Chapter 11: cell-cell interactions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the four types of cell junctions?
1) Tight Junctions (seals cells together)
2) Desmosomes (connect the cytoskeletons of cells)
3) Gap junctions (act as channels between cells)
4) Plasmodesmata (plants only)
What are tight junctions? Functions?
Water-tight seal formed between adjacent cells (composed of specialized proteins)
Prevents passage of molecules between cells
Found between epithelial cells (intestines, lungs, etc)
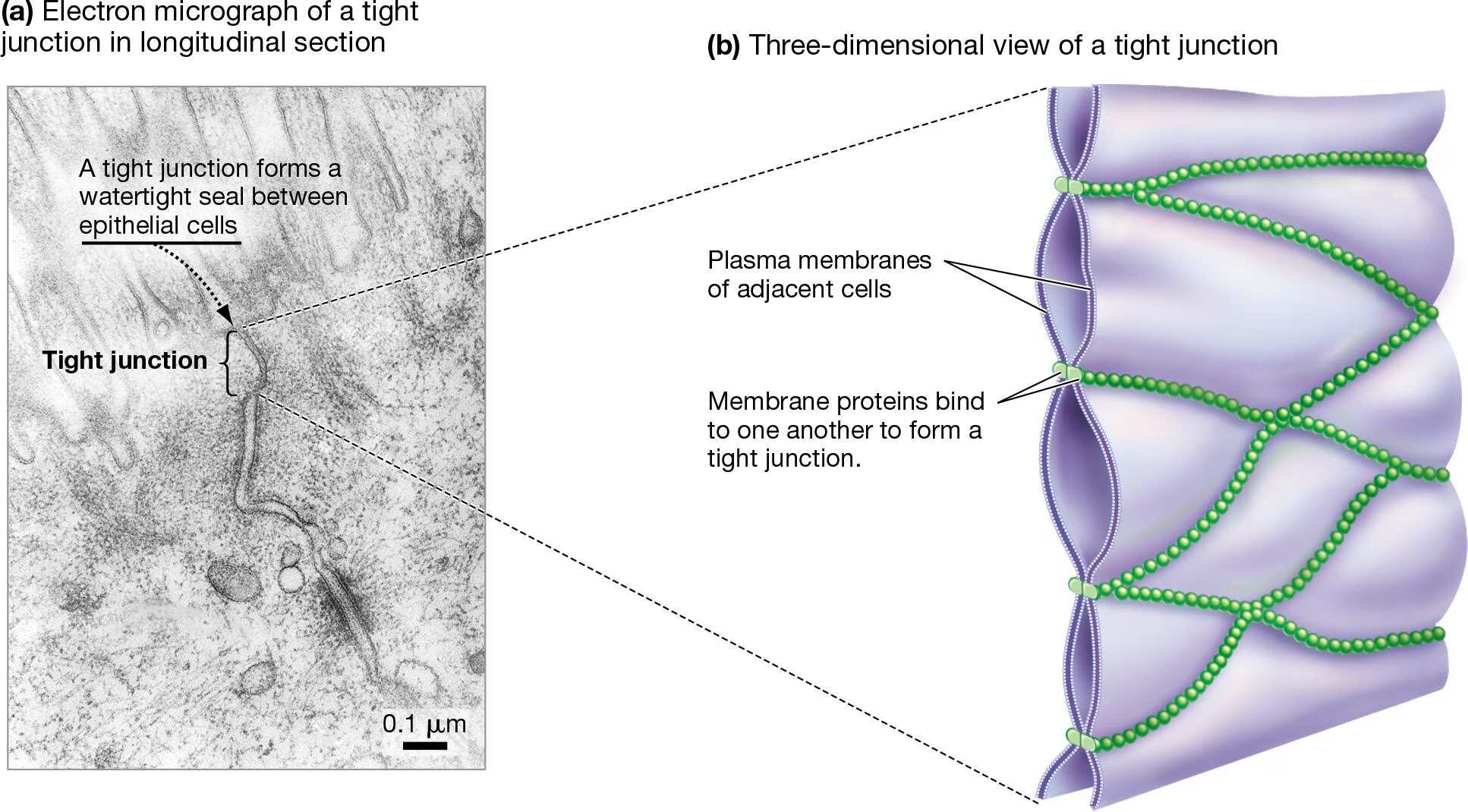
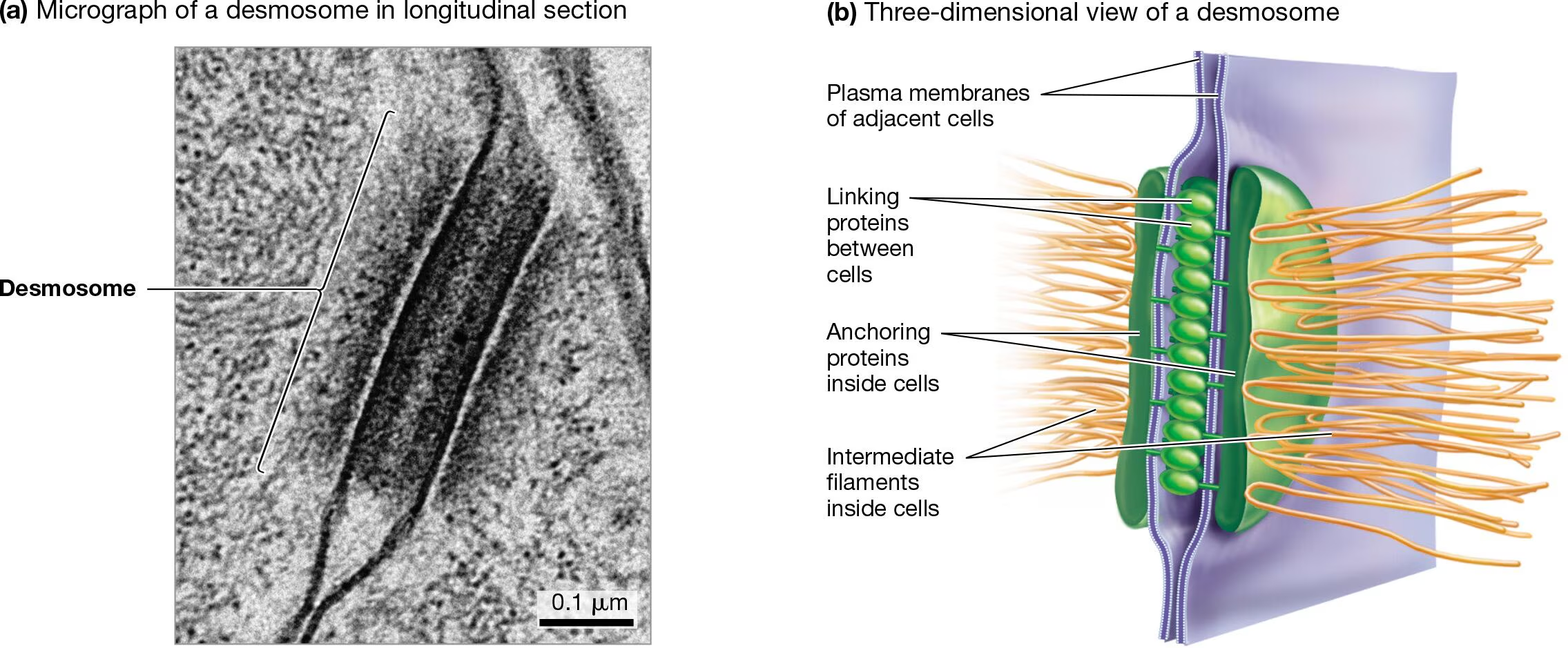
What are desmosomes? Functions?
