IMSE 311: Complement Pathways
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Complement System
Heat labile series of plasma proteins, many of which are enzymes or proteases and has “housekeeping” roles
Lysis of foreign cells (Main function)
Recognizes cellular debris (includes infected host cells)
Opsonize and tag invaders for clearance
Proinflammatory (Diapedesis)
Increase vascular permeability
Recruit phagocytes
Directs the adaptive immune system to site of infection (Chemotaxis)
Liver
Organ that is the major source of complement proteins
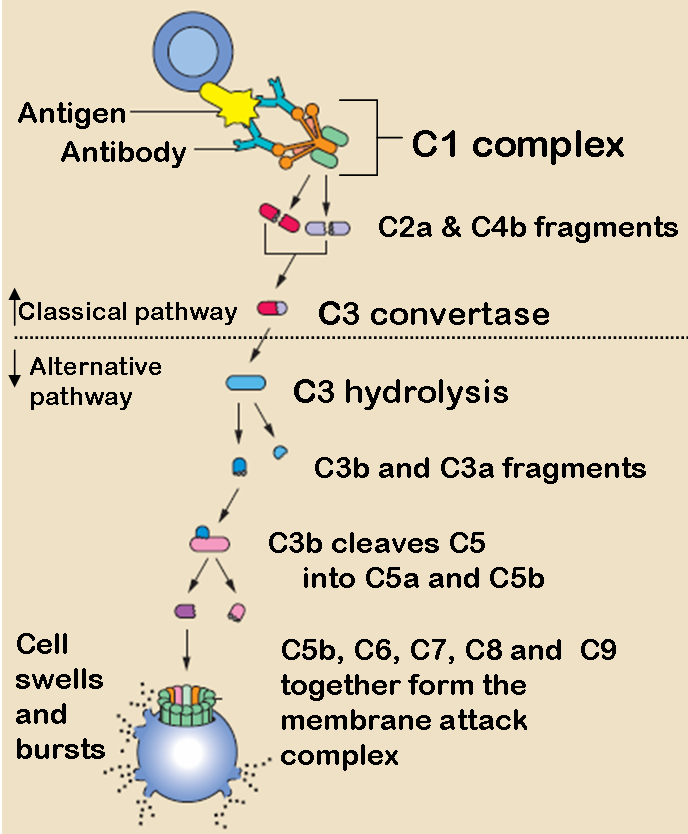
Classical Pathway
Antigen-antibody complexes that involves 9 proteins
Recognition unit: C1 complex + Calcium (maintain structure)
C1q: binds to antibody molecules
C1r: autoactivation; cleaves C1s to activate it
C1s: cleaves C4 and C2 into “a” and “b” fragments
Activation unit:
C4: C4b binds to C2a in the presence of Mg ions
C2: cleaves C3 once bound to C4b
C3: Cleaves C5 once bound to C4b2a
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC): produces a pore in the target membrane of 70-100 Å (Angstrom)
C5: C5b attaches to cell membrane
C6: binds to C5b
C7: binds to C5b6
C8: binds to C5b67
C9: binds to C5b678
C3
Most abundant complement protein with a plasma concentration of 1-1.5 mg/mL
Convergence point of all 3 complement pathways
Cleavage of C3 into C3b
Most significant step in complement activation
C4b2a
Also known as “C3 convertase” of the classical and lectin pathway, with a half-life between 15 secs - 3 mins
Classical Pathway Triggers
IgM (most effective; multiple binding sites)
IgG3
IgG1
IgG2
CRP
Several viruses
Mycoplasma
Some protozoa
Some gram (-) bacteria (Escherichia coli)
C4b2a3b
Also known as “C5 convertase” of the classical and lectin pathway
Carboxy-Terminal End
Hydrophobic part of C9 that anchors the MAC w/n the target membrane
False
True or False: C9 is required for MAC to create a pore for cell lysis
Alternative Pathway
“Properdin System”, relies on spontaneous hydrolysis of C3 into C3b-like molecule or C3H2O and involves 6 proteins + 2 factor proteins
Recognition unit: none
Activation unit:
