Teeling L2: Genomics & Phylogenetic Trees
1/359
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
360 Terms
Phylogenetic tree
Hypothesis about evolutionary relationships among species.
Branch point
Where lineages diverge in a phylogenetic tree.
Sister taxa
Groups sharing an immediate common ancestor.
Rooted tree
Includes a branch for the last common ancestor.
Basal taxon
Diverges early near the common ancestor.
Polytomy
Branch from which more than two groups emerge.
Ancestral lineage
The common ancestor of all taxa in a tree.
Phylogeny
Study of evolutionary relationships among organisms.
Homology
Similarity due to shared ancestry between organisms.
Analogy
Similarity due to convergent evolution, not ancestry.
Homoplasies
Analogous structures or sequences evolved independently.
Convergent evolution
Similar adaptations from similar environmental pressures.
Phenotypic similarities
Similar physical traits indicating evolutionary relationships.
Genetic similarities
Similar DNA sequences suggesting close relatedness.
Systematists
Scientists who classify organisms based on phylogeny.
Shared derived characters
Traits shared by a group, derived from a common ancestor.
Fins and flippers
Example of homologous structures in different species.
Complexity in structures
More complex structures likely indicate homology.
Molecular sequences
DNA comparisons used to determine evolutionary relationships.
Environmental pressures
Factors influencing convergent evolution in different species.
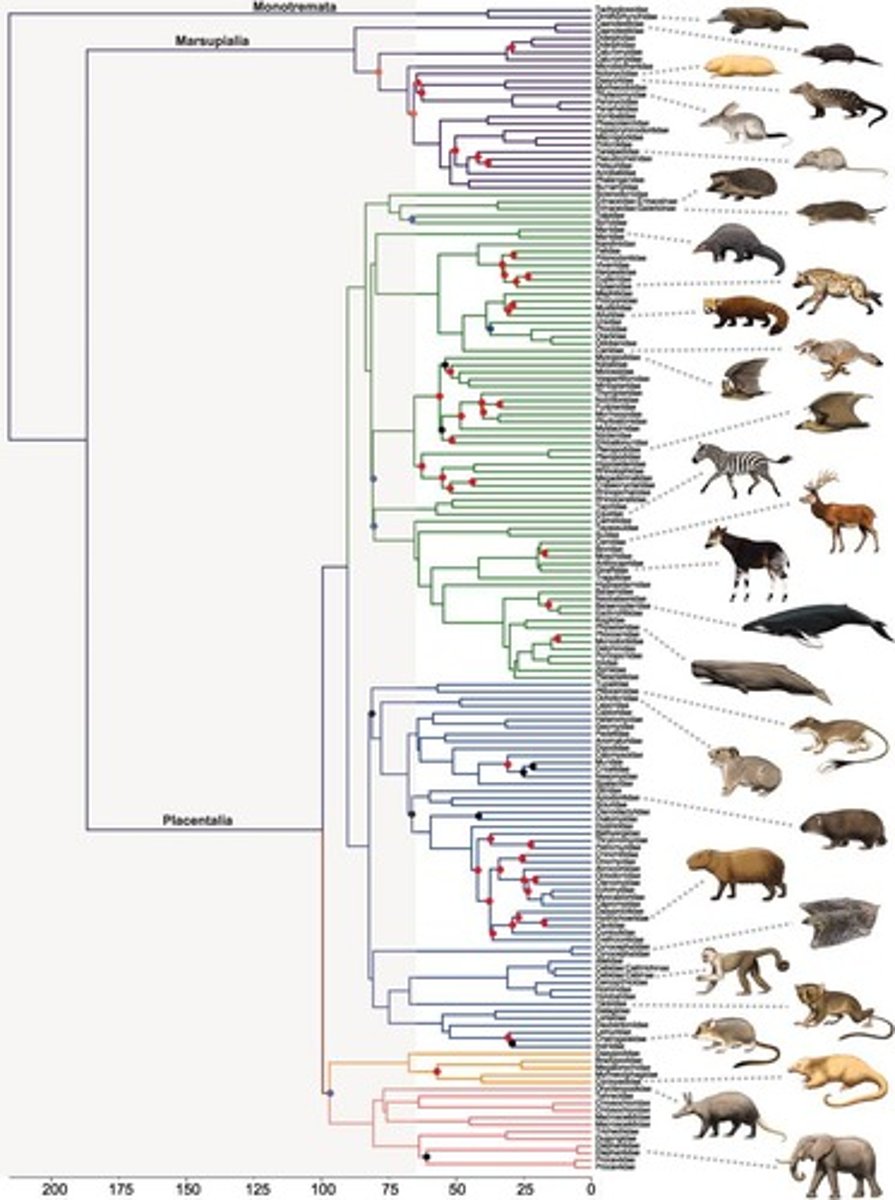
Whale meat identification
Phylogeny used to trace whale species origins.
