Acct 2 - Fall Final - Ch 1-7
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

61 Terms
accounting equation

fiscal period
the length of time for which a business summarizes and reports financial information
sales journal
a special journal used to record only sales of merchandise on account
purchases journal
a special journal used to record only purchases of merchandise on account
general journal
a journal with two amount columns in which all kinds of entries can be recorded
cash receipts journal
a special journal used to record only cash receipt transactions
cash payments journal
a special journal used to record only cash payment transactions
order of posting special journals
sales
purchases
general
cash receipts
cash payments
contra account
an account that reduces a related account on a financial statement

accounts receivable turnover ratio
the number of times the average amount of accounts receivable is collected during a specified period
-days it takes someone to pay us back
calculating accounts receivable turnover ratio
1. Total accounts receivable - allowance for uncollectable accounts = book value of accounts receivable
2. (beginning book value of accounts receivable + ending book value of accounts receivable) / 2 = average book value of accounts receivable
3. Net sales on account / average book value of accounts receivable = accounts receivable turnover ratio
calculating average book value of accounts receivable
accounts receivable - uncollectable accounts
cash discount on purchases
reduces purchases price
departmental margin statements
the revenue earned by a department less cost of merchandise and direct expenses
-shows net income for a department
-like an income statement except for a specific department instead
stock record
a form used to show the kind of merchandise, quantity received, quantity sold, and balance on hand
consignment
Goods that are given to a business to sell but for which title to the goods remains with the vendor
paying employer payroll taxes
in cash payments journal
-debit: each salary expense specific to the department
-credit: all of the taxes in the payroll register
recording payroll taxes
in general journal
-debit: each salary expense payable specific to the department
-credit: SS, Med, unemployment - state and federal
made a deposit using EFTPS
debit the payable accounts of federal income tax, SS, and Med.
how to calculate total earnings
hours worked times the hourly wage
-overtime is then usually time and a half, so multiply the wage by 1.5 and that by the number of overtime hours. Add commission if there is any.
how to journal a sale on account and then receive payment for that sale (w/discount)
debit: accounts receivable
credit: sales discounts and allowances
sales
sales returns and allowances
refunds and price reductions given to customers after goods have been sold and found unsatisfactory
-contra account of sales
schedule of accounts payable
A listing of vendor accounts, account balances, and total amount due all vendors
