osmosis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Osmotic Solutions
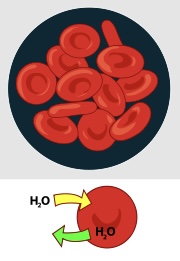
Isotonic Solution
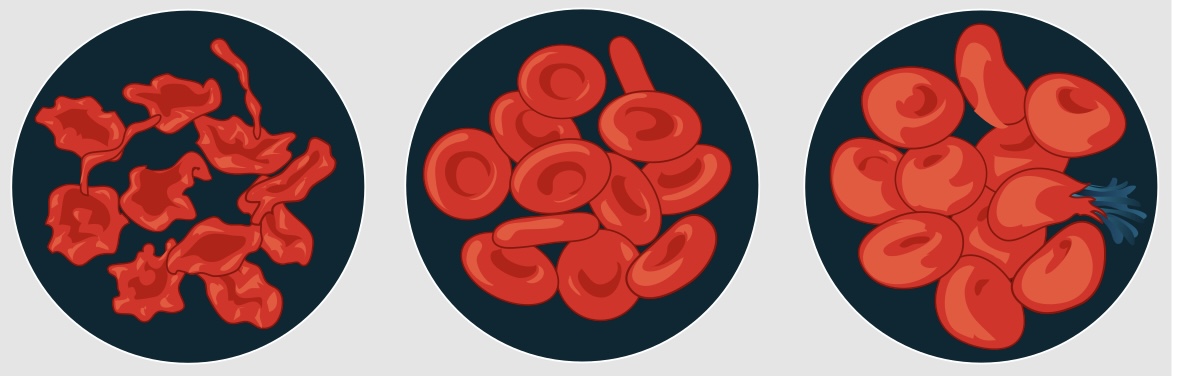
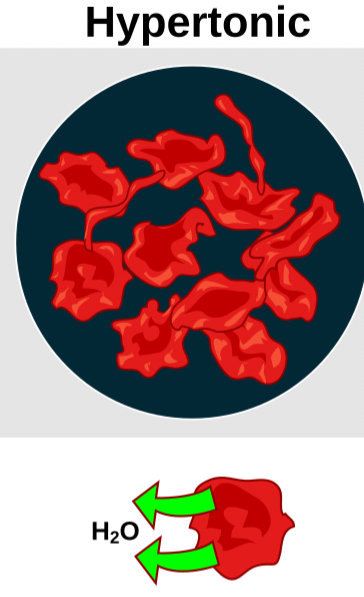
Hypertonic Solution
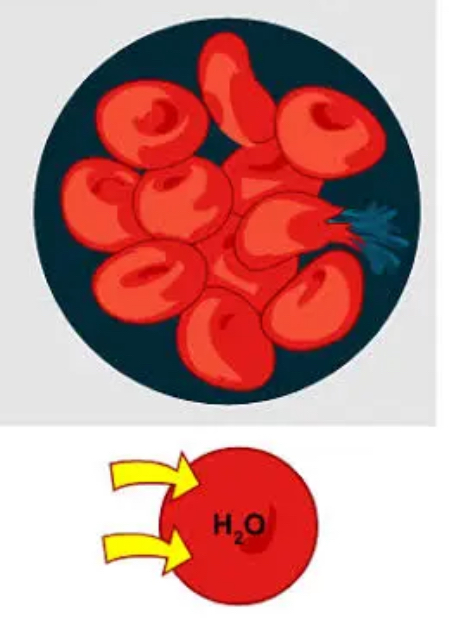
Hypotonic Solution
isotonic solution
one that has the same concentration of solutes both inside and outside the cell.
hypertonic solution
is one that has a higher solute concentration outside the cell than inside.
hypotonic solution
one that has a higher solute concentration inside the cell than outside
Endosmosis
When a substance is placed in a hypotonic solution, the solvent molecules move inside the cell and the cell becomes turgid or undergoes deplasmolysis.

Exosmosis
When a substance is placed in a hypertonic solution, the solvent molecules move outside the cell and the cell becomes flaccid or undergoes plasmolysis.
