Bio1200- Chapter 3
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based off of the slides she provided in class
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Organic Compounds
contain Carbon and Hydrogen
usually connected by covalent bonds
living organisms
May also contain O, N, P, and S
Some are small, but many are large and complex
ex. lipids, fats, proteins, carbs, nucleic acids
Inorganic Compounds
contain different elements
ionic bonds
found in environment
ex. salt and minerals
Microelements
Needed in much smaller amounts, usually used as cofactors for proper enzyme function
Mg, K, Ca, Fe, Cu
Macroelements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur (CHONPS)
Main components of macromolecules
Covalent Bonds
electrons are shared between atoms (strongest bond)
Disulfide bonds
A covalent bond between 2 S atoms
Ionic bond
bond between a neg charged ion and a positive charged ion
Hydrogen bond
bond between an H and an electroneg atom (O or N)
Nonpolar covalent bonds
equally sharing electrons (H2)
Polar covalent bonds
unequally sharing electrons (H20)
Electronegativity
atoms tendency to attract electrons
Functional Groups:
(names, and polar/non, charged or not)
Hydroxyl: R-OH (POLAR)
Carbonyl: R-C=O (POLAR)
Carboxyl: R-COOH (POLAR, charged)
Amino: R-NH2 (POLAR, charged)
Sulfhydryl: R-SH (POLAR)
Phosphate: R-PO4 (POLAR, charged)
Sulfate: R-SO4 (POLAR, charged)
Methyl: R-CH3 (nonpolar)
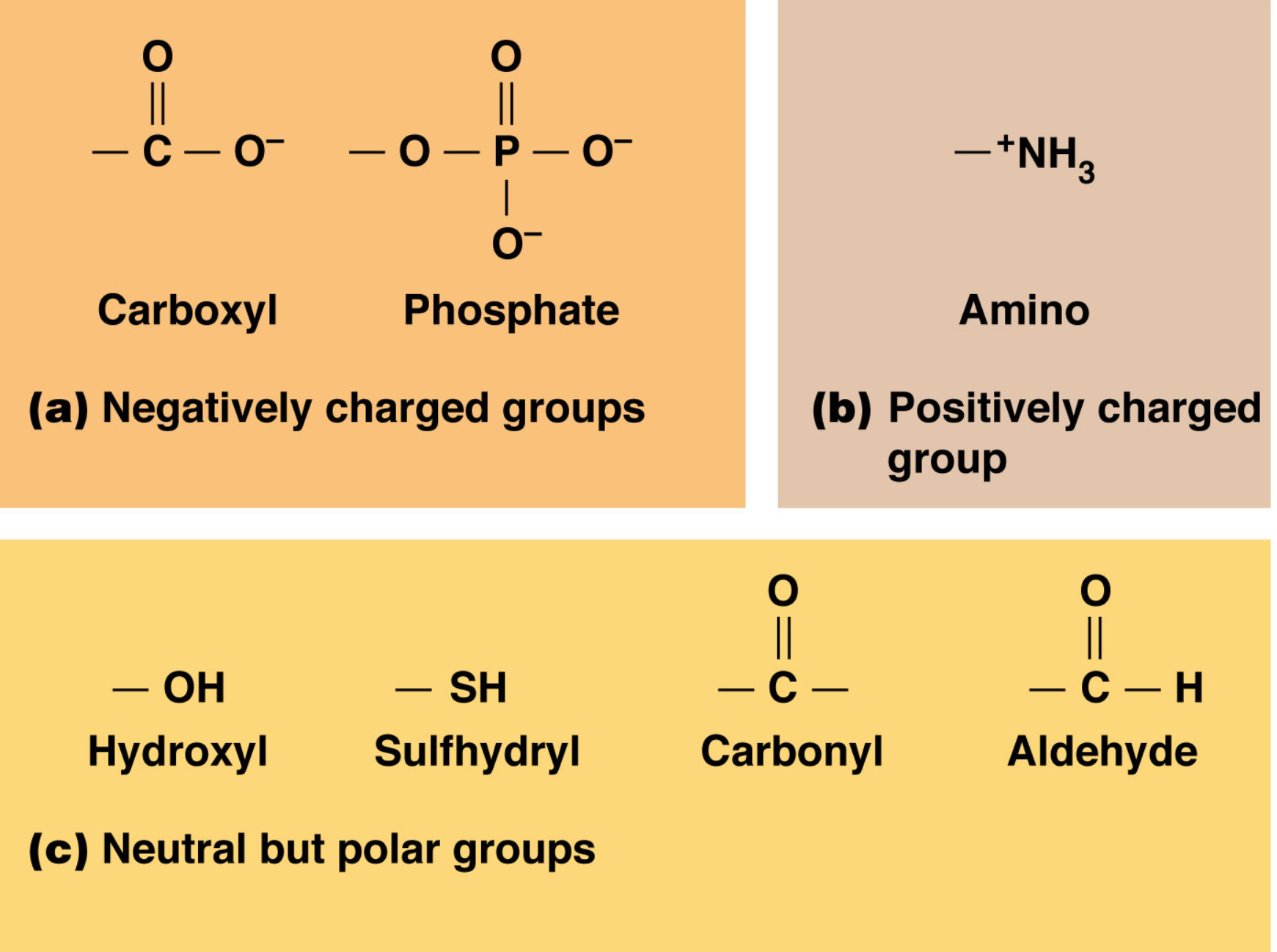
Review Functional Groups on doc camera
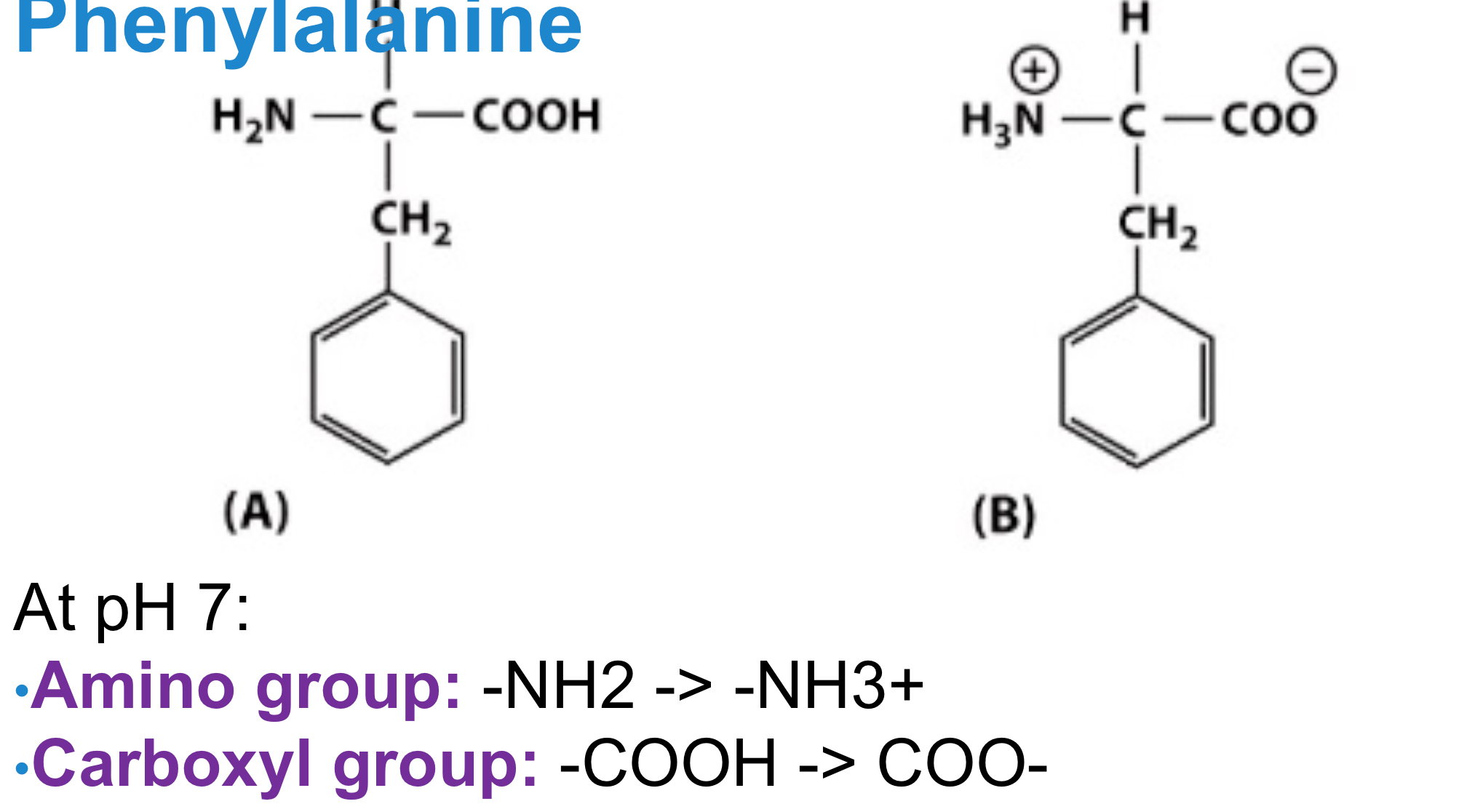
