LAB PRACTICAL TEST qa
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
(no true body cavity) lack coelem (body cavity) between digestive tract and body cavity
ascoelmate
(body cavity between mesoderm and ectoderm)digestive tract lined by endoderm and body cavity partially lined by mesoderm
Pseudocoelamate –
pseudocoelamate example
ex round worm
ascolemate exmaple
ex flatworms
–reduced body canciuty with true coelem completly lines by mesodermla tissue
Eucoelomate
eucoelomate example
ex arthropod
what is spicules
skeletal elements of sponges
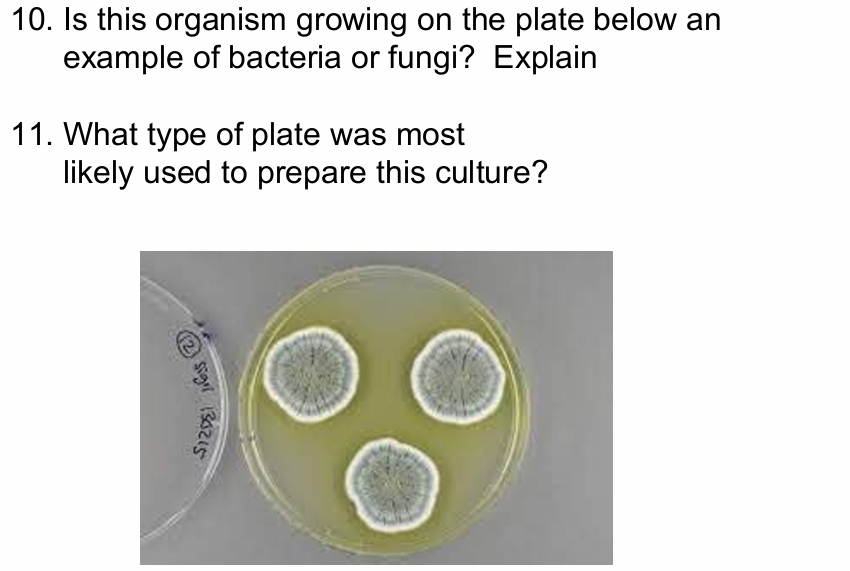
fungi
fuzzy appearance created by hyphae
SDA - it grows fungi because it’s acidic or MEA with antibiotics
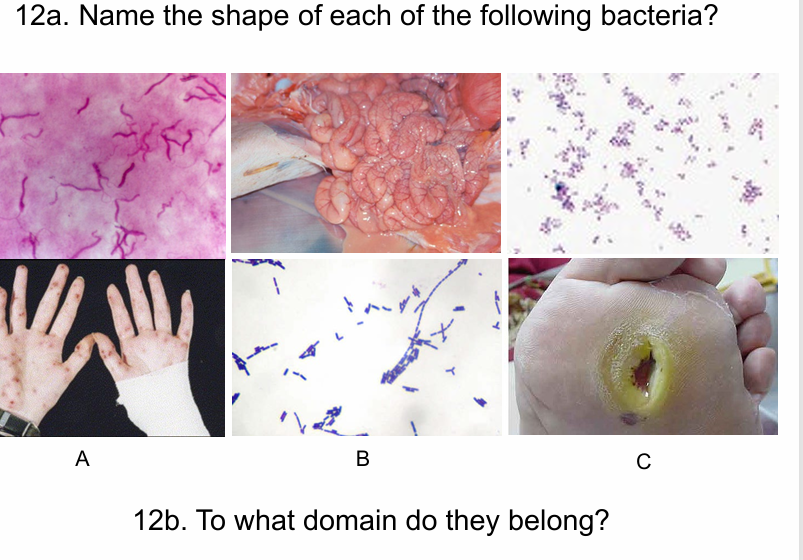
a spirilla b bacillis c cocci
Bacteria and eubacteria
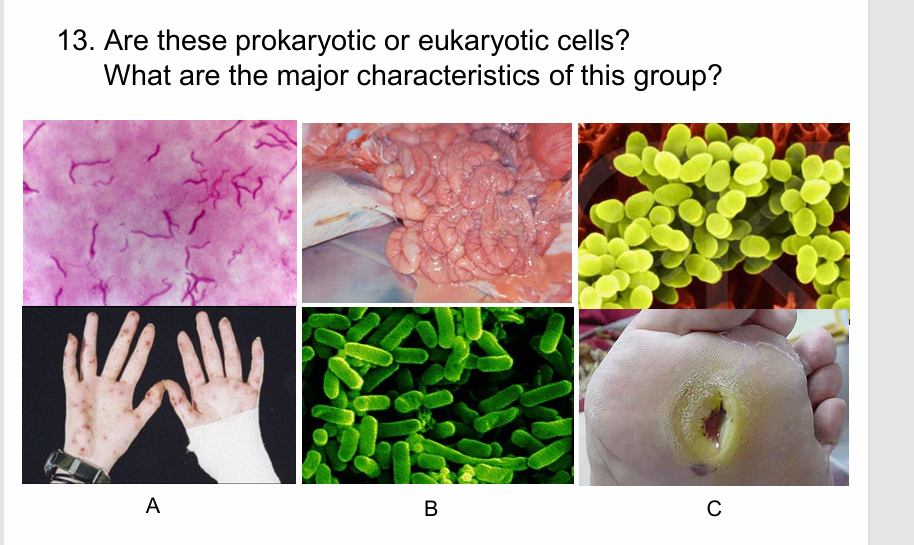
Prokaryotic; No membrane bound organelles; One circular chromosome, and smaller ribosomes.
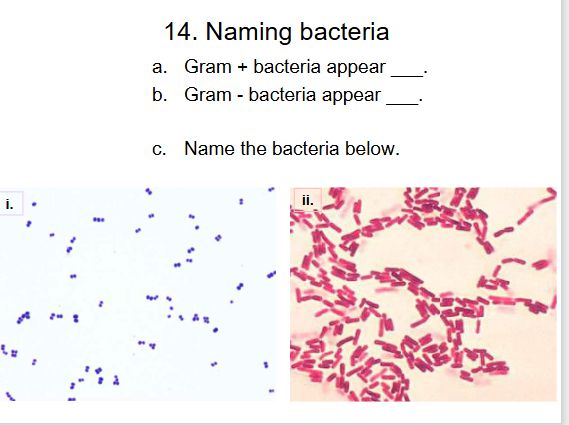
a. purple diplococcus gram positive
B red streptobacillus gram negative
