3.3: Long-Run Costs
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are Increasing Returns to Scale?
When output increases at a rate greater than the inputs increase by.
(E.g. outputs triple when inputs double)
What is Constant Returns to Scale?
When output increases at the same rate as inputs.
(E.g. outputs double after inputs double)
What happens in Decreasing Returns to Scale?
When outputs increase less proportionally to inputs.
(E.g. outputs double even though inputs tripled)
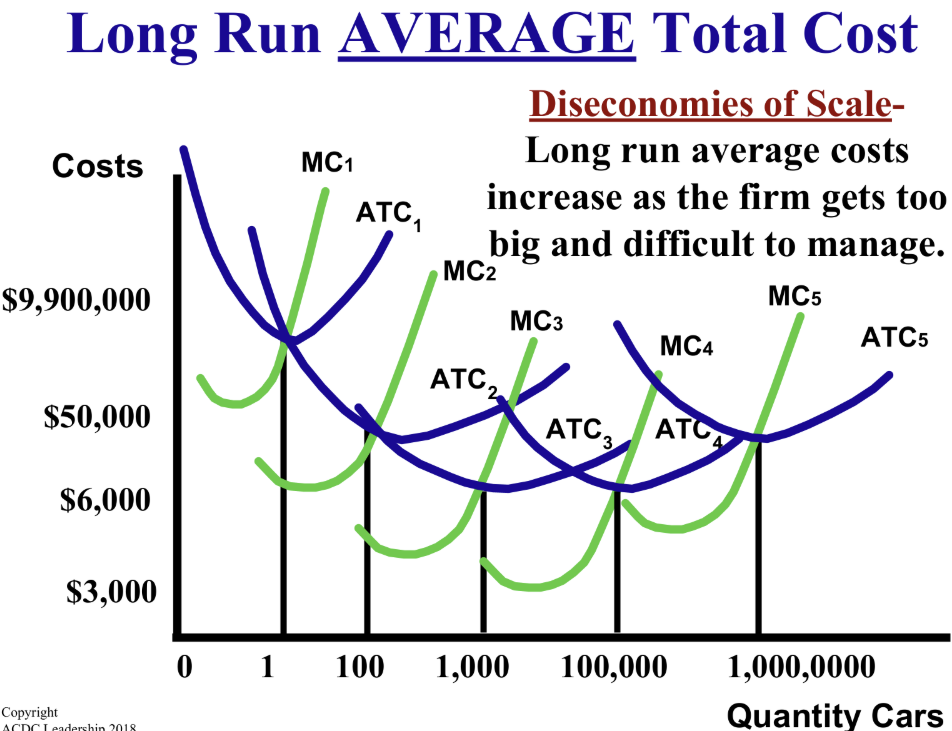
What is the Long Run Average Total Cost (LRATC) curve made up of?
It consists of all the different short-run ATC curves of various production sizes.
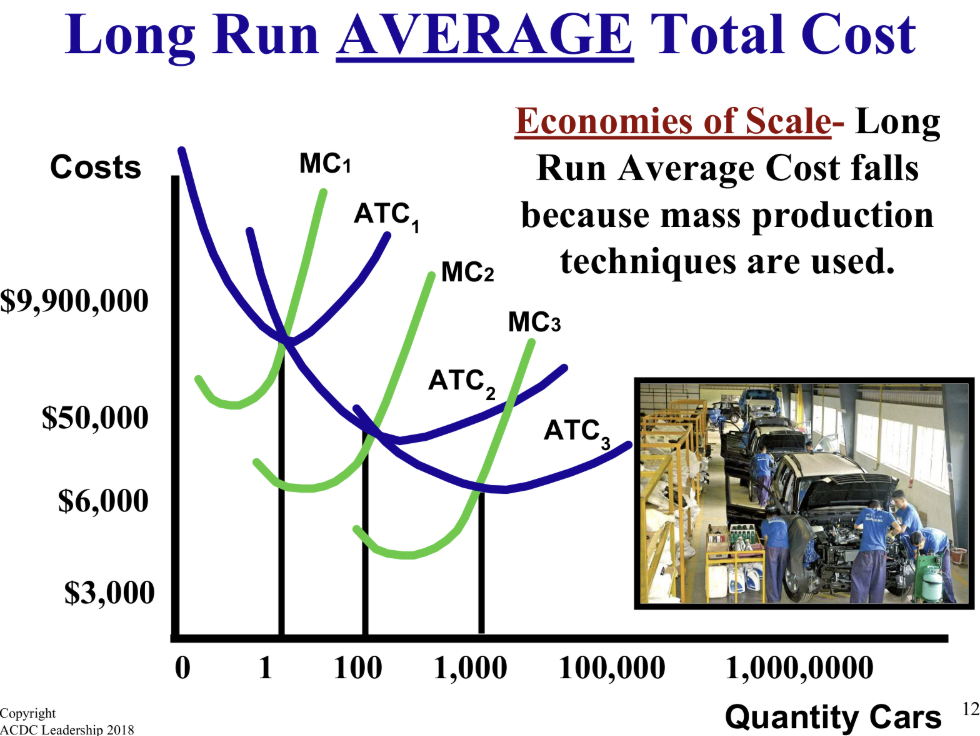
What causes economies of scale?