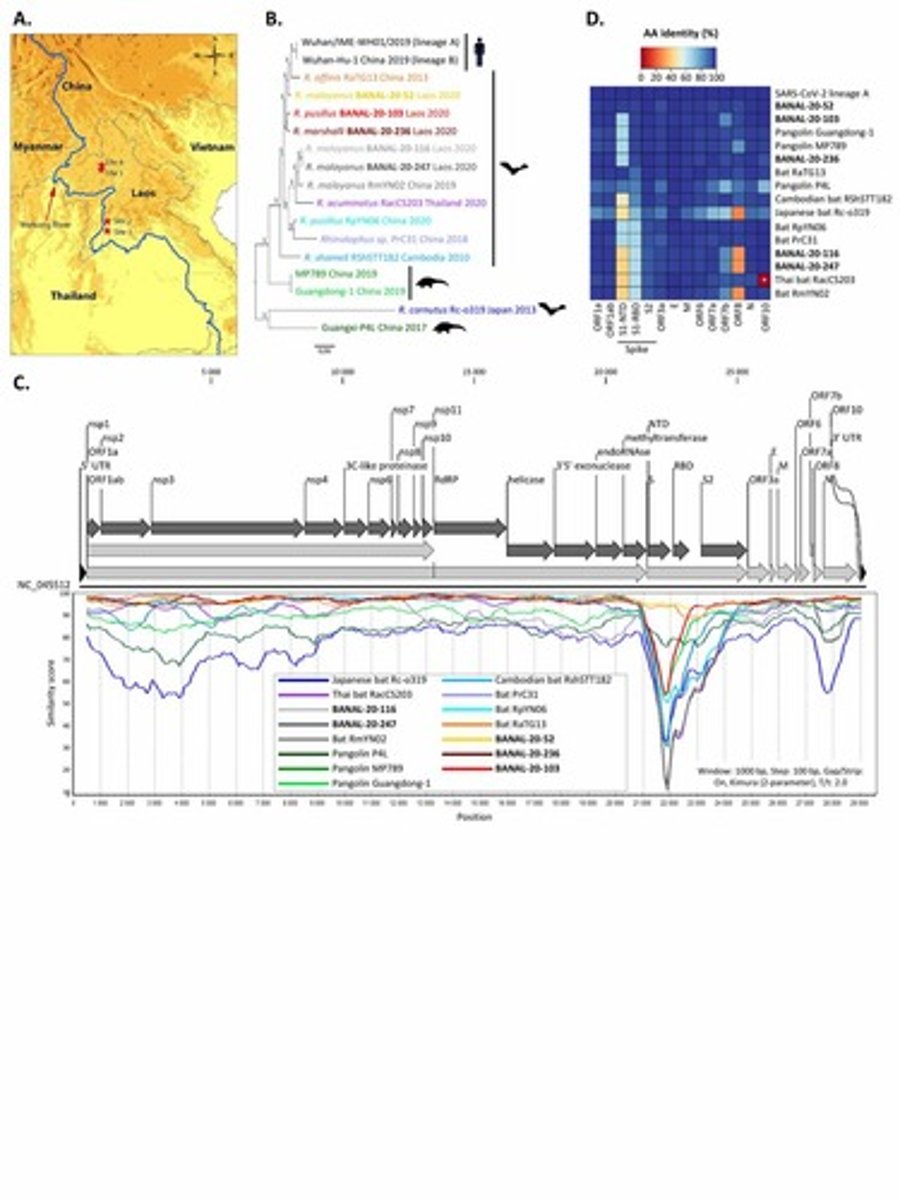
SARS-CoV-2 origin
Investigated using phylogenetic analysis of viruses.
