Unit A Concepts - Motions of Earth & Moon
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Axial Rotation direction
Prograde
Diurnal experience
The apparent motion of celestial objects across the sky over the course of a day/night

Axial Rotation
The day and night cycle is an effect of
Latitude
What stars appear to move across the sky in the diurnal experience depends on
Sidereal Time
A time system based around comparing the movement of earth (or another planet) with distant stars because they are often the most reliable
23 hours, 56 minutes
Sidereal Day (time it takes for earth to rotate once on its axis)
27.32 days
Sidereal month (The time it takes for the moon to make one rotation around earth)
365.256 days
Sidereal Year (time it takes for the Sun to return to the same position in the sky relative to the stars)
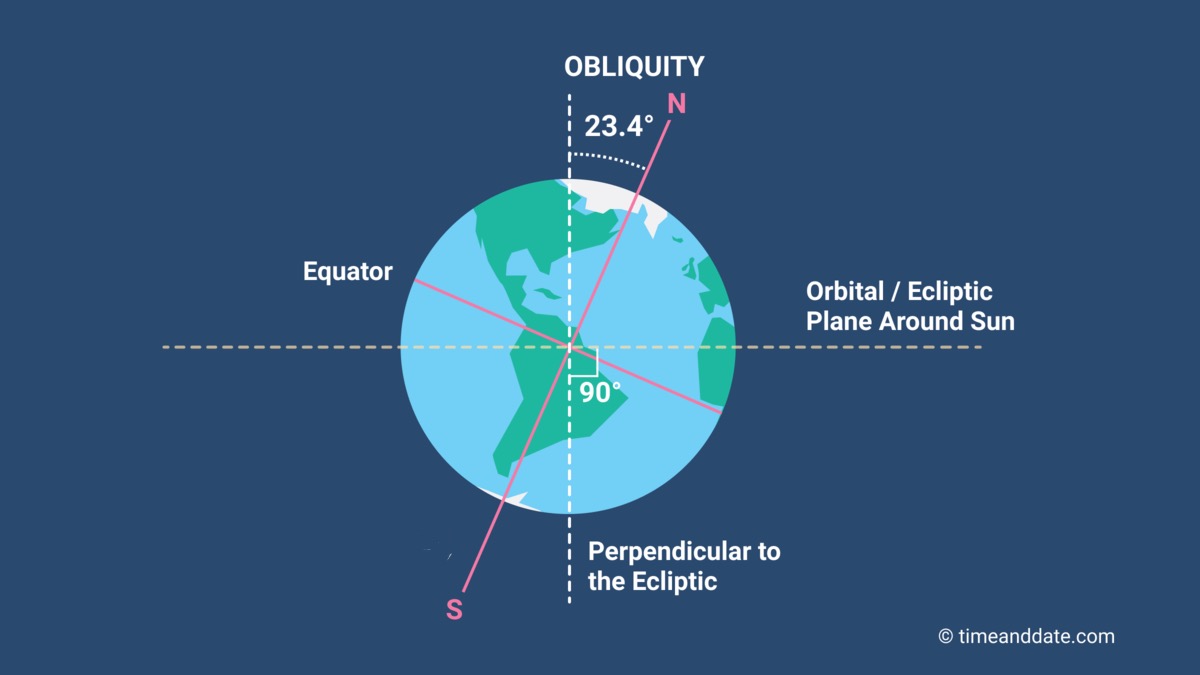
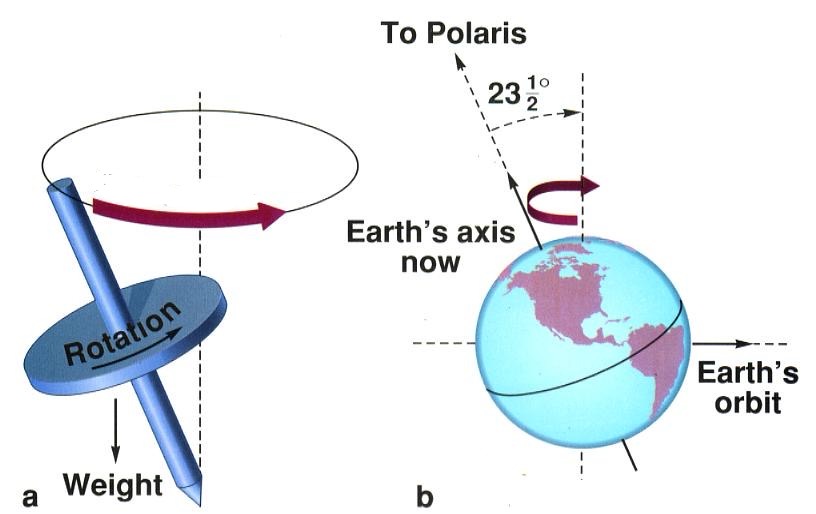
Axial Tilt
The angle between earth’s orbital axis and rotational axis, 23.4 degrees
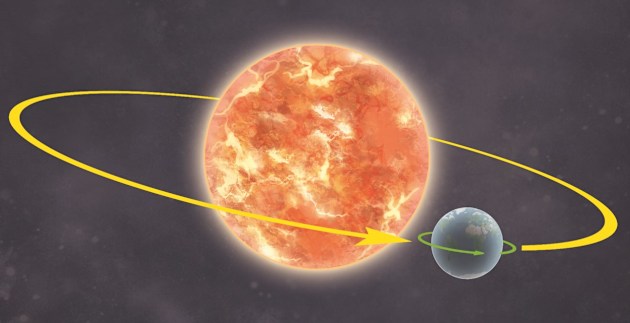
