Pathology of nodules and liver tumors
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
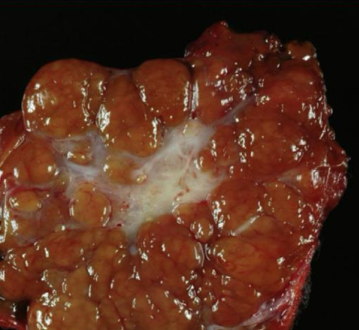
What’s this in liver?
Focal nodular hyperplasia
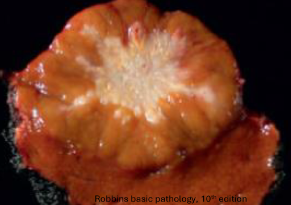
What’s this in liver?
Focal nodular hyperplasia
What’s this in liver?
Focal nodular hyperplasia.
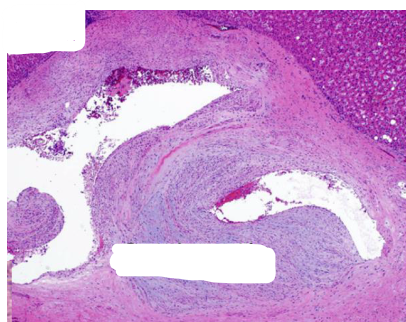
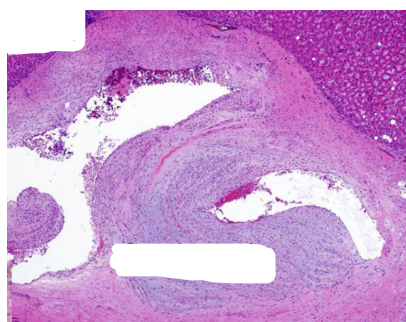
What’s in the center area? This is liver.
Central scar with vascular shunt. Large abnormal vessels in the central scar.
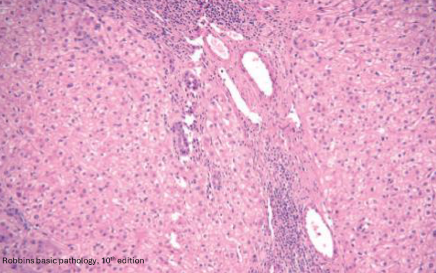
What’s this disease? In liver. Describe the slide.
Focal nodular hyperplasia. Normal hepatocytes separated by thickened sinusoids.
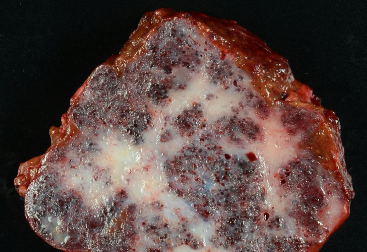
What’s this in liver?
Cavernous hemangioma
What’s the most common benign liver tumor?
Cavernous hemangioma
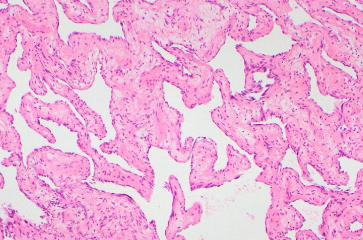
What’s this in liver?
Cavernous hemangioma. Vascular spaces are lined by single layers of flattened endothelial cells.
What increases the risk of developing a hepatocellular adenoma?
Sex hormones (Oral contraceptives or anabolic steroids). Cessation of these may cause the tumor to regress.
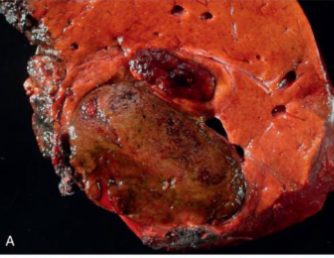
What’s this in liver?
Hepatocellular adenoma
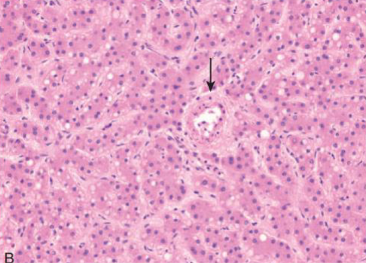
What disease is this in liver?
Hepatocellular adenoma
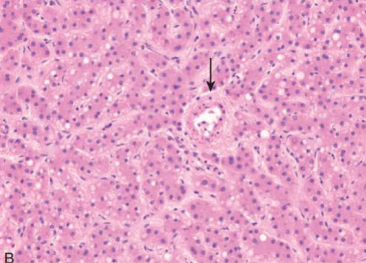
What is the arrow showing? In liver.
In hepatocellular adenoma, there are unpaired arteries and interlobular bile ducts are missing. The arrow shows an artery on its own, not in a portal triad.
Which continent is hepatocellular carcinoma most common?
Asia
Top 2 risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma
1) Viral infections (HBV and HCV). 2) Toxic injury (Alcohol or Aflatoxin)
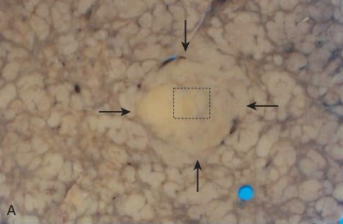
What’s this in liver?
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Large dysplastic nodule.
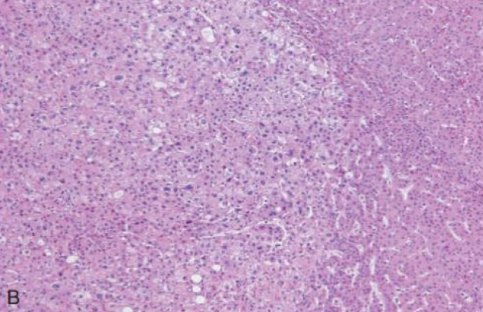
What’s this in liver?
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Well differentiated sub-nodule (left) in the carcinoma.
Scirrhous subtype of HCC is caused by which gene mutations?
TSC1/TSC2
Steatohepatic subtype of HCC is caused by which gene mutations?
IL6/JAK/STAT activation
Macrotrabecular massive subtype of HCC is caused by which gene mutations?
TP53 mutation and FGF19 amplification
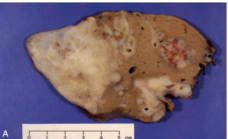
What’s this in liver?
Cholangiocarcinoma
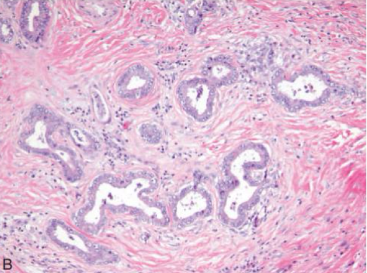
What’s this in liver?
Cholangiocarcinoma. Invasive malignant glands in a reactive, sclerotic stroma.
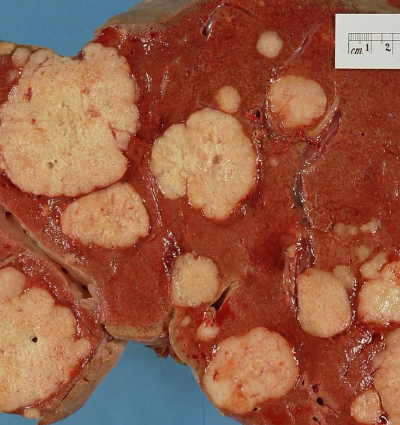
What’s this?
Metastatic liver cancer