Market Equilibrium Quiz
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
How Changes in Demand and/or Supply affect the Equilibrium Price and Equilibrium Quantity
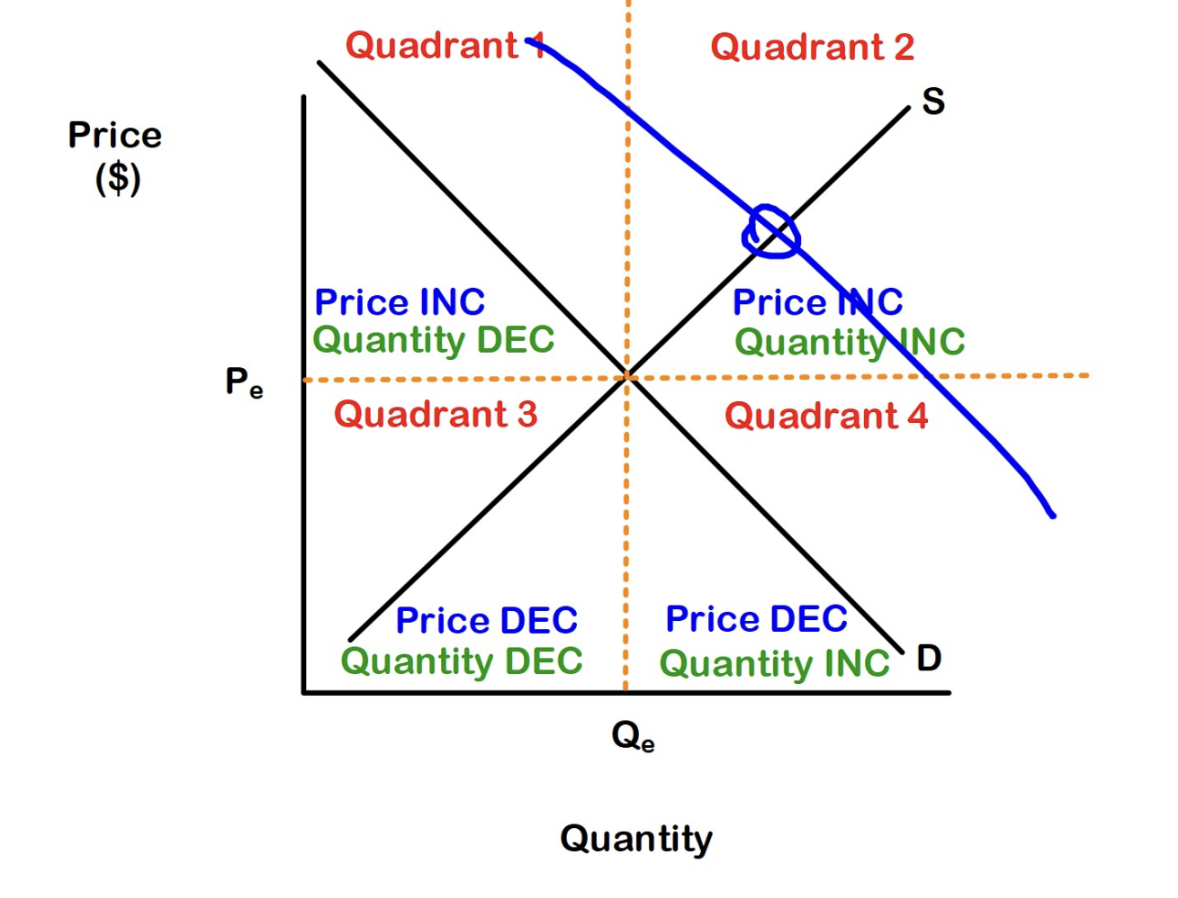
Because price adjustments eliminates shortages and surpluses, markets are normally in equilibrium. When an event disturbs an equilibrium, a new equilibrium soon emerges.
To explain and predict changes in price and quantity…
Only consider EQUILIBRIUM price and quantity
3 Questions to Work out the Effects of an Event on a Market
Does the Event influence demand or supply?
Does the event increase or decrease demand or supply—shift the demand curve or the supply curve rightward or leftward?
What are the new equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity and how have they changed?
