Sexual Reproduction
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What happens during Prophase 1
Centriols and Spinde fibers appear. Chromosomes are visible
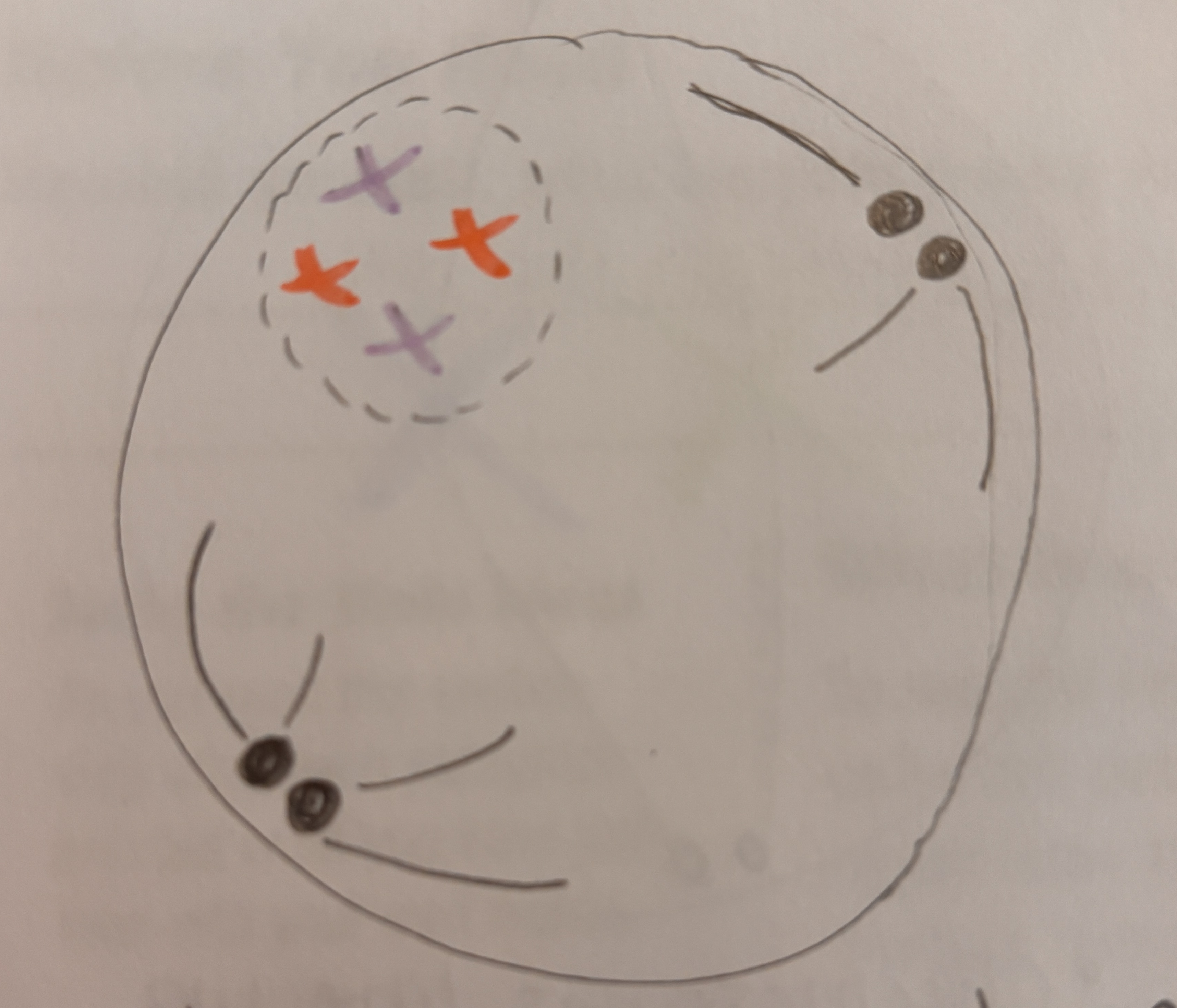
What happens during Metaphase 1
Most important. Chromosomes line up double file with their Homologous pairs. Crossing over and independent assortment occurs.
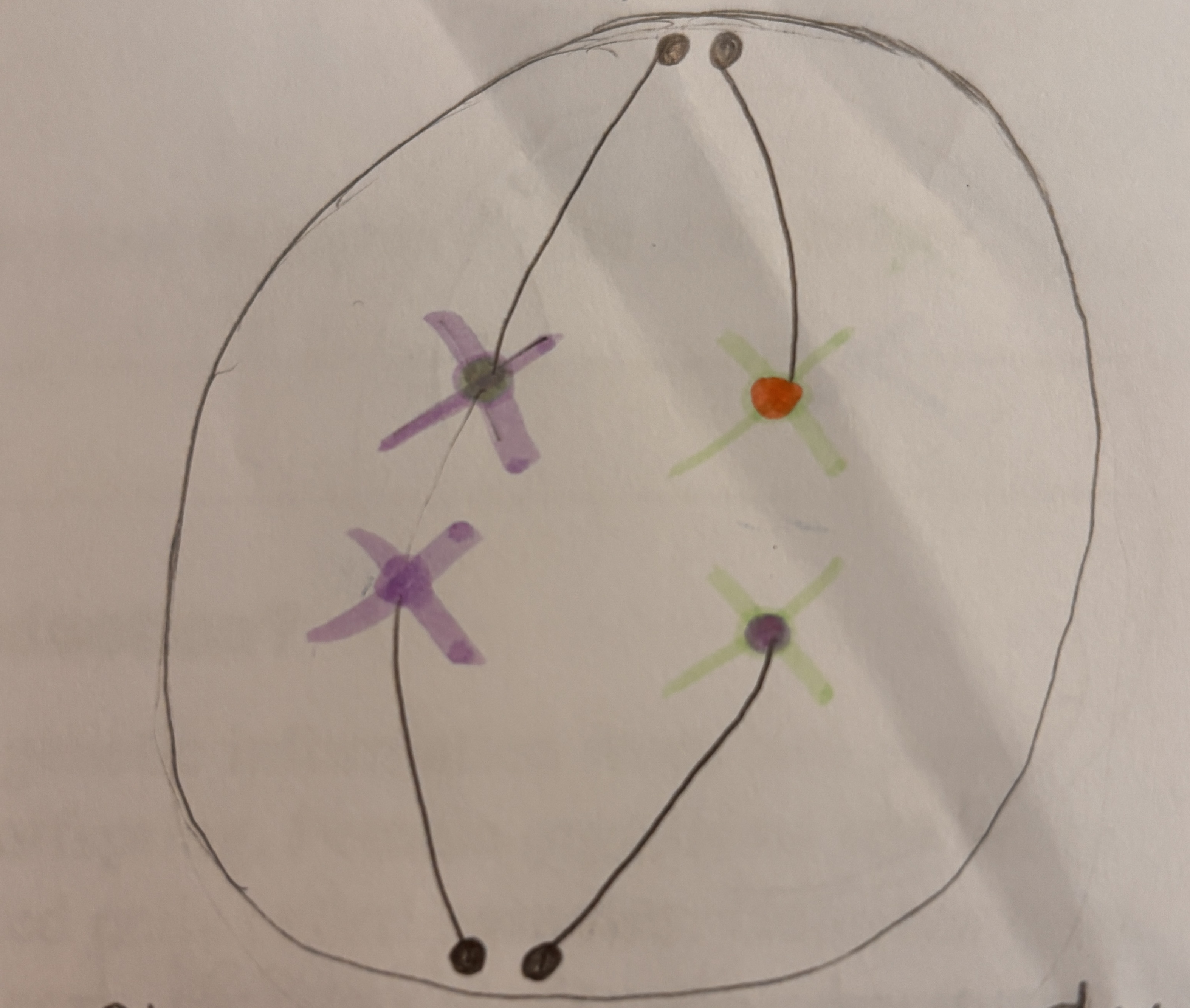
What happens during Anaphase 1
Spindle fibers contract and pull the Homologous pairs apart.
