Chapter 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:37 AM on 2/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Do most types of human cancers act like an infectious disease?
No, because they do not spread from one individual to another like an infectious disease
2
New cards
Which 2 tumor types in the western world could clearly be tied to viruses?
•Cervical carcinomas
•Hepatomas (liver carcinomas)
•Hepatomas (liver carcinomas)
3
New cards
T or F: during the 1970s attempts to isolate viruses from human tumors was mostly successful
False
4
New cards
Transfection
technique to introduce naked DNA into mammalian cells
5
New cards
What did extensively studying infectious agents uncover?
studying these infectious agents uncovered many cellular oncogenes (proto-oncogenes) and tumor suppressor genes
6
New cards
Do cellular oncogenes exist in transformed cells?
No because 3-MC converted previously normal genes into mutant alleles that function as oncogenes
7
New cards
How did they figure out whether or not transformed cells have cellular oncogenes?
Chemically transformed mouse fibroblasts - treated repeatedly with carcinogen and mutagen 3-methylcholanthrene (3-MC) - component of coal tars
8
New cards
What is 3-MC
mutagen 3-methylcholanthrene (3-MC) - component of coal tars
9
New cards
True or False: Cells derived from human carcinomas capable of transforming mouse fibroblasts
True
10
New cards
Can oncogenes work across species to induce cell transformation
Yes
11
New cards
What cancer was amplification of erbB-related gene seen in?
Breast Cancer
12
New cards
What is the relationship between the increase in gene copy number and survival rate
Increase in gene copy number of more than 5 copies per cancer cell correlated with a decreased number of patients who survived
13
New cards
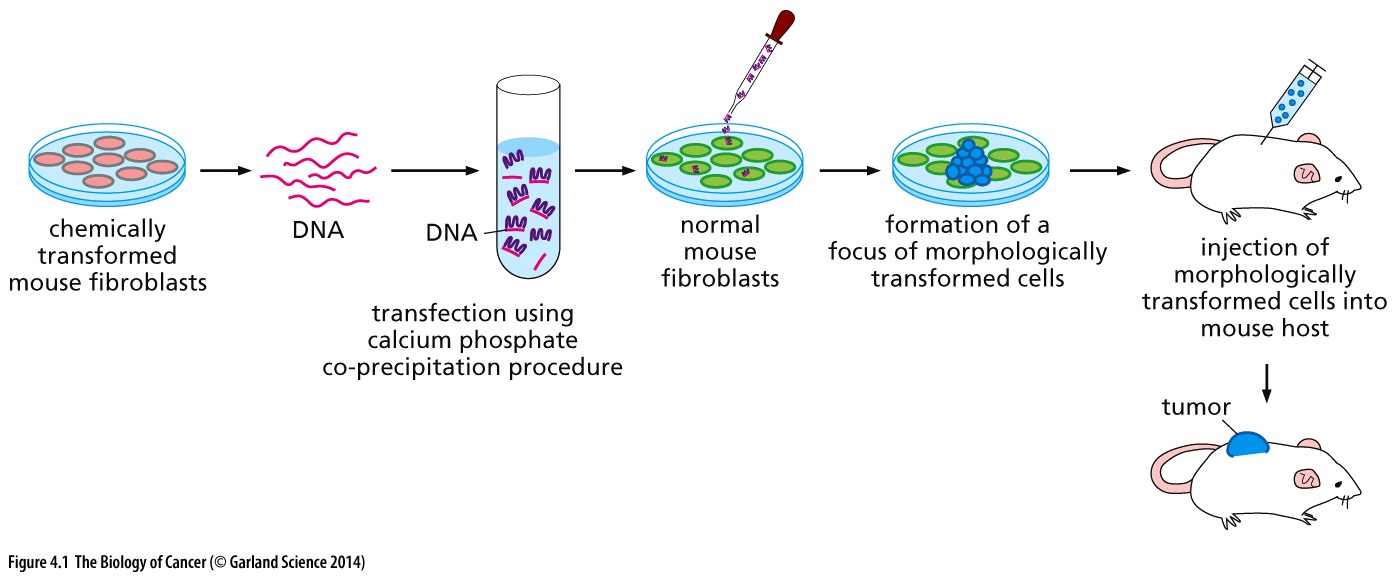
What was the conclusion to this experiment?
