impacts of tectonic plates
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are tectonic hazards?
Hazards related to tectonic activity (eg. earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis)
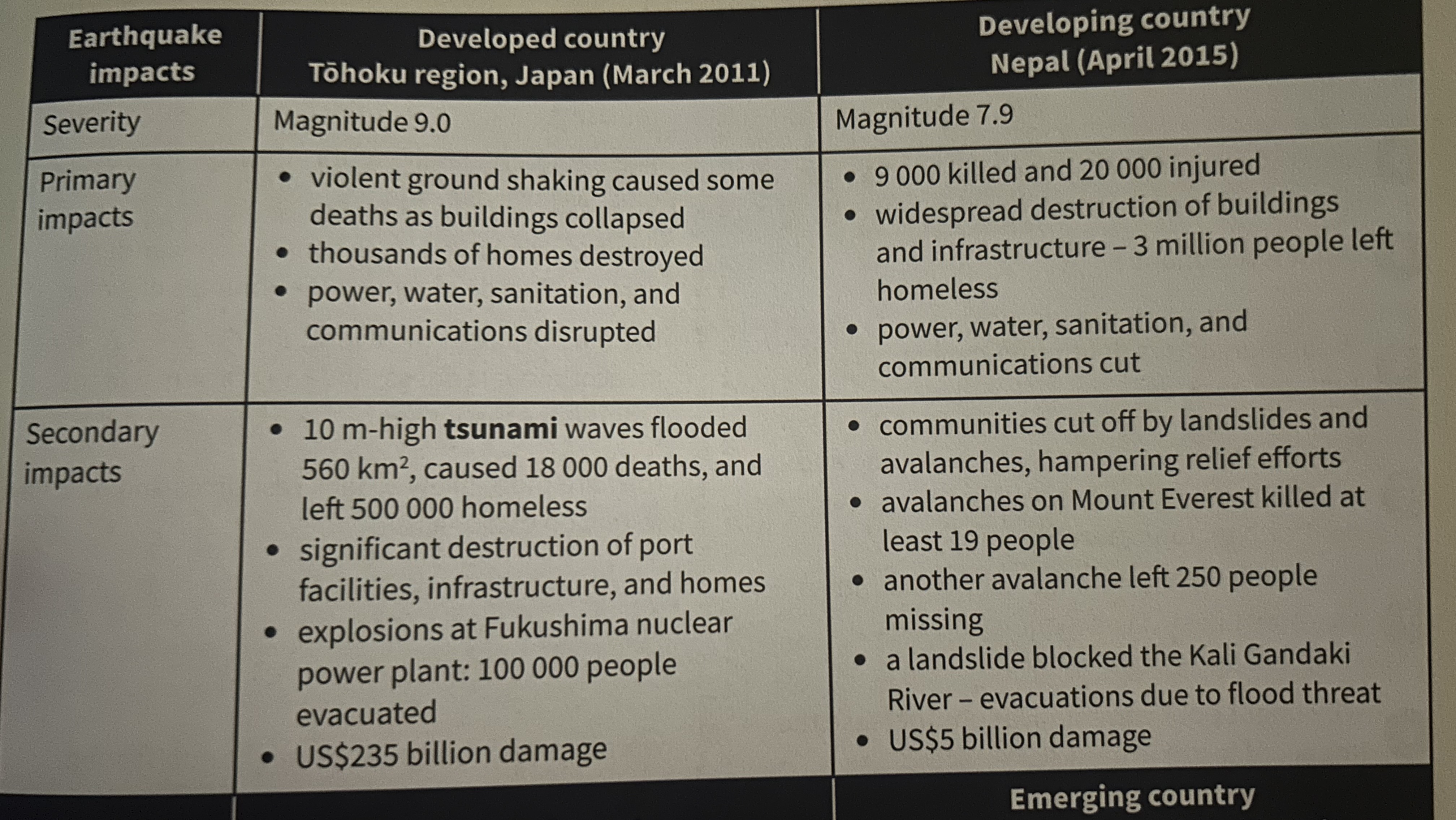
What is an earthquake?