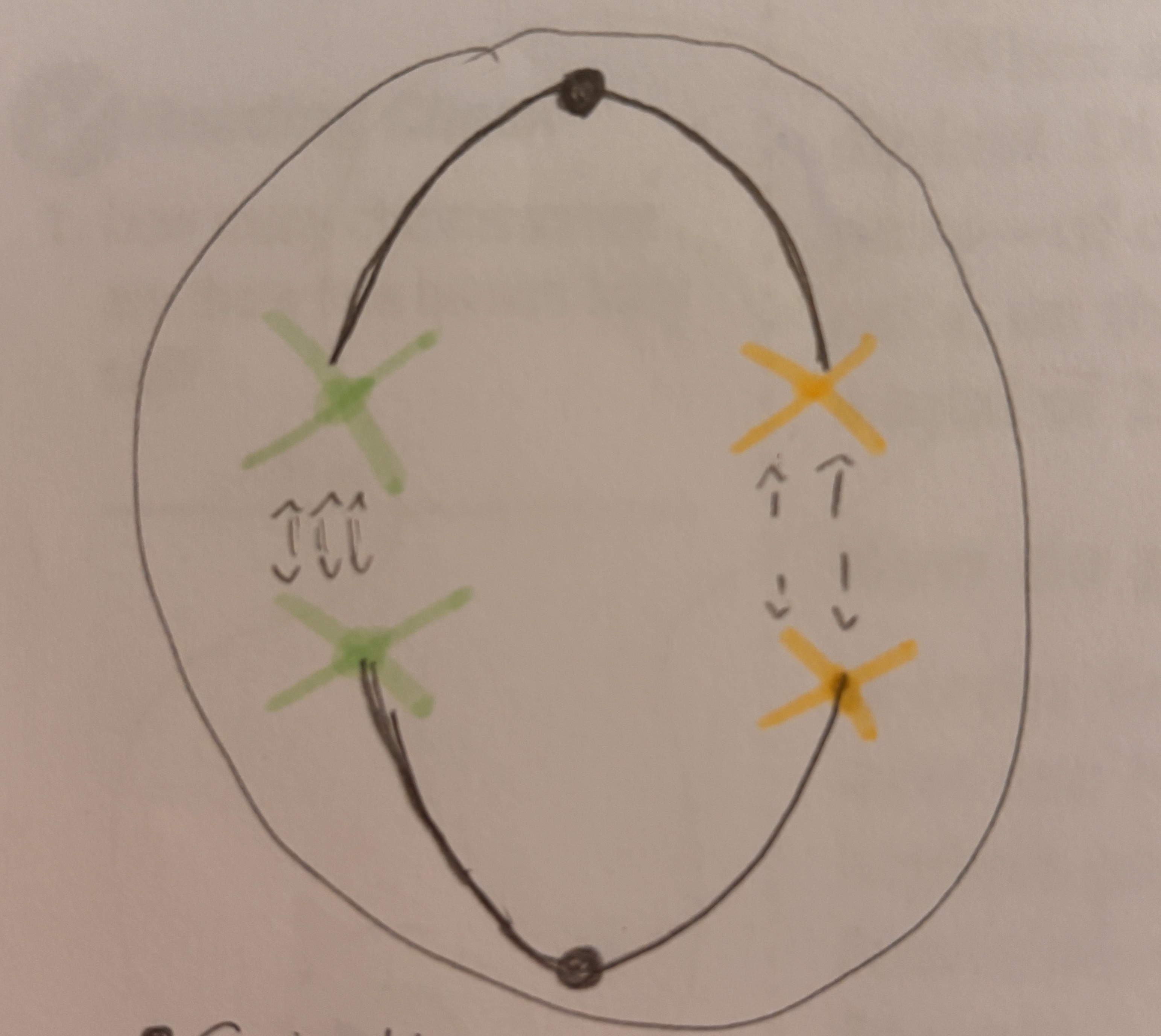
What happens during Telophase 1
Nuclear membrane forms around each new nucleus. Spindle fibers break down. Cell begins to divide (cytokinesis)
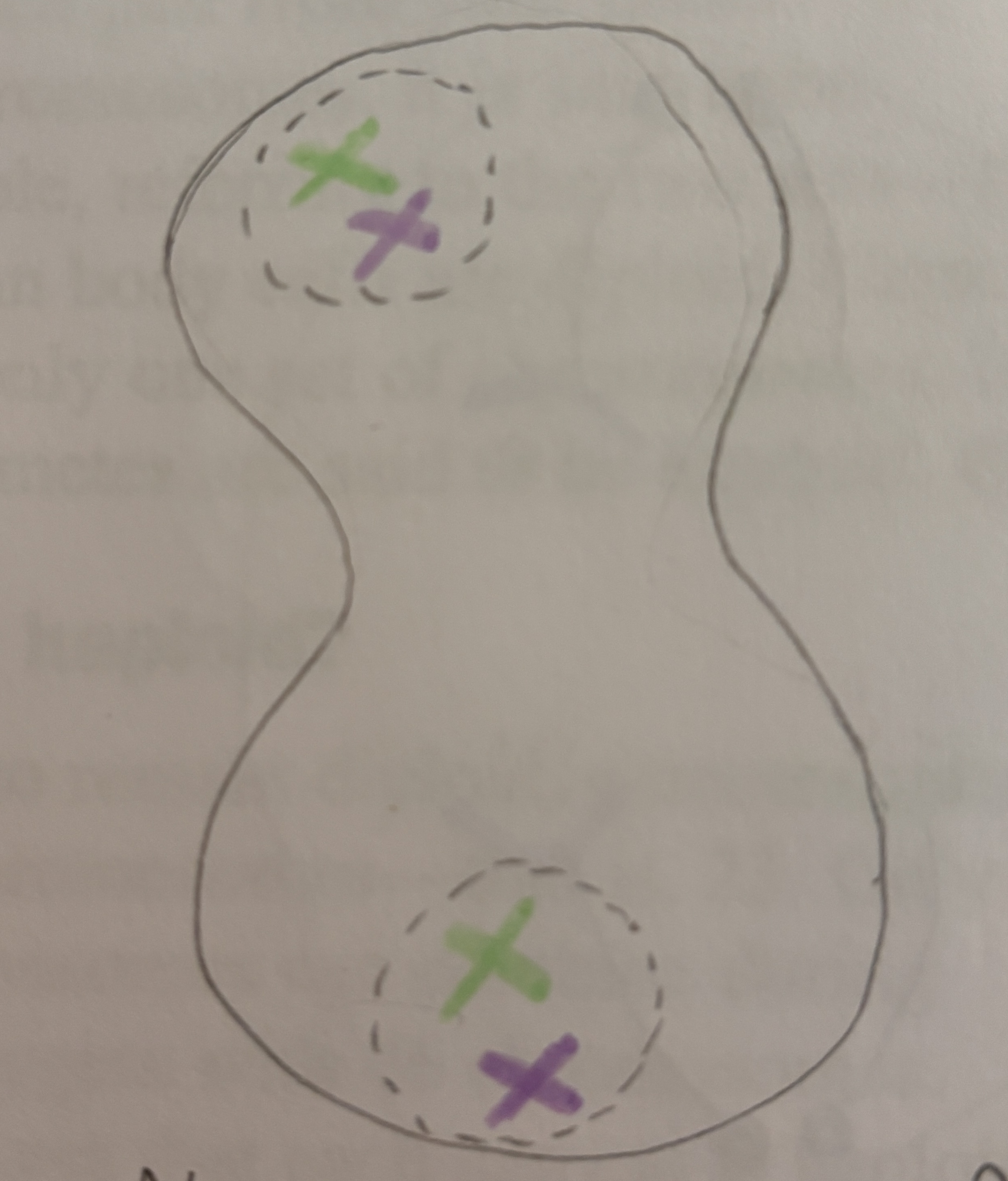
What happens during Prophase 2
Same steps as prophase 1.
What happens during Metaphase 2
Chromosomes line up single file across the middle of the cell.
What happens during Anaphase 2
Spindle fibers contract and pull sister chromatids apart.
What happens during Telophase 2
Same as Telophase 1.
Define Gametes
Are specialized cells necessary for reproduction that are haploid cells. in animals, male gametes are called sperms and female gametes are called eggs.
Define Fertilization
when an egg cell and a sperm cell unite.
Define Haploid Cell
Cells that have 1 copy of every chromosome (23)
Define Diploid Cells
Cells that’s have 2 copies of every chromosome (23+23=46)
Define Zygote
A fertilized cell
two haploid cells become a diploid cell
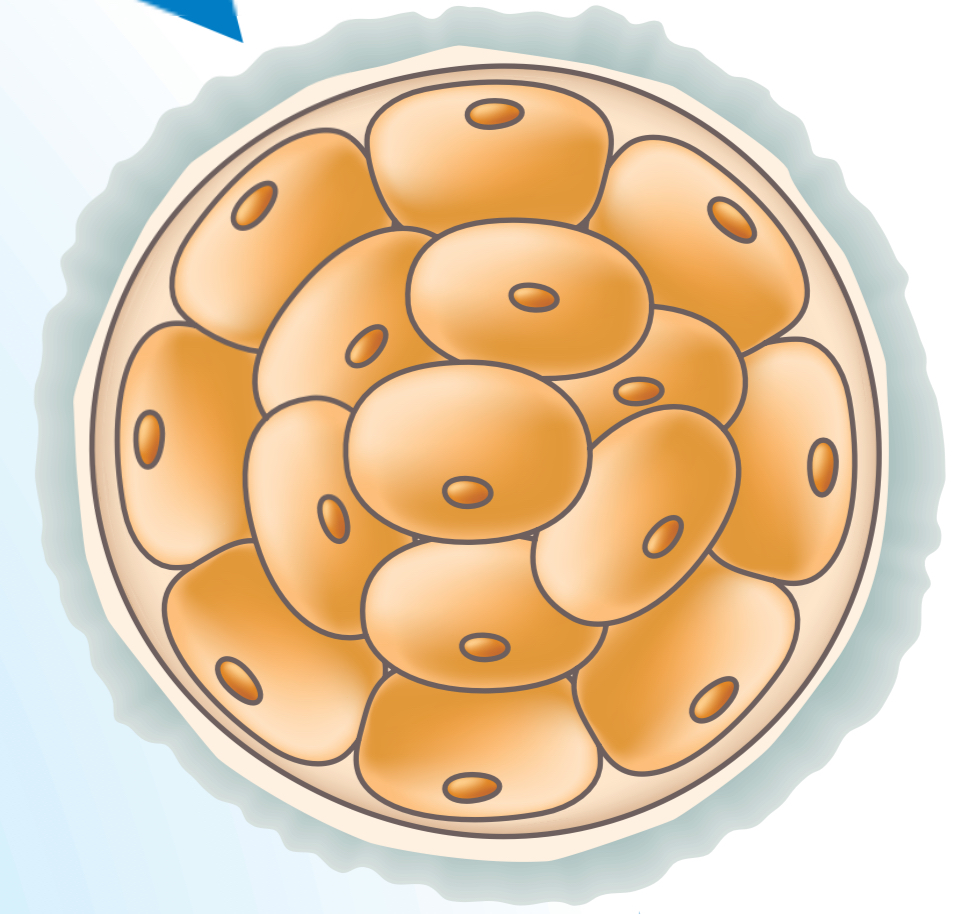
Define Morula
When the zygote divides many times to form a ball of cells (end of first week)
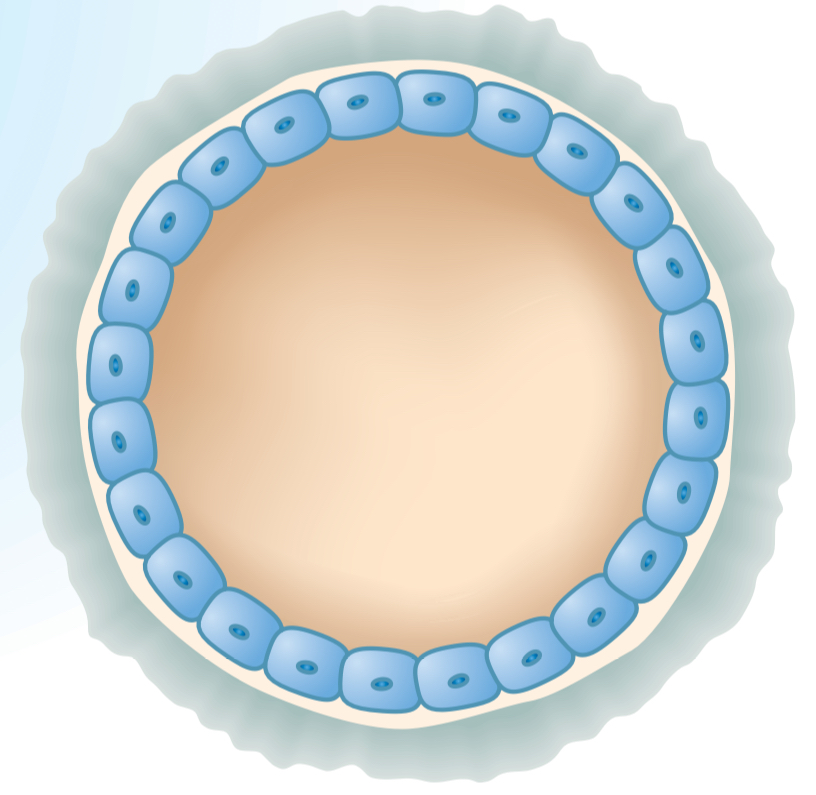
Define Blastula
When a hallow ball of cells forms
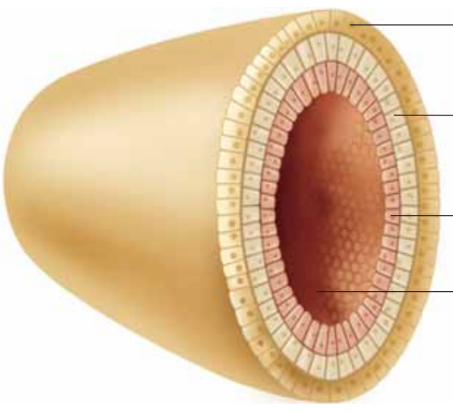
Define Gastrula
the cells of the blastula organize themselves into three layers. The development of the embryo.