3-MC converted previously normal genes into mutant alleles that function as oncogenes
14
New cards
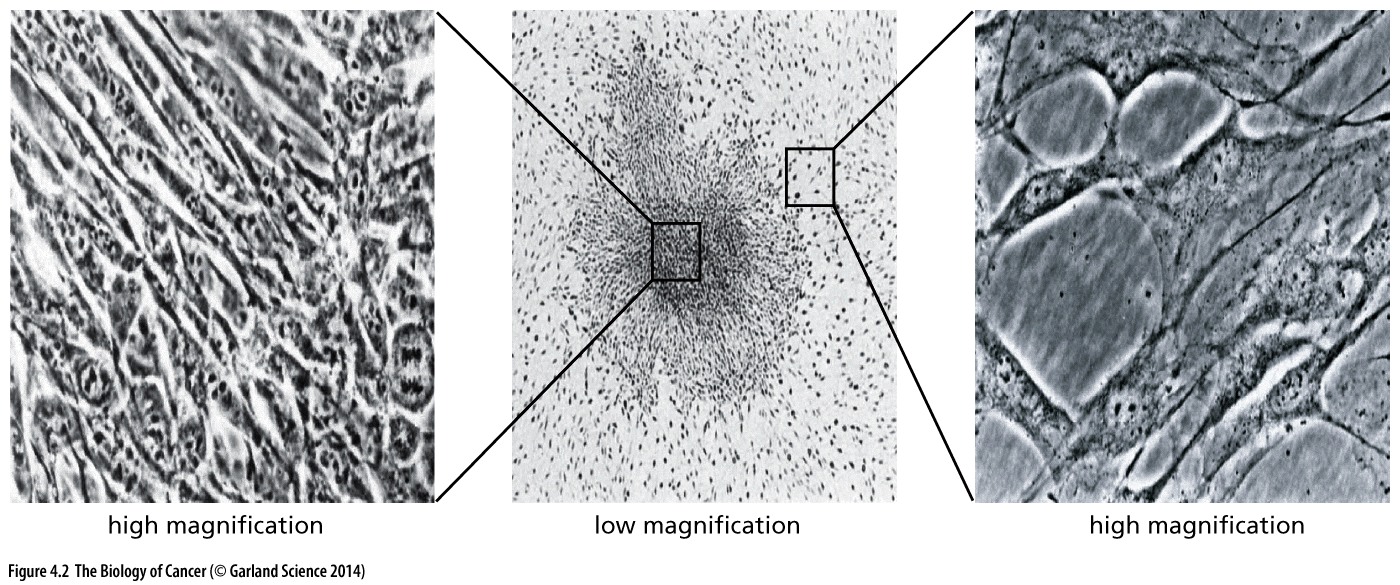
Which picture shows abnormal cells?
The left shows abnormal appearance of the cells in the focus
15
New cards
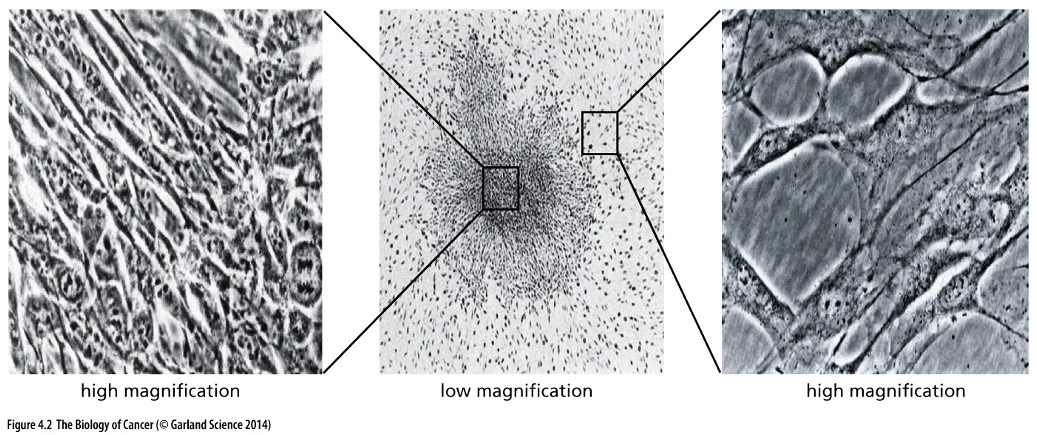
Which picture shows normal cells?