Earth’s revolution
The movement of earth around the sun in an elliptical movement
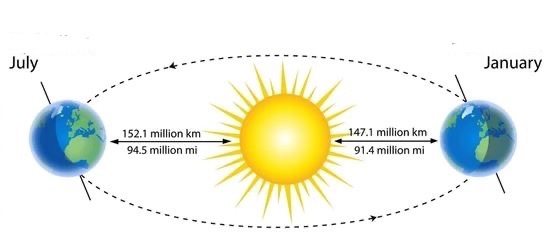
Aphelion
When earth is farthest from the sun in July
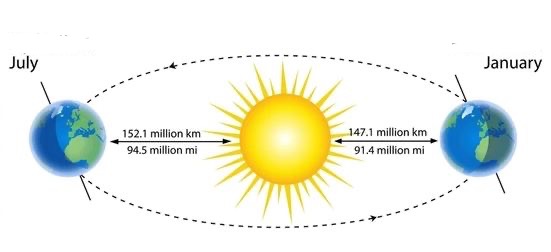
Perihelion
When earth is closest to the sun in January
Ecliptic
The apparent path of the sun and planets across the celestial sphere
Equinoxes
When the sun crosses the celestial equator, making night and day equal in length
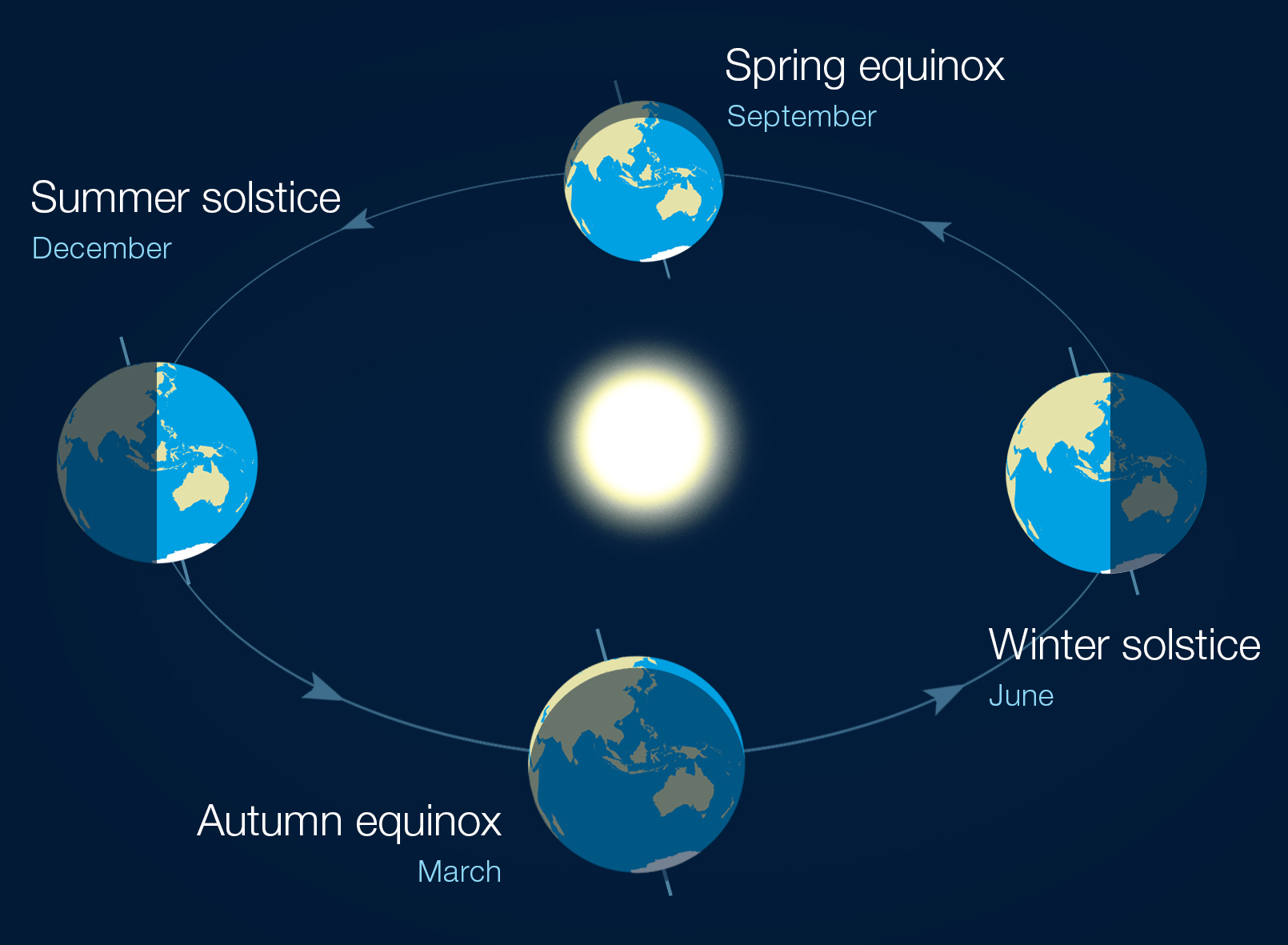
Solstices
When the sun reaches its maximum or minimum declination, making the day either the longest or the shortest of the year depending on whether it is winter or summer
Seasons
The tile of earth’s axis either towards or away from the sun causes
Winter
When it is summer in the northern hemisphere it is _________ in the southern hemisphere
Precession
The gradual shift of our axis over time
Anelemma
plot or graph in the shape of a figure eight that shows the position of the sun in the sky at a given time of day at one specific locale throughout the year.