spirillum does not form clusters or chains)
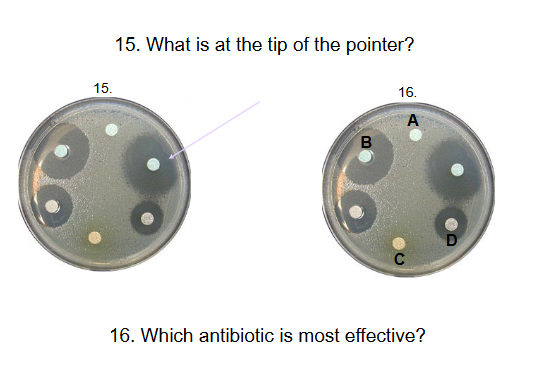
Zone of inhibition - shows effectiveness of antibiotic by showing where bacteria grows or doesn’t
B
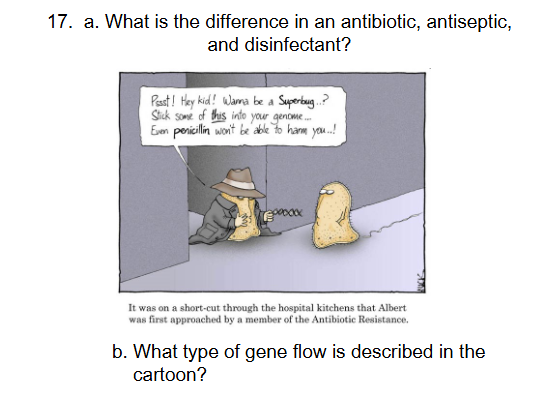
Antibiotic - antibacterial that kill or slow the growth of bacteria taken orally or topically
Antiseptic - antibacterial applied to living tissue
Disinfectant - antibacterial applied to inanimate object
Horizontal gene flow- conjugation
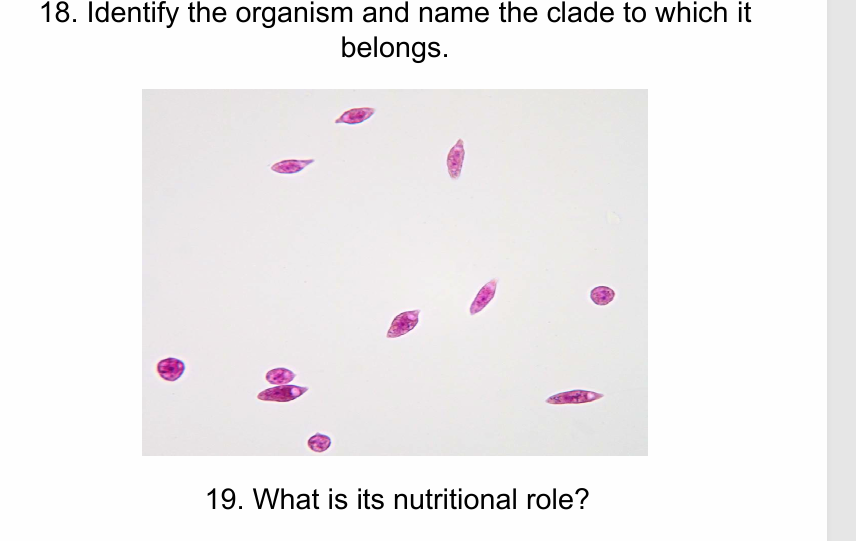
Euglena- excavata
Mixotroph
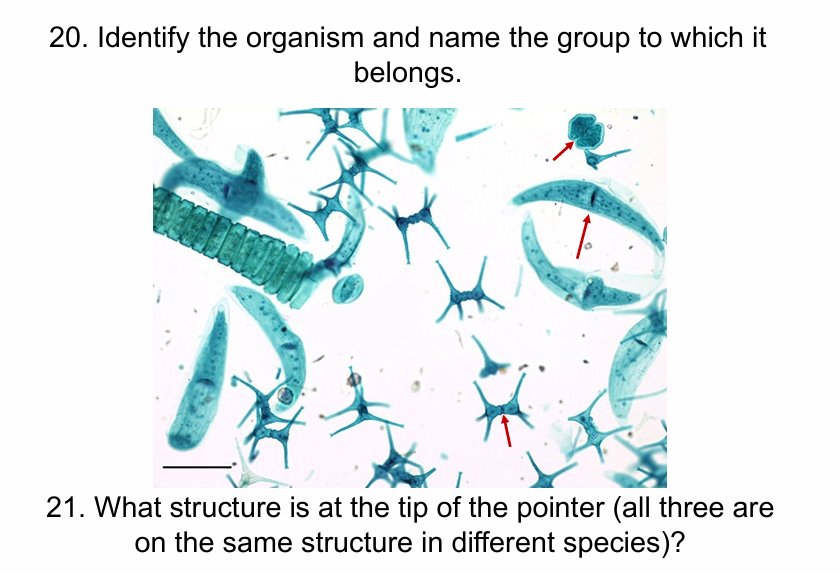
Desmids- archaeplastida
Isthumus between semi cell
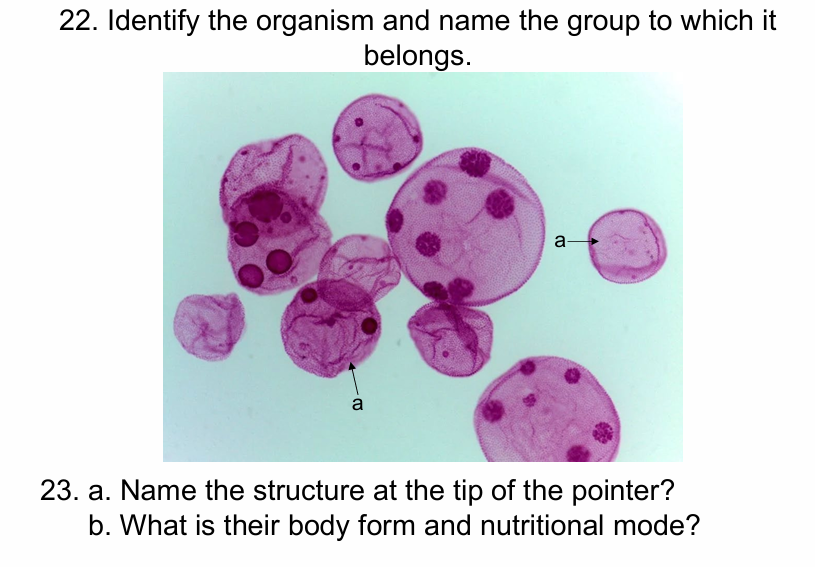
Volvox- archaeplastida
a. Coenobium
B colonial photoautotroph
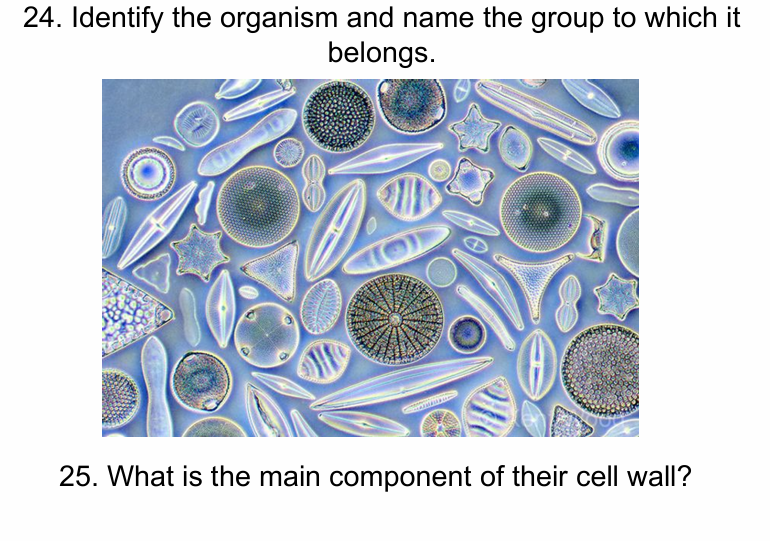
Diatom - SAR clade
Silica
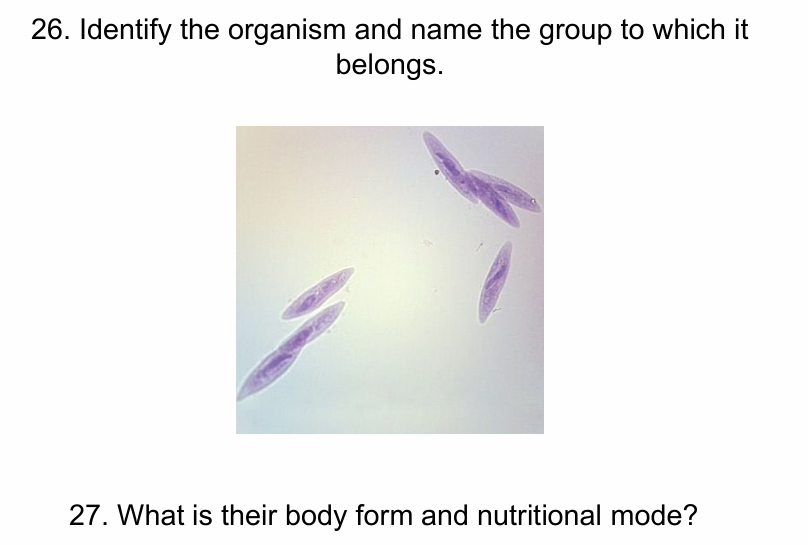
Paramecium- SAR -ciliate
Unicellular free living heterotroph

Amoeba - unikonta
Pseudopodia , cytoplasmic streaming
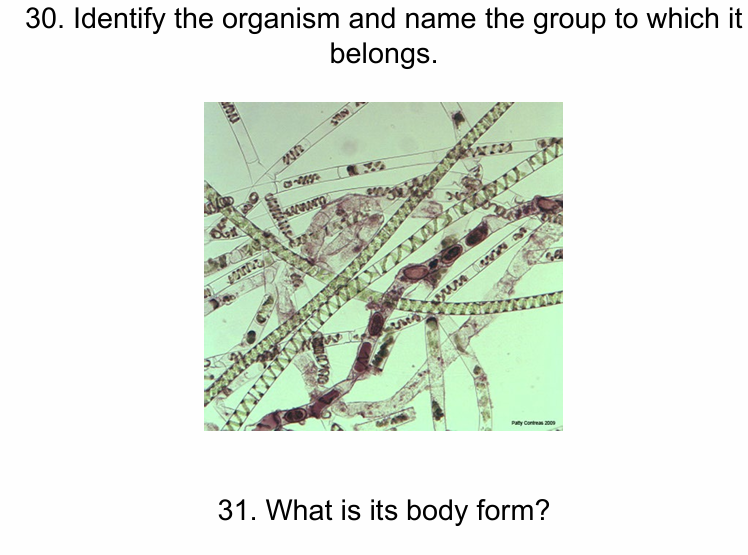
Spirogyra - archaeplastida
Filamentous