Summary of New Equilbirum Price and Quantity based on Change in Demand and/or Supply
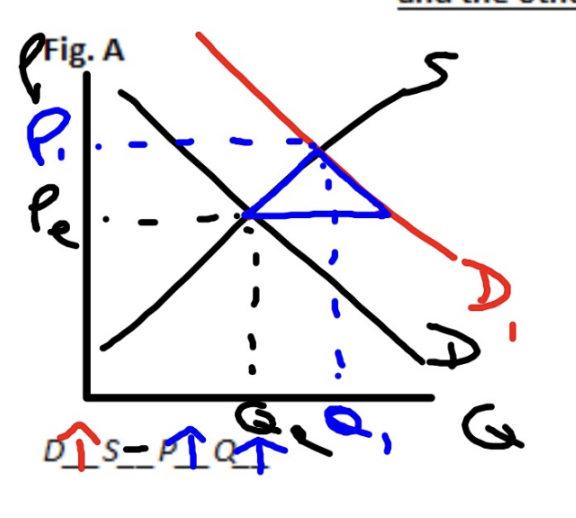
Demand Increases, Supply Constant
Price increases, Quantity Increases (surplus)
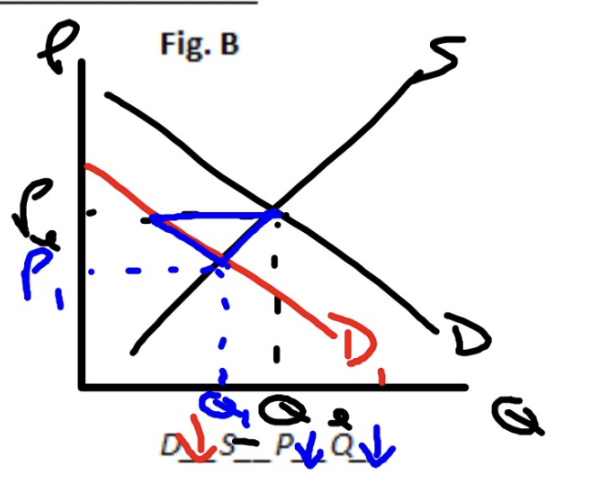
Demand Decreases, Supply Constant
Price Decreases, Quantity Decreases (shortage)
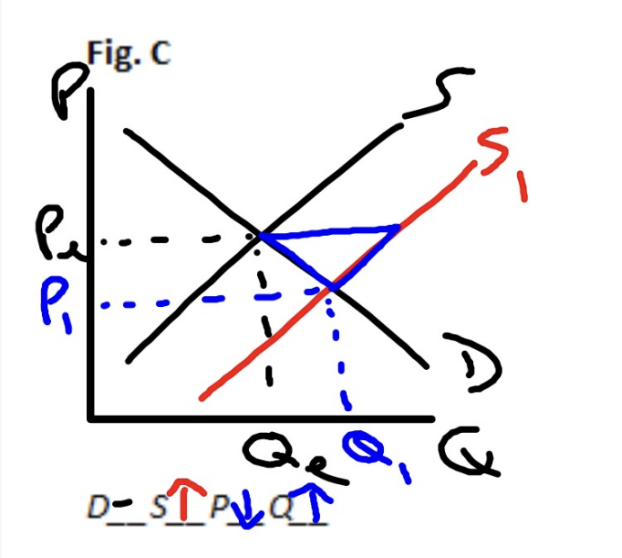
Supply Increases, Demand Constant
Price Decreases, Quantity Increases (surplus)
Supply Decreases, Demand Constant
