C2.2 Neural signalling
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Nerve impulse
Electrical signal passed between two cells, two types
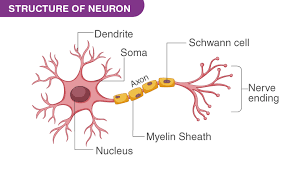
Draw neuron and outline functions of dendrites, axon and cell body
Dendrites → Receive data from another neuron
Axon → Carries electrical impulses
Cell body → Houses nucleus + organelles
Membrane potential
Voltage within membrane due to its distribution of ions
Resting potential
Electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane (-70mv)
Action potential
Rapid change in voltage across membrane
Depolarisation
Membrane potential goes from negative to positive
Repolarisation
Membrane potential goes from positive back to negative
Steps to action potential
Sodium-potassium pump maintains the electrochemical gradient of resting potential (-70mv) → 3 sodium, 2 potassium
Some potassium leaves the membrane
Some sodium voltage gate channels open
Some sodium ions leave the membrane through facilitated diffusion
Once threshold potential is reached, all sodium channels open and sodium continues to leave (-55mv)
Sodium channel gates close and potassium channel gates open
Potassium diffuses out of membrane
Sodium-potassium pump rests and goes back to its resting potential
Self-propagating
Depolarisation in one part triggers depolarisation in the next part
Saltatory conduction
Impulse jumping from node to node, increasing speed
Synapse
Gap between cells through which signals are passed
Steps for release of neurotransmitters from a presynaptic membrane
Action potential reaches the end of presynaptic neuron
Voltage-gated calcium ion channels open
Calcium ions enter the presynaptic neuron (facilitated diffusion)
Calcium ions force vesicles with neurotransmitters to fuse with the membrane
Neurotransmitters are released into the synapse (exocytosis)
Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse
Bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane
Ion channels open
If enough ions enter the post synaptic cell, that generates an action potential
Neurotransmitter is removed from the synapse → to stop this process
Threshold potential
Membrane potential that must be reached in order for voltage-gated ion channels to open
Local current
Movement of sodium ions between polarised and depolarised regions
Oscilloscope
Device that measures/visualises membrane potential
Exogenous chemical
Something that enters the body through an external source
Neonicotinoids
Blocks synaptic transmission by binding to acetylcholine receptors
Cocaine
Promotes synaptic transmission as it blocks the reuptake mechanism for dopamine
Summation
Multiple releases of an excitatory neurotransmitter
Consciousness
Simultaneous awareness of many things
Emergent property
Properties that are evident when components combine but are absent in the individual parts