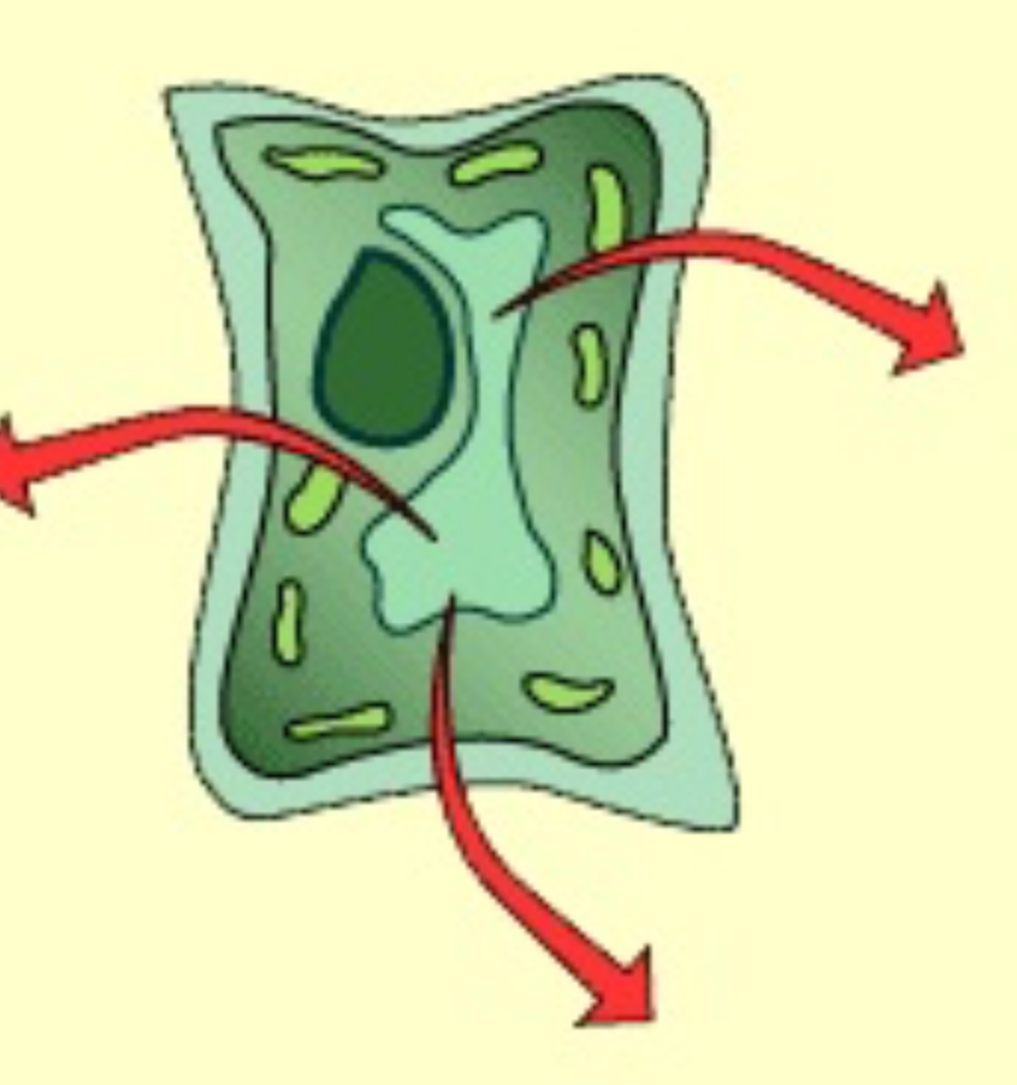
Semipermeable membrane
The cell membrane allows water to pass through but restricts many solutes (salts, sugars, proteins)
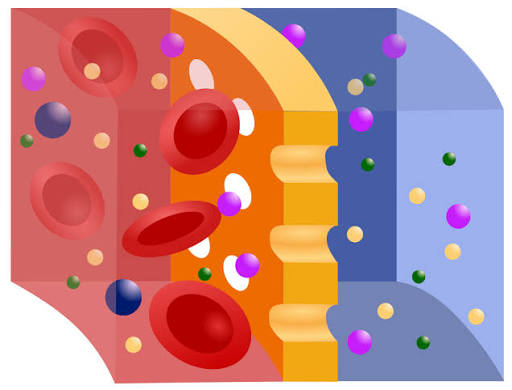
Unequal Solute Concentrations
When one side of the membrane has more solute a concentration difference is created
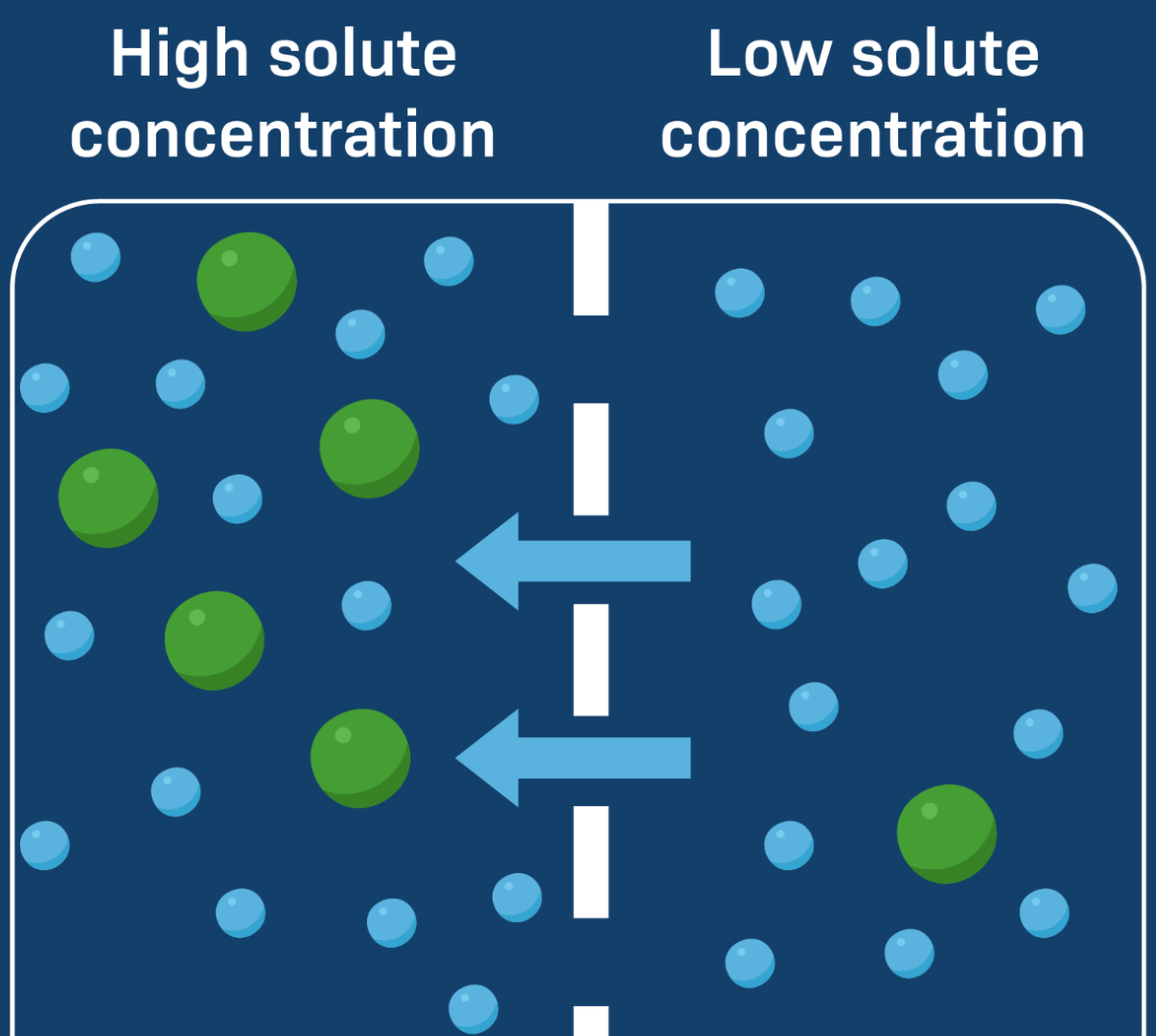
Water movement
Water molecules move through the membrane often with special protein channels called aquaporins, toward the side with the higher solute concentration
Equilibrium