Price Increases, Quantity Decreases (shortage)
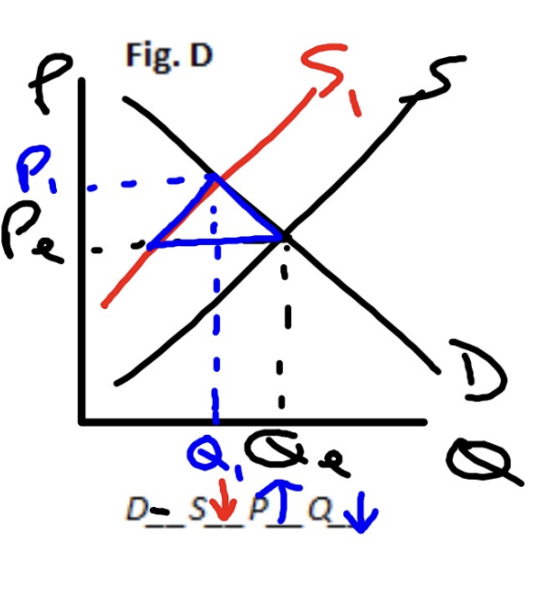
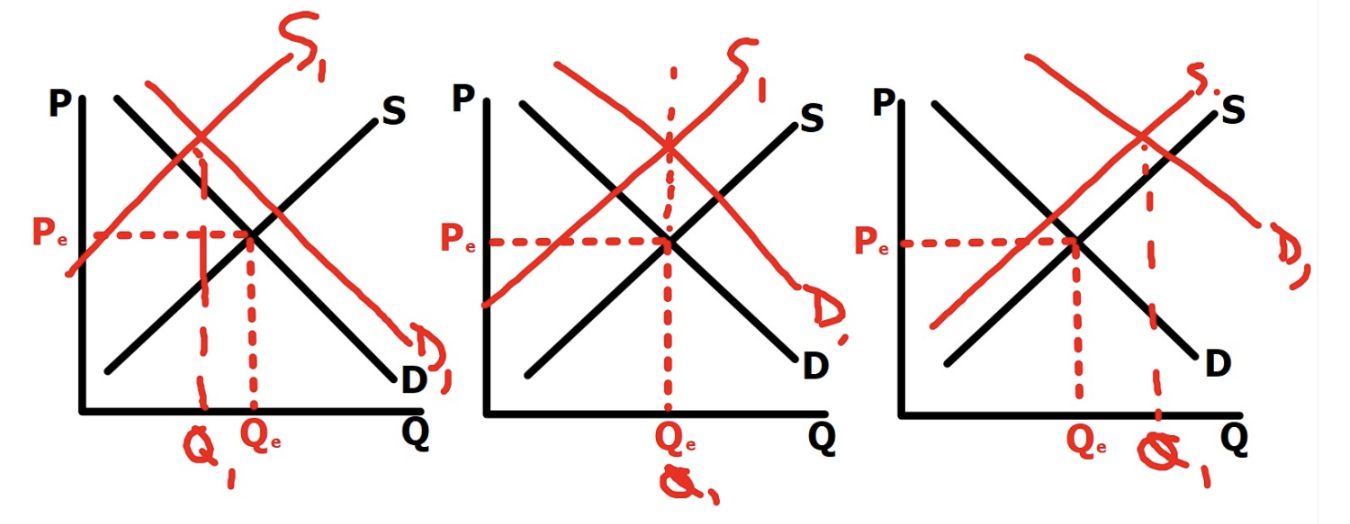
Demand Increases, Supply Decreases
Price increases, Quantity is indeterminate (double shortage)
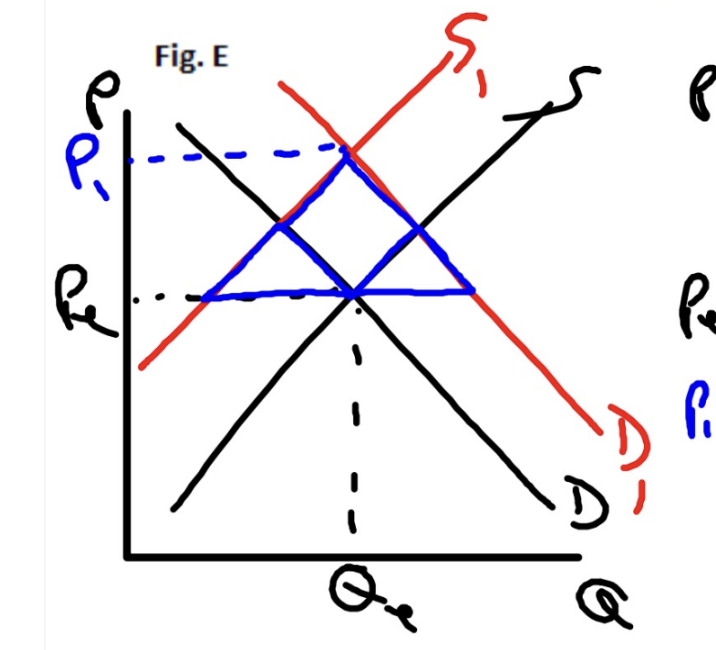
Demand Decreases, Supply Increases
Price Decreases, Quantity is indeterminate (double surplus)
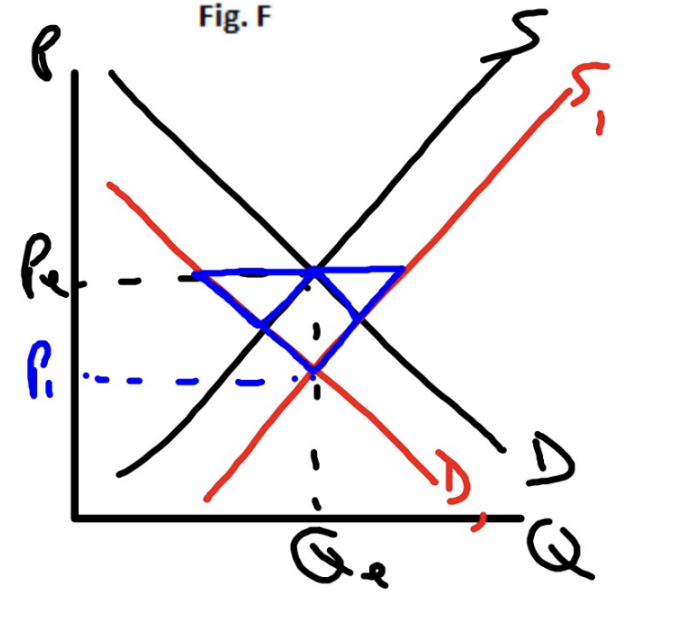
Demand Increases, Supply Increases
Price is indeterminate, Quantity Increases (Shortage from Demand, Surplus from Supply)
