(23.7) Liver, Gallbladder & Pancreas
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Describe Function of the Liver
Production of bile
Role of Bile
Fat emulsifier
Describe Function of the Gallbladder
Stores and concentrates bile that is not needed immediately for digestion
Concentrates it by absorption water and ions
Describe Function of the Pancreas
Supplies most enzymes needed to digest chyme,
Supples bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid
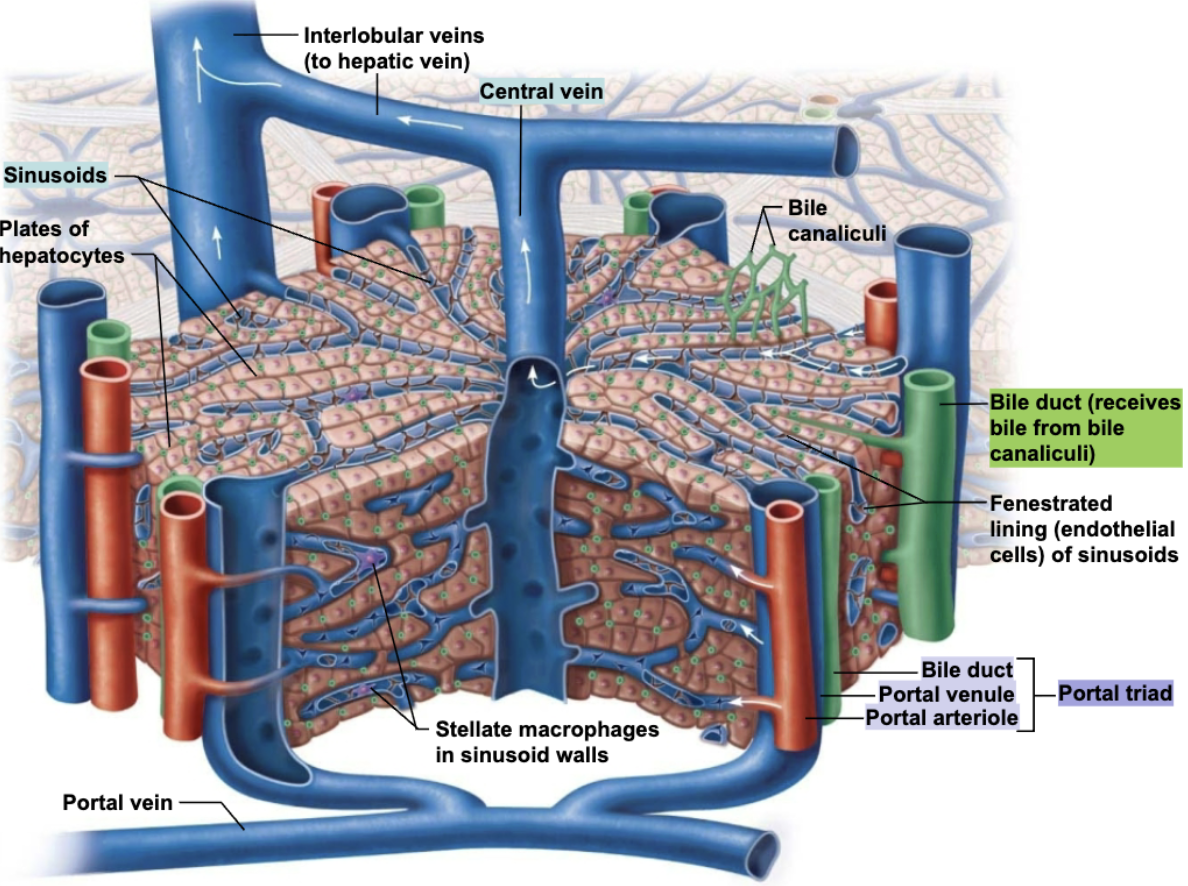
Describe the histologic anatomy of the Liver
Liver lobules
Hexagonal structural and functional units