How is Meiosis II similar to Mitosis
both processes involve the separation of sister chromatids and have similar phases.
How is Meiosis I different from Mitosis?
In meiosis, homologous pair up and are separated reducing the chromosome number in half (diploid to haploid)
Mitosis
Maintains the chromosome number. It produces genetically identical daughter cells for growth, repair, or asexual reproduction.
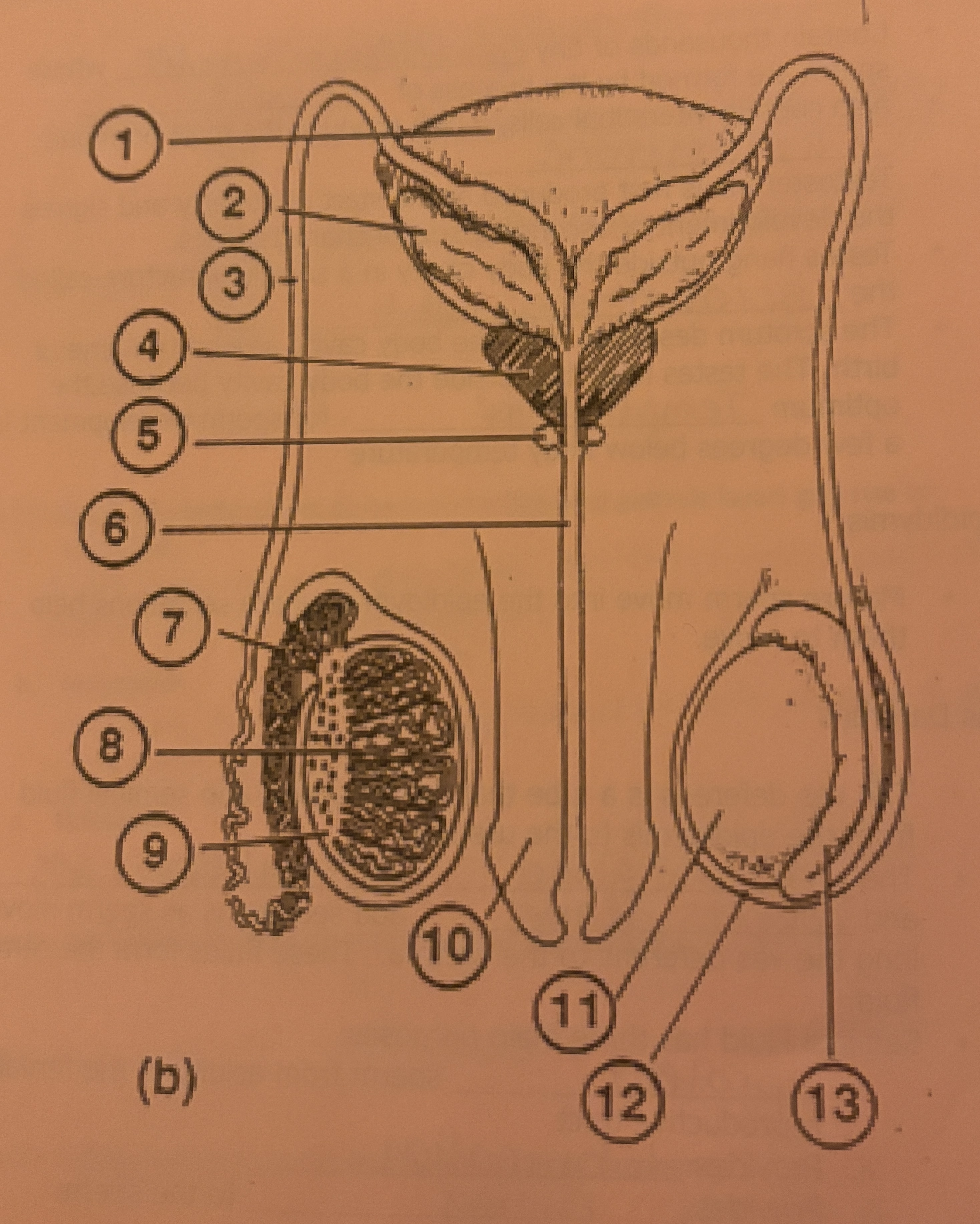
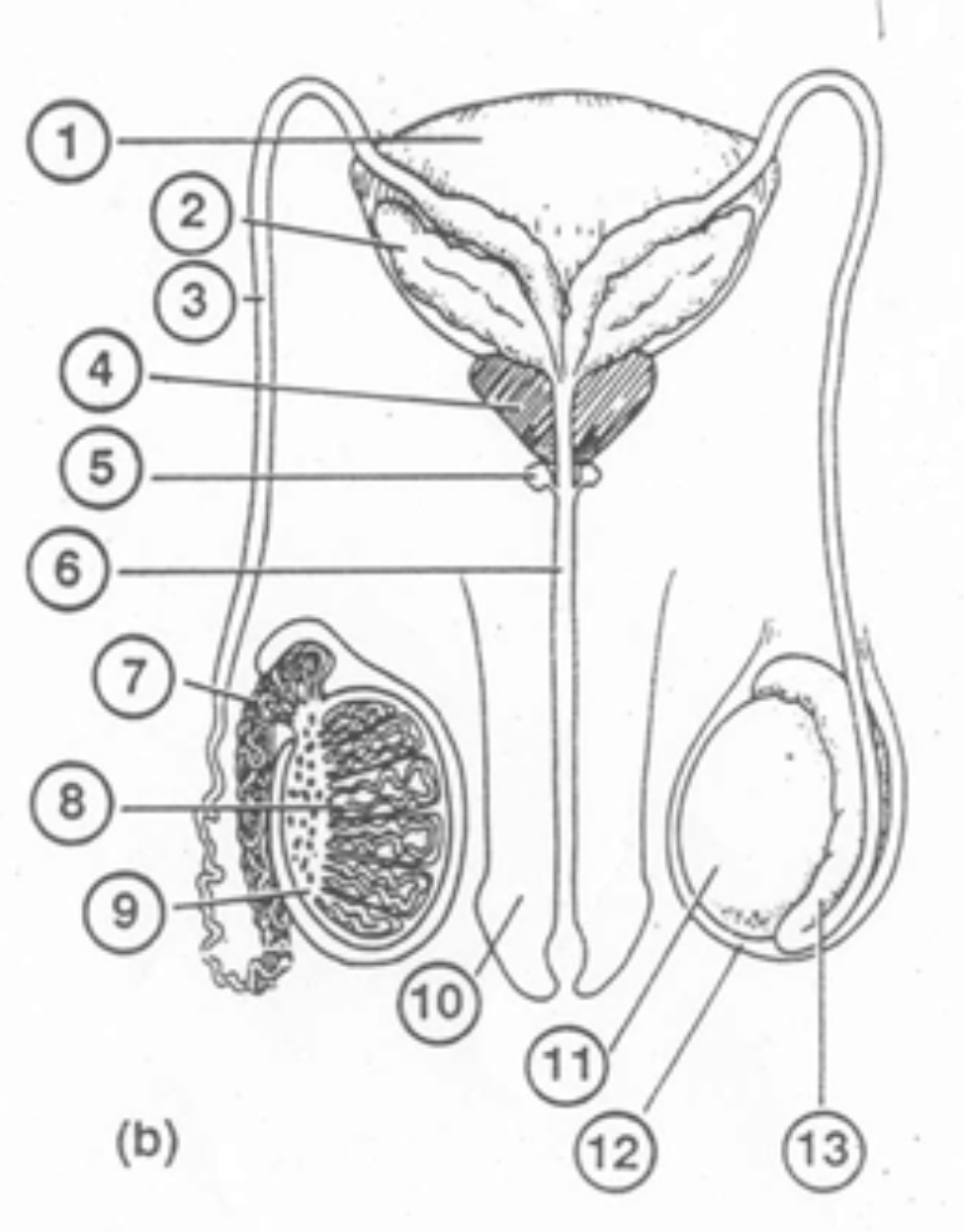
What is #1 called
Bladder
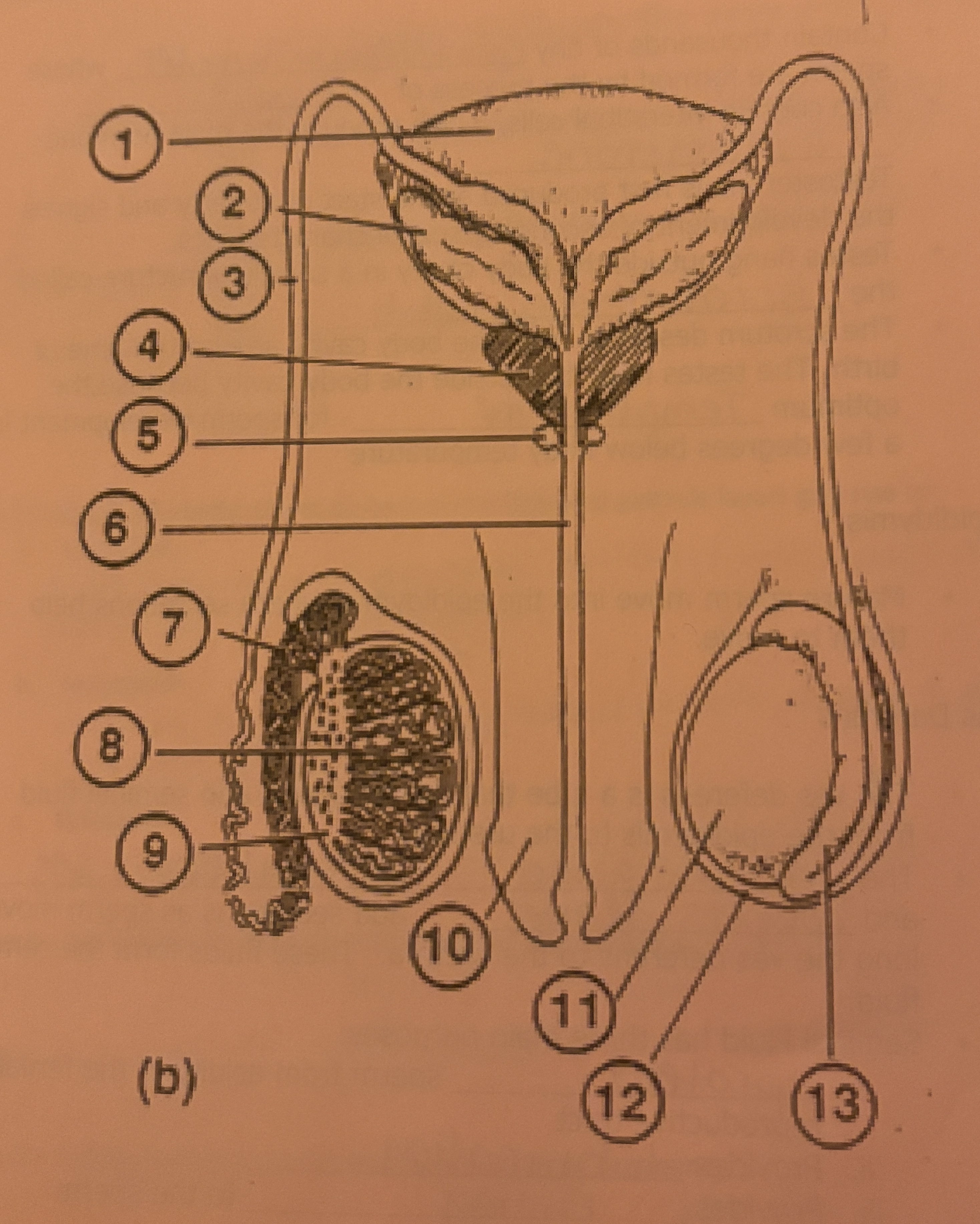
What is #2 called