\-The right shows normal cells.
\-They are untransformed cells outside of the focus
\-They are untransformed cells outside of the focus
16
New cards
True or False: oncogenes work across species to induce cell transformation
True
17
New cards
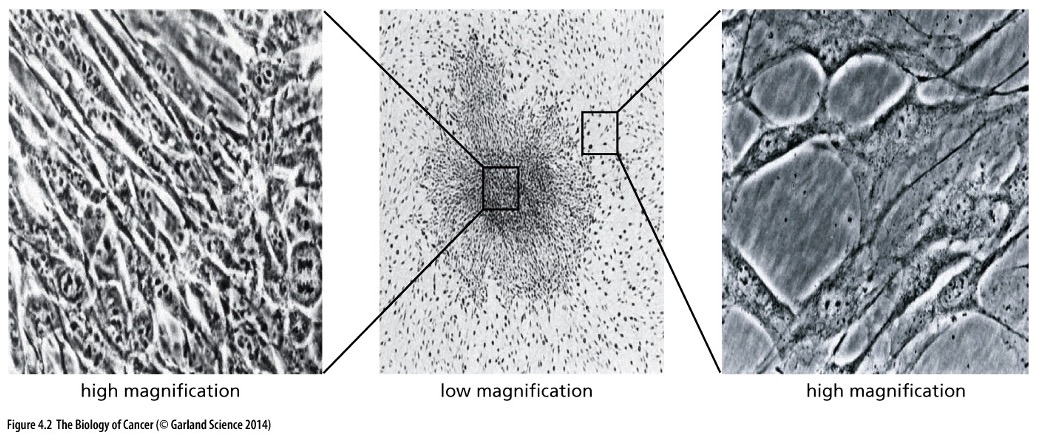
What does this picture show?
Transfection of DNA from the T24 human bladder carcinoma cell line
18
New cards
True or False: Cells derived from human carcinomas are not capable of transforming mouse fibroblasts.
False
19
New cards
Are oncogenes carried by transforming retroviruses related to oncogenes discovered in human tumor cell lines?What
Oncogenes discovered in human tumor cell lines are related to those carried by transforming retroviruses
20
New cards
What technique is used to detect gene amplification in other tumors?
FISH
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (abbreviated FISH) is a laboratory technique used to detect and locate a specific DNA sequence on a chromosome.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (abbreviated FISH) is a laboratory technique used to detect and locate a specific DNA sequence on a chromosome.
21
New cards
Amplicon
unit of DNA amplification
22
New cards
When erB2/HER2 is amplified, what happens to closely linked (nearby) genes?
They are also amplified
23
New cards
Are co-amplified genes important in establishing the cancer cell phenotype?
yes
24
New cards
Are all cancers localized to 1 or 2 chromosomes?
No, some some cancers have altered transcripts in many chromosomes
25
New cards
Are the oncogenes originally discovered through their association with retroviruses normal?
No, many of the oncogenes originally discovered through their association with retroviruses could be found in a __**mutated, activated**__ state in human genomes
26
New cards
When can proto-oncogenes be activated?
Proto-oncogenes can be activated by __**genetic changes affecting protein expression or structure**__
27
New cards
What are ways gene amplification can be achieved?