Earth’s movement
Makes it appear as though all planets and constellations are moving along a similar and predictable path
Inverse
If the earth were to move clockwise instead of counterclockwise, all celestial motions would be
Mare
This is an example of a…

Impact Crater
This is an example of a…

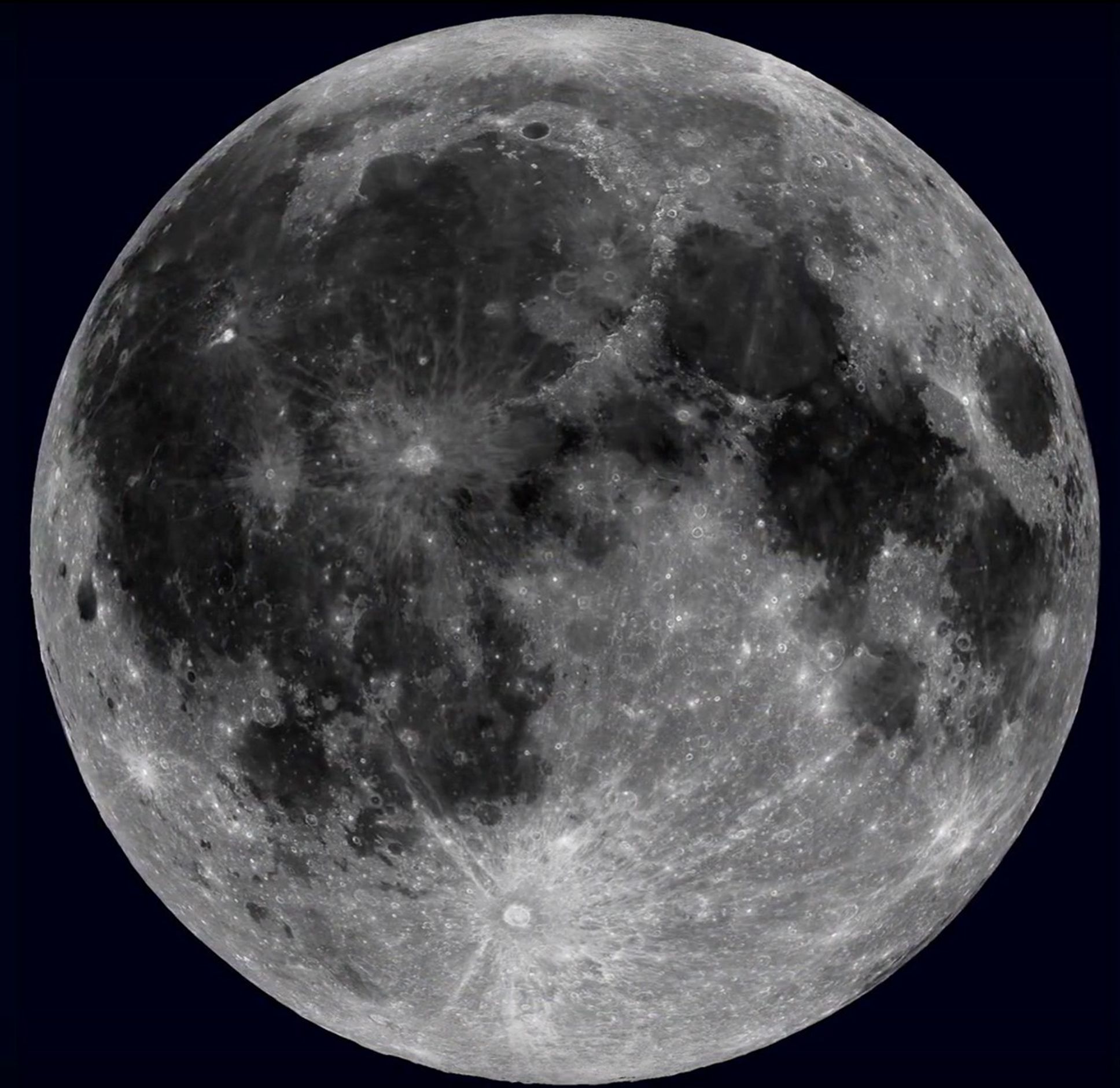
Near side
This is the _____ of the moon