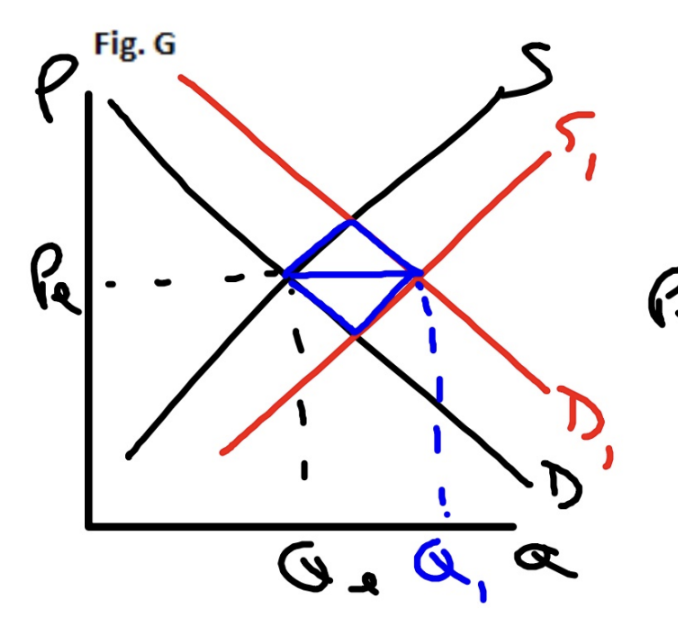
Demand Decreases, Supply decreases
Price is indeterminate, Quantity Decreases (shortage from supply, Surplus from Demand)
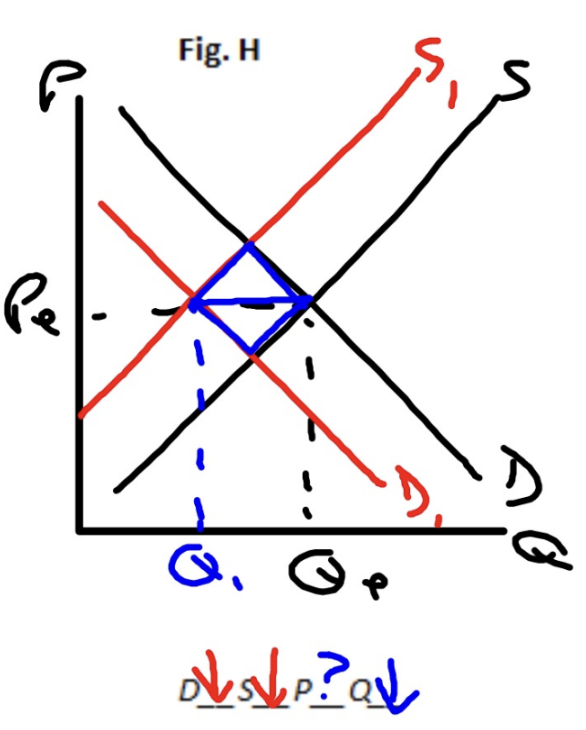
Why is price/quantity indeterminate in complex cases? (when both demand and supply curve shifts)
The impact of each shift on the respective variable can be either reinforcing or conflicting, making it impossible to predict the exact new equilibrium without knowing the magnitude of each shift.