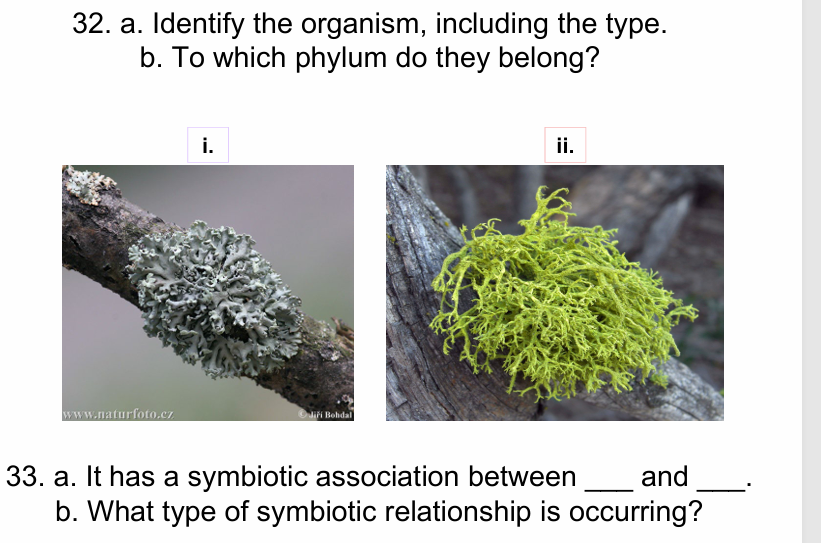
I. Foliose- lichen
Ii. Fruticose lichen
B. Ascomycota
Fungus and green algae or Cyanobacteria
Mutualistic
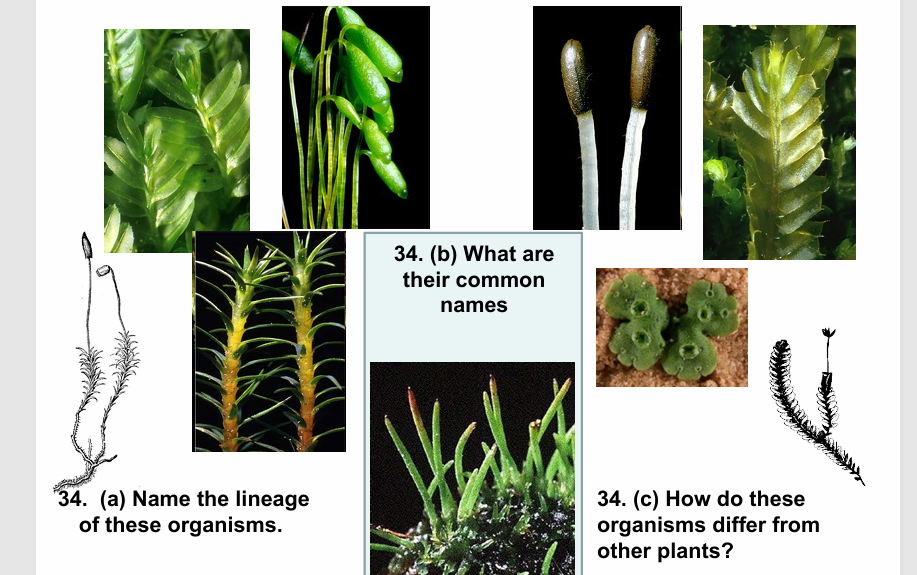

a) Bryophytes,
b) Moss, Hornwort, Liverwort,
c) Small, nonvascular, and
they require water for fertilization
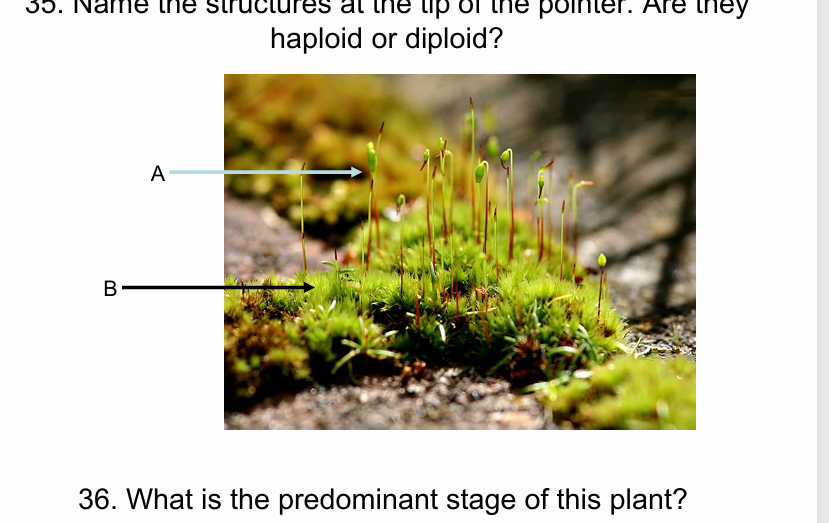
a) sporophyte (diploid)
; b) Gametophyte (haploid)
gametophyte
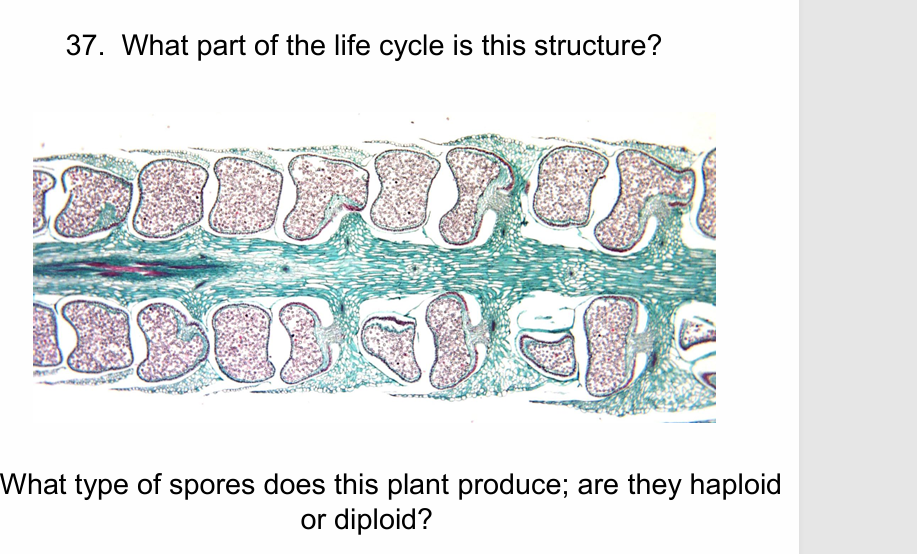
Sporophyte
Homosporous haploid spores
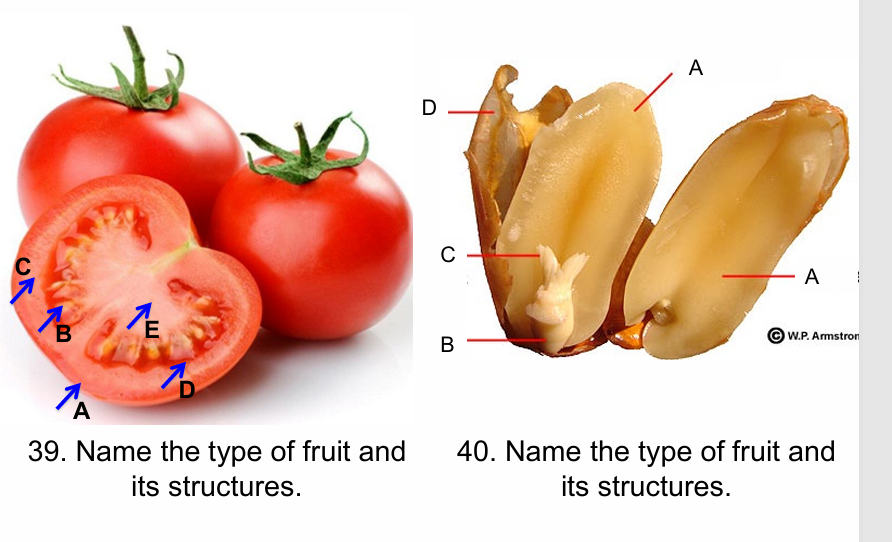
Berry, a) exocarp, b) seed; c) mesocarp, d)endocarp, e) placenta
Legume; a) endosperm cotyledon; b and c) embryonic structures, d) seed coat
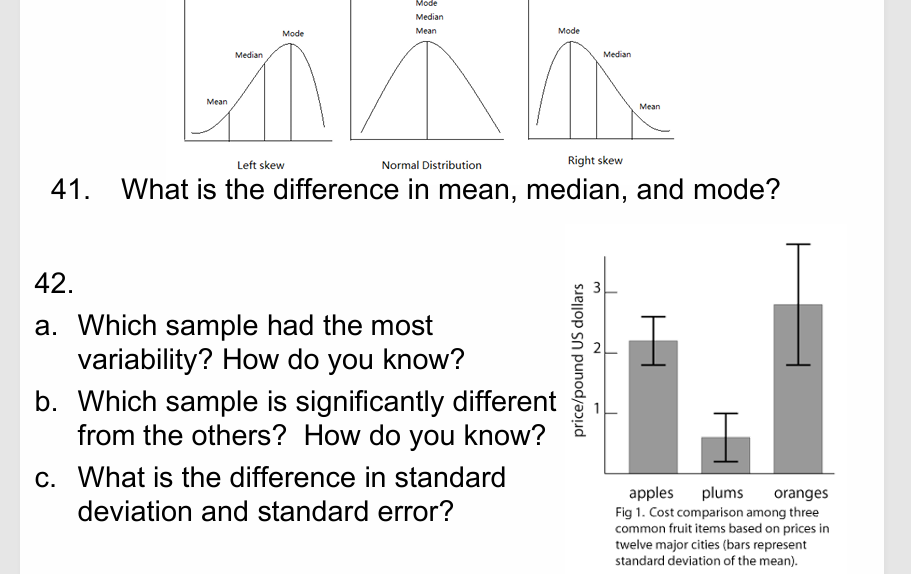
Mean= average, median = middle most data point, mode = most
frequently occurring valuea oranges - it has the largest standard deviation.
b plums - it does not have overlapping error bars with the other two.
c. Standard deviation = amount of variability between samples
Standard error = indicates how closely the sample mean represents.
