Lecture 4: Experiments and survey
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1) EXPERIMENT
(way of data collection)
What is an experiment?
= a research strategy that allows you to test causality
= a procedure designed to investigate a hypothesis, demonstrate a phenomenon, or gather data under controlled conditions.
What does an experiment look like?
think of the picture with this flashcard; try to visualize it!
1. R
= random division of subjects
2. Pre-test
- O1 and O1
3. X
= stimulus manipulation --> one group gets it and one does not (placebo effect)
4. Post-test
- O2 and O2
5. Causal effect
- compare the difference between 2 measurement and then you can draw a conclusion based of off that
- (O2 - O1)x - (O2 - O1)c = effect of X or X has led to a change in Y

What are the requirements for an experiment to be an RTC experiment (classic experiment)? (4)
1) controlled environment
- so you can establish the causality
2) 2 groups
3) only 1 group gets the stimulus
4) calculate the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable
What do you do in regards to the two groups when you don't choose randomly?
matching = definition
What is an RTC experiment (classic experiment)?
- see list on slide!
- double blind --> no one knows who gets the stimulus manipulation, not even the researcher
- this is done to avoid bias
What is a quasi experiment?
- this is the case when there are RTC elements missing
- e.g. pre-test is missing or a controlled environment with more than one variable
When do you use experiments?
to... (2)
... see if there is a causality
... rule out other explanations
What are the downsides of experiments? (2)
1) you can include a limited number of variables
2) weak ecological validity (part of external validity)
--> 'does the research situation actually look like empirical reality?' because a controlled environment is artificial, it doesn't
What is the major pro of conducting an experiment?
= strong internal validity
What are the 5 different types of experiments?
1) lab experiment
2) artefactual experiment
3) survey experiment
4) field experiment
5) natural experiment
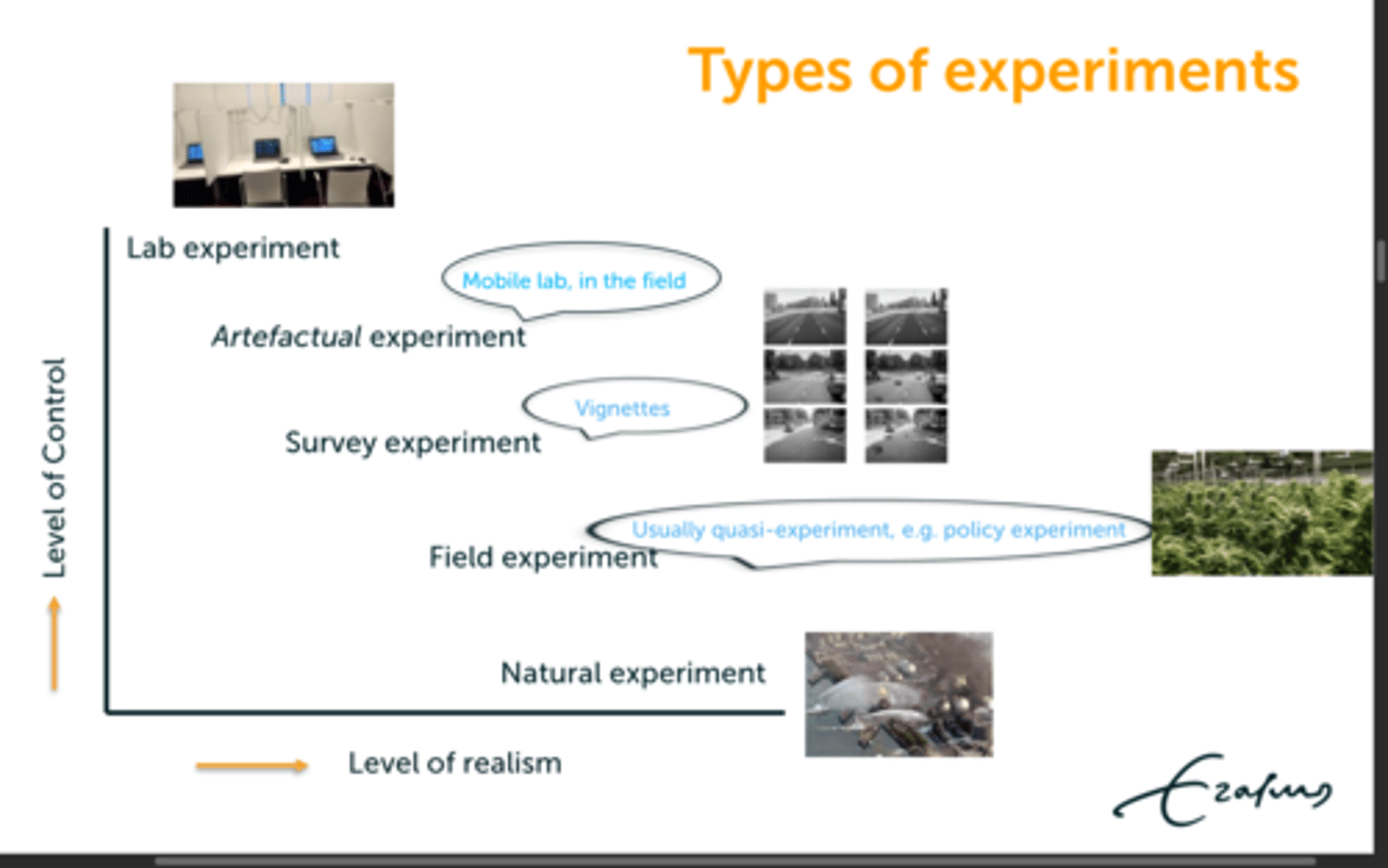
What are the characteristics of a lab experiment?
- RTC experiment
- very few people participate
- controlled environment
- manipulation of variables
- precise measurements
- replicability (being able to repeat an experiment and get similar results)
- control group(s)
- random assignment
What are the characteristics of an artefactual experiment?
- lab is in the field
- still lot of control