Market Equilibrium
When the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied (both suppliers and consumers are happy)
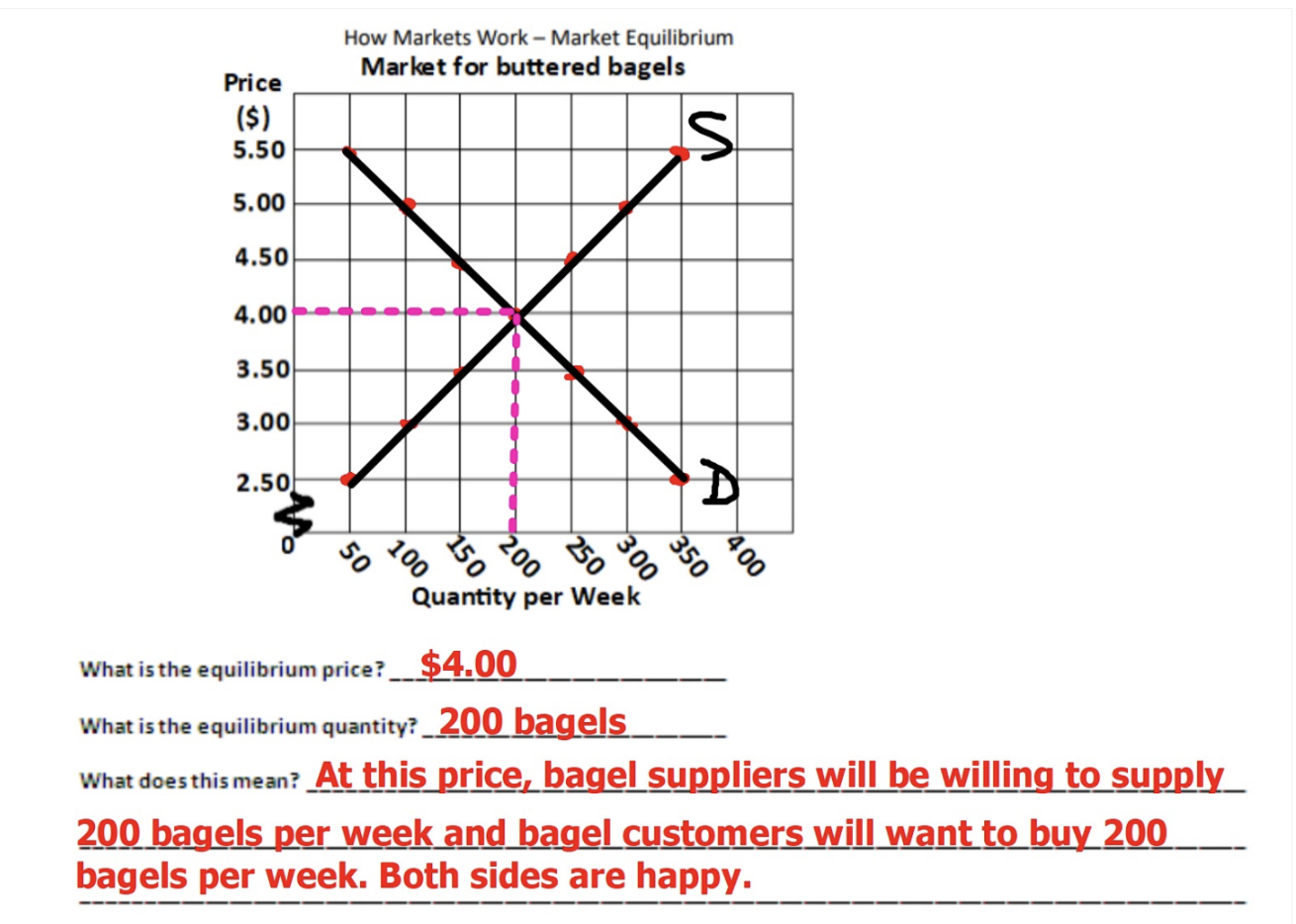
Equilibrium Price
The price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
Equilibrium Quantity
The quantity bought and sold at the equilibrium price
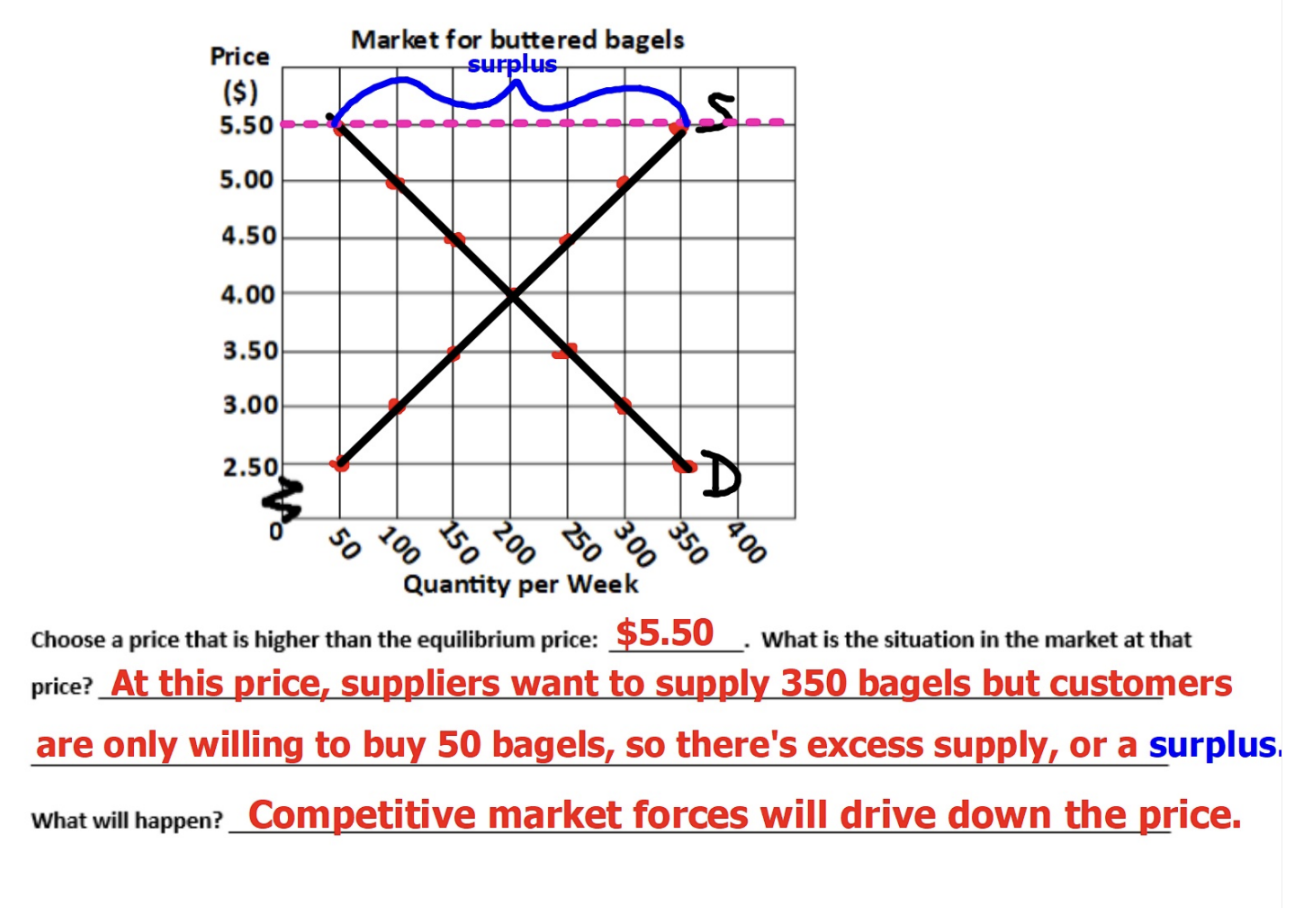
Surplus
A situation in which the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded (competitive market forces will drive down the price)