Morphological similarity
Similar physical traits between species.
Molecular data
DNA sequences used for genetic analysis.
Homologous genes
Genes that share an evolutionary ancestor.
Orthologs
Homologous genes in different species.
Paralogs
Homologous genes within the same species.
Gene duplication
Process creating multiple copies of a gene.
Speciation
Formation of new species through evolution.
Ancestral gene
Original gene from which others are derived.
Shared derived characters
Traits inherited from a common ancestor.
Analogous structures
Similar traits not derived from a common ancestor.
Molecular homologies
Genetic similarities indicating evolutionary relationships.
Molecular homoplasies
Coincidental genetic similarities in unrelated species.
Functional genomics
Study of gene functions using genomic data.
Systematists
Scientists who classify and analyze species relationships.
Insertion and deletion
Changes in DNA sequences affecting gene length.
Evolutionary relationships
Connections between species based on ancestry.
Computer programs
Tools for analyzing DNA sequences.
Mathematical tools
Methods used to analyze genetic data.
Species estimate
Up to 8.7 million species may exist.
Divergence of gene
Evolutionary changes in gene sequences over time.
Evolutionary time
Duration over which species evolve.
Comparable DNA segments
DNA sequences used for comparative analysis.
Phylogenetic tree
Diagram depicting evolutionary relationships among species.
Homologous characters
Traits derived from a common ancestor.
Cladistics
Classification based on common descent.
Clade
Group including an ancestor and all descendants.
Monophyletic group
A clade consisting of an ancestor and all descendants.