A sudden, violent period of ground shaking due to pressure between two tectonic plates suddenly releasing
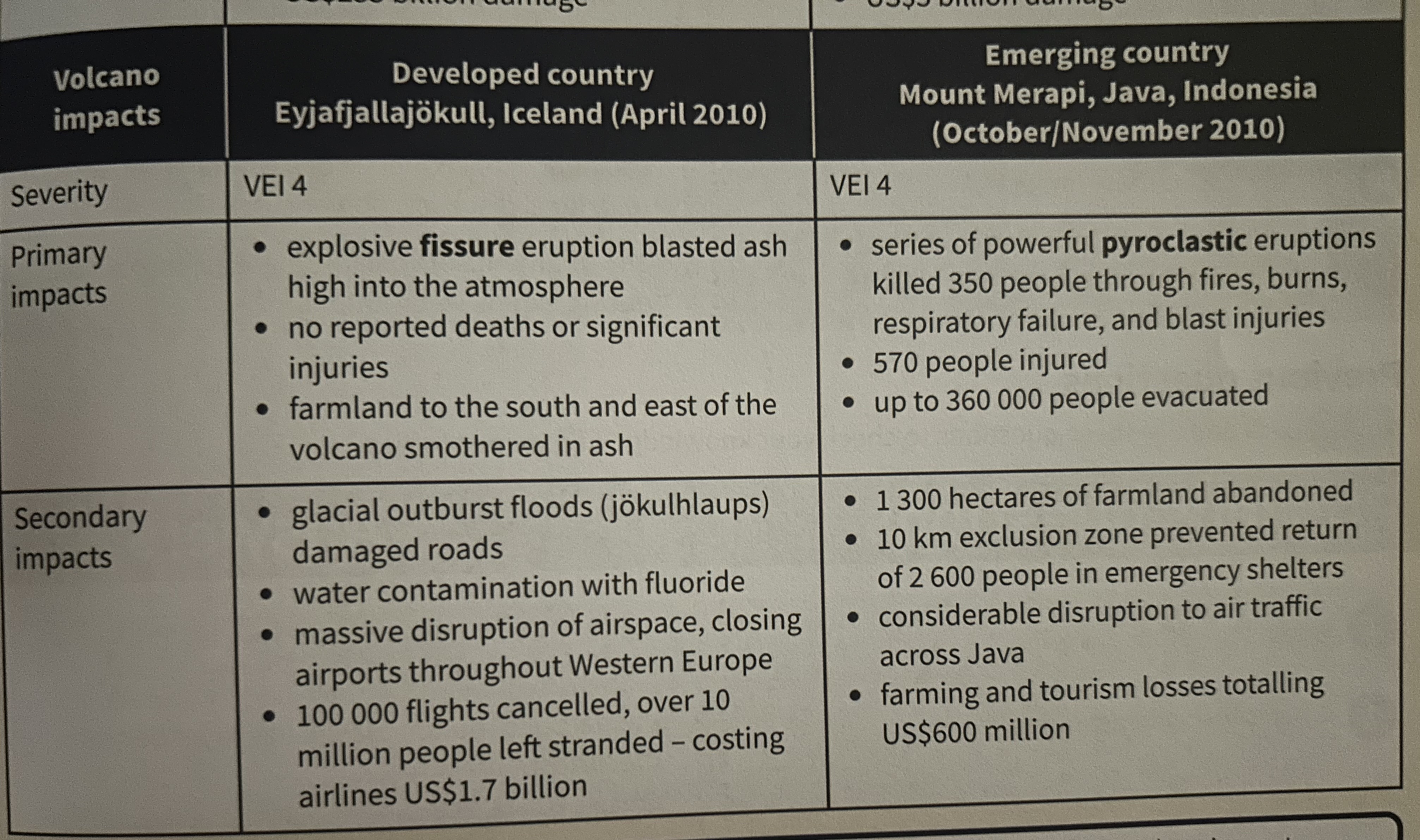
What is a volcanic eruption?
When molten magma erupts through the Earth's crust as lava, ash and gas
What is a tsunami?
Giant, destructive waves generated by undersea earthquakes displacing huge volumes of water
What 4 factors determine the impact of tectonic hazards?
• The magnitude of the event
• The time of day
• The level of preparedness
• The efficiency of the emergency responses
Why are the governments in developing + emerging countries less equipped to deal with tectonic hazards?
They're more likely to lack resources and may have to rely on overseas aid
True or false? People in developed countries are more likely to live in flimsy houses in risky locations
False
Why might poor communications increase the impact of tectonic hazards?
Warnings and evacuations might not happen
What is a primary impact?
The immediate effect of a hazard on people + property (eg. deaths, injuries, collapsed buildings)
What is a secondary impact?
The direct consequence of a primary impact (eg. fires, diseases, power cuts)
‘Pyroclastic’ meaning?
Any fragments of volcanic material thrown out during explosive eruptions


How is a tsunami created? (4)
Two plates get stuck and build tension
An underwater earthquake happens which snaps a plate edge upwards
The height increases as the tsunami reaches shallower coastal areas
The swell reaches the coast and travels very quickly inland