Composed of plates of hepatocytes (liver cells) that filter and process nutrient-rich blood
Central vein located in longitudinal axis
Portal triad in each corner of lobule contains:
Branch of hepatic artery → which supplies oxygen
Branch of hepatic portal vein → which brings nutrient-rich blood from intestine
Bile duct → which receives bile from bile canaliculi
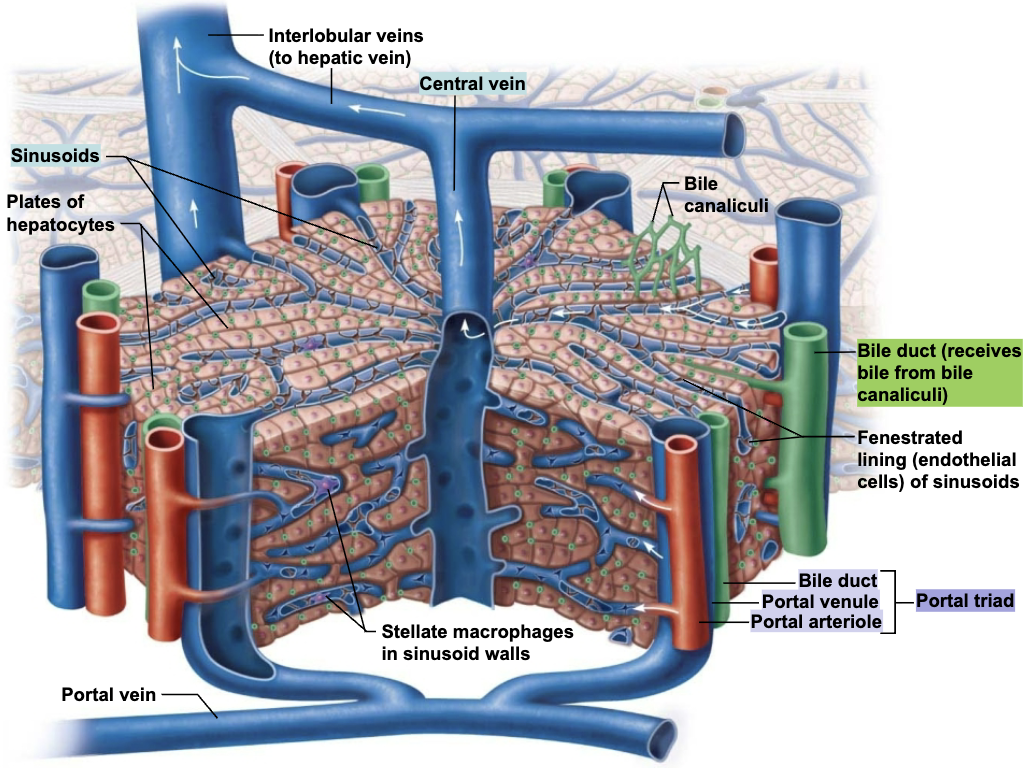
What constitute a portal triad?
A bile duct along with a portal venule and arteriole → the blood vessels provide blood flow to the lobule and the bile duct drains bile.