C3: Cleaved by hydrolysis into C3H2O to start activation of pathway
C3b: binds to Factor B
Factor B: Analogous to C2 in classical pathway
Factor D: Cleaves Factor B
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC): produces a pore in the target membrane of 70-100 Å (Angstrom)
C5: C5b attaches to cell membrane
C6: binds to C5b
C7: binds to C5b6
C8: binds to C5b67
C9: binds to C5b678
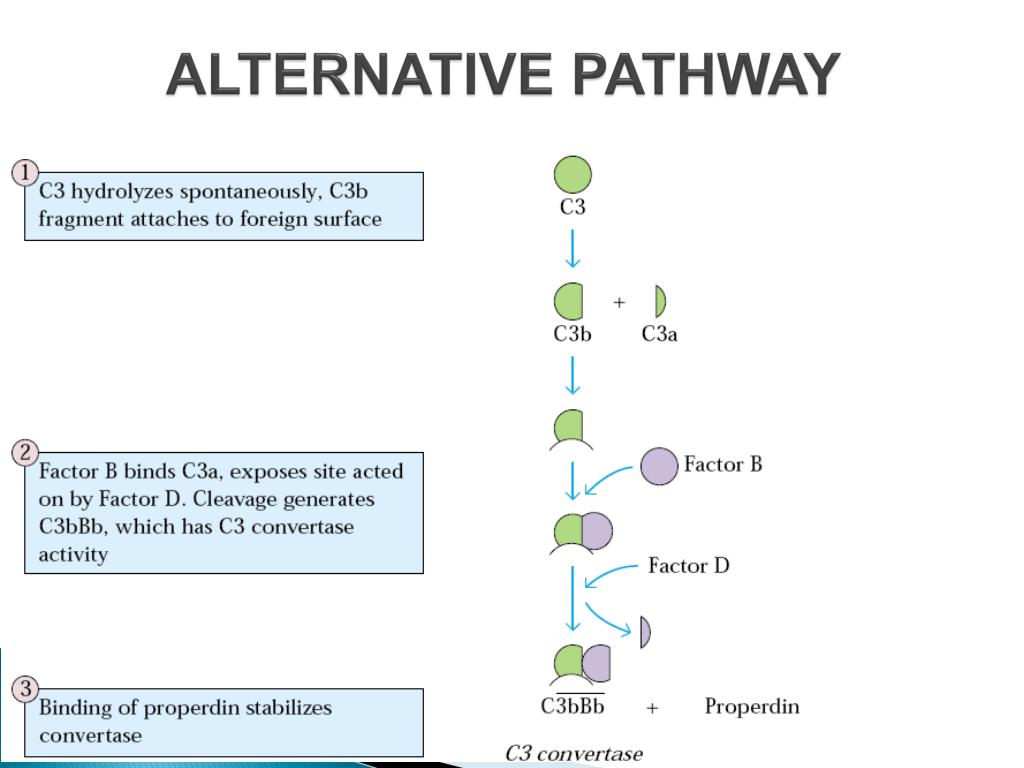
C3bBb
Also known as “C3 convertase” of the alternative pathway; with a half-life of 90 secs
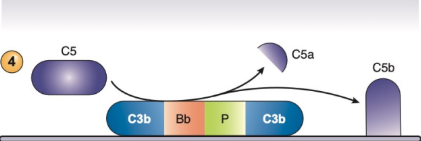
C3bBbPC3b
Also known as “C5 convertase” of the alternative pathway
Properdin
A plasma glycoprotein and the only known positive regulator of the complement system
amplifies and stabilizes C3bBb by binding to it
Alternative Pathway Triggers
Bacterial cell wall w/ lipopolysaccharide
Fungal cell wall
Yeast
Viruses
Virally-infected cells
Tumor cell lines
Some parasites (especially trypanosome)
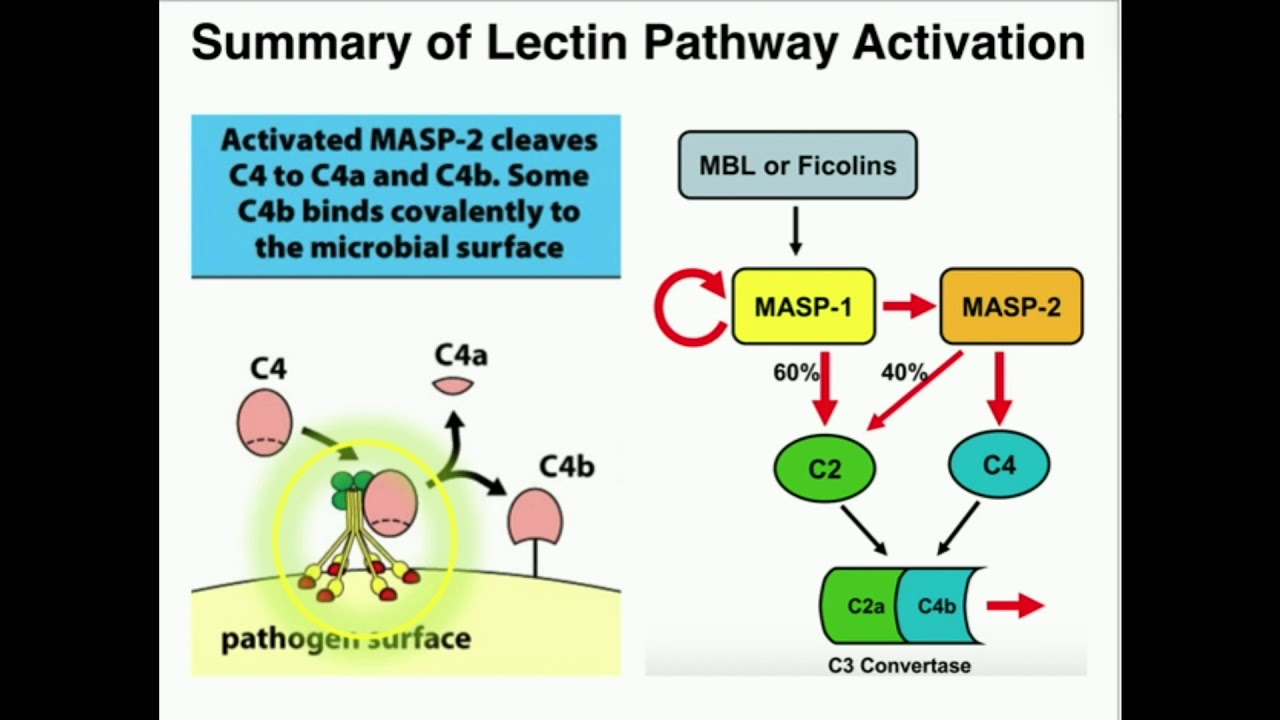
Lectin Pathway
Activated by direct recognition of surface moieties found on pathogens and plays an important role as a defense mechanism in infancy (during the interval between loss of maternal Ab and acquisition of full-fledged Ab response to pathogens) and involves 8 proteins + lectins
Recognition unit:
Lectins, Ficolins, & Collectins: analogous to C1q in classical pathway
Mannose-binding Lectin (MBL): requires Calcium to bind to sugars (PAMPs) found on microbial surfaces
MBL-associated Serine Proteases (MASPs): analogous to C1r and C1s in classical pathway
Activation unit:
C4: C4b binds to C2a in the presence of Mg ions
C2: cleaves C3 once bound to C4b
C3: Cleaves C5 once bound to C4b2a
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC): produces a pore in the target membrane of 70-100 Å (Angstrom)
C5: C5b attaches to cell membrane
C6: binds to C5b
C7: binds to C5b6
C8: binds to C5b67
C9: binds to C5b678
Short Half-Life
Serves as a mechanism of control (“system control”) for complement complex enzymes, keeping the reaction localized
C1 Inhibitor (C1-INH)
Inhibits activation at recognition phases of both classical and lectin pathways by binding to C1r, C1s and MASP-2