Seminal Vesicle
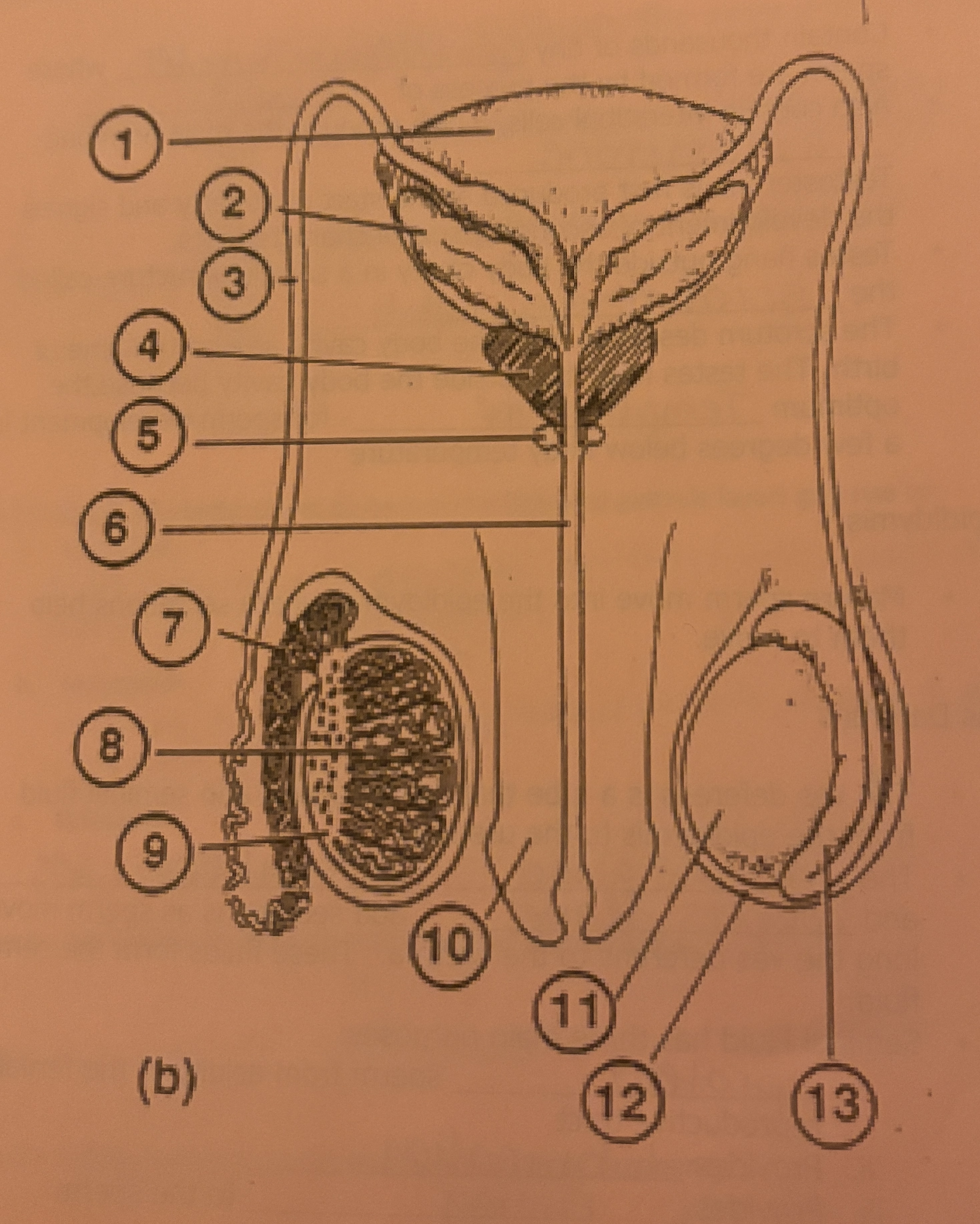
What is #3 called
Vas deferens
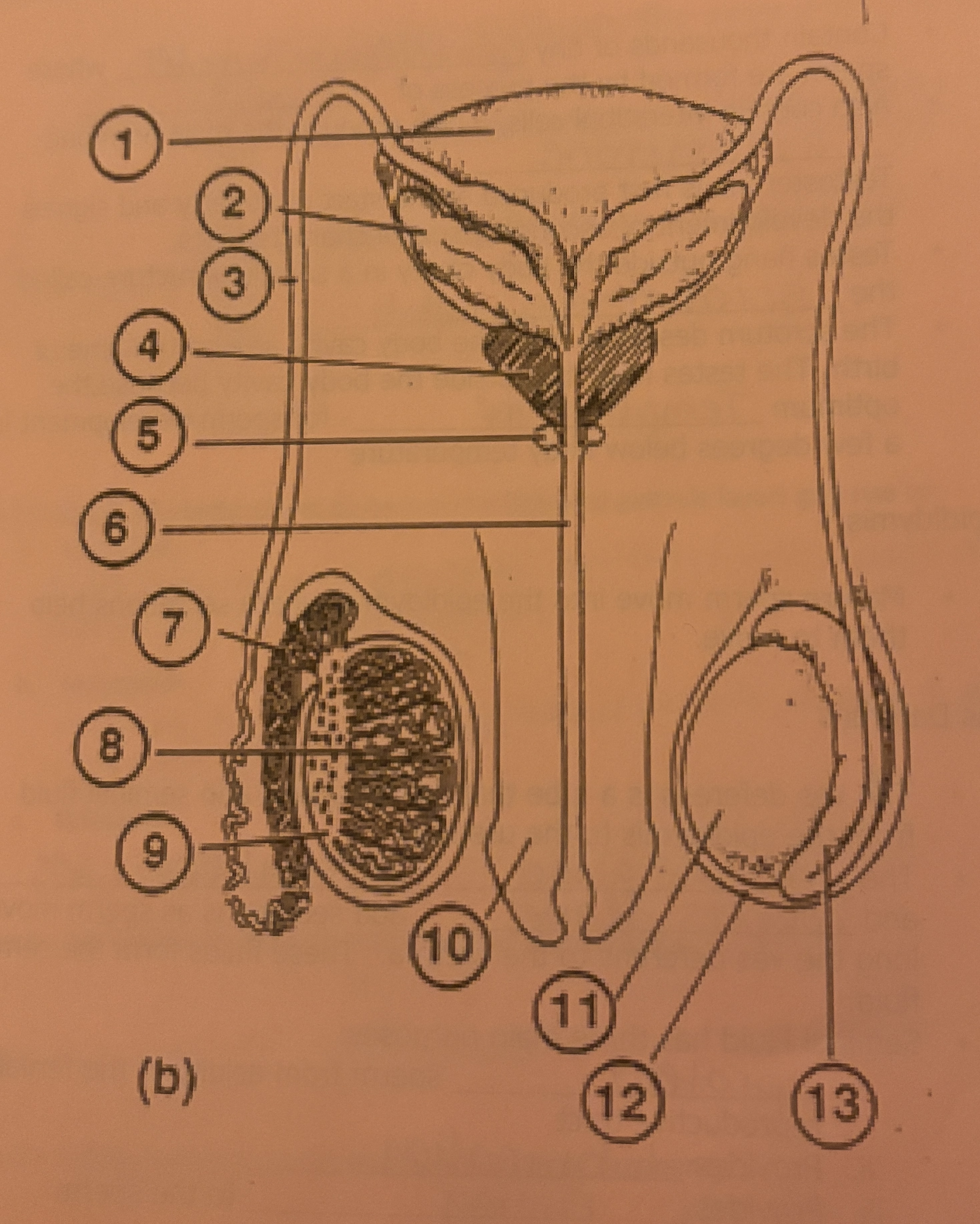
What is #4 called
Prostate Gland
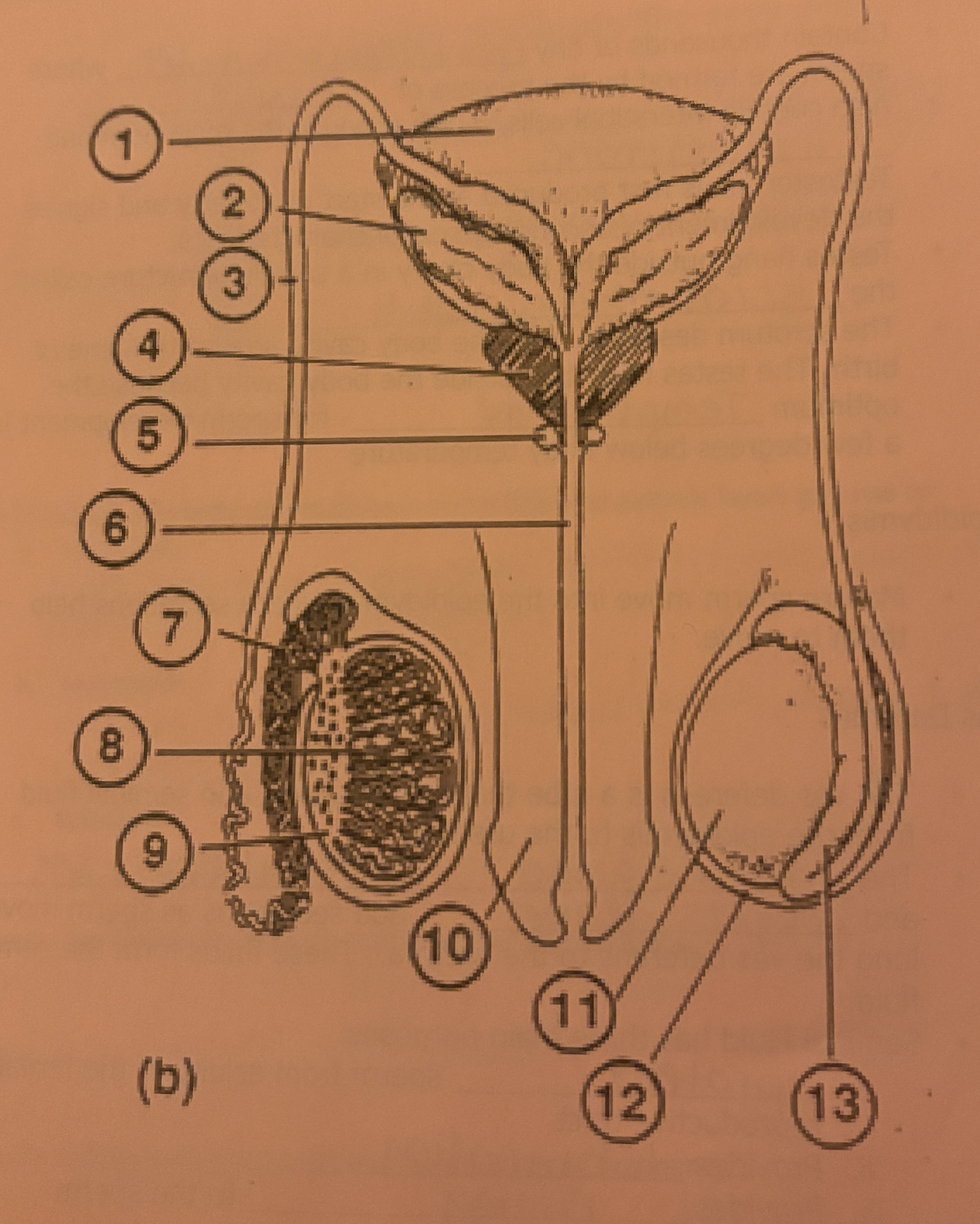
What is #5 called
Cowpers Gland
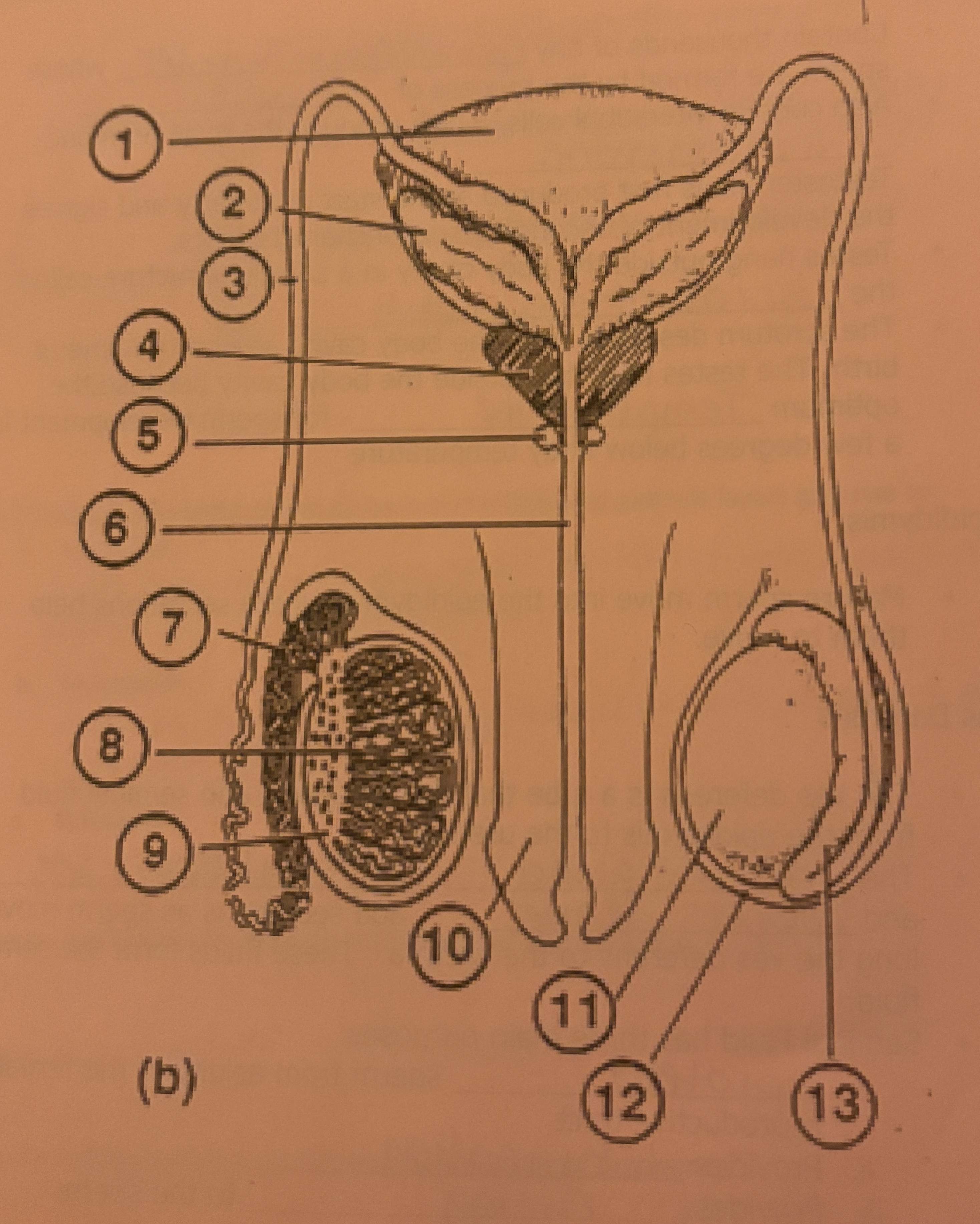
What is #6 called
Urethra
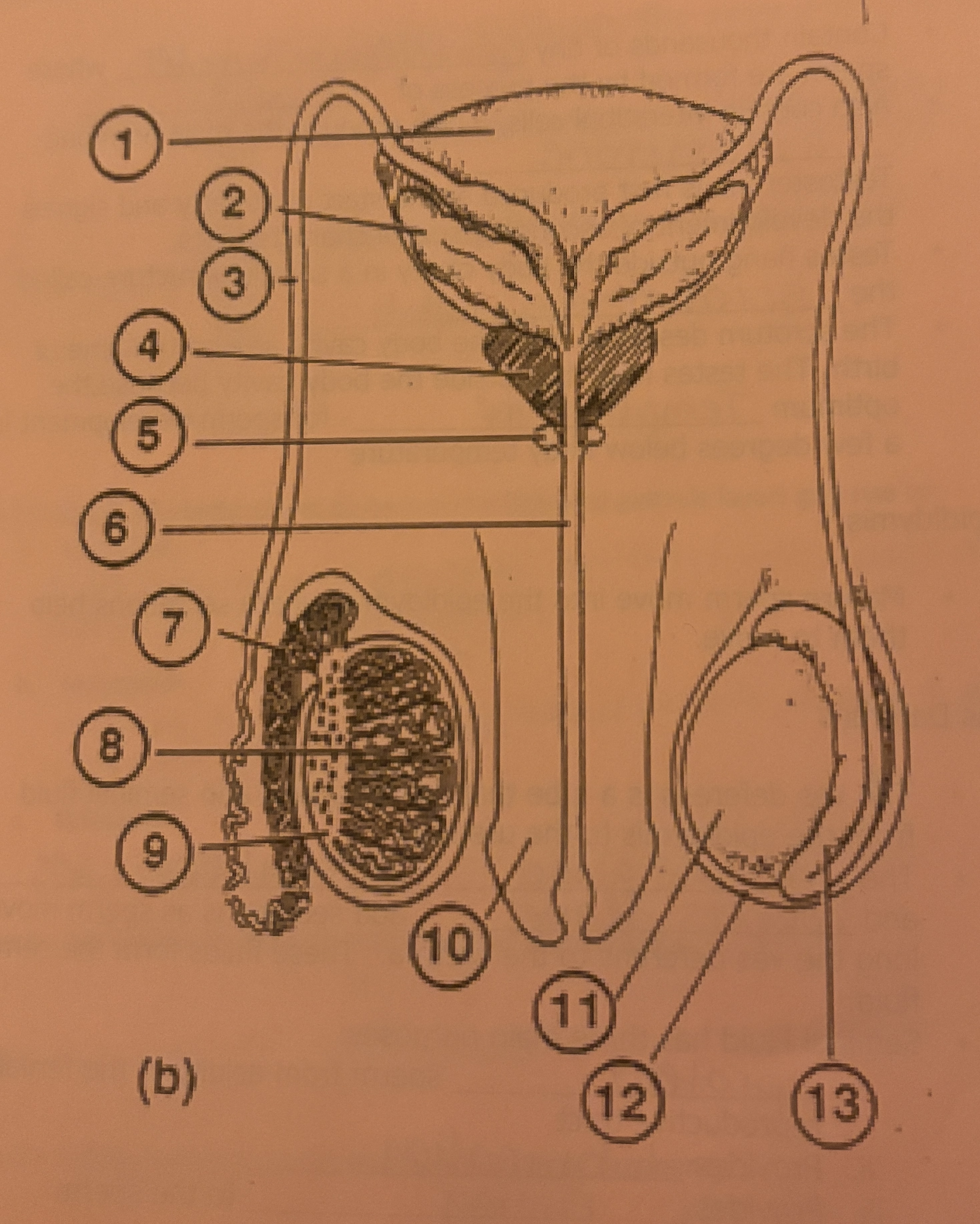
What is #7 called
Epididymis
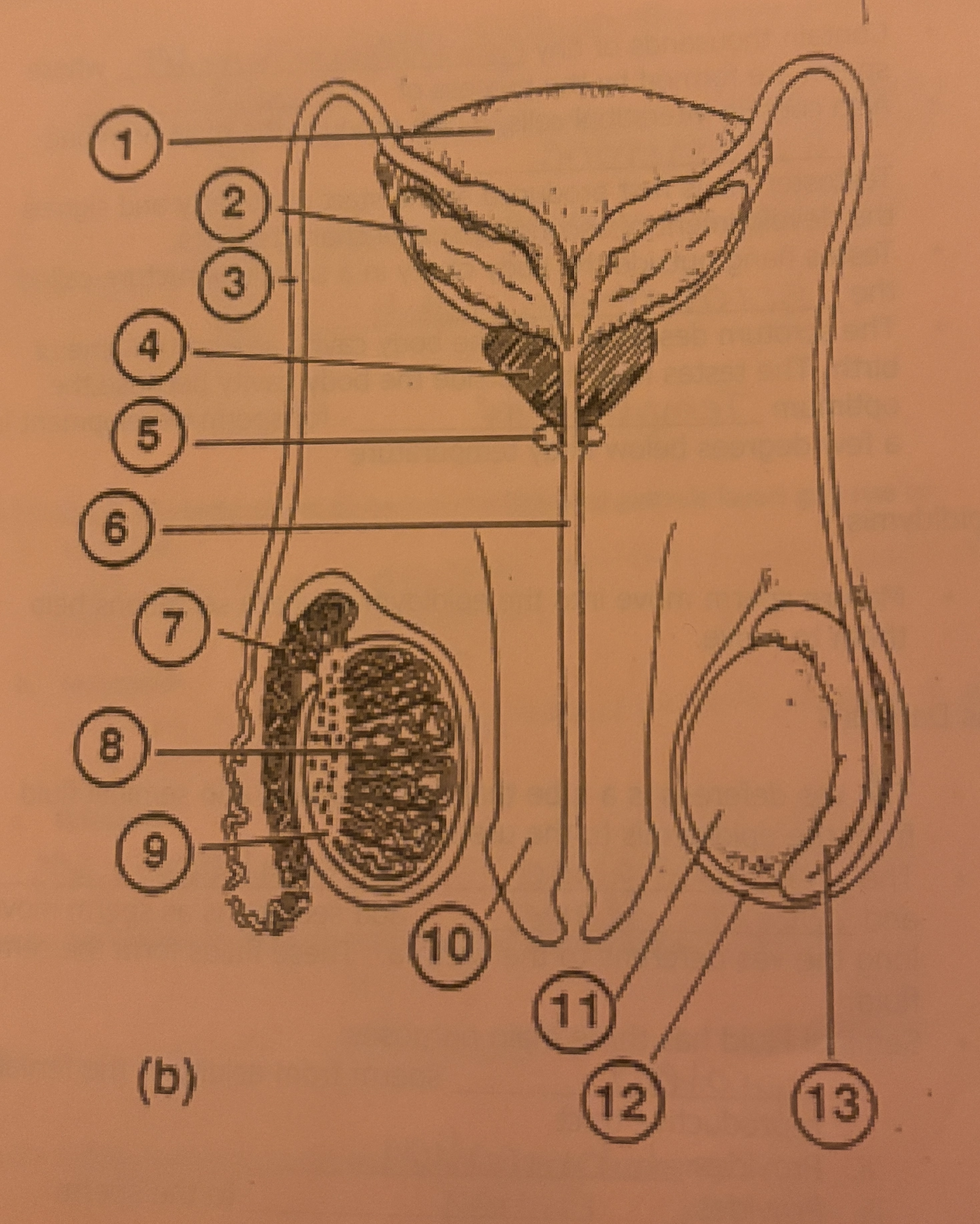
What is #8 called
Seminiferous tubules
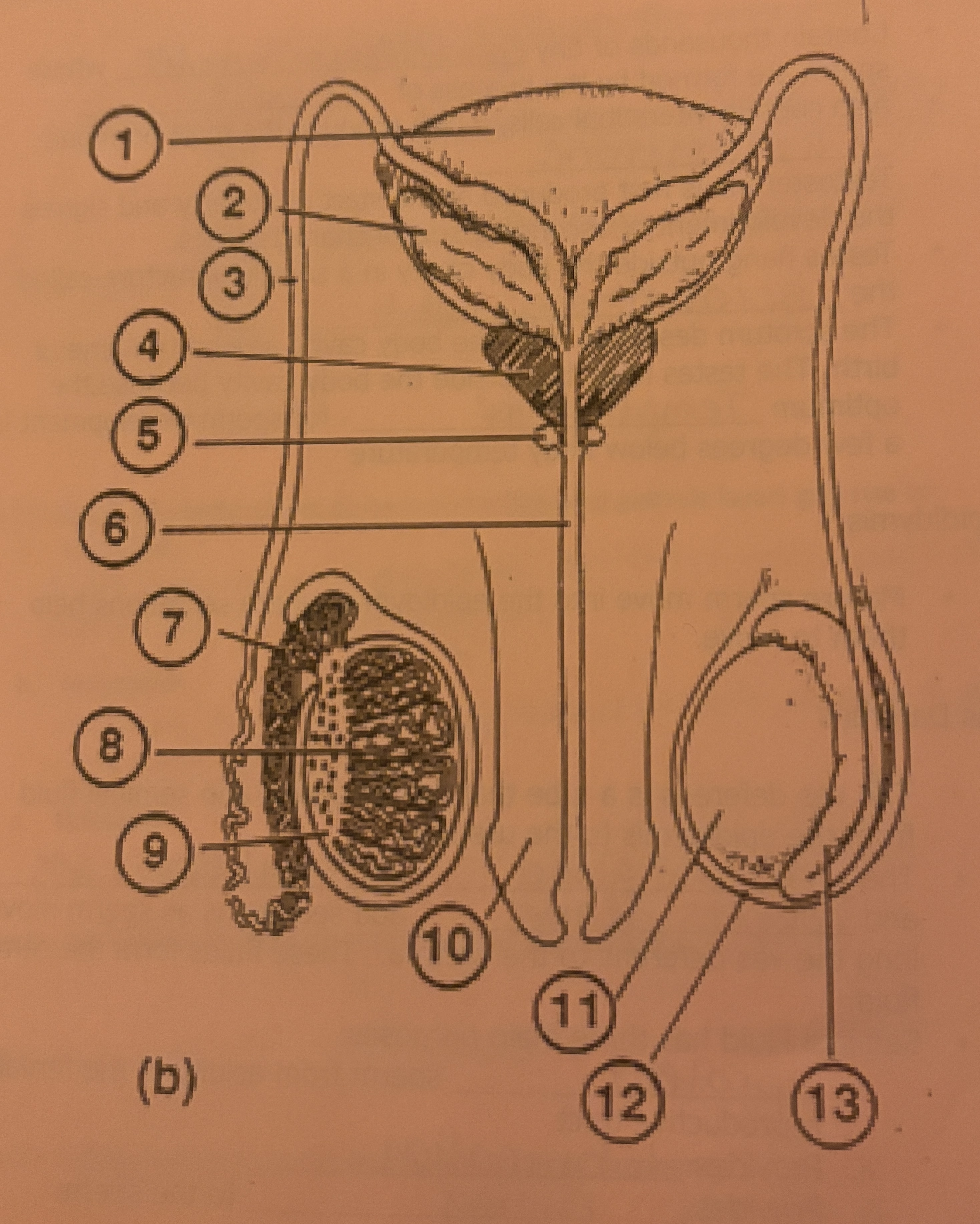
What is #9 called
Interstitial Cells
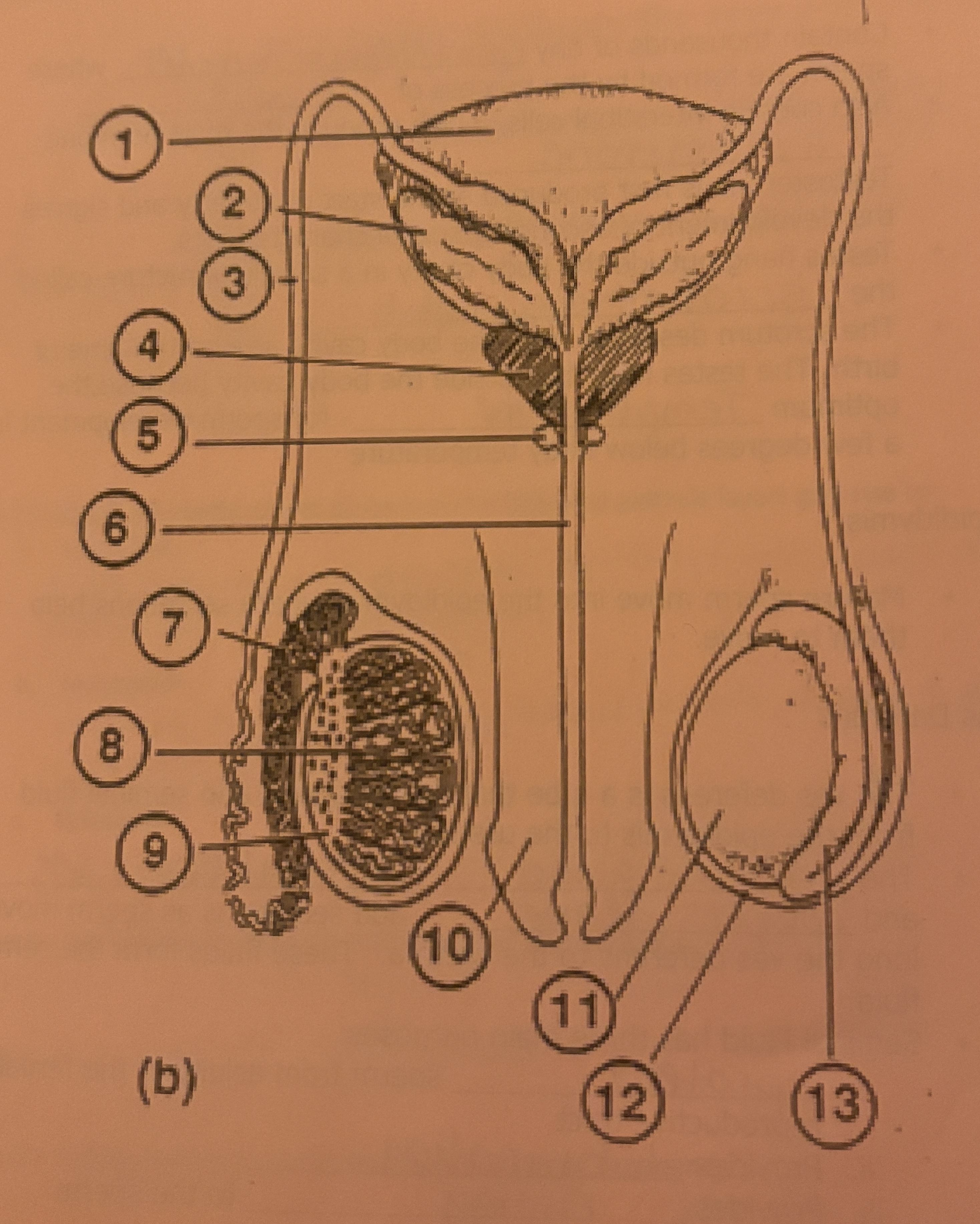
What is #10 called