- expensive because it's a simulated setting
- controlled conditions and manipulation
- replicability (being able to repeat an experiment and get similar results)
- precise measurements
- not very common!
What are the characteristics of a survey experiment?
- can be done with large groups
- combination of survey and questionnaire
- we present people a questionnaire where we have manipulated the variables (vignette) then we ask for their opinion or what they would do in a given situation
- no pre-test
- structured questionnaire or interview
- manipulation of variables
- random assignment
- replicable design
- control over external factors
What are the characteristics of a field experiment?
- e.g. policy experiments
- often quasi experiments
- conducted in a real-world setting
- manipulation of variables
- random assignment
- control over experimental conditions
- potential for less control over external factors compared to lab experiments
What are the characteristics of a natural experiment?
- X is a naturally occurring situation that the researchers has little to no control over
- e.g. earthquakes or other natural disasters
- occurs naturally without researcher intervention
- variables are not manipulated by researchers
- utilizes naturally occurring events or circumstances as quasi-experimental conditions
- lack of control over independent variables
- researchers observe and analyze the effects of naturally occurring variations on dependent variables
1) How are subjects handled in experiments and 2) what are two measurement effects that can arise?
1) They are chosen through sampling: either random or via matching.
2) There might be measurement effects such as:
Hawthorne effect
= people might behave differently when they know they're being measured
- solution: not telling people what the experiment is
- problem: you cannot deceive people!
- solution: ethical committee will decide if you can temporarily deceive people and then afterwards you have to debrief them (they can still decide that the researcher can't use your data)
Observer bias
- you want to keep respondents as naive as possible because of observer bias
What are the methodological considerations of an experiment? (3)
validity?
risks?
ethical considerations?
1) strong on internal validity, while low on external validity
2) risks: experimenter effects, observer bias, subject bias
3) ethical considerations: you need permission from the ethical committee for deception
2) OBSERVATION
(way of data collection)
What is observations and what are the 2 different categories with different options?