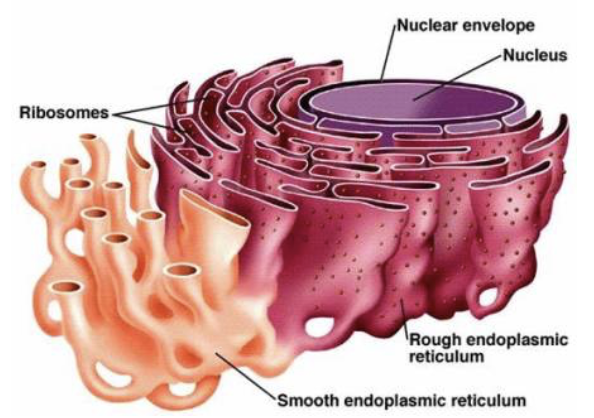
Structure and Function of Hepatocytes
STRUCTURE
Hepatocytes have increased rough and smooth ER, Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, and mitochondria
FUNCTION
Produce ~900 mL bile per day
Process bloodborne nutrients
EX: Store glucose as glycogen and make plasma proteins
Store fat-soluble vitamins
Perform detoxification
EX: Converting ammonia to urea
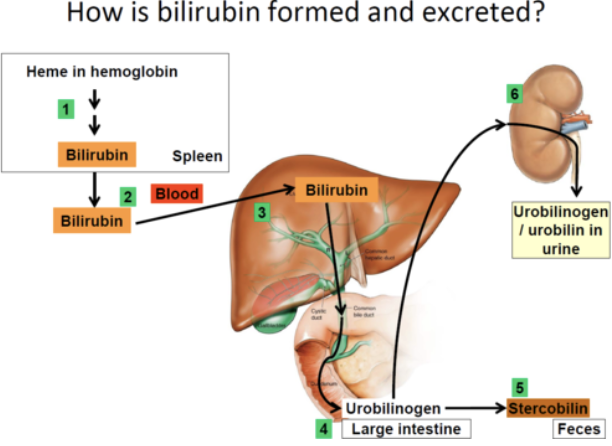
Composition and Enterohepatic circulation of Bile
Yellow-green, alkaline solution containing:
Bile salts
Cholesterol derivates that function in fat emulsification and absorption
Bilirubin
Pigment formed from heme
Cholesterol