* Retroviruses altering the promoter region of a gene and turning it on constitutively (constant)
* By other regulatory molecules in cancer cells
* Single base substitution identified in H-ras oncogene
* Chromosomal Translocation
* Structural changes in proteins- growth factor receptors
* By other regulatory molecules in cancer cells
* Single base substitution identified in H-ras oncogene
* Chromosomal Translocation
* Structural changes in proteins- growth factor receptors
28
New cards
True or False: Gene amplification can only be caused by retroviruses altering the promoter region of a gene and turning it on constitutively
False, there are many ways genes can be amplified
29
New cards
Where is H-ras found?
•present in bladder carcinoma as a single gene copy
•Mutated version of this gene was detected in bladder carcinoma cells
•Mutated version of this gene was detected in bladder carcinoma cells
30
New cards
True or False: changing one nucleotide **won’t** convert a normal gene to an oncogene
False: G→T point mutation responsible for converting H-ras (normal gene) into a potent oncogene
31
New cards
What is the first mutation discovered that lead to neoplastic growth of a human cancer?
G→T point mutation
32
New cards
Where did the point mutation occur in H-ras oncogene?
Reading frame
33
New cards
Reading frame
A nucleotide sequence is read 3 nucleotides at a time (codons) starting at a start codon
34
New cards
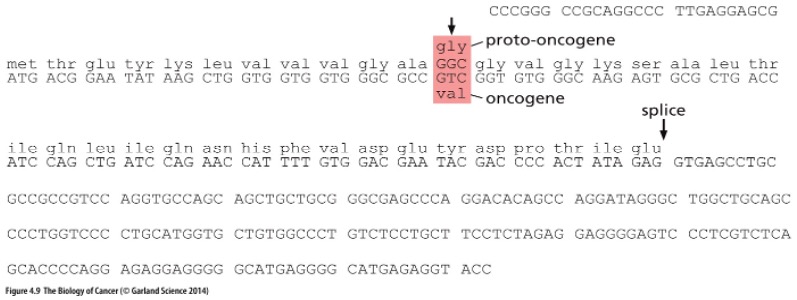
What does this picture show?
A point substitution can change a proto-oncogene into an oncogene
35
New cards
In the H-ras gene what amino acids get switched?
Substitution of glycine for valine in the protein
36
New cards
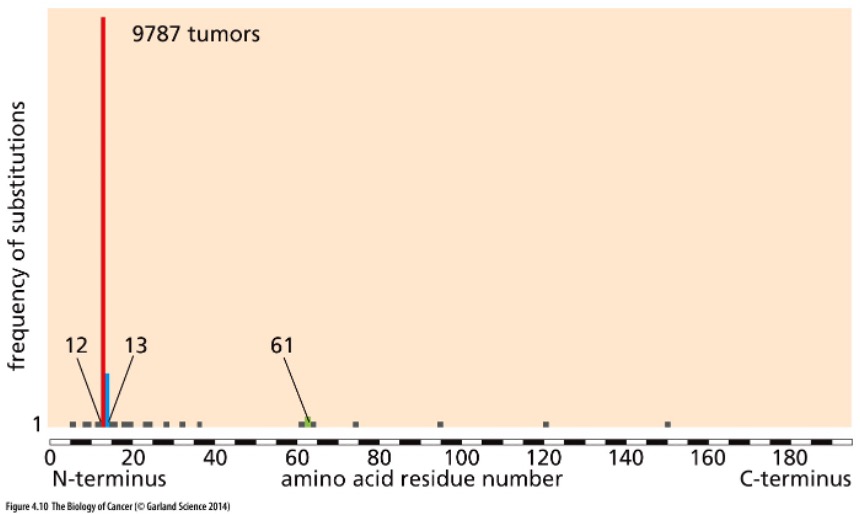
What does this picture show?
