AQA GCSE Geography - Weather hazards
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Economic impact
The effect of an event on the wealth of an area or community.
Environmental impact
The effect of an event on the landscape and ecology of the surrounding area.
Extreme weather
This is when a weather event is significantly different from the average or usual weather pattern, and is especially severe or unseasonal. This may take place over one day or a period of time. A severe snow blizzard or heat wave are two examples of extreme weather in the UK.
Global atmospheric circulation
The worldwide system of winds, which transports heat from tropical to polar latitudes. In each hemisphere, air also circulates through the entire depth of the troposphere which extends up to 15 km.
Immediate responses
The reaction of people as the disaster happens and in the immediate aftermath.
Long-term responses
Later reactions that occur in the weeks, months and years after the event.
Management strategies
Techniques of controlling, responding to, or dealing with an event.
Monitoring
Recording physical changes, such as tracking a tropical storm by satellite, to help forecast when and where a natural hazard might strike.
Planning
Actions taken to enable communities to respond to, and recover from, natural disasters, through measures such as emergency evacuation plans, information management, communications and warning systems.
Prediction
Attempts to forecast when and where a natural hazard will strike, based on current knowledge. This can be done to some extent for tropical storms (and volcanic eruptions, but less reliably for earthquakes).
Primary effects
The initial impact of a natural event on people and property, caused directly by it, for instance buildings being partially or wholly destroyed by a tropical storm.
Protection
Actions taken before a hazard strikes to reduce its impact, such as educating people or improving building design.
Secondary effects