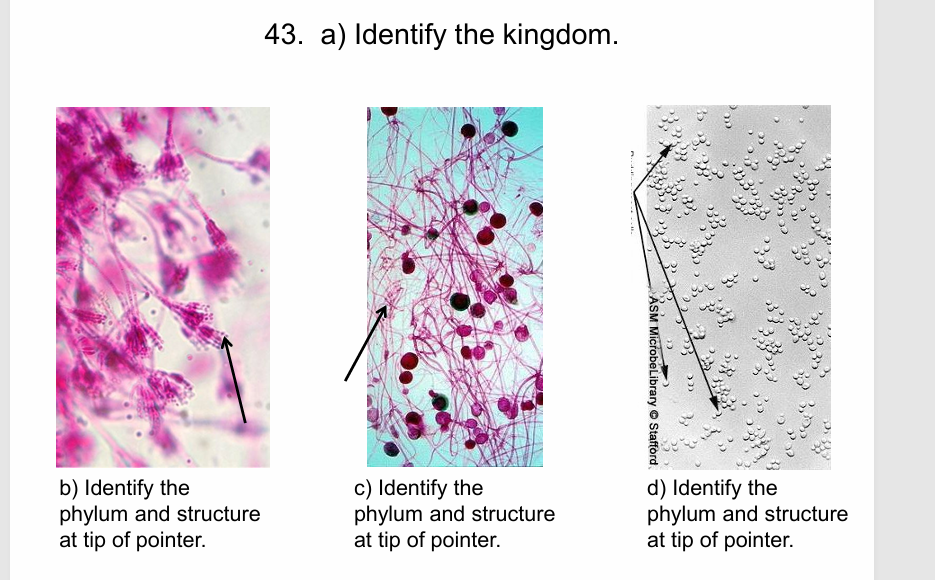
43 a) Fungi,
b) Ascomycetes/Conidia;
c) Mucoromycota /Hyphae
D)Ascomycetes/ Budding yeast

a, Lycophyta and
b) Selaginella megaspore. First time we see heterosporous spores in plants but as a transitional group it contains both types of spores:

Angiosperms/Anthophyta, coevolution with specific cross pollinators

Cnidaria
True

Coniferophyta (pine), Cycadophyta (sago palm), Ginkgophyta (Gingko),