Strong adhesions that anchor the cytoskeleton
Continuous structural support between cells
Found in tissues that experience intense mechanical stress (cardiac muscle, bladder, epithelia)
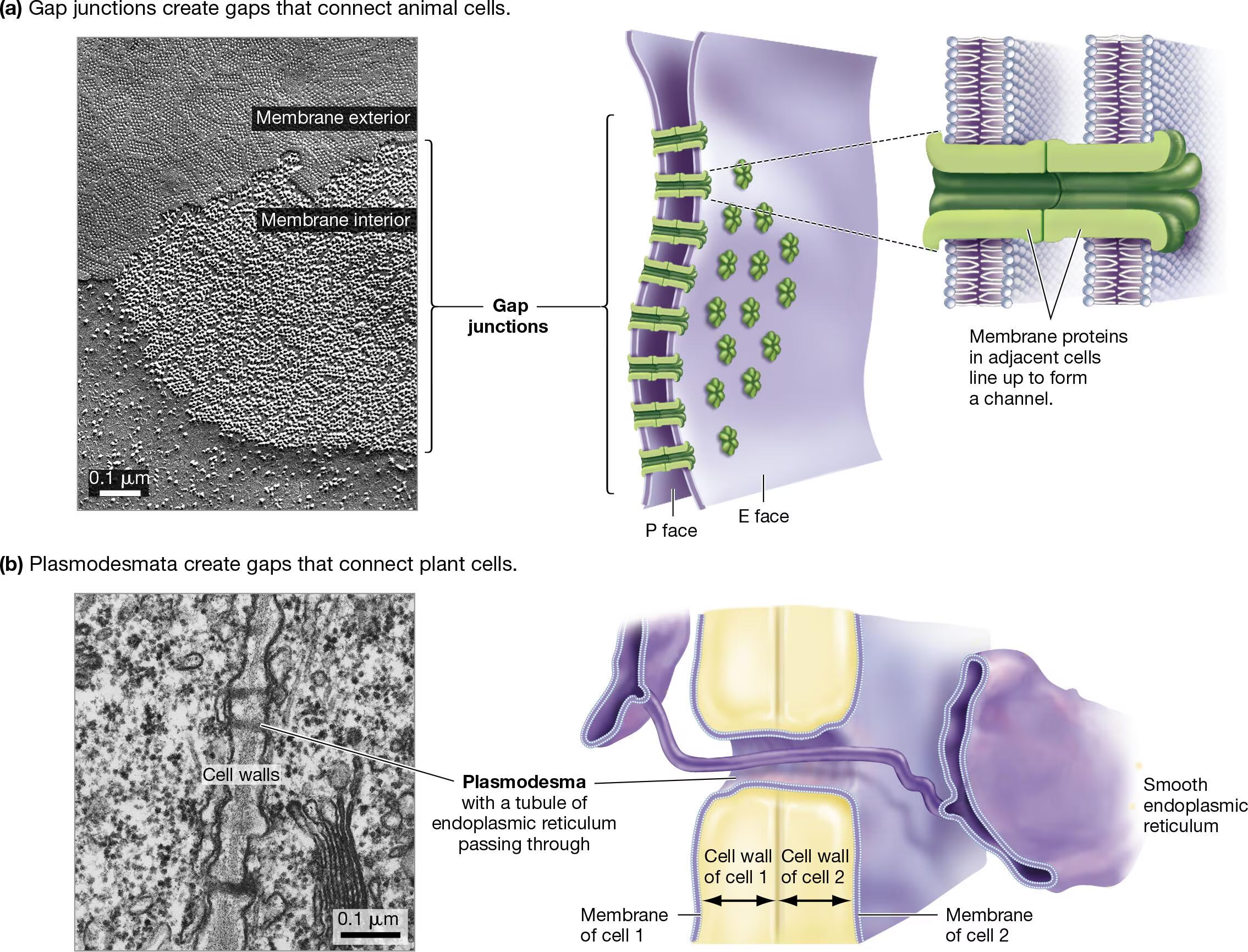
What are Gap Junctions? Functions?
Protein channels between adjacent cells
Allows direct communication between cells
Rapid passage of ions or small molecules
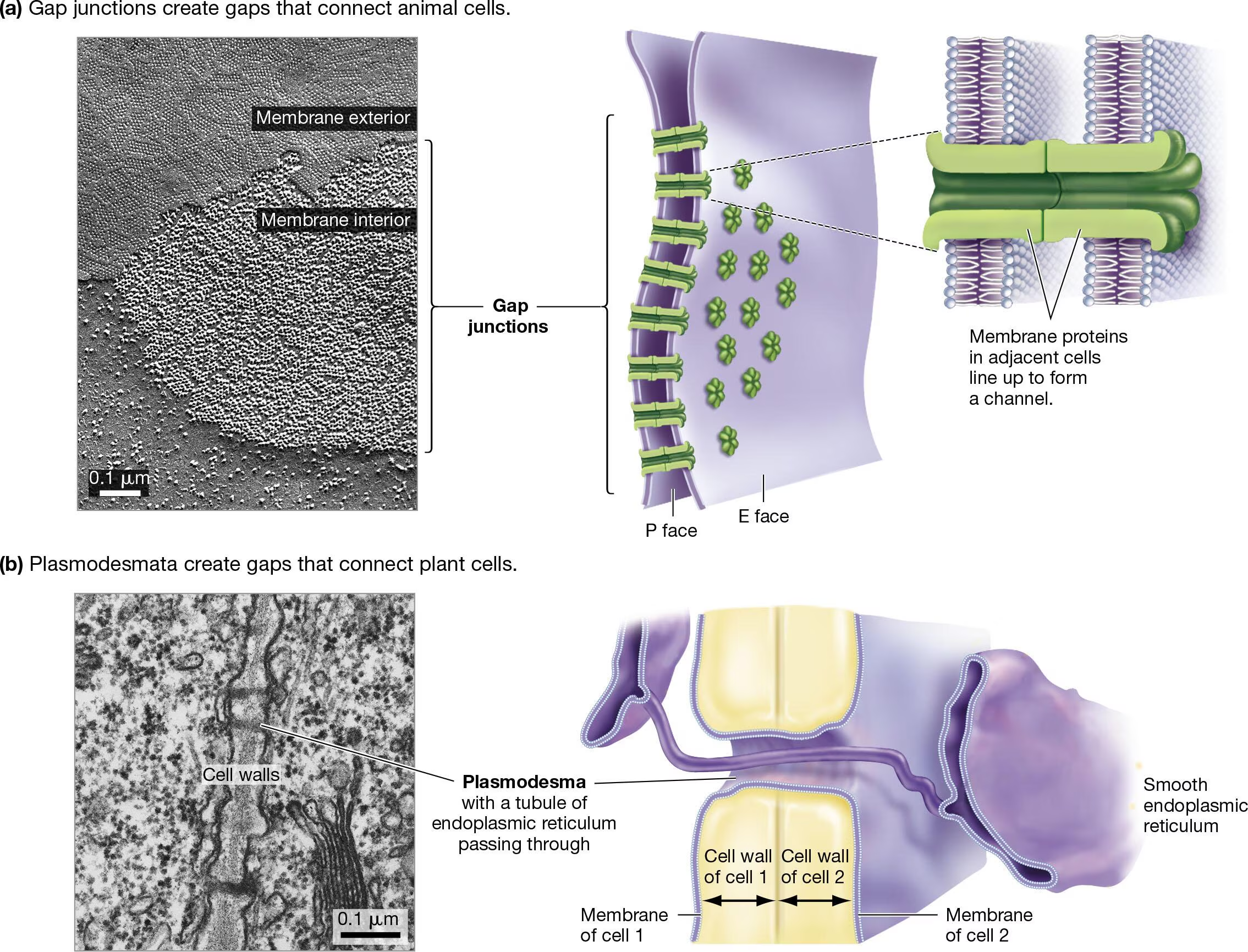
What is plasmodesmata (plants)? Functions?
Gap in cell walls
No proteins involved
Continuous plasma membrane and cytoplasm
Define hormones:
small molecules secreted to act on distant target cells
Steroids (sex), peptides (insulin, HGH), gas (ethylene), amino acid derivatives (adrenaline)
What are the steps of cell-cell signaling?
1) signal reception
different for lipid-soluble vs lipid-insoluble hormones
2) Signal processing (transduction)
second messengers or phosphorylation cascade
3) Signal Response
4) Signal Deactivation
What is a signal receptor?
Any cellular protein that binds to a particular signaling molecular and changes shape and activity after binding to a signal molecule
Where does the interaction between a signaling molecule and its receptor occur—inside the target cell or outside?
The answer depends on the signaling molecule’s ability to pass through plasma membranes.