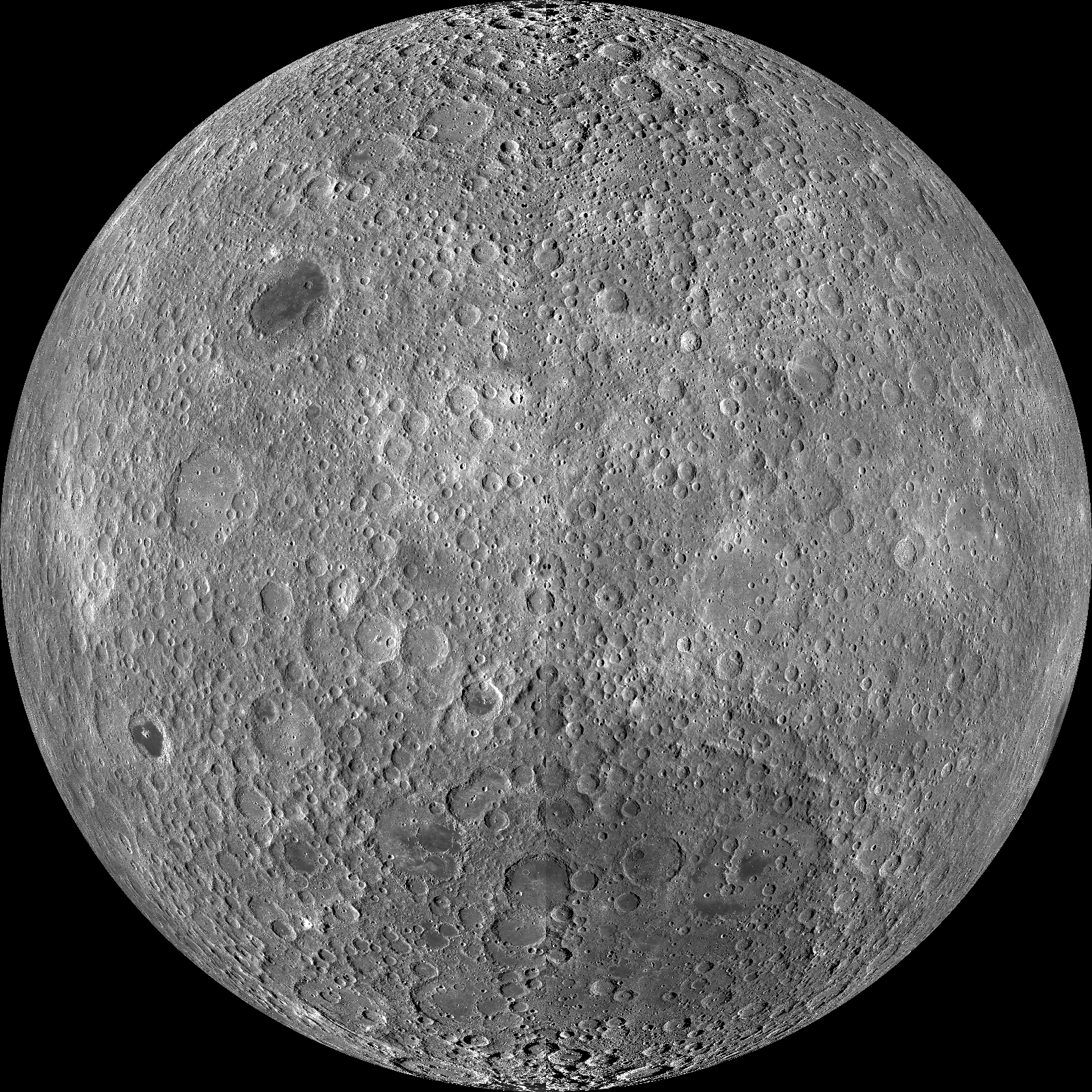
Far side
This is the _______ of the moon

Libration
The oscillation of the moon that causes around 60% of its surface to be visible to earth throughout its cycle
Synchronous Rotation
when an object's rotation period matches its orbital period, so it always shows the same face to the object it's orbiting (Ex: moon to earth)