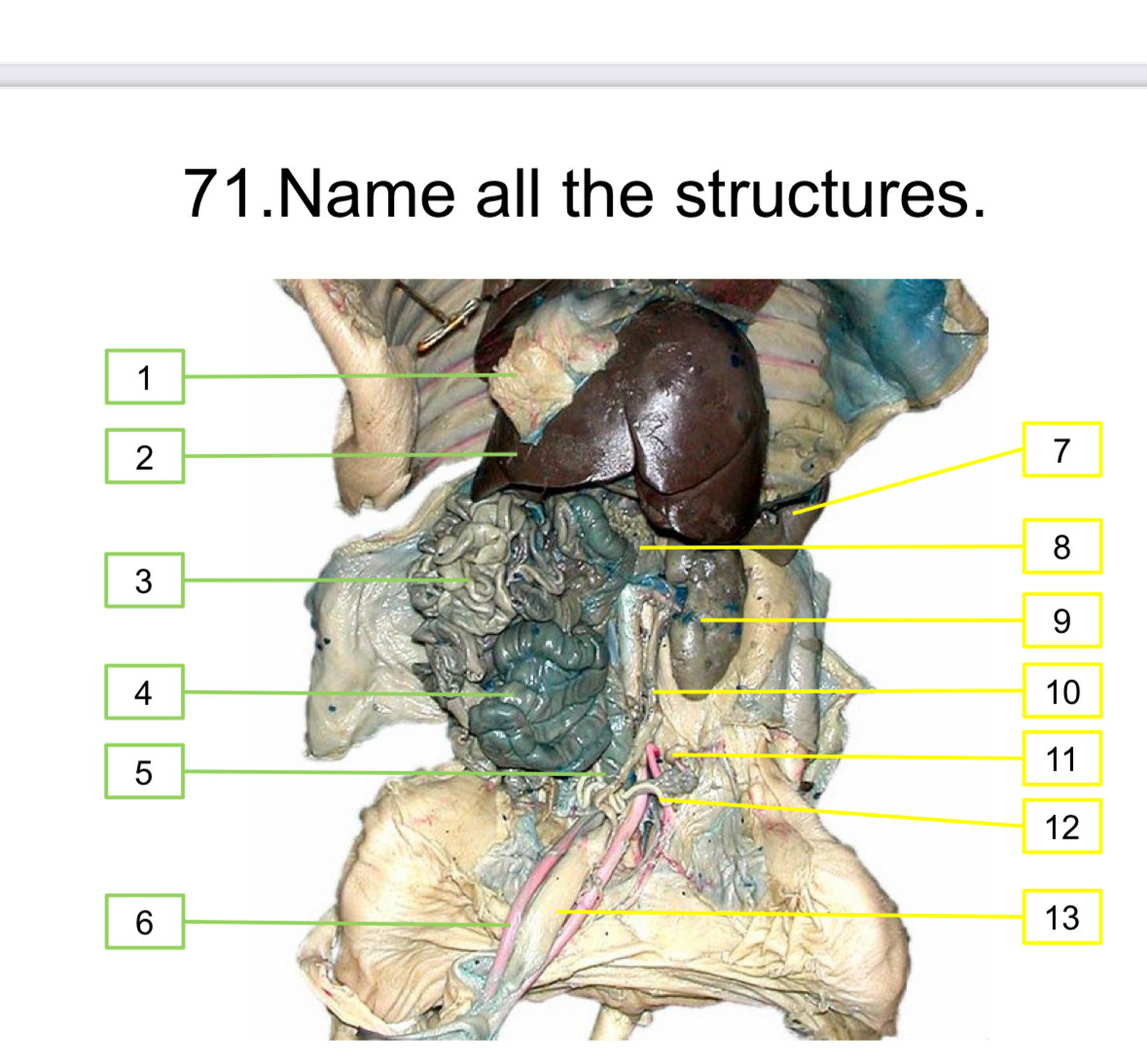
Diaphragm
Liver
Small intestine
Large intestine
Rectum
Umbilical artery
Spleen
Pancreas
Kidney
Ureter
Ovary
Uterus
Urinary bladder
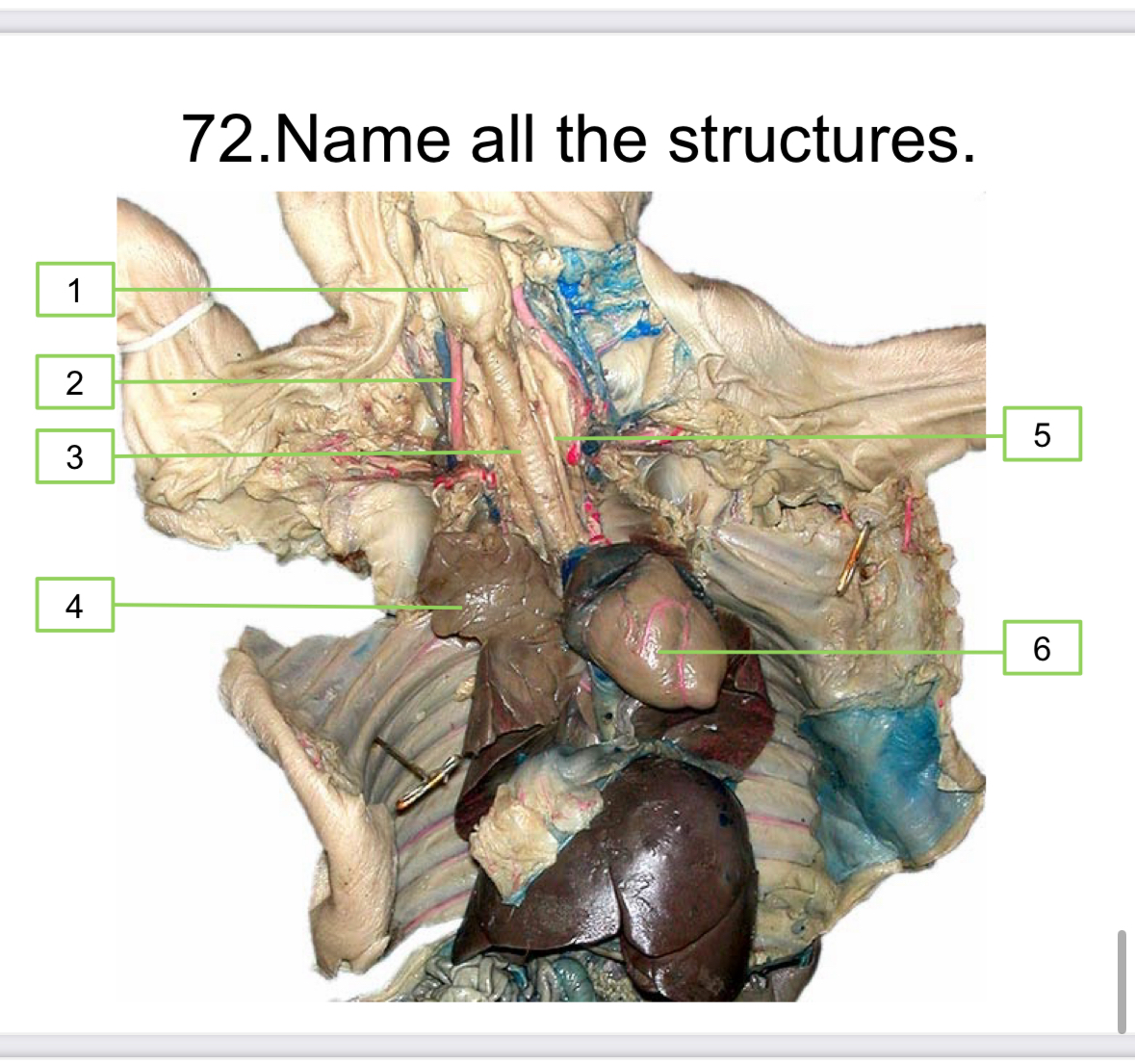
larnyx
Carotid artery
Trachea
Lung
Esophagus
Heart
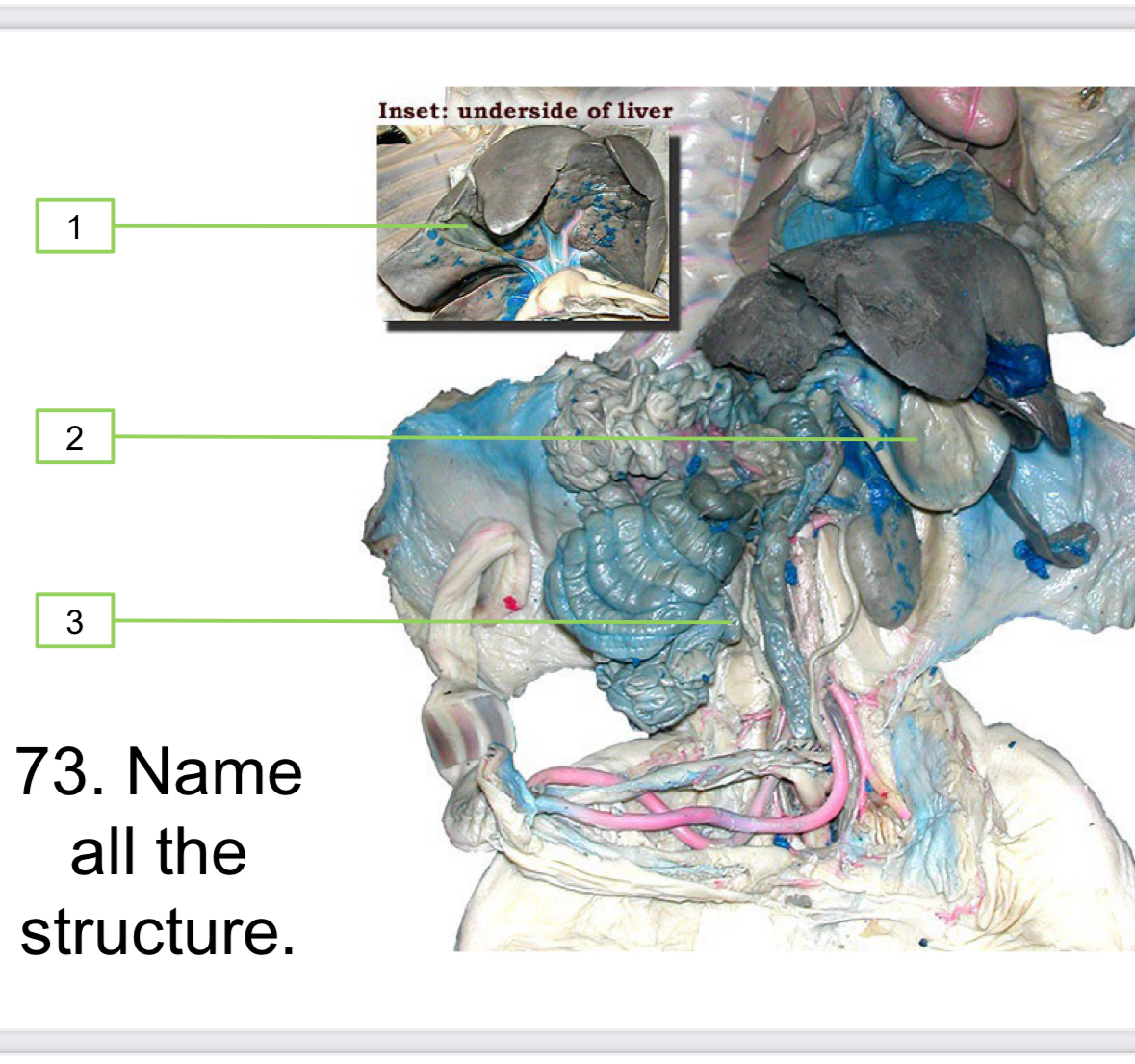
Gall bladder
Stomach
Cecum
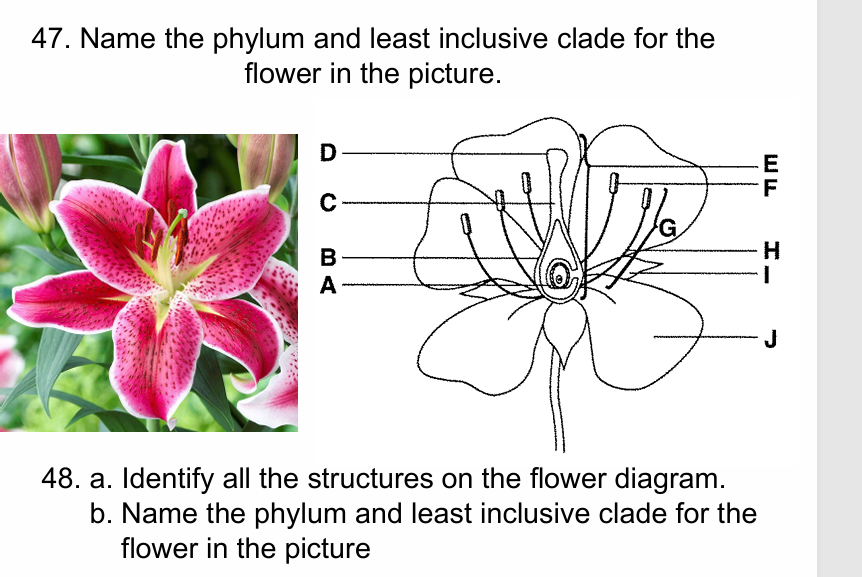
Anthophyta; Monocot (3 petals and 3 sepals of the same color).