Penis
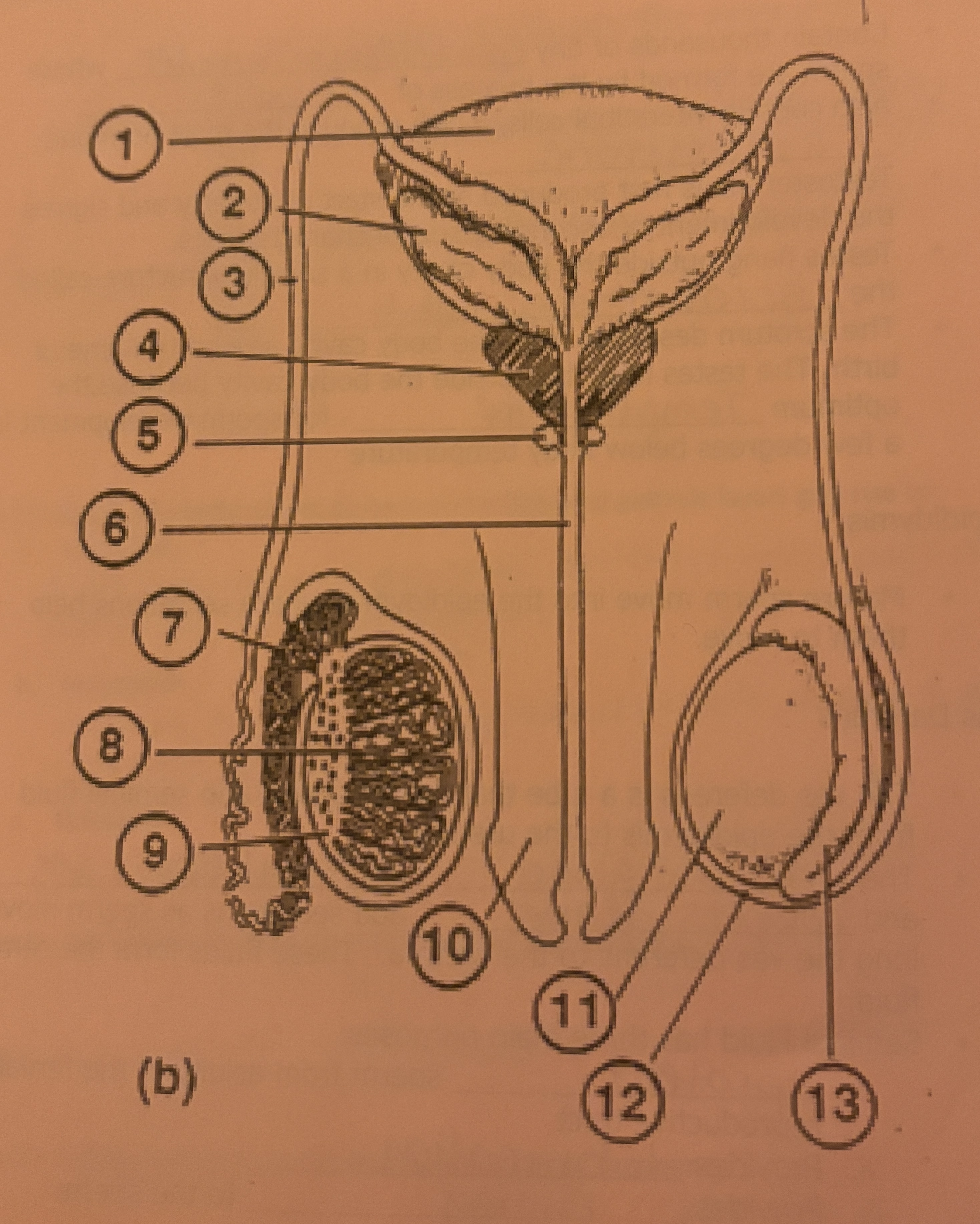
What is #11 called
Testicle
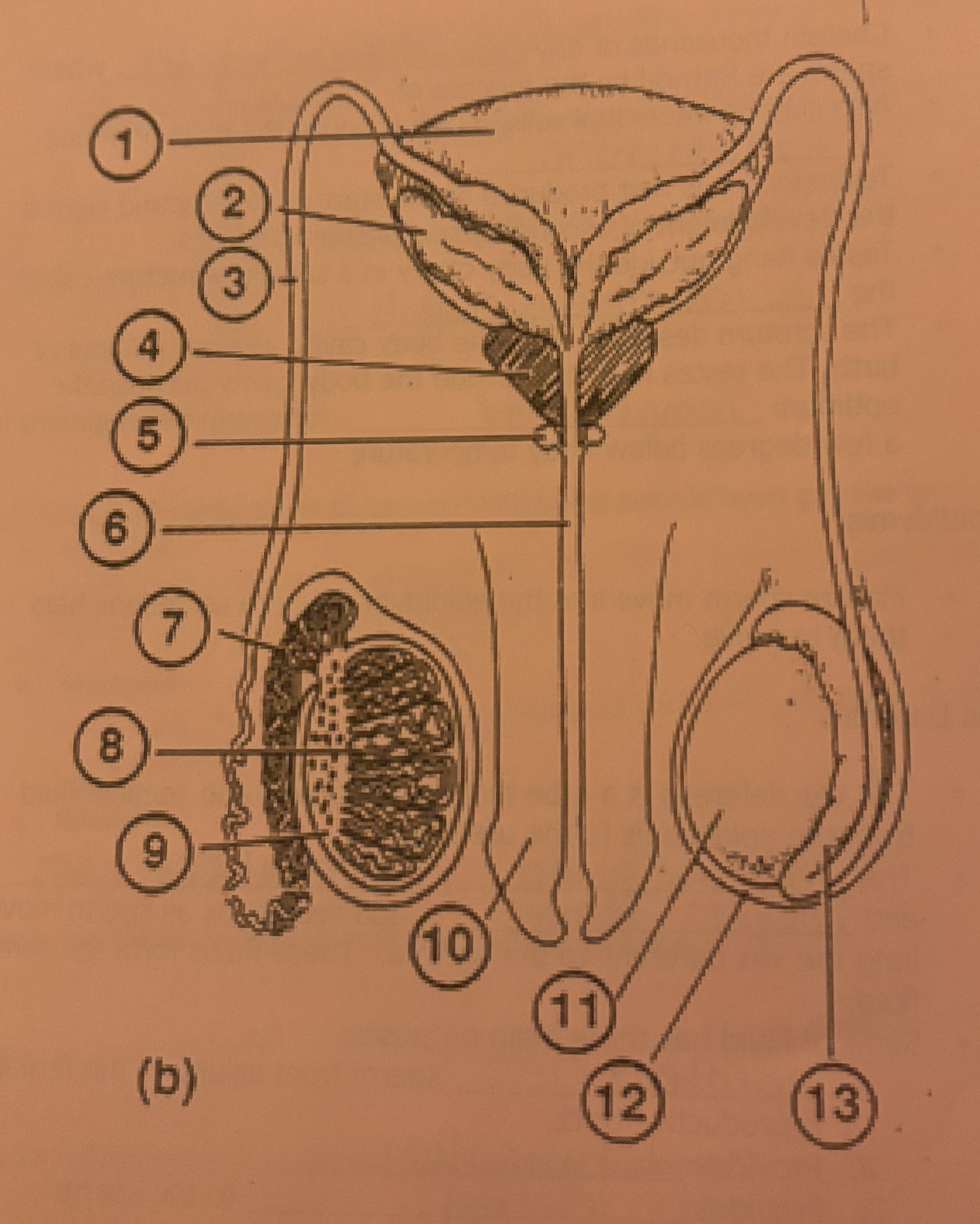
What is #12 called
Scrotum
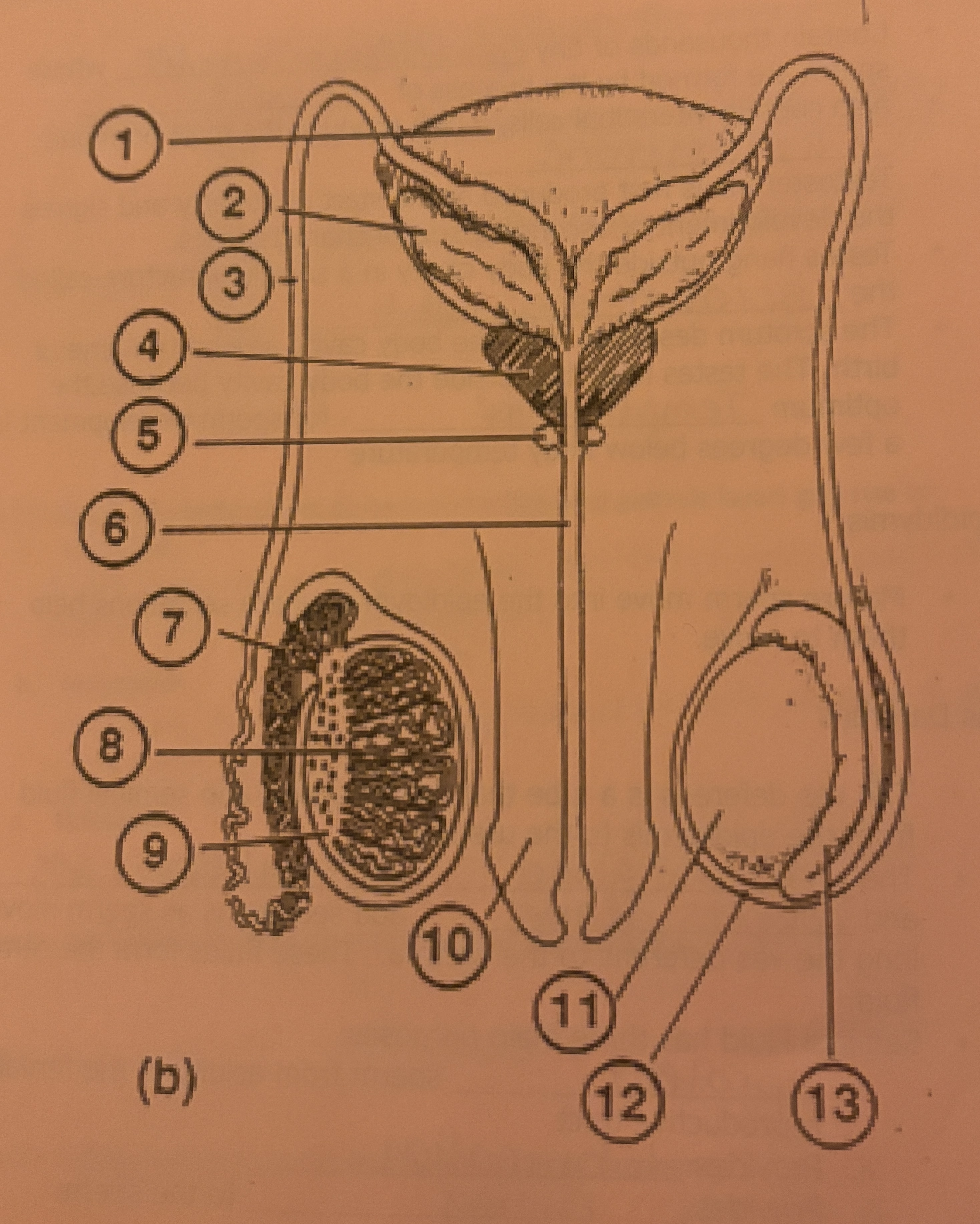
What is #13 called
Epididymis
What do Testicles do?
They contain thousands of tiny Seminiferous Tubules. They also contain interstitial cells which produce the male hormone testosterone.
What does the Epididymis do?
Mature sperm moves into the epididymis, where secretions help them to move.
What does the Vas Deferens do?
Is a tube that carries sperm from and seminal fluid from the epididymis to the urethra.