Orientation
While the phases of the moon are consistent across earth, their ______ varies based on where you are
New Moon, Day 0
0/360 degrees

Waxing Crescent, Day 4
45 degrees
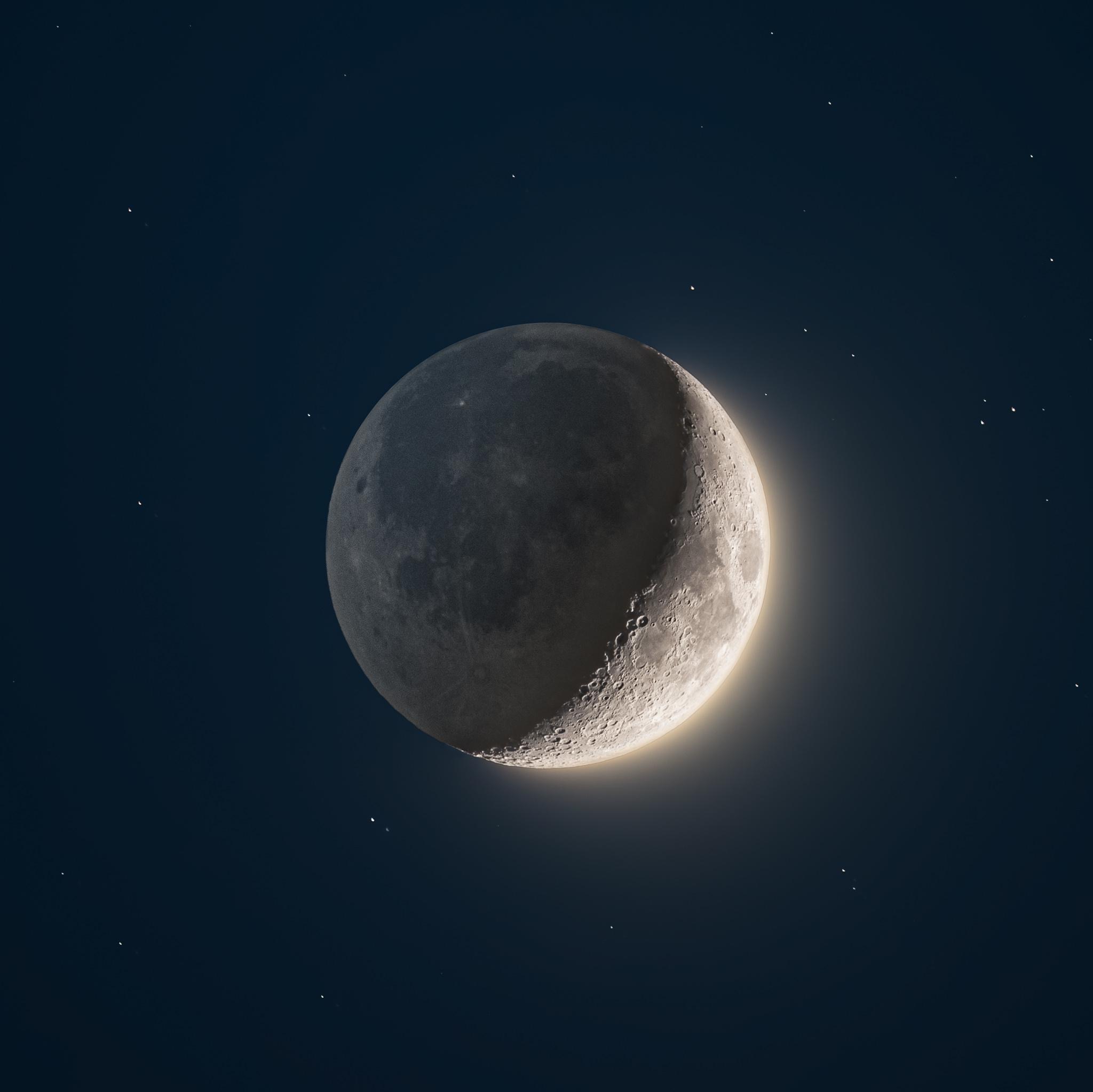

First Quarter, Day 7
90 degrees
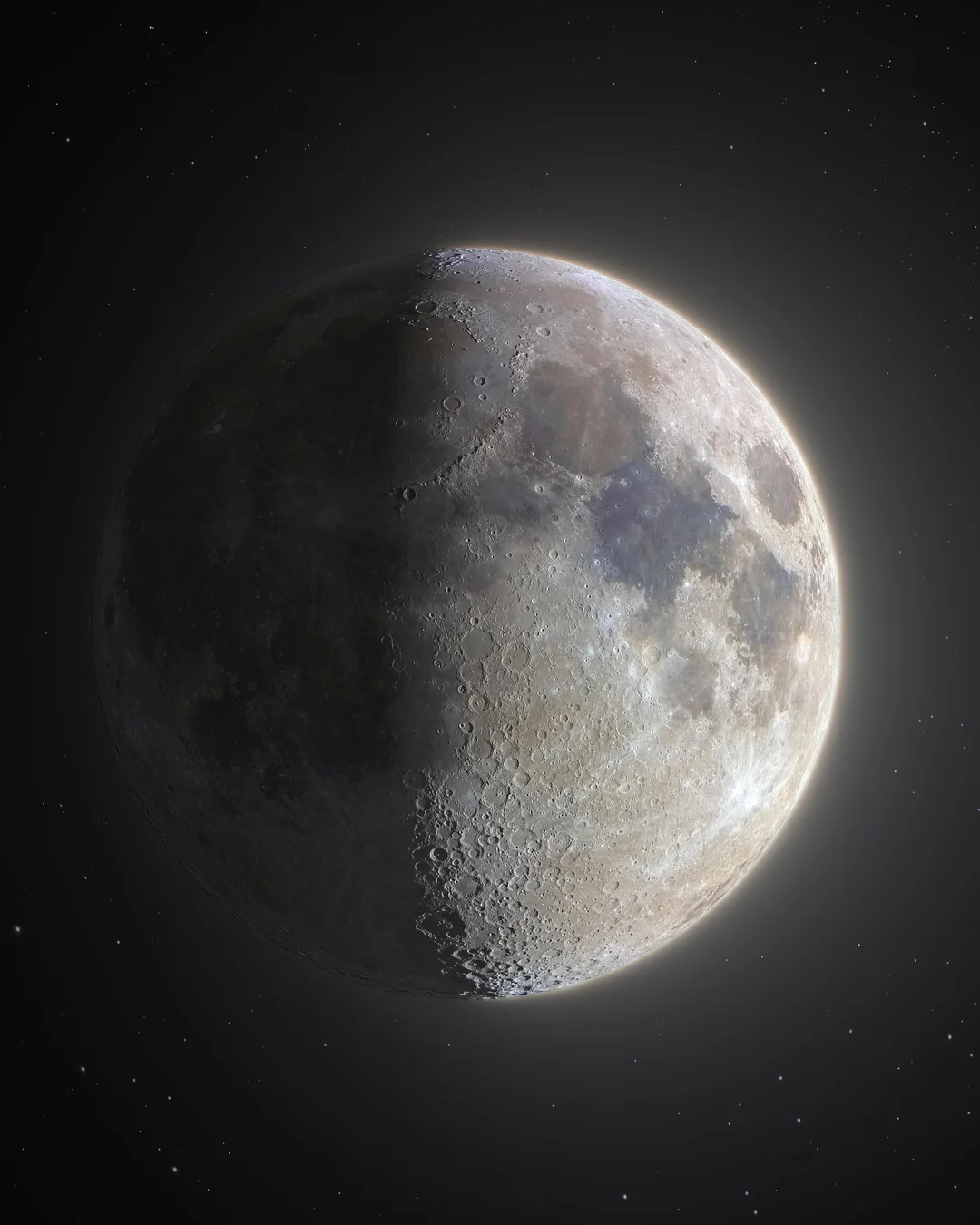

Waxing Gibbous, Day 10
135 degrees
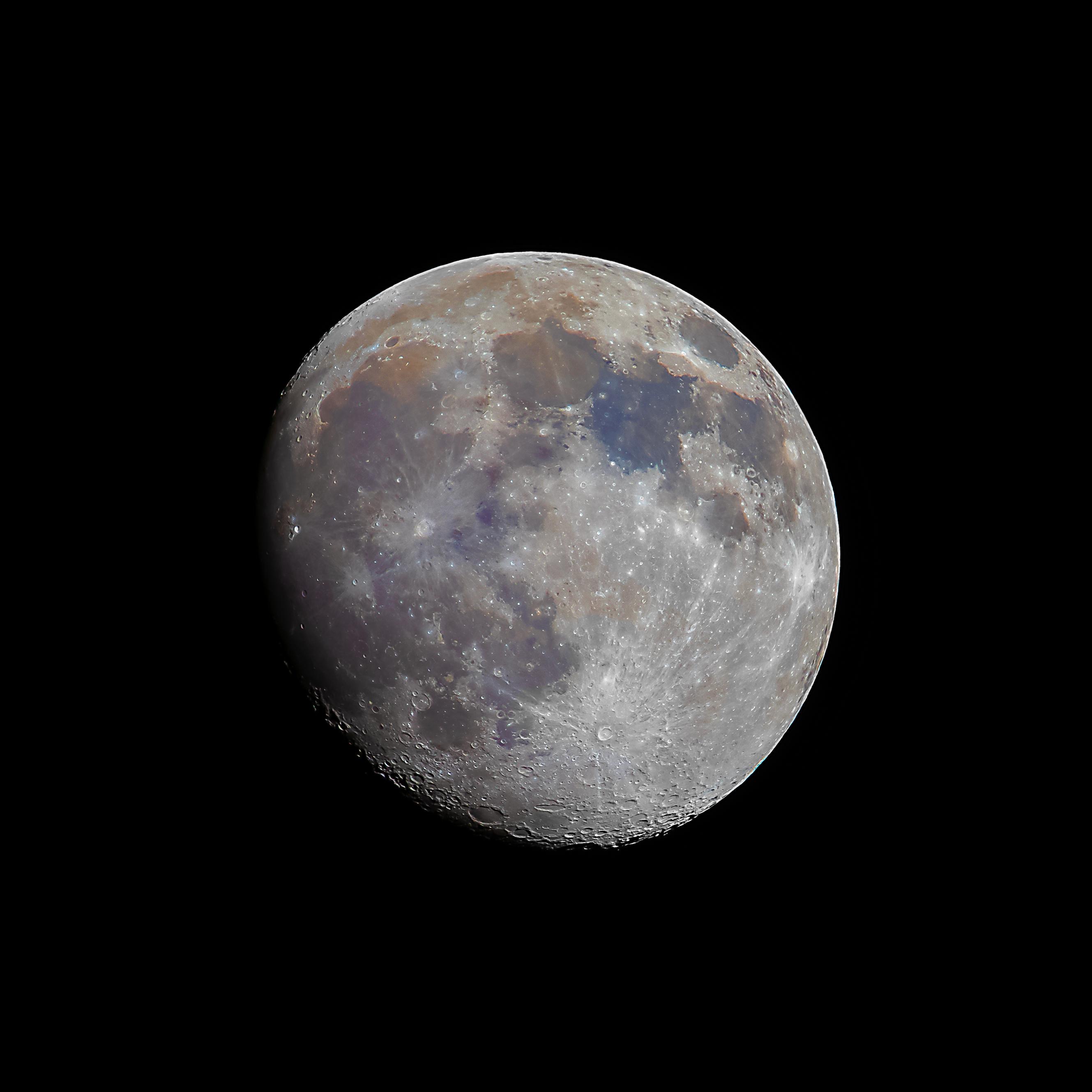