The after-effects that occur as indirect impacts of a natural event, sometimes on a longer timescale, for instance impact on access to potable water can lead to spread of disease.
Social impact
The effect of an event on the lives of people or community.
Tropical storm (hurricane, cyclone, typhoon)
An area of low pressure with winds moving in a spiral around the calm central point called the eye of the storm. Winds are powerful and rainfall is heavy.
Adaptation
Actions taken to adjust to natural events such as climate change, to reduce potential damage, limit the impacts, take advantage of opportunities, or cope with the consequences.
Climate change
A long-term change in the earth's climate, especially a change due to an increase in the average atmospheric temperature.
Mitigation
Action taken to reduce or eliminate the long-term risk to human life and property from natural hazards, such as building earthquake-proof buildings or making international agreements about carbon reduction targets.
Orbital changes
Changes in the pathway of the Earth around the Sun.
Quaternary period
The period of geological time from about 2.6 million years ago to the present. It is characterized by the appearance and development of humans and includes the Pleistocene and Holocene Epochs.
Solar energy
Drives the Earth's atmospheric circulation
Atmosphere
A mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth
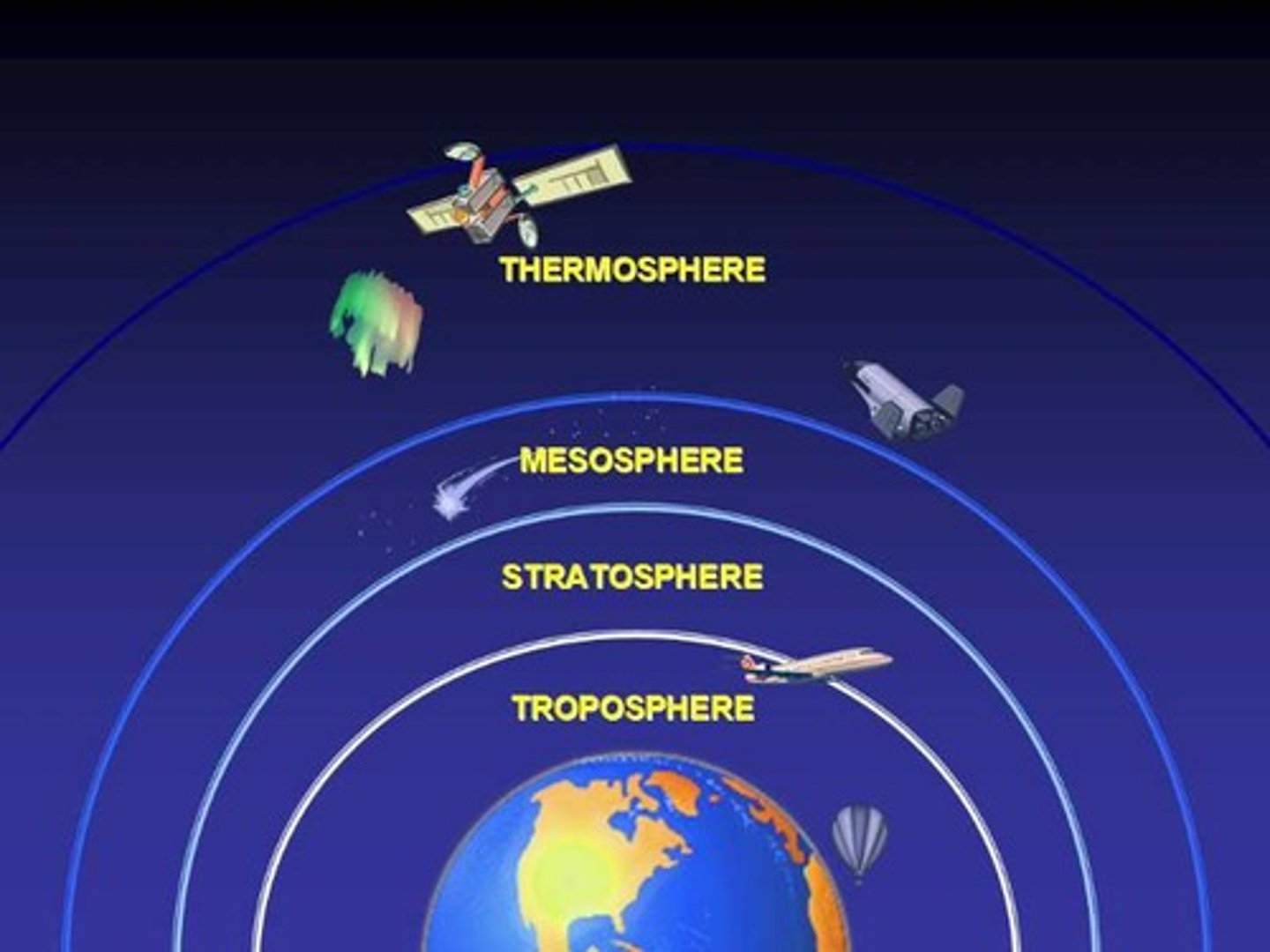