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Electrolytes
Effect and Cause of Hepatitis
EFFECT
Inflammation of the liver
CAUSE
Usually viral infection, drug toxicity, wild mushroom poisoning
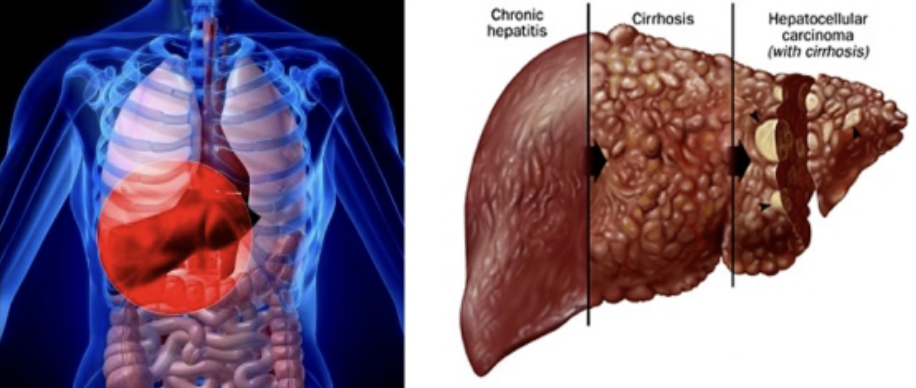
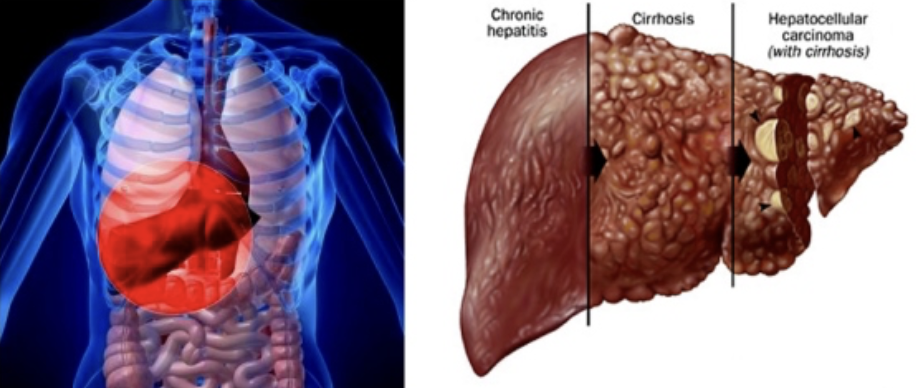
Effect and Cause of Cirrhosis
EFFECT
Progressive, chronic inflammation from chronic hepatitis or alcoholism
CAUSE
Liver → Fatty, fibrous → Portal hypertension
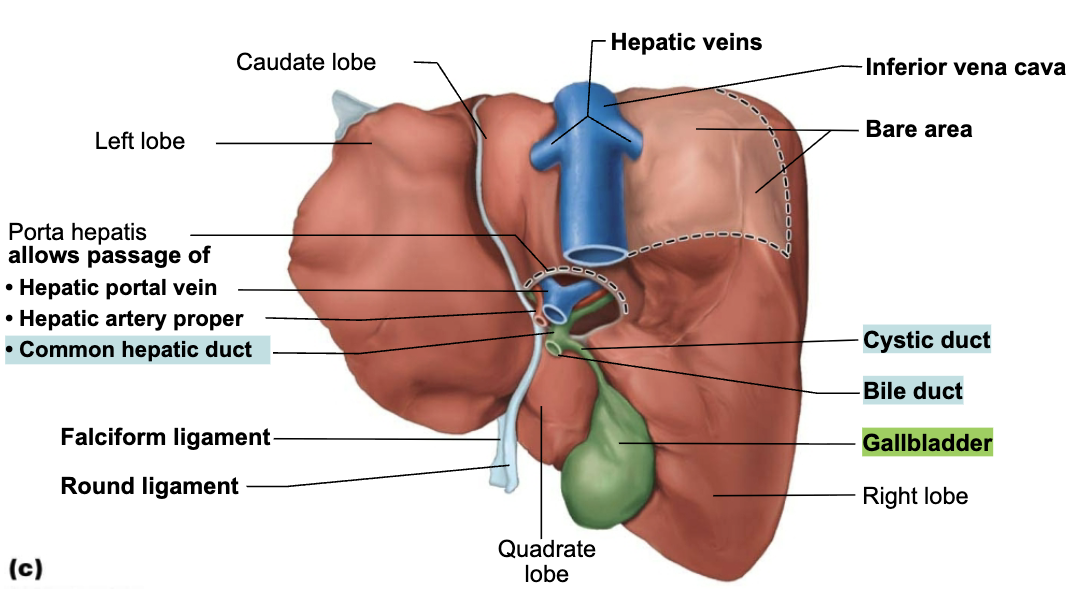
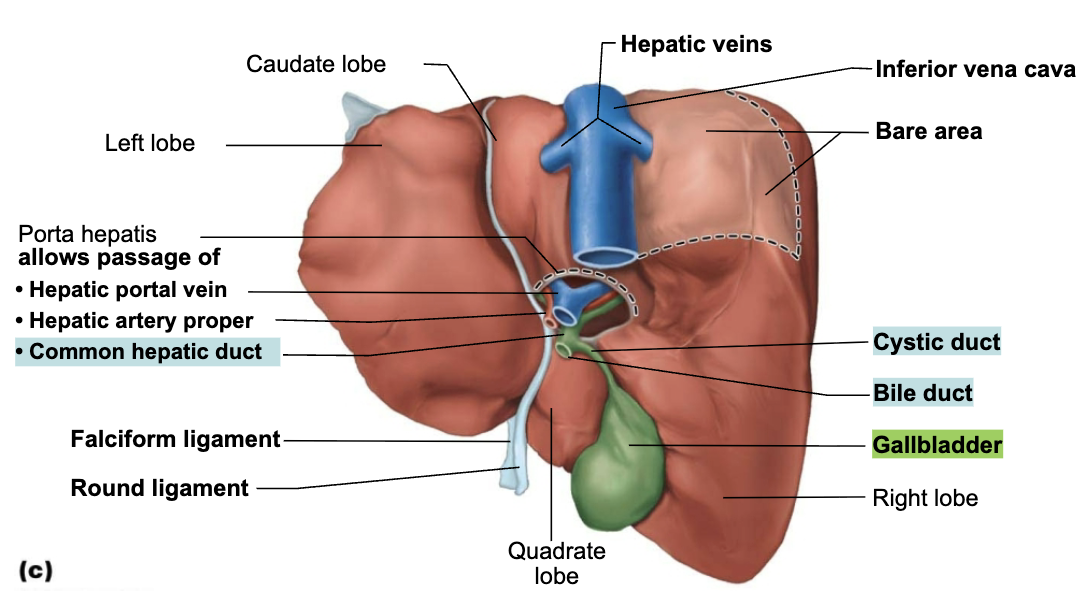
Structure and Function of Gallbladder
STRUCTURE
Muscular contractions release bile via cystic duct, which flows into bile duct
FUNCTION
Store and concentrate bile by absorbing water and ions