Full Moon, Day 14
180 degrees
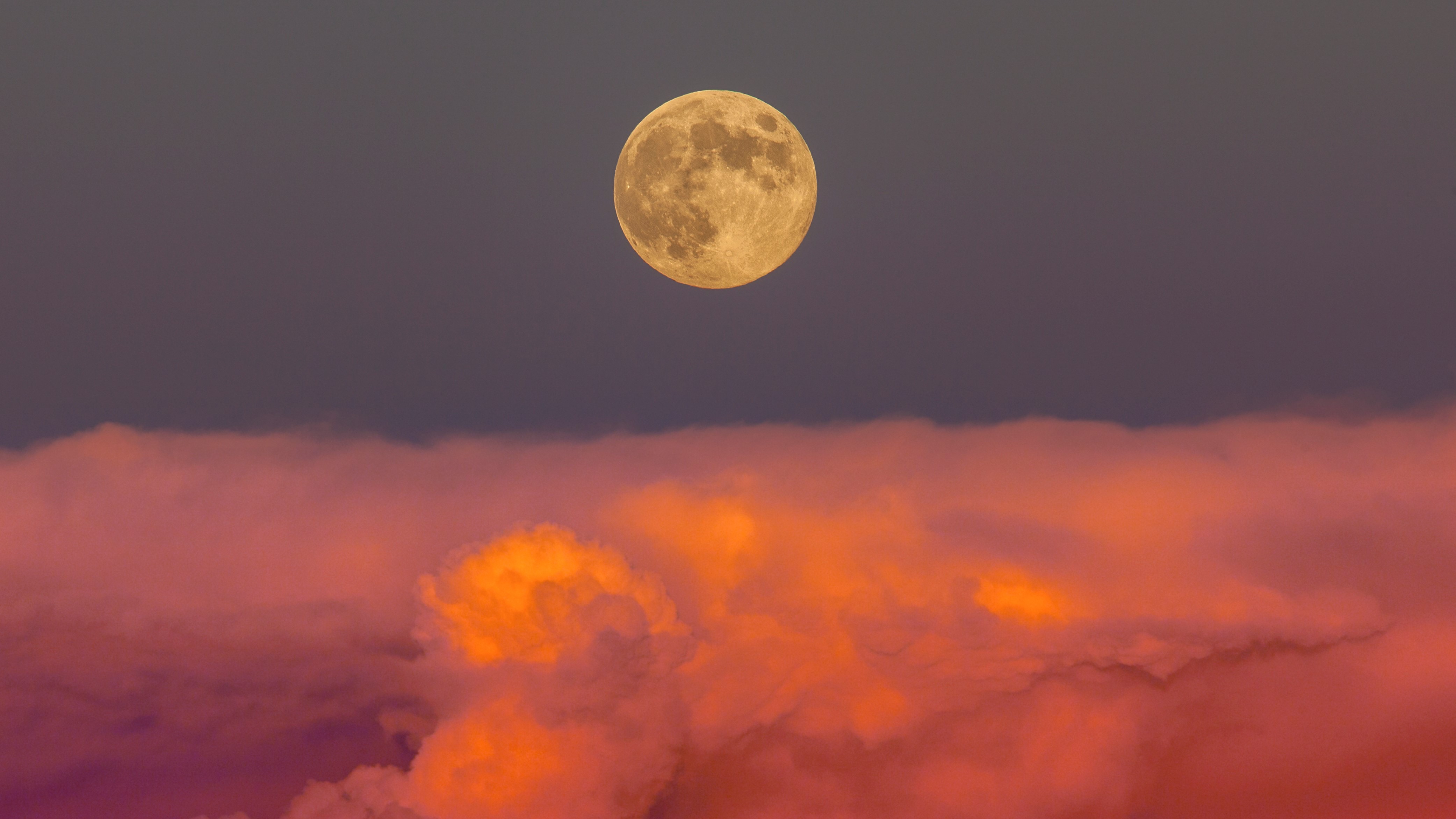

Waning Gibbous, Day 18
225 degrees
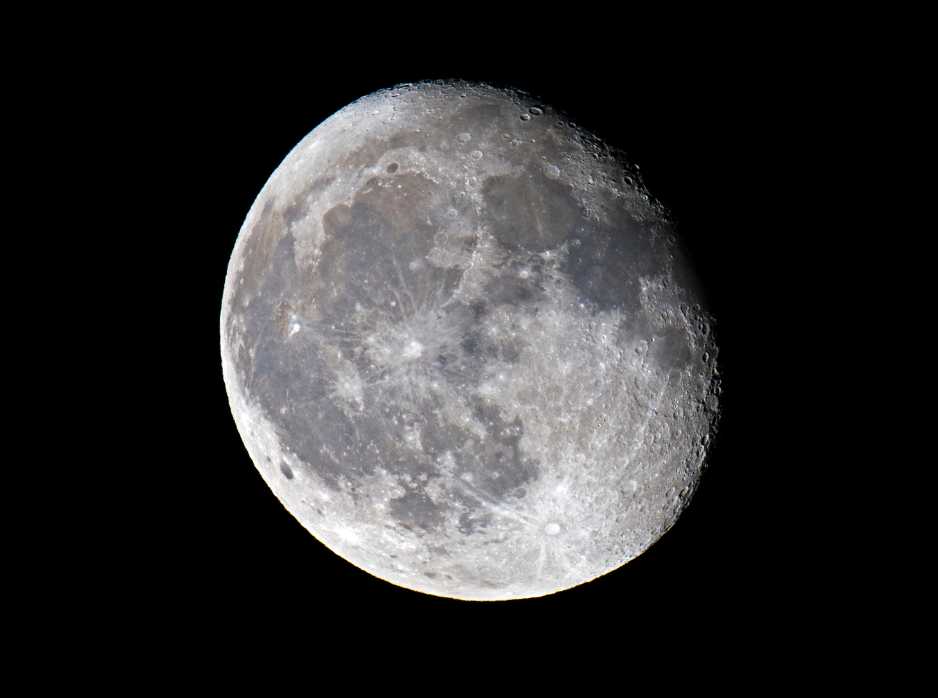

Last Quarter, Day 21
270 degrees
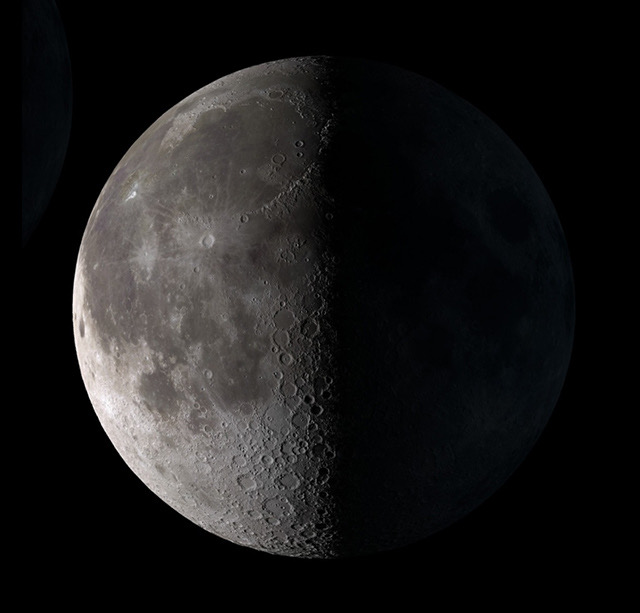

Waning Crescent, Day 25
315 degrees
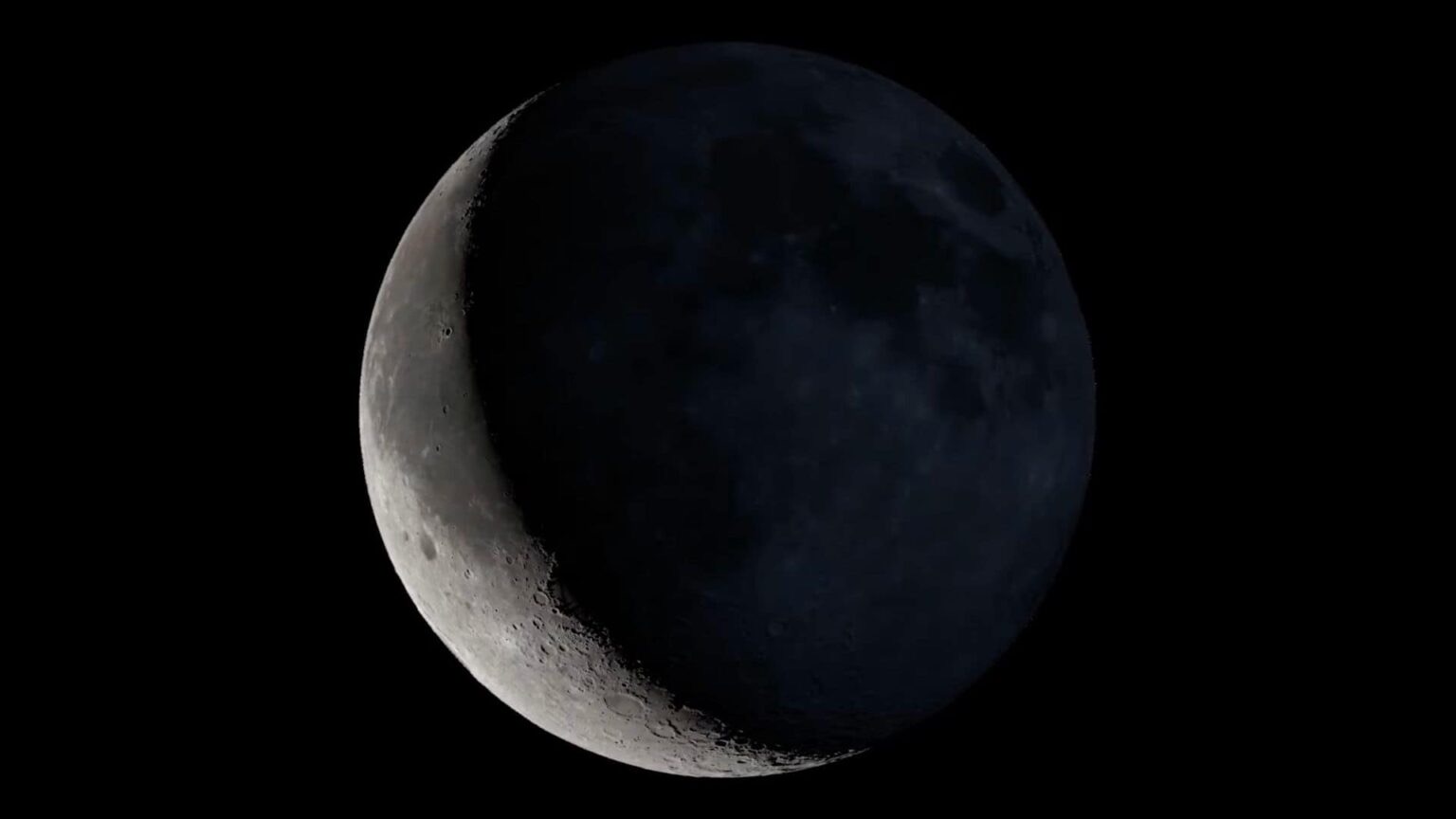

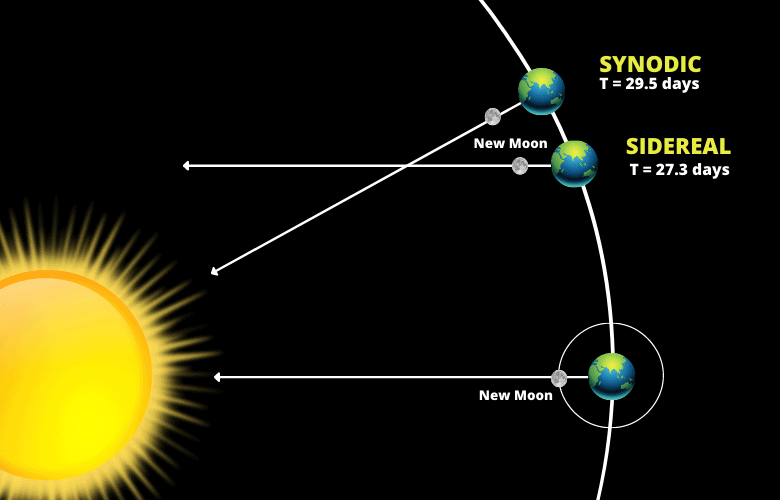
Synodic period