Atmospheric circulation
This process redistributes heat towards the poles and gives the broad patterns of air movement
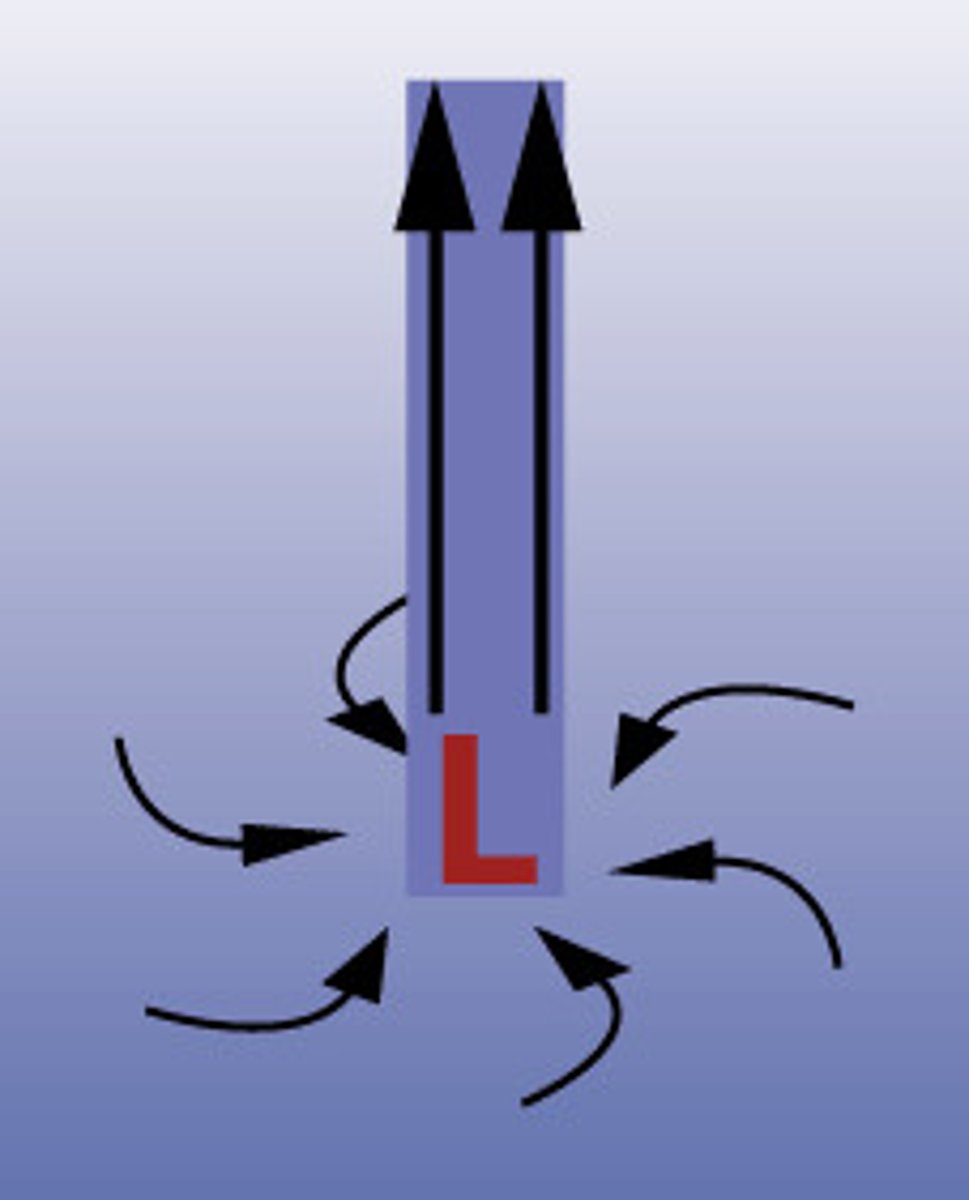
Low Pressure
is where warm air rises usually bringing wet, stormy weather.
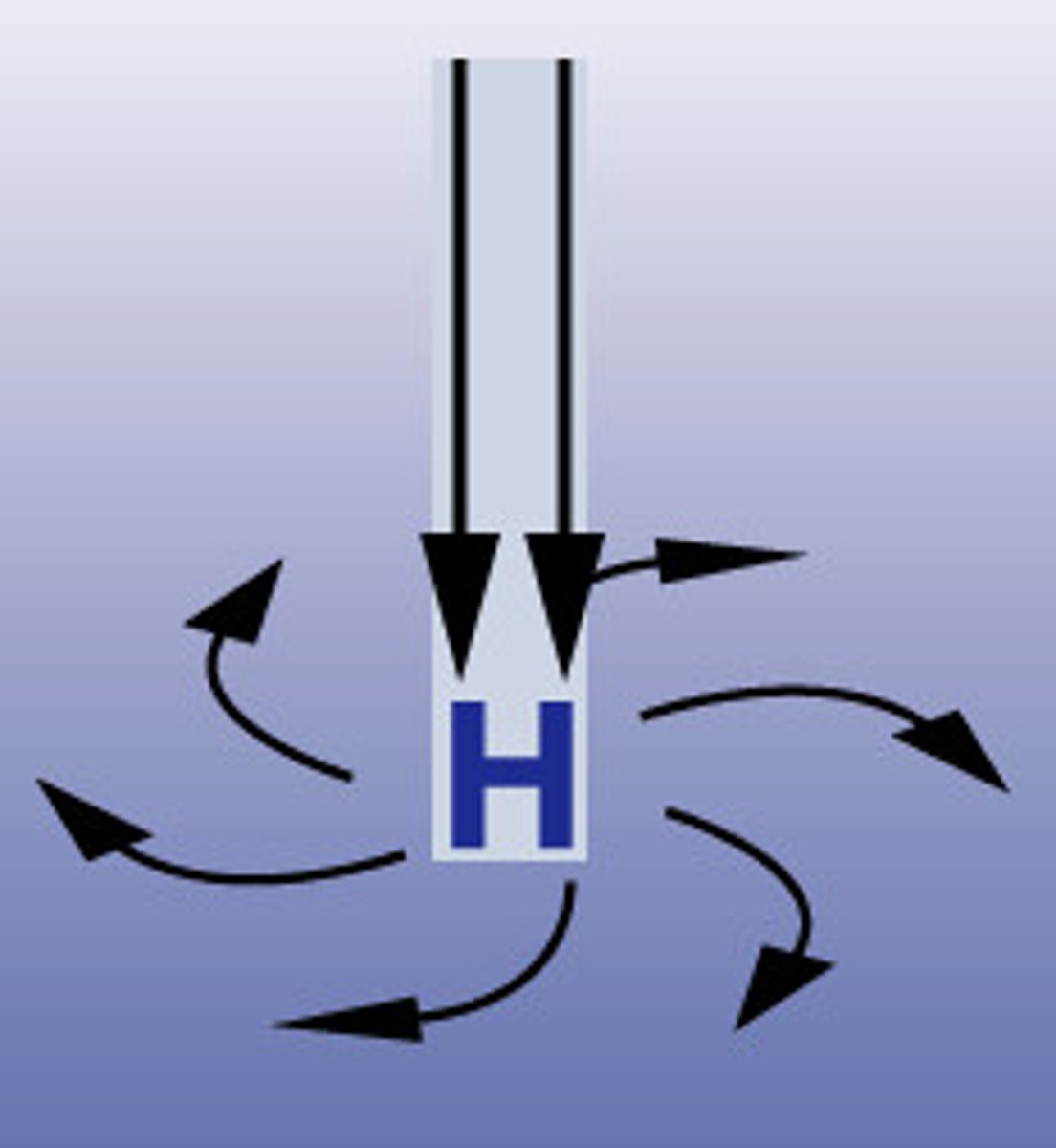
High Pressure
is where air sinks giving dryer, calmer conditions
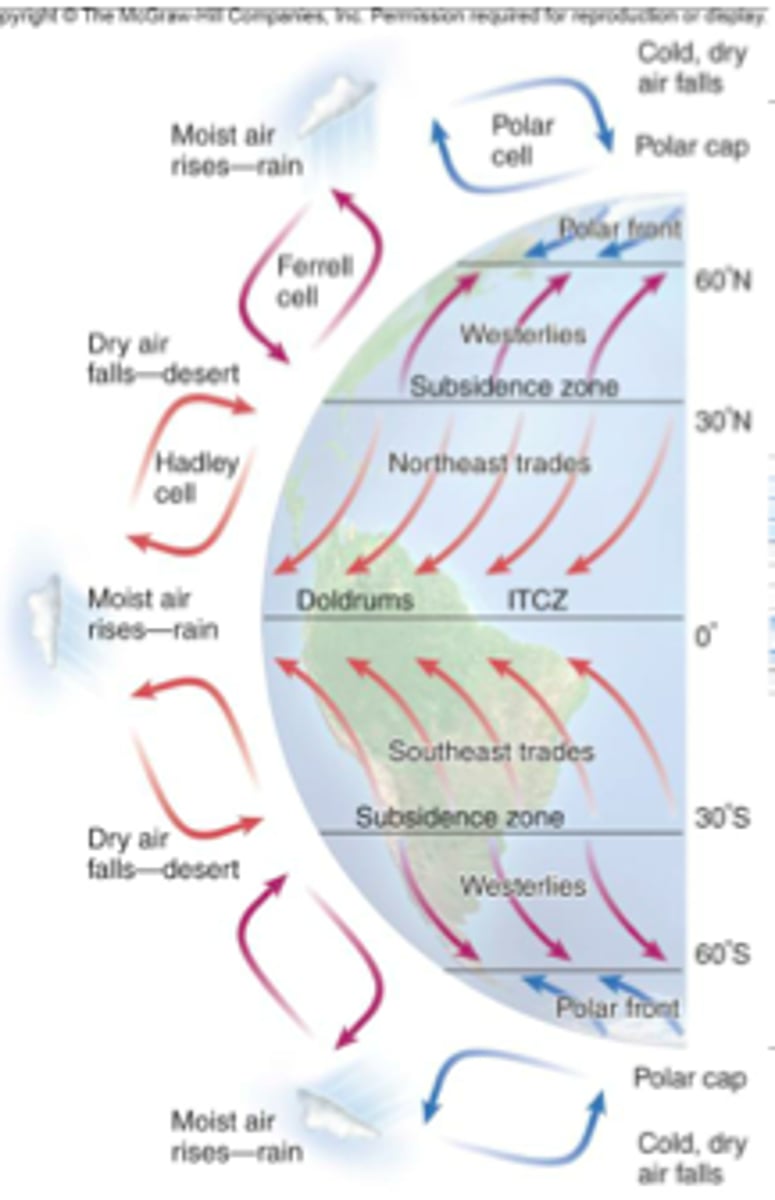
Hadley cell
The cell that drives air around tropical regions
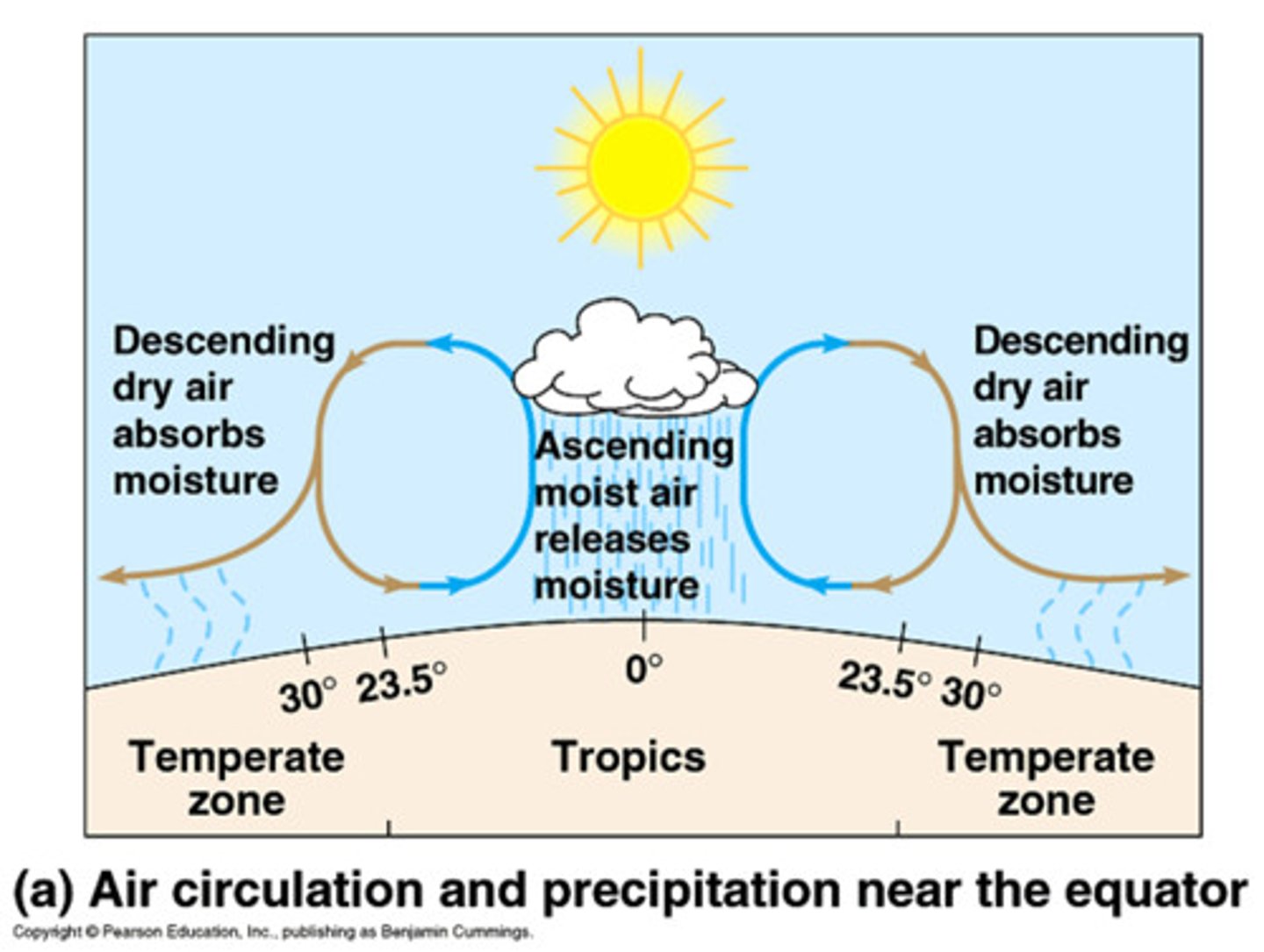
Ferrel Cell
The cell that moves air from 30 degrees to 60 degrees in the mid latitudes
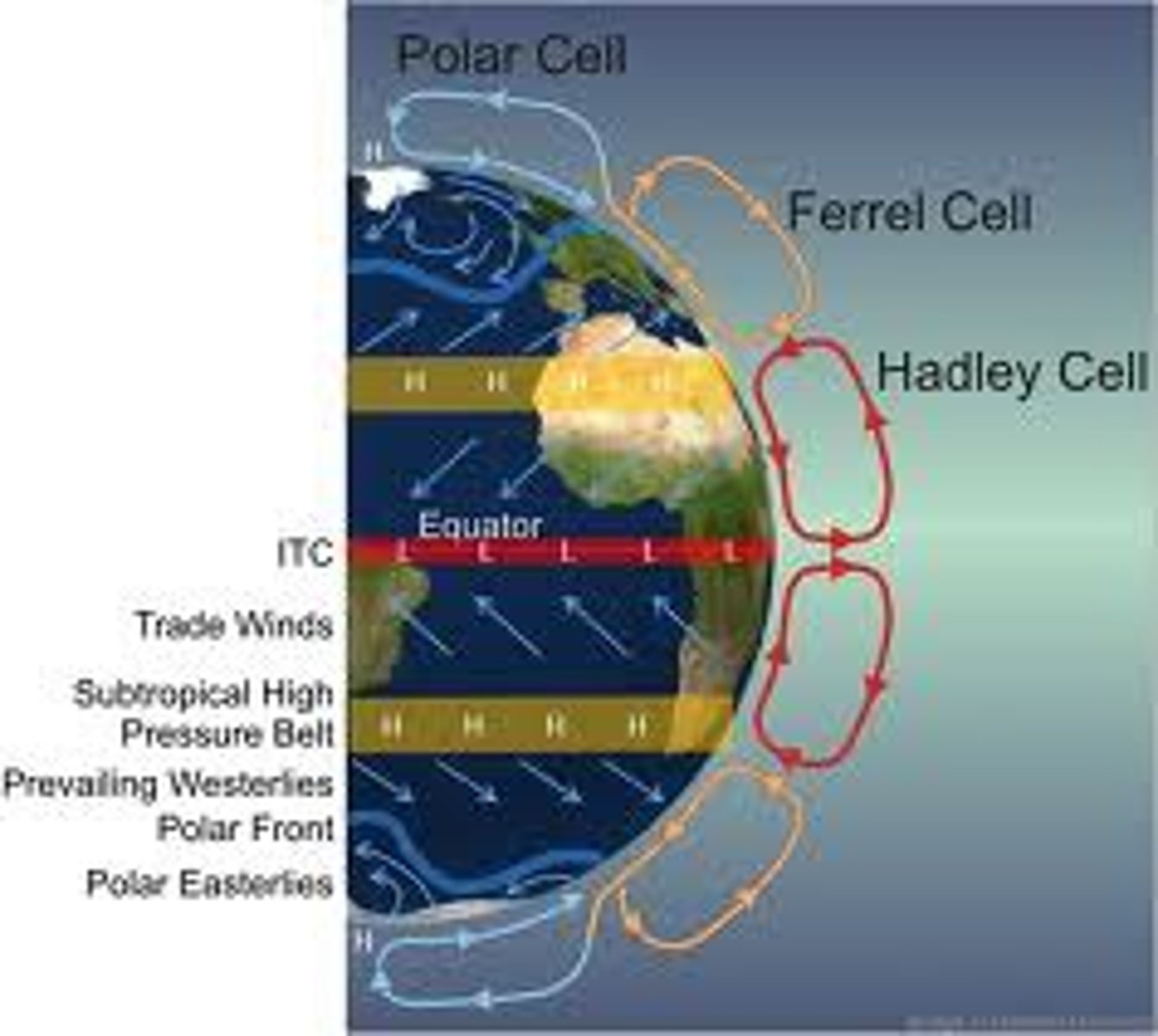
Polar Cell
Weak circulation cell that occurs between 60 and 90 degrees latitude.