C4-binding Protein (C4BP)
Cell-bound Receptors
Complement Receptor Type 1 (CR1)
Membrane Cofactor Protein (MCP or CD46)
Decay-accelerating Factor (DAF or CD55)
Inhibits formation of C3 convertase (inactivates C3b and C4b) together with Factor I (for degradation)
Factor H
Principal soluble regulator of alternative pathway
binds to C3b to inhibit factor B
S Protein (Vitronectin)
Inhibits C5b67 complex binding on cell surface preventing polymerization of C9
note: binding of C8 and C9 still proceeds but polymerization of C9 doesn’t occur
Membrane Inhibitor of Reactive Lysis (MIRL or CD59)
Present on cell membranes (RBCs, endothelial, epithelial, & etc.) to block the formation of membrane attack complex (MAC)
Complement Receptor 1 (CR1 or CD35)
Large polymorphic glycoprotein found mainly on peripheral blood cells that binds to C3b and C4b, but has the greatest affinity for C3b
Complement Receptor 2 (CR2 or CD21)
Present only on mature B-cells and is lost when conversion to plasma cells occurs
binds complement-coated antigen (antigen opsonized by complement molecules) and cross-links it to membrane immunoglobulin to activate B cells
Complement Receptor 3 (CR3 or CD11b/CD18)
Found on monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and natural killer (NK) cells (basically phagocytic cells)
specifically binds particles opsonized with iC3b (C3b degradation product) in calcium-dependent manner
Complement Receptor 4 (CR4 or CD11c/CD18)
Similar function to CR3 but also found in dendritic cells, and activated T- or B-cells,
C5a
An anaphylatoxin (proinflammatory) that also serves as a chemotaxin
Deficiency
C1 complex (C1q, C1r, C1s): Lupus-like syndrome; recurrent infections
C2: Lupus-like syndrome; recurrent infections; atherosclerosis
C3: Severe recurrent infections; glomerulonephritis
C4: Lupus-like syndrome
C5 - C8: Neisseria infections
C9: no known disease association
C1-INH: Hereditary angioedema
DAF and MIRL: Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Factor H or I: Recurrent pyogenic infections
MBL: Pneumococcal diseases; sepsis; Neisseria infections
Properdin: Neisseria infections
MASP-2: Pneumococcal diseases