the average period of the Moon's orbit with respect to the Sun and Earth: around 29.5 (Earth) days
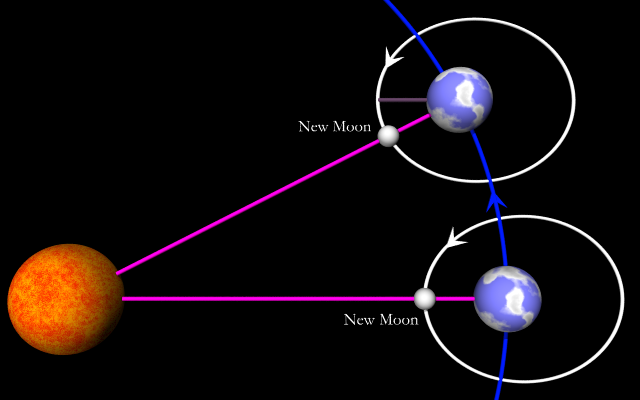
Sidereal period
The average period it takes for the moon to go 360 degrees around earth, as measured with respect to fixed stars: around 27.3 Earth days
Moving
The synodic period longer than the sidereal period because the moon is orbiting around earth, which is __________
1/2
How much of the moon is illuminated by the Sun at all times?
Spherical
The moon is _____ which prevents us from always viewing the illuminated half
Larger
Our moon is ______ compared to other moons in the solar system
Consistent
Our moon is a great time keeper because it’s changes are ________ on a repetitive cycle