= a method for data collection
1. (how visible?)
a) hidden observation (invisible for units)
b) open observation (visible + no interaction)
c) participant observation (visible + interaction)
2. (how is it structured?)
a) structured (schematic; you've thought about what you're going to look for beforehand)
b) unstructured (inductive; you've not thought about what you're going to look for beforehand)
there are different combinations between these possible!!
What are the advantages of observation? (2)
1) it shows real behavior
- what people say they do, is not always what they do
2) it shows non-verbal behavior
- how do people look / expressions
What are the downsides of observation? (3)
1) researchers might miss certain things
2) researchers are not always objective
3) researchers are present and interfere --> validity issues
1) selectivity
might overlook certain things --> why we often use multiple researcher ers because then we can see more or make a recording to capture everything
2) subjectivity
going native = researchers are subjective, however we are all still human and that means you can be less subjective sometimes
3) validity issues
- caused by researchers presence / interference
- in the long run ...
What do researchers aim for when they have an emancipatory aim?
they aim to better the situation for the people
3) SURVEY
(a research strategy)
What is a survey NOT?
a questionnaire!!!
= a way of data collection in a survey study
What is a survey then? (2)
1) large scale study
2) standardized measurements
What is the most frequent way of quantitative data collection for surveys?
questionnaires!
What are panels?
= a way of data collection within a strategy (e.g. survey) where people get paid to fill out questionnaires from time to time
What is the downside of using a pannel as a way of data collection?
the quality of panels be questionable since people just do it for the money and don't really care about the answers they are giving
4) QUESTIONNAIRE
(way of data collection)
What is a questionnaire?
name characteristics (5)
= a series of written questions a researcher presents to subjects
- written or online
- low response rate
- list of closed questions --> standardized measurements
- questions are placed in a certain order e.g. start with easier and build up to more difficult or emotional ones
- demographics nowadays at the end
How do you set up a questionnaire? (5 steps)
1) generate a pool of items
- create questions based on your operationalization
- use existing questionnaires for ideas and validity
2) pilot
- test your questionnaire with a small group
- get feedback on clarity and relevance
3) administering questionnaire to respondents (sampling)
- distribute the questionnaire to your sample population.
4) data inspection and analysis
- review collected responses
- analyze data for patterns and insights
5) reporting --> respondents report
- summarize findings from respondents' answers
- present results to share insights
What are the requirements for good items? (step 1 of making a questionnaire)
they should ... (6)
- be unambiguous
- be clear
- not be suggestive
- no be jargon
- not have double negatives
- have mutually exclusive answer categories (each option provided for a question does not overlap or include the other options)
What should you pay attention to when creating a questionnaire? (5)
1) How you formulate your questions
--> avoid jargon, terminology, double negatives and clear, unambiguous language
2) Create an introduction with an instruction
3) Replication and translation
when translating a questionnaire to a different language make sure to pay attention to culture to not just the language --> some things are not just different language wise but also culture wise
4) Lay-out and routing
5) Pre-testing in a pilot
What is routing?
Routing refers to the path or sequence that participants follow through a survey or questionnaire based on their response. It ensures that respondents are directed to relevant questions based on their previous answers.
e.g. Let's say you're conducting a survey about shopping preferences. If a respondent indicates they prefer online shopping, the routing might direct them to questions specifically about online shopping habits. Conversely, if a respondent prefers in-store shopping, the routing would direct them to questions about their experiences and preferences in physical stores.
What are threats of validity in questionnaires? (3)
and can you name a countermeasure for these threats
1) Social desirability
= respondents giving a socially desirable answer instead of an real answer
Countermeasure:
- use control or reversed items --> one question formulated in a negative way one in a positive way
- use a scale for social desirability
2) Non-response
= when respondents not participate / respond
Countermeasure:
- stratified or quotum sampling, non-response study, statistical corrections
3) Answer tendencies
= artefact in answers, e.g. always answering with 'totally agree' or just giving neutral answers
Countermeasure:
- clear instructions
- forcing non-neutral answers
- routing
- length of the questionnaire