Carboxyl: R-COOH = R-COO-
Amino: R-NH2 = R-NH3
Uncharged and Charged Forms of Amino and Carboxyl in Phenylalanine
See image
Dehydration Synthesis Reaction
to CONNECT subunits together to make a longer polymer (remove H20)
You have two small molecules (like building blocks).
They want to join together to make something bigger.
But to connect, they have to remove a water molecule (H₂O).
One gives up an H (hydrogen).
The other gives up an OH (hydroxyl).
Those two pieces (H + OH) combine to form water.
Now that water is gone, the two molecules are stuck together.
Imagine trying to snap two Lego bricks together, but there’s a tiny piece of gum between them. You have to pull that gum off (that’s the water), and then the bricks can click together.
Hydrolysis Reaction
to BREAK a large polymer into its subunits (add H20)
You have a big molecule (like two building blocks stuck together).
You add a water molecule (H₂O).
The water breaks the bond:
One piece takes the H (hydrogen).
The other takes the OH (hydroxyl).
Now you have two separate smaller molecules again.
Imagine you want to pull two Lego bricks apart, but they’re stuck super tight. You pour a little water on them, and suddenly they come apart. That water helped break the connection.
The 4 Macromolecules
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfate
Carbohydrates: CH2O (Sugars, starch)
Lipids: CHO (Fats, oils)
Proteins: CHONS (Enzymes)
Nucleic Acids: CHONP (DNA, RNA)
Carbohydrates
gen formula: CH20
monosaccharides: simple sugars