*K-ras* oncogene sequencing revealed that most mutations result in amino acid substitutions in residue 12
37
New cards
True or False: tumors that carry the ras oncogene don’t amplify the mutated gene
False
* Many animal and human tumors that carry the *ras* oncogene also amplify the mutated gene
* structure of the protein is affected and also the regulation of the protein/gene is altered
* Many animal and human tumors that carry the *ras* oncogene also amplify the mutated gene
* structure of the protein is affected and also the regulation of the protein/gene is altered
38
New cards
What is *Anopheles gambiae* mosquito a vector for?
vector for malaria
39
New cards
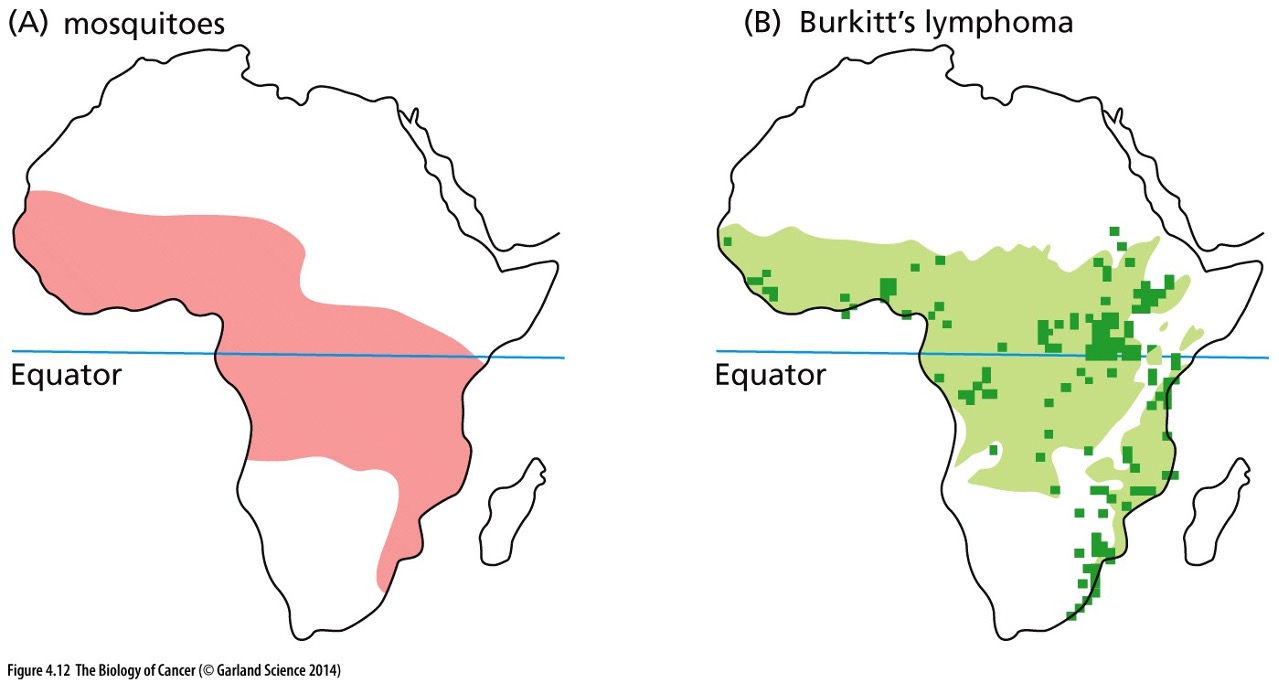
What are the causes of Burkitt’s lymphoma?
* malarial infection
* presence of Epstein Barr virus (EBV)
* presence of Epstein Barr virus (EBV)
40
New cards
What did the tumor cells of Burkitt’s Lymphoma carry?
