Lecture 04 - Cognitive Processing and Academic Skills
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are 2 origins of memory?
Infants remember, forget, and can be prompted to remember things they've forgotten
e.g. mobile and foot experiment with babies
improvements in memory are related to growth in the brain
hippocampus responsible for initial storage of info
frontal cortex develops later and is related to retrieval of stored memories
What four strategies do older children use to remember?
rehearsal
organization
elaboration
chunking
What is rehearsal?
repeating info that must be remembered
What is organization?
structuring material to be remembered so that related info is placed together
What is elaborating?
embellishing info to be remembered to make it more memorable or meaningful to self
What is chunking?
process of organizing related terms into one meaningful group
What is metacognitive knowledge? What occurs as children get older?
knowledge about cognition
improve with age
What is metamemory? How does it develop for children?
memory/knowledge about memory
develops in parallel with metacognitive
What kinds of memory strategies to children often use?
external strategies
e.g. using external aids (writing down events in school agenda)
What basic approach can we use for choosing problem solving strategies?
determine goal → select strategy → use strategy → monitor strategy (was it effective or ineffective?)
Does knowledge help memory or not?
Knowledge helps recall memory AND knowledge can also distort our recall
What are scripts?
memory structures that describe the sequence in which events occurs?
e.g. 'What did you do last Friday?' use a script to help you: 'My day starts with a class at 11:30 oh right I had a quiz in PHIL210, etc.'
Script cued you to remember
What is autobiographical memory?
people’s memory of their own lives
e.g. 'Tell me about what you did over the summer?'
What is infantile amnesia? What age is this usually true?
inability to remember events from early life
before 3 years old, it is difficult to remember things that occurred to you at that age
What was the shrinking machine experiment and what did it tell us about infantile amnesia?
Incredible shrinking machine: box that is supposed to shrink balloons into tennis ball size (e.g. beach ball in machine and someone replaces it with a small beach ball
show this to young children
later ask children when they are older about it and most can't remember it BUT if you show them pictures of it, they remember it better
If you ask them in language about an event when they didn't know language and couldn't encode event in language = difficult to remember
If you show picture about event that they could visually encode years ago = can remember
How can preschoolers’ eyewitness testimony be distorted?
by adults suggestions, learned stereotypes
Briefly describe the Texas death row case in 1987:
Entire case was on a child's testimony
Child's mother had told child on multiple occasions that guy was a 'bad man'
Providing a schema relating to his character before event she allegedly witnessed
Pre-existing knowledge influencing child's memory
From interviews with child, she possessed a deeply inherited stereotype about the man
Child was extensively interviewed about what she said she had witnessed
Interview asked a lot of leading questions
Leading question: question that biases your answer in the way it is formulated (how much blood was on the shirt?)
Child eventually took back statement saying that interviews and pre-existing schemas biased her
Explain the Sam Stone trial? What were the four conditions tested?
control
stereotype
suggestions
stereotype + suggestions
What was the experiment set-up describe the 4 stages?
phase 1:
stereotypes and stereotypes + suggestions were told that this guy Sam is nice but clumsy (he fell down stairs and broke friends barbie)
phase 2:
sam visit daycare centre briefly
phase 3:
interviews (neutral interviews for control and stereotypes and suggestive interviews for suggestions and stereotypes + suggestions_
asking leading questions or planting false info
phase 4:
asked children about Sam and his actions
What were the results from the Sam Stone experiment?
almost half the children in the stereotypes + suggestions condition ‘recalled’ events that never happened!
suggestions next followed by stereotypes and then control
What 3 strategies for children and adolescents use for problem solving?
heuristics
analytical problem solving
collaboration enhances problem solving
What are heuristics?
‘rules of thumb’ based on personal experiences
e.g. availability heuristic = recall things that are more readily available
system 1
What is analytical problem solving?
more effortful and incorporates logical or mathematical rules
not using shortcuts and taking time
system 2
What are different strategies for learning how to read?
word recognition
comprehension
phonological awareness
What is word recgnition?
process of identifying a unique pattern of letters
emphasizing remembering what words look like
focus on whole word
e.g. caregiver is reading with child and points and says 'rabbit' as they point to a rabbit
What is comprehension?
extracting meaning from a sequence of words
semantics of words
remembering what words go with what
What is phonological awareness?
knowing letters and letter sounds
pre-reading skill
sounding out words
Why is learning to read in English so difficult?
wide inconsistencies in pronunciations
What are two approaches to teaching readings?
phonics
research indicates phonics instruction is essential
whole-language reading
What do beginner readers rely heavily on for learning how to read?
rely on sounding out words
BUT even beginning readers retrieve some words from memory
shorter words recalled from memory easier
Example game of learning via phonics?
write several word families (-at, -it, -op)
give letters
see how many real words are possible and read word aloud
reinforces grapheme-phoneme relationships
Example game of learning via whole-language approach?
choose picture book with rich illustrations and read aloud
ask students to predict what will happen next using story context and illustrations
develops comprehension and semantics
Does writing take longer than reading to develop?
yes!
learning to write takes years of effort
What 3 developmental things contribute to improvement in writing?
greater knowledge about topics
the more you know about something, the more you can write about it
greater understanding of how to organize writing
greater ease in dealing with mechanics
verbs, subject and where to place grammar elements
How can children be taught to be better writers?
teaching strategies for planning, drafting and revising
What strategy do we give to younger writers?
writing down info on topic as they retrieve from memory
What strategy do we give to adolescents?
deciding what info to include and how best to organize it for the point they want to convey
Do children have an early understanding of number? How do we know? Use experiment
yes!
Child is more surprised by impossible outcome
They expected the addition of the two rats
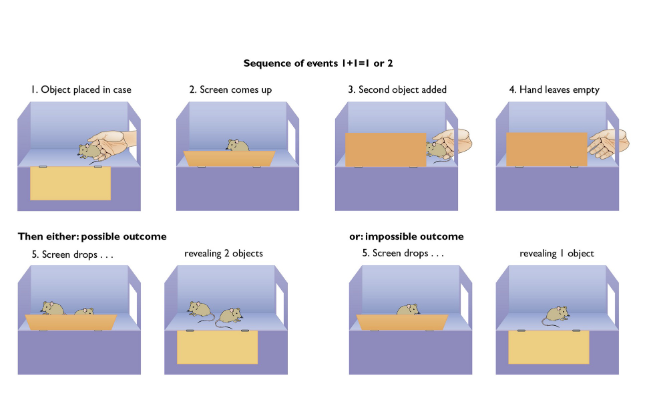
What three basic principles do children use when counting early on?
one-to-one
Each thing has its number when counting something
Four apples: 1, 2, 3, 4
Every apple has its number
Stable-order
Order is always the same
If you put something in order, that order stays
Idea if something is out of order
Cardinality
Last number that you count is bigger number
Last number in sequence is number that you have