disaccharides: 2 sugars connected by a covalent bond
Carbohydrate Dehydration Synthesis Model
2 simple sugars are combined to form a disaccharide (connected by covalent bond)
A molecule of water is removed during the reaction
Sugars are connected by a covalent bond called a glycosidic bond
What shape does the molecule sugar take
Linear and ring form
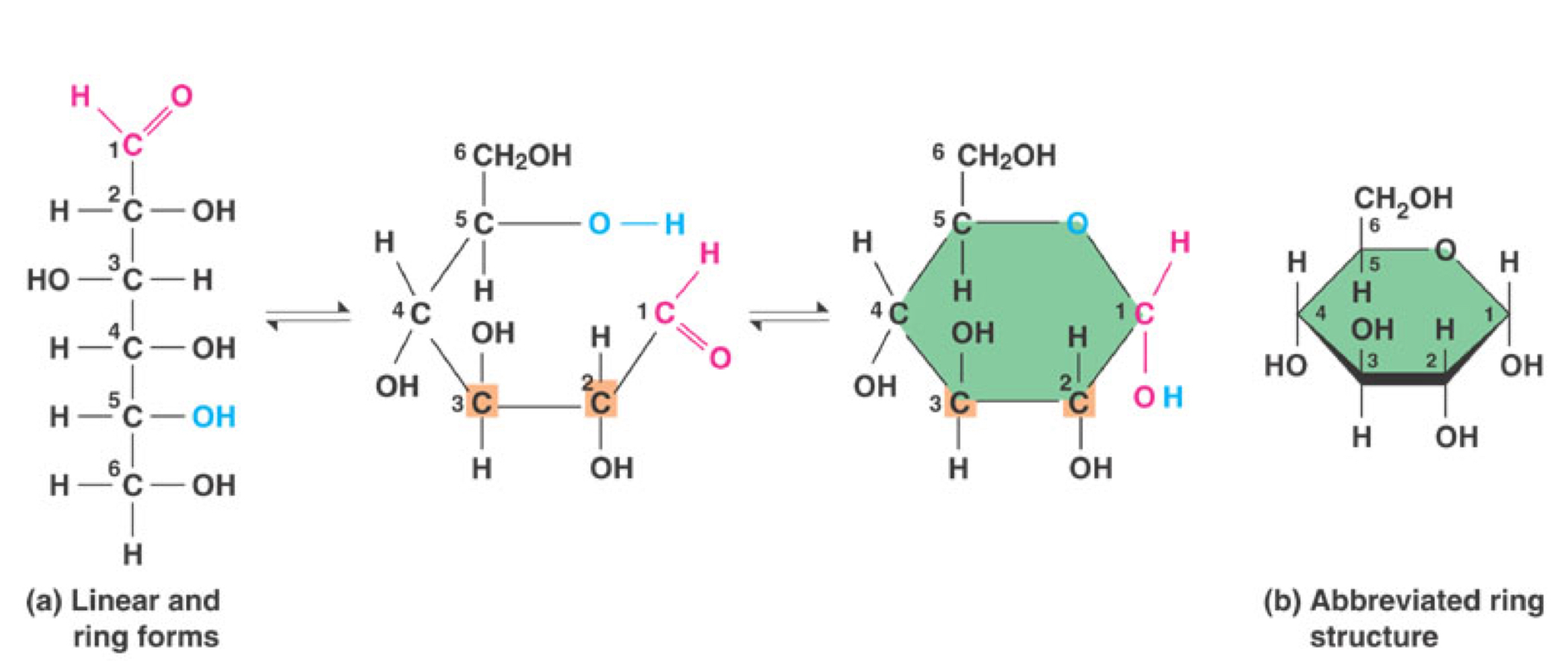
Sugar diagrams- Every angle represents blank
A Carbon atom
Carbohydrate Polysaccharides
long polymer made of sugar subunits
chain of sugars can be straight (unbranched) or branched
Carbohydrate Storage Polysaccharides
Stored form of energy in the cell
They are connected by alpha glycosidic bonds
Most organisms can break alpha glycosidic bonds, so these compounds are easily broken down when the cell needs sugar
ex. starch, glycogen
Storage Carboohydrates
Plants:
Starch
Glucose Polymer unbranched or less branched
alpha glycosidic bonds
Animals:
Glycogen
glucose polymer
branched chain
alpha glycosidic bonds
Structural Polysaccharide
structural component of the cell
sugars are connected by beta glycosidic bonds
most organisms can’t break beta glycosidic bonds, which makes them very stable
ex. cellulose chitin
Cellulose
(structural polysaccharide)
glucose polymer
straight chain
beta glycosidic bonds
Glycoproteins
Proteins with sugars covalently attached to them
Functions of carbohydrates
food/energy- mono/disaccharides- used to make short term chemical energy used in enzyme reactions
storage- storage polysaccharides- stored form of chemical energy, to be used later as food (starch, glycogen)