\
* Tumor cells carried chromosomal **translocations** (region of one chromosome breaks off and then fuses with another chromosome)
\
* Tumor cells carried chromosomal **translocations** (region of one chromosome breaks off and then fuses with another chromosome)
\
41
New cards
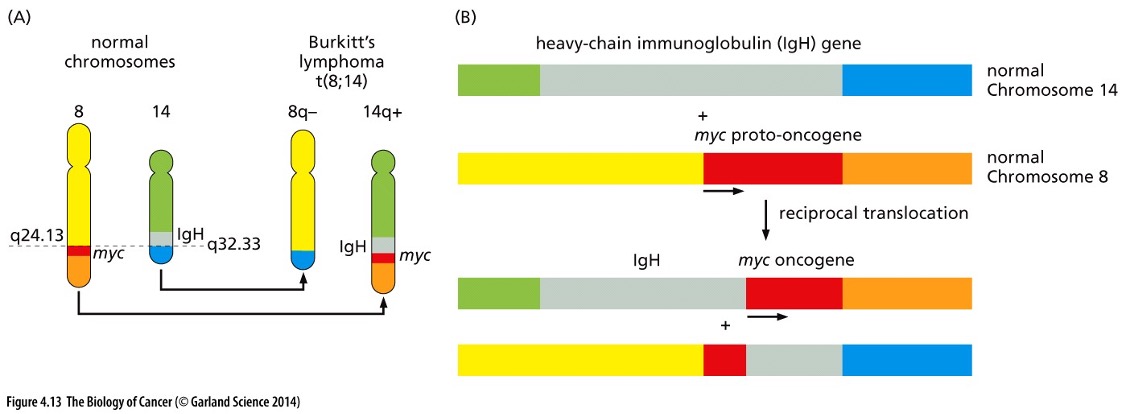
What did the translocations in Burkitt’s lymphoma do?
These translocations separate the *myc* gene from its normal transcriptional promoter and place in under the control of a highly active transcriptional regulator
42
New cards
Are translocation mutations somatic or germ line?
Somatic
43
New cards
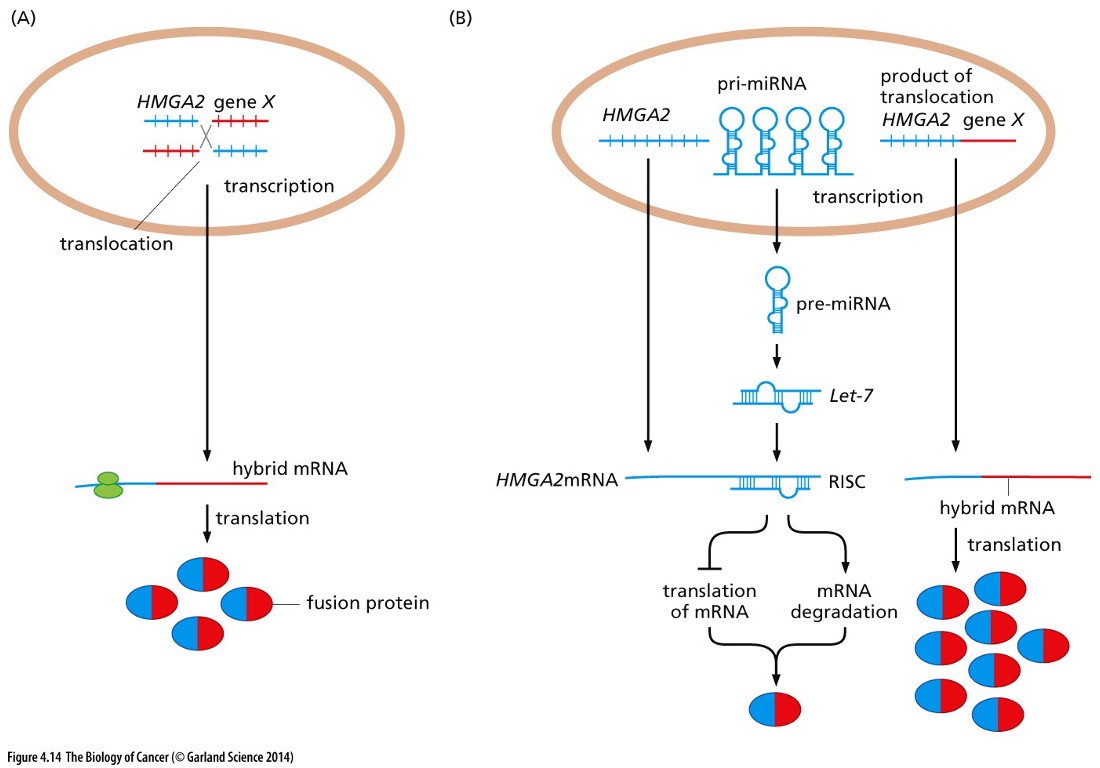
What can translocations lead to ?