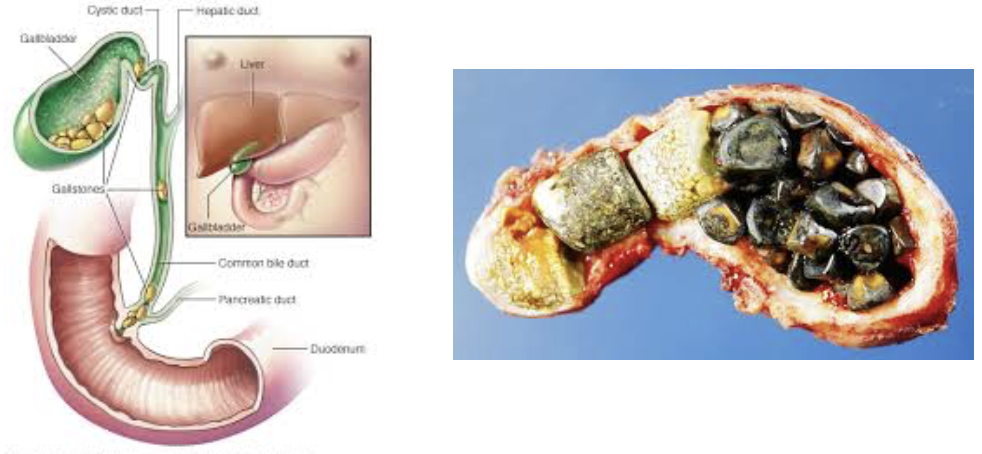
Effect and Cause of Gallstones
Biliary calculi
EFFECT
Can obstruct flow of bile from gallbladder
Painful while gallbladder contracts against sharp crystals
CAUSE
Too much cholesterol or too few bile salts
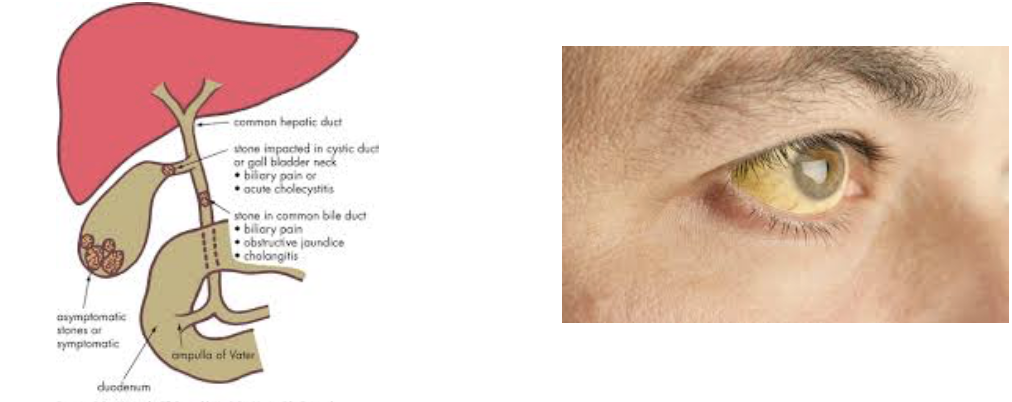
Effect and Cause of Obstructive Jaundice
EFFECT
Blockage can cause bile salts and pigments to build up in blood → resulting in jaundiced (yellow) skin
CAUSE
Gallstones
Liver failure
Location of the Pancreas
Mostly retroperitoneal, deep to greater curvature of stomach
Head is encircled by duodenum; tails abuts spleen
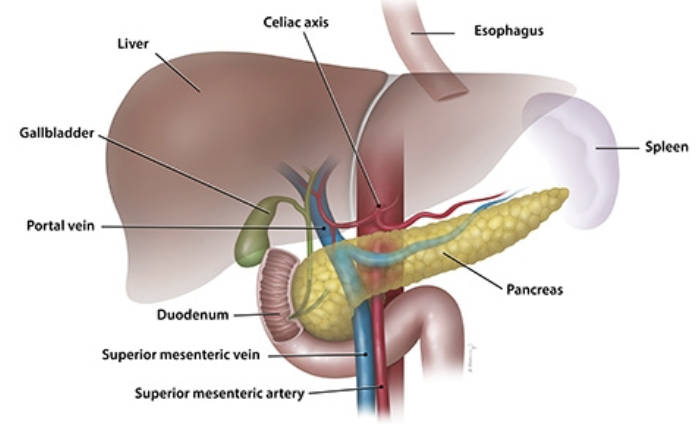
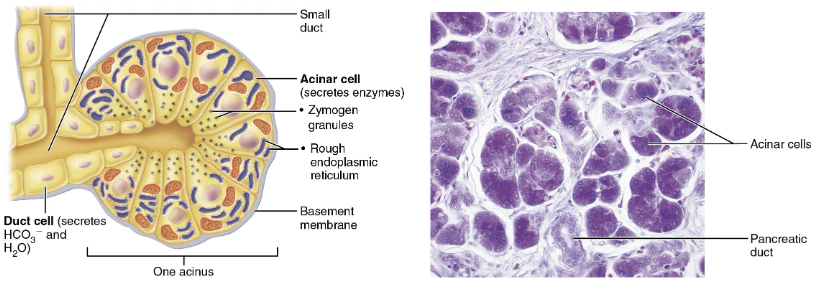