schedule of accounts receivable
a listing of customer accounts, account balances, and total amount due from all customers
double entry accounting
the process of recording equal debits and credits for a single business transaction
post-closing trial balance
prepared to make sure total debits equal total credits after the closing entries are posted
order of closing entries
1) Temporary accounts with credit balances
2) Temporary accounts with debit balances
3) Income Summary
4) Dividends
Why do we calculate accumulated earnings on the employee earning record
to keep track of overall earnings
-this is the amount that is taxed and can't go over the standard to be taxed on
earnings record
only used for one employee for one quarter
-there are 4 a year
payroll register
covers one pay period for all employees
-12 per year
net pay
on payroll register it is the total earnings minus total deductions equals
payroll checks
checks written to each employee for amount due
ledger
group of accounts
Calculating and journalizing depreciation expense
debit depreciation expense
credit accumulated depreciation
how to journalize disposing of a plant asset
1) journalize any additional depreciation
2) debit total accumulated depreciation
3) journalize loss/gain or nothing if broke even
4) credit original cost of plant asset
Calculating book value of a plant asset
the original cost of a plant asset minus accumulated depreciation
double-declining method
type of accelerated depreciation that multiples the book value of an asset by a constant depreciation rate to determine annual depreciation
depletion
reduction in the number or quantity of something
reversing entry
the exact opposite of the adjusting entry made in the previous period
-done if you debit an asset or credit a liability
-this follows on everything except for federal income tax payable which you leave alone
adjusting entry for uncollectable accounts
Debit: Uncollectible Accounts Expense
Credit: Allowance for Uncoll. Accounts
Direct write-off method
recording uncollectible accounts expense only when an amount is actually known to be uncollectible
Journal: General
-Debit: Uncollectible Accounts Expense
-Credit: Accounts Receivable/Company
allowance method
Journal: General
-Debit: Allowance for Uncollectable Accounts
-Credit: Accounts Receivable/Company
income statement
a financial statement showing the revenue and expenses for a fiscal period
balance sheet
a financial statement that reports assets, liabilities, and owner's equity on a specific date
statement of cash flows
reports on a business's cash receipts and cash payments for a specific period

statement of retained earnings
the statement that summarizes the income earned and dividends paid over the life of a business
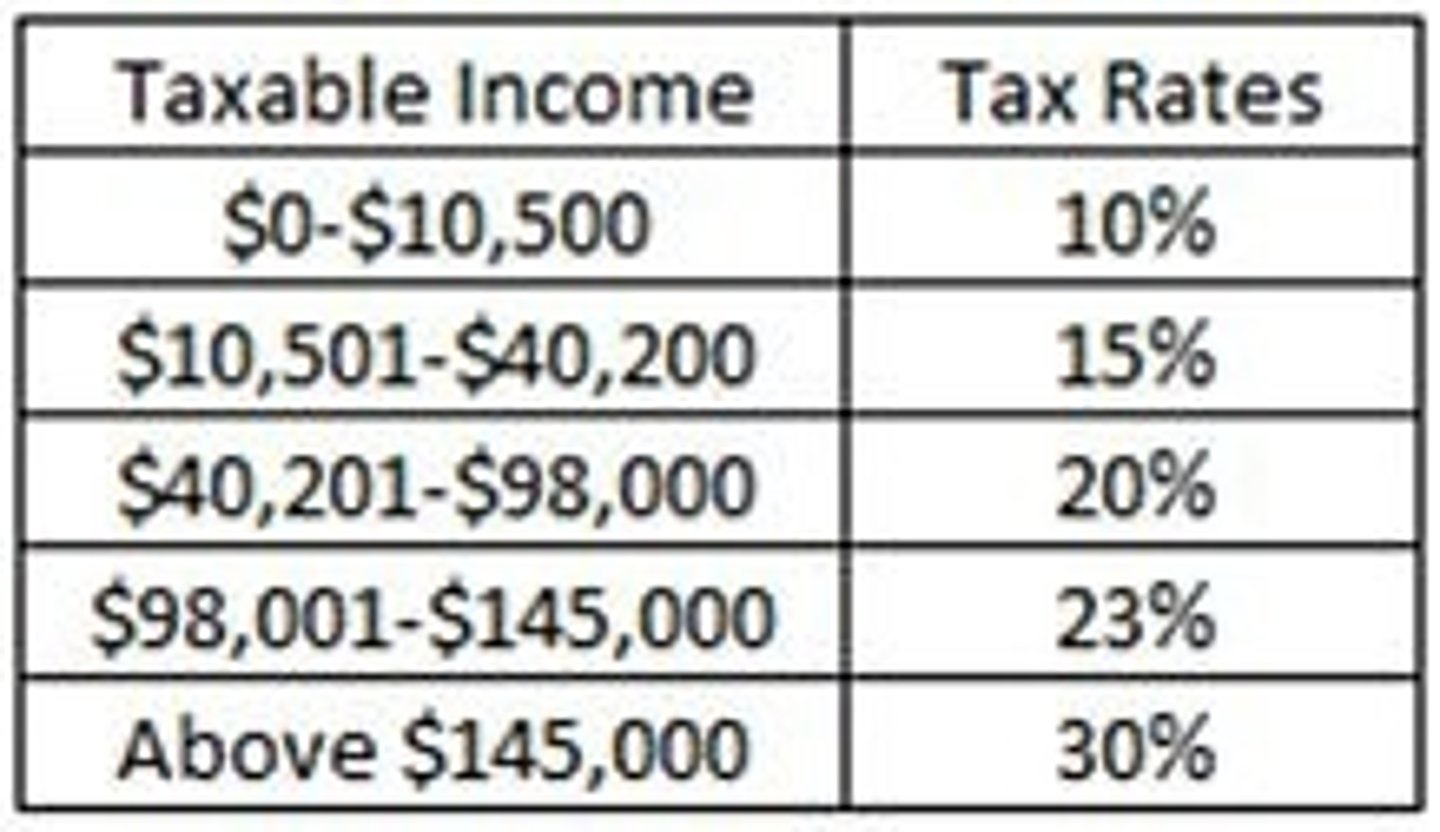
tax bracket
a range of taxable income that is taxed at the same rate
capital stock
total shares of ownership in a corporation
dividends
Company's share profits to the shareholders based on the corporation's performance.