structure- polysaccharides- structural component of cells, like cell wall, shell/ exoskeleton of insects, extracellular matrix of animals (cartilage)- cellulose
Proteins
made up of amino acids
amino group: NH2 or NH3+ (pH7)
carboxyl group: COOH or COO-
Types of Amino Acids
NOT SOLUABLE
Non polar or totally uncharged Amino acids that are hydrophobic
Polar (partially charged) (uncharged)
Polar (charged)
Non polar Amino Acids
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Proline, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Cysteine, Methionine
Polar Uncharged Amino Acids
Serine, Threonine, Asparagine, Glutamine, Tyrosine
Polar, Charged Amino Acids
Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid, Histidine, Lysine, Arginine
Peptide Bonds
SUB GROUP OF COVALENT BONDS
connect amino acids
OH of amino acids combines with an H from AA to form H20
The C if the carboxyl of Amino Acid1 is connected to the N of the amino group 2
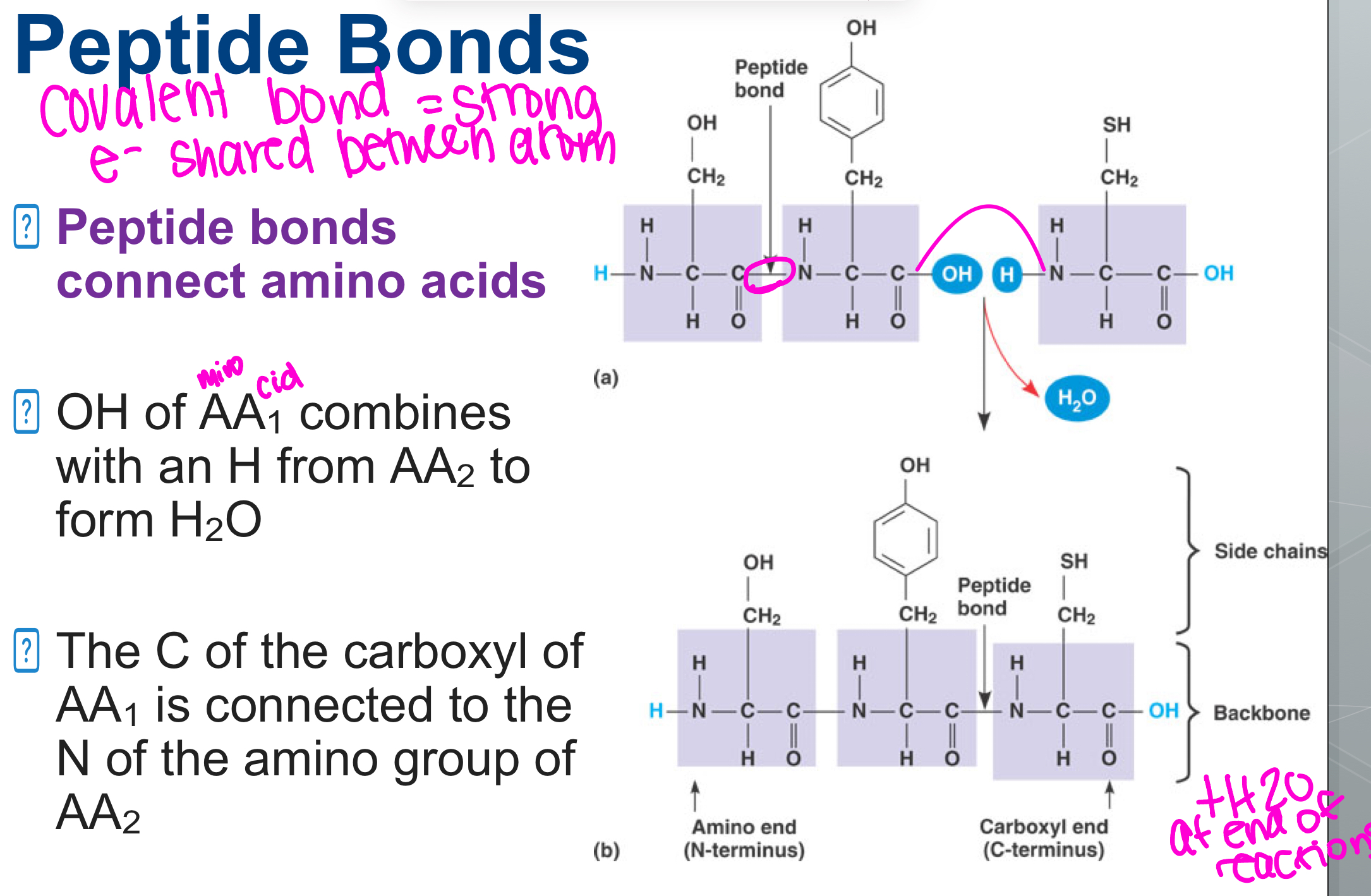
Formation of Peptide Bond
2 amino acids are connected together
a molecule of H2O is produced
Reaction: Dehydration Synthesis
Polypeptide
chain of amino acids
front group- amino group, Nitrogen terminus
rear end- carboxyl group and is called Carbon terminus
Protein structure
primary structure- sequence of amino acids connected by peptide bonds
secondary structure- localized folding of polypeptide chain (interaction between nearby amino acids), held together by H bonds