Structure and Function of Pancreas
STRUCTURE
Acini
Clusters of secretory cells that produce zymogen granules containing proenzymes
Ducts
Secrete to duodenum via main pancreatic duct
Smaller duct cells produce water and bicarbonate
FUNCTION
Exocrine function → produce pancreatic juice containing enzymes and bicarbonate into the small intestine
Composition of Pancreatic Juice
1200-1500 mL/day is produced containing:
Watery
Alkaline solution (pH 8) to neutralize acidic chyme coming from stomach
Electrolytes
Primarily HCO3-
Digestive enzymes
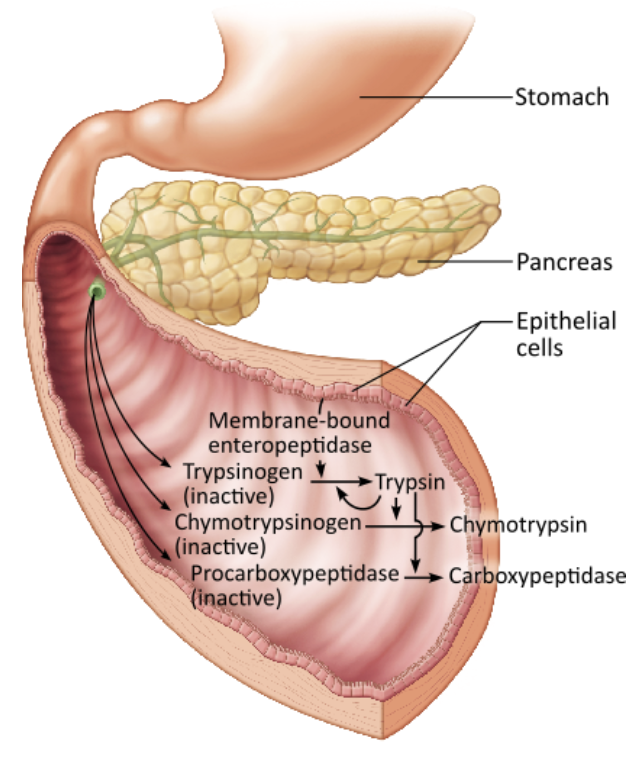
Proteases (for proteins) → secreted in inactive form to prevent self-digestion