lipid-soluble- inside
lipid-insoluble molecules- outside
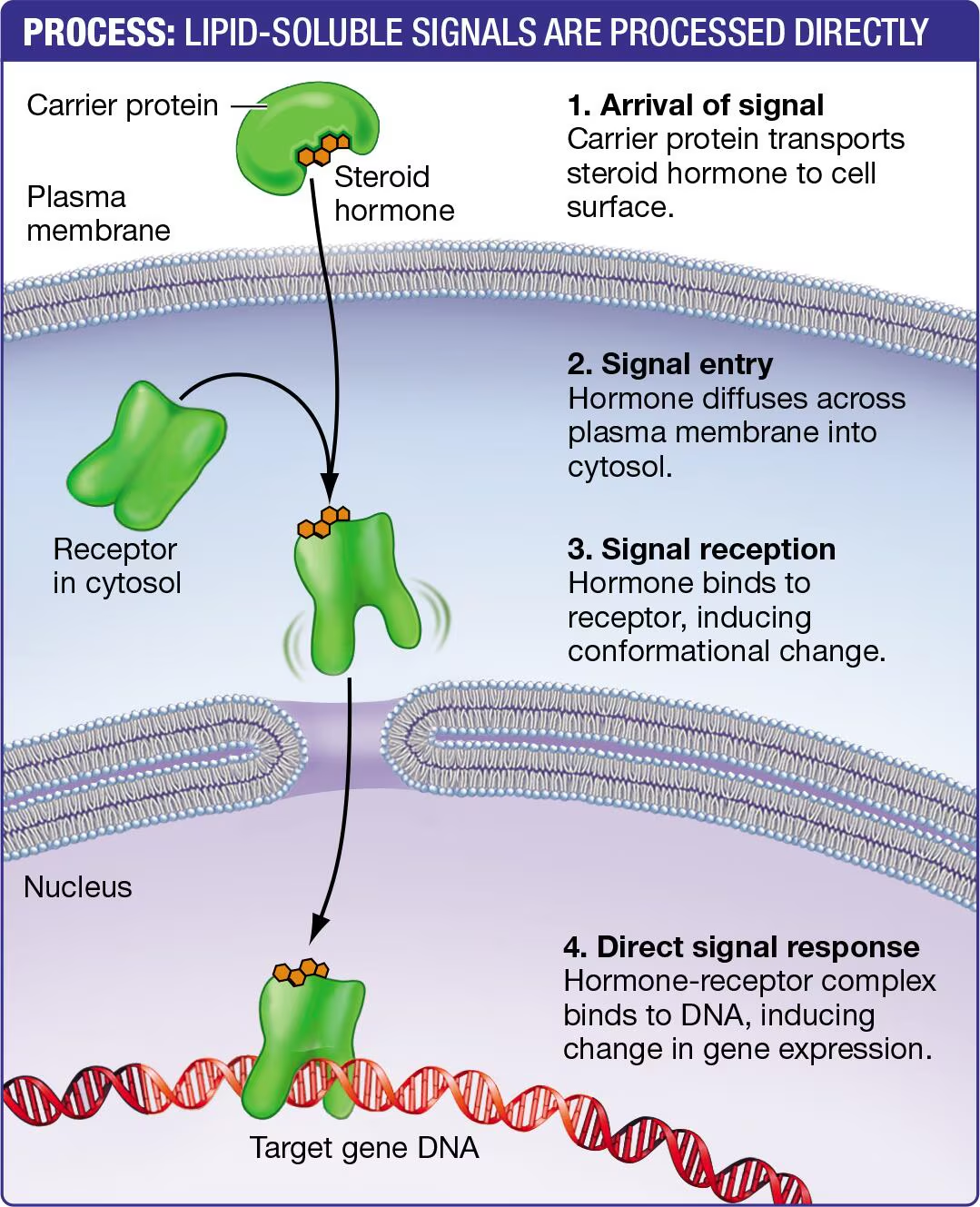
Lipid soluble functions?
Because they are hydrophobic, most lipid-soluble signaling molecules can be diffused across the cell membrane
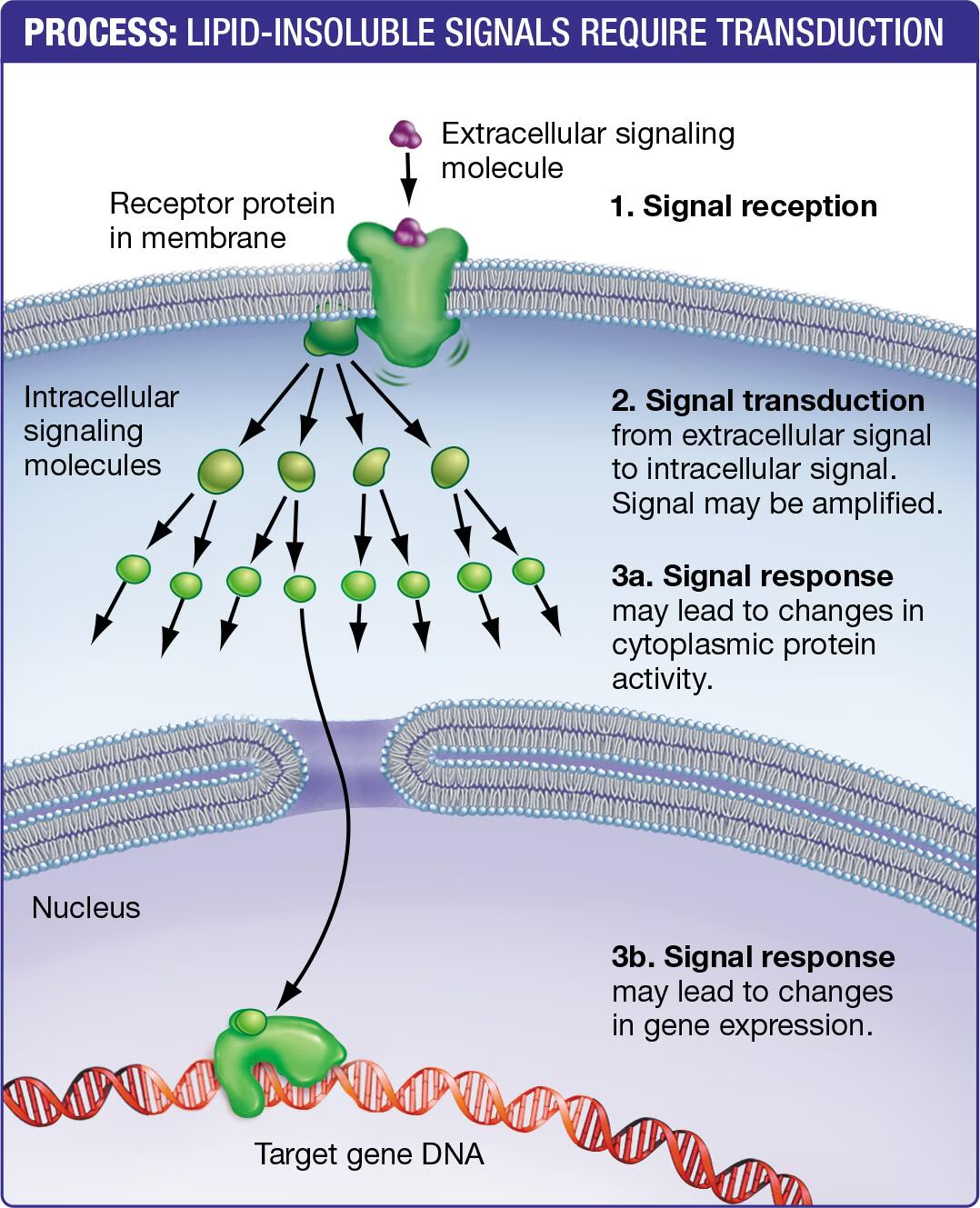
Lipid-insoluble signal reception and function?
Receptors are transmembrane proteins
Signal binding initiates a signaling pathway
Instead of direct response, the receptors trigger signal transduction
Conversion of an extracellular signal to an intracellular signal
Ex/
Second messengers
Phosphorylation cascade
What basic signal pathway must all receptors follow?
Signal molecule binds→receptor undergoes conformation in change→receptor activates signal transduction inside the cell
How do G Protein-couples receptors work?