What does the Urethra do?
The force of secretions (especially those from the prostate gland) and muscular contractions force the semen out of the penis during ejaculation.
What are the 5 Parts of the Female?
Vagina, Cervix, Uterus, Fallopian tubes, Ovaries.
What do ovaries do?
They produce eggs. They also produce two hormones, estrogen, and progesterone.
Describe the path of a sperm cell to an egg
Seminiferous Tubules, Interstitial Cells, Epididymis, Vas Deferens, Seminal Vesicle, Prostate Gland, Cowpers Gland, Urethra.
How many ova mature in a women’s lifetime?
About 400
What are the three layers of the gastrula?
1. Ectoderm
Forms skin + Nervous system
2. Mesoderm
Forms kidneys + skeleton
3. Endoderm
Forms lungs + liver
Main advantage of sexual reproduction
Genetic Diversity
Name 4 Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Artificial Insemination
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
Gamete intrafallopian transfer
Describe Artificial Insemination
Donor sperm is placed in the female
Describe In vitro fertilization (IVF)
egg and sperm are collected and fertilization takes place in a dish. Then the Embryos are placed in the females uterus.
Describe Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
A single sperm is injected directly into an egg.
Describe Gamete intrafallopian transfer
eggs and sperm are collected, mixed, then injected into the women’s fallopian tubes.
Name and describe three ways that sexual reproduction produces variation in a population.
Independent Assortment
Crossing Over
Gamete formation
What are two advantages of internal fertilization over external fertilization?
Higher Fertilization Success Rate
Greater Protection for the Embryo