Amylase (for carbohydrates)
Lipases (for lipids)
Nucleases (for nucleic acids)
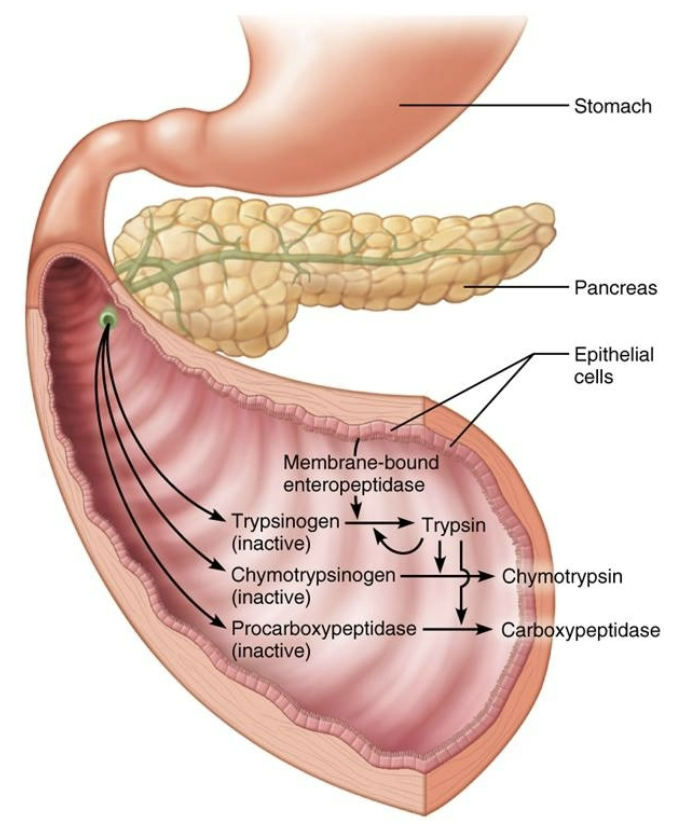
T/F: Proteases are secreted in active form
→ FALSE
Proteases are secreted in an INACTIVE form → they are activated after they reach duodenum
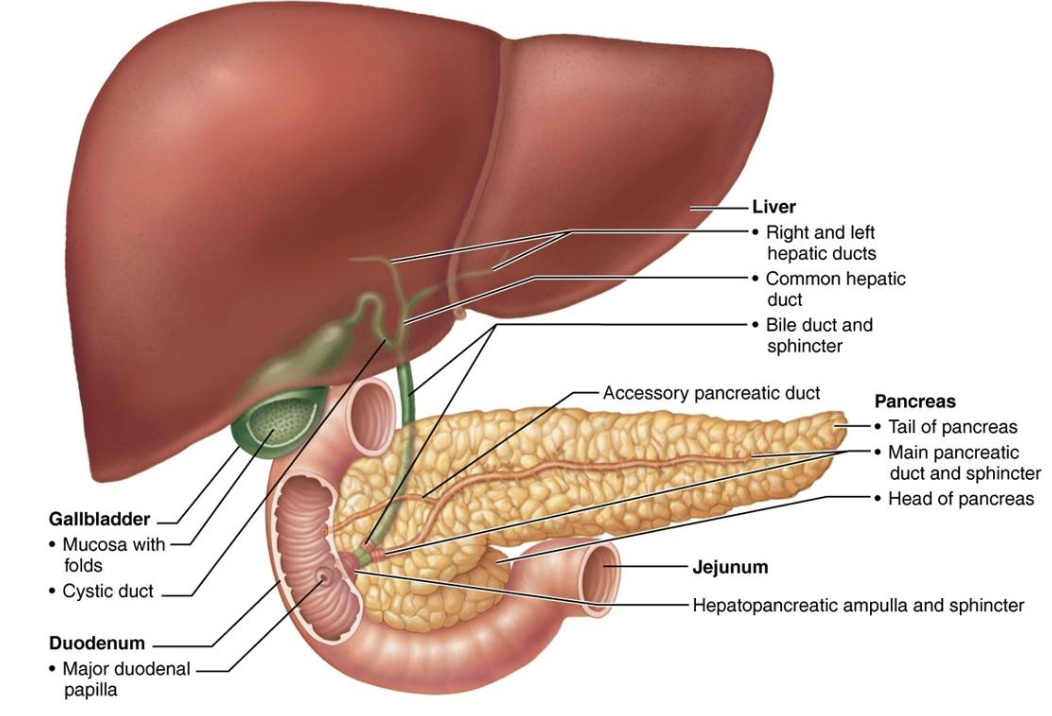
State the roles of bile and pancreatic juice in digestion.
Bile duct from the liver & pancreatic duct join at he duodenal wall and deliver bile and pancreatic juice to the intestine
Bile
Fat emulsifier
Pancreatic juice
Supplies most enzymes needed to digest chyme
Proteases (for proteins) → secreted in inactive form to prevent self-digestion
Amylase (for carbohydrates)
Lipases (for lipids)