Paraphyletic group
Ancestral species with some, but not all, descendants.
Polyphyletic group
Group with species from different ancestors.
Shared ancestral character
Trait originating in a common ancestor.
Shared derived character
Novel trait unique to a specific clade.
Ancestral character
Trait present in the ancestor of a taxon.
Derived character
Trait that evolved in a particular clade.
Evolutionary novelty
New trait that appears in a lineage.
Outgroup
Species used to compare and infer traits.
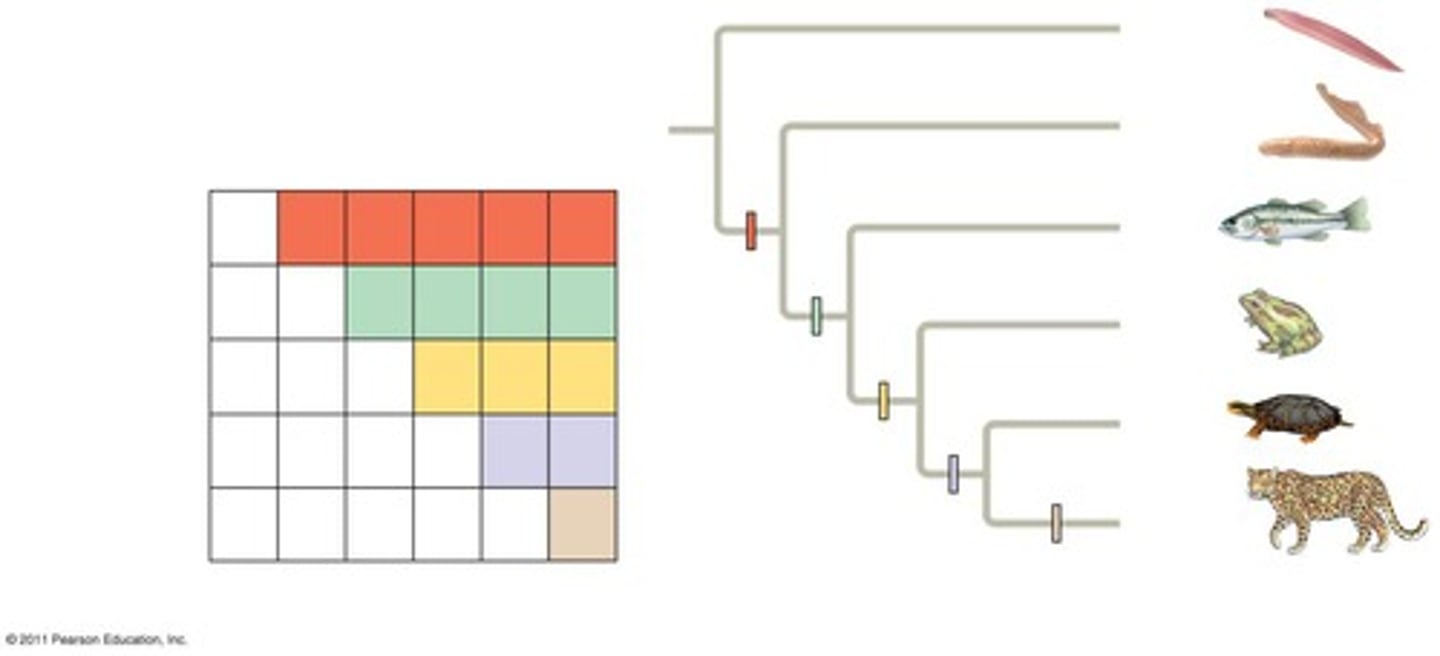
Character table
Matrix displaying traits across different taxa.
Vertebral column
Backbone distinguishing vertebrates from invertebrates.
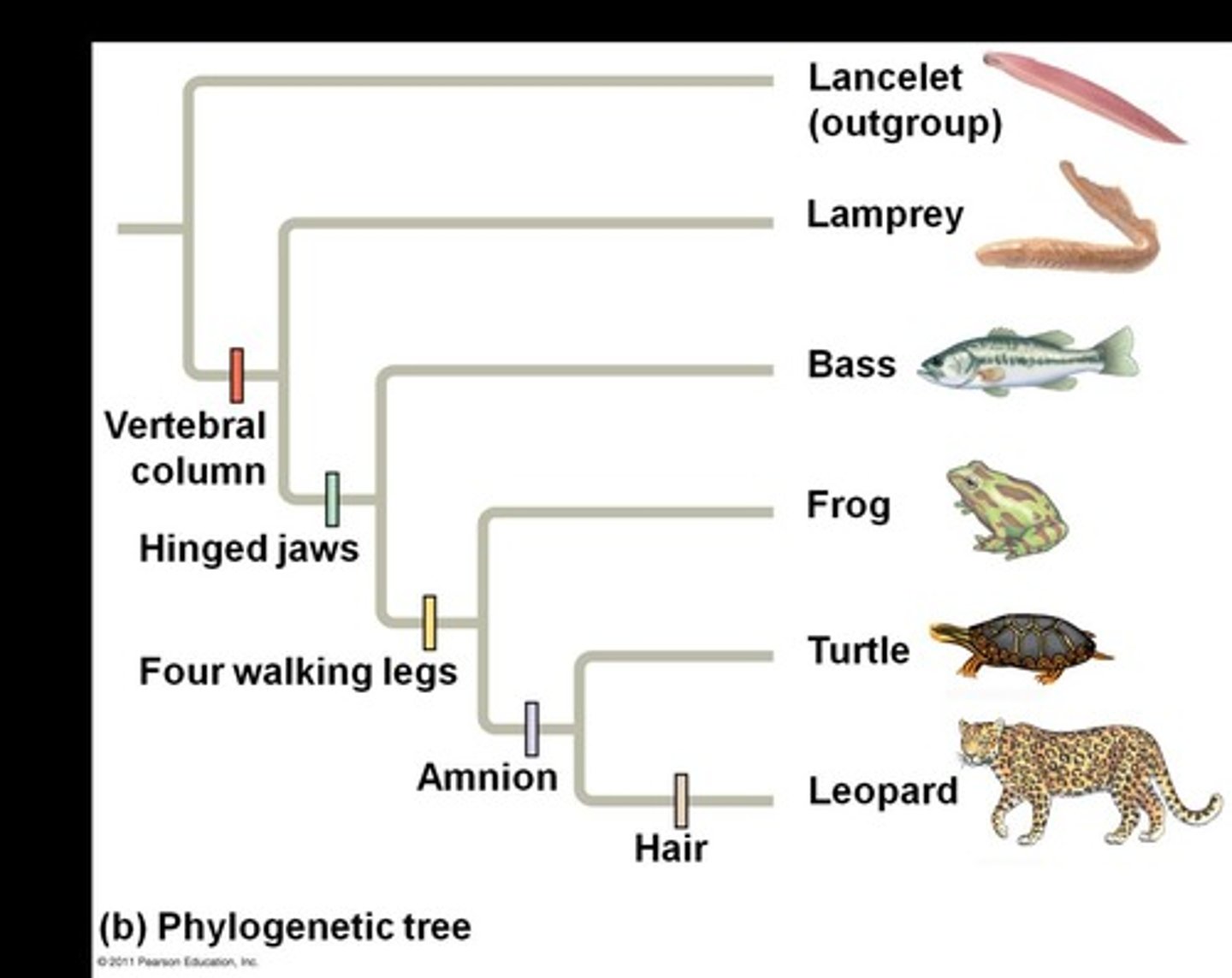
Hinged jaws
Feature that evolved in some vertebrates.
Four walking legs
Characteristic of certain tetrapods.
Amnion
Membrane surrounding embryo in amniotes.
Hair
Unique trait distinguishing mammals from other vertebrates.
Branch point
Node in a phylogenetic tree indicating divergence.
Taxon
Group of one or more populations of organisms.
Evolutionary relationships
Connections based on shared ancestry and traits.
Outgroup
Species closely related to the ingroup studied.
Ingroup
Group of species being analyzed in a study.
Shared derived characteristics
Traits unique to a specific clade.
Shared ancestral characteristics
Traits present before divergence from a common ancestor.
Cladistic analysis
Method to study evolutionary relationships among species.
Lancelet
An outgroup species lacking a backbone.
Vertebral column
Backbone present in all ingroup vertebrates.
Hinged jaws
Feature present in most ingroup vertebrates.
Four walking legs
Characteristic of certain terrestrial vertebrates.