Firms producing more can better use mass production techniques and specialization.
How does average total cost change when a firm increases plant capacity?
It typically falls as more efficient production techniques are utilized.
What happens to average total costs due to Diseconomies of Scale?
They increase as the firm grows too big and difficult to manage.
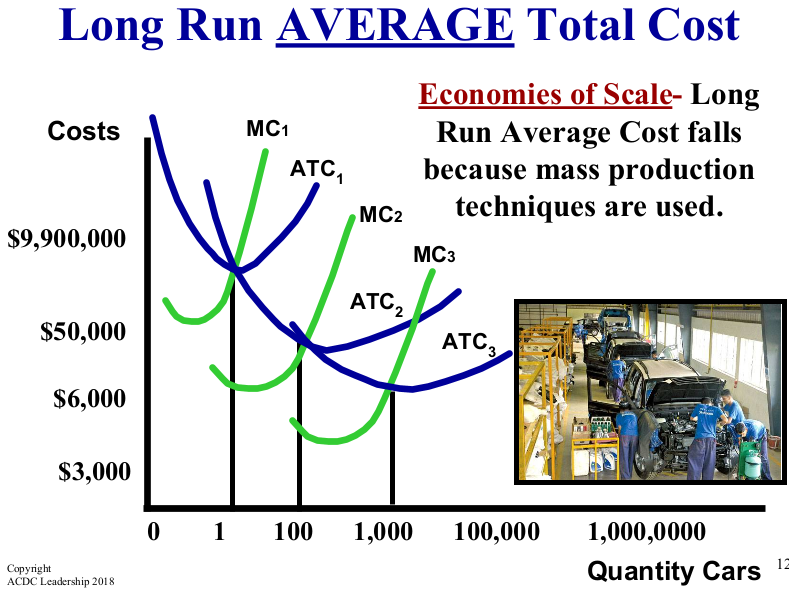
What is the effect of mass production techniques on average costs?
It generally lowers average costs despite potentially higher total costs.
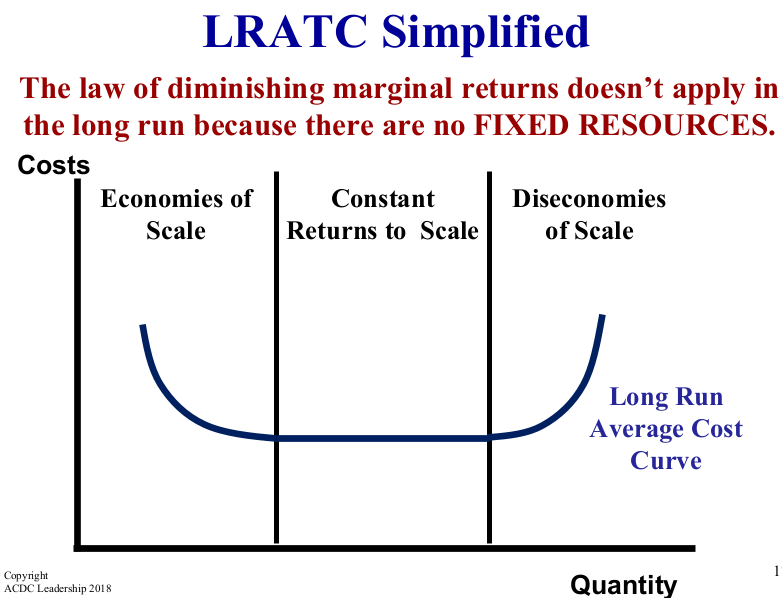
What is meant by the law of diminishing marginal returns in the long run?
It doesn't apply because there are no fixed resources in the long run.
What is the primary goal when firms analyze their long-run average costs?
To minimize per unit costs by adjusting production size and input levels.
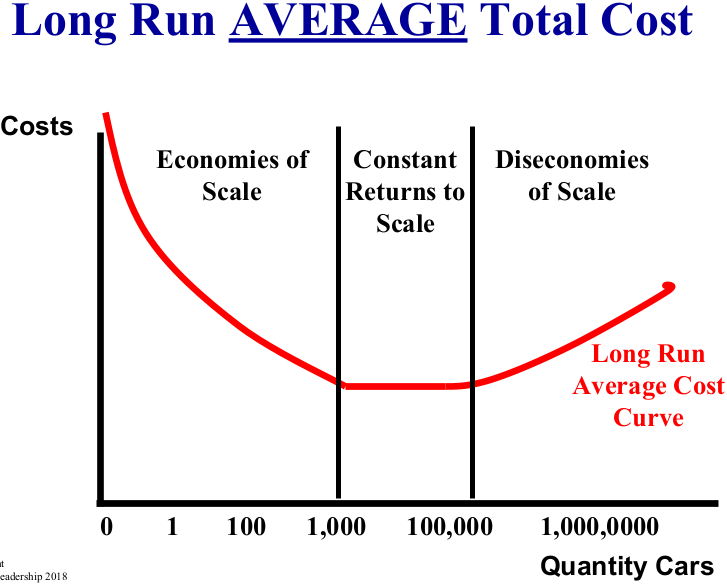
What are the three stages in long run average total cost (LRATC)?
Economies of scale, constant returns to scale, diseconomies of scale