Trade winds
steady winds in tropical latitudes that blow toward the equator from the north and south
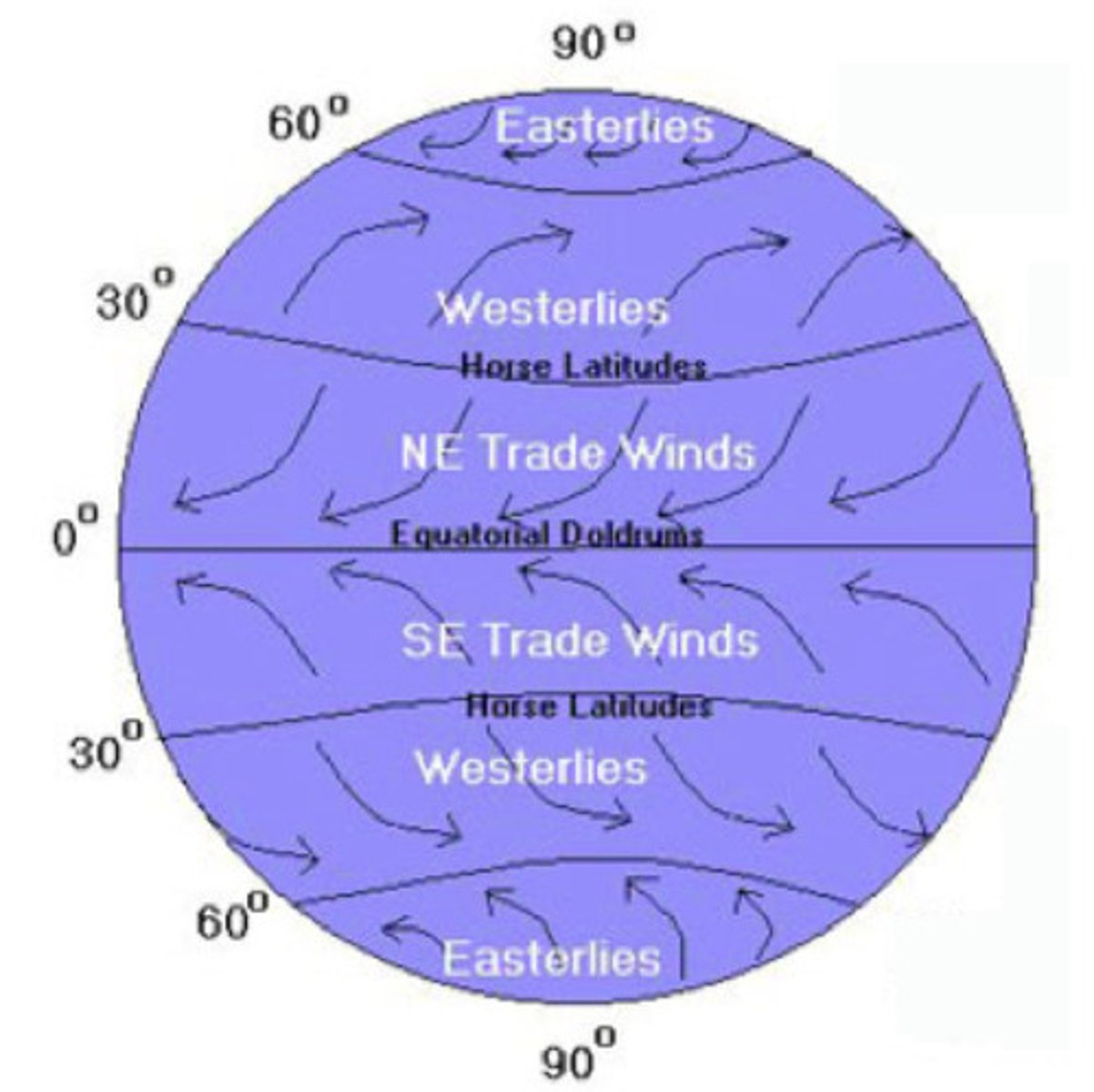
Prevailing westerlies
winds that blow west to east between 30 and 60 degrees in the northern and southern hemispheres
Deserts
are ceated where air sinks on the model