A. a) ovule b) ovary c) style d) stigma e) carpel f) anther g) stamen h) filament i) sepal j) petal B. Anthophyta; Eudicot (5 petals)
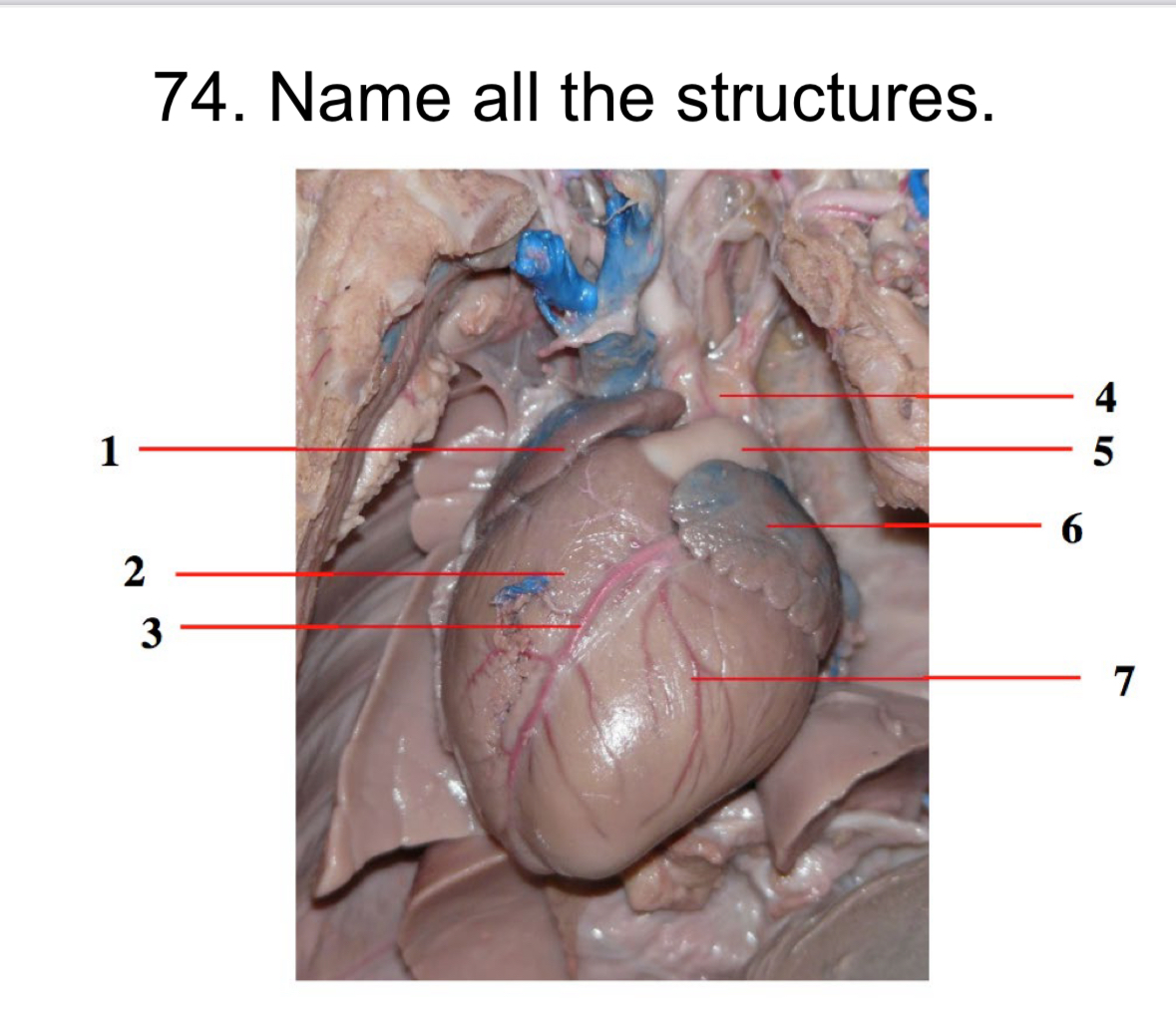
Rt Atrium
Rt Ventricle
Coronary Artery
Aorta
Pulmonary
Trunk
Lt Atrium
Lt ventricle
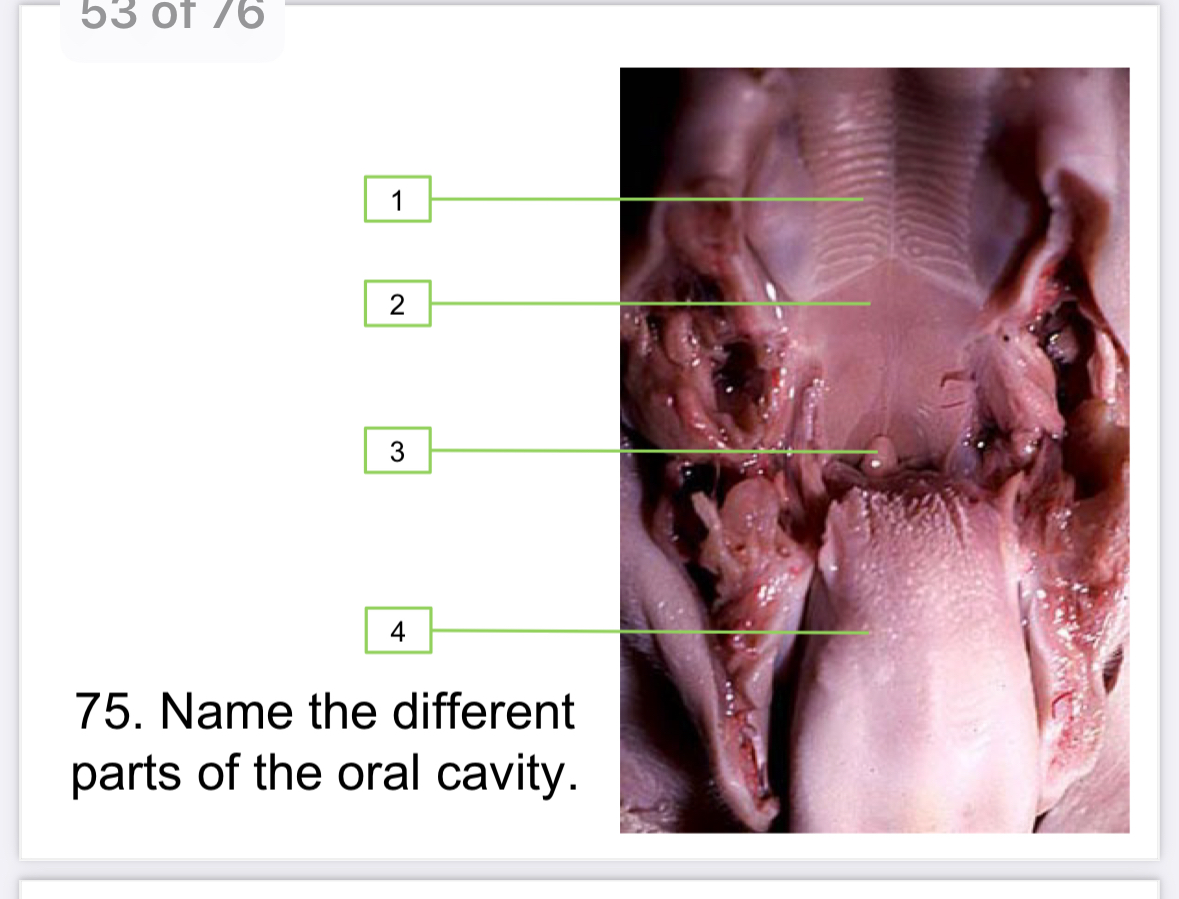
HardPalate
SoftPalate
Epiglottis
Tongue

Porifera
Asymmetry
Spicules
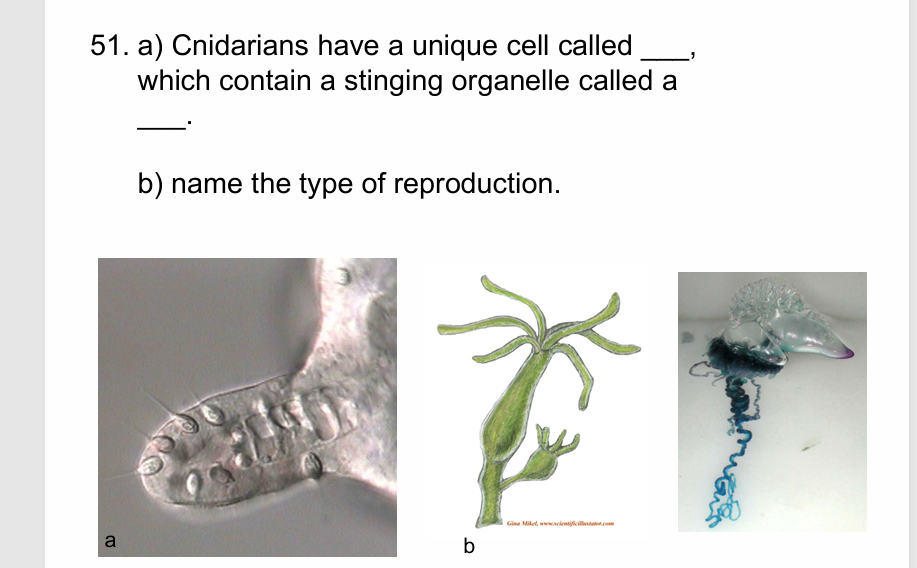
a) Cnidocytes,
nematocyst
b) budding
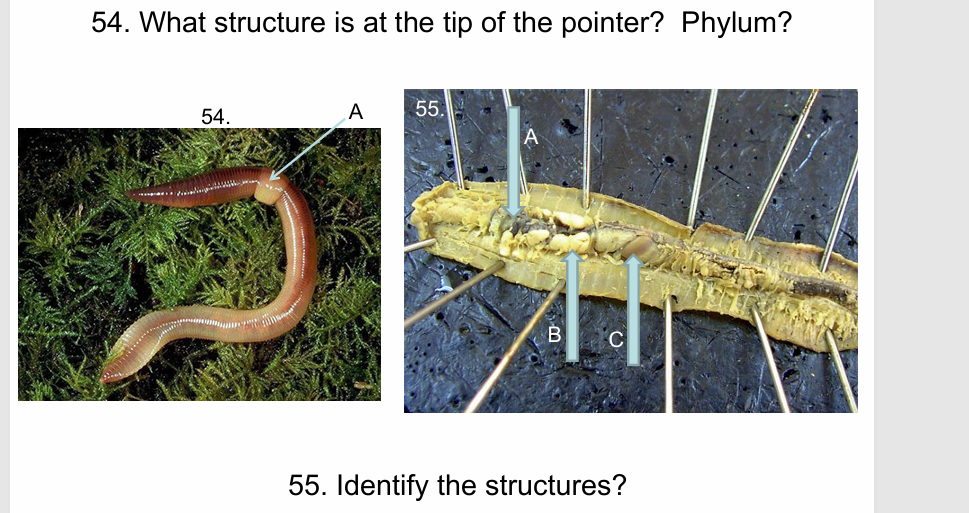
Clitellum, Annelida
A) Heart, B) Seminal vesicles, C) Crop
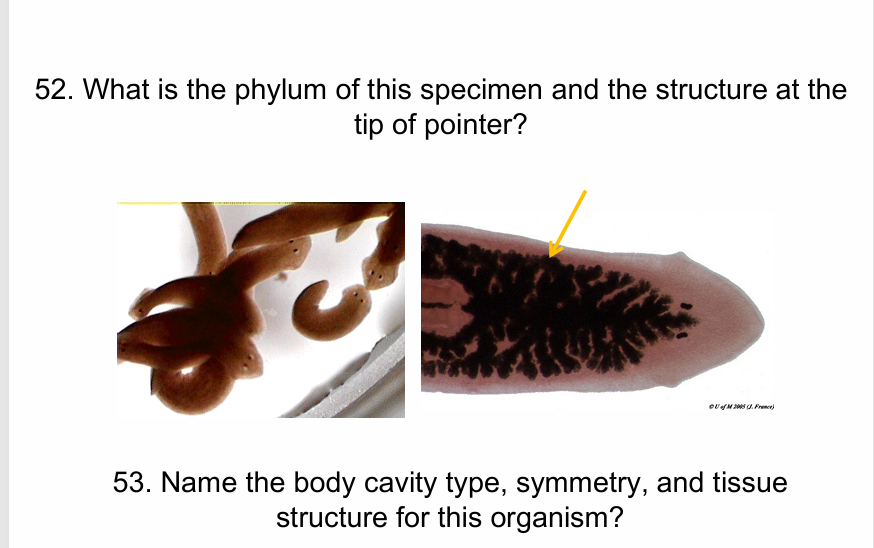
Platyhelminthes, intestines
Acoelomate, Bilateral, triploblastic
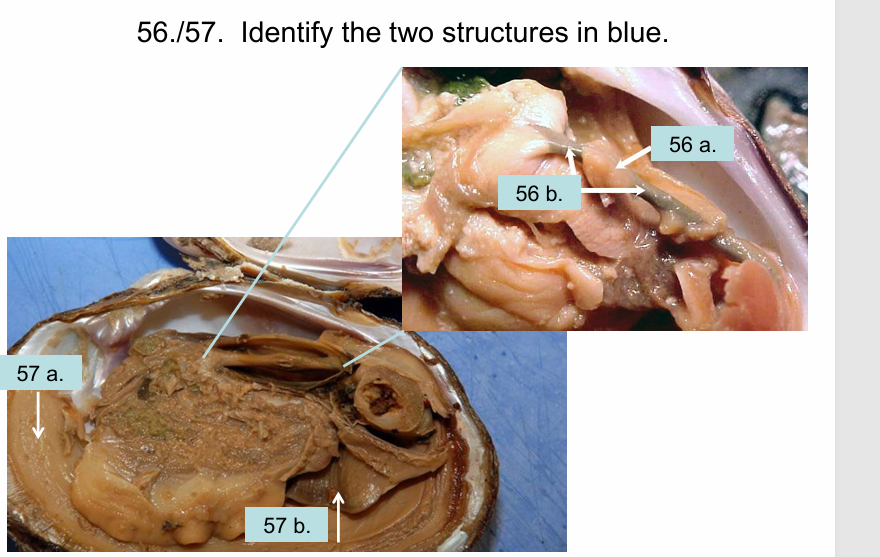