Maximum Parsimony
Principle minimizing the number of evolutionary changes.
Maximum Likelihood
Statistical method estimating tree likelihood based on data.
Convergent evolution
Independent evolution of similar traits in different species.
Reversal evolution
Return to an ancestral trait in a lineage.
Synapomorphy
Shared derived trait among a group of organisms.
Phylogenetic tree
Diagram representing evolutionary relationships among species.
Character table
Matrix showing traits of different taxa.
Paleontology
Study of ancient life through fossils.
Morphology
Study of the form and structure of organisms.
Gene sequences
DNA sequences used to determine evolutionary relationships.
Divergence
Process by which species evolve different traits.
Maximum Parsimony
Tree with fewest evolutionary events is favored.
Maximum Likelihood
Tree reflects most probable DNA change sequence.
Phylogenetic Hypotheses
Different tree structures representing evolutionary relationships.
Parsimony
Minimizing evolutionary changes in tree construction.
Computer Programs
Tools used to identify parsimonious trees.
Shared Derived Characters
Traits that appear in some species but not others.
Branch Length
Indicates number of genetic changes or time.
Phylogenetic Bracketing
Predicting features of ancestors from descendants.
Morphological Data
Physical traits used to construct phylogenetic trees.
Molecular Data
Genetic sequences analyzed for evolutionary relationships.
Fossil Record
Historical evidence supporting evolutionary hypotheses.
Ancestral Sequence
Original DNA sequence from which species diverged.
Evolutionary Events
Occurrences of changes in species over time.
Chronological Time
Time representation in branch lengths of trees.