Hybrid mRNA
44
New cards
How do translocations liberate mRNA?
Because hybrid mRNA can __**NOT**__ be targeted miRNA, it will not get degraded and just keep on increasing
45
New cards
What happens when mutations lead to structural changes in growth factor receptors?
When a receptor is mutated and doesn’t have a extracellular domain (top of receptor that attaches to ligand) it will still emit signals causing the cell to grow and keep dividing
46
New cards
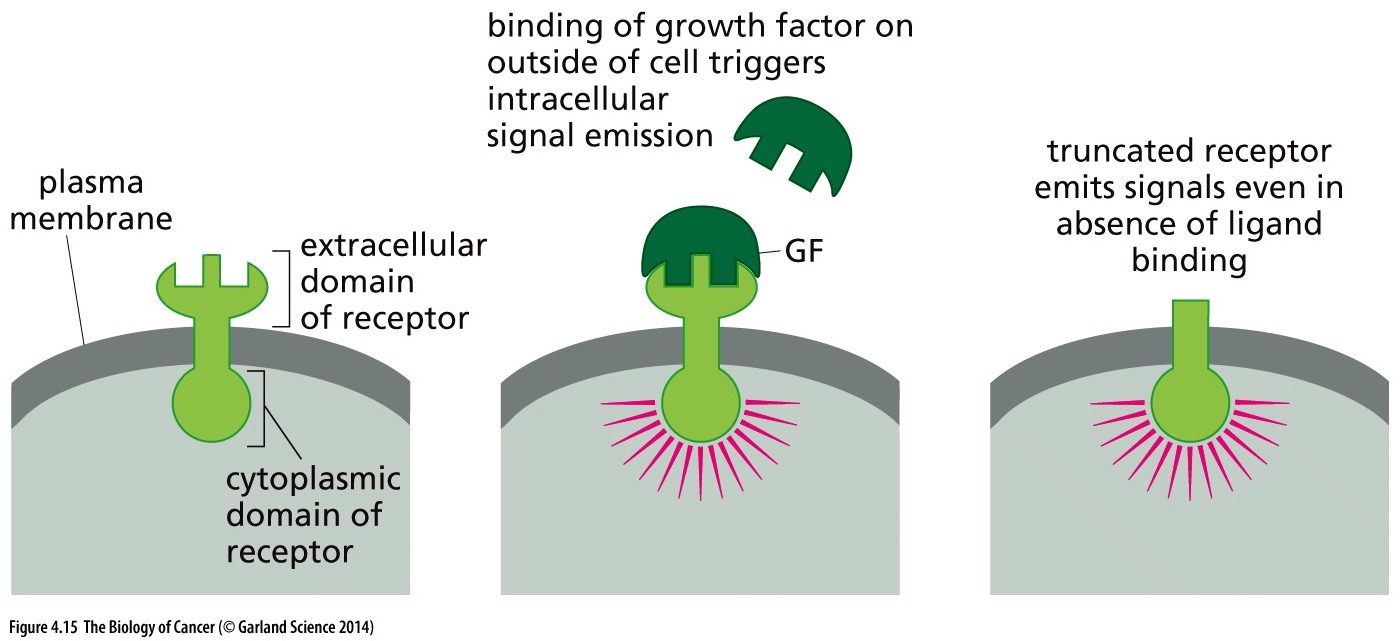
What does this picture show?