1) G protein is inactive (bound to gdp); signal arrives and binds to the receptor
2) Signal-receptor complexes changes; G proteins binds GTP and splits into two
3) Activated G protein binds to an enzyme and starts product of second messenger, which triggers a response
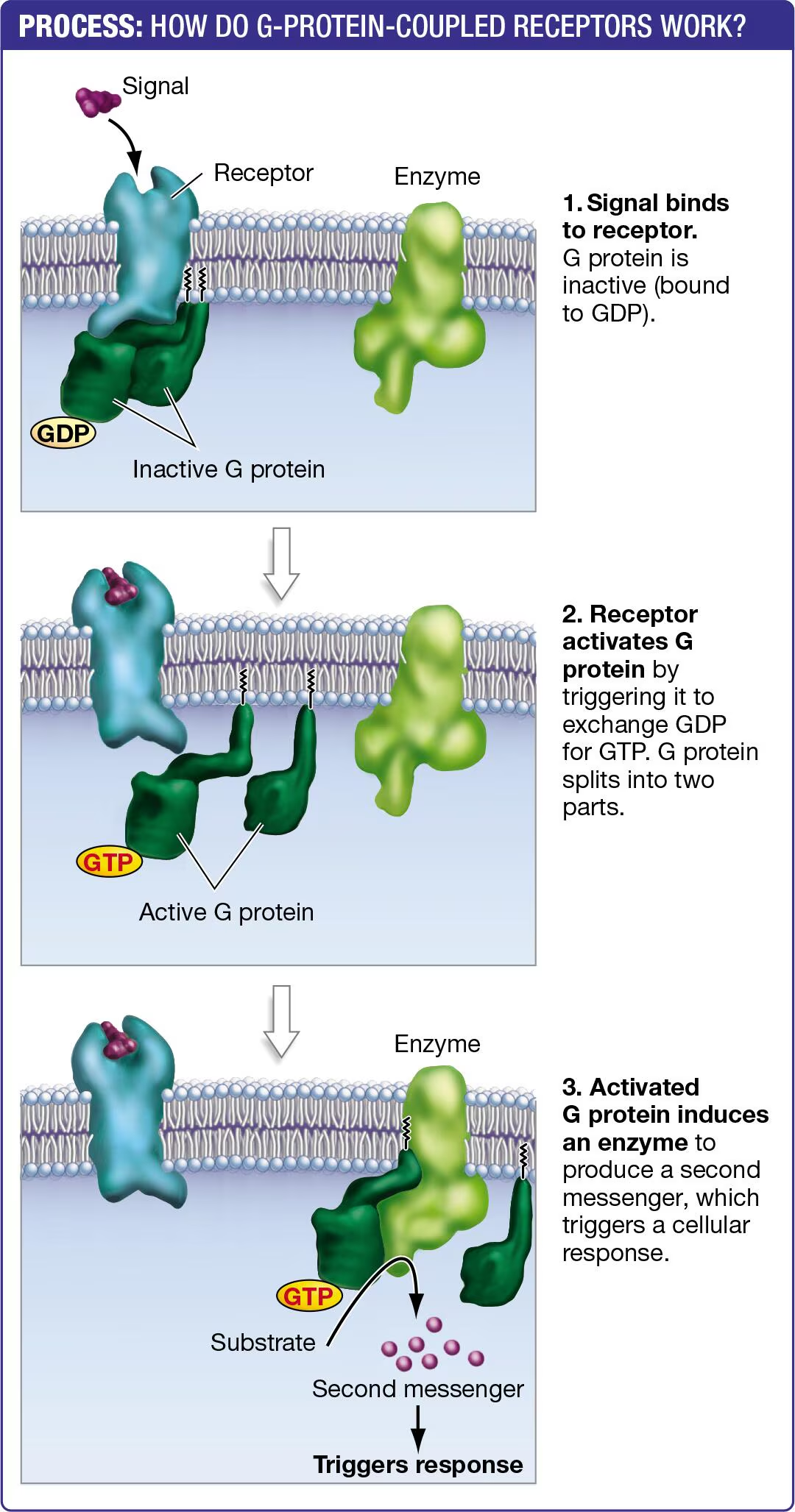
When are G proteins activated and deactivated?
Activated: when they bind to GTP
Deactivated: When a phosphate group is removed from GTP to form GDP
How do RTKs work?
1) a hormone binds to 2 subunits of RTK and cause them to form a dimer
2) The change in the RTK causes it to turn on kinase activity which allows it to phosphorylate itself at tyrosine residues
3) Proteins inside the cell bond to phosphorylated RTK forming a bridge called RAS
4) Ras exchanged GDP for GTP
When G proteins are activated by a signal receptor, they often trigger a key step in signal transduction:
The production of the second messenger
What are second messengers (signal transduction)
Small molecules that relay intraellular signals ( bunch of molecules get released, brute force way )
cAMP (cyclic AMP; derivative of ATP)- activated kinases
Enzymes that add phosphate groups
ions
What is signal transduction?
the process by which cells receive and respond to signals from outside the cell
What is phosphorylation cascade (signal transduction)
Each kinase phosphorylates a different kinase until a response is triggered
(Very step-wise, much more controlled)
Signal Deactivation
Responses and deactivation can occur very rapidly
Deactivation is different for different signal types
What are examples of signal deactivation
G Proteins
Inactivated after GTP hydrolysis
Phosphorylation cascades
Phosphatases remove phosphate groups from components
Second messengers
Ca2+ - membrane pumps return to storage
cAMP, etc - enzymes break down
Where do soluble molecules bind to?
Cytosol
typically transported to the nucleus to affect transcription of DNA