Nucleases (for nucleic acids)
Supples bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid
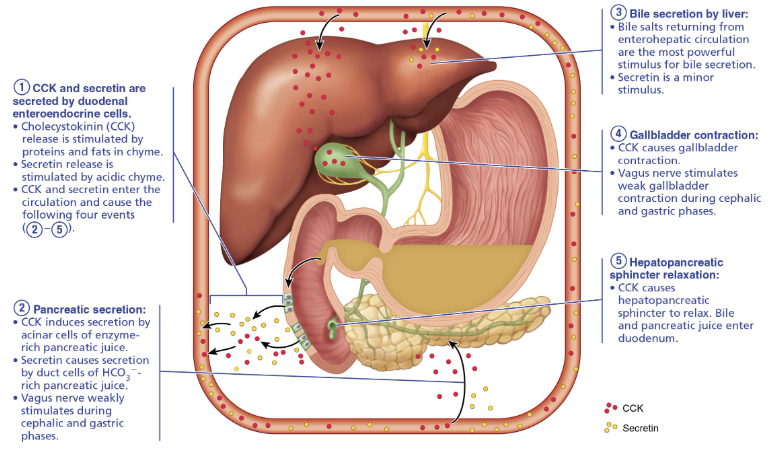
Describe how bile and pancreatic juice secretion into the small intestine are regulated.
Bile and pancreatic juice secretions are BOTH stimulated by neural and hormonal controls
Hormonal controls include:
Cholecystokinin (CCK) → Increases output of enzymatic-rich pancreatic juice.
Secretin → Increases output of pancreatic juice rich in bicarbonate ions
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide → Stimulates insulin release and mildly inhibits HCl production
Gastrin → Increases HCl secretion and stimulates contraction of intestinal muscle