It shows what happens in a normal cell with a functional growth factor receptor vs the mutated one
47
New cards
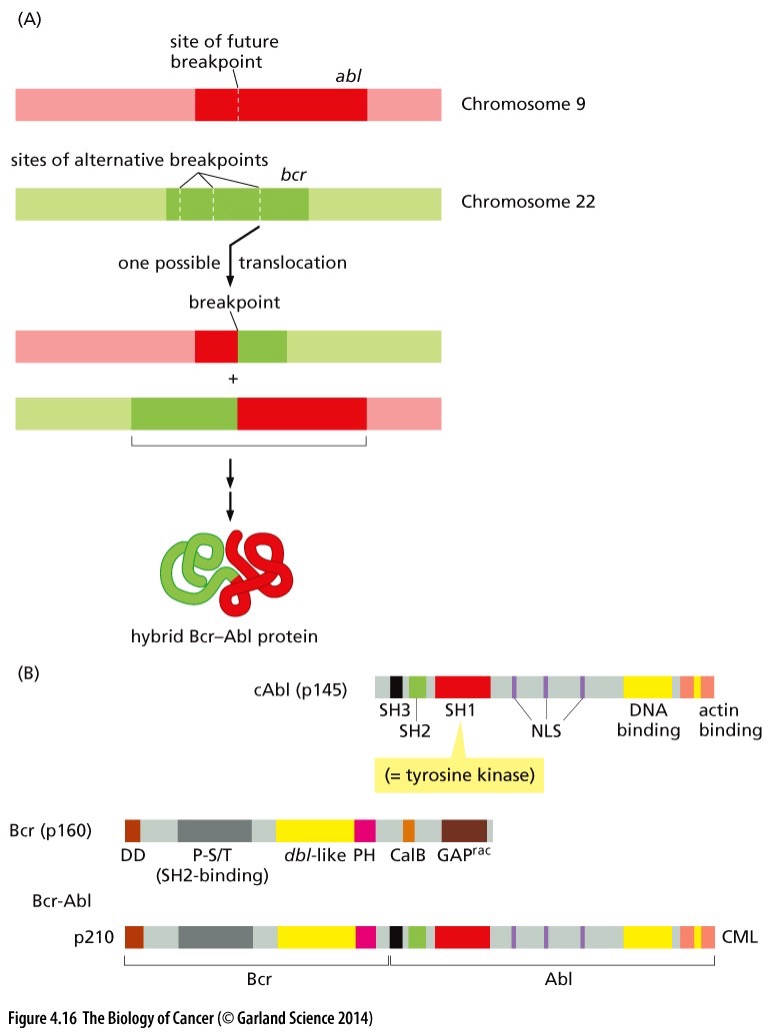
What does this picture show?
Formation of a hybrid protein in CML
48
New cards
How does gene amplification in breast cancers correlate with survival?
Gene amplification lowers survival rate
49
New cards
Why is it significant if a point mutation happens in a reading frame?
If a mutation disrupts this normal reading frame, ***then the entire gene sequence following the mutation will be incorrectly read***. This can cause changes in amino acid sequences, proteins, and structure.
50
New cards
What are the two main etiological factors identified in Burkitt’s Lymphoma?
EBV and malaria
51
New cards
1\.All of the following are proto-oncogenes/oncogenes except _______
A. *myc*
B. *ras*
C. *HER2*
D. *RISC*
A. *myc*
B. *ras*
C. *HER2*
D. *RISC*
D
52
New cards
What effects can translocation have to drive cancer cell transformation?
* In Burkitt’s lymphoma, the translocations separate the *myc* gene from its normal transcriptional promoter and place in under the control of a highly active transcriptional regulator
* Can cause hybrid mRNA which wont be targeted by miRNA and won’t get degraded, increasing the proliferation
* Translocations in human tumors that deregulate proto-oncogene expression and create oncogenes
* Can cause hybrid mRNA which wont be targeted by miRNA and won’t get degraded, increasing the proliferation
* Translocations in human tumors that deregulate proto-oncogene expression and create oncogenes