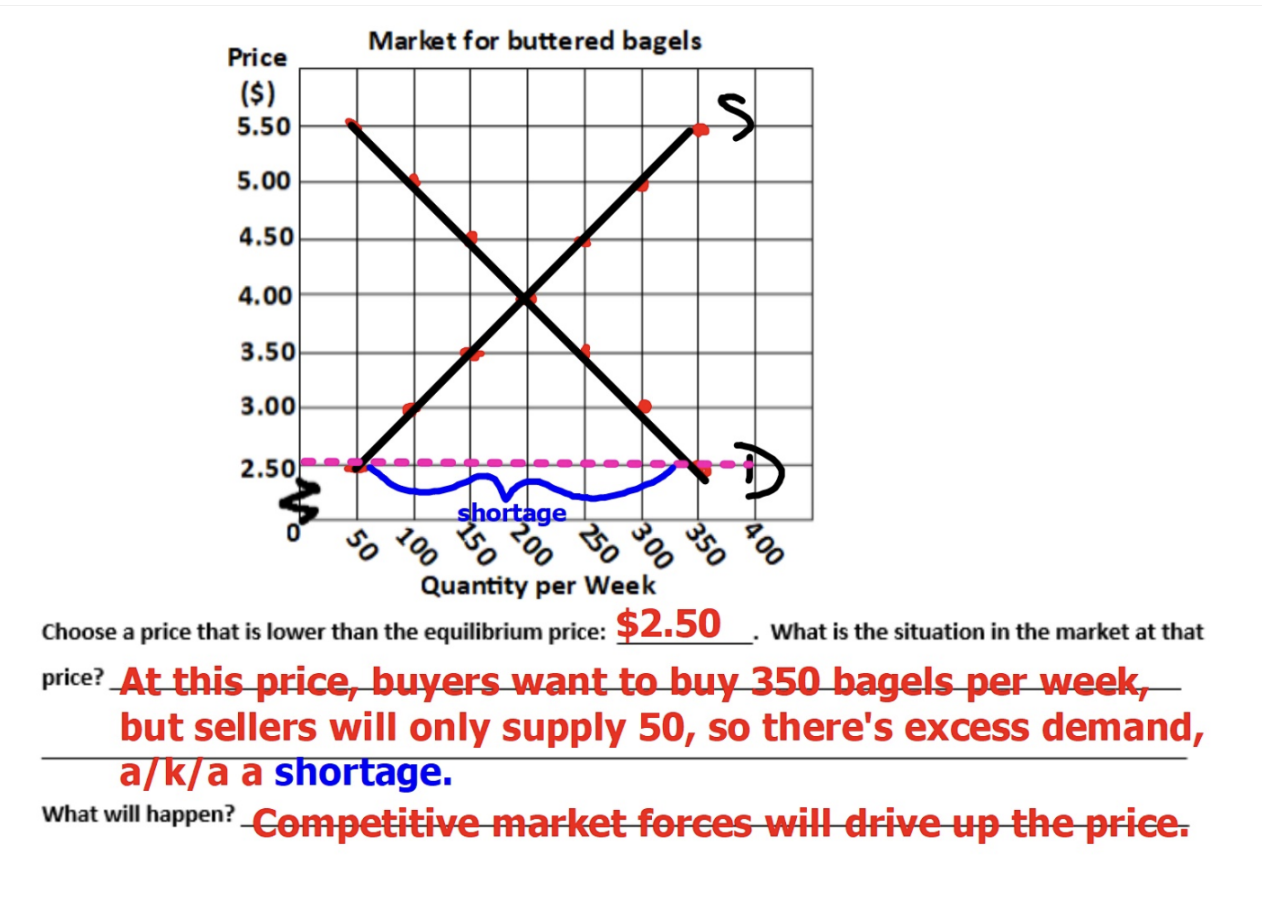
Shortage
A situation in which the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied (competitive market forces will drive up the price)
Equilibrium Quantity is NOT the same as..
supply (and/nor quantity supplied). Equilibrium quantity is the amount (quantity) where buyers and sellers are perfectly satisfied, where the market clears
When Demand and Supply increase/decrease in the SAME direction
Price is indeterminate and Quantity increases/decreases in same direction; opposite direction of shortage/surplus
When Demand and Supply increase/decrease in OPPOSITE directions
Quantity is indeterminate and Price increases/decreases with demand; same direction of shortage/surplus
Double shortage
Occurs when there’s a demand increase and supply decrease (causes equilibrium price to increase)
Double Surplus
Occurs when there’s a demand decrease and a supply increase (causes equilibrium price to decrease)