retained earnings
an amount earned by a corporation and not yet distributed to stockholders
matching revenue with expenses
accurately reflecting the results of operations for a fiscal period
consistent reporting
the same accounting procedures are followed in the same way in each accounting period
full disclosure
providing all information necessary for consumers to make an informed decision
marginal tax rate
the extra taxes paid on an additional dollar of income
calculate inventory turnover ratio
number of times the average amount of merchandise is sold during a specific time period
cost of goods sold/average inventory
-how often inventory is changing
-want this number to be high
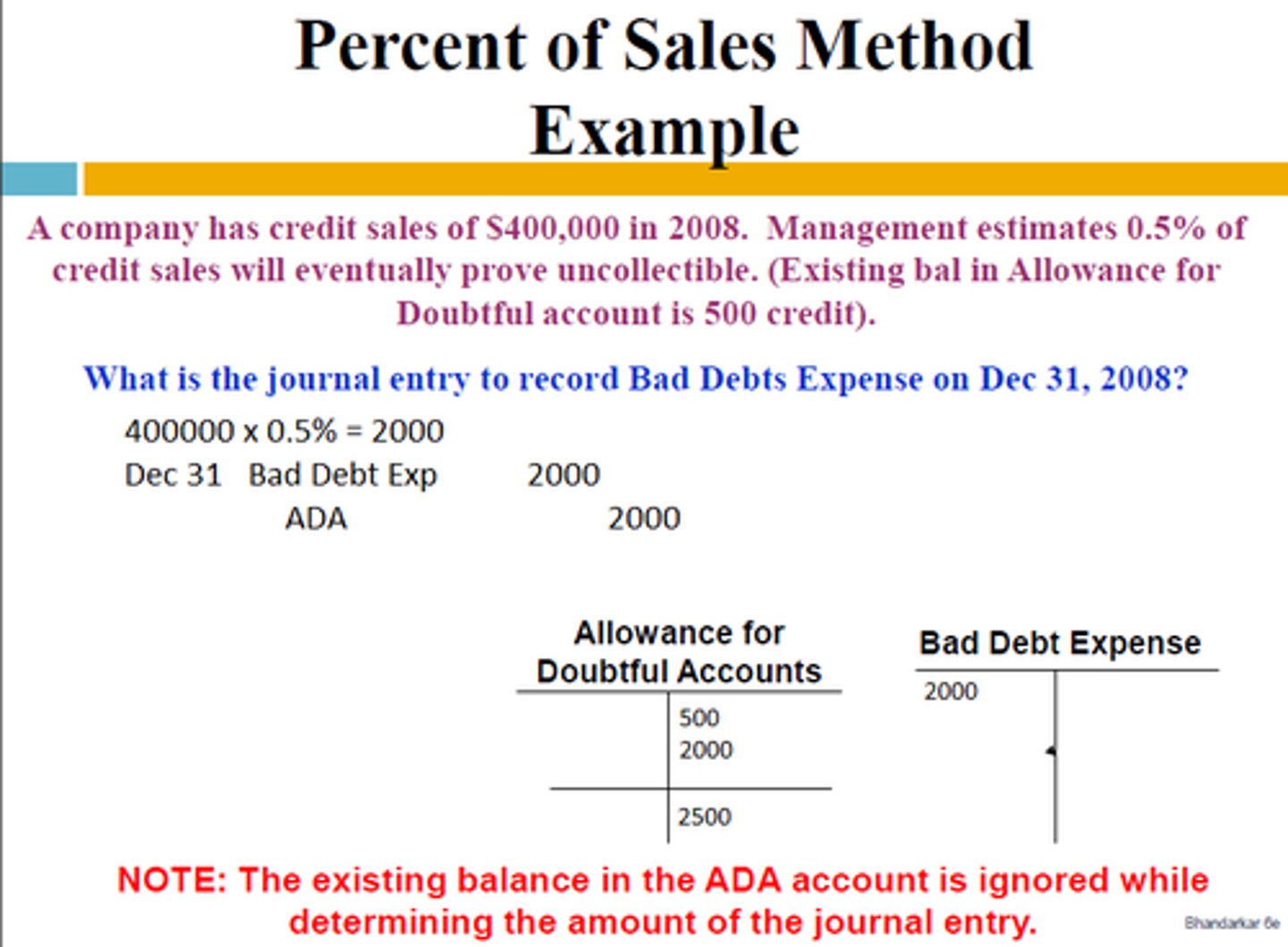
Percent of Sales Method
Estimated Uncollectable Accounts Expense = Net Sales x Percentage
-Answer is the amount of adjusted entry that you will use
-Debit: Uncollectible Accounts Expense
-Credit: Allowance for Uncoll. Accounts
how to write off and reopen an account using direct write off method
*all in general journal
-write off:
Debit: Uncollectible Accounts Expense
Credit: Accounts Receivable/Company
-reopen:
Debit: Account Receivable/Company
Credit: Uncollectable Accounts Expense
how to write off and reopen an account using the allowance method