tertiary structure- final 3D structure of a polypeptide chain, interactions between distant amino acids
quaternary structure- different protein subunits interact to form the whole protein (only proteins that have more than one subunit have this structure)
Protein Denaturation
unfolding of proteins so that they no longer function properly
cause: bonds involved in 3D structure are broken
H bonds, Ionic, Disulfide, Hydrophobic Interactions
Protein Functions
enzymes- perform chemical reactions
structural proteins- can build things out of proteins
receptor proteins- communications
transport proteins- in and out of the cell
hormones- long distant signal molecules
Nucleic Acids
made out of nucleotides
5 carbon sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base
Nucleotide Structure
RNA- sugar ribose in ribonucleotides (NTPs)- breaks easily
DNA- contains sugar deoxyribose in deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs)
Nucleic Acid Nitrogenous Bases
Purines: bases with 2 rings
ex. Adenine, Guanine
Pyrimidines: bases with only 1 ring
ex. Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
Nitrogenous bases in RNA
AGCU
Nitrogenous bases in DNA
AGCT
Phosphodiester Bonds
connect nucleotides on the same strand
covalent bonds
DNA structure
Double stranded
antiparallel
connected by phosphodiester bonds to make sugar-phosphate backbone
bases in opposite strands are connected by H bonds so that they can make base pairs
pairs by complement bases
A-T
G-C
Complementary Bonds
held together by H bonds
Functions of DNA
genetic blueprint