A) Heart, B) Intestine
A) Mantle - produces the shell B) Gill - respiration
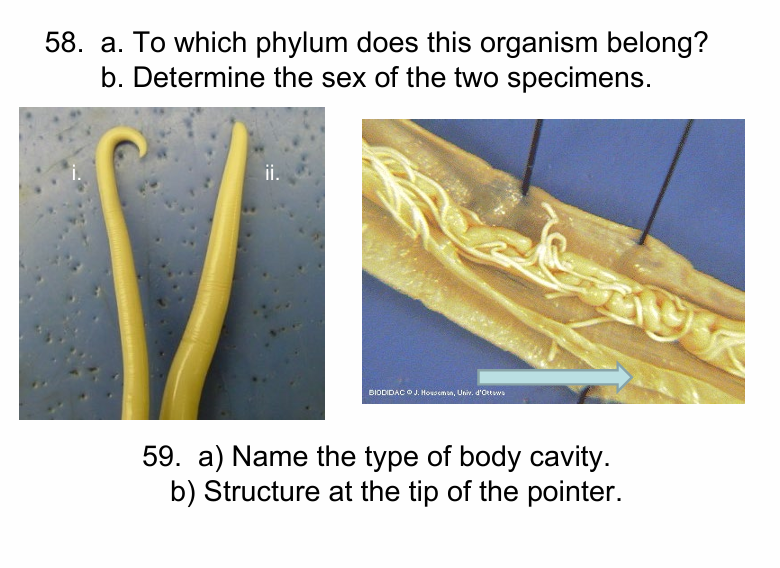
A. Nematoda: i) Male (spicule), i) Female
A) Pseudocoelomate; B) Intestine
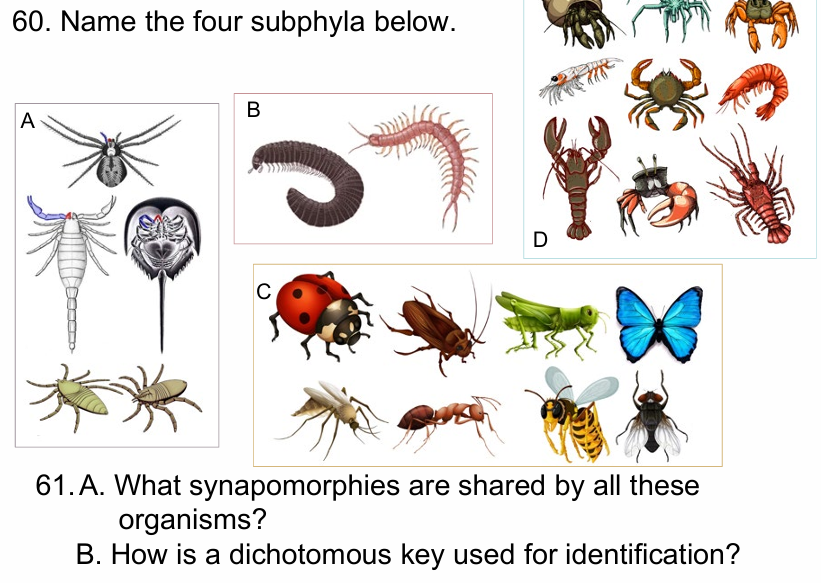
A) Chelicerates, B) Myriapods: C) Hexapods; D) Crustaceans
A) Chitinous exoskeleton; Paired Jointed Appendages, Body
Segmentation
B) It uses key characteristics to all organisms within a clade (ie. phylum, subphylum, genus, species).
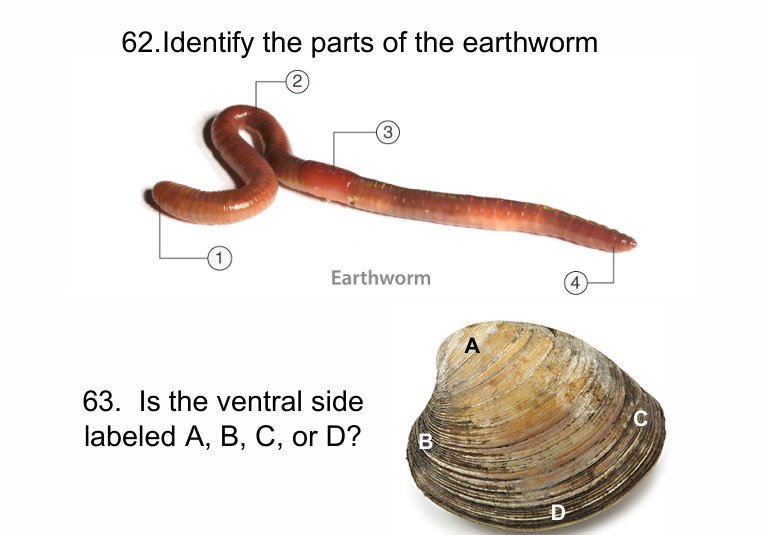
1. anterior end; 2. metameric segmentation; 3. clitellum; 4. posterior end
D; A = dorsal (umbo), B = anterior, C = posterior

Echinodermata
Bilateral in larval stage; Penta-radial symmetry as an adult.

