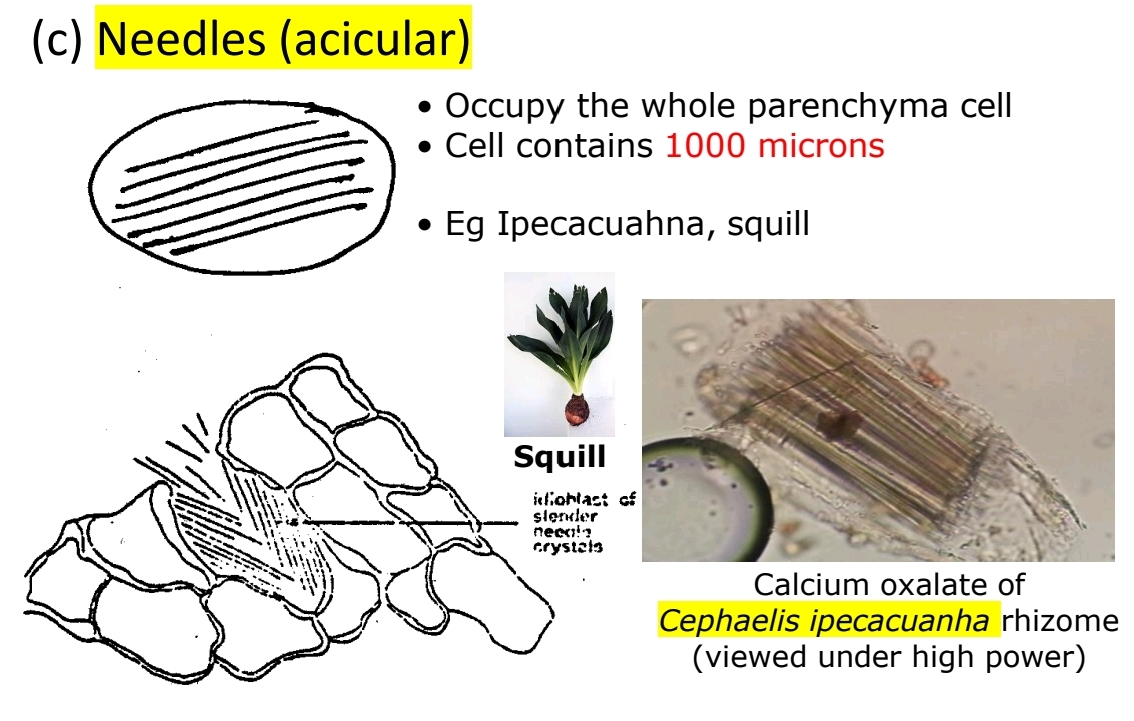
Needle-Shaped Crystals
Acicular type in Ipecacuanha, Squill.
Examples of Secretory Products
Enzymes, pigments (e.g., chlorophyll, anthocyanins, flavonoids), nectar.
Enzyme Functions
Breakdown of carbs, proteins, lipids.
Pigments
Photosynthesis (chlorophyll), coloration (flavonoids, anthocyanins).
Nectar
Secreted to attract pollinators.
Diagnostic Value of Inclusions
Used to identify crude drugs by starch, crystals, trichomes, sclereids.