Movement continues until the concentrations of water and solutes become balanced on both sides.
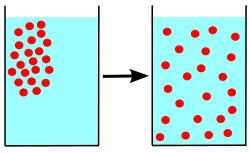
Diffusion (NO ATP)
moves particles from higher to lower concentration without requiring energy.
Facilitated Diffusion
moves down a concentration gradient but requires a protein carrier because the substance cannot cross the membrane easily.
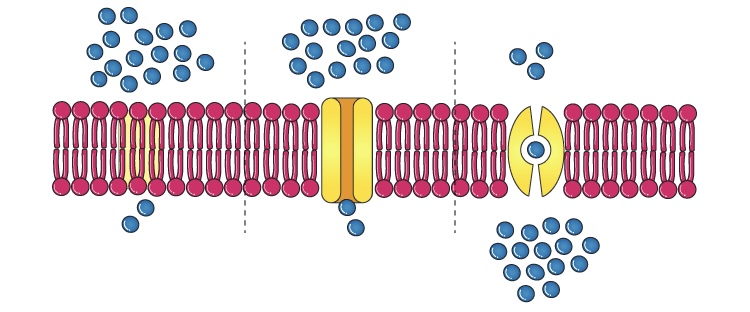
Osmosis (NO ATP)
the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
high concentration of water molecules
Lower concentration of water molecules