*all in general journal
-write off:
Debit: Allowance for Uncollectable Accounts
Credit: Accounts Receivable/Company
-reopen:
Debit: Accounts Receivable/Company
Credit: Allowance for Uncollectable Accounts
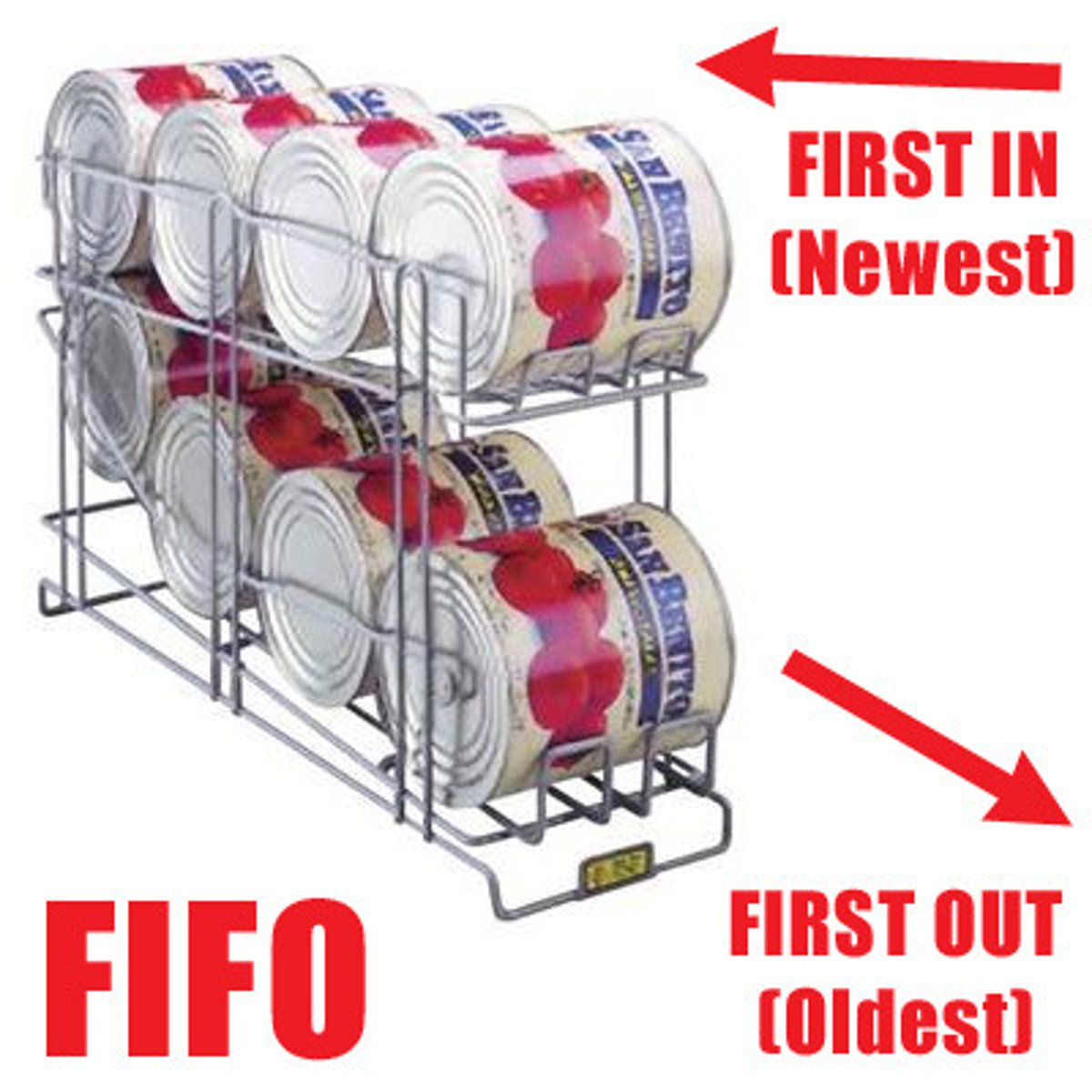
FIFO
using the price of merchandise purchased first to calculate the cost of merchandise sold first
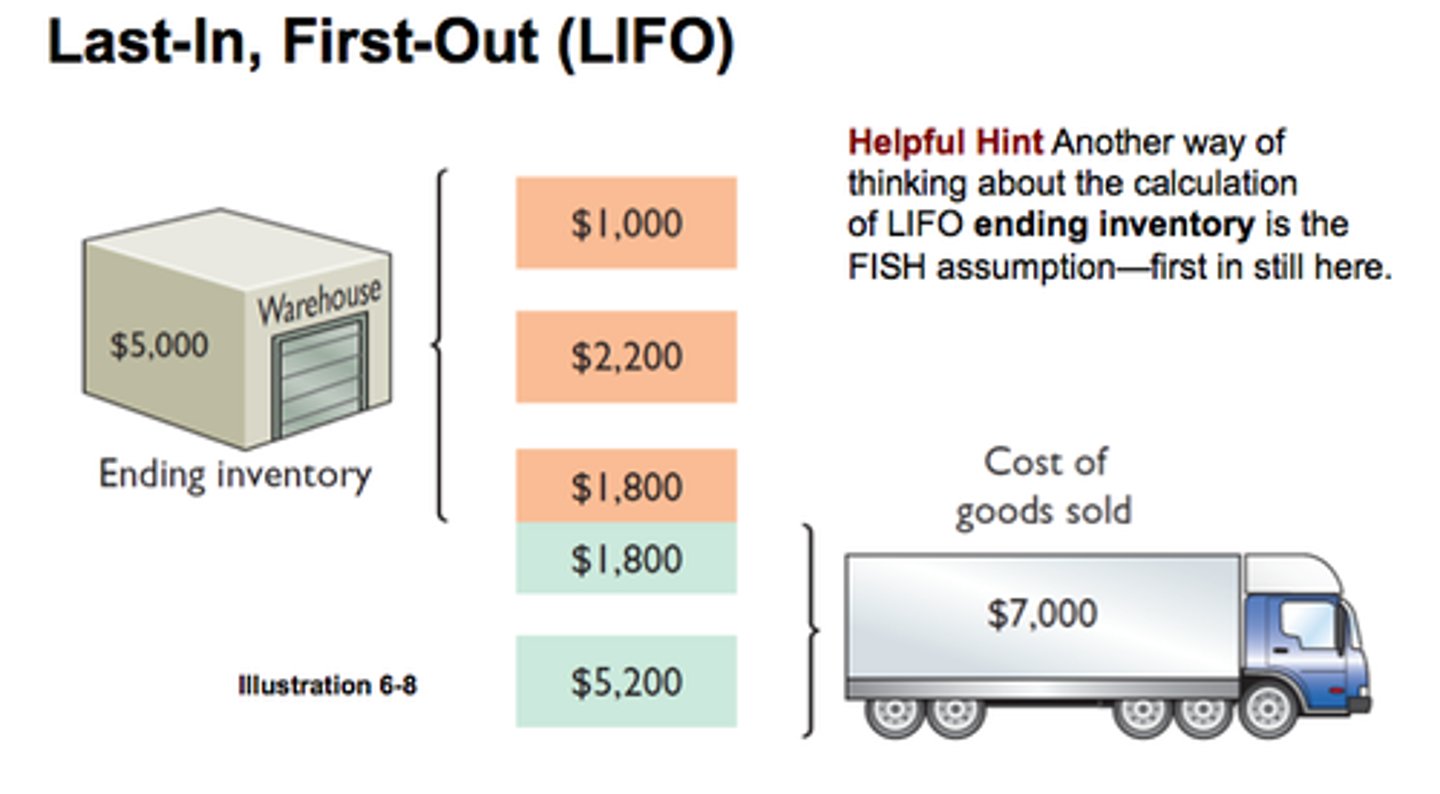
LIFO
using the price of merchandise purchased last to calculate the cost of merchandise sold first
weighted-average method
using the average cost of the beginning inventory plus merchandise purchased during a fiscal period to calculate the cost of merchandise sold