contains genes
genes are code for proteins
What is RNA
made of ribonucleotides= NTPs
sugar=ribose
bases are GACU
single-stranded
Functions of RNA (the different types)
mRNA- codes for proteins
tRNA- brings AA to ribosomes during protein synthesis
rRNA- structural part of the ribosome
snRNA- RNA splicing
Lipids
gen formula- CHO
chem properties- lg and hydrophobic (only group not soluble in water)
ex. fats, oils, steroids, fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipdis
Liquid types
triglycerides- used for stored foods
phospholipids- struct part of membrane
steroids
Lipids as Amphipathic
amphipathic molecules have both a polar and non polar end
ex. fatty acids, phospholipids
Triglycerides/ structure
LIPIDS
function is to store energy
Glycerol, 3 fatty acids, triglyceride
LIPIDS
g- 3C alc
3FA- carboxyl group+ long hydrocarbon chain
T- glycerol + 3 fatty acid molecules
Saturated vs Unsaturated fats
LIPIDS
sat- solid at room temp, single bonds in fatty acids- all three fatty acids are sat
unsat- liquid at room temp and there will be at least one double or triple bond (tendency to kink)- bond has at least one unsat FA, kink
Phospholipids
component of membrane (phospholipid bilayer)
Structure-
glycerol
2 fatty acids
phosphate group
polar headgroup
Phospholipids assemble
into bilayer
hydrophobic tails face one another
polar headgroups- exposed to water
Steriods (structure and function)
LIPID
most are hydrophobic
Structure: 4 characteristic rings, and side chain
Function: component of membranes, hormones