A. Deuterstomes: radial indeterminate cleavage; the blastopore becomes
• the anus and the mesodermal tissue is formed from the archenteron (folding)
B. Echinoderms and chordates

A) 1. Stereoscope or dissecting scope. Used to observe whole structures or
Whole organisms
2. Compound scope. Used to observe thinly sliced organisms or
microorganisms
B) 200 X magnification (10°20)
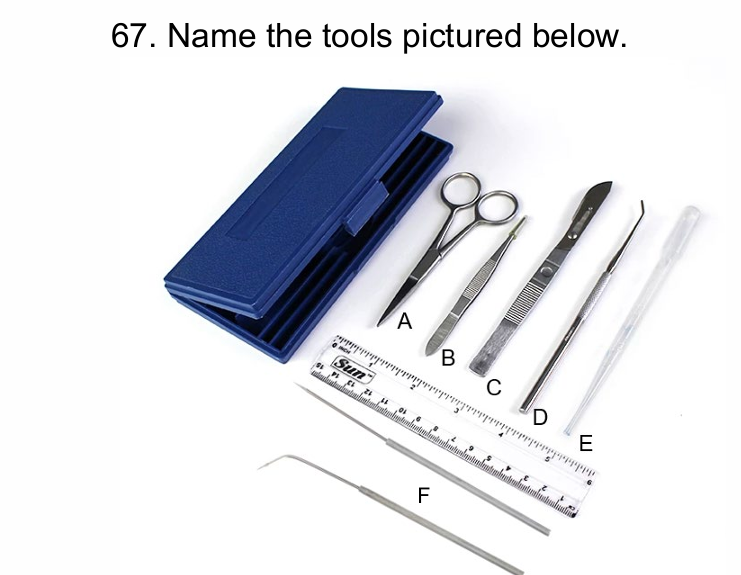
A)Scissors; B) Forceps; C) Scalpel; D) Probe, E) Disposable pipet, F)
Dissecting Needles

This is a chordate, which means it has pharangeal gill slits, notochord. dorsal hollow nerve cord, post-anal tail.
70. Chordata; lancolet (Branchiostoma lanceolatum, previously Amphioxus).
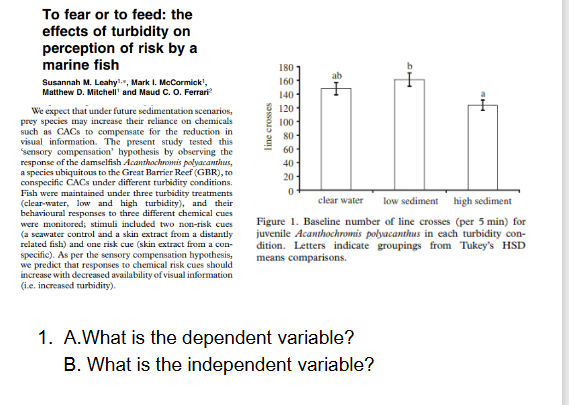
A. Line crosses (number of times fish crossed lines in tank);
B. Water
clarity or water turbidity leve
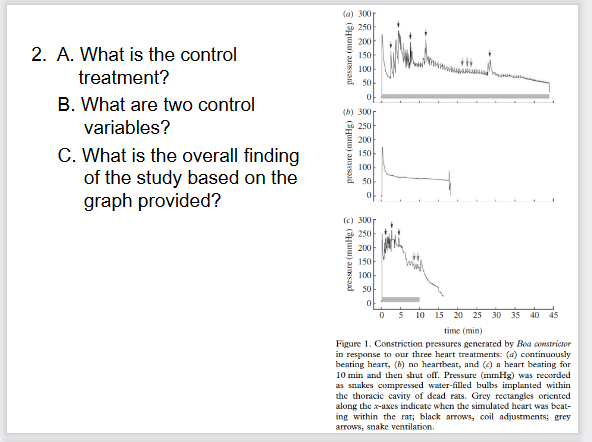
A. No heartbeat; B. Snake health, feeding regime, species,
environmental conditions (light, cage size, cleaning times, etc.) C.
Snakes adjust their constriction based on the prey’s heartbeat.
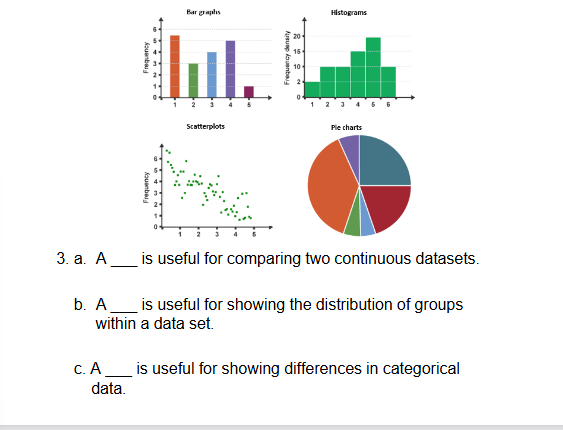
A. Line; B. Histogram; C. Bar

C – this is a hypothesis with a measurable outcome; all the others
have a measurable outcome
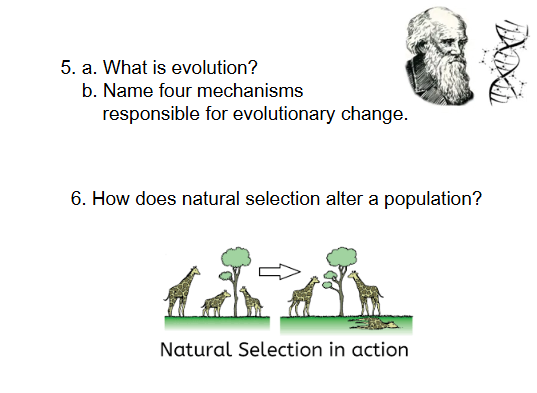
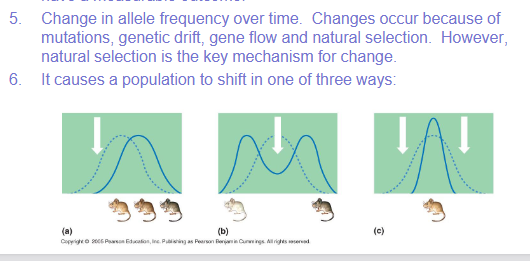

Evolution is the phenomenon and natural selection is the
mechanism. Natural selection is the key event that causes change
in populations, but it is not the only mechanism because it is not
random. Natural selection acts on an individual’s phenotype.
Evolution acts on a population
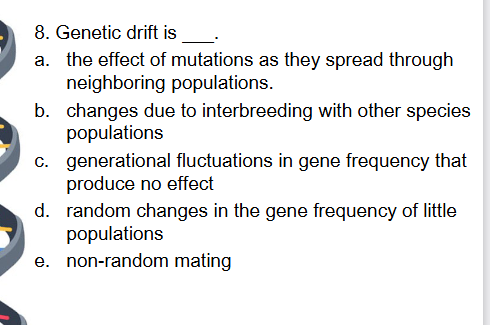
D – occurs in small populations.
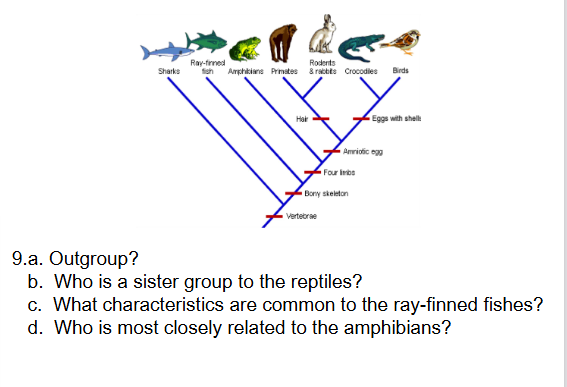
Cladogram:
a. Sharks
b. Reptiles (crocs and birds) are most closely related to the
mammals (primates, rodents, and rabbits).
c. Vertebrae and a bony skeleton
d. Any of the amniotes (mammals and reptiles)
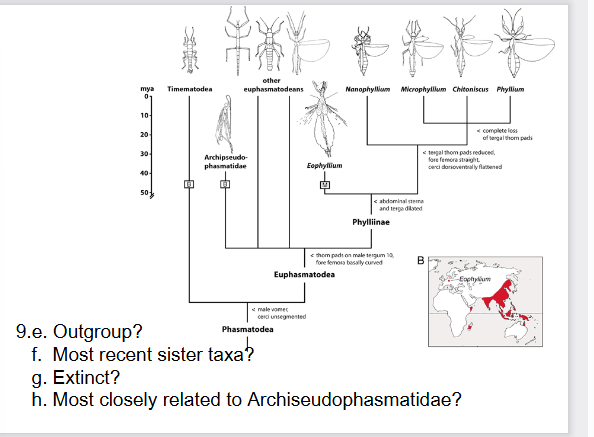
e. Timematodea (branched first)
f. Phyllium, Chitoniscus, Microphyllium (most recent common
ancestor on timeline)
g. Archipseudophasmatidae and Eophyllium (branch does not
extend to present day)
h. other euphasmatodeans and Phyllinae (sister groups)
Note: The lack of dichotomy or presence of a polytomy indicates
that the phylogeny is not well understood for these groups.